Professional Documents
Culture Documents
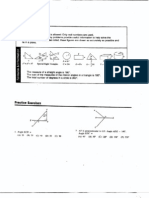
Angles - Maths
Uploaded by
Jannifer Love UCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Angles - Maths
Uploaded by
Jannifer Love UCopyright:
Available Formats
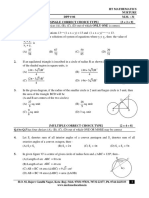
Circles - Angles
Question 1
10
UCLES 2011 0580/23/M/J/11
For
Examiner's
Use
20
f
e
h
g
70
W
V
U
X
A B T
O
NOT TO
SCALE
The diagram shows a circle, centre O.
VT is a diameter and ATB is a tangent to the circle at T.
U, V, W and X lie on the circle and angle VOU = 70.
Calculate the value of
(a) e,
Answer(a) e =
[1]
(b) f,
Answer(b) f =
[1]
(c) g,
Answer(c) g =
[1]
(d) h.
Answer(d) h =
[1]
Question 2
11
UCLES 2010 0580/23/O/N/10 [Turn over
For
Examiner's
Use
23
30
86
50
B
C
D A
O
NOT TO
SCALE
The points A, B, C and D lie on the circumference of the circle, centre O.
Angle ABD = 30, angle CAD = 50 and angle BOC = 86.
(a) Give the reason why angle DBC = 50.
Answer(a)
[1]
(b) Find
(i) angle ADC,
Answer(b)(i) Angle ADC =
[1]
(ii) angle BDC,
Answer(b)(ii) Angle BDC =
[1]
(iii) angle OBD.
Answer(b)(iii) Angle OBD =
[2]
Questions 24 and 25 are printed on the next page.
Question 3
!
0580/23/O/N/13 UCLES 2013
!"#
$%&'()*#+
,+*
"# Write the answer to the Iollowing calculations in standard Iorm.
$%& 600 8000
-)+.*#/&0 ............................................... |2|
$'& 10
8
7 10
6
-)+.*#/10 ............................................... |2|
"(
M
N
D
A
C
O
B
NOT TO
SCALE
42
The vertices oI the rectangle -234 lie on a circle centre 5.
67 is a line oI symmetry oI the rectangle.
-3 is a diameter oI the circle and angle -34 42.
Calculate
$%& angle 3-6,
-)+.*#/&0 Angle 3-6 ............................................... |2|
$'& angle 436.
-)+.*#/10 Angle 436 ............................................... |2|
Question 4
9
UCLES 2010 0580/43/M/J/10 [Turn over
For
Examiner's
Use
(b)
R, H, S, T and U lie on a circle, centre O.
HT is a diameter and MN is a tangent to the circle at T.
Angle RTM = 61.
Find
(i) angle RTH,
Answer(b)(i) Angle RTH =
[1]
(ii) angle RHT,
Answer(b)(ii) Angle RHT =
[1]
(iii) angle RST,
Answer(b)(iii) Angle RST =
[1]
(iv) angle RUT.
Answer(b)(iv) Angle RUT =
[1]
(c) ABCDEF is a hexagon.
The interior angle B is 4 greater than interior angle A.
The interior angle C is 4 greater than interior angle B, and so on, with each of the next interior
angles 4 greater than the previous one.
(i) By how many degrees is interior angle F greater than interior angle A?
Answer(c)(i)
[1]
(ii) Calculate interior angle A.
Answer(c)(ii)
[3]
H
R
U
T
M
N
O
S
61
NOT TO
SCALE
Question 5
14
UCLES 2012 0580/43/M/J/12
For
Examiner's
Use
8 (a)
B
C
D
O
Y
E
A u
v
w
68
88
NOT TO
SCALE
A, B, C, D and E lie on the circle, centre O.
CA and BD intersect at Y.
Angle DCA = 88 and angle CYD = 68.
Angle BAC = u, angle AED = v and reflex angle AOD = w.
