Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ethics - Stumbo
Uploaded by
api-2420829970 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views3 pagesOriginal Title
ethics- stumbo
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views3 pagesEthics - Stumbo
Uploaded by
api-242082997Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
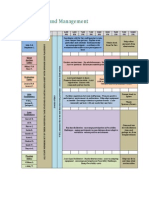
Ethics-Decision Making Model (Stumbo)
Decision making model for ethical situations:
The Decision-Making Model Ethical Situations in Professional Practice/Business
-Norma Stumbo, ATRA 1998
Identify Behavior
Elderly women who has advanced dementia and is a high fall risk desired to participate in
a nature walk. CTRS is unsure if she is cognitively or physically able to make a healthy
decision to participate and self-govern herself with her medical condition of advance
dementia during the group intervention.
Professional Relevance
Patients autonomy to make a decision is at question. The concern for the autonomy of an
individuals competence or capacity to understand the consequences of a particular task
or value their decision making. The judgment of who is able to make the decisions for the
individual is hard because the competence of the person may be incompetent one day and
competent the next.
Considerations:
American Therapeutic Recreation Association Code of Ethics
PRINCIPLE 2: AUTONOMY
- Therapeutic Recreation personnel have a duty to preserve and protect the right of each
individual to make his/her own choices. Each individual is to be given the opportunity to
determine his/her own course of action in accordance with a plan freely chosen.
Differentiate Personal and/or Professional Ideals and Values
Professional-
The safest or most cautious option is the best choice when working with long-term care
patients and when assessing if a patient is able to participate in the program. When the
patient is unable to make a decision based off their medical condition the healthcare
professional should make the best medical decision.
The CTRS job is to provide inclusive recreational activities and intervention programs for
all participants to help increase quality of life and well-being.
RT should work with the interdisciplinary team to determine the best option regarding the
safety and wellbeing of the patient and provide a holistic approach of care to the patient
when making a decision of participating.
Personal-
Not allowing someone to participate in a Recreational Therapy intervention falls on the
CTRS who is implementing the program. The interventions need to have an activity
analysis that will analyze the program and make considerations so all can participate. The
CTRS needs to adjust the intervention to be inclusive and prepare a way that the activity
can be safe for all those who want to participate, regardless of their abilities.
Recreational activities can have extra staff involved so the patient could have someone
monitoring her safety closer, to prevent an accident, allowing participation.
Ethics-Decision Making Model (Stumbo)
The job of a CTRS is to provide inclusive recreation to help increase the well-being of a
patient. The autonomy of a patient is very important to consider when providing a holistic
treatment.
Consider Legal Duties
The possibility of patient falling and causing severe harm and injury is a risk and liability
to the Recreational Therapist. The judgment of who gets to make medical decisions for
the person with dementia is the ability of the person to understand the purpose, risks,
benefits and alternatives of the treatment.
Patient needs to appreciate that she has a choice and understands the medial situation,
prognosis, nature of the recommended care, the risks and benefits of each and the
consequences according to the Alzheimer association on respect for autonomy.
(www.alz.org)
Principles:
Assume capacity unless there is evidence to suggest otherwise.
Dont assume the person lacks capacity simply because they make an unusual or
unwise decision.
The person has a right to be supported to make his or her own decision/s and
communicate the decision/s before it is assumed capacity to do so is lacking.
Any decision or action taken on behalf of the person must:
Benefit the person and be in their best interests
Restrict the persons freedom only so far as it is necessary to gain the benefit needed
Take account of his or her past and present views, wishes, values and beliefs
Take account of the views of relevant others (as specified in legislation)
Encourage the person to use his or her abilities and develop new skills.
(www.nuffieldfoundation.org)
Assess Ethical Obligations
At what point does being cautious impair the ability to perform the job requirements of a
CTRS and prevent treatment from occurring?
At what point is it more important to honor the patients autonomy and let them make a
decision then to take a risk and increase preventive measures to keep them safe?
When does the medical professional have the right to make a decision for a patient with a
mental illness? When does the medical professional allow for the patient to make her own
decisions regarding appropriate treatment?
How advanced does ones medical treatment have to be for their autonomy to be given
up? If patients autonomy is given up who is allowed to make decisions for the patient and
with what motives and guidelines?
ATRA Code of Ethics:
The American Therapeutic Recreation Associations Code of Ethics is to be used as a
guide for promoting and maintaining the highest standards of ethical behavior. The Code
applies to all Recreational Therapy personnel. The term Recreational Therapy personnel
includes Certified Therapeutic Recreation Specialists (CTRS), recreational therapy
Ethics-Decision Making Model (Stumbo)
assistants and recreational therapy students. Acceptance of membership in the American
Therapeutic Recreation Association commits a member to adherence to these principles.
Ethical Obligations:
Make sure the patient is making a decision that will keep her safe and healthy.
Respect the patients wishes and autonomy as much as possible.
Consider the health and well-being of others participating in the program and their safety.
Make sure the decision made is going to help improve patients quality of life.
