Professional Documents
Culture Documents
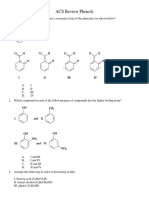
Section-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X X
Uploaded by
Priyansh YadavOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Section-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X X
Uploaded by
Priyansh YadavCopyright:
Available Formats
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
SECTION-I (Single Correct Choice)
1. Arrange the following compounds in the decreasing of their boiling points.
(I) 3-hexanol (II) 1-hexanol (III) 2-methyl-2-pentanol (IV) 1-octanol
(A) I >II >III >IV (B) IV >II >I >III
(C) IV >III >II >I (D) II >III >I >IV
2. Which of the following reagents would be most effective for the following reaction sequence?
(A) KOH (B) Sodium ethoxide
(C) Sodium acetate (D) Butyl lithium
3. Which of the following is the best reagent to convert bromobenzene into benzene?
(A) LiAlH4 (B)NaBH4 (C) H2/Ni (D) Mg in ether ; water
4. Which sequence of steps describes the best synthesis of 2-phenylpropene?
(A) Benzene +2-chloropropene, AlCl3
(B) 1. Benzaldehyde +CH3CH2MgBr, diethyl ether 2. H3O
+
3. H2SO4, heat
(C) 1.Bromobenzene+Mg, diethyl ether 2. Propanal 3. H3O
+
4. H2SO4, heat
(D) 1. Bromobenzene +Mg, diethyl ether 2. Acetone 3. H3O
+
4. H2SO4, heat
5.
If A is an ester and only one alcohol is produced in the above reaction, which of the following could be the structure of A?
(A) CH3CH2COOCH3 (B) CH3COOC2H5
(C) HCOOCH2CH2CH3 (D) HCOOCH(CH3)CH3
6. 1,3-Propanediol can be distinguished from 1,2-ethanediol by
(A) KMnO4 (B) HCl+ZnCl2
(C) HIO4 followed by AgNO3 (D) Na
7. What sequence of steps represents the best synthesis of 4-heptanol?
(A) CH3CH2CH2MgBr +butanal in diethyl ether followed by H3O
+
(B) CH3CH2CH2CH2MgBr +acetone in diethyl ether followed by H3O
+
(C) (CH3CH2CH2)2CHMgBr +formaldehyde in diethyl ether followed by H3O
+
(D) CH3CH2CH2MgBr +ethyl acetate in diethyl ether followed by H3O
+
8. Which of the esters shown, after reduction with LiAlH4 and aqueous workup, will yield two molecules of only a single alcohol?
(A) CH3CH2CO2CH2CH3 (B) C6H5CO2C6H5
(C) C6H5CO2CH2C6H5 (D) None of these
9.
Which of the following can be X?
(A) CH3CHO; H
+
(B) Ethylene oxide; H
+
(C) CH3COCH3; H
+
(D) HCHO; H
+
10. Which of the following alcohols gives the best yield of dialkyl ether on being heated with a trace of sulfuric acid?
(A) 1-Pentanol (B) Cyclopentanol
(C) 2-Pentanol (D) 2-Methyl-2-butanol
HC CH
1.1eq NaNH
2
NaNH
2
NaNH
2
X X
H
2
/Pd
BaSO
4
Na/liq.NH
3
H
3
C
H H
CH
2
CH
2
OH
H
H
3
C H
CH
2
CH
2
OH
1. 1 eq NaNH
2
2. CH
3
I 2. CH
3
I
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
11. Which of the following is the best method to prepare (R)-2-butanol?
CH
3
CH
2
CCH
3
O
1. LiAlH
4
2. H
3
O
+
(A)
C H
3
C
H
H
3
CH
2
C
OCCH
3
O
1. LiAlH
4
2. H
3
O
+
(B)
CH
3
CH
2
CH
O
1. CH
3
MgBr/ether
2.H
3
O
+
(C)
C H
H
3
C
H
3
CH
2
C
1. LiAlH
4
2. H
3
O
+
OCCH
3
O
(D)
12. Which sequence of steps describes the best synthesis of 2-methyl-3-pentanone?
(A) 1. 1-Propanol +(CH3)2CHMgBr, diethyl ether 2. H3O
+
3. PDC, CH2Cl2
(B) 1. 1-Propanol +Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O, heat 2. SOCl2 3. (CH3)2CHCl, AlCl3
(C) 1. 1-Propanol +PCC, CH2Cl2 2.(CH3)2CHLi, diethyl ether 3.H3O
+
4.Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4
(D) 1. 2-Propanol +Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O, heat 2. CH3CH2CH2Li, diethyl ether 3. H3O
+
4. PCC, CH2Cl2
13. Which of the following compounds is unlikely to react with sodium metal?
(A) C2H5OC2H5 (B) C2H5OH (C) C2H5Br (D) C6H5OH
14.
Which of the following can be A?
(A) n-propyl alcohol (B) isopropyl alcohol (C) n-butyl alcohol (D) isobutyl alcohol
15. Which one of the following alcohols will be oxidized by J ones' reagent (CrO3 in 50% sulphuric acid) to a ketone having the
same number of carbon atoms ?
