Professional Documents
Culture Documents
K Cartwright Newandmovedcontent
Uploaded by
S TANCREDOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
K Cartwright Newandmovedcontent
Uploaded by
S TANCREDCopyright:
Available Formats
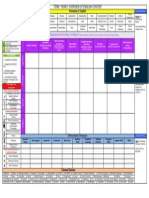
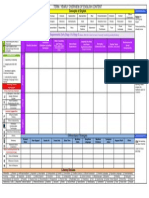
Colour code
new content moved up moved down moved from WM or other strand within the same stage
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
NA Number and Algebra
MAe-4NA
MAe-4NA Whole
Numbers
counts to 30, and orders, reads and
represents numbers in the range 0 to 20 4b
make correspondances between collections, e.g. 'I have four
counters, you have seven counters. So you have more counters
than me' 4d
use the term 'is the same as' to express equality of
groups PAES1.1
MA1-4NA
MA1-4NA Whole
Numbers 1
applies place value, informally, to count,
order, read and represent two- and three-2e
partition two-digit numbers in non-standard forms, eg 32 as 32
ones or 2 tens and 12 ones 2a
count and represent large sets of objects by
systematically grouping in tens WM Stage 1
3b locate and place two-digit numbers on a number line 2b
use and explain mental grouping to count and to assist
with estimating the number of items in large groups WM Stage 1
3f
estimate, to the nearest ten, the number of objects in a
collection and check by counting,
eg estimate the number of children in a room to the nearest
ten 3g solve simple everyday problems with two-digit numbers WM Stage 1
4b
recognise that total amounts can be made using
different denominations, eg 20 cents can be made using
a single coin or two 10-cent coins WM Stage 1
MA1-4NA
MA1-4NA Whole
Numbers 2
applies place value, informally, to count,
order, read and represent two- and three-
digit numbers 2c arrange numbers of up to three digits in ascending order 4c
use and explain mental grouping to count and to assist
with estimating the number of items in large groups WM Stage 1
3a threesany starting point 5b
recognise that there are 100 cents in $1, 200 cents in $2,
WM Stage 1
3c identify number sequences on number charts
4f
partition three-digit numbers in non-standard forms, eg 326
can be 32 groups of ten and
6 ones
5c
identify equivalent values in collections of coins and in
collections of notes, eg four $5 notes
have the same value as one $20 note
MA2-4NA
MA2-4NA Whole
Numbers 1
applies place value to order, read and
represent numbers of up to five digits 2b
use place value to partition numbers of up to four digits, eg
3265 as 3 groups of one
thousand, 2 groups of one hundred, 6 groups of ten and 5 ones
2e
partition numbers of up to four digits in non-standard forms, eg
3265 as 32 hundreds and
65 ones
NOTE: The content descriptors are numbered in order within each part of each sub strand and the content dot points are represented alphabetically, any WM component is represented with an underscore and roman numeral
NOTE: working mathematically components under new dot points are also new content
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
MA2-4NA
MA2-4NA Whole
Numbers 2
applies place value to order, read and
represent numbers of up to five digits 1a up to five digits
1b up to five digits
1c up to five digits
1d up to five digits
1e
partition numbers of up to five digits in non-standard forms, eg
67 000 as 50 000 + 17 000
1f or ten thousand
MA3-4NA
MA3-4NA Whole
Numbers 1
orders, reads and represents integers of
any size and describes properties of
whole numbers 1e
partition numbers of any size in non-standard forms to aid
mental calculation, eg when adding 163 480 and 150 000, 163
480 could be partitioned as 150 000 + 13 480, so that 150 000
could then be doubled and added to 13 480 1f
use numbers of any size in real-life situations, including
in money problems WM Stage 3
2e
determine whether a particular number is a factor of a given
number using digital technologies 2b
determine the 'highest common factor' (HCF) of two
whole numbers, eg the HCF of 16 and 24 is 8 NS4.3
2f
solve problems using knowledge of factors and multiples, eg
'There are 48 people at a party. In how many ways can you set
up the tables and chairs, so that each table seats the same
number of people and there are no empty chairs?' 2d
determine the 'lowest common multiple' (LCM) of two
whole numbers, eg the LCM of 21 and 63 is 63 NS4.3
MA3-4NA
MA3-4NA Whole
Numbers 2
orders, reads and represents integers of
any size and describes properties of
whole numbers 1b
use the term 'integers' to describe positive and negative whole
