Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network:-: Local-Area Networks (Lans)
Uploaded by
Helmi Murad Ebrahim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
134 views35 pagesFundamentals of Computer Networks
Original Title
FCN
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFundamentals of Computer Networks
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
134 views35 pagesNetwork:-: Local-Area Networks (Lans)
Uploaded by
Helmi Murad EbrahimFundamentals of Computer Networks
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 35
1
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
1 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
Introduction
Network:-
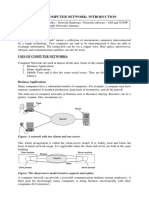
Is a computer network, mostly get back or referred as a network, it contain a lot of
computers, devices connect together through a channels that simplification the
connection between the users, and allow to share data or information with users.
Networks may be classified according to a wide variety of characteristics.
1.0-Type of Networks:-
-Local-area networks (LANs): The computers are geographically close together (that is,
in the same building).A computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs
are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be
connected to other LANs over any distance via telephone lines and radio waves. A
system of LANs connected in this way is called a wide-area network (WAN).
Most LANs connect workstations and personal computers. Each node (individual
computer) in a LAN has its own CPU with which it executes programs, but it also is able
to access data and devices anywhere on the LAN. This means that many users can share
expensive devices, such as laser printers, as well as data. Users can also use the LAN to
communicate with each other, by sending e-mail or engaging in chat sessions.
Local-area
networks
(LANs)
2
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
2 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-Wide-area networks (WANs): The computers are farther apart and are connected by
telephone lines or radio waves.
A computer network that spans a relatively large geographical area. Typically, a WAN
consists of two or more local-area networks (LANs).
Computers connected to a wide-area network are often connected through public
networks, such as the telephone system. They can also be connected through leased lines
or satellites. The largest WAN in existence is the Internet.
Wide-area
networks
(WANs)
3
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
3 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-Campus-area networks (CANs): The computers are within a limited geographic area,
such as a campus or military base.
Acronym for campus-area network. An interconnection of local-area networks within a
limited geographical space, such as a school campus or a military base.
Campus-
area
networks
(CANs)
4
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
4 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-Metropolitan-area networks (MANs): A data network designed for a town or city.
Short for Metropolitan Area Network, a data network designed for a town or city. In
terms of geographic breadth, MANs are larger than local-area networks (LANs), but
smaller than wide-area networks (WANs). MANs are usually characterized by very high-
speed connections using fiber optical cable or other digital media.
Metropolitan-
area networks
(MANs)
5
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
5 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-Home-area networks (HANs): A network contained within a user's home that connects
a person's digital devices.
Short for home area network. A HAN is a network contained within a user's home that
connects a person's digital devices, from multiple computers and their peripheral devices
to telephones, VCRs, televisions, video games, home security systems, "smart"
appliances, fax machines and other digital devices that are wired into the network.
Home-area
networks
(HANs)
6
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
6 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
Requirements:
2.0-Technology Involved:-
-Definition and usage:
The phrase technology derive from a Latina word is originally contain 2 words the first
word is techno (thats mean ART or ACCOPATION), second the LOGY (which mean
STUDY or SCIENCE).
Hence the expression of Technology means or applies for Scientific and knowledge in
every field.
There are two reasons to follow scientific knowledge: for the sake of the knowledge itself
and for the practical uses of that knowledge. Because this second aspect of science affects
the lives of most people, it is more familiar than the first. Knowledge must be gained,
however, before it can be applied, and often the most important technological advances
arise from research pursued for its own sake.
7
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
7 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
Traditionally, new technology has been concerned with the construction of machines,
structures, and tools on a relatively large scale. The development of materials for building
bridges or skyscrapers is an example of this, as is the development of the internal-
combustion engine and the nuclear reactor. While such activities involve all the sciences,
from chemistry to nuclear physics, the overriding goal has been the same: to improve the
human condition by finding better ways to deal with the macroscopic world.
Since World War II, the focus of technological activity has undergone a major change.
While the old activities are still pursued, they have been largely superseded by
applications of technology at the microscopic level. Instead of building large-scale
structures and machines, modern-day technology tends to concentrate on finding
improved ways to transfer information and to develop new materials by studying the way
atom s come together. The silicon chip and microelectronics typify this new
technological trend, as does the blossoming of genetic engineering. The trend can be
expected to continue into the foreseeable future.
8
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
8 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
The dividing line between what we include in the following list as technology and what
we call science elsewhere in this volume is somewhat arbitrary. In general, what we have
done is this: if a term is essential to understanding a particular branch of science, it
appears in the list for that science. Thus, atom appears with the physical sciences, even
though an understanding of atoms is clearly important to the new technology. If,
however, the term involves something that is likely to affect an individual's life, even
though it is not a central concept of a particular branch of science, it is listed under
Technology.
The words in the following section have been chosen because they are likely to appear
without explanation in many publications, particularly in articles and books dealing with
the impact and implications of technology. This section does not emphasize the social
consequences of new technology, but concentrates instead on the basic knowledge
needed to understand how technology works.
3.0-Methods of high Internet Connection:-
(Cable, DSL, Satellite & Wireless Internet connection)
-Wireless:
With recent advances in wireless Internet technology, high speed wireless connections
are now readily available on laptops, cell phones, and other mobile computing devices.
Some emerging forms of wireless technology, such as EV-DO and WiMax, are starting to
turn wireless connectivity into the dominant form of broadband Internet access.
Whether you need a wireless local area network for your home or small office, or
wireless Internet access on your laptop while sitting in your favorite coffee shop, there
are a growing number of wireless ISPs that can provide you with such service -- and at
speeds comparable to residential DSL and Cable.
