Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AN5141
Uploaded by
david_benavidez_30 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views12 pagesCables are used in many high-frequency board designs and can become a critical element in the signal path. If not modeled as part of that system, cables can lead to unexpected system performance degradation. This APPLICATION NOTE discusses the two main loss effects related to cables: the skin effect and dielectric losses. It then presents a simple method of modeling the cable for use in standard SPICE simulators.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCables are used in many high-frequency board designs and can become a critical element in the signal path. If not modeled as part of that system, cables can lead to unexpected system performance degradation. This APPLICATION NOTE discusses the two main loss effects related to cables: the skin effect and dielectric losses. It then presents a simple method of modeling the cable for use in standard SPICE simulators.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views12 pagesAN5141
Uploaded by
david_benavidez_3Cables are used in many high-frequency board designs and can become a critical element in the signal path. If not modeled as part of that system, cables can lead to unexpected system performance degradation. This APPLICATION NOTE discusses the two main loss effects related to cables: the skin effect and dielectric losses. It then presents a simple method of modeling the cable for use in standard SPICE simulators.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Automatic Test Equipment (ATE)
> APP 5141
Keywords: SPICE, simulation, cable model, skin effect, lumped model, transmission line, dielectric loss
APPLICATION NOTE 5141
An Improved and Simple Cable Simulation Model
By: Bernard Hyland, Senior Member of Technical Staff
Oct 22, 2012
Abstract: Nonideal cable dispersive effects can affect system performance. This application note discusses the two
main loss effects related to cables (skin-effect and dielectric losses), and presents a simple method of modeling the
cable for use in standard SPICE simulators.
A similar version of this article appears on EDN, J uly 30, 2012.
Introduction
Cables are used in many high-frequency board designs and can become a critical element in the signal path. This is
especially true for signals that exceed 500MHz. If not modeled as part of that system, cables can lead to unexpected
system performance degradation and to costly time delays in debugging and corrections. Even with this understood,
cables are notoriously difficult to model correctly. Using a simple transmission line model may not effectively model this
element because it is difficult to model a cable both in the frequency and the time domains.
Cable nonideal dispersive effects can affect system performance. These cable effects are seen on drivers, buffers, and
comparators. In the driver or buffer, the low-frequency dribble up (Figure 1) primarily degrades propagation delay
versus pulse-width dispersion; it also degrades minimum pulse time and rise time. In the comparator, the low-
frequency dribble up primarily degrades delay versus pulse width and propagation delay versus overdrive; it also
degrades the minimum pulse width. This application note will discuss the two main loss effects related to cables: the
skin effect and dielectric losses. We will then present a simple method of modeling the cable for use in standard
SPICE simulators.
Figure 1. Example of cable loss effects (simulated results from Figure 3 below).
Why Model a Cable?
As frequencies start to exceed 500MHz, the cable starts to noticeably impact the bandwidth of the signal path and
begins to degrade this path in many ways. To understand the effects of cables at all frequencies, the cable needs to
be modeled. However, based on that model, more intelligent decisions can be made about the type of cable to be
used. Moreover, the parameters of interest that are being degraded in the signal path can then be understood.
Page 1 of 12
Cable Losses
There are two main loss mechanisms with cables: skin-effect and dielectric losses.
Skin-Effect Losses
At high frequencies, the signal tends to propagate along the surface of the conductor. This is known as skin effect.
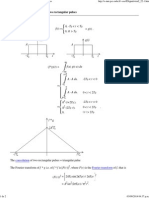
(Note that this application note will not rigorously discuss skin-effect losses.) The skin depth, , is defined as:
(Eq. 1)
Where is the frequency in radian per second; is the conductor's permeability in H (Henries per meter); and is
the conductor's conductivity in S (Siemens per meter).
Equation 1 shows that the skin depth decreases with the square root of the frequency. Alternatively, since the lower
the skin depth the higher the resistance per unit length, then the resistance per unit length, R
L
, increases with the
square root of frequency.
