Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochemistry Exam One Notes
Uploaded by
lucidheroo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views4 pagesNotes for biochem exam number one
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNotes for biochem exam number one
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views4 pagesBiochemistry Exam One Notes
Uploaded by
lucidherooNotes for biochem exam number one
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
8/27
Biochemistry Exam One Notes
1.3: Quick Review
Organic Chemistry
o Phenyl
o Carboxyl
o Aldehyde
o Ester
o Ether
o Amine
o Alcohol
o Ketone
o Schiff Base
o Carboxylic Acid
o Phosphate
o Inorganic Phosphate (PI)
o Phosphodiester
8/27
Biology
o DNA RNA Protein
DNA Gene product
General Chemistry
o Atoms
Most (if not all) properties of atoms are defined by valence electrons
Octet rule states that every atom will want to be stable by having 8 electrons.
Ne 1s
2
2s2
2
p
6
F 1s
2
2s
2
2p
5
Fluorine is unstable and wants one more valence electron to complete its octet.
o Molecules
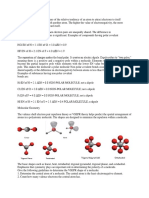
Covalent bonds share electrons equally
Polar bonds share electrons unequally
If the difference in electronegativity is less than .4 than it is a covalent bond
If it is between .5 1.2 than it is a polar bond
If it is greater than 1.21 than it is ionic bonding.
Ex:
8/27
o Molecules interacting with other molecules (InterMolecular Forces)
Van der Waals (induced dipole : induced dipole)
All molecules have VDW
Ex: 2 Alkanes
We will get a partial negative on one end and a partial positive on the adjacent carbon while the other has the opposite charges so that they
may bond.
C4H10 has a lower boiling point than C30H62 because there requires more energy to break apart more
VDW
Hydrogen Bonds (the sharing of a proton)
This bond needs a donor and acceptor
Hydrogen bonds are stronger than VDW
1KJ/mol to break VDW
4-20 KJ/mol to break Hydrogen bonds
350KJ/mol to break covalent bonds
Electrostatic interactions (salt bridges/ionic interactions)
A molecule with a positive or partial positive charge interacts with a molecule with a negative or
partial negative charge.
Hydrophobic interactions
Generates about 7-10 KJ/mol (strongest attraction)
: Nonpolar; no electronegative atoms or polar covalent bonds.
: Polar; negative charge indicates polarity
: Polar; positive charge indicates polarity
: Nonpolar; although the lone pair is present, the molecule is aromatic (stable)
o Nonpolars like nonpolars (hydrophobic) while polar likes polar (hydrophilic).
o Hydrophobic effect: exclusion of nonpolar substances by water
8/27
o S increase in entropy
More disorder = more entropy (positive)
More order = less entropy (negative)
o Alkane in H2O solvent cage
o More alkanes causes more disorder in solvent cage because of VDW forces
o G = H T S
If G is negative then the reaction is spontaeneous
o Amphiles are polar and nonpolar parts of the molecule
o Ketone in H2O
Water
o Water has a high dielectric constant.
o Good for solvating cations and anions by making electrostatic interactions with making ionic bonds weaker
o Water has a high specific heat capacity
o The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1C is 4.184 J/mol C
o Cohere is to interact with similar molecules
o Adhere is to interact with different molecules
o Capillary Action is the ability to move together
o
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chapter 2 Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Basic ChemistryClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- WaterDocument2 pagesWaterMuznah ShahidNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Molecular Orbital Theory: Lumo HomoDocument10 pagesMolecular Orbital Theory: Lumo HomoKristy MohammedNo ratings yet
- Class03 Chemistry G11 NotesDocument16 pagesClass03 Chemistry G11 Notesestarguan1111No ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Review (Students)Document16 pagesBasic Chemistry Review (Students)AnilovRozovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular ForcesDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forcesnoreen doraniNo ratings yet
- MATTER_ BONDING, NAMING, AND COUNTING ITS PARTICLESDocument7 pagesMATTER_ BONDING, NAMING, AND COUNTING ITS PARTICLEStlga.amberdominiquebediaNo ratings yet
- (A) Water and PHDocument53 pages(A) Water and PHSapana SubediNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry - Definitions (V.1) Topic 1 - StoichiometryDocument9 pagesIb Chemistry - Definitions (V.1) Topic 1 - StoichiometryNikole GualdrónNo ratings yet
- Polarity, Solubility and Molecular ShapeDocument38 pagesPolarity, Solubility and Molecular Shapelily smithNo ratings yet
