Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aerobic Processes English
Uploaded by
IR Ika EtyEtyka Dora0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageThe activated sludge process involves suspending microorganisms in wastewater. As the wastewater is aerated in tanks, the microorganisms metabolize and form flocs. The flocs are separated from the treated water via sedimentation. Some activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank while excess sludge is removed. Biofilm processes involve microorganisms settling on carrier materials and forming biofilms. Trickling filters are a type of biofilm process where wastewater is trickled over a layer of carrier material containing biofilms. Biological processes convert organic matter in wastewater into biomass, carbon dioxide, and water through aerobic microorganisms.
Original Description:
Aerobic Processes English
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe activated sludge process involves suspending microorganisms in wastewater. As the wastewater is aerated in tanks, the microorganisms metabolize and form flocs. The flocs are separated from the treated water via sedimentation. Some activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank while excess sludge is removed. Biofilm processes involve microorganisms settling on carrier materials and forming biofilms. Trickling filters are a type of biofilm process where wastewater is trickled over a layer of carrier material containing biofilms. Biological processes convert organic matter in wastewater into biomass, carbon dioxide, and water through aerobic microorganisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageAerobic Processes English
Uploaded by
IR Ika EtyEtyka DoraThe activated sludge process involves suspending microorganisms in wastewater. As the wastewater is aerated in tanks, the microorganisms metabolize and form flocs. The flocs are separated from the treated water via sedimentation. Some activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank while excess sludge is removed. Biofilm processes involve microorganisms settling on carrier materials and forming biofilms. Trickling filters are a type of biofilm process where wastewater is trickled over a layer of carrier material containing biofilms. Biological processes convert organic matter in wastewater into biomass, carbon dioxide, and water through aerobic microorganisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
21
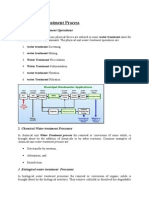
WATER TREATMENT BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES
Activated sludge process
In this process, the microorganisms are suspended in the
wastewater. Aeration of the wastewater in the aeration tank
provides the aerobic microorganisms with oxygen. The
metabolic process causes them to form into flocs the so
called activated sludge. This is separated from the waste-
water by means of sedimentation (secondary clarification).
More biomass is removed from the aeration tank than is
produced in the same period of time. In order to balance
out this loss of biomass in the aeration tank, part of the
activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank (return
sludge). The portion of the activated sludge which is not
returned is termed surplus sludge and is a waste product
of the process.
Biofilm processes
Biofilm processes are based on microorganisms settling on
the surfaces of solids. The resulting layer of microorgan-
isms is called a biofilm. The solids used in this process are
called carrier material. This means the wastewater must be
brought into contact with the biofilm affixed to the carrier
material.
The most important version are trickling filters. Here
the wastewater is trickled over a layer of carrier material
(fixed bed) using a rotating distributor. Whilst the waste-
water passes through the carrier material it is biologically
cleaned by the microorganisms. Aeration of the trickling
filter is normally via natural convection. This is based on
the temperature difference between the outside air and the
inside of the trickling filter.
Carrier materials have high specific surface areas
(approx. 200 m / m). Carrier materials can be of natural
origin (e. g. extrusive rocks) or be artificially produced.
Fundamental principle of the activated sludge process:
1 air, 2 wastewater, 3 return sludge, 4 surplus sludge, 5 treated water, 6 secondary clarifier (sedimentation)
7 aeration tank
Carrier materials for biofilms:
1 artificial carrier material (plastic),
2 natural carrier material (e. g. extrusive rocks)
How a trickling filter works:
1 wastewater, 2 aeration by natural convection, 3 treated water, 4 carrier material, 5 biofilm, 6 distributor
Biological processes enable dissolved biodegrad-
able substances (organic matter) to be removed from
wastewater. The organic matter provides a nutrient
for microorganisms, and is converted under aerobic
conditions into biomass, carbon dioxide and water.
Aerobic microorga nisms need oxygen for respiration.
As well as organic matter, nitrogenous compounds
such as ammonium and nitrate must usually also
be removed from wastewater. Specific micro-
organisms convert ammonium initially into
nitrate (nitrification). Another group of micro-
organisms then reduces the nitrate to nitrogen gas
which escapes to the atmosphere (denitrification).
A distinction is made between biofilm and activated
sludge processes.