Calculate the values of u, v and w.
Answer(a) u =
v =
w =
[4]
(b)
S R
Q
P
NOT TO
SCALE
X
P, Q, R and S lie on the circle. PR and QS intersect at X.
The area of triangle RSX = 1.2 cm
2
and PX = 3 SX.
Calculate the area of triangle PQX.
Answer(b)
cm
2
[2]
15
UCLES 2012 0580/43/M/J/12 [Turn over
For
Examiner's
Use
(c)
J
I
K
O
H
G
F
4x
2x
x
NOT TO
SCALE
GI is a diameter of the circle.
FGH is a tangent to the circle at G.
J and K also lie on the circle.
Angle JGI = x, angle FGJ = 4x and angle KGI = 2x.
Find
(i) the value of x,
Answer(c)(i) x =
[2]
(ii) the size of angle JKG,
Answer(c)(ii) Angle JKG =
[2]
(iii) the size of angle GJK.
Answer(c)(iii) Angle GJK =
[1]
You might also like
- 2 Moons The SeriesDocument39 pages2 Moons The SeriesShifa Fauziah0% (1)
- Shingeki No Kyojin - Linked Horizon - Guren No Yumiya (SNK Opening) (Advanced)Document3 pagesShingeki No Kyojin - Linked Horizon - Guren No Yumiya (SNK Opening) (Advanced)Louis GerrityNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Educationvedant100% (1)
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Educationnisa1673100% (1)
- Trigon Bearing ClassifiedDocument35 pagesTrigon Bearing ClassifiedShaaminiNo ratings yet
- 0607 s10 QP 2Document12 pages0607 s10 QP 2Amalia KorakakiNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMohamed AnsaryNo ratings yet
- 0607 w12 QP 4Document20 pages0607 w12 QP 4AnshulNo ratings yet
- 0580 w11 QP 42Document20 pages0580 w11 QP 42Aryan RajputNo ratings yet
- 0607 w10 QP 2Document12 pages0607 w10 QP 2Amer Al MajedNo ratings yet
- 4024 w08 QP 2Document12 pages4024 w08 QP 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- 0580 s05 QP 2Document12 pages0580 s05 QP 2AdeRayenNo ratings yet
- 0580 s02 QP 4Document8 pages0580 s02 QP 4Khairi AiriNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- 0580 s05 QP 2Document12 pages0580 s05 QP 2MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelKhalid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry WorksheetDocument12 pagesTrigonometry WorksheetRoygunEdwinNo ratings yet
- Arc Length and Area of Sector (MJ 18 To 2005) )Document7 pagesArc Length and Area of Sector (MJ 18 To 2005) )Burhan AzharNo ratings yet
- 0580 w10 QP 42Document20 pages0580 w10 QP 42Aryan RajputNo ratings yet
- November 2011 Question Paper 31coreDocument16 pagesNovember 2011 Question Paper 31coreVikas AbhyankarNo ratings yet
- 0580 w10 QP 41Document16 pages0580 w10 QP 41MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- 4024 w11 QP 22Document24 pages4024 w11 QP 22Hamza NawazNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Core Paper 3 Nov 2011Document16 pagesIGCSE Core Paper 3 Nov 2011rajdeepghai5607No ratings yet
- 0607 Y10 SP 3 PDFDocument16 pages0607 Y10 SP 3 PDFcodybuyeNo ratings yet
- 4024 w04 QP 2Document12 pages4024 w04 QP 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- 0607 s09 QP 4 PDFDocument24 pages0607 s09 QP 4 PDFcodybuyeNo ratings yet
- June 2014 Question Paper 41 PDFDocument24 pagesJune 2014 Question Paper 41 PDFSIDDHI BARVENo ratings yet
- 4024 s15 QP 22Document24 pages4024 s15 QP 22Kevin AarasingheNo ratings yet
- 4024 w07 QP 2Document12 pages4024 w07 QP 2mstudy123456100% (2)
- 4024 s10 QP 21Document12 pages4024 s10 QP 21mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Maths IGCSE Sample Test PaperDocument16 pagesMaths IGCSE Sample Test PaperMarvin LuoNo ratings yet
