Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 2013-2-1
Uploaded by
Min Ko SoeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 2013-2-1
Uploaded by
Min Ko SoeCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Physical Chemistry Assignment
AUTUMN SESSION 2013
School of Science and Health
Due: 1 pm Thursday 6
th
June 2013.
You must submit a hard copy of the answers, and attach a signed
assignment cover sheet.
2
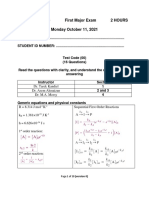
USEFUL FORMULAE AND DATA
w = - nRT ln (V
2
/V
1
) S = nR ln (V
2
/V
1
) G = nRT ln (P
2
/P
1
)
G
0
= H
0
- TS
0
G = G
0
+ RT lnK G
0
= -FE
0
E = E
0
(RT/F) lnK
a
A
=
A
[A] log
= - |z
+
z
-
| 0.509 I
1/2
I = (m
+
z
+
2
+ m
-
z
-
2
) R = 8.314 J K
-1
mol
-1
N
A
= 6.022 x 10
23
mol
-1
h = 6.626 x 10
-34
J s k
B
= 1.381 x 10
-23
J K
-1
F = 96500 C mol
-1
CH
3
CH
2
OH
(g)
CH
3
COOH
(g)
CH
3
CH
2
OOCCH
3(g)
H
2
O
(g)
H
0
/ kJ mol
-1
-231 -435 -443 -242
S
0
/ J K
-1
mol
-1
283 285 363 189
Fe
2+
(aq)
+ 2 e Fe
(s)
E
0
= - 0.41 V
Al
3+
(aq)
+ 3 e Al
(s)
E
0
= -1.66 V
ClO
3
-
(aq)
+ 3 H
+
+ 2 e HClO
2(aq)
+ H
2
O E
0
= 1.21 V
fumarate
2-
+ 2 H
+
+ 2 e
-
succinate
2-
E
0
= 0.03 V
pyruvate
-
+ 2 H
+
+ 2 e
-
lactate
-
E
0
= -0.18 V
lnA
t
lnA
0
= -k
1
t 1/A
t
- 1/A
0
= k
2
t
3
1 Suppose 100 g of ethane (C
2
H
6
) expands isothermally at 350
0
C from 50 mL to 2 L.
Calculate the heat and work done by the system, and the change in Entropy if:
i) the process is via a reversible path (sketch the pathway)
ii) the process is non-reversible (sketch the pathway)
iii) which pathway will require the least work and why?
iv) why are these processes done isothermally?
v) why can a real process never convert completely heat to work?
(10 marks)
2 Calculate the enthalpy and entropy change for the following reaction:
CH
3
CH
2
OH
(g)
+ CH
3
COOH
(g)
CH
3
CH
2
OOCCH
3(g)
+ H
2
O
(g)
(5 marks)
3 The Gibbs Free Energy for the reaction: A + B C was measured as a function of
temperature:
G
0
/ kJ mol
-1
26.6 28.1 29.7 31.3
T
0
C 0 20 40 60
a) Calculate the enthalpy and entropy changes for the reaction
b) Comment on the signs of the change in entropy, enthalpy and the effect of increase in
temperature on the equilibrium constant.
c) Predict the equilibrium constant at 100
0
C.
d) If the initial concentrations are A = 1 M, B = 0.1 M, C = 0.01 M at 100
0
C, will the system
produce reactants or products as the reaction comes to equilibrium? Why?
(15 marks)
4 a) Calculate the standard cell potential for ONE of the reactions (acidic conditions):
Fe
(s)
+ ClO
3
-
(aq)
Fe
2+
(aq)
+ HClO
2(aq)
succinate ion
O
O
-
O
-
O
O
O
-
O
-
O
fumarate ion
OH
O
O
-
lactate ion
+
O
O
O
-
pyruvate ion
+
b) Calculate the change in Gibbs Free Energy for this reaction.
c) Calculate the equilibrium constant at 298.15
0
C. Comment on its magnitude.
(10 marks)
4
5 a) Discuss the general features of the Debye-Hckel theory of electrolyte solutions.
b) Calculate the reduction potential for 0.1 M Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
.