(A) 1-methylcyclohexanol (B) 3,3-dimethylcyclopentanol
(C) 3-methyl-1-hexanol (D) 3-ethyl-3-hexanol
16. What reagent would be suitable for distiguishing 1-methoxy-3-methyl-2-butene from its isomer 4-methyl-3-penten-1-ol?
A) bromine in methylene chloride B) KMnO4 in aqueous base
C) AgNO3 in dilute NH4OH D) sodium metal in hexane
17. A chiral C5H10O ether reacts with hot HI to give a C5H10I 2 product. Treatment of this with hot KOH in ethanol produces 1,3-
pentadiene. What is the structure of the original ether?
O O
O
O
(A) (B) (C) (D)
18.
Select appropriate methods of preparing X and Y from 2-methylpropene.
(A) X- add HBr, then react with Mg in ether Y- add water, acid-catalysis
(B) X- add HBr/H2O2 , then react with Mg in ether Y- react with C6H5CO3H/CH2Cl2
(C) X- add HOBr Y- add B2H6in ether, then NaOH
(D) X- add HOBr Y- add HBr (peroxides) ,then react with Mg in ether
19.
CH
3
-CH-CH
2
Br
CH
3
CH
3
-C-CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
I
CH
3
Select the best series of reagents for the above conversion.
(A) (i ) Mg in ether; .(ii) ethylene oxide (C2H4O); (iii ) HI & heat
(B) (i ) NaCCH in ether; .(ii ) H2 +Lindlar catalyst; (ii i) HI
(C) (i ) KOH in alcohol; (ii) C6H5CO3H in CH2Cl2; (ii i) NaCCH in ; (iv) 2 H2 +Pt
(D) (i ) NaCCH in ether; .(ii ) H3O
+
+HgSO4; (i ii ) HI & heat
X +Y
2,5-dimethyl-2-hexanol
H
3
O
+
A
PBr
3
Mg
dry ether
B
CrO
3
/H
+
1. B
2.H
3
O
+
2,3-Dimethyl-2-butanol
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
20. Select the best combination of reagents for the following conversion.
OH
CH
2
OH
OH
(A) I. PBr3 II. NaNH2 III. O3; Zn/H2O (B) I. H
+
/D II. O3;Zn/H2O III. LiAlH4/ H
+
(C) I. K2Cr2O7 II. LiAlH4; H
+
(D) I. HIO4 II. LiAlH4; H
+
21. A chiral C7H16O2 diol is oxidized by PCC in CH2Cl2 to an achiral C7H12O2 compound. Which of the following would satisfy these
facts?
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
(A) (B) (C) (D)
22. What product is expected from the following reaction?
O
O
excess HI
A
(A) 2 CH3CH2I B) 2 ICH2CH2OH
(C) 2 ICH2CH2I D) CH3CH2I +CH3CH2OH
23.
Which of the following might be A?
(A) 1-penten-3-ol (B) 3-penten-2-ol
(C) 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol (D) 2-methyl-2-buten-1-ol
24. A C6H12O compound does not react with Br2 in CCl4, produces a flammable gas on treatment with LiAlH4, and reacts with
H2CrO4 changing the color from orange to green. Which of the following compounds best agrees with these facts?
(A) 1-methylcyclopentanol (B) methoxycyclopentane
(C) Hex-3-en-1-ol (D) cyclohexanol
25. Two equivalents of OsO4; H2O/NaHSO3 hydroxylate one equivalent of 1,5-cyclooctadiene. How many stereoisomeric
cyclooctane-1,2,5,6-tetraols will be formed?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
26.
(A) CH3CH=CHCH2Cl (B) CH3CH(Cl)CH=CH2
(C) Both A and B (D) CH2=CH-CH=CH2
27.
Major product of the above reaction is
H
O
H
O
H
O
H
HO
(A) (B) (C) (D)
A
H
2
Ni
B
chiral
achiral
MnO
2
C
an aldehyde
which is achiral
(C
5
H
10
O)
O
A
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
28.
(A) Cyclobutene (B) 1,3-Butadiene
(C) 1-Butyne (D) 2-Butyne
29 .
Major product of the above reaction is
(A) (S)-1,2-propanediol (B) (R)-1,2-propanediol (C) ( )-1,2-propanediol (D) (S)-1,3-propanediol
30.
B is
(A) Benzene (B) Benzoic acid (C) Phenol (D) Toluene
31. Cineole is the chief component of eucalyptus oil; it has the molecular formula C10H18O and contains no double or triple bonds.
It reacts with hydrochloric acid to give the dichloride shown:
Cineole +2 HCl
C H
3
C
Cl
CH
3
Cl CH
3
Which of the following can be the structure of cineole?
O
O
C H
3
C
OH
CH
3
H CH
3
C H
3
C
H
CH
3
HO CH
3
(A) (B) (C) (D)
32. Halohydrins, when treated with bulky bases like pyridine, form epoxides in a reaction that can be described as intramolecular
SN2. Identify the major product in the following reaction.