numbers and zero 1d
investigate negative whole numbers and the number
patterns created when counting backwards on a
calculator WM Stage 3
1c interpret integers in everyday contexts, eg temperature 2a
determine whether a number is prime, composite or
neither NS3.3
2b and triangular numbers and record each number... 2b model squarein numerical and diagrammatic form NS2.3 unit 1
MAe-5NA
MAe-5NA Addition and
Subtraction
combines, separates and compares
collections of objects, describes using
everyday language, and records using
informal methods
MA1-5NA
MA1-5NA Addition and
Subtraction 1
uses a range of strategies and informal
recording methods for addition and
subtraction involving one- and two-digit
numbers 1g
create, record and recognise combinations of two numbers
that add to numbers up to and
including 9 1f
recognise, recall and record combinations of two
numbers that add to 10 WM Stage 1
1g_i
model and record patterns for individual numbers by
making all possible whole-number combinations PAS1.1
1h
create, record and recognise combinations of two
numbers that add to numbers from 11 up to and
including 20 WM Stage 1
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
1i
investigate and generalise the effect of adding zero to a
number, eg 'Adding zero to a number does not change
the number' PAS1.1
1j
use concrete materials to model the commutative
property for addition and apply it to aid the recall of
addition facts, eg 4 + 5 = 5 + 4 PAS1.1
1m
use the equals sign to record equivalent number
sentences involving addition, and to mean 'is the same
as', rather than as an indication to perform an
operation, eg 5 + 2 = 3 + 4 PAS1.1
MA1-5NA
MA1-5NA Addition and
Subtraction 2
uses a range of strategies and informal
recording methods for addition and
subtraction involving one- and two-digit
numbers 1a
use concrete materials to model how addition and
subtraction are inverse operations WM Stage 1
2b
select and use a variety of strategies to solve addition
and subtraction problems involving one- and two-digit
numbers WM Stage 1
MA2-5NA
MA2-5NA Addition and
Subtraction 1
uses mental and written strategies for
addition and subtraction involving two-,
three-, four- and five-digit numbers 1a add three or more single-digit numbers 1b
model and apply the associative property of addition to
aid mental computation,
eg 2 + 3 + 8 = 2 + 8 + 3 = 10 + 3 = 13 PAS2.1
2a demonstrate 2a how addition and subtraction are inverse operations WM Stage 1
3a
calculate equivalent amounts of money using different
denominations, eg 70 cents can be
made up of three 20-cent coins and a 10-cent coin, or two 20-
cent coins and three 10-cent
coins, etc 2b
explain and check solutions to problems, including by
using the inverse operation WM Stage 1
3b
perform simple calculations with money, including
finding change, and round to the nearest five cents NS1.2
3c calculate mentally to give change WM Stage 1
MA2-5NA
MA2-5NA Addition and
Subtraction 2
uses mental and written strategies for
addition and subtraction involving two-,
three-, four- and five-digit numbers 1c
solve problems involving purchases and the calculation of
change to the nearest five cents,
with and without the use of digital technologies 1e calculate change and round to the nearest five cents WM Stage 1
1d
solve addition and subtraction problems involving money, with
and without the use of digital
technologies 1f
use estimation to check the reasonableness of solutions
to addition and subtraction
problems, including those involving money WM Stage 2
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
MA3-5NA
MA3-5NA Addition and
Subtraction 1
selects and applies appropriate
strategies for addition and subtraction
with counting numbers of any size 1a
use the term 'sum' to describe the result of adding two or more
numbers, eg 'The sum of 7 and 5 is 12' 1e
check solutions to problems, including by using the
inverse operation WM Stage3
1d
record the strategy used to solve addition and subtraction
word problems
2a
round numbers appropriately when obtaining estimates to
numerical calculations
3a
use knowledge of addition and subtraction facts to create a
financial plan, such as a budget, eg organise a class celebration
on a budget of $60 for all expenses
MA3-5NA
MA3-5NA Addition and
Subtraction 2
selects and applies appropriate
strategies for addition and subtraction
with counting numbers of any size 1a
word problemsincluding problems that require more than
one operation
1b record the strategy used to solveword problems
MAe-6NA
MAe-6NA