(10 marks)
6 a) A radioactive isotope of technetium is produced at Lucas Heights for use in medical
imaging and it has a half life of 61 days. What percent of the initial sample remains
after 2 weeks?
b) The kinetics data for a reaction with the following stoichiometric equation was
measured:
CH
3
COOCH
3(aq)
+ OH
-
(aq)
CH
3
COO
-
(aq)
+ CH
3
OH
(aq)
t / s 0 50 100 150 200
[Ester] / mol L
-1
0.500 0.051 0.027 0.018 0.013
i) Find the overall order of the reaction, the rate constant, and the half-life of the reaction
ii) Comment on the order found from experiment compared to the stoichiometry of this
reaction?
(15 marks)
7 A mechanism for the reaction:
2A + B 2D
is:
2A C
C 2A
B + C 2D
Derive a theoretical rate equation for the production of D from this mechanism using the
steady state approximation, and predict effects on the observed kinetics if k
3
<< k
1
.
(5 marks)
k
1
k
2
k
3
5
8 Give a short answer for two of the following questions:
a) Explain thermodynamic factors such as activity, Gibbs energy, potential and voltage-
gated channels for controlling the flow of ions across biological membranes.
b) Explain hydrophobic interaction in biomolecular and thermodynamic terms. Use
examples of biological molecules.
c) What experimental procedures can be used to measure U and H for a reaction? Sketch
the apparatus.
d) Explain how Collision Theory gives information about the pre-exponential factor and
activation energy of reactions.
(5 marks)
6
7
8
9
You might also like
- Kinetics Homework 3Document4 pagesKinetics Homework 3RizkiNo ratings yet
- Course For Loco Inspector Initial (Diesel)Document239 pagesCourse For Loco Inspector Initial (Diesel)Hanuma Reddy93% (14)
- ASTM A581 A581M-95bDocument3 pagesASTM A581 A581M-95bFeteneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cumulative Review: Multiple ChoiceDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Cumulative Review: Multiple ChoiceJ. LeeNo ratings yet
- Explaining Zambian Poverty: A History of Economic Policy Since IndependenceDocument37 pagesExplaining Zambian Poverty: A History of Economic Policy Since IndependenceChola Mukanga100% (3)
- CHPR3432 Tute 1 QuestionsDocument2 pagesCHPR3432 Tute 1 QuestionsCallum BiggsNo ratings yet
- Run Great Race (Race - Exe) - Turn in The Last Page of The Program With Performance Number.Document6 pagesRun Great Race (Race - Exe) - Turn in The Last Page of The Program With Performance Number.Aman SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13-ChemicalKineticsDocument4 pagesChapter 13-ChemicalKineticsKhurram KhanNo ratings yet
- 2007 ADocument4 pages2007 AAmiro MayraNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document8 pagesProblem Set 1Bj LarracasNo ratings yet
- Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument28 pagesChemical Thermodynamicscorey6No ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Prvs-Qn-6. Thermodynamics Q & ADocument10 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Prvs-Qn-6. Thermodynamics Q & AshineNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics Class 12th Practice PaperDocument8 pagesChemical Thermodynamics Class 12th Practice PaperLiyutsa ZirangeNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No.3Document1 pageProblem Set No.3Jediann BungagNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 119 Ques!!!Document27 pagesChemical Kinetics 119 Ques!!!elifnazNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-5. Thermodynamics Q & ADocument11 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-5. Thermodynamics Q & AarnadicgamingNo ratings yet
- 201B Work 1 KineticsDocument9 pages201B Work 1 Kineticsahraz93No ratings yet
- Tutorial Kit (Chemistry-100 L) - Vol. 2Document30 pagesTutorial Kit (Chemistry-100 L) - Vol. 2Terhemen AnjiraNo ratings yet
- 11 02 2012 Xii Abcd Part Test IIIssssssssssssssssssssssDocument13 pages11 02 2012 Xii Abcd Part Test IIIssssssssssssssssssssssvishal1100850% (1)
- Tutorial 2 StudentDocument6 pagesTutorial 2 StudentIrsyad KamilNo ratings yet
