Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cloreto de Cetilpiridínio
Uploaded by
tuliopdrOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cloreto de Cetilpiridínio
Uploaded by
tuliopdrCopyright:
Available Formats
Cetylpyridinium Chloride
1 Nonproprietary Names
BP: Cetylpyridinium Chloride
PhEur: Cetylpyridinium Chloride
USP: Cetylpyridinium Chloride
2 Synonyms
C16-alkylpyridinium chloride; Cepacol; Cepacol chloride; Ceta-
miun; cetylpridinii chloridum; cetyl pyridium chloride; Dobendan;
hexadecylpyridinium chloride; 1-hexadecylpyridinium chloride;
Medilave; Pristacin; Pyrisept.
3 Chemical Name and CAS Registry Number
1-Hexadecylpyridinium chloride [123-03-5]
1-Hexadecylpyridinium chloride monohydrate [6004-24-6]
4 Empirical Formula and Molecular Weight
C
21
H
38
ClN 339.9 (for anhydrous)
C
21
H
38
ClNH
2
O 358.1 (for monohydrate)
5 Structural Formula
6 Functional Category
Antimicrobial preservative; antiseptic; cationic surfactant; disin-
fectant; solubilizing agent; wetting agent.
7 Applications in Pharmaceutical Formulation or
Technology
Cetylpyridinium chloride is a quaternary ammonium cationic
surfactant, used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations as
an antimicrobial preservative; see Section 10. It is used therapeu-
tically as an antiseptic agent; used alone or in combination with
other drugs for oral and throat care; used in nonparenteral
formulations licensed in the UK; and used in oral and inhalation
preparations at concentrations of 0.021.5 mg (see Section 16).
Mouthwashes containing cetylpyridinium chloride have been
shown to inhibit plaque formation,
(13)
although efficacy is variable
owing to limited published data.
(4,5)
8 Description
Cetylypyridinium chloride is a white powder with a characteristic
odor. It is slightly soapy to the touch.
9 Pharmacopeial Specifications
See Table I.
Table I: Pharmacopeial specifications for cetylpyridinium chloride.
Test PhEur 6.0 USP 32
Absorbance
Acidity
Amines and amine salts
Appearance of solution
Characters
Heavy metals 40.002%
Identification
Melting range 80.084.08C
Pyridine
Residue on ignition 40.2%
Sulfated ash 40.2%
Water 4.55.5% 4.55.5%
Assay 96.0101.0% 99.0102.0%
10 Typical Properties
Antibacterial activity Bactericidal to Gram-positive bacteria;
relatively ineffective against some Gram-negative bacteria.
(6)
Cetylpyridinium chloride is also antibacterial against a number
of oral bacteria;
(7)
see Table II.
(8)
Melting point 80838C
Solubility Freely soluble in water; very soluble in chloroform;
very slightly soluble in ether; insoluble in acetone, acetic acid,
and ethanol.
Critical micelle concentration 0.34 g/L (water, 258C).
(9,10)
Table II: Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for cetylpyridinium
chloride.
(8)
Microorganism MIC (mg/mL)
Staphylococcus aureus <2.0
Bacillus subtilis <2.0
Salmonella typhimurium 8.0
Pseudomonas aeruginosa 16.0
Streptococcus pyogenes <2.0
11 Stability and Storage Conditions
Cetylpyridinium chloride is stable under normal conditions. It
should be stored in well-closed containers.
12 Incompatibilities
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and bases. It is also
incompatible with methylcellulose.
Magnesium stearate suspensions in cetylpyridinium chloride
have been shown to significantly reduce its antimicrobial activity.
This is due to the absorption of cetylpyridinium chloride on
magnesium stearate.
(11)
The cetylpyridinium chloride ion also
interacts with gelatin, resulting in reduced bioavailability.
(12)
13 Method of Manufacture
Cetylpyridinium chloride is prepared from cetyl chloride by
treatment with pyridine.
