Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IHRM Chapter3
Uploaded by
Abhishek SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IHRM Chapter3
Uploaded by
Abhishek SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
1 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Chapter Three
The Context of Cross-
Border Alliances and
SMEs
2 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Chapter Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, you should be able to:
define cross-border mergers and acquisitions (M&As) the
different stages of formation, and phase-specific strategic
HR requirements
describe the formation process of international joint
ventures (IJVs) and identify HR measures and roles
relevant in the development of such cross-border alliances
discuss the internationalization of small and medium-sized
enterprises (SMEs) and their approaches to international
human resource management
3 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Opening Vignette
Mergers and Acquisitions: The Dynamics of
Globalization
increased level of internationalization through M & As
4 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Terms
SME
non-equity cross-border alliance
equity modes
merger
acquisition
born globals
boundary spanning positions
pre-M&A
due diligence
integration planning
implementation planning
resources
processes
values
M&A
IJV
UNCTAD
TNC
5 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Cross-Border Alliances
cooperative agreements between two or more firms from
different national backgrounds, which are intended to
benefit all partners
6 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Non-Equity Cross-Border
Alliance
investment vehicle in which profits and other
responsibilities are assigned to each party according to a
contract
7 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Equity Modes
foreign direct investors purchase of shares of an
enterprise in a country other than its own
8 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Equity and Non-Equity Modes of
Foreign Operation (Figure 3.1)
9 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Cross-Border Mergers and
Acquisitions
Merger
result of an agreement between two companies to join
their operations together
Acquisition
one company buys another company intending to control
the activities of the combined operations
10 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
The Formation Processes of M & As
and HR Challenge (Figure 3.2)
11 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
HR Challenges in M&As
creating new HR practices and strategies that meet the
requirements of the M & A
12 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Cross-Border M&A
merging or takeover of an enterprise in one country by
TNCs from another country
13 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Mergers and Acquisitions in US
Billions (Figure 3.3)
14 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Reason to Engage in M&As
facilitate the rapid entry into new markets
15 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Facts Firms Take into Consideration
When Deciding on a Target Country
the growth aspiration of the acquiring company
risk diversification
technological advantages
a response to government policies in a particular country
exchange rate advantages
favourable political and economic conditions
effort to follow clients
16 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
IHRM and its Role in
Employee Relations (M&A)
The quality of employee relations, ranging from
employee support to employee resistance is influenced
by variables such as the
similarity between management styles of the two
organizations
type of cross-border combinations
combination potential in terms of efficiency gains
extent of organizational integration
17 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Employee Resistance Endangers
M&A Performance
HRM role (task and human integration)
visibility and continuity of leadership
communication processes
integrating mechanisms
acquired personnel retained
voluntary personnel loss
18 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Human Integration Process
especially difficult to manage and takes time
both firms are embedded in their own national,
institutional and cultural settings
19 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Typical Cross-Border M&A
Problems
within first year of merger, up to 20% of executives may
be lost. Over a longer time frame, this tends to increase
even further.
personnel issues are often neglected.
a high number of M & As fail or do not produce the
intended results.
