Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardio Respi
Uploaded by
Kate CruzCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardio Respi
Uploaded by
Kate CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
NUTRITION FOR
CARDIOVASCULAR AND
RESPIRATORY DISEASES
ROLE IN WELLNESS
Physical health dimension
Cardiovascular disease impairs functioning of many body
systems
Intellectual health dimension
Determining ones own risk factors and devising a program to
reduce their effects depends on intellectual skills of
adaptation
Emotional health dimension
Necessary lifestyle modifications for heart health may be
frightening and elicit emotional responses
S
l
i
d
e
2
ROLE IN WELLNESS,
CONTD
Social health dimension
Increased education conducted by health associations and
health departments support socializing
Spiritual health dimension
Ability to cope may depend on optimistic spiritual attitude and
desire to fight back to achieve most positive response of the
body
S
l
i
d
e
3
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE
Atherosclerosis
Underlying pathologic process responsible for coronary artery
disease (CAD)
May gradually lead to arteriosclerosis
Most common manifestation
Angina pectoris
Blood flow to coronary arteries partially occluded
Myocardial infarction
Blood flow to heart completely occluded
S
l
i
d
e
4
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Cholesterol
Most frequent approach in assessing CAD risk measuring
cholesterol and proportions of blood lipoproteins
Plasma lipid profile commonly measured by analyzing 3 major
classes of lipoprotein in blood from fasting individual:
S
l
i
d
e
5
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL)
Contains 10% to 15% of total serum cholesterol (TC)
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
Contains approximately 60% to 70% of TC
High serum causally related to increased CAD risk
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
Usually contains 20% to 30% of TC
Serum levels inversely correlated with CAD risk
S
l
i
d
e
6
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Triglycerides
Most common type of fat found in body
Sources
Foods
Liver makes from carbohydrates, alcohol, and some
cholesterol
Serum triglyceride levels range from about 50 to 250 mg/dL
S
l
i
d
e
7
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Factors that may cause triglyceride levels to be elevated:
Overweight and obesity
Physical inactivity
Cigarette smoking
Excess alcohol intake
Very high carbohydrate intake (>60% of total energy)
S
l
i
d
e
8
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Other diseases (e.g., type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic
renal failure, nephrotic syndrome)
Certain drugs (e.g., corticosteroids, protease inhibitors for
human immunodeficiency virus [HIV], beta-adrenergic
blocking agents, estrogens)
Genetic factors
S
l
i
d
e
9
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
NCEP ATP III
National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult
Treatment Panel III (ATP III) report
Emphasizes LDL cholesterol as primary target for cholesterol-
lowering therapy
LDL-lowering therapy reduces risk for CHD
S
l
i
d
e
1
0
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Association between serum triglyceride and CHD
Elevated serum triglyceride levels factor to identify people
at risk
HDL cholesterol strong independent and inverse risk factor for
increased CHD morbidity and mortality
Low HDL cholesterol defined as <40 mg/dL in men and
women
S
l
i
d
e
1
1
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Dyslipidemia
Characterized by three lipid abnormalities
Elevated triglycerides, small LDL particles, and low HDL
cholesterol
Present in premature CHD
S
l
i
d
e
1
2
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Characteristics of individuals with atherogenic dyslipidemia
Obesity
Abdominal obesity
Insulin resistance
Physical inactivity
Lifestyle modificationweight control and increased physical
activitythe treatment of choice
S
l
i
d
e
1
3
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Nonlipid risk factors
Fixed risk factors
Increasing age
Male gender
Family history of premature CHD
S
l
i
d
e
1
4
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Modifiable risk factors
Hypertension
Cigarette smoking
Diabetes
Obesity
Physical inactivity
Atherogenic diet
S
l
i
d
e
1
5
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Nutrition therapy
Therapeutic lifestyle changes (TLCs)
Reduced intake of saturated fats and cholesterol
Therapeutic dietary options to enhance lowering of LDL
Plant stanols/sterols and increased soluble fiber
Weight reduction
Increased regular physical activity
S
l
i
d
e
1
6
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Saturated fat and cholesterol