Determine Action
Include the patient in the nature walk intervention and respect their autonomy of wanting
to participate.
o The patient is a high fall risk and wonders, she will need to have a staff worker paired
with her to ensure her safety and the safety of the others participating in the group.
o The Recreational Therapist will need to ensure that the nature walk is something that
this patient is capable of doing and if not, find an alternative route that would allow
for the patient to be safe during the intervention. Also, the CTRS should consider if a
wheelchair or walker could be used during the walk to help support the patient.
o The goal and purpose of the intervention must be written out so the client understands
why they are participating and documented so the intervention shows that there is
therapeutic purpose and reason to the walk.
o CTRS should have written consent from the patient that they are asking to participate
in the event and in the case of any injury, it was against medical advice for them to
participate. This ensures that fault wont fall on the CTRS or any other medical
professionals. This is crucial, because of the patients dementia, there needs to be
written documentation to help protect both the RT, the facility and the patient.
You might also like
- MKTG FinalDocument34 pagesMKTG Finalapi-242082997No ratings yet
- Case Study WordyDocument8 pagesCase Study Wordyapi-242082997No ratings yet
- Ethics - ScenarioDocument2 pagesEthics - Scenarioapi-242082997No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Protocol Sandy EditsDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Protocol Sandy Editsapi-242082997No ratings yet
- Assessment ProtocolDocument3 pagesAssessment Protocolapi-242082997No ratings yet
- Article ReviewDocument6 pagesArticle Reviewapi-242082997No ratings yet
- Disability Card FinalDocument4 pagesDisability Card Finalapi-242082997No ratings yet
- Animation PlanDocument2 pagesAnimation Planapi-242082997No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- DemocracyDocument6 pagesDemocracywestelm12No ratings yet
- NCM108 Module 1 EDocument12 pagesNCM108 Module 1 ESheera MangcoNo ratings yet
- Surrogate Humanity - Race, Robot - Neda Atanasoski PDFDocument257 pagesSurrogate Humanity - Race, Robot - Neda Atanasoski PDFjonas esteves100% (2)
- Confucius and Kant: Two Concepts On RespectDocument8 pagesConfucius and Kant: Two Concepts On RespectAlvin Jason BravoNo ratings yet
- 2020 Ewha Brochure EngDocument22 pages2020 Ewha Brochure EngThảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- Ethical DecisionMakingProcess PDFDocument24 pagesEthical DecisionMakingProcess PDFAmrod InglorionNo ratings yet
- The Mediator As Narrator - Paul MedekopDocument12 pagesThe Mediator As Narrator - Paul MedekopfernandombsNo ratings yet
- Ethics Chapter4Document21 pagesEthics Chapter4Rene AjusanNo ratings yet
- Cultivating Good Minds - A Phil - Baehr, Jason - 5523Document563 pagesCultivating Good Minds - A Phil - Baehr, Jason - 5523aquinas03100% (1)
- W340 EmaDocument10 pagesW340 EmaFreddie CookNo ratings yet
- ETHICSDocument5 pagesETHICSRIO ORPIANO100% (2)
- Avedissian, Alayan - 2021 - Adolescent Well-Being A Concept AnalysisDocument11 pagesAvedissian, Alayan - 2021 - Adolescent Well-Being A Concept Analysisisidora2003No ratings yet
- 2006 P 183 202Document20 pages2006 P 183 202KADDOURNo ratings yet
- Transformers SIT - EIB (Round 2)Document57 pagesTransformers SIT - EIB (Round 2)João Rafael BritesNo ratings yet
- Police Ethics and IntegrityDocument12 pagesPolice Ethics and IntegrityJay BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Sociology of Tourism.Document8 pagesChapter 5-Sociology of Tourism.Zeus100% (1)
- Fon Mcqs Whole BookDocument38 pagesFon Mcqs Whole BookRizwan EjazNo ratings yet
- Ethical and Moral Issues in Healthcare by Reason ChivakaDocument15 pagesEthical and Moral Issues in Healthcare by Reason Chivakareach2250% (2)
- Learning Styles in University Students, Types of Strategies, Materials, Supports, Evaluation and Performance. Case StudyDocument17 pagesLearning Styles in University Students, Types of Strategies, Materials, Supports, Evaluation and Performance. Case StudyJorge Eliecer Villarreal FernandezNo ratings yet
- Nursing As A Profession - InduDocument58 pagesNursing As A Profession - InduArchana Sahu100% (2)
- GE606 Professional Ethics in Engineering-2 Marks and 16 MarksDocument40 pagesGE606 Professional Ethics in Engineering-2 Marks and 16 MarksSyed Zia-ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Brazilian Non-Governmental Organizations and Their Relationship With The State: A Promising or Interested?Document26 pagesThe Brazilian Non-Governmental Organizations and Their Relationship With The State: A Promising or Interested?jonhgeocsNo ratings yet
- David LittleDocument7 pagesDavid Littlenaila100% (1)
- Bioethics in Canada 2nd EditionDocument2 pagesBioethics in Canada 2nd Editionolangutan110No ratings yet
- Ood Linical Ractice (GCP) in Clinical Research: Food and Drug AdministrationDocument127 pagesOod Linical Ractice (GCP) in Clinical Research: Food and Drug AdministrationPap PipNo ratings yet
- Streer PatraDocument3 pagesStreer PatraDebjyoti MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- PACFA Code of Ethics 2017Document19 pagesPACFA Code of Ethics 2017yson0087No ratings yet
- Notions of Human RightsDocument22 pagesNotions of Human RightsSwastik PandeyNo ratings yet
- 09 Jacob Hale - Ethical ProblemsDocument16 pages09 Jacob Hale - Ethical ProblemsRachael HarterNo ratings yet
- 1 Learner - Autonomy Week 8Document15 pages1 Learner - Autonomy Week 8Pia Irigoyen SagardíaNo ratings yet