Therefore, R
L
= 1/W, where W is the conductor's cross-sectional width (for a circular wire, W = 2r). Rewriting:
(Eq. 2)
Dielectric Loss
The dielectric constant of insulators has an imaginary component. The dielectric constant, , is defined as = ' + j'' =
'(1 + jtan), where ' is the real component of the dielectric constant; and tand is the loss tangent or dissipation factor
of the dielectric. The dielectric constant affects the capacitance and the C
l
(capacitance per unit length) will change to
C
l
(1 + jtan).
Total Cable Loss
By including the skin-effect and dielectric losses in the model, an ideal cable model (per unit length) can be now
modified to include those losses (Figure 2). Here L
l
, R
l
, and C
l
are the per unit length for inductance, resistance, and
capacitance, respectively.
Figure 2. Ideal cable representation.
The propagation constant is defined as jk = ZY, where Z is the distributed series impedance and Y is the distributed
parallel admittance.
From Figure 2 we see:
(Eq. 3)
Using a Taylor-Expansion approximation:
Page 2 of 12
(Eq. 4)
Further simplifying:
(Eq. 5)
Where Z
o
is the cable's characteristic impedance;
r
is the relative dielectric constant; and c is the speed of light.
We are actually seeking the cable gain, H( ). Therefore, H( ) =e
-jkl
, where l is the length of the line.
Using the findings above:
(Eq. 6)
Where:
(Eq. 7 and 8)
Therefore, skin-effect losses (1) dominate at lower frequencies and dielectric losses (2) dominate at higher
frequencies.
Note that in real-world cables H( ) varies somewhat from the approximations given above. However, this model is
accurate enough for most automated-test-equipment (ATE) work, where the attenuation increases to 6dB at the most.
We will be using Equations 6, 7, and 8 later to model the cable.
SPICE Approximations
Unfortunately, H( ) cannot be modeled well in the time-domain SPICE and electromagnetic (EM) simulators. Typical
EM simulators generate a lumped transmission line approximation. The lumps must be small enough to look like a
transmission line at the frequency of interest, and the lumped elements must vary with frequency. This typically
generates a very big model for longer lines.
S-parameter data from manufacturers can also be used to model the frequency response of the cable. But S-
parameters only model the AC response and not the transient response. S-parameter extraction requires very accurate
equipment, setups, and calibrations, and is not always readily available. You also need to have a different set of S-
parameters for each cable length, which again is difficult to obtain.
Alternatively, H( ) can be approximated by a multiple-pole/zero-fit network. This pole/zero network models both the AC
and transient performance. The pole/zero fits the magnitude very well, but the phase-fit error can be significant.
Because the phase is linear with frequency, it appears as an ideal transmission line and can, thus, be eliminated. A -
3dB pole/zero fit matched an EM simulator within 3 degrees phase error up to the -3dB point.
There are two notable shortcomings to a pole/zero network model:
1. The pole/zero network does not include the ideal phase-dependent part of H( )the part that varies linearly with
frequency. This is usually not needed, since the ideal phase lag looks like an ideal transmission line. If the phase
of H( ) is needed, add an ideal transmission line in series with the pole/zero network.
2. The pole/zero network assumes matched characteristic impedance over all frequencies. L
l
changes with
frequency. For reasonable losses (less than 6dB), the change in L
l
is insignificant. For larger losses, the pole/zero
network would err.
Page 3 of 12
The Model
The model, shown in Figure 3, consists of six cells. Five of these cells are configured with a pole and a zero response.
The sixth cell has just a pole response. Thus, the entire model is made up of six poles and five zeroes. Six poles and
five zeroes were chosen to give a "good" fit. There is no reason why you could not reduce or increase the number of
poles and zeroes. The trade-off will be accuracy. The "dribble up" plot shown in Figure 1 was simulated from Figure 3.
