Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04oct Dec 2012
Uploaded by
Pushkar FegadeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
04oct Dec 2012
Uploaded by
Pushkar FegadeCopyright:
Available Formats
VOLUME XXVII OCTOBER - DECEMBER 2012 NUMBER IV
CONTENTS
RESEARCH ARTICLES
The Impact Of The Lean Technique Of Value Ann Francis 5
Stream Mapping In Indian Construction Sites Ashwin Mahalingam
On Reducing Carbon Emissions
Temporal Data In Three Dimensional Models Abhijeet S. Deshpande 21
For Improved Construction Planning Ossama M. Salem
Richard Alan Miller
A Dynamic Model Study For Real-Life Abhishek V. 29
ESIC Hospital Project Jagadeesh P.
Strength Properties Of Class 'C' Fly Ash Rama Mohan Rao P. 39
Concrete With Variable Aggregate Binder Ratio H. Sudarsana Rao
Application Of Public Private Partnership (PPP) In Siddesh K. Pai 45
Health Care Sector In India Ankit Tripathi
COMMUNICATION
Social Loss Estimation Due To Road Accidents Prasanta K. Sahu 55
Time Waste And Delays In Construction Projects : Safeer Ali Abbas Ali 63
A State Of The Art Report Arun C.
NICMAR
JOURNAL OF CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT
Social Loss Estimation Due To Road Accidents
Prasanta K. Sahu
Abstract : India has a serious road accident problem with over 130,000 deaths
reported annually. These accidents not only cause considerable pain and
suffering but also they lead to direct economic costs and a large waste
of the national resources. The statistical estimates of years of life lost
due to premature mortality and the value of output forgone as a result
of road accident-related injury do not adequately communicate the depth
of human loss, grief, pain and suffering. However, investment decisions
on transport safety and research programs need to be made, and data
on accident numbers and severity, and their economic costs, can improve
the quality of those decisions. One of the prime uses of accident cost
information is assessing the benefits received from various transport
safety measures and programs. These measures and programs also impose
costs on society and it is necessary for the transport planners to determine
the appropriate balance of costs and benefits in order to ensure that
resources are used in a socially acceptable and efficient manner. Therefore,
it was thought to provide a concise review of some accident costing
methods developed worldwide including the key background information.
Keywords : Social Loss; Road Accidents; Human Capital.
COMMUNICATION - I
Application Of Public Private Partnership
(PPP) In Health Care Sector In India
Siddesh K. Pai and Ankit Tripathi
Abstract : Public private partnership or PPP in the context of health sector is an
instrument for improving the health of the population. With the rapid
growth of the Indian economy in recent times and the changing demographics
and socio-economic mix of the Indian population, there has been an
immense change in the healthcare requirements in the country. Today,
the healthcare system in India faces a challenge in raising the service
quality and addressing the increasing health needs of the country. This
challenge needs to be addressed through a concerted effort of both
public and private sectors by their agreeing on suitable public policy
initiatives which incentivize financing and provision of healthcare, and
thereby increase healthcare access to the people.
The paper presents the avenues of collaboration between the public and
private sectors of the healthcare industry, and to recommend public
policy initiatives that would foster Public Private Partnerships (PPPs)
and stimulate investment in healthcare sector to shape the future of
Indian Healthcare Industry. The paper encapsulates the success of PPP
in health sector in India.
Keywords : Public Private Partnership, Healthcare Industry.
Strength Properties Of Class 'C' Fly Ash
Concrete With Variable Aggregate Binder Ratio
Rama Mohan Rao P. and H. Sudarsana Rao
Abstract : In this paper the experimental work has been carried out to study the
strength characteristics of class 'C' fly ash concrete with cement replacement
levels by 30%, 40% and 50%. The aggregate to binder (a/b) ratio of 1.50
and 2.00 with water binder (w/b) ratios of 0.35, 0.40, 0.45 and 0.50
for each concrete mix. In total twenty two fly ash concrete mixes each
of different mix proportions of fly ash, cement, water binder ratios were
cast and their characteristics were studied. For each fly ash concrete mix
consisting of standard sizes of cubes, cylindrical and prisms specimens
were cast and tested for compressive strength at 28 and 90 days and split
tensile strength, flexural strength. at the ages of 28 days. The test results
were analysed and compared among the two aggregate binder ratios. The
water/binder ratio increases, the compressive strength at 28 days for
30%, 40% and 50% fly ash replacement levels were reduced. The concrete
mix having 40% fly ash replacement and water/ binder ratio 0.40 shows
better split tensile strength of aggregate binder ratio of 2.00.