20 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Impact of the Human Integration and
Task Acquisition (Figure 3.4)
21 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Task and Human Integration
Process
Low Integration
if the M&A is carried out for portfolio reasons both
companies remain separate cultures
High Integration
crucial for the M&A to meet the HR requirements of the
phases
22 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Phases of Cross-Border M & A
pre- M & A phase (a screening of alternative partners
based on an analysis of their strengths and weaknesses)
due diligence phase (analyzing the potential benefits of
the merger, product-market combinations, tax
regulations, and compatibility with respect to HR and
cultural issues)
integration planning phase (planning for the new
company)
implementation phase (action plan)
23 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
HR Activities in the Phases of a
Cross-Border M & A (IHRM Notebook 3.1)
24 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Strategic HRM and the Role
of the HR Function in M&As
Starting points in HRM practices
high HRM involvement early in the M&A process
fit between business, M&A and HR strategies
decisions about resources involve staffing and retention
issues, with termination decisions being particularly
important
training and development programs
appraisal and reward systems
25 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Strategic HRM and the Role
of the HR Function in M&As
values that shape employees priorities and decision
making
strategic approach and aligning the HRM activities with
the M&A strategy with respect to resources, processes and
values
26 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Strategic HRM and the Role
of the HR Function in M&As
create a strong team including a mix of both expatriates
and local members of top management
language skills and sensitivity toward cultural differences
crucial skills for M&A success
27 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Strategic HRM and the Role
of the HR Function in M&As
IHRM roles
strategic partner
administrative expert
employee champion
change agent
A Comparative Approach to
HRM in M&A Processes
Post-integration trends in HRM practices
convergence across nationalities in HRM policies
(performance-related pay, training and team-based product
development)
adjustments to suit the local culture
American HRM reflected a short-term individualistic
national business culture
(c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
A Comparative Approach to
HRM in M&A Processes
Japanese HRM reflected long-term, consensual, team-
based, collectivist national philosophies
French companies displayed an ethnocentric approach
German companies were the most anxious to adopt
international practices
(c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
30 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Post-Acquisition Trends in HRM
Practices (IHRM Notebook 3.3)
Cross Border International
Equity Joint Ventures
Joint Venture
legal entity representing holdings of parent
firms located outside the country of operation
(c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
32 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Formation of an International Equity
Joint Venture (Figure 3.6)
33 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
The Main Reasons for
Engaging in an IJV
to gain knowledge and to transfer that knowledge
host government insistence
increased economies of scale
to gain local knowledge
to obtain vital raw materials
34 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
The Main Reasons for
Engaging in an IJV
to spread the risks (e.g. share financial risks)
to improve competitive advantage in the face of increasing
global competition
provide a cost effective and efficient response forced by
the globalization of markets
35 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
The Main Reasons for
IJV Failure
lack of interest in HRM
cross cultural management aspects
36
(c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
IJV Development Stages and HR
Implications (IHRM Notebook 3.4)
Strategic HRM and the Role
of the HR Function in JIVs
IJVs are embedded in their own national, institutional, and
cultural settings
the IHRM challenge is to balance the various interests and
manage these cross cultural differences.
(c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Strategic HRM and the Role
of the HR Function in JIVs
There exists interface and intra-IJV IHRM challenges.
Interface IHRM Challenges (initial stages of IJV formation
process)
manage the relationships at the interfaces of the parent
companies to integrate dualities of rules and practices
focuses on the compatibility of the respective partners
(c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Strategic HRM and the Role
of the HR Function in JIVs
Intra-IJV IHRM Challenges (initial stages of IJV formation
process)
develop IHRM strategies and practices for the new IJV
entity.
focus on managing the mutual learning
processes between the parent companies and
the new joint venture entity.
