Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kinetics Review
Uploaded by
Mario V Lopez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesGeneral Chemistry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGeneral Chemistry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesKinetics Review
Uploaded by
Mario V LopezGeneral Chemistry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Name____________________________
Ch. 14 Kinetics Review
1. What are the 4 factors that can affect the rate of a reaction?
Show your work for every calculation. Round your answer to the correct number of significant figures and record your
final answer with correct units on the line provided.
2. A reaction A + B C obeys the following rate law: Rate = k[A]
2
[B].
a. If [A] is doubled, will the rate constant change? Explain.
b. If [A] is doubled, how will the rate change?
c. What are the reaction orders for A and B? A = B =
d. What is the overall reaction order?
e. What are the units of the rate constant?
3. Consider the following reaction:
2 NO(g) + 2H
2
(g) N
2
(g) + 2H
2
O(g)
a. The rate law for this reaction is first order in H
2
and second order in NO. Write the rate law.
Rate =
b. If the rate constant for this reaction at 1000K is 6.0 x 10
4
M
-2
s
-1
, what is the reaction rate when [NO] = 0.025 M and
[H
2
] = 0.015 M?
c. What is the reaction rate at 1000K when the concentration of NO is increased to 0.10 M while the concentration of H
2
is 0.010 M?
4. The reaction below was studied and produced the results in the table.
2 ClO
2
+ 2 OH
-
ClO
3
-
+ ClO
2
-
+ H
2
O
a. Determine the rate law for the reaction. Rate =
b. Calculate the rate constant.
c. Calculate the rate when [ClO
2
] = 0.010 M and [OH
-
] = 0.025 M.
5. A + 2B 2C
The following results were obtained in experiments designed to study the rate of the reaction above.
Experiment Initial Concentration (mol/L)
[A] [B]
Initial Rate of
Disappearance of A (M/s)
1 0.05 0.05 3.0 x 10
-3
2 0.05 0.10 6.0 x 10
-3
3 0.10 0.10 1.2 x 10
-2
4 0.20 0.10 2.4 x 10
-2
a) Determine the order of the reaction with respect to each of the reactants and write the rate law for the reaction.
b) Calculate the value of the rate constant, k, for the reaction. Include units.
c) If another experiment is attempted with [A] and [B] both 0.02 M, what will be the initial rate of disappearance of B?
d) The following reaction mechanism was proposed for the reaction above.
A + B C + D
D + B C
i) Show that the mechanism is consistent with the balanced reaction.
ii) Show which step is the rate-determining step and explain your choice.
6. 2 NO (g) + Br
2
(g) 2 NOBr (g)
The following results were obtained in experiments designed to study the rate of the reaction above.
Experiment Initial Concentration (mol/L)
[NO] [Br
2
]
Initial Rate of Appearance
of NOBr (M/s)
1 0.0200 0.0200 9.6 x 10
-5
2 0.0400 0.0200 3.8 x 10
-4
3 0.0200 0.0400 1.9 x 10
-4
a) Write the rate law for the reaction b) Calculate the value of the rate constant, k, for the reaction. Include the units.
b) In experiment 2, what was the concentration of NO remaining when 2/3 of the original amount of Br
2
was consumed?
c) Which of the following reaction mechanisms is consistent with the rate law established in (a)? Explain your choice.
