Professional Documents
Culture Documents
005.0 - Esfuerzos Normales, Deformaciones y Tensiones Efectivas PDF
Uploaded by
William Jesus Carrasco OlivaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
005.0 - Esfuerzos Normales, Deformaciones y Tensiones Efectivas PDF
Uploaded by
William Jesus Carrasco OlivaCopyright:
Available Formats
PONTIFICIA UNIVERSIDAD CATLICA DE CHILE
FACULTAD DE INGENIERA
ESCUELA DE CONSTRUCCIN CIVIL
CCL1290. ESTRUCTURAS I
AYUDANTA EXTRA: "ESFUERZOS NORMALES, DEFORMACIN,
TENSIONES EFECTIVAS
PRIMER SEMESTRE 2012. SECCIONES N1 y N2
Profesores: Sr. Cristin Piera Godoy. Ayudantes: Felipe Errzuriz Guzmn
Sr. Pablo Maturana Barahona. William Carrasco Oliva
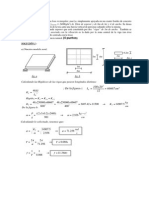
1. Un pilote de hormign de seccin cuadrada, de 20 cm de arista y 3 m de
largo, se encuentra enteramente confinado en una pared rgida e indeformable,
el pilote est sometido a una fuerza vertical de 170 tf.
Considerando que el hormign tiene un mdulo de elasticidad E=210
5
Kgf/cm
2
y que su mdulo de Poisson m = 5, se pide:
a) Calcular las tensiones efectivas en dicho pilote para las condiciones
descritas.
b) Calcular las tensiones efectivas si falla el confinamiento lateral en la
direccin z.
Obs. Desprecie el peso propio del pilote, por ser mucho menor que la carga
aplicada.
2. Calcular las tensiones normales en los elementos elsticos de los sistemas
sometidos a la accin de la fuerza que se indica, considere E=110
5
kgf/cm
2
PONTIFICIA UNIVERSIDAD CATLICA DE CHILE
FACULTAD DE INGENIERA
ESCUELA DE CONSTRUCCIN CIVIL
CCL1290. ESTRUCTURAS I
PAUTA AYUDANTA EXTRA: "ESFUERZOS NORMALES, DEFORMACIN,
TENSIONES EFECTIVAS
PRIMER SEMESTRE 2012. SECCIONES N1 y N2
1. Se tiene el 100% de confinamiento en los ejes X y Z, por lo que se tiene:
2
/ 425
20 20
170000
cm kgf
cm cm
kgf
Y
=
=
0 0 = = efx efx
0 0 = = efz efz
Adems, como se tiene la misma rea normal (3 m x 0,2 m) en X y Z, se tiene:
0 =
Z X
Clculo de tensiones efectivas:
2
2
/ 25 , 106
1 5
/ 425
1
) (
1
0 0 cm kgf
cm kgf
m m
ef
Y
Z X Z Y X X
=
= = + = =
2
/ 25 , 106 cm kgf
X
=
2
/ 25 , 106 cm kgf
Z
=
) 25 , 106 25 , 106 (
5
1
425 ) (
1
= + =
X Z Y Y
m
ef
2
/ 5 , 382 cm kg ef
Y
=
b) Se tiene:
0 0
0
/ 425
2
= =
=
=
X X
Z
Y
ef ef
cm kgf
2
/ 85 425
5
1
1
) (
1
0 0 cm kgf
m m
ef
Y X Z Y X X
= = = + = =
2
/ 408 ) 0 85 (
5
1
425 ) (
1
cm kgf
m
ef
Z X Y Y
= + = + =
2
/ 102 ) 425 85 (
5
1
0 ) (
1
cm kgf
m
ef
Y X Z Z
= = + =
PONTIFICIA UNIVERSIDAD CATLICA DE CHILE
FACULTAD DE INGENIERA
ESCUELA DE CONSTRUCCIN CIVIL
CCL1290. ESTRUCTURAS I
2. Primero confirmamos que debido a la fuerza de 16000 kgf y de 4000 kgf se
cierra el tramo de holgura que existe.