Figure 3 is a model of 30 meters, or 100 ft of RG58U cable. The values of the components for this model will be
developed later and will be shown to match very closely to the measured data. The advantages of the model in Figure
3 are its simplicity, its high-level abstraction that allows for fast simulations, and its accuracy. You can also run both AC
and transient analysis on it. Figure 4 shows the basic representations of the pole/zero and pole configurations used in
the Figure 3 model.
Figure 3. Final model for 100 feet of RG58U cable, modeled with a 6-pole/5-zero approach.
Figure 4. Representation of the pole/zero and pole, cascaded together in Figure 3.
Pole/Zero Derivation (based on Figure 4):
Page 4 of 12
V
OUT
/V
IN
=(1 +R2 C1 S)/(1 +(R1 +R2) C1 S)
Pole =1/(2 (R1 +R2) C1), Zero =1/(2 R2 C1)
Pole Derivation (based on Figure 4)
V
OUT
/V
IN
=1/(1 +R1 C1 S)
Pole =1/(2 R1 C1)
Figure 5 shows the conceptual and graphical representation of how the pole/zero concept is fitted to the real response.
Note that we are modeling a 30m or 100ft. RG58U cable. As will be seen by the GNUPLOT-generated plot, the fit is
very good all the way out to better than -30dB. In general, it is more accurate to model cables out to -6dB.
Figure 5. Graphical representation shows how the 6-pole/5-zero model fits the real response.
Derivation of the Model
Appendix A is a GNUPLOT file that uses the physical constants of the cable. In this example, we use the RG58U
cable and mathematically define the cable response utilizing Equations 6, 7, and 8 above. It then plots this response.
The GNUPLOT file mathematically models the pole/zero and pole responses, as shown in Figure 3, and then calculates
the values of the Rs and Cs. The calculation involves the use of the GNUPLOT "FIT" function. This function will do a
least-square fit to find the poles and the zeroes. It will plot this calculated response, or "fit," and overlay this on the
cable's response, as defined by the physical parameters. Appendix A shows that the real response of the cable,
defined by the cable's physical properties, is accurately matched by the least-square fit, based on a 6 pole/5 zero fit.
Finally the GNUPLOT file calculates the R and C values for Figure 3, which then becomes the model and can be
simulated by any SPICE simulator. Finally, we overlay the real cable response, the least-square approximation, and
then the simulated plot from the model. It will be shown that all three plots agree very closely and, hence, confirm the
model.
Figures 6 and 7 are SPICE simulations from the derived model of the 100ft. RG58U cable.
Page 5 of 12
Figure 6. Frequency response of Figure 3 (our model). SPICE response of the schematic model.
Figure 7. GNUPLOT-generated plot of the physical model and calculated pole/zero model.
Page 6 of 12
Figure 8. AC input impedance plot of Figure 3 (our model); SPICE response of the schematic model.
Procedure to Create the Model
1. Obtain manufacturer's data for the physical characteristics of the cable:
Magnetic permeability (u =1.2e6H/m)
Speed of light (c =300me6 mps)
Conductivity of the signal wire (copper =sigma =58.6e6 spm)
Characteristic impedance of the cable (for RG58U = 50)
Relative dielectric constant for the insulator material (for RG58U, er =2.3 for solid polyethylene)
Loss tangent of the insulator (for RG58U, tand =0.00035)
Signal cable width (for RG58U =4.5e 10
-4
m =0.00045m)
Cable length: this will be the only parameter that will vary and can be passed.
2. Run the GNUPLOT program in Appendix A.
Create the first estimates for wp1 to wp6 and wz1 to wz5 (poles and zeroes). The program in Appendix A
already has these first estimates.
If the error as shown in Appendix B is greater than a few percent, insert the calculated poles and zeros
back into the GNUPLOT program and run and reiterate until the error is below a few %. If you do not do this
and have large errors in the calculated "fit," you will get errors in the calculations of the Rs and Cs for the
final model.