I. NO + NO
N
2
O
2
(fast)
N
2
O
2
+ Br
2
2 NOBr (slow)
II. Br
2
Br + Br (slow)
2NO + Br NOBr (fast)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Translational EquilibriumDocument2 pagesTranslational EquilibriumJossie Razil TolibasNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept HWN 1Document7 pagesMole Concept HWN 1Alina0% (1)
- Functional Groups Alphabetic ListDocument5 pagesFunctional Groups Alphabetic ListYourMotherNo ratings yet
- Band Gap Engineering - Lecture 7Document15 pagesBand Gap Engineering - Lecture 7ldaukiyaNo ratings yet
- ET Contact Options Zavijava To MoonroeDocument276 pagesET Contact Options Zavijava To Moonroeskearney12No ratings yet
- R.T.-1 P-08-05-2011 Paper-1 12th (ABCD) (English) Code-B WADocument12 pagesR.T.-1 P-08-05-2011 Paper-1 12th (ABCD) (English) Code-B WASushmit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Robotics: EverythingDocument11 pagesRobotics: Everythingabu saidNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Model: Review, Ideal Gas Model, Ideal Gas Equation of State, Thermodynamic Properties of Ideal GasesDocument34 pagesIdeal Gas Model: Review, Ideal Gas Model, Ideal Gas Equation of State, Thermodynamic Properties of Ideal GasesJake SyNo ratings yet
- Dfe 4 B 043 Bcca 419825Document11 pagesDfe 4 B 043 Bcca 419825Sarvesh DubeyNo ratings yet
- 50 MM Diameter PipeDocument8 pages50 MM Diameter Pipe阿尔坎塔拉约翰·肯尼斯No ratings yet
- PP2611 XP95 Heat Detector Data SheetDocument2 pagesPP2611 XP95 Heat Detector Data SheetgebreNo ratings yet
- Liquid CrystalsDocument8 pagesLiquid CrystalsSarah TahirNo ratings yet
- Galvanneal - Differences From Galvanize: GalvinfonoteDocument8 pagesGalvanneal - Differences From Galvanize: GalvinfonoteKYAW SOENo ratings yet
- 9800 XRF XRD - ArtigoDocument8 pages9800 XRF XRD - Artigocelestino biasottoNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Week 9Document16 pagesPhysics 1 Week 9Santos, Alexsandria PaulaNo ratings yet
- Tablas de Drill PipeDocument19 pagesTablas de Drill PipeCarito GarciaNo ratings yet
- MSDS Catridge HPDocument7 pagesMSDS Catridge HPdp abdullahNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument14 pagesElectrochemistryOm AgrawalNo ratings yet
- IV. Oxidation and Secondary Enrichment of Gold Deposits: General PrinciplesDocument15 pagesIV. Oxidation and Secondary Enrichment of Gold Deposits: General PrinciplesHAMZA LAMSALAHNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 Solution CIVE207 W24Document11 pagesAssignment2 Solution CIVE207 W24tasnim.tanvir99No ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Electric FieldsDocument12 pagesMODULE 2 Electric FieldsVenus CaringalNo ratings yet
- Dreyer Analysis 1988Document349 pagesDreyer Analysis 1988Yutt WattNo ratings yet
- Pure Biology Chapter 7 Nutrition in PlantsDocument38 pagesPure Biology Chapter 7 Nutrition in Plantshamsterish100% (2)
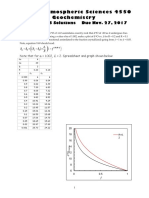
- 455 17ProblemSet08SolutionsDocument5 pages455 17ProblemSet08SolutionsSoundz sevenNo ratings yet
- Mtech CpiDocument1 pageMtech Cpivawom884No ratings yet
- H2 2008 ALL JC Prelims Questions (2013)Document47 pagesH2 2008 ALL JC Prelims Questions (2013)Indrik WijayaNo ratings yet
- CRE1 PAPER - Alif - Farhandi - HannahDocument53 pagesCRE1 PAPER - Alif - Farhandi - HannahFarhandi Fadillah FedrizalNo ratings yet
- Agitan DF 6120 Tds enDocument1 pageAgitan DF 6120 Tds enViktor Ragozin (Nakilon)No ratings yet
- SQP1Document10 pagesSQP1The. Daksh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Commentary To The Leaning Tower of Pisa PresentationDocument2 pagesCommentary To The Leaning Tower of Pisa PresentationTom ChlayonNo ratings yet