(A) O
CH
3
H
H
3
C
H
(B) O
H
CH
3
H
3
C
H
(C) Both A and B (D) Neither A or B
33. Select the best reactant to produce the following product.
CH
3
CH
3
H Cl
H OH
pyridine
O
CH
3
pyridine
Picric acid +NaHCO
3
A (a gas)
A +PhMgBr
followed by hydrolysis
B
O
CH
3
H
2
NaOH;H O
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
CH
3
OH
OH
CH
3
OH
OH
CH
3
OH
Cl
CH
3
OH
Cl
(A) (B) (C) (D)
34. The major product of the following reaction is
H
3
C CH
2
OOH
H
3
O
+
(A) p-methylbenzaldehyde (B) p-cresol
(C) Formadehyde (D) benzaldehyde
35.
Major products of the above reaction are
(I)p-cresol (II) p-nitrophenol (III) phenol (IV)
(A) II only (B) III only (C) I & IV (D) II and IV
36. Given below is the synthetic scheme for the preparation an analgesic, phenacetin.
Which of the following is the structure of phenacetin?
OEt
NH
2
CCH
3
O
OEt
NH
2
CCH
3
O
OEt
NHCCH
3
O
OCCH
3
NHCCH
3
O
O
(A) (B) (C) (D)
37.
Major product is
C O-OH
C
6
H
4
-NO
2
-p
Ph
p-H
3
C-C
6
H
4
H
3
O
+
p-Nitrophenol
1.NaOH/ EtBr
2.Fe,HCl
CH
3
COCCH
3
O O
3.
Phenacetin
O
H
3
O
+
A
Ph-C-C
6
H
4
-NO
2
-p
O
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
OH H
3
C
H
3
C OH
CH
3
HO
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
(A) (B) (C) (D)
38.
3 PhOH
PCl
3
Major product of the above reaction is
(A) 3 PhCl (B) (PhO)3P (C) 3 PhH (D) No reaction
39. A(C4H10O2) reacts with Na metal to liberate 1 mol of H2 gas per mol of A. Although A is inert toward periodic acid, it does react
with CrO3 to form B(C4H6O3). A can be
HO
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
HO
(A) (B) (C) (D)
40. Diglyme(C6H14O3) is a liquid that is inert toward most common reagents like CH3Li, Br2/CCl4, aq.NaOH, m-CPBA, and Na.
When it is warmed with large excess of HI, it gives equimolar amounts of CH3I and C2H5I. Diglyme is
(A) CH3CH2OCH2 OCH2OCH2CH3 (B) CH3CH2OCH2OCH2CH2OCH3
(C)CH3OCH2CH2OCH2CH2OCH3 (D) CH3OCH2CH2OCH2OCH2CH3
41.
The above conversion can be brought by
(A) Red P/HI (B) i. ex HI ii. Na/dry ether (C) i. H
+
ii. Red P/HI (D) None
42. Compound Y, C7H8O, is insoluble in water, dilute HCl, and aqueous NaHCO3; it dissolves in dilute NaOH. When Y is treated
with bromine water it is converted into a compound, C7H5OBr3. What is the structure of Y?
(A) Phenol (B) Cyclohexanol (C) Cyclohexanone (D) None
43
Reactivity if A, B, and C toward H
+
is
(A) A >B >C (B) C >B >A (C) B >C >A (D) A >C >B
44.
B is
(A) p-methylphenylethanoate (B) methylp-methylbenzoate
(C) acetophenone (D) benzophenone
45. Observe the following reaction sequence.
RH
2
Br /hv
RBr
KOH
ROH
O
p-cresol
CH
3
COCl
AlCl
3
A
CH
3
COCl
B
AlCl
3
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
Above reaction sequence is good for preparing
(A) 1-butanol from butane (B) 2-methyl-1-propanol from 2-methylpropane
(C) benzyl alcohol from toluene. (D) (R)-1-phenylethanol from ethyl benzene
46.
OH
COOH
ex. Br
2
H
2
O
The major product of the reaction is
OH
Br
COOH
Br
OH
Br
Br
Br
OH
COOH
Br
OH
COOH
Br
(A) (B) (C) (D)
47. Which of the following reactions is a more effective method for preparing phenyl propylether?
I: C6H5ONa +CH3CH2CH2Br
II: C6H5Br +CH3CH2CH2ONa
(A) Reaction I is more effective. (B) Reaction II is more effective.
(C) Both reactions I and II are effective. (D) Neither reaction I nor reaction II is effective.
48. Which of the following sets of reagents, used in the order shown, would enable preparation of p-chlorophenol from p-
chloronitrobenzene?
(A) 1. Fe, HCl; 2. NaOH; 3. NaNO2, H2SO4; 4. H3PO2
(B) 1. Fe, HCl; 2. NaOH; 3. NaNO2, H2SO4; 4. H2O, heat
(C) 1. Fe, HCl; 2. NaOH; 3. NaNO2, H2SO4; 4. ethanol
(D) 1. NaOH, heat; 2. HCl
49. Treating anisole with the following reagents will give, as the major product,
1. (CH3)3CCl, AlCl3; 2. Cl2, FeCl3; 3. HBr, heat
OH
C(CH
3
)
3
Cl
OH
C(CH
3
)
3
Cl
Br
C(CH
3
)
3
Cl
Br
C(CH
3
)
3
Cl
(A) (B) (C) (D)
50.