- CHEM 3 Quiz 1 - Short Term: Class Discussion: SolutionsDocument7 pagesCHEM 3 Quiz 1 - Short Term: Class Discussion: SolutionsARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- BSC 450 CH 2 NotesDocument15 pagesBSC 450 CH 2 NotesMaddie NNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculeDocument35 pagesPolarity of MoleculeAlyson Kate CastillonNo ratings yet
- 1-Chemistry of Life Part Two StudentDocument21 pages1-Chemistry of Life Part Two StudentteniNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Physical ScienceDocument13 pagesReviewer For Physical ScienceTimothy James Tolentino BruceNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Basic Chemistry, Carbon, Macromolecules 2023Document48 pagesLecture 1 - Basic Chemistry, Carbon, Macromolecules 2023PPNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Properties of Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesDocument23 pages2.1 Properties of Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesmckhiandivinoNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument12 pagesChemical BondingyoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry NotesKisten KallistusNo ratings yet
- Ions + extra (pH & pOH) - Google DocsDocument4 pagesIons + extra (pH & pOH) - Google Docsananyasanvi.bNo ratings yet
- From Last Class: Interatomic BindingDocument27 pagesFrom Last Class: Interatomic BindingPo KaiNo ratings yet
- Jose Camacho Chem LABDocument3 pagesJose Camacho Chem LABLeslieNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Fundamental Biomolecules of LifeDocument60 pagesUnderstanding the Fundamental Biomolecules of Lifecr4zyvi3tNo ratings yet
- Thermo&Molecular Forces 22 PostDocument52 pagesThermo&Molecular Forces 22 PostPedro RamosNo ratings yet
- 2.04-2.05 Intermediate Bonding and Intermolecular ForcesDocument16 pages2.04-2.05 Intermediate Bonding and Intermolecular ForcesDhirenPanchaniNo ratings yet
- Matthew McClain Lab Report Period 4Document4 pagesMatthew McClain Lab Report Period 4mmcclain2014No ratings yet
- Why Don't Covalent Bonds Form Ions?Document10 pagesWhy Don't Covalent Bonds Form Ions?api-470106119No ratings yet
- Week6 Physical+ScienceDocument74 pagesWeek6 Physical+ScienceEKIMISS PHNo ratings yet
- BioChemistry UNIT TEST-2Document16 pagesBioChemistry UNIT TEST-2Kezia BijuNo ratings yet
- BioChemistry UNIT TESTDocument8 pagesBioChemistry UNIT TESTKezia BijuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, Ch. 1,2,3Document15 pagesLecture 1, Ch. 1,2,3S. SpencerNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular ForcesDocument9 pagesIntramolecular ForcesIBstudent10No ratings yet
- Chem Notes CHPTR 5Document6 pagesChem Notes CHPTR 5Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Ionic NetworksDocument3 pagesCharacterizing Ionic NetworksTrinh Tat-TranNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Document88 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 1-4 2 NotesDocument22 pagesChapter 4 1-4 2 NotesKarelene SotoNo ratings yet
- v0.3 Electrolysis ID1324Document54 pagesv0.3 Electrolysis ID1324tamimihsan2763No ratings yet
- Physical Science HandoutsDocument5 pagesPhysical Science HandoutsEllaNatividad100% (1)
- Basic Chemistry ReviewDocument5 pagesBasic Chemistry ReviewArman Neil J. BudogNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 M1bDocument7 pagesGen Chem 2 M1bJohndee Mozart Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Lecture 4Document36 pagesMolecular Biology Lecture 4Anton IrvingNo ratings yet
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: HypothesesDocument3 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab Investigation: HypothesesLeslieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 PagesDocument1 pageChemistry 2 PagesamansingheditorofficialNo ratings yet
- BiologyStudySheetBasicChemistryandWater PDFDocument4 pagesBiologyStudySheetBasicChemistryandWater PDFSam MonellaNo ratings yet
- Christian Lara Lab ReportDocument3 pagesChristian Lara Lab ReportLeslieNo ratings yet
- Biology: The Chemical Basis of Life I: Atoms, Molecules, and WaterDocument18 pagesBiology: The Chemical Basis of Life I: Atoms, Molecules, and WaterMatt LynchNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond (ContDocument18 pagesChemical Bond (ContJachinta JuliusNo ratings yet
- 02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingDocument9 pages02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingNatasha DalalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Polarity PDFDocument33 pagesChemical Polarity PDFEG Tiolo AbadNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity, Bond Polarity & Dipole MomentDocument34 pagesElectronegativity, Bond Polarity & Dipole MomentAtie IekahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding: ChemistryMuneeb MunawarNo ratings yet
- RVCDocument48 pagesRVCfluronineNo ratings yet