Adjust the Rs and Cs as calculated in the GNUPLOT program in Appendix A and printed in Appendix B into
the Figure 3 schematic.
Run an AC sim for Figure 3. Review that the frequency response matches the GNUPLOT responses, as
shown in Figures 6 and 7. If they agree, you are done.
3. You can then run various lengths of the cable to create new models for these different lengths. The schematic
becomes the model and will show both transient and frequency characteristics of the cable.
Summary
This application note showed a simple approach to modeling a signal cable by obtaining just the physical data for that
cable. This process extends to all cables. A cable signal's characteristics are defined by its physical construction and
the materials used. The more normal approach is to obtain S-parameter sweeps or create distributed RLC elements to
model the cable. These do have their place. S-parameters are limited to AC analysis only and must be redone for
Page 7 of 12
every cable and length of that cable. The major limitation of S-parameters is their lack of transient information. S-
parameters can be hard to retrieve. Either the manufacturer supplies these parameters or you must have expensive
equipment to extract these parameters and perform methodical calibration routines. Distributed models allow for AC and
transient modeling, but they are difficult to obtain. Distributed models to obtain an accurate model can also be quite
large and slow down SPICE simulations tremendously.
The greatest advantage of the model presented here is that none of the above restrictions apply. Rather, you get or
determine:
1. A simple modeling interface
2. Need only obtain the physical information of the cable.
3. The pole/zero fit provides a very accurate model of the loss response.
4. The model parameters for the poles and zeros are easily calculated to create the schematic.
5. The only parameter in this model is the length of the cable.
6. It is easy to compose a library of cables from the physical parameters and pass these calculated Rs and Cs to a
circuit that remains the same.
7. Quick, easy "what if analysis" right at your bench
8. Can easily be ported to MATLABfor greater GUI flexibility.
This model does have its limitations, as discussed. Many versions of cable models can be more accurate, but they also
can be very complex and unwieldy. This approach gives a very simple method for modeling a cable, and the method
has very good accuracy over at least a -6dB loss. While it models well past this loss, you would have to account for
impedance and phase differences if these impact the design.
Reference
These cable effects have been seen often by the ATE group at Maxim Integrated. This application note, in fact,
represents its findings; the cable model was developed and tested extensively by that group.
The author would like to acknowledge Charles Sharman, former employee of Maxim Integrated, for his original concept
of a multipole, multizero filter to model the coaxial cable.
Appendix A. GNUPLOT File
# GNUPLOT Fi l e t hat :
#1) Cal cul at es t he f r equency r esponse af t er cal cul at i ng t he ski n ef f ect and di el ect r i c
ef f ect s,
usi ng onl y t he physi cal par amet er s of t he cabl e.
#2) I t t hen pl ot s t he f r equency r esponse caused by t hese physi cal par amet er s and st or es
t hat
i nf or mat i on i n a f i l e cal l ed dr oop. csv.
#3) We t hen def i ne a pol e/ zer o and pol e r esponse, based on f r equency, t he pol e, and t he
zer o.
#4) We cascade f i ve pol e/ zer oes and one pol e.
#5) We t hen cal cul at e t he si x pol es ( wp1 t o wp6) and t he f i ve zer oes ( wz1 t o wz2) usi ng
t he
GNUPLOT " Fi t " f unct i on.
#6) We t hen cal cul at e a SPI CE- equi val ent schemat i c wi t h Rs and Cs def i ned by t he pol es
and zer oes.
#7) We pl ot t he cal cul at ed physi cal r esponse and over l ay t hat wi t h t he mat hemat i cal l y
cal cul at ed
f i t , based on a 6 pol e/ 5 pol e f i t .
#8) The Rs and Cs ar e passed ont o a SPI CE hi gh- l evel schemat i c, and t hi s model s t he
cabl e. Thi s
Page 8 of 12
schemat i c can t hen r un AC or t r ansi ent si mul at i ons.
