Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
Uploaded by
api-19937584100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
1K views26 pagesIntel is expanding its history of innovations with new notebook PC capabilities designed specifically for the mobile world. This technology allows users to work, play and connect without wires and choose from a whole new world of thin and light notebook PCs. With Intel(r)Centrino mobile technology, three components work together to deliver a breakthrough in freedom and capability-work, learn and play on the go.
Original Description:
Original Title
INTEL CENTRINO MOBILE TECHNOLOGY
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIntel is expanding its history of innovations with new notebook PC capabilities designed specifically for the mobile world. This technology allows users to work, play and connect without wires and choose from a whole new world of thin and light notebook PCs. With Intel(r)Centrino mobile technology, three components work together to deliver a breakthrough in freedom and capability-work, learn and play on the go.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
1K views26 pagesIntel Centrino Mobile Technology
Uploaded by
api-19937584Intel is expanding its history of innovations with new notebook PC capabilities designed specifically for the mobile world. This technology allows users to work, play and connect without wires and choose from a whole new world of thin and light notebook PCs. With Intel(r)Centrino mobile technology, three components work together to deliver a breakthrough in freedom and capability-work, learn and play on the go.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
1. INTRODUCTION
Intel is expanding its history of innovations with new
notebook PC capabilities designed specifically for the mobile
world. This technology allows users to work, play and connect
without wires and choose from a whole new world of thin and
light notebook PCs that are designed to enable extended
battery life.
This new innovative technology delivers breakthrough
mobile performance and low power enhancements to enable
extended battery life in notebook PCs, combined with
integrated wireless LAN capability and standards based
security support.
With Intel®Centrino mobile technology, three
components work together to deliver a breakthrough in
freedom and capability-to work , learn and play on the go,
these components include;
• Intel®Pentium® M Processor
• Intel® 855 chipset family
• Intel®PRO/Wireless network connection
The Intel Pentium M processor is offered at speeds of
1.30 GHz, 1.40 GHz, 1.50 GHz, 1.60 GHz and 1.70 GHz. In the
Highest Frequency Mode(HFM), the notebook PCs can achieve
Dept. of CSE 1 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
high performance on the most complex business and Internet
applications. The lowest frequency mode (LFM) speed on all
processor is 600 MHz which reduces power consumption and
enables extended battery life. The on demand performance
switches between HFM,LFM and intermediate Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep technology operating points based on user needs,
optimizing application performance and batterylife.
When an Intel Pentium M processor is used in
conjunction with the Intel® 855 chipset, the resulting platform
provides reliable , balanced performance for today’s
mainstream notebook PCs, with head room to remain
productive as new applications emerge. The Intel® 855
chipset family offers support for DDR memory technology and
offers a system bus frequency of 400 MHz.
The integrated Wi-Fi Certified Intel PRO/wireless 2100
network connection has been validated to work with all of the
Intel Centrino Mobile Technology components and is
interoperable with 802.11b Wi-Fi certified access points. It
supports industry standards- based wireless LAN security such
as 802.1x, WEP and WPA. Intel PRO/ wireless 2100 network
connection also supports WLAN security enhancements for
CISCO compatible extensions on certain models. Subject to PC
manufactures availability and validation this enables
interoperability with CISCO Aironet wireless LAN
infrastructure. For comprehensive security support The Intel
Dept. of CSE 2 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
PRO/ 2100 network connection has been verified with leading
VPN suppliers like CISCO, Microsoft, Intel and CheckPoint.
Notebook PC performance does not depend on the
microprocessor alone. Hardware and software system
components such as the Operating Systems, the Graphics and
the IO subsystems, application software, and memory may
significantly affect performance results. For this reason this
report illustrates Intel Centrino Mobile Technology and its
performance on a consistent PC configuration.
Dept. of CSE 3 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
2. THE INTEL PENTIUM M PROCESSOR
The Intel Pentium M Processor is designed with a mobile
optimized architecture that delivers advanced performance at
very low power.
The highlights of the Intel Pentium M Processor:
• Available at 1.3 GHz, 1.4 GHz, 1.4 GHz, 1.6 GHz, 1.7
GHz.
