Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1: Respiration: Important Concepts
Uploaded by
amiruddin bahadonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1: Respiration: Important Concepts
Uploaded by
amiruddin bahadonCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 : Respiration
Important Concepts
1.1 Human Breathing Mechanism
Quick Refresh
1.2 Transport of Oxygen in the Human Body
Quick Refresh
1.3 Importance of a Healthy Respiratory
System
Quick Refresh
Smart Review
1
Important Concepts
2
Respiration
Harmful
substances
Human respiratory
system
consists
of
Breathing
mechanism
Oxygen
Blood
Respiratory
diseases
Inhalation
Exhalation
takes in
transported
by
Lungs
Nasal cavity
Trachea
Bronchus
Bronchioles
Ribs
Intercostal muscles
Diaphragm
Chapter 1: Respiration
Chapter
1.1
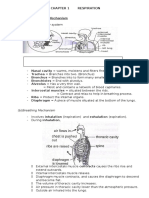
Human Breathing Mechanism
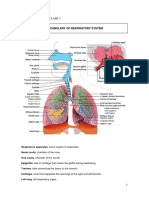
Human respiratory system
nasal cavity
bronchus
ribs
intercostal
muscle
lungs
trachea
diaphragm
bronchioles
3
bronchiole
alveolus
blood
capillary
Chapter 1: Respiration
Chapter
1.1
Human Breathing Mechanism
4
Nostril nose hair help to filter the air from
dust and foreign particles
Nasal cavity to warm and moisten the air that
passes through it
Trachea
Bronchus
Bronchioles
Air
Process of Human Respiratory System
Alveolus has a very thin wall which is
moist and contains a network of
blood capillaries
Chapter 1: Respiration
Component Function
Chapter
1.1
Human Breathing Mechanism
The main organ of the respiratory system
Contains bronchus, bronchioles and alveoli that help gas
exchange
Lungs
The large air-filled space that filter and warm the air as it is
inhaled
Nasal cavity
Also known as the windpipe
Carrying air to the lungs
Trachea
Two air tubes that branch off at the trachea and conducts air
into the lungs
Bronchus
5
Chapter 1: Respiration
Chapter
1.1
Human Breathing Mechanism
Component Function
6
Bronchioles Smaller branches of the bronchus that end with alveoli
Ribs The long curve bones which form the rib cage that protect the
lungs and other internal organs like the heart and so on
Intercostal muscle Muscles that situated between the ribs
They contract and relax during inhaling and exhaling to help
breathing process
Diaphragm
A dome-shaped muscle at the bottom of the lungs that controls
the breathing process
Chapter 1: Respiration
Chapter
1.1
Human Breathing Mechanism
Breathing mechanism
During inhalation
rib muscles
contract (Rib
cage expands)
diaphragm contracted
(moves down)
air inhaled
The diaphragm muscle contracts, that
flatten the diaphragm downwards to
increase the volume of thoracic cavity
7
The external intercostal muscles
contract to expand the rib cage and
further increasing the volume of
thoracic cavity
Increase of volume in thoracic cavity,
lead to lowering air pressure in the
lungs than the atmospheric pressure
This causes the air to be inhaled
through the trachea and into the alveoli
Chapter 1: Respiration
Chapter
1.1
Human Breathing Mechanism
rib muscles
relax (Rib
cage contracts)
diaphragm relaxed
(moves up)
air exhaled
The diaphragm muscle relax that
causes the diaphragm to curve
upwards decreasing the volume of
thoracic cavity
During exhalation
8
The internal intercostal muscles
contract and pull the ribs back to its
original shape
Increase of volume in thoracic cavity
lead to higher air pressure in the lungs
than the atmospheric pressure
This will force the air out of the lungs
Chapter 1: Respiration
Respiratory system is made up of lungs, nasal cavity, trachea, bronchus,
bronchioles, ribs, intercostal muscles and diaphragm
It is healthier to breath through the nose than the mouth because the hair
and mucus in the nose (nasal cavity) helps filter and warm the air as it
comes in
Breathing consists of two phrases, inhalation and exhalation
(a) Inhalation taking air to the lungs
(b) Exhalation expelling air from the lungs
Intercostal muscles , ribs and diaphragm involved in the changes in
volume of thoracic cavity
Q.R.