#9) Last l y, we r un t he SPI CE model and obt ai n t he r esponse and compar e t hi s t o t he
physi cal
r esponse and t he mat hemat i cal r esponse. Al l t hr ee r esponses must l i e on t op of one
anot her t o
ensur e a good model f i t .
# Fr equenci es of i nt er est
f mi n = 1e+6 # mi ni mumf r equency ( Hz)
f max = 1e9 # maxi mumf r equency ( Hz)
# Physi cal const ant s
u=1. 26e- 6 # magnet i c per meabi l i t y ( H/ m)
c=300e+6 # speed of l i ght ( m/ s)
# Li ne- speci f i c const ant s f or cabl e
si gma=58e+6 # copper conduct i vi t y ( S/ m)
z0=50 # char act er i st i c i mpedance ( Ohms)
er =2. 3 # r el at i ve di el ect r i c const ant RG58U cabl e ( sol i d Pol yet hyl ene)
t and=0. 00035 # l oss t angent / di ssi pat i on f act or ( pol yet hyl ene)
w=2*pi *4. 5*10- 4 # cr oss- sect i onal cabl e wi dt h ( m)
#l i s l i ne l engt h ( m)
l =30
# At t enuat i on const ant s
a1=( l / ( 2*w*z0) ) *sqr t ( pi *u/ si gma) # ski n ef f ect . Same as Equat i on 6.
a2=( l *pi *t and*sqr t ( er ) ) / c # Di el ect r i c Ef f ect . Same as Equat i on 7.
pr i nt " a1=" , a1
pr i nt " a2=" , a2
# Pl ot t he l oss i ncl udi ng ski n and di el ect r i c ef f ect s
pl ot [ f =f mi n: f max] exp( - a1*sqr t ( f ) - a2*f ) # Pl ot t i ng Equat i on 8.
set t er mi nal t abl e
set l ogscal e x
set out put ' dr oop. csv'
set t i t l e " Cabl e Response vi a Physi cal Descr i pt on vs Mat hemat i cal Fi t "
set xl abel " Fr equency" ; set yl abel " Ampl i t ude ( v) "
set xr ange [ 1e6: 1e9]
#Set up f or pl ot t i ng t o t er mi nal
r epl ot
set t er mi nal x11
set out put
f scal e=1e9
# Def i ne pol e zer o and pol e equat i ons
# pol e/ zer o
pz( x, p, z) =( 1+( ( 2*pi *x) / ( 2*pi *z) ) **2) / ( 1+( ( 2*pi *x) / ( 2*pi *p) ) **2)
# pol e
p( x, p) =1/ ( 1+( ( 2*pi *x) / ( 2*pi *p) ) **2) # Eq2
Page 9 of 12
# 6- pol e f i t - cascadi ng 6 pol e/ zer o and one pol e ut i l i zi ng pz( x. p. z) and p( x, p) . Wher e
x i s t he f r equency.
f 6( x) =sqr t ( pz( x, wp1, wz1) *pz( x, wp2, wz2) *pz( x, wp3, wz3) *pz( x, wp4, wz4) *pz( x, wp5, wz5) *p( x, wp6) )
# Def i ne our i ni t i al est i mat es
wp1=7e- 3*f scal e; wz1=8e- 3*f scal e; wp2=6e- 2*f scal e; wz2=7e- 2*f scal e; wp3=2. 5e- 1*f scal e;
wz3=3. 5e- 1*f scal e;
wp4=. 25*f scal e; wz4=0. 1*f scal e; wp5=. 5*f scal e; wz5=1*f scal e; wp6=12*f scal e
# Cal l GNUPLOT' s " f i t " f unct i on t o cal cul at e pol es and zer oes by l east squar e met hod
f i t f 6( x) ' dr oop. csv' usi ng ( 10**$1) : 2 vi a wp1, wz1, wp2, wz2, wp3, wz3, wp4, wz4, wp5,
wz5, wp6
#Over l ay t he Cabl e Char act er i st i cs vs t he Mat hemat i cal Fi t .
pl ot ' dr oop. csv' usi ng ( 10**$1) : 2, f 6( x)
#Cal cul at e Rs and Cs f or pol e/ zer o schemat i c nor mal i zed f or a 50 ohmchar act er i st i c
i mpedance.
