Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ME3001 Dynamics of Machinery Problem Set
Uploaded by
Athul John0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views2 pagesThis document contains a problem set for a Dynamics of Machinery course. It includes 12 problems related to static and dynamic force analysis of machines. The problems involve sketching free-body diagrams of machine links and components, determining forces and torques required for equilibrium, and analyzing the effects of friction. Solutions are to be provided on a drawing sheet and submitted by August 13th. An assignment involves using graphical and analytical methods to solve a problem from a textbook on the theory of machines and mechanisms.
Original Description:
Msmt Quest
Original Title
ME3001 Problem Set -1 3-8-2013
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a problem set for a Dynamics of Machinery course. It includes 12 problems related to static and dynamic force analysis of machines. The problems involve sketching free-body diagrams of machine links and components, determining forces and torques required for equilibrium, and analyzing the effects of friction. Solutions are to be provided on a drawing sheet and submitted by August 13th. An assignment involves using graphical and analytical methods to solve a problem from a textbook on the theory of machines and mechanisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views2 pagesME3001 Dynamics of Machinery Problem Set
Uploaded by
Athul JohnThis document contains a problem set for a Dynamics of Machinery course. It includes 12 problems related to static and dynamic force analysis of machines. The problems involve sketching free-body diagrams of machine links and components, determining forces and torques required for equilibrium, and analyzing the effects of friction. Solutions are to be provided on a drawing sheet and submitted by August 13th. An assignment involves using graphical and analytical methods to solve a problem from a textbook on the theory of machines and mechanisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1
ME3001 Dynamics of Machinery Monsoon 2013
Problem set 1 3-8-2013
Exercise 1 Static force analysis of machines (not to be submitted)
Use drawing sheet wherever necessary
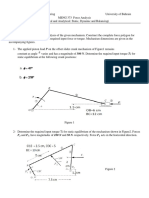
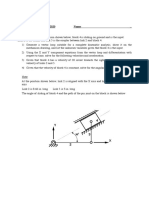
1. Sketch the FBD of each link in Fig.1. What is the force P for static equilibrium?
2. In Fig.2 pinion 2 is the driver and gear 3 is an idler. The gears have a diametral pitch of 6 and 20
o
pressure angle.
Sketch the FBD of gear 3 and show all forces acting. Pinion 2 rotates at 900 rev/min and transmits 25 hp to the
gear set.
Fig.2
Fig.1 O
2
A=100 mm, BA=150mm, BO
4
=125 mm, CO
4
=200mm, CD=400mm, O
2
O
4
=60mm.
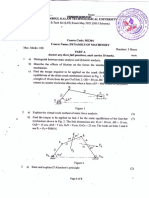
3. Sketch the Free-Body-Diagram (FBD) of each link and show all the forces acing. Obtain the torque T
12
to
be applied on link 2 for static equilibrium of the linkage shown in Fig.3. Also, obtain the forces in the
bearings. Work out the solution both graphically and analytically.
4. (Ref. Q3) Obtain the equilibrium torque using the principle of virtual work.
5. ( ,, ) How will you solve the problem using method of superposition?
6. ( ,, ) Consider the following cases (i) there is friction in the joint A (ii) friction in joints A and B and (iii) friction
in all the four joints. Work out the static force analysis in each case assuming direction of impending motion.
(Does the impending motion in a joint imply the same for other joints?)
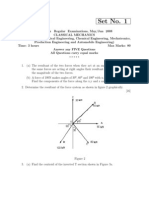
7. Determine the torque M
12
required to drive slider 6 of Fig.4 against a load of P=100N, at a crank angle of =
30
o
.
Fig.4 O
2
A=63 mm, BC=200mm, BO
4
=400 mm
Fig.3 AO
2
=100 mm, CA=350 mm, O
2
O
4
=350mm, CO
4
=250 mm, DO
4
=175 mm, BA=350 mm, BC=200 mm
2
8. In the Q.7 above, assume a coefficients of friction =0.2 between link 1 and 6 and 0.1 between links 3 and 4.
Determine the torque M
12
for equilibrium in this case.
9. Use the method of virtual work to analyse the problem 7.
10. A 16 tooth pinion (Fig.5) on shaft 2 rotates at 1720 rev/min and transmits 5 hp to the double reduction gear train.
All gears have 20
o
pressure angle. The distances between centres of bearings and gears for shaft 3 are shown in
Fig. Find the magnitude and direction of radial force that each bearing exerts against the shaft.
Fig.5
11. Obtain the force transmitted between two spur gears with involute teeth if there is friction between the teeth.
How will the torque ratio (output torque to input torque) vary with respect to the gear rotation? Let N
1
and N
2
be
the number of teeth, is the coefficient of friction, is the pressure angle and m be the module of each gear.