1.1
Quick Refresh
9
Chapter 1: Respiration
You might also like
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Human Breathing Mechanism: RespirationDocument5 pages1.1 Human Breathing Mechanism: RespirationKelly KohNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OkDocument36 pagesRespiratory System Okakselerasi10No ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1Document22 pagesChapter 1.1ieya_yNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Gas Exchange - Lesson 1 - Grade 8Document13 pagesLungs and Gas Exchange - Lesson 1 - Grade 8SAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- MLS221 Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument37 pagesMLS221 Respiratory System PhysiologyAbdirazak AliNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Strcuture and Function of Ventilatory SystemDocument36 pages2.1 Strcuture and Function of Ventilatory SystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
- Gr. 9 Science LM (AG)Document33 pagesGr. 9 Science LM (AG)Aizalonica GalangNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture - 5 PDFDavid JokerNo ratings yet
- Module 9 Lesson 5Document21 pagesModule 9 Lesson 5Faatoots FatsNo ratings yet
- University of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonDocument66 pagesUniversity of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonKNo ratings yet
- Respiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentDocument65 pagesRespiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Normal Oxygen Transport: Susanne A ClarkDocument256 pagesNormal Oxygen Transport: Susanne A Clarkghoncheh0% (1)
- 11.1 The Breathing System: Features of Gas Exchange SurfacesDocument13 pages11.1 The Breathing System: Features of Gas Exchange SurfacesX GamerNo ratings yet
- PDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17FDocument15 pagesPDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17Fgandhitirth147No ratings yet
- Respiratory System Handout Explains Lung Functions & AnatomyDocument10 pagesRespiratory System Handout Explains Lung Functions & AnatomyMr. DummyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System VocabularyDocument9 pagesRespiratory System VocabularyAgustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesRespiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance)Document17 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance)Michelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Respiratory: Email: Phone No. 07703123038Document12 pagesRespiratory: Email: Phone No. 07703123038Wria AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Functions in 5 StepsDocument16 pagesRespiratory System Functions in 5 Stepshellofrom theothersideNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.1 Ventilatory System Sport Science IBDocument4 pagesTopic 2.1 Ventilatory System Sport Science IBAntonio MouNo ratings yet
- Sistem Respirasi-Isti AnindyaDocument18 pagesSistem Respirasi-Isti AnindyaSindia MirnaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System GuideDocument53 pagesRespiratory System GuideFrancesca KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document17 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Saraswati PNo ratings yet
- bio notes respiration in animalsDocument3 pagesbio notes respiration in animalssamanthahuangsamanthaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesThe Respiratory SystemdeepakNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDocument15 pagesPhysiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDivya TripathyNo ratings yet
- BMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemDocument7 pagesBMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System of Human Body FactsDocument12 pagesThe Respiratory System of Human Body FactsjulianneboloronNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument87 pagesRespiratory Systemd...No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Respiratory SystemDocument54 pagesLecture 6 Respiratory SystemLouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-311834149No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Respiratory SystemDocument20 pagesChapter 8 - Respiratory Systemmnurnazri10No ratings yet
- Pulmonary VentilationDocument24 pagesPulmonary VentilationAreeba KhanNo ratings yet
- Prologue 1.1 BackgroundDocument9 pagesPrologue 1.1 BackgroundWulan Yulia DintasariNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SytemDocument2 pagesRespiratory SytemJanet BantigueNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- 1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration ModifiedDocument10 pages1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration Modifiedخالد القرشيNo ratings yet
- 1) Anatomy & Physiology - 202243.15374-CCRN-1505-01 - MANAGEMENT OF CCHC - RESPIRATORYDocument12 pages1) Anatomy & Physiology - 202243.15374-CCRN-1505-01 - MANAGEMENT OF CCHC - RESPIRATORYafshin nikraveshNo ratings yet
- Apec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesApec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- Respiratiob Quick Fire QuestionsDocument2 pagesRespiratiob Quick Fire QuestionsAla' ShehadehNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Notes ExplainedDocument6 pagesGas Exchange Notes ExplainedKai TongNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesThe Human Respiratory Systemjherubedania7No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System Notes (1) ChangesDocument25 pagesThe Respiratory System Notes (1) ChangesAisha BrownNo ratings yet