1
2
7 6
6
3
3
5
5
4
4
2 2
1
2 1
Activated sludge
BASIC KNOWLEDGE
AEROBIC PROCESSES
You might also like
- PHIL University Physics For The Physical and Life Sciences Volume 2 PDFDocument694 pagesPHIL University Physics For The Physical and Life Sciences Volume 2 PDFws1751367% (3)
- Environmental Engineering Sewage TreatmentDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Sewage TreatmentNasirNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment PlantDocument26 pagesWaste Water Treatment Plantkadhim AliNo ratings yet
- Conversion ChartDocument1 pageConversion ChartLibinNo ratings yet
- CSTR StartupDocument7 pagesCSTR StartupIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Chap 6.0 Manufacturing Cost EstimationDocument20 pagesChap 6.0 Manufacturing Cost EstimationIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1Document11 pagesLecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1negaathanipalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatment of Waste WaterDocument36 pagesBiological Treatment of Waste Waternagpal_aakash100% (1)
- LEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDocument5 pagesLEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDysmas100% (1)
- TechnologiesDocument12 pagesTechnologiesHamed MehriNo ratings yet
- WWTP ProcessDocument14 pagesWWTP ProcessShimmer WongNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument67 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantSWATHI ACHARNo ratings yet
- Tet Unit 3 NotesDocument25 pagesTet Unit 3 NotesnesamaniconstructionsNo ratings yet
- Waste WaterDocument6 pagesWaste WaterManish KR AryanNo ratings yet
- Removal of Organic Dissolved SolidsDocument21 pagesRemoval of Organic Dissolved SolidsShravik Patni 18BCL0040No ratings yet
- Biological Wastewater Treatment SystemsDocument41 pagesBiological Wastewater Treatment SystemsJames Korbla Dodzi Hills100% (1)
- Secondry Unit Operation and Process of Wastewater TreatmentDocument11 pagesSecondry Unit Operation and Process of Wastewater Treatmentshivam randiveNo ratings yet
- Paper: DSE1: Semester: VTH Subject: Botany (M)Document4 pagesPaper: DSE1: Semester: VTH Subject: Botany (M)emoghwanreronaNo ratings yet
- Rotating Biological Contractor ReportDocument12 pagesRotating Biological Contractor ReportNavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Sewage TreatmentDocument24 pagesSewage TreatmentGemrex Breva100% (1)
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument10 pagesWaste Water TreatmentPriyank LashkariNo ratings yet
- School of Civil Engineering & Architecture: Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument112 pagesSchool of Civil Engineering & Architecture: Adama Science and Technology UniversityHusen DugoNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Document4 pagesBiological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Environmental BiotechnologyDocument54 pagesEnvironmental BiotechnologyLalita SahNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment IEMDocument37 pagesWaste Water Treatment IEMpawan88502No ratings yet
- Rotating Biological ContactorDocument6 pagesRotating Biological ContactorDebasish NayakNo ratings yet
- ESTII 22 23 TP Lecture 03Document53 pagesESTII 22 23 TP Lecture 03YaraNo ratings yet
- Biofilter: Biofiltration Is A Pollution Control Technique Using A BioreactorDocument6 pagesBiofilter: Biofiltration Is A Pollution Control Technique Using A BioreactorNirmal BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment ProcessDocument4 pagesWaste Water Treatment ProcessDengAwutNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Methods Physical Unit Operations Chemical Unit Operations Biological Unit OperationsDocument34 pagesWastewater Treatment Methods Physical Unit Operations Chemical Unit Operations Biological Unit OperationsNumanNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument28 pagesWaste Water TreatmentSKRY RAYONo ratings yet
- IGNTU EContent 673390684976 B.SC EnvironmentalSciences 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandHumanHealth 3Document34 pagesIGNTU EContent 673390684976 B.SC EnvironmentalSciences 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandHumanHealth 3Riyasath ahamedNo ratings yet
- Secondary Treatment System: Trickling FilterDocument5 pagesSecondary Treatment System: Trickling FilterMaryrose GalapNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Document3 pagesBiological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Primary Wastewater TreatmentDocument12 pagesPrimary Wastewater TreatmentJAY4029364No ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument28 pagesWaste Water Treatmentsaurabhjoshi26108285% (40)
- Rotating Biological ContactorDocument6 pagesRotating Biological Contactorvignesh9489No ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Wastewater Treatment: Snehal Menon Sinhgad College of Engineering, PuneDocument37 pagesPrimary and Secondary Wastewater Treatment: Snehal Menon Sinhgad College of Engineering, PuneSeema NihalaniNo ratings yet