-Wireless Is Becoming Incredibly Fast:
One new wireless technology in development as of early 2009 is poised to increase the
download speeds of wireless even further. WiMax promises to deliver maximum speeds
9
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
9 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
of up to 7 Mbps -- to your laptop, your car, your cell phone, and your home. WiMax is
only just now becoming available in some U.S. cities, but expect to see it in more
locations by the end of the year and throughout 2010.
This increase in speed means that you no longer have to limit your mobile computing
activities to basic email and text messaging. When you use a high speed wireless Internet
service provider, you can download streaming media and other large file formats just as
easily as you could with the broadband Internet connection in your home or at the office.
Nearly every laptop sold today already has a wireless adapter installed in it, plus there are
many new handheld devices that are set up for remote Internet access. The number of
hotspots that the major wireless ISPs have in operation is also constantly increasing. So,
if you like or need to have access to the Internet while on the go, then slow download
speeds and limited availability simply no longer serve as obstacles.
-The First High Internet Connection (Cable):
When you connect to the Internet, you might connect through a regular modem, through a
local-area network connection in your office, through a cable modem or through a digital
subscriber line (DSL) connection. DSL is a very high-speed connection that uses the
same wires as a regular telephone line.
10
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
10 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
Here are some advantages of DSL:
* You can leave your Internet connection open and still use the phone line for voice
calls.
* The speed is much higher than a regular modem
* DSL doesn't necessarily require new wiring; it can use the phone line you already
have.
* The company that offers DSL will usually provide the modem as part of the
installation.
But there are disadvantages:
* A DSL connection works better when you are closer to the provider's central office.
The farther away you get from the central office, the weaker the signal becomes.
* The connection is faster for receiving data than it is for sending data over the
Internet.
* The service is not available everywhere.
In this article, we explain how a DSL connection manages to squeeze more information
through a standard phone line -- and lets you make regular telephone calls even when
you're online.
- DSL:
Stands for "Digital Subscriber Line." It is medium for transferring data over regular
phone lines and can be used to connect to the Internet. However, like a cable modem, a
DSL circuit is much faster than a regular phone connection, even though the wires it uses
are copper like a typical phone line.
An asymmetric DSL (ADSL) connection allows download speeds of up to about 1.5
megabits (not megabytes) per second, and upload speeds of 128 kilobits per second. That
is why it is called ADSL and not just DSL (because of the asymmetric speeds). There is
11
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
11 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
also a "Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line" (SDSL) which is similar to ADSL, but allows
data transfer speeds of 384 Kilobits per second in both directions. Theoretically, this type
of connection allows download speeds of up to 9 megabits per second and upload speeds
of up to 640 kilobits per second. The difficult part in establishing an DSL circuit is that it
must be configured to connect two specific locations, unlike a regular phone line or cable
modem. DSL is often seen as the new, better alternative to the older ISDN standard.
-Type of DSL:
ADSL:
Stands for "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line." ADSL is a type of DSL, which is a
method of transferring data over copper telephone lines. While symmetrical DSL (SDSL)
uploads and downloads data at the same speed, ADSL has different maximum data
transfer rates for uploading and downloading data.
For example, an ADSL connection may allow download rates of 1.5Mbps, while upload
speeds may only reach 256Kbps. Since most users download much more data than they
upload, this difference usually does not make a noticeable impact on Internet access
speeds. However, for Web servers or other computers that send a lot of data upstream,
ADSL would be an inefficient choice.
12
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
12 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-How does satellite Internet operate?
How do you access the Internet other than dial-up if you live too far from a phone
company office for DSL and there is no cable TV on your street? Satellite Internet access
may be worth considering. It's ideal for rural Internet users who want broadband access.
Satellite Internet does not use telephone lines or cable systems, but instead uses a satellite
dish for two-way (upload and download) data communications. Upload speed is about
one-tenth of the 500 kbps download speed. Cable and DSL have higher download speeds,
but satellite systems are about 10 times faster than a normal modem.
13
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
13 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
4.0-The companies that afford internet connection:-
For the companies that offer to the customers the internet line, they are many but the best
one which I feel good about it is (TM net) provide a various internet connection to the
customers and depend of how fast did the customer want or need and the price that is
reasonable to you.
And you can register easy because you will found their clients in everywhere and kind
with you, besides they will explain every single thing that you might use or been useful
for you and ofcourse to make their business get done.
And here is the whole various connection of the company that is called (Streamyx)
Package Combo Price
(RM)
Standard Price
+Rental (RM)
Saving
(RM)
Features
384 Kbps 60 45 + 25 = 70 10 With Modem
512 Kbps 90 77 + 25 = 102 12 Unlimited Access
Lifetime Warranty
1 Mbps 110 99 + 25 = 124 14 1 E-mail
2 Mbps 140 188 + 25 = 213 73 Dynamic IP
4 Mbps 160 268 + 25 = 293 133
www.tmbroadband.com
5.0-Importance of Wi-Fi technology:-
14
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
14 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
WIFI gives you an extremely large amount of freedom because you can basically
use it from anywhere. From your couch to your local shopping mall, wireless
reliability can always lend a helping hand. Also, WIFI is not restricted to certain
groups. No matter who you are, you can use it. And, on top of its convenience,
WIFI is fast, reliable, and easy to use. In the corporate enterprise, wireless LANs
are usually implemented as the final link between the existing wired network and
a group of clients computers. This gives these users wireless access to the full
resources and services of the corporate network across a building or campus
setting.