Keywords : Fly Ash, Aggregate Binder Ratio, Compressive Strength, Split Tensile
Strength, Flexural Strength
A Dynamic Model Study For Real-Life
ESIC Hospital Project
Abhishek V. and Jagadeesh P.
Abstract : All infrastructure projects are said to be inter-dependent, uncertain and
labour-intensive in nature. There is no exception for building services
subsector. For a real time project such as 'The construction, extension
and refurbishment of Employees' State Insurance Corporation (ESIC)
Hospital at Tirupati with total area of 45,000 square feet at an estimated
cost of 110 crores, a generic process model is developed to simulate the
effect of set of identified variables on construction project. The 'Stocks
and Flows' of dynamic model afford relevant insights to project managers,
who apply this knowledge when designing better performance through
more appropriate project planning. It is concluded from the model-based
approach that building services works can be improved through specific
better focussed managerial efforts, such as increasing coordination effectiveness
at the planning stage, clarifying prerequisite conditions prior to installation,
etc. Otherwise, pending works arising from work clashes can lead to
knock-on effects resulting in productivity constraints and pressures, as
well as more rework and demolition. Current study reveals that the
model enables deep insight into various interdependent processes, thereby
improving construction performance levels, by addressing the dynamics
of the various identified critical input parameters.
Keywords : Construction Projects, Construction Project Performance, Dynamic Model
Structure, Endogenous Variables and Exogenous Variables.
Temporal Data In Three Dimensional Models
For Improved Construction Planning
Abhijeet S. Deshpande, Ossama M. Salem and Richard Alan Miller
Abstract : The methods typically used for construction project planning, viz. bar
charts and critical path method are effective in describing only one aspect
of project control, temporal description of the activities that are required
for successful completion of the project. The spatial description of the
activities may be provided textually in the schedule, but the spatial
interaction between various activities is not completely addressed. This
requires a significant effort on the part of project managers and various
subcontractors to ensure that all the subcontractors work harmoniously.
This paper describes a case study involving the construction of a large
industrial project in the US where the temporal data in the CPM schedule
was integrated with the three dimensional model using the Navisworks
software. This integration led to effective co-ordination of various sub-
contractors in the project and enabled the project team to identify
multiple cases of clashes. This case study highlights the use of 4D modeling,
which employs only a sub-set of capabilities of Building Information
Modeling. The potential advantage of use of this technology in construction
projects in India is discussed in this paper.
Keywords : Temporal Data, 4D Modeling, Building Information Modeling.
The Impact Of The Lean Technique Of Value
Stream Mapping In Indian Construction Sites
On Reducing Carbon Emissions
Ann Francis and Ashwin Mahalingam
Abstract : The construction industry is responsible for a considerable amount of
CO
2
and Greenhouse gas emissions. In the present day context, this is
a cause of considerable concern. Can 'Lean' construction techniques that
improve site productivity also improve site sustainability? Preliminary
evidence from other countries indicates that 'Lean' construction can
indeed lead to reduced emissions on construction sites. This paper attempts
to validate this notion on Indian construction sites and also attempts to
compare the extent of productivity enhancement and emission reduction
across a spectrum of construction activities, in order to achieve a better
understanding of where 'Lean' principles can be best used for improving
sustainability. We considered five different construction activities - Piling,
Construction of Open Foundations, Slab Concreting, Blockwork and
Fabricating Steel Trusses. We used Value Stream Mapping (VSM) - a
popularly used and standardized 'Lean' technique to map the current
execution process for each of these activities, and optimize productivity
using Lean techniques. Using simulation techniques, we simulated the
post-optimization performance of these activities. By comparing CO
2
equivalent emissions in the original state and in the optimized state for
each activity type, we were able to assess the role of Lean practices in
promoting sustainable construction. Our results indicate that while Lean
construction can lead to Green construction across all the activities that
we considered, the extent of emission reductions was highest in the
construction of open foundations followed by block work and piling.
Only negligible improvements were visible in concreting and structural
steel fabrication. Our findings are of relevance to policy makers, practitioners
and academics as they seek to make the construction industry more
sustainable.
Keywords : Sustainability, Lean Construction, Value Stream Mapping, Simulation,
CO
2
Equivalent Emissions.
Time Waste And Delays In Construction
Projects : A State Of The Art Report
Safeer Ali Abbas Ali and Arun C.
Abstract : Delays in construction sites occur due to systematic additions of time
waste in various activities that are part of the construction process. Time
waste of a particular activity is the waste in productive time that could
have been made productive. Different activities have different reasons
that contribute to time wastes of that particular activity.