• Supported by the Intel 855 chipset family.
• Featuring a high performance, low power mobile
optimized micro architecture.
• On-die, primary 32KB instruction cache and 32KB write-
back data cache.
• On-die, 1MB level-2 cache with Advanced Transfer
Cache Architecture.
• Advanced power management including enhanced Intel
speed step technology support with multiple operating points.
• Fully compatible with existing Intel architecture based
software.
• Streaming SIMD Extension 2.
• Intel MMX media enhancement technology.
• Available in Micro FCPGA and micro FCBGA packages.
Dept. of CSE 4 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
• Based upon Intel’s advanced 0.13µ maufacturing
process.
3. INTEL PENTIUM M PROCESSOR PRODUCT
FEATURE HIGHLIGHTS
The Intel Pentium M Processor micro-architecture is
optimized for high performance and low power. It includes a
number of features including Enhanced Intel SpeedStep
technology support, a high performance power optimized
400MHZ system bus, 32KB level1 instruction and data cache,
1MB level 2 advanced transfer cache , streaming SIMD
Extension 2 support and advanced thermal monitoring
capabilities. These features and resulting benefits are
described in more detail below:
High performance and low power core
The Intel Pentium processor features a high
performance core architecture that uses techniques like
Micro–op fusion and Advanced Stack Management to
maximize performance. Micro-op fusion combines micro-ops
derived from the same macro-op. Advanced Stack
Management reduces the number of micro-ops in the stack
related operations by tracking relative stack pointer changes
locally. Reduction in the number of micro-ops results in more
efficient scheduling and better performance at lower power.
Dept. of CSE 5 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
The Intel Pentium M Processor core can operate at very low
voltages and use advanced techniques to minimize clock and
signal switching resulting in very low power dissipation in the
active state. The processor features dynamic power
management states that consists of Stop Grant, Sleep, Deep
Sleep, and Deeper Sleep Alert states that allow the processor
to quickly enter and exit from these states to provide fast
responsiveness and significant power savings.
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology
The Intel Pentium M processor features Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep® technology. Unlike previous implementations of
Intel SpeedStep technology, this technology enables the
processor to switch between multiple frequency and voltage
points instead of two. This will enable superior performance
with optimal power savings. Switching between states is
software controlled unlike previous implementations where
the GHI# pin is used to toggle between two states. The
following are the key features of Enhanced Intel SpeedStep
technology:
• Multiple voltage/frequency operating points provide
optimal performance at the lowest power.
• Voltage/Frequency selection is software controlled by
writing to processor MSR’s (Model Specific Registers)
thus eliminating chipset dependency.
Dept. of CSE 6 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
• The processor controls voltage ramp rates internally
to ensure glitch free transitions.
• Low transition latency and large number of transitions
possible per second.
• No bus master arbiter disable required prior to
transition and no processor cache flush necessary.
• Improved Intel Thermal Monitor mode.
400 MHz System Bus with low power features
The Intel Pentium M processor supports Intel’s highest
performance mobile system bus by delivering 3.2 GB of data
per second into and out of the processor .this is accomplished
through a physical signaling scheme of quad pumping the
data transfers over a 100-MHz clocked system bus and a
buffering scheme allowing for sustained 400-MHz data
transfer .the system bus features the following low power
enhancement:
• Low voltage swing
• Intelligent disabling of data, address and
control signal buffers
• Dynamic on-die termination disabling
32KB Level 1 Instruction and Data Caches
Dept. of CSE 7 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
Both instruction and data Caches on the Intel Pentium
processor are 32KB in size. Large L1 caches provide fast
access to critical instructions and data, resulting in very high
performance.
1MB Level 2 Advanced Transfer Cache
The Level 2 Advanced Transfer Cache (ATC) is 1MB in
size and delivers an extremely high data throughput channel
between the level 2 Cache and the processor core. The
Advanced Transfer Cache transfers data on each core clock.