Wireless Fidelity is important to the wireless LAN world, because it is securely
tested to assure ability of equipment of the same frequency band and feature.
WIFI is the certification logo given by the WIFI Alliance for equipments that
passes the tests for compatibility for IEEE 802.11 standards. The WIFI Alliance
organization, is a nonprofit organization that promotes the acceptance of 802.11
wireless technology and they ensures all WIFI certified 802.11 based wireless
networking equipments works with all other WIFI certified equipments of the
same frequency. The WIFI Alliance works with technical-groups like the IEEE
and other companies that are developing new wireless networking equipments.
6.0-How Technology can affect human and life social?
-The bright side of Wi-Fi Technology:
Technology with its rapid growing speed is influencing old ways of doing daily
affairs. We don't need any more to move around to handle different tasks and
chores since all of them will be done in a matter of pushing a button located on a
remote control.
Nobody can deny that technology has brought comfort to our lives, but almost all
of us confess this fact that technology by itself has got a lot of deficits that in long
term will cause a lot of side effects either physically or emotionally. This is a fact
that through the multi-media and the wide spread range of webs ( Internet) the
15
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
15 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
concept of time and distance have been vanished and people can keep in touch
with each other by means of such facilities. The negative view is the fact that they
keep in touch in a virtual world not natural. Via the webs and mail the emotional
feelings and thoughts cant be transferred. People can convey their attitudes and
thoughts much more effectively when they are close to each other.
-The bad side of Wi-Fi Technology:
One bad effect of technology on life is that with more technology placing barriers
between people, face to face meetings happen less.
This small, simple change leads to a whole host of very serious problems with
society in general. People are becoming more lazy; choosing to stay at home and
play video games than go to a basketball game or get together with friends.
On top of that, the new barriers that are made because of technology gives those
who are most effected by them a decaying sense of pride in their country. In fact,
it is this lack of pride that has spurred many of the anti-American feelings that are
felt and publicized by people of this very country.
Not all technology is bad or evil, but we do need to be careful that we don't
become slaves (meaning obsessed with, not actual slaves) to our own creations.
Newspapers and local agencies and music stores have been forced to shut down
since items are available online.
6.0-Criteria Requirements of Wi-Fi Technology:-
-Scope:
The term Wi-Fi was used for 802.11b only in the beginning, But today applies to
the 802.11 substandard.
Certifying and owning the Trademark: The Wi-Fi Alliance, http://www.wi-fi.org/
Standard frequency gross data rate modulation
16
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
16 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
802.11a 5._ GHz 54 Mbps OFDM
802.11b 2.4 GHz 11 Mbps DSSS
802.11g 2.4 GHz 54 Mbps OFDM, PBCC
-Criteria:
How to choose the right standard what area a, b and g good for?
802.11b oldest, robust, good for indoors and outdoors, cheapest
802.11g same frequency as 802.11b, higher bandwidth, BUT, because of
ODFM, a lot less robust for outdoor long haul links! For this, it is not a good
choice!
802.11a because of higher frequency, it does not go through obstacles as well.
But, it makes for excellent high bandwidth long haul links, When LOS is given.
Indoors, it suffers from LOS problems.
-How to choose standards and products:
As always: your requirements what do you want to do?
Budget & availability
Especially for wireless gear: consider price development!
Dont buy for 500 today, what next year might cost 100.
Legal considerations:
What is legally & practically :) possible where you are?
Where applicable: support/drivers for your Operating system?
Environmental specs: temperature! Humidity!
Power consumption
-Types of Wi-Fi hardware:
Access Point
(Includes Access Points, Residential Gateways, DSL & Cable Products)
17
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
17 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
Cellular Convergence
(Products that enable both Wi-Fi and cellular communications)
Compact Flash
Embedded Client
(Includes Notebooks, etc.)
Ethernet Client Device
(Includes Wireless-to-Ethernet Station Adapters & Converters)
External Card
(Includes PC Cards, PCMCIA Cards, Card Bus & SD Cards)
Internal Card
(Includes Mini PCI Cards & PCI Cards)
PDAs
USB Client Device
(Includes Dongles & Adapters)
Wireless Printers and Print Servers
This was the list of types as used by the expert
However, the line between types of hardware is not a strict one.
Especially when you build and modify yourself, it makes sense to think of it as radio +
chipset + surrounding hardware + software + all the externals (antennas, power supply ...)
Types of usage change over time and may be hard to classify, e.g. point to point links,
bridges, repeaters, mesh nodes (where the line between client and AP/server disappears).
18
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
18 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
Anatomy of an AP/router
WAN or
Internet
port
Reset
button
Radio card
Antenna
Connection
Chipset
Broadcom
Unused connectors
(Sometimes)
Pigtail
Power supply
LAN ports
19
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
19 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-Features: output and sensitivity:
Examples for output power and receive sensitivity info
Receive Sensitivity
1. -94dBm at 1 Mbps;
2. -88dBm at 2 Mbps;
3. -87 dBm at 5.5 Mbps;
4. -84dBm at 11 Mbps
5. Output Power (at the N connector)
6. +17.5dBm (max) to
7. +11.5dBm (min)
20
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
20 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-Some Products:
The following examples of wireless hardware focus mostly on infrastructure related
hardware, i.e. access points, gateways, bridges, point-to-point links rather than pure client
cards.
These examples are of course just a personal pick -based on an overview of many
international projects. Alvarion/ Breezecom
There are many many more vendors to name a few we have omitted here:
Cisco, 3COM, Gemtek, Tranzeo, Intel, Alvarion/Breezecom Pricing info in this
presentation is meant as a very rough first orientation prices change fast and are
extremely dependent on quantity.Local availability, pricing and skills easily can be the
most important buying points.(Antennas are subject of a separate presentation later in this
course, and not being covered here).
