Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Valves: 3.1 Classification
Uploaded by
Raju NaiduOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Valves: 3.1 Classification
Uploaded by
Raju NaiduCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3
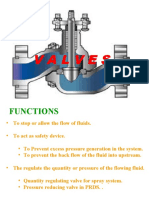
VALVES
3.1 CLASSIFICATION
Piping
61
Valves are classified according to their action performed.
Isolation
Regulation.
Checking
Switching
Discharging
ISOLATION VALVES.
Gate valve
Ball valve
Plug valve
Piston valve
Diaphragm valve.
Butterfl valve.
REGULATION VALVES.
Glo!e valve.
"eedle valve.
Butterfl valve.
Diaphragm valve.
Piston valves.
CHECKING VALVES.
Check valve.
#oot valve.
SWITCHING VALVES.
$ultiport valve.
Diverting valve.
DISCHARGING VALVES.
Safet valve.
Relief valve.
Safet relief valve.
#lush !ottom valve.
Rupture disc.
3.2 VALVES ASSEMBLY
Piping
62
#ollowing are the parts of valve%
Disc:- &he moving part that directl effect the flow is called as disc.
Seat:- &he non'moving part on which the disc !ears is called as seat.
Port:- &he ma(imum internal opening of the valve in full open position.
Stem:- &here are two tpes of screwed stem. &he rising ) non rising stem.
&he rising stem can either !e inside screw or outside screw .&he outside screw
tpe has a oke on !onnet ) referred to as *outside screw ) oke+ , -S)./. the
hand wheel can either rise with the stem or stem can rise through the hand
wheel.
In "on' rising stem hand wheel ) stem are in the same position whether the
valve is open or closed. &he screw is inside the !onnet.
Bonnet 0'&he !onnet is connected to the !od . &he tpe of connection can !e
flanged !olted1 !ellow sealed1 screwed 2on1 welded1 union1 pressure sealed etc.
Body 0'&he valves are connected to pipe1 fittings or vessel ! their !od ends1
which ma !e flanged1 screwed1 !utt or socket welding.
TERMS USED FOR VALVE SPECIFICATION.
P-T ratings :- &he ma(imum allowa!le sustained non'shock pressure at the
corresponding ta!ulated temperature. &hese are listed in 3"SI B 45.67 ) 3"SI
B 45.8.
Class:- &he valve is specified ! the pressure rating of the !od of the valves.
&he 3merican standard specifies the following class.
Class 489 :
Class 699 :
Class 799 :
Class 599 :
Class ;99 :
Class 4899 :
Class <899:
Class =99:
Class 7899:
Piping
63
Trim:- &he trim mainl comprises of stem1 seat surface1 !ushing ) other internal
parts1 which are in contact with the fluid.
3PI 599 specifies trim "o0 ) the material that can !e used for parts with its
tpical specification ) grade.
&a!le 6.4 3PI 59 Standard for &rim
3.3 VALVE TYPES
Piping
64
3.3.1 GATE VALVE
It is an isolation valve1 can+t !e used for regulation.
Designed to operate full open or full closed.
#luid hammer is minimum as it operates slowl.
Pressure drop through gate valve is less.
In full closed position gate valve provide positive seal under high
pressure.
>nder low pressure there can !e seepage of 8psi.which is not considered
a!normal.
Si?e range @A 2 4<A
#igure 6.4 Gate Valve
3.3.2 BALL VALVE.
Piping
65
Ball valve is an isolation valve !ut in some case it can !e used as a
regulation valve.
It is designed to operate full open or full closed.
Ball valve is Buarter turn valve hence it can !e Buickl opened or closed.
It is suita!le for gas1 compressed air ) slurr services.
Cuick opening D closing causes fluid hammering.
Pressure drop is less.
#igure 6.4 Ball Valve
3.3.3 GLOBE VALVE.
Piping
66
Glo!e valve is a regulation valve.
It open ) closes slowl so fluid hammer is minimum.
&here is leakage under low pressure in full close position.
Pressure drop is comparativel higher gate1 !all.
$ain disadvantage is the *E+ pattern design which restrict the flow more
then gate1 !all or !utterfl valve.
Si?e range is @A 2 4<A
#igure 6.6 Glo!e Valve
3.3. NEEDLE VALVE.
It is a tpe of glo!e valve. -nl the wedge in the shape of needle.