O
HO
Cu
350
0
C
A
Compound A, when dissolved in H2O or ethanol, is converted cleanly into a compound B, which is an isomer of A. Compound
B is
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
(A)
O
O
(B) O
O
(C) OH
OH
(D) OH
51.
2 eq. of CH
3
COOH
O
Number of isomers (including stereoisomers) formed in the above reaction is
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 6
52.
O
A
A
KOH
A
B
1. O
3
Zn/H
+
C +D
*
(C* =C
14
)
C and D are
OH
CHO
+CH
3
CHO
*
OH
CHO
+CH
3
CHO
*
OH
CH
2
CHO
+HCHO
*
OH
CH
2
CHO
+HCHO
*
(A) (B) (C) (D)
53. What is the major product of the following reaction?
OH
H
+
A
(A) (B) (C) (D)
54. What is the major product of the following reaction?
OH
OH
H
+
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
O
O
O
O
(A) (B) (C) (D)
55. Select the most appropriate sequence of reagents for the following conversion.
O
O
I. CH3MgBr; H
+
II. Cold dil. KMnO4 III. H
+
/A
(A) I, III, II (B) II, I, III (C) I, III, II, III (D) I, II, III
SECTION-II (Multi-correct)
56. Which of the following is/are soluble in aqueous NaHCO3?
(A) Phenol (B) Paranitrophenol
(C) 2,4-Dinitrophenol (D) 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol
57. An optically inactive mixture contains equal moles of A and B. There is another compound C which is isomeric with A and B.
All the three compounds have the molecular formula C4H10O2. All the three compounds give acetaldehyde when treated with
HIO4. Which of the conclusions can definitely be made from the above information?
(A) A and B are enantiomers (B) A and C are diastereomers
(C) A, B and C give same product with H
+
(D) C is optically inactive
58. (R)-2-butanol (R)-2-methoxybutane
The above conversion can be brought about by
(A) i. TsCl ii. CH3ONa (B) i. Na ii. CH3I
(C) CH2N2 (D) i. Na ii. (CH3)2SO4
59. Which of the following compounds give(s) phenol on heating strongly with NaOH?
A) Benzoic acid B) chloro benzene
C) sodium benzene sulfonate D) toluene
60. In which of the following reaction(s), given products are obtained as major products ?
61. Reaction of excess CH3MgBr with diethyl carbonate followed by hydrolysis yields
(A) isopropyl alcohol (B) tert.butyl alcohol (C) n-propyl alcohol (D) ethyl alcohol
62.
The above conversion can be brought about by
A) i. Cl2/H2O; ii. AgNO3 , iii. Red P/HI B) i. cold KMnO4 ii. H
+
/ A, iii. Zn-Hg/HCl
C) i. RCO3H ii. CH3MgX iii. PCC D) None
63. Which of the following combinations of reagents will yield a chiral product after hydrolysis in aqueous acid?
(A)
H
O
+CH
3
MgBr
(C)
CH
3
CH
2
COCH
3
O
+2 CH
3
MgBr
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
(C)
O
+CH
3
MgBr
(D)
CH3CHO +C2H5MgBr
64.
Select the correct option(s)
C(CH
3
)
2 HO
OH
X is
OH
CH
2
OH
X is
O
Y is
O
CH
3
CCH
3
Z is
(A) (B) (C) (D)
65.
Select the correct sequence(s) of reagents for the above conversion?
(A) H3O
+
(B) I.B2H6;THF II.H2O2;NaOH
(C) I.Hg(OAc)2;H2O II. NaBH4 (D) I. PhCO3H II.LiAlH4 III. H3O
+
66. In which of the following reactions, an aldehyde is obtained as a major product?
(A) CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
-O-OH (B) CH
3
-O-CH=CH
2
(C) CH
3
CH
2
CHCl
2 (D)
OH
CHCl
3
KOH
H
+
H
+
NaOH
67.
Select the correct statement(s) regarding A, B, C and D.
(A) A and B are enantiomers (B) C and D are enantiomers
(C) A and B are diastereomers (D) C and D are diastereomers
68. Which of the following give(s) an aldehyde as a major product with CHCl3/KOH?
(A) Phenol (B) Aniline (C) Pyrrole (D) Benzene
(CH
3
)
3
CCH=CH
2
(CH
3
)
3
CCHCH
3
OH
O
Mixture of A and B
Mixture of C and D
1.CH
3
MgBr/
dry ether
2.H
3
O
+
H
3
O
+
A
COCH
3
O O
1. ex.CH
3
MgBr
X +(CH
3
)
3
COH
2. H
3
O
+
X
Y +Z (C
3
H
6
O) +HIO
3
H
3
CCO
HIO
4
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
69.