- MR Sat PacketDocument5 pagesMR Sat PacketbriandmcneillNo ratings yet
- 4024 s09 QP 2Document12 pages4024 s09 QP 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- 0580 s06 QP 2Document12 pages0580 s06 QP 2John MayoresseNo ratings yet
- Merged Files Int Math QuestionsDocument460 pagesMerged Files Int Math Questionsdhruv goelNo ratings yet
- Vectors: Not To ScaleDocument7 pagesVectors: Not To ScaleJannifer Love UNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSEDocument12 pagesCambridge IGCSEHannah LohNo ratings yet
- 4024 s13 QP 11Document20 pages4024 s13 QP 11Ruwan BandaraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Mathematics Model Paper - 3Document9 pagesIGCSE Mathematics Model Paper - 3Kothakonda Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 0580 w10 QP 22Document12 pages0580 w10 QP 22Haider AliNo ratings yet
- 0580 s05 QP 2Document12 pages0580 s05 QP 2Elissar129No ratings yet
- 0580 s10 QP 42Document20 pages0580 s10 QP 42MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- O Level Mathematics Past QuestionsDocument24 pagesO Level Mathematics Past QuestionsnurlNo ratings yet
- Ssc-Geometry Questions PDFDocument13 pagesSsc-Geometry Questions PDFShobhit Mishra0% (1)
- 0580 s12 QP 41Document16 pages0580 s12 QP 41Darwin ManoNo ratings yet
- MR - Yasser Elsayed Mobile No: +966451482868 / +201114057545 1Document363 pagesMR - Yasser Elsayed Mobile No: +966451482868 / +201114057545 1tranquil_452889939No ratings yet
- H.O. 92, Rajeev Gandhi Nagar, Kota (Raj.) Mob. 97831-97831, 70732-22177, Ph. 0744-2423333 WWW - Nucleuseducation.inDocument2 pagesH.O. 92, Rajeev Gandhi Nagar, Kota (Raj.) Mob. 97831-97831, 70732-22177, Ph. 0744-2423333 WWW - Nucleuseducation.inSatyanshu JhaNo ratings yet
- 0607 s09 QP 3 PDFDocument16 pages0607 s09 QP 3 PDFcodybuyeNo ratings yet
- 4024 s04 QP 2Document12 pages4024 s04 QP 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- 0580 s04 QP 3Document16 pages0580 s04 QP 3Andrea UmarNo ratings yet
- C2 Geometry and Trigonmetry+solutionsDocument7 pagesC2 Geometry and Trigonmetry+solutionsIrrationalNo ratings yet
- GeomeDocument13 pagesGeomesomu646No ratings yet
- 575 P1 Lit Mock 2020Document8 pages575 P1 Lit Mock 2020Labssen FaithNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Additional Mathematics Paper 2 Version 1 Summer 2012Document16 pagesIGCSE Additional Mathematics Paper 2 Version 1 Summer 2012Veshalini Naidu100% (1)
- 0580 s10 QP 41Document20 pages0580 s10 QP 41Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Diploma Engineering MCQFrom EverandEnvironmental Engineering Diploma Engineering MCQRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- MARK SCHEME For The November 2005 Question PaperDocument10 pagesMARK SCHEME For The November 2005 Question PaperJannifer Love UNo ratings yet
- Business Foundation Timetable For Semester 1, 2015-2016 at 5-10-2015Document2 pagesBusiness Foundation Timetable For Semester 1, 2015-2016 at 5-10-2015Jannifer Love UNo ratings yet
- 0580 s05 QP 2Document12 pages0580 s05 QP 2MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- CBL Peer Review Form 2014Document2 pagesCBL Peer Review Form 2014Jannifer Love UNo ratings yet
- Course Profile - Maths J2Document2 pagesCourse Profile - Maths J2Jannifer Love UNo ratings yet
- Algebra - Maths ExerciseDocument15 pagesAlgebra - Maths ExerciseJannifer Love UNo ratings yet
