Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Methodologieschart
Uploaded by
Marwah ZagzougCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Methodologieschart
Uploaded by
Marwah ZagzougCopyright:
Available Formats
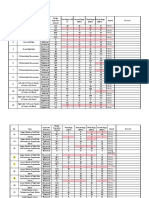
Summary of Research Methodologies by Paula Muirhead
Area of Research:
Legend
Appealing I CT Conceptual Theorist Holistic and imaginative
Unappealing II AS Analytical Scientist Exactness, precision and unambiguous situations
No Opinion III PH Particular Humanist Personal and rational knowledge
? Possibility IV CH Conceptual Humanist Holistic knowledge to better humanity
(Adapted from Week One Lecture >> Choosing Your Research/Topic: What type of cook (researcher) are you?)
Relation
to Topic
Research Method Archetype Brief Overview
CT AS PH CH
1 Action Research III Action learning and collaboration
2 Appreciative Inquiry IV Action research that leads to developmental changes
3 Case Study Research IV Observation and analysis to determine patterns
4 Casual Comparative
Research
The use of variables to determine outcomes
5 Content Analysis IV Quantifies and analyzes data and make inferences
6 Correlational Research Collects data to determine relationships between two or more quantifiable
variables
7 Critical Incident
Technique (CIT)
III Studies focus on human behavior and quantifying it
8 Delphi Research I IV Using data/findings to predict future problems and foresee solutions
9 Descriptive Research I Utilizes elements of qualitative and quantitative research to gather data for
correlational, developmental, and observation studies
10 Design-Based Research
or Decision Analysis
II Links process to outcomes
11 Ethnographic Investigation of cultural norms, beliefs, patterns, and social structures
12 Evaluation Research Determines effectiveness of current programs and evaluate different areas such as
outcomes, costs, etc.
13 Experimental Research II Variables are manipulated and results are analyzed
14 Factor Analysis Uses a statistical approach to analyze interrelationships
15 Grounded Theory III IV Uses theory to explain a process or action to discover the implicit in data
16 Hermeneutic Research III Activities and things are studied for what they mean
17 Historical Research IV Utilizes elements of qualitative and quantitative data to show meanings and
significance of activities, etc.
18 Meta-Analysis
Research
Data are collected from several sources to find patterns that will guide future
decisions or actions
19 Narrative Research Data is collected through stories that reports on individual experiences
20 Needs Assessment Systematic process of asking questions and comparing answers for developing
new programs, etc.
21 Phenomenography III IV Empirical research designed to answer questions about thinking and learning
22 Phenomenology Qualitative research based on lived experiences
23 Quasi-experimental II Involves manipulation of one or more independent variables
24 Q-Method I Systematic study of subjectivity
25 Regression
Discontinuity Design
(RD)
II Determines effectiveness of current program or treatment
26 Retrospective Record
Review
II Data is collected to compare two similar groups
27 Semiology II III Research focuses on the meaning of symbols that models after human thoughts
and actions
28 Situational Analysis Postmodern approach to grounded theory that seeks to reveal complex
connections
29 Trend Analysis
Research
II Research focus is on prediction and forecast of future direction or trends
30 True Experimental
Research
Research situation isolates variable of interests and controls
Note: Column two is unique to the researcher. , x, - ?
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Fuse Box Diagram JeepDocument7 pagesFuse Box Diagram JeepSumedin Nisic100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Fall 17 Masters GuideDocument50 pagesFall 17 Masters GuideShivam Agarwal80% (5)
- Wilkins, A Zurn Company: Demand Forecasting: AssignmentDocument9 pagesWilkins, A Zurn Company: Demand Forecasting: AssignmentYogendra RathoreNo ratings yet
- Project SynopsisDocument2 pagesProject SynopsisEkam JotNo ratings yet
- Man Pa-4000Document18 pagesMan Pa-4000JOEY76BYNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Quality in XeroxDocument29 pagesEvolution of Quality in XeroxJappreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Serdes HandbookDocument98 pagesSerdes HandbookRamesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Obtaining Technology - ImplementationDocument13 pagesObtaining Technology - ImplementationEric EugenioNo ratings yet
- Working of Fingerprint ScannerDocument5 pagesWorking of Fingerprint ScannerSahana BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Oops-Program 10-MduDocument6 pagesOops-Program 10-MduAtul MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Participatory EvaluationDocument4 pagesParticipatory EvaluationEvaluación Participativa100% (1)
- K Sera Sera CaseDocument12 pagesK Sera Sera CaseAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Sci20 Unitb 1 8Document8 pagesSci20 Unitb 1 8api-207957230No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Hydraulic JumpDocument31 pagesChapter 5 Hydraulic JumpUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Expansion Indicator Boiler #1Document6 pagesExpansion Indicator Boiler #1Muhammad AbyNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument42 pagesPDFMohd Nizamuddin Mohamad NoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Step 2 Comprehend Intellectual Property: Valuation and Negotiation of TechnologyDocument16 pagesUnit 1 - Step 2 Comprehend Intellectual Property: Valuation and Negotiation of TechnologyGiovanny MicNo ratings yet
- Mamuli N22Document28 pagesMamuli N22doubeNo ratings yet
- Gmail - CAMPUS DRIVE NOTIFICATION - Himadri Speciality Chemical LTDDocument2 pagesGmail - CAMPUS DRIVE NOTIFICATION - Himadri Speciality Chemical LTDShresth SanskarNo ratings yet
- Fluid FrictionDocument10 pagesFluid FrictionUmesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Buku Program Kopo 18Document20 pagesBuku Program Kopo 18Mieza Binti YusoffNo ratings yet
- Employee Departure Clearance FormDocument1 pageEmployee Departure Clearance FormJery TomNo ratings yet
- 5 Star SynopsisDocument22 pages5 Star Synopsisabdul wahidNo ratings yet
- Amca - 201 Fans and SystemsDocument80 pagesAmca - 201 Fans and SystemsenricoNo ratings yet
- Material Submittal R0-BMS - 10 Schools PDFDocument216 pagesMaterial Submittal R0-BMS - 10 Schools PDFElektrikal InhinyeroNo ratings yet
- Linguistic Determinism & Linguistic RealismDocument1 pageLinguistic Determinism & Linguistic RealismTünde KovácsNo ratings yet
- Title Proposal Form For StudentsDocument3 pagesTitle Proposal Form For StudentsHelen AlalagNo ratings yet
- EM Console Slowness and Stuck Thread IssueDocument10 pagesEM Console Slowness and Stuck Thread IssueAbdul JabbarNo ratings yet
- Don Honorio Ventura Technological State University: Dr. Enrique G. BakingDocument1 pageDon Honorio Ventura Technological State University: Dr. Enrique G. BakingJulianne DucutNo ratings yet
- Proses Manufaktur: Machining Operation and Machine ToolsDocument34 pagesProses Manufaktur: Machining Operation and Machine ToolsLyndaNo ratings yet