A (C
14
H
12
O)
Optically active
B (C
14
H
14
O
2
)
Optically inactive
HIO
4
only benzaldehyde
H
3
O
+
Select the correct statement(s).
(A) A is trans-2,3-diphenylepoxyethane (B) B is meso-1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diol
(C) A is cis-2,3-diphenylepoxyethane (D) B is racemic-1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diol
70. Select the product(s) formed in the following reaction.
OH
1. NaOH
2.CH
3
I
OCH
3
OH
OH
OH
(A) (B) (C) (D)
SECTION-III (Passages)
Passage :1 (Q.NO: 71-73)
+
3 4
7 14 2 4 2 2 4
4
7 14 2
1.O 2.Zn/H KMnO
A C 3-hexanol
A(C H )decolorisesBr /CCl andreactswithHg(OAc) /H O;NaBH toformB,whichisresolvable
KMnO
HBO
D(isomerof A&G) E(chiral) F,C H O (chiral carboxylicacid)
G(i
+
3 4
1.O 2.Zn/H KMnO /
somerof A&D) H 2-methyl-3-pentanol
71. A is
(A) 1-heptene (B) 2-ethyl-1-pentene (C) 3-methyl-2-hexene (D) 3-heptene
72. D is
(A) 3-methyl-3-hexene (B) 3-methyl-1-hexene
(C) 3-methyl-2-hexene (D) 4-methyl-2-hexene
73. When G is treated with Hg(oAc)2/H2O; NaBH4
(A) a chiral alcohol is produced
(B) a primary alcohol is produced as a major product.
(C) an achiral alcohol is produced
(D) None
Passage:2 (Q.No 74-75) : Phenacetin(PHT) and Acetyl salicylic acid (ASS) are well-known analgesics (pain relievers). See the
following reaction sequences.
74. Select the correct statement.
(A) ASS is more soluble in H2O at P
H
2 than at P
H
9
(B) A further ArSE in ASS occurs at ortho to COOH.
(C) The conjugate base of ASS is less water soluble than the acid.
ONa
0
+
2
9 8 4
CO /100C
H
A B ASS(C H O )
(CH
3
CO)
2
O
H
3
PO
4
NO
2
0
3 2 4 2 2
SO/H SO SnCl /HCl Ac O
NaOH/300C
C D E F
10 13 2
EtBr
F PHT(C H NO )
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
(D) ASS is more acidic than benzoic acid.
75. Select the correct statement regarding PHT and ASS.
. (A) At P
H
9 PHT is more polar than ASS
(B) Both can be deprotonated by NaHCO3.
(C) The ring in PHT is more electron rich than in ASS.
(D) PHT is chiral.
Passage:3 (Q.No: 76-78)
76. M contains
(A) Enantiomers (B) Diastereomers
(C) Positional isomers (D) Functional isomers
77. O contains
(A) Enantiomers (B) Diastereomers
(C) Positional isomers (D) Functional isomers
78. Select the incorrect statement.
(A) S is optically inactive as a result of internal compensation
(B) S has two chiral centers
(C) R has two chiral centers
(D) S is optically inactive as a result of external compensation
Passage:4 (Q.No 79-81)
79. Select the correct statement about E.
(A) It is a racemic mixture. (B) It gives turbidity with Lucas reagent in 5-10 minutes
(C) It is a pure compound and optically inactive. (D) It gives red color with FeCl3.
80. Select the correct statement about B.
(A) It is a racemic mixture. (B) It gives turbidity with Lucas reagent in 5-10 minutes
(C) It is a pure compound and optically inactive. (D) It liberates H2 with Na.
A (C
8
H
16
)
E
n-octane
1. OsO
4
2. NaHSO
3
D
(isomer of C
and non-resolvable)
m-CPBA
B (C
8
H
16
O)
1. LiAlH
4
2. H
2
O
C (C
8
H
18
O
2
)
H
3
O
+
C can be resolved.
1. B
2
H
6
;THF
2. H
2
O
2
,OH
-
E
H
2
/Ni
3 2 2 2
3
3 2
3
2 13 28 13 28
(R)-1-bromo-2,4-dimethylpentane+Mg L
L+(CH ) CHCH CHO,thenH O M,amixture
M+CrO N
N+CH MgBr,thenH O O,amixrure
O+POCl /py P(amixture)+Q(amixture)
PorQ+H /Ni R(C H ) + S(C H )
opt.active opt.ina
ctive
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
81. Select the correct statement.
A) D is a racemic mixture. B) A is 4-octene
C) A is 3-octene D) E is 5-octanol
SECTION-IV (Matching)
82.
COLUMN-I COLUMN-II (Distinguishing reagents)
(A) OH
NO
2
NO
2
O
2
N
OH
&
(P) Na
(B) OH
C
2
H
5
OH
&
(Q) NaHCO3
(C) C2H5OH & CH3OCH3 (R) FeCl3
(D) CH2=CHCH2OH & CH3CH2CH2OH (S) MnO2
(T) Br/H2O
83. Match column-I (containing pairs of compounds) with column-II (containing distinguishing reagents)
COLUMN-I COLUMN-II
(A) CH3CH=CH2 and (CH3)3COH
(P)
| |
3 2
Ag(NH )
+
(B) CH3CH=CH2 and CH3CHOHCH3 (Q) Br2/H2O
(C) CH3CH=CH2 and CH3C CH (R) KMnO4
(D) CH3CH2CH2OH and CH3OCH3 (S) Na
84.