12. Illustrate the effect of friction in a slider-crank mechanism if there is friction in all the joints. A known force P is
applied on the slider. Obtain the torque T to be applied on the crank for static equilibrium. Also obtain all the
bearing forces. Assume a suitable direction for the impending motion. Work out the problem graphically by
assuming numerical values. Indicate the steps involved in the obtaining the forces.
.
Assignment 1 Dynamic force analysis of machines Submit on 13-8-13
Give the entire answers in the drawing sheet.
1. Ref. Pr. 12.7, P.496, Uicker, Pennock and Shigley, Theory of machines and mechanisms, 3
rd
ed. 2009. Work out
the problem (i) graphically and (ii) analytically.
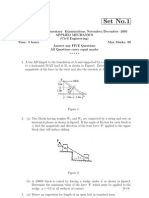
2. The crank in the slider-crank mechanism shown in Fig.1 has a constant angular velocity of 100 rad/s ccw. The
mass of the connecting rod is 0.2 kg and the moment of inertia about the centre of mass is 300 kg.mm
2
.
Determine the crank torque T
1
required for dynamic equilibrium at the position shown if slider has a mass of 0.3
kg. Neglect external loads and inertia of crank 1. Work out the problem (a) graphically (b) by method of virtual
work. [Ans: T
1
=4.4 Nm ccw]
Fig.1
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 6710 NotesDocument45 pages6710 NotesAndrés SuquilloNo ratings yet
- MOH Formulary Drug List 2014Document115 pagesMOH Formulary Drug List 2014mahmud000No ratings yet
- Violent Extremism in South AfricaDocument20 pagesViolent Extremism in South AfricaMulidsahayaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Circular MotionDocument22 pagesPhysics Project On Circular Motionishan67% (3)
- Beams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsFrom EverandBeams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Problem Set 9: Gear Design and Shaft Critical Speed ProblemsDocument31 pagesProblem Set 9: Gear Design and Shaft Critical Speed ProblemsAshley Moreira67% (3)
- Ralph M. McInerny (Auth.) - The Logic of Analogy - An Interpretation of ST Thomas (1971, Springer Netherlands)Document191 pagesRalph M. McInerny (Auth.) - The Logic of Analogy - An Interpretation of ST Thomas (1971, Springer Netherlands)cuba esquivel amadeoNo ratings yet
- S4PE ME2014 Mechanics of Machines Winter 2018-19Document1 pageS4PE ME2014 Mechanics of Machines Winter 2018-19AswinNo ratings yet
- Question Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Force Analysis Problems (Kinematics)Document8 pagesForce Analysis Problems (Kinematics)AkibNo ratings yet
- R05010105-APPLIED-MECHANICS apr/may 2007 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂™Document12 pagesR05010105-APPLIED-MECHANICS apr/may 2007 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂™badboy_rockssNo ratings yet
- DOM Cycle Test - I 2022 AnswerkeyDocument7 pagesDOM Cycle Test - I 2022 AnswerkeyL04 BHÀRÁTHÏ KÀÑÑÁÑNo ratings yet
- Mech4005y 5 2010 2Document4 pagesMech4005y 5 2010 2Balgo BalgobinNo ratings yet
- NR 10105 Engineering MechanicsDocument13 pagesNR 10105 Engineering MechanicsVijay PrakashNo ratings yet
- DOM-Mid SemDocument3 pagesDOM-Mid SemsdfvsrferNo ratings yet
- End Term TOM 2020-2021Document3 pagesEnd Term TOM 2020-2021Nivash KumarNo ratings yet
- ME3001 A3 Balancing of Reciprocating MassesDocument2 pagesME3001 A3 Balancing of Reciprocating MassesAkshay KakaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: BDA 31003 Finite Element MethodDocument3 pagesAssignment 1: BDA 31003 Finite Element MethodIzwan SaifudinNo ratings yet
- I B.Tech Regular Examinations Engineering MechanicsDocument12 pagesI B.Tech Regular Examinations Engineering MechanicsGanesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Shafts: Calculating Shear Strain in Circular ShaftsDocument0 pagesTorsion of Shafts: Calculating Shear Strain in Circular ShaftsJavier_MoliNo ratings yet
- 22203-AME Question Bank-1Document2 pages22203-AME Question Bank-1Shubham ModakNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Eng Ses Main 2016 First PDFDocument8 pagesMechanical Eng Ses Main 2016 First PDFSumeet TiwariNo ratings yet
- Btes103 203 em QBDocument10 pagesBtes103 203 em QBSurajNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question PaperDocument0 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question PaperBala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument18 pagesEngineering MechanicsSiva ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Dec 2013Document11 pagesEngineering Mechanics Dec 2013api-248483124No ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument2 pagesKinematics of Machinessameer_m_daniNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocument15 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question BankKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Vibration Paper3Document32 pagesVibration Paper3Debabrata PaulNo ratings yet