21
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
21 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-Some Products: PC client cards:
Many vendors. Older cards for 802.11b, g/b newer cards are typically a/b/g and based
on Atheros chipset.Sometimes with antenna connectors.
Radio quality (output, sensitivity) varies a lot! Vendors worth looking at: Avaya (ex
Orinoco) (old b cards!) Senao (200 mW cards, ext. ant.) Linksys,D-Link
Home user equipment that can do many things more, as proven in many projects around
the world. Hard to beat in price /performance. Some of their gear runs on GPLed Linux
firmware, e.g. the Linksys WRT54G (b+g standards), for which a growing number of
Firmware hacks exist, including mesh implementations. Comparable vendors in the low
price range: e.g. D-Link, Net gear.
Good entry points for WRT54G info:
22
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
22 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
http://www.talug.org/events/20050115/Wireless_Linux/WRT54G_firmware.html
http://www.seattlewireless.net/index.cgi/LinksysWrt54g
-Some Products: Mikrotik:
From Latvia, this company makes 2.4/5 Ghz routers, boards and WISP oriented software.
Very interesting multi-radio (a/b/g) configurations.
1600 rm (check list!) for single AP, 3200 rm for a link
Www http://www.mikrotik.com
23
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
23 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-Some Products: Smart bridges:
Very good series of point to (multi)point links (airhaul), APs (airpoint), clients. Good
global distribution, track record of rural deployments, incl. Mt. Everest.Rated -
40 ... +65 Celsius! AP from 650 rm, Links from 1300 rm
Www http://www.smartbridges.com
-Some Products: Motorola Canopy:
24
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
24 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
Products in (900 MHz), 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Focus on WISP, carriers, enterprise.
Point to point and multipoint links. Proprietary (non-802.11) modulation very robust.
1300 to 1600 rm per end),( 500 rm for reflector)
-Some Products: 4G Access cube:
The 4G access cube is a little 2-4 radios
Linux mesh box.
* Dimensions: small (7x5x7cm) cube
* Waterproof outdoor casing
* No moving parts
* Low power consumption (ca. 4W)
* Power over Ethernet (802.3af standard)
* Up to 4 WLAN (802.11a/b/g) interfaces
* 400MHz MIPS processor AMD Au1500 aka Alchemy
* 32MB flash
* 64MB RAM
* USB host, USB device
870 rm (2 radios)
25
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
25 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
Www http://meshcube.org
http://4g-systems.biz
-WI-Fi Software:
-WI-Fi Software Tools for Multiple Platforms
Aircrack-ng is a WEP and WPA-PSK key cracking program for use on 802.11 networks.
The primary purpose for the program is to recover a lost or unknown key once enough
data is captured. Aircrack-ng has the following advantages over the original Aircrack
release:
Updated and better documentation
Updated drivers, including new drivers not originally supported in Aircrack
New and faster WEP attack algorithm PTW
Supports Unix, Windows, and Zaurus
Includes fragmentation in attacks
Better cracking performance
Dictionary support for WEP attacks
Use multiple cards to capture simultaneously
New tools including airtun-ng, packetforge-ng (improved arpforge), wesside-ng (still
under development), and airserv-ng(still under development)
Code optimizations and bug fixes
-Wi-Fi Software Tools for Windows:
26
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
26 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
KNSGEM II
KNSGEM II is a program that takes the survey logs produced by NetStumbler, Kismet,
or WiFiHopper and compiles the data with data Google earth to provide colorized 3D
coverage maps.
Nets tumbler
Nets tumbler is a Wi-Fi tool for Windows that allows you to detect Wireless Local Area
Networks (WLANs) using 802.11b, 802.11a and 802.11g. It has many uses:
Verify that your network is set up the way you intended.
Find locations with poor coverage in your WLAN.
Detect other networks that may be causing interference on your network.
Detect unauthorized "rogue" access points in your workplace.
Help aim directional antennas for long-haul WLAN links.
Use it recreationally for War Driving.
Omni Peek
Omni peek is the next generation version of commercial wireless analysis software from
wild packets which combines the legacy applications AiroPeek and Ether Peek.
Features of Omni Peek include the ability to:
Analyze any network interface, including 10Gigabit, Gigabit, and WAN adapters
Analyze media and data traffic simultaneously
View results in normal document formats such as PDF, HTML or just through
email or IM clients
27
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
27 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
View high level details of traffic in a dashboard, or drill down into the individual
packet payloads
View local, remote, or previously stored captures, including view multiple active
captures at once.
View capture details by conversation pairs to quickly identify useful or
problematic events
Change capture filters at will without restarting the capture sequence
Stumbverter
StumbVerter is a standalone application which allows you to import Network Stumbler's
summary files into Microsoft's MapPoint 2004 maps. The logged WAPs will be shown
with small icons, their color and shape relating to WEP mode and signal strength.
As the AP icons are created as MapPoint pushpins, the balloons contain other
information, such as MAC address, signal strength, mode, etc. This balloon can also be
used to write down useful information about the AP.
Lucent/Orinoco Registry Encryption/Decryption
Lucent Orinoco Client Manager stores WEP keys in the Windows registry under a certain
encryption/obfuscation. This Wi-Fi tool can be used to encrypt WEP keys into a registry
value or to decrypt registry values into WEP keys.
Wi-Fi Hopper
Wi-Fi Hopper is a windows network discovery and connection client. Wi-Fi Hopper can
assist auditors with Site Surveys, Connection parameter testing, and Network Discovery.