#Pol e Zer o1
r 1= 50*( ( wz1/ wp1) - 1) ; c1=1/ ( 2*pi *50*wz1)
#Pol e Zer o2
r 2= 50*( ( wz2/ wp2) - 1) ; c2=1/ ( 2*pi *50*wz2)
#Pol e Zer o3
r 3= 50*( ( wz3/ wp3) - 1) ; c3=1/ ( 2*pi *50*wz3)
#Pol e Zer o4
r 4= 50*( ( wz4/ wp4) - 1) ; c4=1/ ( 2*pi *50*wz4)
#Pol e Zer o1
r 5= 50*( ( wz5/ wp5) - 1) ; c5=1/ ( 2*pi *50*wz5)
#Last Pol e
c6=1/ ( 2*pi *50*wp6)
pr i nt " r 1=" , r 1; pr i nt " c1=" , c1
pr i nt " r 2=" , r 2; pr i nt " c2=" , c2
pr i nt " r 3=" , r 3; pr i nt " c3=" , c3
pr i nt " r 4=" , r 4; pr i nt " c4=" , c4
pr i nt " r 5=" , r 5; pr i nt " c5=" , c5
pr i nt " c6=" , c6
pause - 1 ' Hi t r et ur n t o cont i nue'
Appendix B. Output Log of GNUPLOT File Run in Appendix A
Af t er 480 i t er at i ons t he f i t conver ged.
Fi nal sumof squar es of r esi dual s: 5. 84016e- 06
Rel . change dur i ng l ast i t er at i on: - 4. 6111e- 06
Degr ees of f r eedom( ndf ) : 89
r ms of r esi dual s ( st df i t ) = sqr t ( WSSR/ ndf ) : 0. 000256164
Var i ance of r esi dual s ( r educed chi squar e) = WSSR/ ndf : 6. 56198e- 08
Page 10 of 12
Fi nal set of par amet er s Asympt ot i c St andar d Er r or
======================= ==========================
wp1 = 646510 +/ - 1. 679e+04 ( 2. 596%)
wz1 = 670473 +/ - 1. 775e+04 ( 2. 647%)
wp2 = 5. 03764e+06 +/ - 1. 362e+05 ( 2. 703%)
wz2 = 5. 27773e+06 +/ - 1. 462e+05 ( 2. 77%)
wp3 = 8. 39629e+07 +/ - 1. 863e+06 ( 2. 219%)
wz3 = 9. 95475e+07 +/ - 2. 375e+06 ( 2. 385%)
wp4 = 2. 22295e+07 +/ - 5. 627e+05 ( 2. 531%)
wz4 = 2. 43028e+07 +/ - 6. 414e+05 ( 2. 639%)
wp5 = 2. 8391e+08 +/ - 4. 841e+06 ( 1. 705%)
wz5 = 3. 99073e+08 +/ - 7. 35e+06 ( 1. 842%)
wp6 = 9. 06085e+08 +/ - 6. 952e+06 ( 0. 7673%)
r 1=1. 85319306240795
c1=4. 74754480502755e- 09
r 2=2. 38294740571777
c2=6. 03118500463386e- 10
r 3=9. 28066392395646
c3=3. 19756688710695e- 11
r 4=4. 66322485796558
c4=1. 30976817734003e- 10
r 5=20. 2815653367384
c5=7. 97623211328647e- 12
c6=3. 51302554048115e- 12
Hi t r et ur n t o cont i nue
MATLAB is a registered trademark of The MathWorks Inc.