Piping
67
>sed for the precise flow of fluid.
Generall used for instrument1 gauge ) meter line service.
#igure 6.7 "eedle Valve
3.3.! BUTTERFLY VALVE.
It is an isolation valve.
It can !e used for regulation !ut not for e(tended period.
Piping
68
3dvantage is the low weight1 compact design hence preferred over gate
valve in large !ore.
Fike !all valve it operates with a 4D7
th
turn.
It is designed for handling large flow of gases or fluid including slurries.
Si?e range <A' 4<A
#igure 6.8 Butterfl Valve
3.3." PLUG VALVE.
Plug valve is an isolation valve.
Fike !all valve it reBuire onl ;9G turns to open it.
Piping
69
Valve design is ver compact.
It reBuires little headroom.
Steam corrosion is minimum as there is no screw thread.
Suita!le for highl viscous fluid.
3vaila!le in much higher si?e then the !all valve
#igure 6.5 Plug Valve
3.3.# DIAPHRAGM VALVE.
$ainl an isolation valve !ut cat can !e used for regulation also.
$ainl used for low pressure corrosive fluid or where high degree of purit
is reBuires e.g.. Pharmaceutical ) food processing industries.
Diaphragm moves ups ) down to operate the valve.
Piping
70
Bod ) !onnet is made of casting. Bod is lined with corrosive resistant
materials. Diaphragm is generall made of ru!!er or P&#H.
&here is no 3PI or 3"SI standard availa!le for this valve. these are
covered ! British standards ) $SS'SP standards.
Op$n p%&i'i%n C(%&$ p%&i'i%n
#igure 6.I Diaphragm Valve
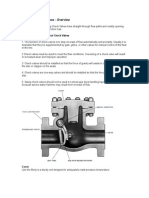
3.3.) CHECK VALVE.
Check valves are directional control valve1 which prevent the !ack flow in
lines.
&he common tpes of check valves used are lift tpe1 swing tpe ) wafer
tpe.
FI#& CJHCK V3FVH
&hese are operated ! lifting action of the disk D elements. &he different tpe of
lift check valve availa!le are
Piston lift check 0' It can !e placed in hori?ontal pipe line onl.
Ball lift check0 ' It comes in !oth hori?ontal ) vertical pattern hence can !e used
in !oth the position.
Piping
71
#igure 6.= Fift check valve
SWING CHECK VALVE
Swinging action of disk operates these valves. &he pressure of the fluid lifts the
hinged disk ) allows the flow. &he disk return to seat ! its own weight. It can !e
used in !oth hori?ontal ) vertical position.
Piping
72
#igure 6.; Swing Check Valve
L3#HR CJHCK V3FVH
&hese are the flangeless swing check valves. &here are two tpe of wafer check
valve
4. Single plate wafer check valve
<. Dual plate wafer check valve
Piping
73
Lafer check valves are availa!le from <A to 7=A
Covered under the regulator code 3PI 8;7.
Compact in design.
Fess pressure drop across the valve.
Fess water hammering.
3.3.* FLUSH + BOTTOM VALVE.
>suall it+s a glo!e valve tpe.
>sed to drain out piping1 vessel1 reactor.
&he disk in close position matches with the !ottom surface of tanks or
piping.
>suall inlet is one si?e higher then the outlet si?e.
&he outlet port is at an angle of 78G' 59G to the inlet port.
3vaila!le in the si?e range of 4A ' 4<A.
3vaila!le ma(imum rating of :699.
Fig,-$ 3.1. F(,&/ B%''%0 V1(2$
3.3.1. SAFETY VALVE.
3n automatic pressure relieving device actuated ! the static pressure
upstream of the valve. Characteri?ed ! rapid full opening or pop action.
>sed for steam gas or vapor service.
Piping
74
#igure 6.44 Safet Valve
3.3.11 RELIEF VALVE.
3n automatic pressure relieving device actuated ! the static pressure
upstream of the valve. Lhich opens in proportion to the sstem pressure. 3lso
the valve reseat when the pressure is reduced !elow the set pressure.
>sed primaril in liBuid service.
Piping
75
#igure 6.4< Relief Valve.
