Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Es 13 Thy Prob Set 1 I. Stresses: Max Max
Uploaded by
Michael Sean DeangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Es 13 Thy Prob Set 1 I. Stresses: Max Max
Uploaded by
Michael Sean DeangCopyright:
Available Formats
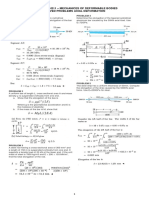
ES 13 THY PROB SET 1
I. Stresses
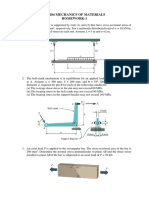
1. Two wooden boards (300mm wide and 25mm thick) designed to carry a 10-kN load are
joined together by two 300-mm wide plywood gussets glued above and below the boards as
shown below. There is a 5-mm gap between the two wood boards at the joint. Assuming that
the failure of the glue governs, what is the required strength of the glue? Use a factor of
safety of 1.50.
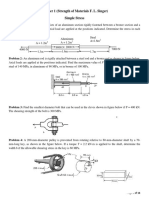
2. Steel plates B and C are fully glued to member A thus, forming a compound member as
shown in the figure. This will be used to punch two holes in a 12-mm thick wooden plank. If
the maximum average shearing stress in the glue is 570 MPa, and the allowable normal
stress in member A is 800 MPa, (thickness of A, B, and C is 25 mm) determine:
a. P
max
that can be applied to the compound member.
b. Is this force P
max
enough to punch holes in the plank if the failure shearing stress in the
plank is 750 MPa?
P
A A
80 mm
60 mm
B C
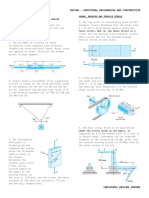
II. Strain
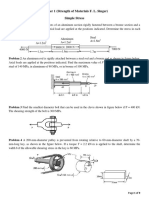
1. Load P is applied on the rigid bar BD causing a shearing strain at point B equal to 0.09
radians. Knowing angle ABC is initially 90 and AB = BC = 0.3 m, determine:
a. normal strain at AB
b. normal strain at BC
c. normal strain on 0.5-m post E
III. Material Properties
1. A square plate in the figure on the right has
the following dimensions before normal
stresses are applied: L
x
= L
y
= 160 mm,
t=20 mm. Its Poissons ratio, = 0.283, and
its modulus of rigidity, G = 30 GPa. It is
then subjected to normal stresses on ALL
its faces and deforms.
a) If the normal stresses are
x
= 444 MPa,
y
= 222 MPa, and its new length along
the x-direction is 160.8437 mm, find
z
.
b) Find the new thickness of the plate, t.
c) Find the new length along the y direction
2. At the proportional limit, a 200-mm gage length of a 15-mm diameter alloy bar has
elongated 0.90 mm and the diameter has been reduced 0.022 mm. the total axial load carried
was 58.4 kN. Determine the following properties of this material:
a. The modulus of elasticity
b. Poissons ratio
c. The proportional limit
y
z
0.5 m 0.5 m
20 mm
B
A C
D
E
P
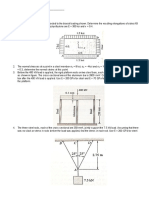
IV. Axially Loaded Members
A. Statically Determinate
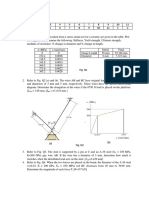
1. A 10-mm-diameter cable AC is made of steel with E = 200 GPa and attached to a rigid
bar BC. Knowing that the maximum stress in the cable must not exceed 190 MPa, and
that elongation of the cable must not exceed 8 mm, find the maximum load P that can
be applied as shown.
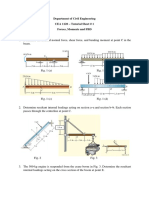
2. Bar ABCD is subjected to the following loads as shown. Determine the maximum
value of force P that can be applied to the bar if
allow
used for design is based on
ultimate strength and
allow
(of bar ABCD) = 1.2 mm.
Note: Member AB at inner diameter is hollow.