(c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
40 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Strategic HRM and the Roles of
the HR Function in IJVs
IHRM roles
partnership
change facilitator and strategy implementer
innovator
collaborator
41 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
The Importance of Cross-Cultural
Management ( M&As and IJVs)
different national, institutional, and
cultural environments; cultural differences matter in
collaboration, decision making and loyalty
top management multicultural team; different cultural
expectations, management styles and strategic objectives
42 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
EU Defining Standards for SMEs
(Table 3.1)
43 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Access Barriers to International
Markets by SMEs (IHRM Notebook 3.5)
shortage of working capital to finance exports
identifying foreign business opportunities
limited information to locate/analyze markets
inability to contact potential overseas customers
obtaining reliable foreign representation
lack of managerial time to deal with internationalization
44 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Access Barriers to International
Markets by SMEs (IHRM Notebook 3.5)
inadequate quantity of and/or untrained personnel for
internationalization
difficulty in managing competitors prices
lack of home government assistance/incentives
excessive transportation/insurance costs
45 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Typical Challenges for IHRM in
Internationalized SMEs
importance of the founder/owner
recruitment, selection, and retention
human resource development; the challenge of learning
expatriate management
limited resources of the HR department and outsourcing
46 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Importance of the
Founder/Owner
Specific skills of the founder have an impact on the
internationalization process of SMEs
international work experience or established
networks and relationships abroad
positive perceptions of the international environment
47 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Recruitment, Selection and
Retention
SMEs
more difficulties than large firms in recruiting adequate
international managers
perceived to lack legitimacy as employers with a strong
international orientation
perceived as having disadvantages; career/international
work opportunities, pay/benefits, progressiveness of
company, training
48 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Recruitment, Selection and
Retention
IHRM activities for SMEs
communicate the company has a strong position in
international markets and offers international career
opportunities
use selection criteria that defines international
competencies
improve and emphasize benefits; training, career paths,
financial
49 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
SME Employer Image and
Internationalization (Figure 3.8)
50 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Human Resource Development:
The Challenge of Learning
SMEs
short term oriented
informal learning
tacit knowledge
51 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Human Resource Development:
The Challenge of Learning
IHRM activities for SMEs
learning processes are critically important
improve capacity to perceive relevant environmental
developments: strategy and communication training
resist the temptation to impose large firm thinking
52 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Learning in Small
Organizations (IHRM Notebook 3.6)
53 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Expatriate and Limited
IHRM Resources
SMEs
informal
IHRM activities for SMEs
cultural integration
outsourcing IHRM
54 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Discussion Questions
1. Describe the formation process of cross-border mergers,
acquisitions and international joint ventures. What are
the major differences?
2. Describe the development phases of an M&A and the
respective HR implications.
3. Outline the development phases of an IJV and the
respective HR implications.
55 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Discussion Questions
4. In which ways do cultural and institutional differences
impact the HR integration in M&As and in IJVs?
5. What are the barriers to internationalization for SMEs?
6. What are some of the typical challenges for HRM in
internationalized SMEs?