14 Safety
Cetylpyridinium chloride is used widely in mouthwashes as a
bactericidal antiseptic. It is generally regarded as a relatively
C
157
You might also like
- Pharmacognosy & PhytochemistryDocument73 pagesPharmacognosy & PhytochemistryAsif Hasan Niloy100% (2)
- Extracting Dna From Whole BloodDocument21 pagesExtracting Dna From Whole BloodJaninepaciaNo ratings yet
- Fish Farming Manual Fish Farming ManualDocument51 pagesFish Farming Manual Fish Farming ManualPeter MukunzaNo ratings yet
- Merox Operating ManualDocument76 pagesMerox Operating ManualManish Kalra50% (2)
- The Pesticide Manual PDFDocument561 pagesThe Pesticide Manual PDFthaingolamvien71% (21)
- A New Generation of Preservatives For Cosmetic FormulationsDocument5 pagesA New Generation of Preservatives For Cosmetic FormulationsKingson_786100% (1)
- 10 MCQDocument40 pages10 MCQPragnesh Parmar0% (1)
- Maleic Anhydride - WikipediaDocument31 pagesMaleic Anhydride - WikipediaObaidullah ObaidiNo ratings yet
- Glycerol: Glycerine (Song)Document17 pagesGlycerol: Glycerine (Song)Chaeyoung SonNo ratings yet
- 5.polymer ProfileDocument5 pages5.polymer ProfileLoki MrPerfectNo ratings yet
- Model Answer: Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological UniversityDocument7 pagesModel Answer: Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological UniversityPrathiNo ratings yet
- Opinion SCCS On Acid Blue 62Document19 pagesOpinion SCCS On Acid Blue 62Nana AyraNo ratings yet
- Cetyl ChlorideDocument4 pagesCetyl ChlorideDeniz ışıkNo ratings yet
- Kathon CG MsdsDocument9 pagesKathon CG MsdsKhairil MahpolNo ratings yet
- Application A1047 Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose As A Food Additive in Wine Risk and Technical Assessment ReportDocument8 pagesApplication A1047 Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose As A Food Additive in Wine Risk and Technical Assessment ReportSyarifatul IzzaNo ratings yet
- Dequalinium chloride monograph summaryDocument2 pagesDequalinium chloride monograph summaryMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Dey-Engley Neutralizing BrothDocument2 pagesDey-Engley Neutralizing BrothAnonymous WxIzg7tNo ratings yet
- CREMOPHORDocument6 pagesCREMOPHORNezz InezNo ratings yet
- Potassium Hydroxide TR 1 - 22 - 16Document13 pagesPotassium Hydroxide TR 1 - 22 - 16Nurul RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- 1965 - Ohta - Pyridoxine-3,4-Diacylates and Their Use in CosmeticsDocument10 pages1965 - Ohta - Pyridoxine-3,4-Diacylates and Their Use in CosmeticsymiyazyNo ratings yet
- Vitamin C: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument8 pagesVitamin C: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDanny FentomNo ratings yet
- Acrolein: Acrolein (Systematic Name: Propenal) Is The SimplestDocument7 pagesAcrolein: Acrolein (Systematic Name: Propenal) Is The SimplestDjordje IvanovicNo ratings yet
- Glutaradehyde: CAS N°: 111-30-8Document83 pagesGlutaradehyde: CAS N°: 111-30-8gplese0No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Excipient ProfileDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Excipient ProfileSandeepNo ratings yet
- NadeemDocument6 pagesNadeemmalik usamaNo ratings yet
- CapreomycinDocument1 pageCapreomycinAnonymous JXKgWBjerNo ratings yet
- Citricidal Brochure PDFDocument5 pagesCitricidal Brochure PDFtvt_loverNo ratings yet
- Optimizing granulation of DCPT tabletsDocument40 pagesOptimizing granulation of DCPT tabletsDhaval DudhatNo ratings yet
- M031IDocument3 pagesM031Idarrendelfinoy9No ratings yet
- Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesSafety Data SheetDaine MarconNo ratings yet
- M080. LSTDocument3 pagesM080. LSToktaNo ratings yet
- CM0995 Burkholderia Cepacia Agar Base - TDSDocument2 pagesCM0995 Burkholderia Cepacia Agar Base - TDSAna ParaveNo ratings yet
- Retinol Product InformationDocument3 pagesRetinol Product InformationMarrauNo ratings yet
- Calcium Carbonate - Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument4 pagesCalcium Carbonate - Pharmaceutical ExcipientsRoger (Sisfarma)100% (4)
- 3 CaCO3Document3 pages3 CaCO3Yesid CepedaNo ratings yet
- Salicyl Alcohol - WikipediaDocument1 pageSalicyl Alcohol - WikipediathhNo ratings yet
- Adipic Acid - Wikipedia PDFDocument24 pagesAdipic Acid - Wikipedia PDFKalpesh DetheNo ratings yet
- ISR IH ISR 2000-17 BHTPDocument7 pagesISR IH ISR 2000-17 BHTPMaria Inês HarrisNo ratings yet
- Acrylonitrile: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument5 pagesAcrylonitrile: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchsheetalNo ratings yet
- TDS M198Document3 pagesTDS M198Muhammad ErdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology: - AntibioticsDocument20 pagesMolecular Biology: - Antibioticsrw333333No ratings yet
- Diphenyl Ether Is The Organic CompoundDocument17 pagesDiphenyl Ether Is The Organic CompoundIslamic WorldNo ratings yet
- Bab8 Msds LibrDocument5 pagesBab8 Msds LibrFajri Ashfi RayhanNo ratings yet
- Access 25 (OH) Vitamin D Assay Total IFUDocument16 pagesAccess 25 (OH) Vitamin D Assay Total IFUcarineNo ratings yet
- Spec Tween 80 PDFDocument2 pagesSpec Tween 80 PDFtary_nuryanaNo ratings yet
- P 4780 PisDocument2 pagesP 4780 Pisabhi200291No ratings yet
- Citric Acid Anhydrous AUDocument3 pagesCitric Acid Anhydrous AUTrisNo ratings yet
- AcetonitrileDocument7 pagesAcetonitriletechzonesNo ratings yet
- Oligopeptide 10 Productinformation ExperChem PDFDocument2 pagesOligopeptide 10 Productinformation ExperChem PDFLndNo ratings yet
- EksipienDocument4 pagesEksipienAgung PermataNo ratings yet
- SRB-Hydraulic 46ES Oil MSDSDocument4 pagesSRB-Hydraulic 46ES Oil MSDSBen WigginsNo ratings yet
- 107 - Uk51081 Ifu 25oh-Direct ElisaDocument8 pages107 - Uk51081 Ifu 25oh-Direct Elisad208dgNo ratings yet
- Citric 032012 FRDocument37 pagesCitric 032012 FRAlbin JolyNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To Information: IS 5057 (1997) : Potassium Nitrite, Food Grade (FAD 8: Food Additives)Document8 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To Information: IS 5057 (1997) : Potassium Nitrite, Food Grade (FAD 8: Food Additives)akNo ratings yet
- Vit DDocument8 pagesVit Dzara0% (1)
- Mercolite PSSDocument1 pageMercolite PSSDoru StefanNo ratings yet
- Clostridial Agar: Intended UseDocument3 pagesClostridial Agar: Intended Usesg.comNo ratings yet
- Methacrylic AcidDocument19 pagesMethacrylic AcidEr Bali PandhareNo ratings yet
- Texapon R K 12 P PH eDocument4 pagesTexapon R K 12 P PH ePedro MelendezNo ratings yet
- Litmus SM Broth: Intended Use: CompositionDocument3 pagesLitmus SM Broth: Intended Use: Compositionyayu sainaNo ratings yet
- Application Note: 0008 - Bilberry For Anthocyanidins by HPLCDocument4 pagesApplication Note: 0008 - Bilberry For Anthocyanidins by HPLCFábio Teixeira da SilvaNo ratings yet
- C 9394 PisDocument2 pagesC 9394 PisSandy BelNo ratings yet
- Glycochemical Synthesis: Strategies and ApplicationsFrom EverandGlycochemical Synthesis: Strategies and ApplicationsShang-Cheng HungNo ratings yet