Aluminum Steel
Copper
Properties Aluminum Copper Steel
E (GPa) 70 120 200
yp
(MPa) 180 200 300
ult
(MPa) 310 400 580
FS 2 4 3
A
B
C
4m
3m
P
B. Statically Indeterminate
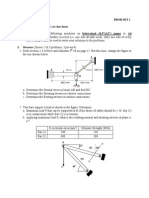
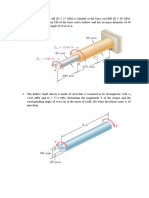
1. Three bars AB, AC, and AD, are pinned together to support a load of 20 kN.
Horizontal movement is prevented at joint A by a horizontal strut AE. Note: All
supports are pin-connected.
Bars AB and AD:
E = 70 GPa
A = 400 mm
2
Bar AC:
E = 200 GPa
A = 200 mm
2
Determine
a.
avg
in each bar (AB, AC, and AD)
b. Force in the strut AE
2. In the figure shown below, each of the two vertical steel posts (E = 200 GPa, =
1210
-6
/C) has a height of 300 mm and a diameter of 50 mm. If the springs each has a
stiffness of 0.5 kN/m, determine the resulting stress in the steel posts if the temperature
is raised by 70C. Assume that springs are initially unstretched. Neglect the masses of
the rigid members.
3. A system of bars is attached to a spring with spring constant k = 5000 kN/m. Bar B is
assumed to be rigid, and bars A & C are deformable with properties given in the Table.
Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the displacement of pin p when
the system is subjected to a 60C increase in temperature.
You might also like
- 2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNDocument2 pages2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- MEC103 Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument24 pagesMEC103 Mechanics of Deformable BodiesLorene Ropeta.No ratings yet
- Strain ProblemsDocument4 pagesStrain ProblemsBianca GuevarraNo ratings yet
- ME-2127 Solid Mechanics-MSEDocument14 pagesME-2127 Solid Mechanics-MSEFazle RabbyNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 2Document5 pages1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 2onenoteforlocadNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-2Document4 pagesTutorial 2-2nageshNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2017 Tutorial ProblemsDocument2 pagesSolid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2017 Tutorial ProblemsMihir Kumar MechNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2019 Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Tutorial-3Document2 pagesSolid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2019 Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Tutorial-3Kamini GoyalNo ratings yet
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Document3 pagesEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoNo ratings yet
- AXIALLY LOADED MEMBER: Statically Determinate: (Note: You Can Only Have Displacement/s at Axis/axes With No Support)Document4 pagesAXIALLY LOADED MEMBER: Statically Determinate: (Note: You Can Only Have Displacement/s at Axis/axes With No Support)Marsha Fatima PascualNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1Document5 pages1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1onenoteforlocadNo ratings yet
- Es 13 Thr1 Prob Set 1Document6 pagesEs 13 Thr1 Prob Set 1Tim AcostaNo ratings yet
- Es 13 Prob Set 1Document5 pagesEs 13 Prob Set 1Julian de LaraNo ratings yet
- SolveDocument2 pagesSolveJea Clarie Mendioro Espinas67% (3)
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1furkandemirgsNo ratings yet
- 183Document3 pages183Mridul PantNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesStrength of Materialsjerold_arandiaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Document4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Jesus RodeloNo ratings yet
- Es 13 Prob Set 1Document5 pagesEs 13 Prob Set 1onenoteforlocadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1TanmayNo ratings yet
- ME-1203 Solid Mechanics-EEE (Solved Problem Slide)Document9 pagesME-1203 Solid Mechanics-EEE (Solved Problem Slide)sadfNo ratings yet
- Prob SheetDocument20 pagesProb SheetAditya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Rods and Cables Design ProblemsDocument5 pagesRods and Cables Design ProblemslewisbardsonNo ratings yet
- MEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial QuestionsDocument7 pagesMEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial Questionsha haNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Axial DeformationDocument20 pagesSolved Problems in Axial DeformationElizabeth Jovie ViolaNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics QuestionsDocument3 pagesSolid Mechanics QuestionsUnknownNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocument20 pagesTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- LE1 Problem Set PDFDocument14 pagesLE1 Problem Set PDFJunhong BapNo ratings yet
- Axial LoadingDocument4 pagesAxial LoadingAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5A SкNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Chapter 2: Axial Load: (Ans 73.7 Gpa)Document12 pagesTutorial 2 Chapter 2: Axial Load: (Ans 73.7 Gpa)ha haNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1Document2 pagesQuiz No 1Tris ZackNo ratings yet
- Strength Matls Board ReviewDocument20 pagesStrength Matls Board ReviewErika RamosNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials 1 PDFDocument2 pagesMechanics of Materials 1 PDFEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of MaterialDocument3 pagesMechanics of MaterialChhaya Sharma100% (1)
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1anandNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagrams, Stress Analysis, and Material BehaviorDocument7 pagesPhase Diagrams, Stress Analysis, and Material BehaviorMOHAMMAD AELEEF BIN PATRICK A20ET0356No ratings yet
- Quiz No 1 - Set D PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz No 1 - Set D PDFMayoune Nasinopa GalvezNo ratings yet
- Assignment For IPEDocument4 pagesAssignment For IPEAbirHasanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsDocument3 pagesSheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsAhmed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Solving Simple Strain ProblemsDocument2 pagesSolving Simple Strain ProblemsFerrolinoLouieNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Strength of Materials 1Document3 pagesProblem Sets Strength of Materials 1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- Ans. σ = 70 psi; τ = 40.4 psi: ExercisesDocument2 pagesAns. σ = 70 psi; τ = 40.4 psi: ExercisesJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- Homework Chapter 2 - Statically Indeterminate BarDocument2 pagesHomework Chapter 2 - Statically Indeterminate BarPhat Nguyen TrungNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1محمد معوضNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2anonymouscheNo ratings yet
- SOM AssignmentDocument6 pagesSOM Assignmentshreyas shahNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems Axial DeformationDocument6 pagesSolved Problems Axial DeformationChristopher Largado100% (1)
- Exercises Axial Forces and Deformation + TranversalDocument4 pagesExercises Axial Forces and Deformation + TranversalsesNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering ReviewDocument4 pagesStructural Engineering ReviewHazel VidallonNo ratings yet
- SOMDocument14 pagesSOMAditya ojhaNo ratings yet
- Mec32 HW3Document4 pagesMec32 HW3Isabelle LunaNo ratings yet
- Ce003 PsDocument4 pagesCe003 PsJaimeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 On-Line Edition PDFDocument11 pagesAssignment 2 On-Line Edition PDFEm CervasNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Tutorial on Stress and Strain CalculationsDocument4 pagesMechanical Engineering Tutorial on Stress and Strain CalculationsSujay BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Questions On Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesQuestions On Strength of MaterialsAiswarya Ramesh me21b011No ratings yet
- Ternary DiagramDocument1 pageTernary DiagramMichael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- ChE 125 WFR/WFU Ideal Reactor Sample ProblemsDocument2 pagesChE 125 WFR/WFU Ideal Reactor Sample ProblemsMichael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics Sample ProblemsDocument2 pagesReaction Kinetics Sample ProblemsMichael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- Process Variables Problem SetDocument1 pageProcess Variables Problem SetMichael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Process Calculation ExamplesDocument1 pageIdeal Gas Process Calculation ExamplesMichael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document1 pageLab 6Michael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics Practice ProblemsDocument1 pageFluid Statics Practice ProblemsMichael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- ChE 122 ExamplesDocument1 pageChE 122 ExamplesMichael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Process Calculation ExamplesDocument1 pageIdeal Gas Process Calculation ExamplesMichael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- 3 - Absolute, Effective and Relative PermeabilitiesDocument34 pages3 - Absolute, Effective and Relative PermeabilitiesAhmad MammadovNo ratings yet