56 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Case: HR in the Daimler
Chrysler Merger
1. Why do you think the board member responsible for
human resources was not included in the Chairmans
Integration Council? Can you think of any consequences
for the two companies?
1. How could the HR function of the two merging
companies have addressed organizational and national
cultural differences before they became problems?
57 (c) 2009 by Nelson Education Ltd.
Case: HR in the Daimler
Chrysler Merger
3. If you compare the information given about the Daimler
Chrysler merger with the list of HR activities outlined in
IHRM Notebook 3.1, you can analyze the strengths and
the weaknesses from an HR perspective. What lessons
could be learned from this process?
You might also like
- The Context of Cross-Border Alliances and Smes: Chapter ThreeDocument57 pagesThe Context of Cross-Border Alliances and Smes: Chapter ThreeKulbhushan Nagarkar50% (2)
- IHRM Chapter 7Document22 pagesIHRM Chapter 7Tausiff Hossain0% (1)
- IHRM-Labour & IRDocument20 pagesIHRM-Labour & IRapi-3771917100% (4)
- IHRM Question BankDocument5 pagesIHRM Question Bankruchi agrawalNo ratings yet
- Ihrm NotesDocument3 pagesIhrm NotesNeha KashyapNo ratings yet
- The Enduring Context of IhrmDocument23 pagesThe Enduring Context of Ihrmhurricane2010No ratings yet
- IhrmDocument12 pagesIhrmHarpreet Singh0% (1)
- IHRM Module 2Document62 pagesIHRM Module 2deepeka_rathi24No ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Performance ManagementDocument34 pagesChapter - 6 Performance ManagementPreeti BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 IHRMDocument23 pagesChapter 04 IHRMSujit Sekhar0% (1)
- IHRM in The Host-Country Context: Chapter EightDocument21 pagesIHRM in The Host-Country Context: Chapter EightXahra Mir100% (1)
- Case Study About SHRM Air NationalDocument4 pagesCase Study About SHRM Air NationalHari Krishnan Ampady0% (1)
- IHRM Module 2Document32 pagesIHRM Module 2Pavithra SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Report On IHRMDocument12 pagesReport On IHRMmanishsingh6270100% (1)
- Human Resource Selection and Development Across Cultures: Learning Objectives and Summary of The ChapterDocument31 pagesHuman Resource Selection and Development Across Cultures: Learning Objectives and Summary of The ChapterLinh HoangNo ratings yet
- SIHRMDocument2 pagesSIHRMDolly ParhawkNo ratings yet
- EJMCM - Volume 8 - Issue 1 - Pages 1200-1212Document13 pagesEJMCM - Volume 8 - Issue 1 - Pages 1200-1212Morrison Omokiniovo Jessa Snr100% (1)
- Module 3Document82 pagesModule 3Reet Jain100% (1)
- Chap018 PDFDocument44 pagesChap018 PDFLuân Nguyễn100% (1)
- IHRM Notes 5unitsDocument46 pagesIHRM Notes 5unitsRani BiswasNo ratings yet
- Financing Infrastructure Projects PDFDocument4 pagesFinancing Infrastructure Projects PDFshubham agarwalNo ratings yet
- IHRMDocument30 pagesIHRMtrilokrarotia7656No ratings yet
- Ihrm AssignmentDocument5 pagesIhrm AssignmentShagor AhamedNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues in HRMDocument9 pagesContemporary Issues in HRMVenky NaiduNo ratings yet
- QQ-P2-Strategic HRM 2Document15 pagesQQ-P2-Strategic HRM 2Assign Us100% (1)
- (Economic Themes) Impact of National Culture On International Human Resource ManagementDocument20 pages(Economic Themes) Impact of National Culture On International Human Resource ManagementAshleyKumarNo ratings yet
- International HR StrategyDocument31 pagesInternational HR StrategyHanisha RaviNo ratings yet
- Questions HrisDocument2 pagesQuestions HrisCharmi PoraniyaNo ratings yet
- Recruitment, Selection & InductionDocument28 pagesRecruitment, Selection & Inductionvidisha sharmaNo ratings yet
- International HRMDocument31 pagesInternational HRMSweta BakshiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behaviour-Ass 1Document4 pagesOrganizational Behaviour-Ass 1Sukhi MakkarNo ratings yet
- IHRM - Individual Assignment (CB3090)Document10 pagesIHRM - Individual Assignment (CB3090)Rimaz FiazNo ratings yet
- HRM ModelsDocument6 pagesHRM ModelshannaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Process of SQUARE Group of Ltd. of BangladeshDocument28 pagesSupply Chain Process of SQUARE Group of Ltd. of Bangladeshabid746No ratings yet
- North South University MKT627 (1) - Summer 2020 Quiz-1, Marks-10 Name: Tasnova Lutfor ID: 1825062090 SL No: (SL - 11)Document1 pageNorth South University MKT627 (1) - Summer 2020 Quiz-1, Marks-10 Name: Tasnova Lutfor ID: 1825062090 SL No: (SL - 11)Tasnova Lutfor 1825062090No ratings yet