Features of the ATC include:
• Non-blocking, full speed, on-die Level 2 Cache
• 8-way set associativity
• data clocked into and out of the cache every clock cycle
Advanced Branch Prediction and Data Prefetching
The Intel Pentium M processor features an advanced
branch prediction architecture that combines three types of
predictors –Global, Bi-Modal and Loop Detector. The processor
automatically selects the most optimal algorithm to use,
significantly reducing the number of mis-predicted branches.
The processor also features an advanced data prefetcher that
can track up to 8 upstream and 4 downstream operations
simultaneously. Data is perfected from main memory to the L2
Dept. of CSE 8 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
cache in advance, resulting in higher performance by reducing
the need to access system memory.
Dept. of CSE 9 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
Streaming SIMD Extensions 2(SSE2)
The Intel Pentium M processor supports the complete
SSE2 instruction set. These instructions include 128-bit SIMD
integer arithmetic and 128-bit SIMD double-precision floating-
point operations. These instructions reduce the overall
number of instructions required to execute a particular
program task and as a result can contribute to an overall
performance increase.
Features used for test and performance/thermal
monitoring
• Built in Self test (BIST) provides single stuck at fault
coverage of the micro code and large logic arrays, as well as
the testing of the instruction cache, data cache, translation look
aside buffers(TLBs) and ROMs.
• IEEE 1149.1 standard test access port and boundary scan
mechanism enables testing of the Intel Pentium M Processor
and system connections through a standard interface.
• Internal performance counters can be used for
performance monitoring and event counting.
Dept. of CSE 10 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
• Includes an on–die thermal diode and Intel thermal
monitor feature for thermal management purpose. The Intel
Pentium M processor features a new thermal monitor mode
which uses Enhanced Intel Speed Step technology instead of
clock control. This technique achieves efficient thermal
management with minimal performance impact.
• The Intel Pentium M processor has a maximum junction
temperature (TJ) specification of 100 degree Celsius.
Dept. of CSE 11 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
4. INTEL 855PM CHIPSET PRODUCT FEATURE
HIGHLIGHTS
As the next step in the evolution of Intel Hub
architecture for note book PCs using Intel Centrino mobile
technology, the Intel 855 PM Chipset was designed in tandem
with the Intel Pentium M processor.
The Intel 855 PM memory controller hub delivers
support for either PC 1600 and PC 2100 DDR memory
technology and a 400 MHz system bus , providing the latest
graphics support through 1.5 v ADP4X technology. Together
these features deliver the highest total bandwidth capabilities
to the PC platform. The enhanced 82801 DBM I/O Controller
Hub 4 (ICH4-M) delivers twice the I/O bandwidth over
traditional bridge architecture and provides dedicated data
path to fully optimize the additional bandwidth. The ICH4-M
makes a direct connection from the graphics and memory for
faster access to peripherals and provides the features and
bandwidth required for a high performance note book PC.
In addition to advanced application support , the Intel
855 chipset was designed with the following features to
enhance the end-user experience:
Dept. of CSE 12 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
• 400MHz system bus delivers a high bandwidth connection
between the Intel Pentium M processor and the platform
• The DDR channel memory delivers up to 2.1 GB per
second of memory bandwidth to the processor. High memory
bandwidth, coupled with an efficient protocol, deliver a
balanced platform support and provide the memory bandwidth
necessary to extract the highest performance from the Intel
Pentium M processor.
• AGP4X interface allows graphics controllers to access main
memory over 1 GB/s, twice that of previous AGP platform
• Support for high speed USB 2.0 with backward
compatibility with USB 1.1
• AC97 2.2 interface with support for a third codec to
provide 20 bit resolution. The latest AC97 audio delivers six
channels of audio for enhanced sound quality and full surround
sound capability for live broadcast and other digital dashboard
programming.
• LAN Connect Interface (LCI) provides flexible network
solutions such as home phone line, 10/100 Mbps Ethernet, and
10/100Mbps Ethernet with LAN manageability.
• Dual Ultra ATA-100 controllers support the fastest IDE
interface for transfer to storage devices.
• Support for ACPI-defined power states C1-C4, S1, S3-S5.
• Support for enhanced Intel Speed Step Technology.
• Support for “deeper sleep” power state.
• Allows wake up from sleep states S1-S4.