(Las unidades de longitud son despreciables, ya que trabajaremos con
diferencias de longitudes)
78 , 2
30 3 / 10
750 ) 4000 16000 (
30 8 , 1 / 10
600 16000
2 2 5 2 2 5
=
+
= +
cm cm kgf
kgf kgf
cm cm kgf
kgf
L L
CD BC
Donde se ve claramente que se cierra la junta, por lo que ahora se tiene que
analizar de la siguiente forma:
Grado de restriccin 2R-1Ec=1
Estructura hiperesttica de grado 1
i. kgf Rd Ra F
X
12000 0 = + =
ii. Condicin de deformacin:
CD BC AB AD
L L L L + + =
30 3 10
750 ) 12000 (
30 8 , 1 10
600 ) 16000 (
30 10
450
0 , 2
5 5 5
=
Ra Ra Ra
kgf Ra 06 , 2258 =
kgf Rd 94 , 9741 =
Ra F
AB
= = -2258,06 kgf
1 P Ra F
BC
= = 13741,94 kgf
1 P Ra F
CD
= = 9741,94 kgf
2
2
1
/ 27 , 75
30
06 , 2258
cm kgf
cm
kgf
=
=
2
2
2
/ 48 , 254
30 8 , 1
94 , 13741
cm kgf
cm
kgf
=
=
PONTIFICIA UNIVERSIDAD CATLICA DE CHILE
FACULTAD DE INGENIERA
ESCUELA DE CONSTRUCCIN CIVIL
CCL1290. ESTRUCTURAS I
2
2
3
/ 24 , 108
30 3
94 , 9741
cm kgf
cm
kgf
=
You might also like
- Sistemas de puesta a tierra: Diseñado con IEEE-80 y evaluado con MEFFrom EverandSistemas de puesta a tierra: Diseñado con IEEE-80 y evaluado con MEFRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Problemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesFrom EverandProblemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Cimentaciones Zapatas Conectadas PDFDocument8 pagesCimentaciones Zapatas Conectadas PDFBryan Meza100% (2)
- UF1670 - Reparación de equipos mecánicos y eléctricos de plantas de tratamiento de agua y plantas depuradorasFrom EverandUF1670 - Reparación de equipos mecánicos y eléctricos de plantas de tratamiento de agua y plantas depuradorasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Diseño de Tijerales de MaderaDocument22 pagesDiseño de Tijerales de MaderaSr. Gracie100% (2)
- Experiencias sobre circuitos eléctricos en serie operados por corriente directaFrom EverandExperiencias sobre circuitos eléctricos en serie operados por corriente directaNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Edificios Con Elementos PrefabricadosDocument16 pagesDiseño de Edificios Con Elementos PrefabricadosAlex GalindoNo ratings yet
- Estructuras Metalicas Tema 16.ejerciciosDocument12 pagesEstructuras Metalicas Tema 16.ejerciciosluisandradeNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Escaleras de Todo Tipo Wilder NancyDocument23 pagesDiseño de Escaleras de Todo Tipo Wilder NancyFernando Smith TorresNo ratings yet
- Montaje y mantenimiento de redes eléctricas subterráneas de alta tensión.From EverandMontaje y mantenimiento de redes eléctricas subterráneas de alta tensión.No ratings yet
- Ejercicios de PuentesDocument14 pagesEjercicios de PuentesEmilio ZayagoNo ratings yet
- Cimentaciones Zapatas ConectadasDocument8 pagesCimentaciones Zapatas ConectadasAndres Romero Quevedo75% (4)
- Grilla para La Observacion de Clases 2018Document4 pagesGrilla para La Observacion de Clases 2018Adriano Fernando Rivas100% (2)
- Mathcad - 01 - Memoria de Calculo - ColumnasDocument18 pagesMathcad - 01 - Memoria de Calculo - Columnas777ecor0% (1)