- 1429r05210804 Engineering MechanicsDocument11 pages1429r05210804 Engineering MechanicsSaivenkat PenuguduruNo ratings yet
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KompsnasabariNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics July 2021Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics July 2021DANDEM SAIRAMNo ratings yet
- Me304 Dynamics of Machinery, May 2022Document4 pagesMe304 Dynamics of Machinery, May 2022Alok DineshNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics 3rd Sem GTU IMPDocument9 pagesEngineering Mechanics 3rd Sem GTU IMPSwastik PanchalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 1Document16 pagesTutorial 3 1abinNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- 5826Document6 pages5826zubbbuNo ratings yet
- HW-8 - CHDocument20 pagesHW-8 - CHMuzamil Shah0% (1)
- Classical MechanicsDocument14 pagesClassical MechanicsinaylakNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomDocument6 pagesMechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomIoana BoilaNo ratings yet
- Applied MechanicsDocument13 pagesApplied Mechanicsapi-26349602100% (1)
- (Join AICTE Telegram Group) 22303 (MOS) Mechanics of StructuralDocument4 pages(Join AICTE Telegram Group) 22303 (MOS) Mechanics of StructuralVivek Sharma0% (1)
- Second Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. TechDocument7 pagesSecond Semester Examination, 2002-2003: B. Techlatendra kumar srivastavNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 Plane Kinematics of Rigid Bodies and Lagrangian DynamicsDocument2 pagesTutorial 8 Plane Kinematics of Rigid Bodies and Lagrangian Dynamicsrockbottom 123No ratings yet
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KomRajueswarNo ratings yet
- ENCI 317 - Lab 2 Material - Fall 2022Document17 pagesENCI 317 - Lab 2 Material - Fall 2022Sherry YousafNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics EquationsDocument16 pagesEngineering Mechanics Equationsgovind4ever5No ratings yet
- EME2204 - Assignment - Balancing - 2023Document2 pagesEME2204 - Assignment - Balancing - 2023Jamiza shenningNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Torsional Test of A Round Steel BarDocument9 pagesLab 2 - Torsional Test of A Round Steel BarTaha KhanNo ratings yet
- nov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂Document14 pagesnov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂badboy_rockssNo ratings yet
- ME101 Midsem 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesME101 Midsem 2020 PDFRohan MittalNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I SYSTEM OF FORCES - SOLVED NUMERICALS (4)Document44 pagesUNIT - I SYSTEM OF FORCES - SOLVED NUMERICALS (4)vanshpkothari2005No ratings yet
- Torsion of Shafts Theory and Numerical ExamplesDocument49 pagesTorsion of Shafts Theory and Numerical Exampleser.jaspreetNo ratings yet
- Tutorial emDocument3 pagesTutorial emBeesam Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations Engineering Mechanics Aug/Sep 2008Document3 pagesI B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations Engineering Mechanics Aug/Sep 2008sanagavarapuNo ratings yet
- Design Area Exam - Fall 2020 Name - Problem 1Document4 pagesDesign Area Exam - Fall 2020 Name - Problem 1PriyadarshanSinghNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Systems 334 (308814 v1) End of Semester 1 Examinations, June 2007Document12 pagesDynamic Systems 334 (308814 v1) End of Semester 1 Examinations, June 2007Jill Dagreat100% (1)
- Kinematics Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesKinematics Exam QuestionsShyloo GsaNo ratings yet
- R13 Engineering Mechanics TitleDocument3 pagesR13 Engineering Mechanics TitlePrudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- 20220825022418am 1460238122 10595448 1852907624 - Ahl23Document7 pages20220825022418am 1460238122 10595448 1852907624 - Ahl23pm engineeringsNo ratings yet
- Bench ViceDocument10 pagesBench ViceAthul John100% (3)
- Procedure To Teach Sight Words in Unit 1Document1 pageProcedure To Teach Sight Words in Unit 1Athul JohnNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument11 pagesMini ProjectAthul John100% (1)
- Lamp 1Document11 pagesLamp 1Athul JohnNo ratings yet
- ME3001 Tut 2 16-8-13 PDFDocument1 pageME3001 Tut 2 16-8-13 PDFBivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Ch08 - Design of ExperimentsDocument19 pagesCh08 - Design of ExperimentsAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- Grade CardDocument2 pagesGrade CardAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- Grade CardDocument2 pagesGrade CardAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument1 pageBrochureAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- ME3003 - Project Presentation GuidelinesDocument4 pagesME3003 - Project Presentation GuidelinesAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- Computer Forensics and ExplorationDocument6 pagesComputer Forensics and ExplorationAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- Alby TRV Ded 22mayDocument2 pagesAlby TRV Ded 22mayAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- Alby Ded Cok 29mayDocument2 pagesAlby Ded Cok 29mayAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Environment Studies For Undergraduate Courses - Erach Bharucha PDFDocument260 pagesTextbook of Environment Studies For Undergraduate Courses - Erach Bharucha PDFPari Athouba100% (2)