Dept. of CSE 13 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
The 855PM Chipset is designed for low power and great
performance supporting architectural features for power
reduction techniques including:
• Chipset MCH core voltage reduced to 1.2V for reduced
power consumption
• Management of DDR SO-DIMM (platform) power by using
aggressive use of CKE Power-Down when memory interface is
idle and enhancement of per-bank page-closing policy for the
memory interface.
• Management of Intel 855PM MCH DDR I/O power with
aggressive tri-stating of control signals when not needed and
partial drive of command signals when possible and including
during idle cycles reducing toggle rates of control line.
• Support for DDR Read Throttling via External Thermal
Sensor to prevent memory overheating, disabling of I/O buffers
and DDLs when possible, turning off Hub interface and Host
PLLs also add to increased power savings for the 855PM chipset.
Some of the features added to the Intel 855PM Chipset
design to boost MCH performance include:
• Significant timing improvements to allow a robust DDR266
channel with a combination of significant logic changes and I/O
changes.
• Shorter memory refresh sequence with shorter memory
controller queues provides additional bandwidth.
• Reduction in page miss occurrences due to significant
improvements in page closing algorithms
Dept. of CSE 14 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
5. INTEL PRO /WIRELESS 2100 NETWORK
CONNECTION
To access the Internet wirelessly, a laptop uses radio
signals to communicate with a wireless LAN via base band
circuitry, a media access controller, and a radio. (Centrino
does this with three chips.) A wireless LAN operates with one
of two IEEE standard protocols finalized in 1997 and differing
in data rate and signal frequency. The two standards are the
802.11a and 802.11b, the latter often called Wi-Fi. The
802.11a operates at 5 GHz and can transmit data at up to 54
Mb/s. The 802.11b operates at 2.4 GHz and transmits data at
11 Mb/s. The two protocols are not compatible: a laptop
equipped with 802.11b circuitry alone cannot access the
Internet at a hotspot running 802.11a. A newer protocol, IEEE
802.11g, is being finalized and should be out this summer. It
has the same data rate as 802.11a but operates on the same
frequency as 802.11b and is compatible with it.
According to Shane Rau, senior research analyst at
International Data Corp. (Framingham, Mass.), Centrino’s
success, at least initially, will not be due to its wireless
component. First, it uses separate chips for the 802.11b base
band and media access controller functions, whereas many
companies combine them on the same chip, and so are able
to provide a more compact two-chip set that includes the
radio. Second, although dual-band a+b chips are being sold by
Intersil Corp. (Irvine, Calif.), Atheros Communications Inc.
Dept. of CSE 15 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
(Sunnyvale, Calif.), and others, Intel’s chips contain only the
radio for 802.11b and not the one for 802.11a. So a Centrino-
based machine can access the Internet only at 802.11b
hotspots. “The consensus is that to be competitive, you at
least need a dual-band solution,” says Rau.
Another source of dismay may well be that only one of
the three chips, the media access controller, was designed
and built by Intel. IDC’s Ken Furer told IEEE Spectrum that
Intel’s original plan was to develop its own 802.11a+b chipset
as a part of Centrino. “However, it was apparent Intel was still
having some problems with the 802.11a RF component, so
they launched Centrino in a tiered approach.” The current
version uses an 802.11b base band chip that incorporates a
good deal of intellectual property from Symbol Technologies
Inc. (Holtsville, N.Y.) and is manufactured by Texas
Instruments Inc. (Dallas). Intel is buying 802.11b radio chips
from Royal Philips Electronics NV (Amsterdam, the
Netherlands).
According to Intel spokesperson Howard High, the
company had built 802.11a radio ICs before the Centrino
launch, but decided it needed more time to ensure the chip
lived up to Intel’s reliability and quality standards. The RF
circuitry for 802.11a should be ready by midyear. The 802.11a
base band circuitry is already part of the media access
controller chip.