Filters allow you to easily limit the details displayed, as well as what kinds and
configurations of equipment will be tested.
28
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
28 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
APTools
APTools is a utility that queries ARP Tables and Content-Addressable Memory (CAM)
for MAC Address ranges associated with 802.11b Access Points. It will also utilize Cisco
Discovery Protocol (CDP) if available. If an Access Point that is web managed is
identified, the security configuration of the Access Point is audited via HTML parsing.
-Windows tools useful when associated with Wi-Fi tools:
MacIdChanger
MacIdChanger allows you to easily and temporarily change the MAC Address of your
windows network adapter without much fuss. This is generally used to conceal the unique
mac id that is on every network adapter. This software only operates on Windows
XP/2003.
Technetium MAC Address Changer
Free, and very verbose and functional tool to change your network adapters MAC
Address. The tool works regardless of which network adapter or driver is installed in
your system. Supported platforms are Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows XP and
Windows Vista.
-Wi-Fi Implementation Cost:
Citywide blanket coverage of wireless Internet access sounds great, but companies aren't
going to go around setting up Wi-Fi base stations out of sheer kindness. Who's going to
pay for Wi-Fi?
It depends how it will be used. There are two ways Wi-Fi can be implemented -- as a
zone for wireless connections that single users go to when they want to connect to the
Internet on a laptop (the non-line-of-sight "super Wi-Fi" implementation), or as a line-of-
29
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
29 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
sight hub used to connect hundreds of customers to a steady, always-on, high-speed
wireless Internet connection.
Under the "super Wi-Fi" plan, cities might pay to have WiMAX base stations set up in
key areas for business and commerce and then allow people to use them for free. They
already do this with Wi-Fi, but instead of putting in a bunch of Wi-Fi hot spots that cover
a few hundred square yards, a city could pay for one WiMAX base station and cover an
entire financial district. This could provide a strong draw when city leaders try to attract
businesses to their area.
Some companies might set up WiMAX transmitters and then make people pay for access.
Again, this is similar to strategies used for WiFi, but a much wider area would be
covered. Instead of hopping from one hot spot to another, WiMAX-enabled users could
have Internet access anywhere within 30 miles of the WiMAX base station. These
companies might offer unlimited access for a monthly fee or a "pay as you go" plan that
charges on a per-minute or per-hour basis.
The high-speed wireless hub plan has the potential to be far more revolutionary. If you
have high-speed Internet access now, it probably works something like this: The cable (or
phone) company has a line that runs into your home. That line goes to a cable modem,
and another line runs from the modem to your computer. If you have a home network,
first it goes to a router and then on to the other computers on the network. You pay the
cable company a monthly fee, which reflects in part the expense of running cable lines to
every single home in the neighborhood.
30
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
30 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
The other good thing for people wanting to set up a Wi-Fi network is that the prices of
Wi-Fi access points and radios are falling sharply. The cost of a Wi-Fi radio chip which
was around 50 rm in 2002 will drop to under 7 rm in 2006.Similarly the cost of Wi-Fi.
Access points which were around 3200 rm in 2002 are under 320 rm now and are
expected to fall further. Also the Wi-fi card that was around 2200 rm in 2000 is almost
under 160 rm now and is approaching to be provided as a standard feature in most of the
new PC's being manufactured today. Because of these low price to set up a Wi-Fi
network and without any licence fees to be paid millions of wi-Fi networks have been set
up as they also provide better speeds as compared to the traditional broadband and
cellular networks.
The default installed cost per unit for a single access point is 3200 rm. The overall cost
estimate (default, suggested values) for a wireless network with 13 access points is
251,520 rm, providing support for 250 employees. This cost includes 32,000 rm for the
design (site survey), 800 rm for each of the 13 Ethernet drops, and 800 rm for each of the
13 power supplies (including Power-over-Ethernet).
-Special considerations of Wi-Fi implementation:-
-Safety:
Wireless networks use radio waves to transmit information between wired router stations
and the wireless adapter cards in laptop computers. The radio waves emitted by Wi-Fi
networks are typically at frequencies of 2.4 Gigahertz (GHz) or 5.8 GHz - well within
that portion of the electromagnetic spectrum defined to be radiofrequency radiation. This
radiation is much lower in energy than ionizing radiation (e.g. the type of radiation
emitted by x-ray machines), and the biological effects associated with exposure are much
different.
The long-recognized and well understood adverse biological effect resulting from
exposure to high levels of RF exposure is tissue and cell heating. More recently concerns
have been raised about whether there may be effects, including carcinogenicity, at RF
levels below those levels that produce detectably harmful heating. Many studies have
31
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
31 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
been conducted to determine whether there is a causal relationship between low-level
radiofrequency exposure and harmful effects such as cancer and adverse pregnancy
outcomes.
-security:
Nowadays Wi-Fi is becoming more and more popular used by the people in varied
places, home, office, malls, new buildings, and even in parks. So as we need to create a
Wi-Fi network we have to ensure that our security point isnt accessible to anyone can
get our network easily or hack through the network because it can be dangerous on our
precious files and information that we keep it in our personal computers.
Almost all routers and access points have an administrator password that's needed to log
into the device and modify any configuration settings. Most devices use a weak default
password like "password" or the manufacturer's name, and some don't have a default
password at all. As soon as you set up a new WLAN router or access point, your first
step should be to change the default password to something else. You may not use this
password very often, so be sure to write it down in a safe place so you can refer to it if
needed. Without it, the only way to access the router or access point may be to reset it to
factory default settings which will wipe away any configuration changes you've made.