Multiplication and
Division
groups, shares and counts collections of
objects, describes using everyday
language, and records using informal
methods
MA1-6NA
MA1-6NA
Multiplication and
Division 1
uses a range of mental strategies and
concrete materials for multiplication and
division 3a
recognise when there are equal numbers of items in groups, eg
'There are three pencils in each group'
3c
model division by sharing a collection of objects into groups of
a given size to determine the number of groups, eg determine
the number of groups when 20 objects are shared into groups
of four
MA1-6NA
MA1-6NA
Multiplication and
Division 2
uses a range of mental strategies and
concrete materials for multiplication and
division 1b
recognise when items have been arranged into groups, eg 'I can
see two groups of three pencils'
2b
model division by sharing a collection of objects into groups of
a given size, and by arranging it into rows or columns of a given
size in an array, eg determine the number of columns in an
array when 20 objects are arranged into rows of four
2d
solve multiplication and division problems using objects,
diagrams, imagery and actions
MA2-6NA
MA2-6NA
Multiplication and
Division 1
uses mental and informal written
strategies for multiplication and division 1c and use the symbol 1c
recognise ... the symbols for multiplied by (), divided by
() and equals (=) NS1.3
MA2-6NA
MA2-6NA
Multiplication and
Division 2
uses mental and informal written
strategies for multiplication and division 2a multiply three or more single-digit numbers, eg 5 3 6 1d
recall multiplication facts up to 10 10, including zero
facts, with automaticity WM Stage 2
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
2c using area model 1h
use the equals sign to record equivalent number
relationships involving multiplication, and to mean 'is
the same as', rather than to mean to perform an
operation, eg 4 3 = 6 2 PAS2.1
2f use a variety of
MA3-6NA
MA3-6NA
Multiplication and
Division 1
selects and applies appropriate
strategies for multiplication and division,
and applies the order of operations to
calculations involving more than one
operation 1a using an area model 3b
use estimation to check the reasonableness of answers
to multiplication and division calculations, eg '32 253
will be about, but more than, 30 250' WM Stage 3
1b using an area modelfactorising the numbers
1c use digital technologies to multiply numbers of up to four digits
1d word problems
1e record the strategy used to solveword problems
2a
use the term 'quotient' to describe the result of a division
calculation, eg 'The quotient when 30 is divided by 6 is 5'
2f
show the connection between division and multiplication,
including where there is a
remainder, eg 25 4 = 6 remainder 1, so 25 = 4 6 + 1
2g
use digital technologies to divide whole numbers by one- and
two-digit divisors
2h word problems
2j record the strategy used
3a
round numbers appropriately when obtaining estimates to
numerical calculations
MA3-6NA
MA3-6NA
Multiplication and
Division 2
selects and applies appropriate
strategies for multiplication and division,
and applies the order of operations to
calculations involving more than one
operation 1d word problems 1c ...numbers by1000 NS3.4
2a
use the term 'operations' to describe collectively the processes
of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division 1e
recognise symbols used to record speed in kilometres
per hour, eg 80 km/h MS3.1
2b
investigate and establish the order of operations using real-life
contexts 1f
solve simple problems involving speed, eg 'How long
would it take to travel 600 km if the average speed for
the trip is 75 km/h?' WM MS3.1
2c
recognise that the grouping symbols and are used in number
sentences to indicate operations that must be performed first
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
2d
recognise that if more than one pair of grouping symbols are
used, the operation within the
innermost grouping symbols is performed first
2e
perform calculations involving grouping symbols without the
use of digital technologies
2f
apply the order of operations to perform calculations involving
mixed operations and
grouping symbols, without the use of digital technologies
2g
recognise when grouping symbols are not necessary, eg 32 + (2
4) has the same answer
as 32 + 2 4
MAe-7NA
MAe-7NA Fractions and
Decimals describes two equal parts as halves
MA1-7NA
MA1-7NA Fractions and
Decimals 1
represents and models halves, quarters
and eighths
MA1-7NA
MA1-7NA Fractions and
Decimals 2