Dept. of CSE 16 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
Highlights of the Intel PRO/ wireless 2100 network connection
include:
• Single band support ,providing the ability to connect to
802.11b networks
• Industry standards and extended wireless security
support(WEP,802.1X and Cisco LEAP)
• Available Intel PROSet software with advanced profile
management support, allows multiple setup profiles to connect
to different WLAN networks
• Available Intel PROSet software with automatic WLAN
switching support enables automatic switching between wired
and wireless LAN connections
• Available Intel PROSet software supports
Cisco*,Checkpoint*,Microsoft* and Intel VPN connections
• Intel Wireless Coexistence system support enables
reduced interfernce between PRO /Wireless and Bluetooth*
devices
• Per-packet antenna section enables optimized WLAN
performance
• Intel Intelligent Scanning Technology, reduces power by
controlling the frequency of scanning for access points
• Power Save Protocol(PSP) is a user selectable feature
with five different power states, which allows the user to make
their own power versus performance choice when in battery
mode.
Dept. of CSE 17 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
6. PERFORMANCE SUMMARY
Mobile Experience- Mobile Mark *2002
Mobile Mark *2002 is used to evaluate notebook PC
user experience by measuring both performance and battery
life at the same time on the same workload. Mobile Mark
*2002 is a tool that measures notebook PC performance on
popular business- oriented applications in Microsoft*
Windows* operating environment. The productivity usage
model provides computations representing today’s business
users using popular Office productivity and content creation
applications. This usage model reports a performance score
and a battery life score.
The productivity workload of Mobile Mark *2002
consists of emerging usage model and popular productivity
applications including;
• Adobe Photoshop 6.0.1
• Macromedia Flash 5.0
• McAfee Virus Scan 5.13
• Microsoft Excel 2002
• Microsoft Outlook 2002
• Microsoft PowerPoint 2002
• Netscape Communicator 6.0
• WinZip 8.0
Dept. of CSE 18 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
Dept. of CSE 19 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
Dept. of CSE 20 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
7. CONCLUSION
Although the wireless package is less than ideal,
Centrino shines at improving battery life and performance.
Power consumption is less than 60 percent that of the mobile
version of Intel’s Pentium IV, while performance is better by
15 percent, as measured by the notebook PC benchmark
Mobile Mark 2002.
These pluses are largely due to Centrino’s centerpiece,
the Pentium M processor, which was designed to save power
by weighing the benefits of each processor function against its
power consumption. Also, an enhanced version of Intel’s
Speed- Step technology, included in the processor, saves
power by stepping the operating voltage and frequency up or
down to match the processing demands of the application
running on the processor. Granted, previous Pentium mobile
processors have also included SpeedStep. But for the Pentium
M, designers have increased the number of steps over which
frequency and voltage can be varied, to better match
processor speeds to the needs of the application.
Power is also saved by turning off clocks and circuits
when they are not needed and running the secondary on chip
cache more slowly than the processor. All told, then, laptop
batteries can last much longer on a single charge. For
example, Robert Enochs, IBM’s product manager for the T-
Dept. of CSE 21 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
series ThinkPad, told Spectrum that the company’s Centrino-
based T40 can run up to 5.5 hours on a single charge of the
standard T40 battery—almost three times the battery life of
previous models. An optional high-capacity battery gives 7.2
hours of use, which can be extended a further 2.5 hours by
plugging a second battery into the computer’s peripheral bay.
The low power consumption can also do away with the need
for fans, allowing notebook makers to design slimmer, lighter
notebooks.
Dept. of CSE 22 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
8. REFERENCES
• www.intel.com
• www.pcquest.com
• www.ibm.com
• www.whitepapers.com
Dept. of CSE 23 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
ABSTRACT
Intel announced a new brand name for its next
generation mobile processor technology: Centrino. It was
designed to help manufactures to build notebooks that use
less power and offer extended battery life along with better
wireless networking facilities. Centrino family will also include
supporting chipsets and wireless radio modules designed to
allow new notebooks to use 802.11 wireless networking. The
Pentium–M Chip runs at speed of about 1.4 GHz. Centrino
extends its performance by adding features extended battery
life and introducing enhanced speed step technology. The
performance is also increased by using large caches. A wide
range of notebook manufactures are expected to adopt the
Centrino technology in a multitude of so called thin and light
notebook models weighing 5 pounds or less.