Reduce your WLAN transmitter power:
You won't find this feature on all wireless routers and access points, but some allow you
lower the power of your WLAN transmitter and thus reduce the range of the signal.
Although it's usually impossible to fine-tune a signal so precisely that it won't leak
outside your home or business, with some trial-and-error you can often limit how far
outside your premises the signal reaches, minimizing the opportunity for outsiders to
access your WLAN.
-Rules and Regulation:
32
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
32 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
The Ministry of Communications, Department of Telecommunications (DoT) Malaysia
has introduced significant new compliance requirements for all ISPs providing Wi-Fi
services. The regulation goes beyond just public hotspots to include residential and
business Wi-Fi applications, extending requirements of centralized management,
authentication and provisioning by the ISP even for all customers who may have installed
Wi-Fi access points within their premises.
SP must ensure that all Wi-Fi access points be encrypted & secured. The list of
locations includes:
Public hotspots including airports, transportation hubs, schools
Hotels, restaurants, guest houses, malls & similar locations
Business and offices who use leased lines and install their own Wi-Fi Access
Points (APs) also need to be secured
Residential & Retail customers who install Wi-Fi Access Points also need to be
secured or risk suspension of their Internet access
Service providers must offer central authentication and tracking system to secure
all Wi-Fi end points ensuring each subscribers access sessions are authorized and
tracked.
o Records of subscriber records need to be kept for minimum 1 year.
o Records must also include user metrics for full audit trace
Identity verification of each subscriber is mandatory and must be accomplished in
the following ways:
o Photo identity based verification using well established address proof
documents such as PAN, Passport, Driver License;
o Personal Identification needs to be copied and retained for 1 year;
o SMS based authentication of each session/subscriber thereby establishing
a direct co-relation between a pre-verified mobile phone and a subscriber.
Avoiding Internet DoT License Suspension requires ISPs to:
Ensure only secure and authorized subscribers are allowed network access at all
wireless end points;
Accurately ascertain network access and retain records of subscriber activity
including IP address & location where / when an authorized user accessed a
specified Internet resource;
ISPs must, upon lawful request, enable interception and tracking capabilities for
agencies to track unlawful activity.
-Advantages and Disadvantages of Wi-Fi Technology:-
33
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
33 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
-Advantages / strengths for implementing Wi-Fi technology:
Wi-Fi uses unlicensed radio spectrum and does not require regulatory approval
for individual deplorers.
It allows local area networks (LANs) to be setup with cabling. The can reduce
associated costs of network connection and expansions. Places where cables
cannot be run, such as outdoor areas and historical buildings can use wireless
LANs.
Wi-Fi products are extensively available in the market. There are different brands
of access points and user's network interfaces are able to inter-operate at a very
basic service level.
Prices are considerably lower as competition amongst vendors' increases.
Wi-Fi networks can support roaming. This allows mobile users with laptop
computer to be able to move from one access point to another.
Numerous access points and network interfaces support various degrees of
encryption to protect traffic from interception.
-Disadvantages / strengths for implementing Wi-Fi technology:
Due the fact that Wi-Fi is still relatively new, there are considerably more disadvantages
to users. Let's have a look at them:
The use of Wi-Fi band that is 2.4 GHz does not require a license in most countries
provided that is stays below limit of 100mW and one accepts interference from
other sources; including interference which causes the users devices to no longer
function.
The spectrum assignments and operational limitations are not consistent
worldwide.
Power consumption is fairly high compared to some other standards, making the
battery life and heat a concern to some users.
Wi-Fi uses the unlicensed 2.4GHz spectrum, which often crowded with other
devices such as Bluetooth, microwave ovens, cordless phones, or video sender
devices, and among many others. This may cause degradation in performance.
Wi-Fi networks have limited range. A typical Wi-Fi home router might have a
range of 45m (150ft) indoors and 90m (300ft) outdoors. Ranges may also vary as
34
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
34 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
Wi-Fi is no exception to the physics of radio wave propagation with frequency
band.
The most common wireless encryption standard, wired equivalent privacy or
WEP has been shown to be breakable even when it has been correctly configured.
Access points could be used to steal personal and confidential information
transmitted from Wi-Fi consumers.
Intervention of a closed or encrypted access point with other open access points
on the same or a nearby channel can prevent access to the open access points by
others in the area. It poses a high problem in high-density areas such as large
apartment blocks where many residents are operating Wi-Fi access points.
Inter-operability issues between brands or deviations can cause limited connection
or lower output speeds.
Free access points can be used by the malicious to anonymous to initiate an
attack that would be extremely difficult to track beyond the owner of the access
point.