- HT2Document178 pagesHT2dhruvNo ratings yet
- Clapeyron Equation ProblemsDocument23 pagesClapeyron Equation ProblemsGhalintia Vanesa RekasariNo ratings yet
- PENSTOCK Optimization ResearchDocument3 pagesPENSTOCK Optimization ResearchAnjan SigdelNo ratings yet
- Drag Coefficient PDFDocument9 pagesDrag Coefficient PDFphutd09No ratings yet
- Blast Resistant Design of RC StructuresDocument5 pagesBlast Resistant Design of RC StructuresBalaji SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Ressa Reslope and MsewDocument2 pagesRessa Reslope and Msewchehalis0% (1)
- Archimedes' Principle and Buoyant ForcesDocument20 pagesArchimedes' Principle and Buoyant ForcesAnonymous yfkitRbSvZNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Piping DesignDocument19 pagesCryogenic Piping Designsatishchemeng80% (10)
- Article JAS Cyclone Revised R2 PDFDocument24 pagesArticle JAS Cyclone Revised R2 PDFAinaNo ratings yet
- Mokveld Product Sheet Axial Control Valve 1Document2 pagesMokveld Product Sheet Axial Control Valve 1Belos SahajiNo ratings yet
- Flow Modelling of Scroll Compressors and ExpandersDocument351 pagesFlow Modelling of Scroll Compressors and ExpandersYang LeechinNo ratings yet
- Base Plate, Anchor & Foundation (Pipe)Document39 pagesBase Plate, Anchor & Foundation (Pipe)nizardsouissiNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Viscoelastic Materials in AbaqusDocument5 pagesSimulation of Viscoelastic Materials in AbaqusRahulprabhakaran VannostranNo ratings yet
- Beam Design ExcelDocument3 pagesBeam Design Excelprashanth palaniNo ratings yet
- Compact Rooftop Heat Pump Technical SpecificationsDocument10 pagesCompact Rooftop Heat Pump Technical SpecificationsRonald MonzónNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Schematic (ISO Control Pattern) 316 (S/N 522811001 AND ABOVE) (S/N 522911001 AND ABOVE)Document2 pagesHydraulic Schematic (ISO Control Pattern) 316 (S/N 522811001 AND ABOVE) (S/N 522911001 AND ABOVE)Леонид ЮртаевNo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain Curve - WikipediaDocument3 pagesStress-Strain Curve - WikipediaTomy GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Pin Connected Tension MemberDocument2 pagesPin Connected Tension MemberAUNGPSNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Fill EfficiencyDocument11 pagesCooling Tower Fill EfficiencyMubarik Ali100% (1)
- IJETR041973Document5 pagesIJETR041973erpublicationNo ratings yet
- Added MassDocument3 pagesAdded MassAli PungaNo ratings yet
- Latihan Kelompok Mekanika Fluida Dan PartikelDocument2 pagesLatihan Kelompok Mekanika Fluida Dan PartikelrizkaNo ratings yet
- Final - PTPresentation - 060525Document50 pagesFinal - PTPresentation - 060525Tran VietcuongNo ratings yet
- Machine Design: Stress Concentration FactorsDocument30 pagesMachine Design: Stress Concentration FactorsM.HNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Hydraulic Conductivity of Porous Material Using A Rigid-Wall, Compaction-Mold PermeameterDocument8 pagesMeasurement of Hydraulic Conductivity of Porous Material Using A Rigid-Wall, Compaction-Mold PermeameterOpu Debnath100% (1)
- ECSS E HB 32 20 - Part2A PDFDocument434 pagesECSS E HB 32 20 - Part2A PDFVesa RäisänenNo ratings yet
- Seismic CPT Whitepaper - Final - May2020Document9 pagesSeismic CPT Whitepaper - Final - May2020Lei QiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 - Embankment - PLAXIS Consolidation and Safety AnalysisDocument19 pagesExercise 2 - Embankment - PLAXIS Consolidation and Safety AnalysisRelu MititeluNo ratings yet
- StrukturDocument73 pagesStrukturRhea SeneNo ratings yet