Dept. of CSE 24 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
CONTENTS
1. Introduction
2. Intel Pentium M processor
3. Intel Pentium M processor Product Feature highlights
4. Intel 855PM Chipset product feature highlights
5. Intel PRO /Wireless 2100 Network Connection
6. Performance Summary
7. Conclusion
8. Reference
Dept. of CSE 25 MESCE, Kuttippuram
Seminar Report ’03 Intel Centrino Mobile Technology
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
I express my sincere thanks to Prof. M.N
Agnisarman Namboothiri (Head of the Department,
Computer Science and Engineering, MESCE), Mr. Sminesh
(Staff incharge) for their kind co-operation for presenting the
seminar.
I also extend my sincere thanks to all other members
of the faculty of Computer Science and Engineering
Department and my friends for their co-operation and
encouragement.
ARUN SIDHAN
Dept. of CSE 26 MESCE, Kuttippuram
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Ntroduction: Computer Memory Based On The Protein Bacterio-RhodopsinDocument19 pagesNtroduction: Computer Memory Based On The Protein Bacterio-Rhodopsinapi-19937584No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Glimpse Into The Technology of 21 Century NanotechnologyDocument24 pagesA Glimpse Into The Technology of 21 Century Nanotechnologyapi-19937584100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Quantum CryptographyDocument33 pagesQuantum Cryptographyranga231980No ratings yet
- Tempest & EchelonDocument30 pagesTempest & Echelonapi-19937584No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Voice User InterfaceDocument16 pagesVoice User InterfacebeinsyncNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Www.bestneo.comDocument30 pagesWww.bestneo.comakhisarNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Artificial EyeDocument31 pagesArtificial Eyeapi-19937584No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Smart Dust Full ReportDocument26 pagesSmart Dust Full ReportDivya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Wavelet Video Processing Technolog Full ReportDocument20 pagesWavelet Video Processing Technolog Full ReportKrishna Kumari Sahoo100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- SpectDocument31 pagesSpectapi-1993758480% (5)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Sensors On 3D DigitizationDocument21 pagesSensors On 3D DigitizationUnni KrishnanNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Speed Detection of Moving Vehicle Using Speed CamerasDocument22 pagesSpeed Detection of Moving Vehicle Using Speed Camerasapi-19937584No ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Synthetic Aperture Radar System Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesSynthetic Aperture Radar System Seminar ReportsasankrpNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- SATRACKDocument22 pagesSATRACKapi-19937584100% (6)
- Ovonic Unified MemoryDocument28 pagesOvonic Unified Memoryapi-19937584No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Proteomics Full ReportDocument24 pagesProteomics Full ReportI'am AjasNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency Light SourcesorigDocument21 pagesRadio Frequency Light Sourcesorigapi-19937584No ratings yet
- Rfid Technolqogy Full ReportDocument29 pagesRfid Technolqogy Full ReportManjula Huded100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Moct Seminar ReportDocument21 pagesMoct Seminar ReportSohail AliNo ratings yet
- NavBelt and GuideCane Seminar ReportDocument29 pagesNavBelt and GuideCane Seminar ReportkanavkanotraNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Interactive Voice Response System Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesInteractive Voice Response System Seminar ReportMurali Dhar Kankati100% (1)
- Multi Sensor Fusion and Integration Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesMulti Sensor Fusion and Integration Seminar ReportJijo FrancisNo ratings yet
- Landmine Detection Using Impulse Ground Penetrating Radar Seminar ReportDocument24 pagesLandmine Detection Using Impulse Ground Penetrating Radar Seminar ReportthejasgvNo ratings yet