- What is Wastewater TreatmentDocument28 pagesWhat is Wastewater Treatmentramonik08100% (4)
- Sewagetreatment1 130927055820 Phpapp01Document56 pagesSewagetreatment1 130927055820 Phpapp01Divakar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Actvated Sludge Process SSWMDocument28 pagesActvated Sludge Process SSWMGREENLAB ECL TECHNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Mini ReviewDocument26 pagesWastewater Treatment Mini Reviewnininick805No ratings yet
- Trickling Filter: Aerobic Biological Wastewater Treatment ProcessDocument10 pagesTrickling Filter: Aerobic Biological Wastewater Treatment Processpriodeep chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Wastewater TrainDocument3 pagesWastewater TrainLester Mercado100% (1)
- Tinjauan Aspek Teknis Pemilihan Media Biofilter Untuk Pengolahan Air LimbahDocument10 pagesTinjauan Aspek Teknis Pemilihan Media Biofilter Untuk Pengolahan Air LimbahHasnanurfajriahNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Processes EnglishDocument1 pageAerobic Processes EnglishplennyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15 - Trickling FiltersDocument10 pagesLesson 15 - Trickling FiltersShane RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Steps in Waste Water TreatmentDocument7 pagesSteps in Waste Water Treatmentex_travaganza87No ratings yet
- Sewage Water TreatmentDocument8 pagesSewage Water Treatmentsivani rayavarapuNo ratings yet
- Ipal UmumDocument17 pagesIpal UmumDannysArifKusumaNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument9 pagesExamDileepa NeranjanaNo ratings yet
- Secondary Wastewater Treatment Microorganisms RoleDocument39 pagesSecondary Wastewater Treatment Microorganisms RoleAregaNo ratings yet
- Lect 2Document64 pagesLect 2Patricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNo ratings yet
- Biological Wastewater Treatment Processes ExplainedDocument40 pagesBiological Wastewater Treatment Processes ExplainedashuNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document3 pagesPresentation 3SarahNo ratings yet
- Sewage TreatmentDocument5 pagesSewage TreatmentbalachandransheebaNo ratings yet
- Effluent TreatmentDocument21 pagesEffluent TreatmentRadhika AnandkumarNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Methods ComparisonDocument54 pagesWastewater Treatment Methods ComparisonPamela MendozaNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment From Municipal Waste Using Biological MethodDocument20 pagesWastewater Treatment From Municipal Waste Using Biological Methodnoorain zulkapliNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument28 pagesWaste Water TreatmentRoseNavyaNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution ControlFrom EverandWater Pollution ControlSuresh T. NesaratnamNo ratings yet
- Aquaponics system, fish. Volume 1: Sistemas de acuaponíaFrom EverandAquaponics system, fish. Volume 1: Sistemas de acuaponíaNo ratings yet
- Art21 PDFDocument5 pagesArt21 PDFIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Water and Wastewater Treatment ProcessesDocument32 pagesWater and Wastewater Treatment ProcessesMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- How To Answer UPSR Science Paper II - Soalan Ramalan UPSR PT3 SPM 2015Document4 pagesHow To Answer UPSR Science Paper II - Soalan Ramalan UPSR PT3 SPM 2015IR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Maldonado 1Document66 pagesMaldonado 1vazzoleralex6884No ratings yet
- Is 13425 1992Document14 pagesIs 13425 1992IR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Rasterbation of Audrey HepburnDocument9 pagesRasterbation of Audrey HepburnIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- SedmentationDocument6 pagesSedmentationJorge Olortiga OrtizNo ratings yet
- Appendix A Flow Chart of The Mini Project of The Chemical Reaction Engineering I SubjectDocument1 pageAppendix A Flow Chart of The Mini Project of The Chemical Reaction Engineering I SubjectIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Conversion Tables For Units: Chapter 1 - 1Document9 pages1.6 Conversion Tables For Units: Chapter 1 - 1Yamel MorenoNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Formulae-ImpDocument4 pagesCooling Tower Formulae-ImptpplantNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 Pinch TechDocument30 pagesCHP 3 Pinch TechIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Ciss Probs SolutionDocument4 pagesCiss Probs SolutionIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Corrosion NotesDocument7 pagesCorrosion NotesIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- CHE 481-Project 2 ReportDocument7 pagesCHE 481-Project 2 ReportIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- The STP Guide-Design, Operation and MaintenanceDocument74 pagesThe STP Guide-Design, Operation and MaintenanceRajesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Resultresult Thin Film - Docx Thin FilmDocument4 pagesResultresult Thin Film - Docx Thin FilmIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Technology Fact SheetDocument7 pagesWastewater Technology Fact SheetIrving VazquezNo ratings yet