- 2014 Midterm SolutionsDocument11 pages2014 Midterm SolutionsDuncan StrayerNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry 2010 Free-Response Questions Form B: The College BoardDocument13 pagesAP Chemistry 2010 Free-Response Questions Form B: The College BoardDharul Handri PranawaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics AP ChemistryDocument17 pagesThermodynamics AP ChemistryprojayjayNo ratings yet
- Kinetics AnswersDocument19 pagesKinetics AnswersAlielson Botelho100% (1)
- III Kinetics & Equilibrium-ReviewDocument3 pagesIII Kinetics & Equilibrium-ReviewChinmaya Ranjan BiswalNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1212 202002 Exam 1 Form A KeyDocument7 pagesCHEM 1212 202002 Exam 1 Form A KeyHamza AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 122 Kinetics and Equilibrium Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesChemistry 122 Kinetics and Equilibrium Exam ReviewKyle GeryczNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 2011Document3 pagesChemistry 1 2011MuhammadUsman KhanNo ratings yet
- CM1502 Tutorial 6: P, M 2 - 1 - 1 2 - 1 - 1 2 - 1 - 1 Fus - 1 Vap - 1Document2 pagesCM1502 Tutorial 6: P, M 2 - 1 - 1 2 - 1 - 1 2 - 1 - 1 Fus - 1 Vap - 1Jim HippieNo ratings yet
- CHEM311 211 Major2 SolvedDocument9 pagesCHEM311 211 Major2 SolvedhussainNo ratings yet
- CHEM2 Long Quiz 2Document4 pagesCHEM2 Long Quiz 2Maria Leonora PaltaoNo ratings yet
- Handout 7Document20 pagesHandout 7axganiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Manual CH1002Document18 pagesTutorial-Manual CH1002Gift Chulu100% (2)
- S-Cool A Level Chemistry Practice Questions and AnswersDocument28 pagesS-Cool A Level Chemistry Practice Questions and AnswersMaruf Hassan100% (1)
- Review Questions: Medicinal Chemistry 300550Document49 pagesReview Questions: Medicinal Chemistry 300550vanyarufusNo ratings yet
- NS102 200902 ProblemSet4Document7 pagesNS102 200902 ProblemSet4Peren CoşkunNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium WorksheetDocument6 pagesEquilibrium WorksheetGiselleNo ratings yet
- Exam I Review QuestionsDocument9 pagesExam I Review QuestionsRylan SmolikNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Multiple Choice ReviewDocument33 pagesEquilibrium Multiple Choice ReviewXUNo ratings yet
- Kinetics ReviewDocument5 pagesKinetics ReviewbrittanypriyaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam I - AnswerDocument5 pagesMidterm Exam I - AnswerJames_Kuo_80No ratings yet
- AP Ch. 12-13 Kinetics & Equilibrium Review AnswersDocument35 pagesAP Ch. 12-13 Kinetics & Equilibrium Review AnswersRucar Rad0% (1)
- CHM 096 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesCHM 096 Tutorial 1Muhammad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- C CC CDocument9 pagesC CC CAkhil KhannaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial XIDocument2 pagesTutorial XIhetNo ratings yet
- Practice Final Exam - CHEM102 - Spring 2023Document7 pagesPractice Final Exam - CHEM102 - Spring 2023mmmNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam Example Midterm KeyDocument7 pagesPractice Exam Example Midterm KeymebrahtomNo ratings yet
- 2011 Final AnswerDocument8 pages2011 Final Answerxuan1002No ratings yet
- Chemistry XI PT-2 Final PAPERDocument3 pagesChemistry XI PT-2 Final PAPERJoshua ZongteNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 ReviewDocument3 pagesExam 1 ReviewShanty FelizNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - THTDocument25 pagesThermodynamics - THTannodalNo ratings yet
- Eamcet 2008 EnggDocument15 pagesEamcet 2008 EnggjanmanchiNo ratings yet
- 2020-2021.HK2 - cuối kìDocument8 pages2020-2021.HK2 - cuối kìthuan phamNo ratings yet
- Phase EquilibriaDocument6 pagesPhase EquilibriaIlwandy KosasihNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Problem SetDocument6 pagesChemical Kinetics Problem Setascd_msvuNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Mc1Document6 pagesKinetics Mc1hylee102594No ratings yet