- Powercommand 40-02 TRANSFER Switch ControlDocument5 pagesPowercommand 40-02 TRANSFER Switch ControlWagnerNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- PL 300Document15 pagesPL 300Gabriel Mignani100% (2)
- 4 Selecting Relevant LiteratureDocument11 pages4 Selecting Relevant LiteratureHeather Kang100% (1)
- BLC Project PDFDocument23 pagesBLC Project PDFFakibazz frndsNo ratings yet
- Combined Science Step Ahead Book 4-1 PDFDocument1 pageCombined Science Step Ahead Book 4-1 PDFmadhuvu tadiwanashe60% (5)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- CS6310 Udacity TranscriptsDocument309 pagesCS6310 Udacity TranscriptsPhillip DieppaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Firstprelim Cdi 9Document3 pagesWeek 1 Firstprelim Cdi 9Ella BanlasanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Maya Commands - Arguments PDFDocument11 pages1 - Maya Commands - Arguments PDFGustavoLadinoNo ratings yet
- LogDocument65 pagesLogChristian EmerencianaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Systems and Services: InstructionsDocument3 pagesVirtual Systems and Services: InstructionsJahanzaib LodhiNo ratings yet
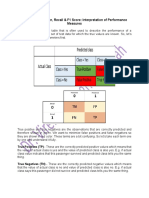
- Accuracy, Precision, Recall & F1 Score Interpretation of Performance MeasuresDocument5 pagesAccuracy, Precision, Recall & F1 Score Interpretation of Performance MeasuresFriday JonesNo ratings yet
- GalleonOne 1 3KVA Tower RT ManualDocument34 pagesGalleonOne 1 3KVA Tower RT Manualevanilsonsantana100% (1)
- Ej2 Aspnetcore DocsDocument1,499 pagesEj2 Aspnetcore Docscesar64091No ratings yet
- FSE Application Form - MSF 4203 REV 0123 PDFDocument3 pagesFSE Application Form - MSF 4203 REV 0123 PDFVadym DerevyanchukNo ratings yet
- Testmax Xlbist: X-Tolerant Logic Built-In Self-Test (BIST)Document3 pagesTestmax Xlbist: X-Tolerant Logic Built-In Self-Test (BIST)Hitesh PradhanNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chapter 7 Validation and VerificationDocument38 pagesChapter 7 Validation and VerificationMoses GeorgeNo ratings yet
- MIS605 Systems Analysis and DesignDocument5 pagesMIS605 Systems Analysis and DesignAbhilasha Dahiya100% (1)
- Comprehensive Report: Acunetix Threat Level 3Document38 pagesComprehensive Report: Acunetix Threat Level 3Yudha Trias RusmanaNo ratings yet
- The Economic Value of Prevention in The ReportDocument51 pagesThe Economic Value of Prevention in The ReportIkponmwosa AghimienNo ratings yet
- JDB - Java Debugger, Which Help Us To Find Errors in Our ProgramsDocument6 pagesJDB - Java Debugger, Which Help Us To Find Errors in Our ProgramsJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Sem I 2020-2021 Software Quiz (Chapters 2, 3 5)Document5 pagesSem I 2020-2021 Software Quiz (Chapters 2, 3 5)Syahema SalehNo ratings yet
- Srs Template With ExplanationDocument90 pagesSrs Template With ExplanationBetrand AjebuaNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocument22 pagesCustomer Relationship ManagementAffan PrinceNo ratings yet
- FIORI AppsDocument1,319 pagesFIORI Appsmusoohansa100% (1)
- Standard Telephone Set: Old Telephone Services (POTS), Which Involves Subscribers Accessing The PublicDocument2 pagesStandard Telephone Set: Old Telephone Services (POTS), Which Involves Subscribers Accessing The PublicjeevanNo ratings yet
- XDA 1 ManualDocument22 pagesXDA 1 Manualneo2025No ratings yet
- Unit1 and 2 Meshram SirDocument104 pagesUnit1 and 2 Meshram SirsiddheshNo ratings yet
- CT071-3-3-DDAC-Class Test Paper #2 - QuestionDocument8 pagesCT071-3-3-DDAC-Class Test Paper #2 - QuestionPurnima OliNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Networks (EIE418) : Prof. E. Adetiba (PH.D, R.Engr. (COREN) )Document52 pagesData Communication and Computer Networks (EIE418) : Prof. E. Adetiba (PH.D, R.Engr. (COREN) )John DavidNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Submission of Eforms For Creation of NIC E-Mail IDDocument10 pagesProcedure For Submission of Eforms For Creation of NIC E-Mail IDKrishNo ratings yet
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (228)
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandCyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsHoubing H. SongNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)