Piping
76
You might also like
- Operator's Manual-TT55-TT65-TT75-English PDFDocument129 pagesOperator's Manual-TT55-TT65-TT75-English PDFvalgorunescu@hotmail.com88% (16)
- Classification and Selection of Industrial ValvesDocument76 pagesClassification and Selection of Industrial ValvesABVSAI100% (6)
- Valve Selection Handbook: Engineering Fundamentals for Selecting the Right Valve Design for Every Industrial Flow ApplicationFrom EverandValve Selection Handbook: Engineering Fundamentals for Selecting the Right Valve Design for Every Industrial Flow ApplicationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Repair Manual B200Document460 pagesRepair Manual B200slawny7789% (9)
- Objective and Scope and Importance of Mineral Beneficiation With Special Reference To IndiaDocument4 pagesObjective and Scope and Importance of Mineral Beneficiation With Special Reference To IndiaVidya Sagar100% (1)
- Pipe Fittings, ValvesDocument10 pagesPipe Fittings, Valvesaasatti100% (1)
- Valves Gate DamperDocument54 pagesValves Gate DamperLalit MeenaNo ratings yet
- KTM512 Extended Guide ENDocument12 pagesKTM512 Extended Guide ENFilip SerafimovNo ratings yet
- Walworth Check ValvesDocument24 pagesWalworth Check ValvesFahad RockingNo ratings yet
- Valves Details and UsageDocument72 pagesValves Details and UsageKagira Drawing Soltuion100% (1)
- ValvesDocument31 pagesValvesJuber KhatibNo ratings yet
- Guide to Valve Types, Uses, Maintenance and ControlDocument44 pagesGuide to Valve Types, Uses, Maintenance and Controlأحمد محمد قدريNo ratings yet
- Control Valves ExplainedDocument58 pagesControl Valves ExplainedNIKHIL SHINDENo ratings yet
- Control Valve PDFDocument39 pagesControl Valve PDFRush SfNo ratings yet
- Conventional Valves GuideDocument23 pagesConventional Valves GuidePower PlantNo ratings yet
- Sohel Ffo ProjectDocument13 pagesSohel Ffo ProjectSANIKA TALATHINo ratings yet
- Control Valve - Theory & SizingDocument32 pagesControl Valve - Theory & SizingAmanda Porter100% (1)
- ValveDocument20 pagesValveShekhar KurmiNo ratings yet
- Actuating Systems Lecure 28Document25 pagesActuating Systems Lecure 28shahzaibkhan ccpNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Course 2.Document67 pagesInstrumentation Course 2.FACE BOOK100% (1)
- ValvesDocument108 pagesValvesGautam Wayse100% (1)
- Valve: Final Element of ControlDocument23 pagesValve: Final Element of ControlReech Dirt EpNo ratings yet
- Valve Type Used in Power PlantDocument14 pagesValve Type Used in Power PlantGourav Choudhuri0% (1)
- Piping ValvesDocument51 pagesPiping ValvesRohit Kamble100% (2)
- 9-Valves Rating9Document29 pages9-Valves Rating9Mohamed FouadNo ratings yet
- Control ValveDocument37 pagesControl Valvevipin12krishnan100% (2)
- Valves: Submitted By: Group 3 Submitted ToDocument23 pagesValves: Submitted By: Group 3 Submitted ToShruti jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Control ValvesDocument20 pagesControl ValvesSakthivel PalaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Final Control ElementsDocument79 pagesUnit 2 Final Control ElementsHatif AlamNo ratings yet
- Proces ValveDocument98 pagesProces Valvehimansh871100% (1)
- Application of Valves 1687106274Document93 pagesApplication of Valves 1687106274Muhammed RaheesNo ratings yet
- Control ValveDocument39 pagesControl Valveryukyu100% (1)
- CONTREN Series Valves GuideDocument57 pagesCONTREN Series Valves GuideKristian UretaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 ValvesDocument57 pages1.1 ValvesKristian UretaNo ratings yet
- Control Valves in 38 CharactersDocument111 pagesControl Valves in 38 CharactersAndrei SabaterNo ratings yet
- Valves: CONTREN Series # 40109-07Document57 pagesValves: CONTREN Series # 40109-07Sakthivel SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- 7 - Andre VolschenkDocument24 pages7 - Andre VolschenkPieter Vd MerweNo ratings yet
- Model 115-3: Digital Electronic Control ValveDocument36 pagesModel 115-3: Digital Electronic Control ValveBruno GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Valves Technology: Ahmed Yehia MohamedDocument71 pagesValves Technology: Ahmed Yehia Mohamedرابح أبو عبد الرحمانNo ratings yet