- Vetiver (Type of Grass)Document12 pagesVetiver (Type of Grass)p6a4nduNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 4th Edition by Mathews Holde Appling Cahill ISBN Test BankDocument12 pagesBiochemistry 4th Edition by Mathews Holde Appling Cahill ISBN Test Bankdoris100% (24)
- 11 Cbse Chemistry Organic ChemistryDocument22 pages11 Cbse Chemistry Organic ChemistryKrish KakkarNo ratings yet
- Technical Documentation AnchorFix 2Document17 pagesTechnical Documentation AnchorFix 2TimoNo ratings yet
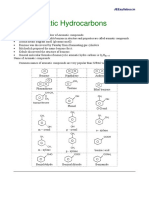
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonskailashNo ratings yet
- 1.1 (P) Oxidation & ReductionDocument10 pages1.1 (P) Oxidation & ReductionChel SonNo ratings yet
- Purine Intake, Knowledge Level Linked to Uric Acid LevelsDocument11 pagesPurine Intake, Knowledge Level Linked to Uric Acid Levelssiti nurhidayahNo ratings yet
- 3G Metric A4 Overview PDFDocument8 pages3G Metric A4 Overview PDFDiadam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cleaner TechnologiesDocument40 pagesCleaner TechnologiesMisganaw MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Vaishali Randive, Et AlDocument8 pagesVaishali Randive, Et AlOENDRIL DASNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science - PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesIntegrated Science - PhotosynthesisResh JagessarNo ratings yet
- Wells Plastics Additives For Polyethylene ExtrusionDocument4 pagesWells Plastics Additives For Polyethylene ExtrusionmohammedNo ratings yet
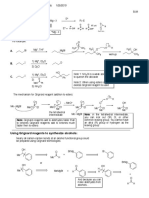
- Using Grignard Reagents To Synthesize Alcohols:: O H C CHDocument3 pagesUsing Grignard Reagents To Synthesize Alcohols:: O H C CHSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Photodegradation of Pharmaceutical Antibiotics OnDocument13 pagesPhotodegradation of Pharmaceutical Antibiotics OnNAMRATA KAMATNo ratings yet
- Sample & Assay TechnologiesDocument4 pagesSample & Assay Technologieskeven319hk4304No ratings yet
- IPEP Certification Guide for QEP and EPI ExamsDocument20 pagesIPEP Certification Guide for QEP and EPI ExamsNada HajriNo ratings yet
- Hydration of Acetylene To Acetaldehyde Using K (Run' (EDTA-II) C11211a0Document7 pagesHydration of Acetylene To Acetaldehyde Using K (Run' (EDTA-II) C11211a0Syuhadah NoordinNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences P2 May-June 2017 EngDocument19 pagesPhysical Sciences P2 May-June 2017 EngThando ChebaseNo ratings yet
- Li Et Al., 2020Document13 pagesLi Et Al., 2020niranjan gowdaNo ratings yet
- Nestle Coc 2016 SeptDocument9 pagesNestle Coc 2016 SeptGruuNo ratings yet
- Transition Elements AND COORDINATION CHEMISTRY PDFDocument50 pagesTransition Elements AND COORDINATION CHEMISTRY PDFAniruddha KawadeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry PDFDocument4 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry PDFdela2No ratings yet
- LYOCELLDocument5 pagesLYOCELLKingson_786100% (1)
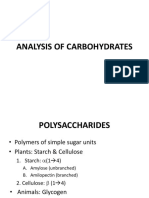
- Carbohydrate Post Lab DiscussionDocument28 pagesCarbohydrate Post Lab Discussionanon nymouseNo ratings yet
- Nh4H2Po4/Sio2: A Recyclable, Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst For Crossed Aldol Condensation ReactionDocument29 pagesNh4H2Po4/Sio2: A Recyclable, Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst For Crossed Aldol Condensation ReactionPARUL KUMAR SHARMANo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Previous Year Question Paper 2012Document8 pagesICSE Class 10 Chemistry Previous Year Question Paper 2012megha rohillaNo ratings yet