- A1 - Mathcad - VIGA Pasarela L 25.50m-SIDocument25 pagesA1 - Mathcad - VIGA Pasarela L 25.50m-SIJavier CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Hormigón armado. Tomo II - 2.a edición: Introducción a nueva norma CIRSOC 201/05 A.C.I. 318From EverandHormigón armado. Tomo II - 2.a edición: Introducción a nueva norma CIRSOC 201/05 A.C.I. 318Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Manual de Procedimientos Del RepejDocument13 pagesManual de Procedimientos Del RepejStheePanyAlexaAyalaNo ratings yet
- 2022-EPn09 - MET - Dimensionamiento Viga IPE (2021)Document8 pages2022-EPn09 - MET - Dimensionamiento Viga IPE (2021)Ariana ReyNo ratings yet
- Curso Cirsoc - 301 2008 SismoDocument18 pagesCurso Cirsoc - 301 2008 SismoJohn Pier Delgado PerezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Integrales de Línea, Superficie y VolumenFrom EverandEjercicios de Integrales de Línea, Superficie y VolumenRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Problemas 1gdlDocument7 pagesProblemas 1gdlJonathan Mendieta BarriosNo ratings yet
- UNE166002 2006 Gestion I D IDocument124 pagesUNE166002 2006 Gestion I D IVictorNo ratings yet
- Elasticidad EjerciciosDocument16 pagesElasticidad EjerciciosjuanNo ratings yet
- TAREA9 LT BARRENO Ecua de Estado y Vano DesniveladoDocument10 pagesTAREA9 LT BARRENO Ecua de Estado y Vano DesniveladoLuis Miguel BarrenoNo ratings yet
- 002.2 - Estructuras Reticuladas PDFDocument7 pages002.2 - Estructuras Reticuladas PDFWilliam Jesus Carrasco OlivaNo ratings yet
- EJEMPLOS DE CONCRETO REFORZADO (Basilio J. Curbelo) CivilGeeks - Com APLICANDO Concreto Estructural Del Reglamento Colombiano de Construcción Sismo Resistente NSR-10 PDFDocument194 pagesEJEMPLOS DE CONCRETO REFORZADO (Basilio J. Curbelo) CivilGeeks - Com APLICANDO Concreto Estructural Del Reglamento Colombiano de Construcción Sismo Resistente NSR-10 PDFGuillermo De la BarreraNo ratings yet
- (Zapatas Trapezoidales Combinadas - Diseño Estructural) PDFDocument34 pages(Zapatas Trapezoidales Combinadas - Diseño Estructural) PDFBrunno Claure Garcia100% (3)
- HAP1 20112012 Practica FisuracionDeformacionAnclaje v2Document27 pagesHAP1 20112012 Practica FisuracionDeformacionAnclaje v2Carlitos AndreuNo ratings yet
- Examen Calculo de PerdidasDocument10 pagesExamen Calculo de PerdidasRafael Alberto Guilarte BravoNo ratings yet
- Portico de La Iglesia - 1Document15 pagesPortico de La Iglesia - 1Salomon Balderrama YauriNo ratings yet
- Informe de Concreto Armado I - Diseño Metodo ElasticoDocument20 pagesInforme de Concreto Armado I - Diseño Metodo ElasticoHeber Barboza Fustamante100% (1)
- Capítulo 4 - Diseno de Vigas A FLEXION - 2017 (CORREGIDO)Document16 pagesCapítulo 4 - Diseno de Vigas A FLEXION - 2017 (CORREGIDO)kleber89No ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Dinamica Parte Mas 12-22Document12 pagesEjercicios de Dinamica Parte Mas 12-22MaxRamirezCastroNo ratings yet
- GRUPO7 Agrietado NoagrietadoDocument8 pagesGRUPO7 Agrietado NoagrietadoalexanderNo ratings yet
- Estabilidad 2Document29 pagesEstabilidad 2LndIngenieriaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Mecánica de SólidosDocument16 pagesEjercicios Mecánica de SólidosAnonymous oxqdXAKJ50% (2)