COLUMN-I COLUMN-II (Products with HIO4)
(A)
HO
OH
O
OH
(P) CH3CH2COOH and OHCCH2CHO
(B)
HO
OH
O
O
(Q) HCOOH, CO2 and OHCCH2CHO
(C)
O
O
OH
(R) 2 HCOOH and OHCCH2CHO
(D)
HO
OH
OH
OH
(S) CO2, HCOOH, and OHCCH2COOH
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS AND PHENOLS E M RAO
85.
COLUMN-I COLUMN-II
(A)
H
3
O
+
(P)
OH
(B)
1.Hg(OAc)
2
/H
2
O
2. NaBH
4
(Q) OH
(C)
*
1.B
2
H
6
/THF
2. H
2
O
2
;NaOH
(R) OCH
3
(D)
1.Hg(OAc)
2
/CH
3
OH
2. NaBH
4
(S)
OH
ANSWERS
1.B 2.D 3.D 4.D 5.D 6.C 7.A 8.C 9.B 10.A
11.B 12.C 13.A 14.B 15.B 16.D 17.B 18.B 19.A 20.D
21.B 22.A 23.A 24.D 25.B 26.B 27.B 28.B 29.A 30.B
31.B 32.B 33.D 34.A 35.C 36.C 37.B 38.B 39.B 40.C
41.B 42.A 43.A 44.A 45.C 46.B 47.A 48.B 49.B 50.C
51.C 52.A 53.B 54.A 55.C 56.CD 57.ABCD 58.BCD 59.BC 60.AC
61.BD 62.AB 63.AD 64.ACD 65.CD 66.ABCD 67.BC 68.A 69.AB 70.AB
71.B 72.B 73.A 74.D 75.C 76.B 77.B 78.D 79.A 80.C
81.B
82. A-QT B-RT C-P D-ST
83. A-QRS B-QS C-PS D-RS
84. A-Q B-S C-P D-R
85. A-P B-Q C-S D-R
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry I Exam 4 20101 KeyDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry I Exam 4 20101 KeyAlicia ShortNo ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes & Cyclic HydrocarbonsDocument17 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes & Cyclic HydrocarbonsEllaŠtrbac100% (1)
- ch8 1Document8 pagesch8 1yonggyeNo ratings yet
- ALDEHYDES, KETONES, ACIDS-01-170419: Neet-Crash-2017 Chemistry TestDocument6 pagesALDEHYDES, KETONES, ACIDS-01-170419: Neet-Crash-2017 Chemistry TestPoorvaBakshiNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument8 pagesAlkyl HalideMegh Raj BhattNo ratings yet
- Alcohols TestDocument2 pagesAlcohols TestAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Chem 1040 Final Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesChem 1040 Final Exam ReviewUzair AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 MergedDocument38 pagesChapter 08 MergedreemNo ratings yet
- ACS Review: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocument12 pagesACS Review: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesJana BazziNo ratings yet
- ACS Review 24 PhenolsDocument10 pagesACS Review 24 PhenolsJana BazziNo ratings yet
- ACS Review 15 Alcohols Diols and ThiolsDocument10 pagesACS Review 15 Alcohols Diols and ThiolsJana BazziNo ratings yet
- ACS Review 18 Enols and EnolatesDocument11 pagesACS Review 18 Enols and EnolatesJana BazziNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry I Practice Exam ADocument13 pagesOrganic Chemistry I Practice Exam ANoleNo ratings yet
- All Year Chemistry Up To 2018 PDFDocument37 pagesAll Year Chemistry Up To 2018 PDFAGAH LUCKYNo ratings yet
- ACS Review 9 AlkynesDocument9 pagesACS Review 9 AlkynesMohamad HabbabaNo ratings yet
- Chem MCQ FinalDocument258 pagesChem MCQ FinalDare DevilNo ratings yet
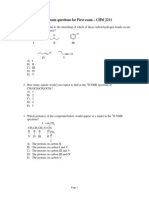
- Sample exam questions for First exam – CHM 2211Document10 pagesSample exam questions for First exam – CHM 2211abhijit.salvekarNo ratings yet
- Benzene Derivatives: Key Concepts and ReactionsDocument14 pagesBenzene Derivatives: Key Concepts and ReactionsRaj ModiNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDocument10 pagesAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesPanda Boy100% (2)
- ACS Review 17 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic AdditionDocument14 pagesACS Review 17 Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic AdditionJana Bazzi100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Assignment QuestionsDocument21 pagesOrganic Chemistry Assignment QuestionsChocolaMeilleurNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions AnswersDocument29 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions AnswersRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Kristia Stephanie BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones For IitjeeDocument65 pagesAldehydes and Ketones For Iitjeevarundhall1994No ratings yet
- Fall 2008 Old - Exam - 4Document12 pagesFall 2008 Old - Exam - 4alfredNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 & 4 - Equilibria & Application of Rates and EquilibriumDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 & 4 - Equilibria & Application of Rates and EquilibriumAhmad Taufiq Mohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 20 MC PracticeDocument17 pagesTopic 10 20 MC PracticePipen 5No ratings yet
- APCHEM Review Practice Test 1Document16 pagesAPCHEM Review Practice Test 1M. JosephNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 3 - Makox MCQsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 3 - Makox MCQsنونه الحنونةNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Exam One CH201Document7 pagesSample Test Exam One CH201Ashly PhilipNo ratings yet