- IHRM Extended WritingDocument10 pagesIHRM Extended Writing瑞婷No ratings yet
- Chapter 03 IHRMDocument38 pagesChapter 03 IHRMSujit SekharNo ratings yet
- 08-0753 HRM Case Study IM v3Document36 pages08-0753 HRM Case Study IM v3Janry SimanungkalitNo ratings yet
- Steps in MBODocument10 pagesSteps in MBOAnu DmzzNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Nike HRM: Managing People in Sport and EventsDocument19 pagesCase Study: Nike HRM: Managing People in Sport and EventsPrashant TodkarNo ratings yet
- CSR BookDocument13 pagesCSR BookCj LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 International HRMDocument19 pagesChapter 4 International HRMMony MstNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes:: Variables That Moderate The Difference Between HRM and IHRMDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Notes:: Variables That Moderate The Difference Between HRM and IHRMHUỲNH TRẦN THIỆN PHÚCNo ratings yet
- An Analysis On Turning Talent Management Into A Competitive AdvantageDocument2 pagesAn Analysis On Turning Talent Management Into A Competitive AdvantagePruthviraj RathoreNo ratings yet
- Tech MahindraDocument9 pagesTech MahindraUdaya Shankar SNo ratings yet
- CRM Relationship, Theories - 2Document51 pagesCRM Relationship, Theories - 2Divanshu Tiwari75% (4)
- Cross-Cultural Project On Human Resource Management: An OverviewDocument15 pagesCross-Cultural Project On Human Resource Management: An OverviewHamza MechehatNo ratings yet
- Emerald List of JournalsDocument10 pagesEmerald List of JournalsKuldeep Singh BidhuriNo ratings yet
- Expatriate Failure and The Role of Expatriate TrainingDocument11 pagesExpatriate Failure and The Role of Expatriate TrainingDinesh RvNo ratings yet
- HRM Assignment Questions (Human Resources Management)Document21 pagesHRM Assignment Questions (Human Resources Management)kvvalencia2128valNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1 (HRM)Document2 pagesQuiz No 1 (HRM)Aiman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 (Recruiting and Selecting Staff For International Assignments)Document35 pagesCh-5 (Recruiting and Selecting Staff For International Assignments)eisaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Assignment - SemIIDocument11 pagesHuman Resource Management Assignment - SemIIAkhilesh100% (1)
- Ihrm Chapt 5Document28 pagesIhrm Chapt 5Anonymous qFdWnrRZNo ratings yet
- BUS 251 Project Report Plummy Fashions LTDDocument21 pagesBUS 251 Project Report Plummy Fashions LTDAhsanul Karim MontyNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument19 pagesStaffingJessica JohnsonNo ratings yet
- International Strategic Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandInternational Strategic Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Organisations and Leadership during Covid-19: Studies using Systems Leadership TheoryFrom EverandOrganisations and Leadership during Covid-19: Studies using Systems Leadership TheoryNo ratings yet
- Managing Britannia: Culture and Management in Modern BritainFrom EverandManaging Britannia: Culture and Management in Modern BritainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cross-Border Alliances and SME's: 1 (C) 2009 by Nelson Education LTDDocument37 pagesCross-Border Alliances and SME's: 1 (C) 2009 by Nelson Education LTDSuzi StojkovskiNo ratings yet
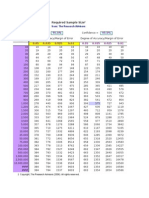
- Required Sample Size: From: The Research AdvisorsDocument3 pagesRequired Sample Size: From: The Research AdvisorsAbhishek Sharma100% (1)
- BJP Membership Online July2010Document1 pageBJP Membership Online July2010Ankit GahlotNo ratings yet
- Personal-Banking Investments Customer-Investment-profile en Cip QuestionnaireDocument7 pagesPersonal-Banking Investments Customer-Investment-profile en Cip QuestionnaireAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Axa Insurance: Champion SaverDocument6 pagesAxa Insurance: Champion SaverAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- ISM SOE11139 Assessment InformationDocument4 pagesISM SOE11139 Assessment InformationAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- AiaDocument2 pagesAiaAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Constructing Qudity-Satisfaction-Loyalty Chain System: An Empirical Study Insurance Industry in ChinaDocument5 pagesConstructing Qudity-Satisfaction-Loyalty Chain System: An Empirical Study Insurance Industry in ChinaAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- MSC IBM FT 1st SemDocument1 pageMSC IBM FT 1st SemAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- IBC Slides 1Document30 pagesIBC Slides 1Abhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- HOFSTEDE - Cultures and Organizations-Software of The MindDocument29 pagesHOFSTEDE - Cultures and Organizations-Software of The MindMita2010No ratings yet