- Imprimir 4PCDocument10 pagesImprimir 4PCKatherine ViverosNo ratings yet
- Pase VehicularDocument8 pagesPase Vehicularandy esteban sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios DinámicaDocument10 pagesEjercicios DinámicaHimel TolozaNo ratings yet
- Problemas TracciónDocument11 pagesProblemas TracciónGuille SanchezNo ratings yet
- EscalerasDocument8 pagesEscalerasRaúl López SánchezNo ratings yet
- Cimentaciones Zapatas ConectadasDocument9 pagesCimentaciones Zapatas ConectadasIrwin Bazàn BustamanteNo ratings yet
- MetodovariableDocument16 pagesMetodovariableMauricio Ayala MendozaNo ratings yet
- Formulario CIV 209Document7 pagesFormulario CIV 209hvo_ts5441No ratings yet
- Carga Equivalente Concreto PresforzadoDocument10 pagesCarga Equivalente Concreto PresforzadoFinley Pozo Sedano100% (1)
- Memoria de Cálculo VerificacionDocument22 pagesMemoria de Cálculo Verificacionjesus25No ratings yet
- RESOLUCIÓN PRACTICO I (Prop. de Los Fluidos)Document17 pagesRESOLUCIÓN PRACTICO I (Prop. de Los Fluidos)Risotada50% (4)
- Ejercicios Resueltos en ClaseDocument22 pagesEjercicios Resueltos en ClasePaul A. Villacis100% (2)
- Estructuras de Concreto Armado ACI318-05Document0 pagesEstructuras de Concreto Armado ACI318-05PEDROUPAONo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de ZapatasDocument15 pagesEjercicios de Zapatasfcv007No ratings yet
- Escuela Politecnica NacionalDocument8 pagesEscuela Politecnica NacionalJonathan Gabriel Astudillo PortillaNo ratings yet
- Cercha de Cordones ParalelosDocument9 pagesCercha de Cordones ParalelosJoaquin MagnetNo ratings yet
- 01-Resolucion - Ejercicios Propiedades MecanicasDocument9 pages01-Resolucion - Ejercicios Propiedades MecanicassolangevenegasvillarroelNo ratings yet
- Calculo de Un DintelDocument17 pagesCalculo de Un DintelTrini Peña RuizNo ratings yet
- cALCULO PUENTE GRUA ESF PDFDocument14 pagescALCULO PUENTE GRUA ESF PDFHernan Apcho MoralesNo ratings yet
- 012.1 - Método Pendiente Deflexión PDFDocument8 pages012.1 - Método Pendiente Deflexión PDFWilliam Jesus Carrasco OlivaNo ratings yet
- 010.1 - Pandeo PDFDocument4 pages010.1 - Pandeo PDFWilliam Jesus Carrasco OlivaNo ratings yet
- 011.2 - Teorema de Clapeyron y Método Pendiente Deflexión PDFDocument1 page011.2 - Teorema de Clapeyron y Método Pendiente Deflexión PDFWilliam Jesus Carrasco OlivaNo ratings yet
- 011.1 - Teroema de Clapeyron y Método Pendiente-Deflexión PDFDocument9 pages011.1 - Teroema de Clapeyron y Método Pendiente-Deflexión PDFWilliam Jesus Carrasco OlivaNo ratings yet
- 006.2 - Flexión Compuesta, Excentricidad Simple y Fundaciones PDFDocument5 pages006.2 - Flexión Compuesta, Excentricidad Simple y Fundaciones PDFWilliam Jesus Carrasco OlivaNo ratings yet
- 007.1 - Solicitaciones Combinadas y Torsión PDFDocument6 pages007.1 - Solicitaciones Combinadas y Torsión PDFWilliam Jesus Carrasco OlivaNo ratings yet
- 006.1 - Flexión Compuesta, Excentricidad Simple y Fundaciones PDFDocument7 pages006.1 - Flexión Compuesta, Excentricidad Simple y Fundaciones PDFWilliam Jesus Carrasco Oliva100% (1)
- Solucion Pantalla Negra de La Canaima Modelo EF10MI2Document3 pagesSolucion Pantalla Negra de La Canaima Modelo EF10MI2Daniel Quintero100% (1)