represents and models halves, quarters
and eighths 1a an eighth of a whole object 1h
use fraction language in a variety of everyday contexts,
eg the half-hour, one-quarter of the class WM Stage 1
1c or eighths
1d and eighth
1e or an eighth of
1f or eighths
1g and eighth
MA2-7NA
MA2-7NA Fractions and
Decimals 1
represents, models and compares
commonly used fractions and decimals 1a denominators35
2a
identify and describe 'mixed numerals' as having a whole-
number part and a fractional part
2c thirds
2d thirds on number lines
2e thirds
MA2-7NA
MA2-7NA Fractions and
Decimals 2
represents, models and compares
commonly used fractions and decimals 1a with denominators of3 and 6
2c
use place value to partition decimals of up to two decimal
places,
2d
partition decimals of up to two decimal places in non-standard
forms
MA3-7NA
MA3-7NA Fractions,
Decimals and
Percentages 1
compares, orders and calculates with
fractions, decimals and percentages 1b and orderwith denominators of3, 4, 5, 610, 12, and 100 1b compareunit fractionsof 28 NS2.4
2a
identify and describe 'proper fractions' as fractions in which the
numerator is less than the denominator
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
2b
identify and describe 'improper fractions' as fractions in which
the numerator is greater than
the denominator
2e model and represent
2g
model and represent strategies, including using diagrams, to
add mixed numerals with the
same denominator
2i word problems
4b
interpret zero digit(s) at the end of a decimal, eg 0.170 has the
same value as 0.17
4c up to three decimal places
MA3-7NA
MA3-7NA Fractions,
Decimals and
Percentages 2
compares, orders and calculates with
fractions, decimals and percentages 1f simplest form 4a
add and subtract decimals with the same number of
decimal places, with and without the use of digital
technologies NS2.4
2b solve word problems 4c
round a number of up to three decimal places to the
nearest whole number NS4.3
3c solve word problems 5b
multiply decimals of up to three decimal places by whole
numbers of up to two digits, with and without the use of
digital technologies NS4.3
4d use estimation and rounding to check 5c
divide decimals by a one-digit whole number where the
result is a terminating decimal, eg 5.25 5 = 1.05 NS4.3
4e solve word problems 7a recognise that the symbol % means 'percent NS2.4
5c terminating decimals 7b
represent common percentages as fractions and
decimals NS2.4
5d solve word problems 7c
represent simple fractions as decimals and as
percentages NS4.2
8a equate 10% to 1/10 , 25% to 25/100 and 50% to 50/100 NS2.4
8c
use mental strategies to estimate discounts of 10%, 25%
and 50% WM Stage 3
8d
calculate the sale price of an item after a discount of
10%, 25% and 50%, with and without the use of digital
technologies, recording the strategy and result WM Stage 3
MAe-8NA
MAe-8NA Patterns and
Algebra
recognises, describes and continues
repeating patterns 1a sort and classify a group of familiar objects into smaller groups
1b
recognise that a group of objects can be sorted and classified in
different ways
MA1-8NA
MA1-8NA Patterns and
Algebra 1
creates, represents and continues a
variety of patterns with numbers and
objects 1c
recognise, copy and continue given number patterns
that increase or decrease, eg
1, 2, 3, 4,
20, 18, 16, 14, PAES1.1
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
1e
recognise, copy and continue patterns with objects or
symbols WM in PAS2.1
1f
create, record and describe patterns with objects or
symbols WM in PAS2.1
g
describe a repeating pattern of objects or symbols in
terms of a 'number' pattern PAES1.1
MA1-8NA
MA1-8NA Patterns and
Algebra 2
creates, represents and continues a
variety of patterns with numbers and
objects 2b
solve problems involving addition or subtraction by using
number sentences 1a
describe a number pattern in words, eg 'It goes up by
threes PAS2.1
2a
complete number sentences involving one operation of
addition or subtraction by calculating the missing
number, PAS2.1
MA2-8NA
MA2-8NA Patterns and
Algebra 1
generalises properties of odd and even
numbers, generates number patterns,
and completes simple number sentences
by calculating missing values 1a from any starting point 1c
create and continue a variety of number patterns that
increase or decrease, WM Stage 2
1b modelrecord 2a model even and odd numbers with two rows PAS1.1
1c in more than one way
2a of up to two digits using arrays
2b
describe and generalise the conditions for a number to be even
or odd