- Primark Final ReportDocument97 pagesPrimark Final ReportShahid Rana75% (4)
- Toyota Completes New Facilities in China, Reaffirms Commitment To Localized R&D and ProductionDocument2 pagesToyota Completes New Facilities in China, Reaffirms Commitment To Localized R&D and ProductionAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Memo - T&C For Student Pass HoldersDocument1 pageMemo - T&C For Student Pass HoldersAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- XIMB Batch Profile HRM 2012-14Document11 pagesXIMB Batch Profile HRM 2012-14Abhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- v550 EnglishDocument3 pagesv550 Englishdangtuan27No ratings yet
- Nestle Pakistan HR ProjectDocument21 pagesNestle Pakistan HR ProjectAbdullah KashifNo ratings yet
- Antifoam U 310Document9 pagesAntifoam U 310syeddanishrasoolNo ratings yet
- Employee EngagementDocument76 pagesEmployee EngagementRaveendra Reddy Vallapu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Submission of Request For Inclusion of All Newly Hired Elementary School Teachers and Division Office Employees To The RpsuDocument2 pagesSubmission of Request For Inclusion of All Newly Hired Elementary School Teachers and Division Office Employees To The RpsuHercules M VillamorNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument7 pagesHuman Resource ManagementtashneetNo ratings yet
- ICWAI Prospectus FinalDocument40 pagesICWAI Prospectus Finalffcm1No ratings yet
- IE Feasibility Study FormatDocument5 pagesIE Feasibility Study FormatiecscstNo ratings yet
- AuthorDocument5 pagesAuthorjbvhchjsvNo ratings yet
- Zulita - ILR DENR OrientationDocument2 pagesZulita - ILR DENR OrientationCENRO GSC100% (2)
- 2022 OPEC Job Offer StatuteDocument8 pages2022 OPEC Job Offer StatuteHiraeth WeltschmerzNo ratings yet
- PA-Employee Attrition Factors Analysis2Document33 pagesPA-Employee Attrition Factors Analysis2Ranjan SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Introduction of BRAC BANKDocument4 pagesIntroduction of BRAC BANKTarannum TahsinNo ratings yet
- HR OpportunityDocument4 pagesHR OpportunityAli AyubNo ratings yet
- Job Evaluation MethodsDocument5 pagesJob Evaluation MethodsSai KumarNo ratings yet
- The Political Theory of Universal Basic IncomeDocument23 pagesThe Political Theory of Universal Basic IncomesuditiNo ratings yet
- Charging For Civil Engineering Services - Group 6Document7 pagesCharging For Civil Engineering Services - Group 6Donna MelgarNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Policy and ProceduresDocument7 pagesRisk Management Policy and ProceduresOhms BrangueloNo ratings yet
- Edp Case StudyDocument9 pagesEdp Case StudyPema ChodenNo ratings yet
- Merin Vs NLRCDocument7 pagesMerin Vs NLRCPrincess Aiza MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Rapid Population ... EconDocument44 pagesImpact of Rapid Population ... EconMELAKU100% (3)
- Interview ReportDocument2 pagesInterview Reportariotriot100% (1)
- 108.3.3.3 Schedule Revisions at Request of Department:: Section 108: Prosecution and Progress Page 76Document3 pages108.3.3.3 Schedule Revisions at Request of Department:: Section 108: Prosecution and Progress Page 76Opata OpataNo ratings yet
- HRM 370 Assignment 01: Independent University, Bangladesh (IUB)Document16 pagesHRM 370 Assignment 01: Independent University, Bangladesh (IUB)Najia MuktaNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Strategic Planning in The Uk Construction IndustryDocument14 pagesEnhancing Strategic Planning in The Uk Construction Industryshamen AmarasekaraNo ratings yet
- Um Tagum Campus Tagum City College of Accounting Education W AiverDocument1 pageUm Tagum Campus Tagum City College of Accounting Education W AiverApple Mae SaleraNo ratings yet
- Advt No 02Document5 pagesAdvt No 02parveen790No ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis On Construction IndustriesDocument21 pagesSWOT Analysis On Construction IndustriesPawan2186% (35)
- OteDocument394 pagesOtebring it onNo ratings yet
- CARSURINDocument8 pagesCARSURINInang Sarge0% (1)