- Che 232 Test 1 Sptember 2007Document16 pagesChe 232 Test 1 Sptember 2007BONOLO RANKONo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Revision QuestionsDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Revision Questionsmalikimran28No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Alkynes SolutionsDocument11 pagesChapter 9 Alkynes SolutionsRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- Assignment 151Document5 pagesAssignment 151Hai Xuan DoNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases StudentDocument24 pagesAcids and Bases StudentVictor BritoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes - Addition Reactions: Trans-1,2-Dimethylcyclopentane Cis-1,2-DimethylcyclopentaneDocument21 pagesChapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes - Addition Reactions: Trans-1,2-Dimethylcyclopentane Cis-1,2-DimethylcyclopentaneRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- FREETESTPAPER.com - Chemistry Exam SolutionsDocument35 pagesFREETESTPAPER.com - Chemistry Exam SolutionsUZAIR MAHBUB BHUYAINNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document38 pagesChapter 4Rebecca Campbell100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Nucleophilic Substitution: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanDocument16 pagesChapter 8 Nucleophilic Substitution: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- Alkenes SeatworkDocument5 pagesAlkenes SeatworkJhefNo ratings yet
- A) Iron's Molar Mass Must Be Known To Calculate The Moles of Iron in SolutionDocument5 pagesA) Iron's Molar Mass Must Be Known To Calculate The Moles of Iron in SolutionBla NkNo ratings yet
- Exam Three Practice TestDocument13 pagesExam Three Practice TestBUCH203100% (1)
- Ap Chemistry Acid-Base Exam Part I Multiple Choice: K (Hco) (Co) (H O) K (Co) (Co) (OH)Document8 pagesAp Chemistry Acid-Base Exam Part I Multiple Choice: K (Hco) (Co) (H O) K (Co) (Co) (OH)Max SaubermanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and PhenolsDocument9 pagesAlcohols and Phenolsdivya divyaNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Cmpds AnskeyDocument6 pagesAromatic Cmpds AnskeyAaron LeeNo ratings yet
- ICSE Chemistry Board Paper19 PDFDocument9 pagesICSE Chemistry Board Paper19 PDFPrajakta DigheNo ratings yet
- Ketones and Carboxylic Acids GuideDocument5 pagesKetones and Carboxylic Acids GuideAnindya AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Directions: This Examination Contains A Total of 80 Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pagesDirections: This Examination Contains A Total of 80 Multiple ChoiceLemi NegesoNo ratings yet
- CH203 Fall 2014 Exam Two Practice Test With AnswersDocument10 pagesCH203 Fall 2014 Exam Two Practice Test With AnswersBUCH203No ratings yet
- Chem52 Su13 PracticeExam1ADocument11 pagesChem52 Su13 PracticeExam1Aamarka01No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC20CHEMISTRY20POST20TESTDocument13 pagesORGANIC20CHEMISTRY20POST20TESTJan Mill100% (1)
- MFT Samp Questions ChemistryDocument13 pagesMFT Samp Questions ChemistryМаријана КрговићNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocument29 pagesChapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionAnonymous Ngsu7C4aNo ratings yet
- Org Part 1 With AnsDocument7 pagesOrg Part 1 With AnsDeepak PradhanNo ratings yet
- Model Answer: The Following Questions Answer Choose The Correct Answer: (20Document4 pagesModel Answer: The Following Questions Answer Choose The Correct Answer: (20Khalid AbeedNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Part-A I. Answer ALL The Questions (Each Question Carries One Mark) 10x1 10Document3 pagesInstructions:: Part-A I. Answer ALL The Questions (Each Question Carries One Mark) 10x1 10anon_850201470No ratings yet
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIFrom EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Alkyl Halides, Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides: 1. What Is The IUPAC Name For CHDocument17 pagesAlkyl Halides, Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides: 1. What Is The IUPAC Name For CHEllaŠtrbacNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law ProjectDocument15 pagesAdministrative Law ProjectPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- JaisalmerDocument3 pagesJaisalmerPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- Memo PunditsDocument2 pagesMemo PunditsPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- Mess Menu Week PlanDocument1 pageMess Menu Week PlanPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- All Editorial 27 July 2019 PDFDocument15 pagesAll Editorial 27 July 2019 PDFPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- Monday: Shoulder Tuesday: Legs Wednesday: Chest Thursday: Friday: Saturday: SundayDocument1 pageMonday: Shoulder Tuesday: Legs Wednesday: Chest Thursday: Friday: Saturday: SundayPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- CasesDocument3 pagesCasesPriyansh Yadav100% (1)
- Going Out of The Box Is A NECESSITY Be Open Minded Understand How The Left and Right Brain WorksDocument1 pageGoing Out of The Box Is A NECESSITY Be Open Minded Understand How The Left and Right Brain WorksPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- Lead The CompetitionDocument8 pagesLead The CompetitionPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- English Aug Nirdeshak PDFDocument97 pagesEnglish Aug Nirdeshak PDFrs0728No ratings yet
- Lead The CompetitionDocument5 pagesLead The CompetitionPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs of Feb16Document12 pagesCurrent Affairs of Feb16Parth UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Generate Profits from Bottled Water Using Atmospheric Water GeneratorsDocument20 pagesGenerate Profits from Bottled Water Using Atmospheric Water GeneratorsJose AndradeNo ratings yet
- 4 6051111060339957657Document361 pages4 6051111060339957657Oviedo OviedoNo ratings yet
- Sunflower Herbicide ChartDocument2 pagesSunflower Herbicide ChartpapucicaNo ratings yet
- Causes of DyspneaDocument9 pagesCauses of DyspneaHanis Afiqah Violet MeowNo ratings yet
- Deadline Anchors BrochureDocument3 pagesDeadline Anchors Brochurejlmunozv100% (2)
- Marital Satisfaction in Dual Earner FamilyDocument4 pagesMarital Satisfaction in Dual Earner FamilyInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- The Truth About EtawahDocument4 pagesThe Truth About EtawahPoojaDasgupta100% (1)
- Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Detection of Postnatal Depression. Development of The 10-ItemDocument6 pagesEdinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Detection of Postnatal Depression. Development of The 10-ItemKyze LQNo ratings yet
- Report Experiment 5 STK1211Document9 pagesReport Experiment 5 STK1211NurAkila Mohd YasirNo ratings yet
- EMI InstructionsDocument2 pagesEMI InstructionsAKSHAY ANANDNo ratings yet
- The Congressional Committee and Philippine Policymaking: The Case of The Anti-Rape Law - Myrna LavidesDocument29 pagesThe Congressional Committee and Philippine Policymaking: The Case of The Anti-Rape Law - Myrna LavidesmarielkuaNo ratings yet
- Guide To Admissions 2024-25Document159 pagesGuide To Admissions 2024-25imayushx.inNo ratings yet
- Company Law AssignmentDocument5 pagesCompany Law AssignmentABISHEK SRIRAM S 17BLA1008No ratings yet
- Bio ViberDocument7 pagesBio ViberMarco BuntNo ratings yet
- Somali Guideline of InvestorsDocument9 pagesSomali Guideline of InvestorsABDULLAHI HAGAR FARAH HERSI STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Eltra Cs 530Document122 pagesEltra Cs 530ahalonsoNo ratings yet
- Lab 9-Measurement of Filtrate Loss and Mud Cake Thickness of Drilling Mud Sample Using Dead Weight Hydraulic Filter Press Considering API Standard.Document17 pagesLab 9-Measurement of Filtrate Loss and Mud Cake Thickness of Drilling Mud Sample Using Dead Weight Hydraulic Filter Press Considering API Standard.Sunny BbaNo ratings yet
- Buhos SummaryDocument1 pageBuhos Summaryclarissa abigail mandocdocNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of Galactomannan From Sugar PalmDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Galactomannan From Sugar PalmRafaél Berroya Navárro100% (1)
- Restaurant Supervisor Job Description Job SummaryDocument3 pagesRestaurant Supervisor Job Description Job SummaryKumarSvNo ratings yet
- Density of Aggregates: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDensity of Aggregates: ObjectivesKit Gerald EliasNo ratings yet
- 6V Plush Ride-On: Owner'S ManualDocument26 pages6V Plush Ride-On: Owner'S ManualVisas LaredoNo ratings yet
- Undas Deployment PadsDocument15 pagesUndas Deployment PadsVic NairaNo ratings yet
- GDCR Final PDFDocument311 pagesGDCR Final PDFHrushikesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Human Diseases A Systemic Approach 8th Edition-Páginas-15-26Document12 pagesHuman Diseases A Systemic Approach 8th Edition-Páginas-15-26Karime LopezNo ratings yet
- Disha Symbiosis 20th JulyDocument2 pagesDisha Symbiosis 20th JulyhippieatheartbalewadiNo ratings yet
- Partial Defoliation of Vitis Vinifera L. Cv. Cabernet SauvignonDocument9 pagesPartial Defoliation of Vitis Vinifera L. Cv. Cabernet Sauvignon1ab4cNo ratings yet
- Hydropad InstructionsDocument2 pagesHydropad Instructionsmohamed hindawiNo ratings yet
- Steroids ActivityDocument1 pageSteroids Activityfaqed ilzakiraNo ratings yet
- Specialized Connective TissueDocument15 pagesSpecialized Connective TissueSebNo ratings yet