- The human respiratory system: how breathing worksDocument8 pagesThe human respiratory system: how breathing worksChilla Adis ViolitaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Respiratory System, Gaseous ExchangeDocument4 pagesNotes On Respiratory System, Gaseous Exchangeshelter musasaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document15 pagesPresentation 4achsanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemElle MateoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory system-3Document18 pagesRespiratory system-3samaranadotzulfiqarNo ratings yet
- The Function of The Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesThe Function of The Respiratory Systemkevinramirezzz365No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory Systemkakai0.0No ratings yet
- Human Biology: Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesHuman Biology: Respiratory SystemSaikrishna RaoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AnatomyDocument35 pagesRespiratory Anatomyapi-217919217No ratings yet
- ACFrOgCYzyAtlOdYv5jafLv-AubsWO2slT5n-CLAKbsxs37xlcq301vUs KfW9yPahBUJ3tJd68DH3Rf-H3JFeaJn BOx82c QRBoNJMxjZCNQIg-sy KVTI5Rx7OB93lfvgdTKZs1 3ImlTKcEhDocument37 pagesACFrOgCYzyAtlOdYv5jafLv-AubsWO2slT5n-CLAKbsxs37xlcq301vUs KfW9yPahBUJ3tJd68DH3Rf-H3JFeaJn BOx82c QRBoNJMxjZCNQIg-sy KVTI5Rx7OB93lfvgdTKZs1 3ImlTKcEhEmmanuel David PereaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Respiratory Systempaulo_camuaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemMichael QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Respiratory System LessonsDocument19 pagesGrade 7 Respiratory System LessonsclaireNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument74 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- How To Write Recommendations in ResearchDocument5 pagesHow To Write Recommendations in ResearchEden MonforteNo ratings yet
- ESIC Staff Nurse 2012 and 2011Document35 pagesESIC Staff Nurse 2012 and 2011Dr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Module 5-Respiratory SystemDocument64 pagesModule 5-Respiratory SystemBorja MelanieNo ratings yet
- Nine Purification Breaths InstructionsDocument3 pagesNine Purification Breaths InstructionsElefanti SomaNo ratings yet
- Living Things and Their Environment: Quarter 1: Module 1-4Document30 pagesLiving Things and Their Environment: Quarter 1: Module 1-4ar0411No ratings yet
- مذكرة شرح علوم الصف الرابع الابتدائي لغات 2015 science for primary 4 second term 2015 Prim 4secondTERM2015Document29 pagesمذكرة شرح علوم الصف الرابع الابتدائي لغات 2015 science for primary 4 second term 2015 Prim 4secondTERM2015rabei95% (55)
- Cardiopulmonary Practice PatternsDocument909 pagesCardiopulmonary Practice PatternsDuncan D'Amico0% (1)
- Respiratory System PDFDocument202 pagesRespiratory System PDFGokul RamNo ratings yet
- Manual de Usuario LP6 Plus Puritan BennettDocument56 pagesManual de Usuario LP6 Plus Puritan BennettAmmisadday Sordo0% (1)
- Jurnal Pursed Lips BreatingDocument6 pagesJurnal Pursed Lips BreatingLya RahmaNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument16 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesMoses DumbuyaNo ratings yet
- CAPNOGRAPHYDocument10 pagesCAPNOGRAPHYJessica GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ga Machine Slide11Document94 pagesGa Machine Slide11Wong KinYouNo ratings yet
- Insights From Breath by James Nestor: "Am I Nasal Breathing?"Document1 pageInsights From Breath by James Nestor: "Am I Nasal Breathing?"Vivek TyagiNo ratings yet
- The Crane Frolics: The Path From Qihai To TanzhongDocument4 pagesThe Crane Frolics: The Path From Qihai To Tanzhongapi-268467409100% (1)
- Chicken AnatomyDocument24 pagesChicken Anatomybrianmore10No ratings yet
- Premature Ejaculation GoodbyeDocument28 pagesPremature Ejaculation GoodbyeDaniyal Abbas100% (1)
- Mechanical VentilationDocument262 pagesMechanical VentilationShalini Garg0% (1)
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 10Document8 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 10opsharpedgeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 3 Exam ReportsDocument115 pagesSyllabus 3 Exam ReportsHani MikhailNo ratings yet
- CPT ChecklistDocument3 pagesCPT ChecklistMa. Angelica Alyssa RachoNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange.Document71 pagesGaseous Exchange.wittyshooterclan100% (2)
- Sudharsana KriyaDocument2 pagesSudharsana KriyasureshbabubnysNo ratings yet
- Stephan Ventilator ABV - Service Manual PDFDocument23 pagesStephan Ventilator ABV - Service Manual PDFtallrajNo ratings yet
- Arnold Jacobs BreathingDocument7 pagesArnold Jacobs Breathingelementjunction100% (3)
- Pulmonary Function Test of Forced Vital Capacity and Slow Vital Capacity Using Spirometry in Young Adults With Respect To Body Mass Index A Normative StudyDocument18 pagesPulmonary Function Test of Forced Vital Capacity and Slow Vital Capacity Using Spirometry in Young Adults With Respect To Body Mass Index A Normative StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Gas exchange and transport in the human bodyDocument20 pagesGas exchange and transport in the human bodyAlva WongNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Just Go With The FlowDocument24 pagesActivity 3 - Just Go With The FlowJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- Ventilator Graphics and Bilevel - UAB HandoutDocument10 pagesVentilator Graphics and Bilevel - UAB HandoutRahul AmteNo ratings yet
- Z Neurology-Respiracion DiafragmaDocument61 pagesZ Neurology-Respiracion Diafragmaelmer1612No ratings yet