Reduce
Saturated fat (<7% of total energy intake)
Cholesterol (<200 mg/day)
S
l
i
d
e
1
7
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Dose response relationship between saturated fats and LDL
cholesterol levels
For every 1% increase in kcal from saturated fats as
percent of total energy, serum LDL cholesterol increases
roughly 2%
1% decrease in saturated fats lowers serum cholesterol
by about 2%
S
l
i
d
e
1
8
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Weight reduction
Loss of even few pounds reduces LDL cholesterol levels
Weight reduction using a kcal-controlled diet low in
saturated fats and cholesterol enhances and maintains
LDL cholesterol reductions
Reducing dietary cholesterol to <200 mg per day decreases
serum LDL cholesterol in most people
S
l
i
d
e
1
9
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Monounsaturated fat
Recommendation to substitute monounsaturated fat for
saturated fats up to 20% of total energy intake
Monounsaturated fats lower LDL cholesterol levels relative to
saturated fats without decreasing HDL cholesterol or
triglyceride levels
Best sources of monounsaturated fats: plant oils and nuts
S
l
i
d
e
2
0
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Polyunsaturated fats
Polyunsaturated fats, in particular linoleic acid, reduce LDL
cholesterol levels
Best sources: liquid vegetables oils, semiliquid margarines,
and other margarines low in trans fatty acids
Recommend intakes up to 10% of total energy intake
S
l
i
d
e
2
1
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Total fat
Saturated fats and trans fatty acids increase LDL cholesterol
levels
Serum levels of LDL cholesterol do not appear affected by
total fat intake
Provided saturated fats decreased to goal levels, not essential
to limit total fat to reduce LDL cholesterol levels
S
l
i
d
e
2
2
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Carbohydrate
Replacing saturated fats with carbohydrates decreases LDL
cholesterol
Very high intakes of carbohydrates (>60% total energy intake)
associated with:
Reduction in HDL cholesterol
Increase in serum triglyceride
Increasing soluble fiber to 5 to 10 g per day accompanied by
roughly 5% reduction in LDL cholesterol
S
l
i
d
e
2
3
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Protein
Dietary protein negligible effect on serum LDL cholesterol
level
Substituting plant-based proteins for animal proteins appears
to decrease LDL cholesterol
Fat-free and low-fat dairy products, egg whites, fish, skinless
poultry, and lean cuts of beef and pork low in saturated fat
and cholesterol
All foods of animal origin contain cholesterol
S
l
i
d
e
2
4
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Further dietary options to reduce LDL cholesterol
Daily consumption of 5 to 10 g soluble fiber
Soluble fiber such as oats, barley, psyllium, pectin-rich
fruit, and beans
Roughly reduces LDL cholesterol by 5%
Considered therapeutic alternative
S
l
i
d
e
2
5
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Daily intakes of 2 to 3 g plant sterol/sterol esters
Isolated soybean and tall pine tree oils shown to lower
LDL cholesterol by 6% to 15%
S
l
i
d
e
2
6
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Drug therapy
If treatment with TLC alone unsuccessful after 3 months,
initiation of drug treatment recommended
Implement nutrition therapy regardless of use of
LDL-lowering medications
Nutrition therapy affords further CHD risk reduction beyond
drug efficacy
S
l
i
d
e
2
7
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Combined use of TLC and LDL-lowering medications
Intensive LDL lowering with TLC, including therapeutic
dietary options may prevent need for drugs
Augments LDL-lowering medications
May allow for lower doses of medications
S
l
i
d
e
2
8
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Weight control plus increased physical activity
Reduces risk beyond LDL cholesterol lowering
Constitutes principal management of metabolic syndrome
Raises HDL cholesterol
S
l
i
d
e
2
9
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Trial of nutrition therapy of about 3 months advised before initiating
drug therapy
Medications should not be withheld if needed to reach targets
in people with short-term and/or long-term CHD risk
S
l
i
d
e
3
0
CORONARY ARTERY
DISEASE, CONTD
Initiating drug therapy simultaneously with TLC
Severe hypercholesterolemia
Nutrition therapy alone cannot attain LDL cholesterol
targets
CHD or CHD risk equivalents
Nutrition therapy alone will not attain LDL cholesterol
targets
S
l
i
d
e
3
1
HYPERTENSION
Hypertension (HTN)
A cardiovascular disease and a risk factor for CAD
Average systolic blood pressure 140 mm Hg and/or a
diastolic pressure 90 mm Hg (or both)
One in every three adults has HTN
S
l
i
d
e
3
2
HYPERTENSION,
CONTD
Incidence higher in following groups:
Until age 45, higher percentage of men than women have
HTN
Ages 45 to 54, percentage of women with HTN slightly higher
Older than 54, higher percentage of women than men have
HTN
African Americans, Puerto Ricans, Cuban Americans, and
Mexican Americans more likely to have HTN than white
Americans
S
l
i
d
e
3
3
HYPERTENSION,
CONTD
Primary or essential hypertension
About 95% of HTN cases
Cause unknown
Secondary hypertension
Cause of HTN identifiable
Conditions that are possible causes:
Renal insufficiency
Renovascular diseases
Cushings syndrome
Primary aldosteronism
S
l
i
d
e
3
4
HYPERTENSION,
CONTD
Nutrition therapy
Prescribed treatment regimens
Vary because disease differs in severity
First line of treatment usually nonpharmacologic or focused
on lifestyle modifications
Modifying dietary intake predominant element of
nonpharmacologic treatment
Weight loss most effective means of lowering blood pressure
S
l
i
d
e
3
5
HYPERTENSION,
CONTD
Other lifestyle modifications include:
Possible beneficial effects of reducing weight, if overweight
Decreasing alcohol consumption
Increasing physical activity, if sedentary
Terminating cigarette smoking
Decreasing sodium intake
Increasing dietary intake of other minerals such as potassium,
magnesium, and calcium
S
l
i
d
e
3
6
HYPERTENSION,
CONTD
Weight loss
Weight reduction facilitates lowered blood pressure even when only
a loss of 10 to 15 pounds
Diet for weight loss and control includes:
Specific kcal restriction
Exercise (aerobic) prescription
S
l
i
d
e
3
7
HYPERTENSION,
CONTD
Sodium
Average daily sodium intake in U.S. estimated approximately
4 to 6 g (175 to 265 mEq)
Dietary sodium comes from:
Mostly added sodium during processing and
manufacturing
Discretionary use of table salt (sodium chloride)
Small amount of natural sodium in foods
S
l
i
d
e
3
8
HYPERTENSION,
CONTD
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet
Recommended for prevention and management of HTN
Diet rich in:
Fruits
Vegetables
Low-fat dairy products
Reduced saturated and total fats
S
l
i
d
e
3
9
HYPERTENSION,
CONTD
Larger drop in blood pressure when combined with sodium
restriction
Greatest reduction in blood pressure with DASH at sodium
intake level of 1500 mg/day
Perceived as moderately severe restriction
Difficult to achieve given sodium added during processing
and manufacturing
Salt substitute may be prescribed
S
l
i
d
e
4
0
MYOCARDIAL
INFARCTION
Myocardial infarction (MI)
Occlusion of a coronary artery
Sometimes called heart attack
Disability or death can result after an MI
Depends on extent of muscle damage
Single largest killer of adult men and women in U.S.
S
l
i
d
e
4
1
MYOCARDIAL
INFARCTION, CONTD
Nutrition therapy
Purpose of nutrition therapy to reduce workload of heart
Smaller, frequent meals usually better tolerated than large
meals
Caffeine-containing beverages sometimes restricted to avoid
myocardial stimulation
S
l
i
d
e
4
2
MYOCARDIAL
INFARCTION, CONTD
Control of sodium, cholesterol, fat, and kcal (if weight loss
indicated) according to patients needs
Omega-3 fatty acids recommended
Appears to reduce risk of blood clots that may cause MI
Sources: tuna, salmon, halibut, sardines, and lake trout
S
l
i
d
e
4
3
CARDIAC FAILURE
Cardiac failure
Also referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), heart failure,
and cardiac decompensation
Location of congestion depends on ventricle involved
Left ventricular failure results in pulmonary congestion
Right ventricular failure results in systemic congestion
Causes poor perfusion to all organ systems
Also reported resulting from left heart (ventricular) failure
S
l
i
d
e
4
4
CARDIAC FAILURE,
CONTD
Nutrition therapy
Mild to moderate heart failure
Sodium restriction of 3000 mg/day
Severe CHF
2000 mg/day sodium restriction
Fluid restriction of 1 to 2 L
Fluid requirements depends on medical status and use of
diuretics
S
l
i
d
e
4
5
CARDIAC FAILURE,
CONTD
Nutrition therapy
Energy requirements
May be 20% to 30% above basal needs
Protein and energy intake sufficient to maintain body weight
Barriers to meeting increased nutrient and energy
requirements
Early satiety, gastrointestinal congestion, shortness of
breath, anorexia, and nausea
S
l
i
d
e
4
6
CARDIAC FAILURE,
CONTD
Cardiac cachexia
Cachexia: general ill health and malnutrition, marked by
weakness and emaciation
Additional kcal and protein needed to prevent further
catabolism
Caution must be used when increasing energy not to
overfeed
S
l
i
d
e
4
7
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES
Chronic long-term changes in respiratory function
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Collective phrase for chronic bronchitis, asthma, and
emphysema
Second leading cause of disability in U.S.
Goal of nutrition therapy
Maintain respiratory muscle strength and function
Prevent or correct malnutrition
S
l
i
d
e
4
8
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES, CONTD
Acute changes in respiratory function
Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
Acute respiratory failure (ARF)
Critical illness, shock, severe injury, or sepsis
Goal of nutrition therapy
Inhibit tissue destruction
Provide extra nutrients for hypermetabolic conditions
without contributing to declining respiratory function
S
l
i
d
e
4
9
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES, CONTD
COPD
Malnutrition multifactorial
Contributing factors:
Altered taste (chronic mouth breathing and excess sputum)
Fatigue
Anxiety
Depression
Increased energy requirements
Frequent infections
Side effects of multiple medications
S
l
i
d
e
5
0
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES, CONTD
Nutrition therapy
Anorexia, early satiety, nausea, and vomiting common
25 to 45 kcal/kg
Depends on whether maintenance kcal or repletion (less
than 90% ideal body weight) kcal
Adequate protein, but not excessive, known to stimulate
ventilatory drive
1.2 to 1.9 g protein/kg for maintenance
1.6 to 2.5 g/kg of body weight for repletion
S
l
i
d
e
5
1
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES, CONTD
Proper combination of carbohydrate, protein, and fat
important to reduce production of carbon dioxide and maintain
respiratory function
Particularly crucial for ventilator-dependent patient
Respiratory quotient (RQ)
Ratio of carbon dioxide produced to amount of oxygen
consumed
S
l
i
d
e
5
2
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES, CONTD
Carbohydrate metabolism produces greatest amount of
carbon dioxide
Produces highest RQ
Fat metabolism produces least amount of carbon dioxide
Produced lowest RQ
RQ >1 is evidence of accumulating carbon dioxide
Respiration more difficult with COPD
S
l
i
d
e
5
3
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES, CONTD
Nonprotein kcal should be divided evenly between fat and
carbohydrate
Important to provide adequate nutrition without overfeeding
patient
Overfeeding produces excessive amount of carbon dioxide
Reflected in RQ >1
S
l
i
d
e
5
4
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES, CONTD
ARF and RDS
Almost half of all patients with ARF suffer from malnutrition
Impairs recovery
Prolongs weaning from mechanical ventilation
S
l
i
d
e
5
5
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES, CONTD
Recommended diet minimizes carbon dioxide production
while maintaining good nutrition
Most patients in ARF require mechanical ventilation
Enteral or parenteral nutrition support
S
l
i
d
e
5
6
RESPIRATORY
DISEASES, CONTD
Nutrition therapy
Nutrition support should be initiated as soon as possible to
help wean patient from ventilator
Nutritional recommendations similar to COPD:
High kcalorie, high protein
Moderate to high (50% nonprotein kcal) fat
Moderate (50% nonprotein kcal) carbohydrate
S
l
i
d
e
5
7
You might also like
- Molecular Methods For Diagnosis of Viral Encephalitis: Roberta L. Debiasi and Kenneth L. TylerDocument23 pagesMolecular Methods For Diagnosis of Viral Encephalitis: Roberta L. Debiasi and Kenneth L. TylerKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Review ArticleDocument10 pagesReview ArticleKate CruzNo ratings yet
- 0084 03 PDFDocument23 pages0084 03 PDFKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Should Blood Cultures Be Performed For Patients With Acute Prostatitis?Document4 pagesShould Blood Cultures Be Performed For Patients With Acute Prostatitis?Kate CruzNo ratings yet
- D CAdfghjklDocument2 pagesD CAdfghjklKate CruzNo ratings yet
- 0084 03 PDFDocument23 pages0084 03 PDFKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKate Cruz75% (8)
- ART TherapyDocument3 pagesART TherapyKate CruzNo ratings yet
- SDFGHJDocument1 pageSDFGHJKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Pag-Iwas Sa Pulmonya, Ating Kayang-Kaya!: Ust-SnDocument2 pagesPag-Iwas Sa Pulmonya, Ating Kayang-Kaya!: Ust-SnKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Atonic Seizur Clonic Seizur Tonic Seizur Myocloni CDocument1 pageAtonic Seizur Clonic Seizur Tonic Seizur Myocloni CKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Biblio Lung CancerDocument4 pagesBiblio Lung CancerKate CruzNo ratings yet
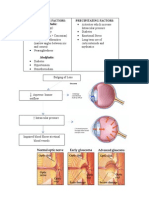
- Precipitating Factors: Predisposing Factors:: Non-ModifiableDocument2 pagesPrecipitating Factors: Predisposing Factors:: Non-ModifiableKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKate CruzNo ratings yet