Time management for construction activities is not activity oriented, but
process oriented. Scheduling of projects using bar charts, milestone
charts, Critical Path Method (CPM), Programme Evaluation and Review
Technique (PERT) or even Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)
is done to maximize the project value by finishing the project at the
earliest by managing various activities most judiciously depending on the
sophistication of the method employed. However, these techniques are
less activity oriented, if the work is not discretized to minute level.
Studies indicating activity oriented time wastes for reduction in delay are
not many. Very few authors have studied certain activities in construction
in detail, while the detailed study on time waste generation, its reasons
and techniques for its reduction are almost nonexistent.
This paper gives a good insight into all presently available studies pertaining
to activity oriented as well as non-activity oriented time waste generation.
It is seen that the lean technique implementation has reduced wastages
in construction, reducing time wastes in the process. Further, studies
explaining delay analysis, ways to reduction of delay and betterment of
process are reported by a number of scholars. But time waste studies are
nominal and a lot of effort is required to be put into this area of study.
In case of delay in construction, which is chronic in today's sites delays
are to be eradicated or at least reduced substantially.
Keywords : Time Wastes, Time Management, Lean Construction, Construction Activities.
COMMUNICATION - II
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Corporation Law Quiz AnswersDocument3 pagesCorporation Law Quiz AnswerswivadaNo ratings yet
- Perkin Elmer Singapore Distribution CaseDocument3 pagesPerkin Elmer Singapore Distribution CaseJackie Canlas100% (1)
- Apostles CreedDocument141 pagesApostles Creedjerome mecca0% (2)
- 600 2 Sub-Zero Built-In Series Refrigerator Service ManualDocument188 pages600 2 Sub-Zero Built-In Series Refrigerator Service Manual911servicetechNo ratings yet
- Project On Bid ProcessDocument13 pagesProject On Bid ProcessPushkar Fegade100% (1)
- Raman Spectroscopy: 1 Theoretical BasisDocument9 pagesRaman Spectroscopy: 1 Theoretical BasisJèManziNo ratings yet
- 6 - English-How I Taught My Grandmother To Read and Grammar-Notes&VLDocument11 pages6 - English-How I Taught My Grandmother To Read and Grammar-Notes&VLManav100% (2)
- Teaching Plan FM 2013-14Document3 pagesTeaching Plan FM 2013-14Pushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Application of Cad in RP TechnologyffDocument13 pagesApplication of Cad in RP TechnologyffPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- 16 Ivg Engfuelreg 11 hb130 FinalDocument24 pages16 Ivg Engfuelreg 11 hb130 FinalPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan: Automobile EnggDocument2 pagesTeaching Plan: Automobile EnggPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- P G ChaudharyDocument2 pagesP G ChaudharyPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Be Syllabus AutoDocument1 pageBe Syllabus AutoPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Name of Students Mobile Number RemarksDocument1 pageSr. No. Name of Students Mobile Number RemarksPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
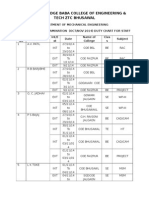
- Shri Sant Gadge Baba College of Engineering & Tech ZTC BhusawalDocument3 pagesShri Sant Gadge Baba College of Engineering & Tech ZTC BhusawalPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Name of Students Mobile Number RemarksDocument1 pageSr. No. Name of Students Mobile Number RemarksPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
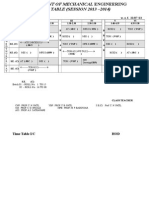
- Mech-Time Table First Sem Mech 13-14 Second Shift Legal DisplayDocument1 pageMech-Time Table First Sem Mech 13-14 Second Shift Legal DisplayPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Be Syllabus AutoDocument1 pageBe Syllabus AutoPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Auto Teaching Plan NbaDocument4 pagesAuto Teaching Plan NbaPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- CGDocument1 pageCGPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- 2007-08 TE Engg MechDocument35 pages2007-08 TE Engg Mechmspiso2000No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering TYDocument25 pagesMechanical Engineering TYShailendrasingh DikitNo ratings yet
- MCADocument19 pagesMCARajasekaran ChNo ratings yet