- 2014 Metrology Lab S6MA1 Practical Exam ScheduleDocument1 page2014 Metrology Lab S6MA1 Practical Exam ScheduleAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- 2013 Monsoon Final TimetableDocument2 pages2013 Monsoon Final TimetableAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- 2013 Monsoon Final Timetable DRAFTDocument2 pages2013 Monsoon Final Timetable DRAFTAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- ME3003 - Module One Part Two PDFDocument12 pagesME3003 - Module One Part Two PDFAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- Nitc Mechanical Btech Syllabus and CurriculumDocument110 pagesNitc Mechanical Btech Syllabus and Curriculumpikasoc1No ratings yet
- ME3003 - Module One Part Two PDFDocument12 pagesME3003 - Module One Part Two PDFAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- ME3003 - Module Two Part Two PDFDocument13 pagesME3003 - Module Two Part Two PDFAthul JohnNo ratings yet
- Director VP Program Manager in Raleigh NC Resume Mary Paige ForresterDocument6 pagesDirector VP Program Manager in Raleigh NC Resume Mary Paige ForresterMaryPaigeForresterNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Arabic ManuscriptsDocument46 pagesConservation of Arabic ManuscriptsDr. M. A. UmarNo ratings yet
- Progressivism Lesson 3 The PresidentsDocument3 pagesProgressivism Lesson 3 The Presidentsapi-302923213No ratings yet
- DTF - Houses of The FallenDocument226 pagesDTF - Houses of The FallenShuang Song100% (1)
- Lower and Upper Bound Theory ExplainedDocument37 pagesLower and Upper Bound Theory ExplainedTsuki ZombinaNo ratings yet
- IEEE COMMUNICATIONS LETTERS, VOL. 10, NO. 6, JUNE 2006Document3 pagesIEEE COMMUNICATIONS LETTERS, VOL. 10, NO. 6, JUNE 2006Regina PittsNo ratings yet
- Crane's Manual - CV ValuesDocument14 pagesCrane's Manual - CV Valuesnghiemta18No ratings yet
- ELC650-Movie Critique Yusri, YassinDocument14 pagesELC650-Movie Critique Yusri, YassinYusri MalekNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument23 pagesAbstractaashish21081986No ratings yet
- Reactor (CSTR)Document12 pagesReactor (CSTR)fatiehah93100% (1)
- Sap Interface PDFDocument1 pageSap Interface PDFAwais SafdarNo ratings yet
- Organization and Workflow Management of Central ST PDFDocument5 pagesOrganization and Workflow Management of Central ST PDFravsab GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Sanjay Chandra Vs Cbi On 23 November, 2011Document21 pagesSanjay Chandra Vs Cbi On 23 November, 2011SaiBharathNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Measurement, Evaluation and AssessmentDocument11 pagesDifferences Between Measurement, Evaluation and Assessmentfaizy216No ratings yet
- Understanding Cholesterol: Classification of A LipoproteinDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Cholesterol: Classification of A LipoproteinJacky FaragNo ratings yet
- History of English - IntroductionDocument58 pagesHistory of English - IntroductionPaul Edward GuevarraNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio Rubric For HHS4C: Criteria Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Overall Expectation ADocument4 pagesE-Portfolio Rubric For HHS4C: Criteria Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Overall Expectation Aapi-312895913No ratings yet
- Essential Leadership Qualities and StylesDocument20 pagesEssential Leadership Qualities and StylesDanica Rose Daza MacahiloNo ratings yet
- SAP FICO Asset Accounting 1Document3 pagesSAP FICO Asset Accounting 1Ananthakumar ANo ratings yet
- VC3 TranslationDocument313 pagesVC3 TranslationFuyuki Maxwell ArashiNo ratings yet
- SLI ProfileThe title "TITLE SLI Profile" is less than 40 characters and starts with "TITLEDocument3 pagesSLI ProfileThe title "TITLE SLI Profile" is less than 40 characters and starts with "TITLEcringeNo ratings yet
- Sigram Schindler Beteiligungsgesellschaft PetitionDocument190 pagesSigram Schindler Beteiligungsgesellschaft PetitionjoshblackmanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics - IntroductionDocument55 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics - IntroductionTeacher DennisNo ratings yet
- Swadhin Bangla Betar KendraDocument21 pagesSwadhin Bangla Betar KendraMusfiqur Rahman ApuNo ratings yet
- Bailable and Non BailableDocument10 pagesBailable and Non BailableasthaNo ratings yet