- E CIGDocument2 pagesE CIGKate CruzNo ratings yet
- ART TherapyDocument3 pagesART TherapyKate CruzNo ratings yet
- ART TherapyDocument3 pagesART TherapyKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Non Marital RelationshipDocument8 pagesNon Marital RelationshipKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Trust Vs MistrustDocument1 pageTrust Vs MistrustKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial PartialsdffghbjnkmlDocument1 pagePsychosocial PartialsdffghbjnkmlKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Biblio Lung CancerDocument4 pagesBiblio Lung CancerKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Role in Wellness: Nutrition For Cardiovascular and Respiratory Diseases Physical Health DimensionDocument8 pagesRole in Wellness: Nutrition For Cardiovascular and Respiratory Diseases Physical Health DimensionKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Family Coping IndexDocument2 pagesFamily Coping IndexKate CruzNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Asthma Review PDFDocument12 pagesAsthma Review PDFdanielc503No ratings yet
- GUIDELINES Management and Treatment of Common InfectionsDocument152 pagesGUIDELINES Management and Treatment of Common Infectionsmarc daouNo ratings yet
- P1 RleDocument34 pagesP1 RleMary Jean GicaNo ratings yet
- Reviews: Lung Function Testing Assessment by Impulse Oscillometry in Chronic Lung DiseaseDocument7 pagesReviews: Lung Function Testing Assessment by Impulse Oscillometry in Chronic Lung DiseaseCristiana LibuNo ratings yet
- COPD Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesCOPD Practice QuestionsMikaella CondeNo ratings yet
- HemoptoeDocument7 pagesHemoptoeAnonymous h0DxuJTNo ratings yet
- NurseLabs QnA#4Document36 pagesNurseLabs QnA#4Jill Noelle100% (1)
- Implications of Low Muscle Mass Across The Continuum of Care A Narrative ReviewDocument20 pagesImplications of Low Muscle Mass Across The Continuum of Care A Narrative ReviewAngelica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument20 pagesAir PollutionSheraz Ali50% (2)
- 281 FullDocument8 pages281 FullbcgvpilotNo ratings yet
- CDC 2Document39 pagesCDC 2Erica May Formacion SeverinoNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument8 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAlexandra BeldimanNo ratings yet
- NOTES (Pneumonia & Lobectomy)Document6 pagesNOTES (Pneumonia & Lobectomy)Kim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Ambient Air Pollution and Health in Accra, Ghana: Pierpaolo MuduDocument44 pagesAmbient Air Pollution and Health in Accra, Ghana: Pierpaolo MuduJeff Derbi-OkaeNo ratings yet
- Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesCommon Medical AbbreviationsalallaallalaNo ratings yet
- HSE From WeldingDocument7 pagesHSE From WeldingMichael RujuwaNo ratings yet
- Gold Guidlines 2023 1Document24 pagesGold Guidlines 2023 1api-649066372No ratings yet
- COPD Physio-Pedia PDFDocument17 pagesCOPD Physio-Pedia PDFsazi01No ratings yet
- DOH Standard For Primary Healthcare in The Emirate of Abu DhabiDocument21 pagesDOH Standard For Primary Healthcare in The Emirate of Abu DhabiManishaNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - Edexcel - Biology - Health, Disease and The Development of Medicines - KnowIT - GCSE 2Document49 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - Edexcel - Biology - Health, Disease and The Development of Medicines - KnowIT - GCSE 2Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- ARDS QuizDocument6 pagesARDS QuizMeliza BancolitaNo ratings yet
- COPD and Heart FailureDocument3 pagesCOPD and Heart Failureyyfan98No ratings yet
- Patented Therapeutic Drug Delivery Strategies For Targeting Pulmonary DiseasesDocument36 pagesPatented Therapeutic Drug Delivery Strategies For Targeting Pulmonary DiseasesMayson BaliNo ratings yet
- Grandjean 2000Document13 pagesGrandjean 2000Ivan VeriswanNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Practice Questions With RationaleDocument196 pagesNCLEX Practice Questions With RationaleKharen Herrera88% (8)
- 1 Preoperative Health Status EvaluationDocument21 pages1 Preoperative Health Status EvaluationNuno CoelhoNo ratings yet
- MKSAP 17 Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine PDFDocument192 pagesMKSAP 17 Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine PDFRoxana Enachescu100% (3)
- Respiratory Symptoms Campbell All ChapterDocument67 pagesRespiratory Symptoms Campbell All Chaptermelanie.grant662100% (12)
- Health Impact of Air PollutionDocument15 pagesHealth Impact of Air Pollutionapi-304969581No ratings yet
- Rembe 1Document8 pagesRembe 1Steve ColbertNo ratings yet