- Important As DefinitionsDocument3 pagesImportant As DefinitionsmiammyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - 254 PDFDocument27 pagesChemical Bonding - 254 PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL-BOND IdkDocument15 pagesCHEMICAL-BOND Idk14A - BANTANG, Mark Joshua R.No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic ChemistryDocument50 pagesChemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic Chemistryyayooo200450% (2)
- Key TermsDocument9 pagesKey TermsLayan HalasaNo ratings yet
- Division Celular Mitosis y MeiosisDocument5 pagesDivision Celular Mitosis y MeiosisGiovanna Macías100% (1)
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Natural SolutionsDocument25 pagesIrritable Bowel Syndrome Natural SolutionsBrettNo ratings yet
- Cancer DiseaseDocument7 pagesCancer Diseasenbs saraswathiNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs-Test-1-QuestionsDocument7 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs-Test-1-QuestionsDrishya Bioplannet100% (2)
- Optimizing Ba and Iba Concentrations For Micro Propagation of Spineless Yucca Yucca Elephantipes IJERTV8IS010004Document5 pagesOptimizing Ba and Iba Concentrations For Micro Propagation of Spineless Yucca Yucca Elephantipes IJERTV8IS010004SHUBHAM JIBHAKATENo ratings yet
- Kantor Cabang: BANJARMASIN - 1701 FKTP: Kertak Hanyar - 17040601Document6 pagesKantor Cabang: BANJARMASIN - 1701 FKTP: Kertak Hanyar - 17040601Ic-tika Siee ChuabbieNo ratings yet
- How It Works Book of The HumanDocument180 pagesHow It Works Book of The Humanyassomelek100% (1)
- Kurukshetra University Date-Sheets for BA/BSc Part ExamsDocument12 pagesKurukshetra University Date-Sheets for BA/BSc Part ExamsabhishekNo ratings yet
- Root Resorption: Challenge To The Endodontist: Acta Scientific Dental SciencesDocument11 pagesRoot Resorption: Challenge To The Endodontist: Acta Scientific Dental SciencesMuhammadDeniRahmanNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care StepsDocument21 pagesNewborn Care StepsRaida Marañon Ibrahim100% (2)
- Biology 2000 Paper I Marking SchemeDocument4 pagesBiology 2000 Paper I Marking Schemeapi-2642329075% (4)
- HEMOLYTIC ANEMIAS AND ACUTE BLOOD LOSS: CAUSES, SIGNS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTDocument4 pagesHEMOLYTIC ANEMIAS AND ACUTE BLOOD LOSS: CAUSES, SIGNS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Ncps For CvaDocument14 pagesNcps For Cvalouie roderos0% (2)
- ElectrophysiologyDocument32 pagesElectrophysiologyAbdelrehim SirajNo ratings yet
- Bag-Valve-Mask Ventilation (BVM)Document1 pageBag-Valve-Mask Ventilation (BVM)Aidan RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Q and A DactylosDocument56 pagesQ and A DactylosJUNN REE MONTILLA100% (2)
- Secondary Growth of PlantsDocument13 pagesSecondary Growth of PlantsAngie Kong Su Mei50% (2)
- Illusions The Magic Eye of PerceptionDocument12 pagesIllusions The Magic Eye of PerceptionArctic Illusion100% (2)
- Evolutionary Reclassification of Protozoa and Chromista KingdomsDocument4 pagesEvolutionary Reclassification of Protozoa and Chromista KingdomsWormInchNo ratings yet
- Dental Sedation TechniquesDocument28 pagesDental Sedation TechniquesRamesh CandyNo ratings yet
- MKFP Mat-Xs Clinical 16052012 enDocument8 pagesMKFP Mat-Xs Clinical 16052012 ensuharyantoNo ratings yet
- Kidney PowerPoint Presentation TemplateDocument14 pagesKidney PowerPoint Presentation TemplateMedicinePPT100% (1)
- How Finally I Straightened My Spine OutDocument169 pagesHow Finally I Straightened My Spine OutGiuseppe Medina100% (1)
- Essentials Lab Resource Guide 12 22Document67 pagesEssentials Lab Resource Guide 12 22Aijeleth Shahar Gunay AwacayNo ratings yet
- Chem 205 Lecture 5: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Derived From Voet, 2011)Document37 pagesChem 205 Lecture 5: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Derived From Voet, 2011)Rab BaloloyNo ratings yet
- Pure Bio CH 4 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 pagesPure Bio CH 4 Textbook Answers PDFlee0% (1)
- Asthma Care Quick Reference - Diagnosing and Managing AsthmaDocument18 pagesAsthma Care Quick Reference - Diagnosing and Managing AsthmaMarizka Putri AftriaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Subphylum UrochordataDocument12 pages4 - Subphylum UrochordataStudent 365No ratings yet
- Reduce sodium guide for food industryDocument82 pagesReduce sodium guide for food industryperunikicaNo ratings yet
- Rhopalocera (Butterfly) : FunctionsDocument18 pagesRhopalocera (Butterfly) : FunctionsChris Anthony EdulanNo ratings yet
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsFrom EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryFrom EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Process Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentFrom EverandProcess Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet