Professional Documents
Culture Documents
366 369economics Xi
Uploaded by
api-259591583Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
366 369economics Xi
Uploaded by
api-259591583Copyright:
Available Formats
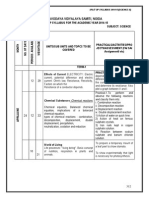
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2014-15(ECONOMICS-XI)
366
NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA SAMITI, NOIDA
SPLITUP SYLLABUS FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2014-2015
CLASS: XI SUBJECT: ECONOMICS
M
O
N
T
H
N
O
.
O
F
D
A
Y
S
P
E
R
I
O
D
S
A
V
A
I
L
A
B
L
E
W
E
I
G
H
T
A
G
E
UNITS/SUBUNITS AND TOPICS TO BE COVERED
U
N
I
T
T
E
S
T
S
/
A
S
S
I
G
N
M
E
N
T
S
/
P
R
O
J
E
C
T
S
TERM -1
A
P
R
I
L
/
J
U
N
E
,
2
0
1
4
24/
25
32/
36
13
PART-A : STATISTICS FOR ECONOMICS
Unit-1 Introduction
What is Economics?
Meaning, scope and importance of statistics in economics
Unit-2-Collection, organization and presentation of data
Collection of Data-Sources of data-Primary and secondary
sources.
How basic data is collected?
Methods of collecting data.
Some important sources of secondary data.
Census of India, National sample survey organization.
UT-1
AS-1
J
U
L
Y
,
2
0
1
4
26 36
27
Organization of Data: Meaning and types of variables-
Frequency distribution
Presentation of Data: Tabular presentation and diagrammatic
presentation of data.
1. Geometric forms (Bar Diagram and Pie Diagram)
2. Frequency diagrams.(Histogram, polygon and ogive
curve)
Arithmetic lines graphs(Time series graph)
Unit-3-Statistical tools and interpretation
1.Measures of central tendency
a) Mean- simple and weighted
b) Median and mode
UT-2
AS-2
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2014-15(ECONOMICS-XI)
367
A
U
G
U
S
T
,
2
0
1
4
24 32
2.Measures of dispersion
Absolute dispersion
a) Range
b) Quartile deviation
c) Mean deviation and standard deviation
3) Relative dispersion
Coefficient of quartile deviation
Coefficient of mean deviation
Coefficient of variation
Lorenz curve-Meaning and its
Applications
UT-3
AS-3
PROJE
CT-1
ORAL-1
S
E
P
T
E
M
B
E
R
,
2
0
1
4
26 32
13
Correlation Meaning- scattered diagram-Measures of
correlation, Karl Pearsons methods(Two variable ungrouped
data)
Spearmens rank correlation
Introduction to index numbers.
1. Meaning and types
2. Wholesale price index
3. Consumer price index
4. And index of industrial production
Uses of index numbers
Inflation and index number
Some mathematical tools used in economics: Equation of a
line, slope of a line and slope of a curve.
PART B- Indian economic development
UNIT-4 Development policies and experience (1947-1990)
1. A brief introduction of the state of Indian economy on
the eve of independence.
2. Common goals of 5 year plans. Main features,
problems and policies of agriculture.(institutional
aspects and new agricultural strategy etc)
Industry (industrial license, etc)and
Foreign trade
UT -4
As -4
TERM
TEST -1
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2014-15(ECONOMICS-XI)
368
O
C
T
/
N
O
V
E
M
B
E
R
,
2
0
1
4
5+24
=29
3
0
12
10(
OT
BA
)
UNIT-4 Economic reforms since 1991
Need and main features- liberalisation, globalisation and
privatisation
An appraisal of LPG policies.
UNIT-5 Current challenges facing Indian economy
Poverty- absolute and relative
Main programmes for poverty alleviation; a critical
assessment
Rural development
Key issues- credit and marketing, Role of cooperatives
Agriculture diversification, Alternative farming- organic
farming
D
E
C
E
M
B
E
R
,
2
0
1
4
26
3
2
Human capital formation
How people become resource, Role of human capital
formation in economic development, Growth of
education sector in India
Employment
Formal and informal, Growth and other issues
Problems and policies, Inflation- problems and policies
INFRASTRUCTURE:-
Meaning and types, case studies, Energy and
Health Problems and policies, A critical
assessment.
Sustainable economic development
Meaning, effects of economic development on
resource and environment, including global warming
UT-5
AS-5
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2014-15(ECONOMICS-XI)
369
J
A
N
U
A
R
Y
-
2
0
1
5
20 27
15
10
Pro
ject
wor
k
UNIT-6
Development experiences of India
A comparison with neighbours -India and Pakistan. India and
china,
Issues :Growth, population, sectoral development and other
developmental indicators
Part C Developing projects in Economics ( Project work)
The students may be encouraged to develop projects which
have primary data, secondary data or both. Case studies of few
organizations/ outlets may also be encouraged.
Some of the examples of the projects are as follows.(These are
not mandatory but suggestive)
a) A report on Demographic structure of your
neighbourhood.
b) Consumer awareness among house holds
c) Changing prices of few vegetables in your market
d) Study of a cooperative institution. Ex. Milk
Cooperatives.
e) Case studies on public private partnership, outsourcing
and outward foreign direct investment.
f) Global warming.
g) Designing eco friendly projects applicable in school
such as paper and water cycle.
UT-6
AS-6
PRO-2
ORAL-2
F
E
B
-
2
0
1
5
22 32
Revision
Revision
test
M
A
R
-
2
0
1
5
26
2
nd
TERM EXAMINATION
TERM
TEST-2
Note:
a )PART C Project work for 10 mark.
b) The question paper will include a section on open text based assessment of 10 marks from
unit 5 of part B. From this unit no other questions will be asked in the theory
examination. The OTBA will be asked only during the annual examination to be held in the
March2015.
c) Question paper will be set for annual examination as per the CBSE guidelines
given in the curriculum 2015-16 .
d) The teacher concerned is requested to refer to the CBSE curriculum 2014-15 for further
clarifications, if any.
*****
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Chapter 4 Measures of Dispersion (Variation)Document34 pagesChapter 4 Measures of Dispersion (Variation)yonasNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument489 pagesManagerial Economicsbenjudsr100% (3)
- E 456 - 96 Standard Terminology For Relating To Quality and Statistics1Document8 pagesE 456 - 96 Standard Terminology For Relating To Quality and Statistics1JORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTA100% (1)
- Book 4Document16 pagesBook 4api-259591583No ratings yet
- Book 1Document14 pagesBook 1api-259591583No ratings yet
- Book 3Document14 pagesBook 3api-259591583No ratings yet
- Desm S ChemistryDocument13 pagesDesm S Chemistryapi-259591583No ratings yet
- Desm S ChemistryDocument13 pagesDesm S Chemistryapi-259591583No ratings yet
- Book 2Document16 pagesBook 2api-259591583No ratings yet
- MehndiDocument4 pagesMehndiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- VIII BDocument4 pagesVIII Bapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 297 306english XDocument10 pages297 306english Xapi-259591583No ratings yet
- ViibDocument4 pagesViibapi-259591583No ratings yet
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Prabhat Pattan Class-Xib: TERM TEST - II - (SESSION 2014-15)Document2 pagesJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Prabhat Pattan Class-Xib: TERM TEST - II - (SESSION 2014-15)api-259591583No ratings yet
- 266 270maths IxDocument5 pages266 270maths Ixapi-259591583No ratings yet
- ViiaDocument4 pagesViiaapi-259591583No ratings yet
- VIII ADocument4 pagesVIII Aapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 260 265englis IxDocument6 pages260 265englis Ixapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 338 343english XiDocument6 pages338 343english Xiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 271 275science IxDocument5 pages271 275science Ixapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 307 311maths XDocument5 pages307 311maths Xapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 438 440economics XiiDocument4 pages438 440economics Xiiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 312 316science XDocument5 pages312 316science Xapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 382 383geography XiDocument2 pages382 383geography Xiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 413-416english Core-XiiDocument4 pages413-416english Core-Xiiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 349 353physics XiDocument5 pages349 353physics Xiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 380 381history XiDocument2 pages380 381history Xiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 360 365biology XiDocument6 pages360 365biology Xiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 344 348maths XiDocument5 pages344 348maths Xiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 438 440economics XiiDocument4 pages438 440economics Xiiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 421 425physics XiiDocument5 pages421 425physics Xiiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- 447-448history XiiDocument2 pages447-448history Xiiapi-259591583No ratings yet
- P6LabManual1 AY11-12Document134 pagesP6LabManual1 AY11-12roxy8marie8chanNo ratings yet
- CAIIB Paper 1 Module A ABM STATISTICS by Ambitious Baba New SyllabusDocument91 pagesCAIIB Paper 1 Module A ABM STATISTICS by Ambitious Baba New Syllabusaswin ganesh rajaNo ratings yet
- IT 102A - Lesson 5Document5 pagesIT 102A - Lesson 5John Patrick MercurioNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariabilityDocument11 pagesMeasures of VariabilityGomer MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 NSUDocument68 pagesLecture 1 NSUHarjotBrarNo ratings yet
- Statistics Materials: Data Science: Week 9Document22 pagesStatistics Materials: Data Science: Week 9ARCHANA RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.Document24 pagesChapter 2.Roha CbcNo ratings yet
- Business StatisticsDocument219 pagesBusiness StatisticsAnjana NairNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Statistical Quality Control (SQC)Document31 pagesChapter Four Statistical Quality Control (SQC)fekadeNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument76 pagesUnit IIVidhi MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Assignment W12Document8 pagesAssignment W12Pathi Narasimha saiNo ratings yet
- Data Types - Research MethodologyDocument34 pagesData Types - Research MethodologyVetri PadiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - StatisticsDocument30 pagesModule 3 - StatisticsJomil CompelNo ratings yet
- Statistics - Descriptive StatisticsDocument22 pagesStatistics - Descriptive StatisticsDamimi 21No ratings yet
- Measure of DispersionDocument10 pagesMeasure of Dispersiondr.neupane27No ratings yet
- Note-145 Biostat Prof. Abdullah Al-Shiha PDFDocument157 pagesNote-145 Biostat Prof. Abdullah Al-Shiha PDFAdel Dib Al-jubeh100% (2)
- Intermediate Statistics Using Spss 1st Edition Knapp Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesIntermediate Statistics Using Spss 1st Edition Knapp Solutions ManualJamesGrantfzdmo100% (22)
- Math 7-Q4-Module-6Document16 pagesMath 7-Q4-Module-6Cher Anna MarieNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 1-9Document7 pagesWorksheet Chapter 1-9yoftahe habtamuNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion ExplainedDocument25 pagesMeasures of Dispersion ExplainedNinad AbhyankarNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 10Document28 pagesLecture No 10Wra ArirmiwniNo ratings yet
- G7 Math 7 Exam 4thDocument7 pagesG7 Math 7 Exam 4thMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Measure of DispersionDocument66 pagesMeasure of DispersionPuttu Guru PrasadNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion: Range, Quartile Deviation, and Coefficient of VariationDocument7 pagesMeasures of Dispersion: Range, Quartile Deviation, and Coefficient of Variationsakhie hassanNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics: Methods For Describing Sets of DataDocument103 pagesBusiness Statistics: Methods For Describing Sets of DataDrake AdamNo ratings yet
- Quality ProgressDocument68 pagesQuality Progressمحمد يسرNo ratings yet
- 03 Descriptive StatisticsDocument71 pages03 Descriptive StatisticsS R SainiNo ratings yet