- Vectors: Not To ScaleDocument7 pagesVectors: Not To ScaleJannifer Love UNo ratings yet
- ChopinDocument6 pagesChopinJannifer Love UNo ratings yet
- Kelly Alexander Resume 2015Document1 pageKelly Alexander Resume 2015api-235202010No ratings yet
- Basis2 Steel enDocument107 pagesBasis2 Steel enNguyen HaiNo ratings yet
- Quantitative and Qualitative Aptitude ProblemsDocument21 pagesQuantitative and Qualitative Aptitude ProblemslembdaNo ratings yet
- Smops 2018Document13 pagesSmops 2018Marilyn Citadel0% (1)
- Trigonometric Functions - by TrockersDocument122 pagesTrigonometric Functions - by TrockersGracious ChiweraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 - MTH101 IIT KanpurDocument3 pagesLecture 21 - MTH101 IIT KanpurAsish MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Expectations For Cooperating School SitesDocument3 pagesExpectations For Cooperating School Sitesapi-247649236No ratings yet
- Lesson 2-09 Areas Under A Standard Normal CurveDocument12 pagesLesson 2-09 Areas Under A Standard Normal CurveJamiefel PungtilanNo ratings yet
- Integral (Kalkulus 2)Document7 pagesIntegral (Kalkulus 2)pitoNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Refresher SetDocument3 pagesAnalytic Geometry Refresher SetRowena Remorosa Galay100% (3)
- Test 1-9Document19 pagesTest 1-9Mounira DebibiNo ratings yet
- XF - KR: Lakdfyr Ijh (KK &I &Document54 pagesXF - KR: Lakdfyr Ijh (KK &I &selva.uae8207No ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Classifying Learners Grades Per Learning AreasDocument8 pages2nd Grading Classifying Learners Grades Per Learning Areasemelyn tumpagNo ratings yet
- Maths CH-12 Special Product and ExpansionDocument6 pagesMaths CH-12 Special Product and ExpansionfmzirkNo ratings yet
- 2023 Annual Playwriting Festival - List of HonoreesDocument4 pages2023 Annual Playwriting Festival - List of HonoreesGlynnis NadelNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7-The Straight LinesDocument18 pagesMODULE 7-The Straight Linesidaman2905No ratings yet
- Trial SPM 2021 - Soalan Maths k2Document33 pagesTrial SPM 2021 - Soalan Maths k2ROSNIZA BT AB. GHANI MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Deductive GeometryDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Deductive GeometryEric Mooi100% (1)
- Part 1 Set 1 FinalDocument18 pagesPart 1 Set 1 Finalapi-237793444No ratings yet
- My ProfileDocument2 pagesMy Profileapi-459074614No ratings yet
- GCSE VectorWorksheetDocument7 pagesGCSE VectorWorksheetRocioNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL 2021 Maths All 21 Sets 525 PYQDocument67 pagesSSC CGL 2021 Maths All 21 Sets 525 PYQkamalNo ratings yet
- Cutting WatermelonDocument5 pagesCutting WatermelonlizbethsingsNo ratings yet
- Isometric Drawing 1.0Document32 pagesIsometric Drawing 1.0Najed SallehNo ratings yet
- ContinueDocument5 pagesContinueGoldBirdNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument4 pagesNarrative Reportfrancis vale NavitaNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Division and SubtractionDocument4 pagesThe Relationship Between Division and SubtractionalissavictorNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 - Math Practice PDFDocument41 pagesGrade 3 - Math Practice PDFcoed_emc100% (1)
- Grade 10: International Junior Math OlympiadDocument13 pagesGrade 10: International Junior Math OlympiadMehdi MoradiNo ratings yet