35
CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
35 CE51100-1 - Fundamentals of Computer Networks 2010
You might also like
- Final Project ReportDocument49 pagesFinal Project ReportAllen NagarNo ratings yet
- Ee Act 2Document12 pagesEe Act 2Isip, Dirk Lou V.No ratings yet
- Artikel Dan Contoh Soal (Bahasa Inggris)Document15 pagesArtikel Dan Contoh Soal (Bahasa Inggris)BWfool100% (1)
- Networking Concepts and Technologies ExplainedDocument18 pagesNetworking Concepts and Technologies ExplainedTiki BlossomNo ratings yet
- DCN Chapter 1 - Part 2Document66 pagesDCN Chapter 1 - Part 2Esta AmeNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer NetworkingDocument46 pagesWhat Is Computer NetworkingramprasadNo ratings yet
- Saiku Viva DocumentationDocument45 pagesSaiku Viva DocumentationSai KumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Computer NetworksDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Computer Networkssasi_17No ratings yet
- Computer Communication (MIS Project)Document16 pagesComputer Communication (MIS Project)harshvardhan_sheoranNo ratings yet
- Uses of InternetDocument8 pagesUses of Internetigwe nnabuikeNo ratings yet
- Wireless Network ProDocument30 pagesWireless Network ProDilip YadavNo ratings yet
- IMP Introduction-To-Mobile-ComputingDocument43 pagesIMP Introduction-To-Mobile-ComputingakttripathiNo ratings yet
- LAN and WAN ConnectivityDocument11 pagesLAN and WAN Connectivitydebabratalogon50% (2)
- MplsDocument124 pagesMplsmgitecetechNo ratings yet
- BT205 BCE Unit 4Document29 pagesBT205 BCE Unit 4deepak kushwahNo ratings yet
- InternetNotes PDFDocument11 pagesInternetNotes PDFSungram SinghNo ratings yet
- CSEC IT NOTES - Term 2 Week 11 - Computer Networks Lecture 1Document58 pagesCSEC IT NOTES - Term 2 Week 11 - Computer Networks Lecture 1kxng ultimateNo ratings yet
- Troduction To NetworkingDocument10 pagesTroduction To NetworkingHero EnglishNo ratings yet
- Business Driven Technology - Networks and Telecoms ManualDocument7 pagesBusiness Driven Technology - Networks and Telecoms ManualThao TrungNo ratings yet
- LO 1 NewDocument52 pagesLO 1 NewEdgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Wireless Local Area NetwoDocument8 pagesAn Overview of Wireless Local Area NetwoHọc Sinh Mới LớnNo ratings yet
- Module1-Introduction To NetworkDocument14 pagesModule1-Introduction To NetworkUsop AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet In: Computer Systems ServicingDocument12 pagesLearning Activity Sheet In: Computer Systems ServicingCarvalds 0315No ratings yet
- UNIT-I Introduction of Computer NetworsDocument128 pagesUNIT-I Introduction of Computer NetworsSARKARI BABUNo ratings yet
- 2.0 NetworkDocument24 pages2.0 NetworkChinta QaishyNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Ch-1 Computer Network NotesDocument13 pagesClass 8 Ch-1 Computer Network NotesHaresh NathaniNo ratings yet
- History and evolution of the Internet and World Wide WebDocument18 pagesHistory and evolution of the Internet and World Wide WebHimanshi JainNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Notes For Students - 2Document49 pagesUNIT 3 Notes For Students - 2deepesh_gaonkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document30 pagesChapter 7Nixon Yusach SihombingNo ratings yet
- Internet: To YouDocument14 pagesInternet: To YouMurali VasuNo ratings yet
- Cornell Data Networking: Wired vs. Wireless?: Prepared by R. David VernonDocument8 pagesCornell Data Networking: Wired vs. Wireless?: Prepared by R. David VernonNour HrsNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Wireless LANDocument31 pagesTerm Paper Wireless LANUrvija DuttNo ratings yet
- On Computer Networking and SecurityDocument14 pagesOn Computer Networking and SecurityshitaltadasNo ratings yet
- Project Chapter OneDocument3 pagesProject Chapter Oneomoniyioluwatobi35No ratings yet
- CcnaDocument21 pagesCcnaYoo Hoo BinNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument67 pagesComputer NetworkWaqas AliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Network (5 Hours)Document18 pagesIntroduction To Computer Network (5 Hours)karan subediNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Introduction To NetworkDocument15 pagesMODULE 1 Introduction To NetworkChiew Hui LooNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Peer-To-peer NetworksDocument13 pagesPresentation On Peer-To-peer NetworksDhara R. PatelNo ratings yet
- CDCDocument9 pagesCDCMelvin P. FiguraNo ratings yet
- Researchcub 504 2394Document4 pagesResearchcub 504 2394Reygen TauthoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer Network?Document55 pagesWhat Is A Computer Network?AnuNo ratings yet
- Trabalho Redes 2Document5 pagesTrabalho Redes 2Vinicius FreitasNo ratings yet
- Hardware and Network Servicing Level III: Determine Best Fit TopologyDocument14 pagesHardware and Network Servicing Level III: Determine Best Fit TopologyDagneWalleNo ratings yet
- CN 1 - MergedDocument32 pagesCN 1 - MergedLo VeNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications in Mobile ComputingDocument12 pagesWireless Communications in Mobile Computingapi-19799369No ratings yet
- Wired and Wireless NetworkDocument5 pagesWired and Wireless Networkjimoh emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Wireless Tech Guide to Voice, Data & InternetDocument11 pagesWireless Tech Guide to Voice, Data & InternetAdemola AdesiyiNo ratings yet
- Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) PresentationDocument14 pagesWireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) PresentationsonuchandiniNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - Information, People, and TechnologyDocument8 pagesComputer Networks - Information, People, and TechnologyMike MikkelsenNo ratings yet
- "Computer Networks" Redirects Here. For The Periodical, "Datacom" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See Datacom (Disambiguation)Document13 pages"Computer Networks" Redirects Here. For The Periodical, "Datacom" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See Datacom (Disambiguation)sheikhkhalidNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument13 pagesUnit Iabdulbasithboss46No ratings yet
- Graphic Communication Lecture on NetworkingDocument9 pagesGraphic Communication Lecture on Networkingalrafi antorNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Etworks: Prepared by Senait KDocument11 pagesData Communication and Etworks: Prepared by Senait KSenait Kiros100% (1)
- Wireless Lan PDFDocument9 pagesWireless Lan PDFSafwan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Mark Carlo Sanorjo Bscpe - 3B: Review Questions Fill in The BlanksDocument5 pagesMark Carlo Sanorjo Bscpe - 3B: Review Questions Fill in The Blanksmark carlo SanorjoNo ratings yet
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Investigation The Relationship Between Teamwork With Employees' Job SatisfactionDocument6 pagesInvestigation The Relationship Between Teamwork With Employees' Job SatisfactionHelmi Murad EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Impact of Process Protocol Design On Virtual Team EffectivenessDocument190 pagesImpact of Process Protocol Design On Virtual Team EffectivenessHelmi Murad EbrahimNo ratings yet
- High-Performance Work Practices, Career Satisfaction, and Service Recovery PerformanceDocument17 pagesHigh-Performance Work Practices, Career Satisfaction, and Service Recovery PerformanceHelmi Murad EbrahimNo ratings yet
- FCN - Second MoldDocument39 pagesFCN - Second MoldHelmi Murad EbrahimNo ratings yet
- OOM Group AssignmentDocument36 pagesOOM Group AssignmentHelmi Murad EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things Iot InfrastructuresDocument147 pagesInternet of Things Iot Infrastructuresx01001932100% (1)
- WI FI TechnologyDocument27 pagesWI FI Technologyshivammathur25No ratings yet
- Bts3911b PicoDocument38 pagesBts3911b PicoGeorgeNo ratings yet
- ZTE H1600 Maintenance Management GuideDocument109 pagesZTE H1600 Maintenance Management GuideandreasmonNo ratings yet
- True of False: H12-111-Enu Hcia-Iot V2.5 ExamDocument20 pagesTrue of False: H12-111-Enu Hcia-Iot V2.5 ExamSeif Riahi100% (4)
- RN-131 Eval GuideDocument46 pagesRN-131 Eval Guidemorcov19No ratings yet
- HP Pro Mini 400 G9 Desktop PCDocument99 pagesHP Pro Mini 400 G9 Desktop PCyovocNo ratings yet
- ACOEM (OneProd) Vs CSI 2140 ComparisonDocument2 pagesACOEM (OneProd) Vs CSI 2140 ComparisonSyed Huzaifa Ahmed (Larf Nalavale)100% (1)
- PDFDocument24 pagesPDFAnonymous 2lMI3jbZbNo ratings yet
- Cisco SBA COL TelephonyUsingCiscoUCMConfigurationFilesGuide-Feb2013Document41 pagesCisco SBA COL TelephonyUsingCiscoUCMConfigurationFilesGuide-Feb2013kayudo80No ratings yet
- 4G TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS AND TECHNOLOGIESDocument6 pages4G TECHNOLOGY APPLICATIONS AND TECHNOLOGIESAchmad YukrisnaNo ratings yet
- URC MX-1400/MX-1400i SpecsDocument1 pageURC MX-1400/MX-1400i SpecsCorey DownsNo ratings yet
- Strategic Information Managemnet and E-Business Group 3 Presentation RevisedDocument34 pagesStrategic Information Managemnet and E-Business Group 3 Presentation Revisedmichellechirimuta0No ratings yet
- FT - AutoMesh Training Final PartnerDocument36 pagesFT - AutoMesh Training Final PartnerRokhan NasseryNo ratings yet
- Verizon Jetpack 4g Lte Mobile Hotspot Ac791l Manual OriginalDocument2 pagesVerizon Jetpack 4g Lte Mobile Hotspot Ac791l Manual Originalfawzan fawzNo ratings yet
- FireTV 4Series Omni OmniQLED US UsermanualDocument108 pagesFireTV 4Series Omni OmniQLED US UsermanualjasonphxNo ratings yet
- Computer Concepts Illustrated Introductory 9th Edition Parsons Test BankDocument12 pagesComputer Concepts Illustrated Introductory 9th Edition Parsons Test Bankkevinsnyder22051995fne100% (24)
- Fortigate Managing Devices 50 PDFDocument33 pagesFortigate Managing Devices 50 PDFmatemhkNo ratings yet
- BGT ASAP User GuideDocument198 pagesBGT ASAP User Guideobads1No ratings yet
- Samsung Galaxy S4 Mini I9190 - Schematic DiagarmDocument133 pagesSamsung Galaxy S4 Mini I9190 - Schematic DiagarmJhoel Tapia TirinaNo ratings yet
- DSL-224 Quick Setup GuideDocument36 pagesDSL-224 Quick Setup GuideMarco DiazNo ratings yet
- Mobile MarketingDocument42 pagesMobile MarketingRui TengNo ratings yet
- ICT 7 2Q Chapter 5 Activity SheetDocument2 pagesICT 7 2Q Chapter 5 Activity SheetRaymond PunoNo ratings yet
- Ceh v7 and v8 ComparisonDocument21 pagesCeh v7 and v8 ComparisonRicardo J. Bendita LaricoNo ratings yet
- D-Link Router Setup and Installation Using Dlinkrouter - Local LoginDocument2 pagesD-Link Router Setup and Installation Using Dlinkrouter - Local LoginDlink-Router-LocalNo ratings yet
- Satellite L300 Series User's GuideDocument220 pagesSatellite L300 Series User's GuideNaveen SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Quick Installation Guide: Set UpDocument2 pagesQuick Installation Guide: Set UpMarcello BenucciNo ratings yet
- DebeshDocument13 pagesDebeshroom liveNo ratings yet
- User Manual 2276949Document15 pagesUser Manual 2276949Roberto Di MarcoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 DCC NotesDocument11 pagesUnit 4 DCC NoteskharateojasNo ratings yet