Related Parts
MAX19000 Dual DCL with Integrated Level Setters Free Samples
MAX19001 Quad Driver with Integrated Level Setters Free Samples
MAX9249 Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link Serializer with LVDS System
Interface
Free Samples
MAX9259 Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link with Spread Spectrum and Full-
Duplex Control Channel
Free Samples
MAX9260 Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link with Spread Spectrum and Full-
Duplex Control Channel
Free Samples
MAX9263 HDCP Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link Serializer/Deserializer Free Samples
MAX9264 HDCP Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link Serializer/Deserializer Free Samples
MAX9265 HDCP Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link Serializer with LVDS System
Interface
Free Samples
MAX9266 HDCP Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link Deserializer with LVDS
System Interface
Free Samples
Page 11 of 12
MAX9268 Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link Deserializer with LVDS System
Interface
MAX9979 Dual 1.1Gbps Pin Electronics with Integrated PMU and Level-
Setting DACs
Free Samples
More Information
For Technical Support: http://www.maximintegrated.com/support
For Samples: http://www.maximintegrated.com/samples
Other Questions and Comments: http://www.maximintegrated.com/contact
Application Note 5141: http://www.maximintegrated.com/an5141
APPLICATION NOTE 5141, AN5141, AN 5141, APP5141, Appnote5141, Appnote 5141
Copyright by Maxim Integrated
Additional Legal Notices: http://www.maximintegrated.com/legal
Page 12 of 12
You might also like
- Convolution of Two Rectangular PulsesDocument2 pagesConvolution of Two Rectangular Pulsesdavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument42 pagesInheritancedavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- MDLX Atc App Note Pi 026Document0 pagesMDLX Atc App Note Pi 026david_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument9 pagesSolutionsdavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- 7292571Document32 pages7292571david_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- Interfet Application Notes: Junction Field Effect TransistorsDocument11 pagesInterfet Application Notes: Junction Field Effect Transistorsrmtsro_pcNo ratings yet
- PCB Pspice Simulation DsDocument4 pagesPCB Pspice Simulation Dsdavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- How To Use The BootrecDocument2 pagesHow To Use The Bootrecdavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- Build A Bootable BCD From Scratch With BcdeditDocument2 pagesBuild A Bootable BCD From Scratch With Bcdeditdavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- How To Use The BootrecDocument2 pagesHow To Use The Bootrecdavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- Histrory and Development of The National Innovation Systems (NIS) Conceptual ApproachDocument36 pagesHistrory and Development of The National Innovation Systems (NIS) Conceptual Approachdavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- Oscillators 1Document25 pagesOscillators 1Vo Phong PhuNo ratings yet
- Tl-wr340g - wr340gd User GuideDocument86 pagesTl-wr340g - wr340gd User Guidedavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- Agilent Spectrum Analysis Basics: Application Note 150Document64 pagesAgilent Spectrum Analysis Basics: Application Note 150suthecNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument28 pagesInternet of Thingstihitat100% (1)