- Bract's VIT Mechanical Engineering Course Structure and SyllabusDocument164 pagesBract's VIT Mechanical Engineering Course Structure and SyllabusPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- AbbreviationDocument2 pagesAbbreviationPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- 2 AbstractDocument1 page2 AbstractPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- SE Thermodynamics Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesSE Thermodynamics Exam QuestionsPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- References: Jianhui Chen and Ning ZhongDocument2 pagesReferences: Jianhui Chen and Ning ZhongPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Practical Internal Combustion Engine Laser Spark Plug: DevelopmentDocument5 pagesPractical Internal Combustion Engine Laser Spark Plug: DevelopmentPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Robo SoccerDocument1 pageRobo SoccerPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- 01jan March 2011Document8 pages01jan March 2011Pushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Hydrogène Internal Combustion Engine: MR - Yusuf Mulani Ms. Tejashri Khochare Collège of Engineering, PandharpurDocument11 pagesHydrogène Internal Combustion Engine: MR - Yusuf Mulani Ms. Tejashri Khochare Collège of Engineering, PandharpurPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Texomech14: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageTexomech14: Department of Mechanical EngineeringPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- m34 Shiv SanvedDocument9 pagesm34 Shiv SanvedPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- M16 - New Heat Exchanger Design Allows Improved CoolingDocument9 pagesM16 - New Heat Exchanger Design Allows Improved CoolingPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- H-1 Nationalism in Europe NotesDocument5 pagesH-1 Nationalism in Europe Noteskanishk kumarNo ratings yet
- Culture of BMWDocument6 pagesCulture of BMWhk246100% (1)
- Readingdev 7Document2 pagesReadingdev 7api-190328610No ratings yet
- The Meaning of Al FatihaDocument11 pagesThe Meaning of Al Fatihammhoward20No ratings yet
- Paul Daugerdas IndictmentDocument79 pagesPaul Daugerdas IndictmentBrian Willingham100% (2)
- General Ledger Journal Import ProcessDocument13 pagesGeneral Ledger Journal Import ProcessMadhavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Dwi Athaya Salsabila - Task 4&5Document4 pagesDwi Athaya Salsabila - Task 4&521Dwi Athaya SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Vinzenz Hediger, Patrick Vonderau - Films That Work - Industrial Film and The Productivity of Media (Film Culture in Transition) (2009)Document496 pagesVinzenz Hediger, Patrick Vonderau - Films That Work - Industrial Film and The Productivity of Media (Film Culture in Transition) (2009)Arlindo Rebechi JuniorNo ratings yet
- The City - Populus' As A Self-Governing CorporationDocument24 pagesThe City - Populus' As A Self-Governing Corporation马寅秋No ratings yet
- Christian Storytelling EvaluationDocument3 pagesChristian Storytelling Evaluationerika paduaNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Risks of Dexamethasone in Noncardiac Surgery: Clinical Focus ReviewDocument9 pagesBenefits and Risks of Dexamethasone in Noncardiac Surgery: Clinical Focus ReviewAlejandra VillaNo ratings yet
- Bible Study RisksDocument6 pagesBible Study RisksVincentNo ratings yet
- Havighurst ThePirenneThesis (BW)Document133 pagesHavighurst ThePirenneThesis (BW)tmarr014100% (1)
- A Case of DrowningDocument16 pagesA Case of DrowningDr. Asheesh B. PatelNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court: Lichauco, Picazo and Agcaoili For Petitioner. Bengzon Villegas and Zarraga For Respondent R. CarrascosoDocument7 pagesSupreme Court: Lichauco, Picazo and Agcaoili For Petitioner. Bengzon Villegas and Zarraga For Respondent R. CarrascosoLOUISE ELIJAH GACUANNo ratings yet
- Telesure Mock 8Document13 pagesTelesure Mock 8Letlhogonolo RatselaneNo ratings yet
- Adina CFD FsiDocument481 pagesAdina CFD FsiDaniel GasparinNo ratings yet
- Guide To Djent ToneDocument6 pagesGuide To Djent ToneCristiana MusellaNo ratings yet
- Reconsidering Puerto Rico's Status After 116 Years of Colonial RuleDocument3 pagesReconsidering Puerto Rico's Status After 116 Years of Colonial RuleHéctor Iván Arroyo-SierraNo ratings yet
- Are Moral Principles Determined by SocietyDocument2 pagesAre Moral Principles Determined by SocietyKeye HiterozaNo ratings yet
- Mr. Honey's Large Business DictionaryEnglish-German by Honig, WinfriedDocument538 pagesMr. Honey's Large Business DictionaryEnglish-German by Honig, WinfriedGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Answer Here:: FAMILY NAME - FIRST NAME - CLASSCODEDocument4 pagesAnswer Here:: FAMILY NAME - FIRST NAME - CLASSCODEUchayyaNo ratings yet
- Functional Appliances 2018Document45 pagesFunctional Appliances 2018tonhanrhmNo ratings yet
- PIC16 F 1619Document594 pagesPIC16 F 1619Francisco Martinez AlemanNo ratings yet