- Piping ValvesDocument51 pagesPiping ValvesRohit KambleNo ratings yet
- Valves 110722053925 Phpapp01Document77 pagesValves 110722053925 Phpapp01Jogi Oscar SinagaNo ratings yet
- Figure 7-7 - Plug Valve Detail: Ball ValvesDocument8 pagesFigure 7-7 - Plug Valve Detail: Ball ValvesEmad SaadNo ratings yet
- Flow Control ValvesDocument9 pagesFlow Control Valvesaryan patilNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Actuators and Control ValvesDocument35 pagesIntroduction to Actuators and Control ValvesEvans HopeNo ratings yet
- Marine Valve Types and UsesDocument31 pagesMarine Valve Types and UsesSoumya SameerNo ratings yet
- Webinar Slides Tank Blanketing 101Document28 pagesWebinar Slides Tank Blanketing 101edgardiaz5519No ratings yet
- Valves: Presented by D.Nagababu (Get-Pp)Document54 pagesValves: Presented by D.Nagababu (Get-Pp)SatishSathyamevaJayatheNo ratings yet
- Minggu12 13 PIDDocument19 pagesMinggu12 13 PIDBerdi Nak GbaNo ratings yet
- Minggu12 13 PIDDocument19 pagesMinggu12 13 PIDMuhammad Khairul FikriNo ratings yet
- Dorot S100Document36 pagesDorot S100joseph katongoNo ratings yet
- Pengetahuan - ValvesDocument8 pagesPengetahuan - ValvesivansanjayaNo ratings yet
- 3590 - Marine Piping Systems - VALVES On Shipbuilding ApplicationDocument14 pages3590 - Marine Piping Systems - VALVES On Shipbuilding ApplicationZhafira OspNo ratings yet
- Control ValveDocument39 pagesControl ValvewirawansatriaNo ratings yet
- Study of Different Types of Pipe FittingsDocument17 pagesStudy of Different Types of Pipe FittingsIzi50% (2)
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryFrom EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsFrom EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- PHS Support User GuideDocument3 pagesPHS Support User GuideRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- PHS Support User GuideDocument3 pagesPHS Support User GuideRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Variable Effort SupportsDocument29 pagesVariable Effort SupportssanmukhaNo ratings yet
- POWERGRID recruitment for Diploma TraineesDocument9 pagesPOWERGRID recruitment for Diploma TraineesRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Kalyani RevuDocument1 pageCurriculum Vitae Kalyani RevuRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Offer LaerDocument4 pagesOffer LaerRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- 2.7 PMS Rev-ADocument227 pages2.7 PMS Rev-ARaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- ChceDocument1 pageChceRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- How To Install Smartplant 3D (Step-By-Step Guide)Document2 pagesHow To Install Smartplant 3D (Step-By-Step Guide)Raju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Attachment#2 - B224-FCC-LT-111-PP-SP-0007 - REV 01Document28 pagesAttachment#2 - B224-FCC-LT-111-PP-SP-0007 - REV 01Raju NaiduNo ratings yet
- PMS - B224-FCC-LT-111-PP-SP-0001 - Rev 02. A11ADocument10 pagesPMS - B224-FCC-LT-111-PP-SP-0001 - Rev 02. A11ARaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Pipe Hanger & SupportsDocument220 pagesPipe Hanger & SupportsK.S.MAYILVAGHANANNo ratings yet
- Notepad++ ReadmeDocument5 pagesNotepad++ ReadmeRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- User Access Review GuideDocument13 pagesUser Access Review GuideRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Customisation Guide PDFDocument268 pagesCustomisation Guide PDFRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Software Customisation Reference ManualDocument336 pagesSoftware Customisation Reference ManualJorge Enrique Reyes SztayzelNo ratings yet
- BWC Company Profile Brief PLMDocument11 pagesBWC Company Profile Brief PLMRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Administrator Command Reference ManualDocument201 pagesAdministrator Command Reference ManualĐình NamNo ratings yet