- Respondidas 27-02-2015Document402 pagesRespondidas 27-02-2015Leidy Muñoz de GaldamesNo ratings yet
- Tutoría en Investigación EducativaDocument49 pagesTutoría en Investigación EducativaMargarett CoronaNo ratings yet
- Desafiante OposicionistaDocument16 pagesDesafiante OposicionistaIsraelOloNo ratings yet
- Cap 6-Valor Anual Uniforme EquivalenteDocument5 pagesCap 6-Valor Anual Uniforme EquivalenteJuan Sebastian Sanchez PadillaNo ratings yet
- Neurología Argentina: Valores Normativos para El Test Del Hotel en Adultos Jóvenes de Buenos AiresDocument7 pagesNeurología Argentina: Valores Normativos para El Test Del Hotel en Adultos Jóvenes de Buenos AiresAndrea PinoNo ratings yet
- Comunicación OrganizacionalDocument98 pagesComunicación OrganizacionalMaria jose BernalNo ratings yet
- Sec. 1 Pueblos Originarios 4toDocument9 pagesSec. 1 Pueblos Originarios 4toFernanda GavioliNo ratings yet
- LA INTELIGENCIA EMOCIONAL - Industrial DataDocument3 pagesLA INTELIGENCIA EMOCIONAL - Industrial DataDvs TrademarkNo ratings yet
- Los Tres Tiempos Del EdipoDocument5 pagesLos Tres Tiempos Del EdipoelizurtNo ratings yet
- Mapa Conceptual - SociologíaDocument1 pageMapa Conceptual - SociologíaAlfredito BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Politica ObjDocument6 pagesPolitica ObjAlan CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Tarea Semanal 8 KevinDocument7 pagesTarea Semanal 8 KevinJuan T NoaNo ratings yet
- Monografía Planeamiento EstratégicoDocument28 pagesMonografía Planeamiento EstratégicoEstephanyEspinozaHuamanNo ratings yet
- MR 228 TSP 20222Document8 pagesMR 228 TSP 20222Ronny ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Investigacion de Accidentes e IncidentesDocument7 pagesInvestigacion de Accidentes e IncidentesCarolina GomezNo ratings yet
- La Capacidad y El Nivel de ActividadDocument35 pagesLa Capacidad y El Nivel de ActividadEstanislao SuardiazNo ratings yet
- Folleto Caja de Herramientas de SeguridadDocument2 pagesFolleto Caja de Herramientas de SeguridadFernando MuñozNo ratings yet
- Curso Universitario de Especialización en Dirección de Recursos Humanos, Gestión Laboral y PRLDocument18 pagesCurso Universitario de Especialización en Dirección de Recursos Humanos, Gestión Laboral y PRLENyDNo ratings yet
- Manual AutowareDocument303 pagesManual Autowarehoward_pernia75% (4)
- Etica Empresarial UberDocument2 pagesEtica Empresarial Uberjuan0% (1)
- Padres Que Crian Solo A Sus HijosDocument3 pagesPadres Que Crian Solo A Sus HijosKimberly HoustonNo ratings yet
- El Problema Que Ayudó A Plantear Alfred MarshallDocument1 pageEl Problema Que Ayudó A Plantear Alfred Marshallpciscar2No ratings yet
- Lineas GeodesicasDocument5 pagesLineas GeodesicasEdgar Aguirre RomeroNo ratings yet
- Los VulgarismosDocument12 pagesLos Vulgarismosaula_proyectos25670% (2)
- Ensayo Sobre La Identidad y Las Instituciones para DurkheimDocument5 pagesEnsayo Sobre La Identidad y Las Instituciones para DurkheimLuis MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cuestionario Capitulo 5 Apa 3Document15 pagesCuestionario Capitulo 5 Apa 3cmarroquin73No ratings yet