- Conceptests in Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Unit 3: Fluid Phase Equilibria in MixturesDocument68 pagesConceptests in Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Unit 3: Fluid Phase Equilibria in MixturesLance MeyersNo ratings yet
- 1-8 Reaction Kinetics PDFDocument8 pages1-8 Reaction Kinetics PDFBerry101No ratings yet
- Ki KBR H C Ki BR H C: Oducts B ADocument2 pagesKi KBR H C Ki BR H C: Oducts B AnaverfallNo ratings yet
- Paper: Chemistry:: Chemistry MCQ: Chemical KineticsDocument10 pagesPaper: Chemistry:: Chemistry MCQ: Chemical KineticsShakeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chem 1120 - Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium Practice Quiz 1Document10 pagesChem 1120 - Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium Practice Quiz 1Danielle Lois AbagNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Selected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionFrom EverandSelected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Feasibility Study of Creating Spaces For Cultural Tourism Under The Floating Market Concept at Nong Han Lake, Sakon Nakhon, ThailandDocument5 pagesFeasibility Study of Creating Spaces For Cultural Tourism Under The Floating Market Concept at Nong Han Lake, Sakon Nakhon, ThailandInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument29 pagesElectricity and MagnetismNashrul HaqNo ratings yet
- Responsible Living: Mantri DevelopersDocument15 pagesResponsible Living: Mantri Developersnadaf8No ratings yet
- Aabroo Recyclable Waste Program Survey: 1. Demographic InformationDocument2 pagesAabroo Recyclable Waste Program Survey: 1. Demographic InformationIqra KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Text 5Document7 pagesText 5santoshkumarray490No ratings yet
- Soal Pat Bahasa Inggris Kelas 5Document5 pagesSoal Pat Bahasa Inggris Kelas 5Tini Bastuti Joyolaksono100% (1)
- tmpE0D4 TMPDocument7 pagestmpE0D4 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- 2019 BMS1021 Practice Questions Answers PDFDocument12 pages2019 BMS1021 Practice Questions Answers PDFaskldhfdasjkNo ratings yet
- Research Argumentative EssayDocument6 pagesResearch Argumentative EssayHoney LabajoNo ratings yet
- List of Irc Publications Referred To in The Specifications: AppendicesDocument17 pagesList of Irc Publications Referred To in The Specifications: AppendicesPrasad BoniNo ratings yet
- SMA - Core 1 - IEC62109-2 - 0 Test ReportDocument6 pagesSMA - Core 1 - IEC62109-2 - 0 Test ReportFurqan HamidNo ratings yet
- Moving Money Box: Pig (Assembly Instructions) : The Movements Work Better With Heavier CoinsDocument6 pagesMoving Money Box: Pig (Assembly Instructions) : The Movements Work Better With Heavier CoinsjuanNo ratings yet
- The Greek LettersDocument18 pagesThe Greek LettersSupreet GuptaNo ratings yet
- 0707-Passive VoiceDocument6 pages0707-Passive VoiceKhôi TrầnNo ratings yet
- TL K1 2 1 04 VSD35 Varyset DE enDocument25 pagesTL K1 2 1 04 VSD35 Varyset DE enAkilaJosephNo ratings yet
- National Railway Museum Annual Review 04-05Document40 pagesNational Railway Museum Annual Review 04-05sol.loredo1705530No ratings yet
- Yoga ProjectDocument5 pagesYoga ProjectSouri Rajan CaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFIfwat ThaqifNo ratings yet
- Question Paper - GIAN - 19 - ModifiedDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper - GIAN - 19 - Modifiedsayan mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Unit-1 (Network Operating System) : Session: 2021-22Document17 pagesLecture Notes Unit-1 (Network Operating System) : Session: 2021-22Pradeep BediNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic DesignDocument38 pagesDigital Logic DesignAri BaderNo ratings yet
- 8v92ta DetroitDocument554 pages8v92ta Detroit10000389% (9)
- HandbikeDocument10 pagesHandbikeLely JuniariNo ratings yet
- LC Magna Leaflet 2019Document2 pagesLC Magna Leaflet 2019saemiNo ratings yet
- Meal Planning Guide e BookDocument7 pagesMeal Planning Guide e BookA'isha TijjaniNo ratings yet
- Union Fork & Hoe No. 19Document68 pagesUnion Fork & Hoe No. 19Jay SNo ratings yet