- Eb Vs No ExplainedDocument10 pagesEb Vs No Explaineddavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- CAD Glosario TérminosDocument38 pagesCAD Glosario TérminospafinouNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- BMED Duplex Vertical 3-5HP Oil-Less Rotary Vacuum NFPA Technical Datasheet EN 4107951081Document2 pagesBMED Duplex Vertical 3-5HP Oil-Less Rotary Vacuum NFPA Technical Datasheet EN 4107951081ARN18No ratings yet
- PixelNet Domain Control User ManualDocument251 pagesPixelNet Domain Control User ManualPedro MarquezNo ratings yet
- MS132-2.5 Manual Motor Starter: Product-DetailsDocument7 pagesMS132-2.5 Manual Motor Starter: Product-Detailsysabel112No ratings yet
- Pump XJ - SeriesDocument36 pagesPump XJ - SeriesFERNANDA ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Drive Spares Old PDFDocument3 pagesDrive Spares Old PDFmiguel angel vanegas medinaNo ratings yet
- FXSQ-A EEDEN20 Data Books EnglishDocument37 pagesFXSQ-A EEDEN20 Data Books EnglishommfcNo ratings yet
- RDE10.1 Datasheet enDocument8 pagesRDE10.1 Datasheet enReparatii CncNo ratings yet
- ScapyDocument478 pagesScapyaravindh aravindhNo ratings yet
- SPX Hes SeriesDocument48 pagesSPX Hes SeriesSunni GallegosNo ratings yet
- I Region Width ModulationDocument4 pagesI Region Width ModulationSinisa HristovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2Nazrul KocyNo ratings yet
- Innolux V500HJ1-ME1 Datasheet, Specification, Stocks, Overview - Lcd-SourceDocument2 pagesInnolux V500HJ1-ME1 Datasheet, Specification, Stocks, Overview - Lcd-SourceJackeline MosquedaNo ratings yet
- 54AC/74AC14 Hex Inverter With Schmitt Trigger Input: General DescriptionDocument7 pages54AC/74AC14 Hex Inverter With Schmitt Trigger Input: General DescriptionJose FeghaliNo ratings yet
- Mpms Combi Controller Fault CodesDocument4 pagesMpms Combi Controller Fault CodesFatih YÜKSELNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument4 pagesDownloadAlbertNo ratings yet
- LED ChaserDocument7 pagesLED ChaserMegan Skinner100% (1)
- Option EntryDocument6 pagesOption EntryManoj RajahulliNo ratings yet
- The Most Complete Starter Kit For UNO V1.0.19.09.18Document223 pagesThe Most Complete Starter Kit For UNO V1.0.19.09.18Kuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Altivar Process ATV600 - ATV630C31N4Document13 pagesAltivar Process ATV600 - ATV630C31N4Lester MuscaNo ratings yet
- Features Description: LT3755/LT3755-1/LT3755-2 40V, 75V LED ControllersDocument28 pagesFeatures Description: LT3755/LT3755-1/LT3755-2 40V, 75V LED ControllersMick Thomson RcNo ratings yet
- Raptor Techn RevCA 704010EN WebDocument194 pagesRaptor Techn RevCA 704010EN WebFranciscoNo ratings yet
- IoT Based Water Quality Monitoring System For Smart CitiesDocument6 pagesIoT Based Water Quality Monitoring System For Smart CitiesEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Polymer Memory: Bachelor of Technology IN Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument25 pagesPolymer Memory: Bachelor of Technology IN Electronics and Communication EngineeringSateesh Kuna100% (1)
- XBee - XBee-PRO® S2C Zigbee® RF ModuleDocument309 pagesXBee - XBee-PRO® S2C Zigbee® RF ModulerodviljosNo ratings yet
- Ericsson ReviewDocument40 pagesEricsson ReviewMiguel Ángel CoriaNo ratings yet
- SBAS365710027ENR0Document24 pagesSBAS365710027ENR0Rizqi PerdanaNo ratings yet
- M3310.093 MG15CFX-MG30CFX-MG50CFX-MG101CFX-MG102CFX-MG100HFX PDFDocument27 pagesM3310.093 MG15CFX-MG30CFX-MG50CFX-MG101CFX-MG102CFX-MG100HFX PDFRaphael Barboza100% (1)
- Def Stan 59-411 Part 5Document294 pagesDef Stan 59-411 Part 5Deepto BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- LG 32lf2500 32lf2510 Chassis Ld91aDocument78 pagesLG 32lf2500 32lf2510 Chassis Ld91appashevNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Growatt MIC 3000 TL-XDocument2 pagesDatasheet Growatt MIC 3000 TL-XYongki Adi Pratama PutraNo ratings yet