- db5c3e3e5365eb334855d7d818ef53d9Document20 pagesdb5c3e3e5365eb334855d7d818ef53d9reasonorgNo ratings yet
- Liquid Extraction Process Design and TechniquesDocument7 pagesLiquid Extraction Process Design and TechniquesIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- List of Questions and Answers For WastewaterDocument22 pagesList of Questions and Answers For WastewaterIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Me443 CH6Document28 pagesMe443 CH6IR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- List of Questions and Answers For WastewaterDocument22 pagesList of Questions and Answers For WastewaterIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Integrals in Cylindrical & Spherical CoordinatesDocument2 pagesIntegrals in Cylindrical & Spherical CoordinatesIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Mott Calc Well DeliverabilityDocument8 pagesMott Calc Well DeliverabilityIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- 124 Lle4Document31 pages124 Lle4bluestardiverNo ratings yet
- Mott Calc Well DeliverabilityDocument8 pagesMott Calc Well DeliverabilityIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- Deccan TrapsDocument5 pagesDeccan TrapsNTA UGC-NETNo ratings yet
- The University of DodomaDocument20 pagesThe University of DodomaIsrael MwanyeleleNo ratings yet
- Edexcel AS Physics Experiment Questions Unit 1Document7 pagesEdexcel AS Physics Experiment Questions Unit 1RaShid KhAnNo ratings yet
- Coriolis Flow MeasurementDocument19 pagesCoriolis Flow MeasurementtetiospamNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ConversionDocument24 pagesAmmonia ConversionKashan AslamNo ratings yet
- GeegDocument2 pagesGeegjefferson100% (1)
- Snay Soler Part3Document3 pagesSnay Soler Part3jajceNo ratings yet
- Jinsoon Choi Dong Jin Suh (2007) - Catalytic Applications of Aerogels., 11 (3)Document11 pagesJinsoon Choi Dong Jin Suh (2007) - Catalytic Applications of Aerogels., 11 (3)EcNo ratings yet
- MS - Hyprene L1200 7-25-08Document1 pageMS - Hyprene L1200 7-25-08Abe KobNo ratings yet
- 2-Vle Part 2Document22 pages2-Vle Part 2Arfa Zulkifli01No ratings yet
- Topic: Earth: The Living PlanetDocument4 pagesTopic: Earth: The Living PlanetLesly Ann De VeraNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Hysteresis in Ferromagnetic Materials: Sajag - Kumar@niser - Ac.inDocument4 pagesMagnetic Hysteresis in Ferromagnetic Materials: Sajag - Kumar@niser - Ac.inSajag KumarNo ratings yet
- Alkalinity and Acidity ExperimentDocument4 pagesAlkalinity and Acidity ExperimentSaivenkateshBantupalliNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis PDFDocument13 pagesDimensional Analysis PDFMspamNo ratings yet
- DRAP Monthly Progress ReportDocument7 pagesDRAP Monthly Progress ReportKhawaja AsadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project on Cosmetic ChemistryDocument48 pagesChemistry Project on Cosmetic ChemistryShubham SehgalNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Kimia 1Document11 pagesLab Report Kimia 1nur anith aqilahNo ratings yet
- TT 200 1 SC TT 200 2 SC Sample Concentrator DatasheetDocument4 pagesTT 200 1 SC TT 200 2 SC Sample Concentrator Datasheetlehieua8No ratings yet
- Tds Polintek L&P Plus For Metal-Dmi IndustriDocument1 pageTds Polintek L&P Plus For Metal-Dmi IndustriYosep SasadaNo ratings yet
- Mass For Of: Scale Based On Resolution Mass Spectrometry Organic CompoundsDocument9 pagesMass For Of: Scale Based On Resolution Mass Spectrometry Organic CompoundsoreamigNo ratings yet
- PT Chapter 1Document13 pagesPT Chapter 1shubhamNo ratings yet
- 3310 Atf Dexron III H Pds Vesion 3Document2 pages3310 Atf Dexron III H Pds Vesion 3luayhabibbNo ratings yet
- Geog 213Document365 pagesGeog 213Fatima TwumasiNo ratings yet
- The Geographers Tools PDFDocument27 pagesThe Geographers Tools PDFAhou Ania Qouma JejaNo ratings yet
- Steinmueller Engineering Produktbroschuere Steam GenerationDocument7 pagesSteinmueller Engineering Produktbroschuere Steam GenerationTC Capulcu Mustafa MNo ratings yet
- Notes Electrochemistry 2021 IIDocument117 pagesNotes Electrochemistry 2021 IISavvy GuptaNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Novel Lepidium Perfoliatum Linn Biodiesel Using Zirconium Modified Montmorillonite Clay CatalystDocument17 pagesOptimization of Novel Lepidium Perfoliatum Linn Biodiesel Using Zirconium Modified Montmorillonite Clay CatalystGanesh T NaikNo ratings yet
- PROTECT WORKER HEALTH WITH INDUSTRIAL HYGIENEDocument31 pagesPROTECT WORKER HEALTH WITH INDUSTRIAL HYGIENEDANICA JORIELLE PALOGANNo ratings yet
- 09 Exp 11 Buffer SolutionsDocument8 pages09 Exp 11 Buffer SolutionsShainmaugne AdvientoNo ratings yet