- Restaurant BillDocument6 pagesRestaurant BillRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- 04 TM 1812 AVEVA Everything3D 1 1 Structural Modelling Rev 1 0 PDFDocument2 pages04 TM 1812 AVEVA Everything3D 1 1 Structural Modelling Rev 1 0 PDFRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Query Reference ManualDocument1 pageQuery Reference ManualRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Stepped View PDFDocument8 pagesStepped View PDFRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- PdmsDocument699 pagesPdmsRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- TM 1812 AVEVA Everything3D 1 1 Structural Modelling Rev 1 0 PDFDocument221 pagesTM 1812 AVEVA Everything3D 1 1 Structural Modelling Rev 1 0 PDFtrawri007No ratings yet
- Query Reference ManualDocument35 pagesQuery Reference ManualManny Mendoza100% (1)
- ISomanDocument250 pagesISomanmtirones01100% (1)
- PDMS CommandsDocument24 pagesPDMS CommandsShahrouz Raeisi85% (13)
- Government of India Ministry of Railways Railway Recruitment BoardsDocument2 pagesGovernment of India Ministry of Railways Railway Recruitment BoardsRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- Pduv PDFDocument434 pagesPduv PDFRaju NaiduNo ratings yet
- ISomanDocument250 pagesISomanmtirones01100% (1)
- WM2077CW Service ManualDocument44 pagesWM2077CW Service ManualMichael David SharkeyNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatograph OptimizationDocument18 pagesGas Chromatograph OptimizationUmair KazmiNo ratings yet
- Method of Lighting CalculationsDocument3 pagesMethod of Lighting CalculationsSpencer Josh RegedorNo ratings yet
- Rpdir-L12 Shielding WebDocument73 pagesRpdir-L12 Shielding WebWiie ArdiNo ratings yet
- Cause Effect Analysis of Oil Loss in Edible Oil IndustryDocument60 pagesCause Effect Analysis of Oil Loss in Edible Oil IndustrySaurabh RaiNo ratings yet
- Total Rewinding and Reconditioning of 3KW MotorDocument5 pagesTotal Rewinding and Reconditioning of 3KW MotorCBD COLLEGE INCNo ratings yet
- WCR For Canon Motor Relay FailureDocument1 pageWCR For Canon Motor Relay FailureIqmal WahabNo ratings yet
- SUPER PPTPPTDocument15 pagesSUPER PPTPPTsrinuNo ratings yet
- A Novel ZVS-ZCS Bi-Directional Flyback DC-DCDocument6 pagesA Novel ZVS-ZCS Bi-Directional Flyback DC-DCArceu CamposNo ratings yet
- Nikunj Sir FinalDocument32 pagesNikunj Sir FinalSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Impact of Industrial RobotsDocument14 pagesAssessing The Impact of Industrial RobotsKarthik SRSNo ratings yet
- Ed Current DynamometerDocument3 pagesEd Current DynamometerOM MUNGELWARNo ratings yet
- Enatel's microCOMPACT Power SystemDocument2 pagesEnatel's microCOMPACT Power SystemomarpatNo ratings yet
- Universal Gen Controller Manual - Digital Display, 8 Inputs, 4 RelaysDocument21 pagesUniversal Gen Controller Manual - Digital Display, 8 Inputs, 4 RelaysBrianHazeNo ratings yet
- HKBEAMDocument0 pagesHKBEAMTse Lam ChanNo ratings yet
- Air Motor Torque and Horsepower LabDocument7 pagesAir Motor Torque and Horsepower LabMelody KimNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Cutout Cylinder CutoutDocument12 pagesCylinder Cutout Cylinder CutoutIsrael Miranda ZamarcaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONICDocument13 pagesELECTRONICMahmoued YasinNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement TechniquesDocument29 pagesGround Improvement TechniquesMeEr AahilNo ratings yet
- O359h MilDocument90 pagesO359h MilNisar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Led ComponentsDocument226 pagesLed Componentselcomsrl100% (1)
- Numatics Series 342Document6 pagesNumatics Series 342Jebran FarazNo ratings yet
- Esite Bauer Poseidon Edition VE 300 850 Hengitysilmakompressori enDocument4 pagesEsite Bauer Poseidon Edition VE 300 850 Hengitysilmakompressori enrolandoNo ratings yet
- Repair and RehabilitationDocument22 pagesRepair and RehabilitationConstro FacilitatorNo ratings yet
- ZhangDocument21 pagesZhangjajajaja21No ratings yet
- Enclosed Control Product Guide: April 2008Document456 pagesEnclosed Control Product Guide: April 2008MED-ROBIN2000No ratings yet