2c identify even or odd numbers of up to four digits
MA2-8NA
MA2-8NA Patterns and
Algebra 2
generalises properties of odd and even
numbers, generates number patterns,
and completes simple number sentences
by calculating missing values 1b on both sides of the equals sign 1b
find the missing number in a number sentence involving
operations of addition or subtraction PAS3.1
2a
investigate and generalise.and multiplying pairs.odd x odd =
odd 2a
the result of adding, subtractingeven numbers, pairs
of odd numbers, one even amd one odd number WM Stage 2
3a
generate number patterns using multiples of 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 and 9,
eg 3, 6, 9, 12, 5b
represent and solve multiplication and division word
problems using number sentences, eg 'I buy six pens and
the total cost is $24. What is the cost of each pen?' WM Stage 2
4a
use the word 'term' when referring to numbers in a number
pattern
MA3-8NA
MA3-8NA Patterns and
Algebra 1
analyses and creates geometric and
number patterns, constructs and
completes number sentences, and
locates points on the Cartesian plane 1a identify, continue and create 1c
create, with materials or digital technologies, a variety
of patterns using whole numbers, fractions or decimals PAS2.1
1d
use a number line or other diagram to create patterns
involving fractions or decimals WM Stage 3
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
MA3-8NA
MA3-8NA Patterns and
Algebra 2
analyses and creates geometric and
number patterns, constructs and
completes number sentences, and
locates points on the Cartesian plane 1a continue and create 1e
make generalisations about numbers and number
relationships, eg 'If you add a number and then subtract
the same number, the result is the number you started
with WM Stage 3
2a
recognise that the number plane (Cartesian plane) is a visual
way of describing location on a grid 2b
recognise that the number plane consists of a horizontal
axis (x-axis) and a vertical axis (y-axis), creating four
quadrants PAS4.5
2c
identify the point of intersection of the two axes as the
origin, having coordinates (0, 0) PAS4.5
2d
plot and label points, given coordinates, in all four
quadrants of the number plane PAS4.5
2e
identify and record the coordinates of given points in all
four quadrants of the number plane PAS4.5
SG Space and Geometry
MAe-9MG MAe-9MG Length
describes and compares lengths and
distances using everyday language 1g
compare lengths indirectly by copying a length, e.g. using the
same strip of paper to compare lengths
MA1-9MG MA1-9MG Length 1
measures, records, compares and
estimates lengths and distances using
uniform informal units, metres and
centimetres
MA1-9MG MA1-9MG Length 2
measures, records, compares and
estimates lengths and distances using
uniform informal units, metres and
centimetres 1a
relate the term 'length' to the longest dimension when
referring to an object
MA2-9MG MA2-9MG Length 1
measures, records, compares and
estimates lengths, distances and
perimeters in metres, centimetres and
millimetres, and measures, compares
and records temperatures 1c and order
1i and checking by measuring
MA2-9MG MA2-9MG Length 2
measures, records, compares and
estimates lengths, distances and
perimeters in metres, centimetres and
millimetres, and measures, compares
and records temperatures 2a
identify temperature as a measure of how hot or cold
something is 1b
select and use an appropriate unit to estimate, measure
and compare lengths and
distances MS3.1
2b
use everyday language to describe temperature, eg 'cold',
'warm', 'hot' 1c
recognise the features of a three-dimensional object
associated with length that can be
measured, eg length, height, width, perimeter SGS2.2a
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
2c recognise the need for formal units to measure temperature
2d
use a thermometer to measure and compare temperatures to
the nearest degree Celsius
2e
record temperatures to the nearest degree Celsius using the
symbol for degrees ()
MA3-9MG MA3-9MG Length 1
selects and uses the appropriate unit and
device to measure lengths and distances,
calculates perimeters, and converts
between units of length 1f
estimate lengths and distances using an appropriate unit and
check by measuring
2a
use the term 'dimensions' to describe the 'lengths' and 'widths'
of rectangles
2d record
MA3-9MG MA3-9MG Length 2
selects and uses the appropriate unit and
device to measure lengths and distances,
calculates perimeters, and converts
between units of length 1b
interpret decimal notation for lengths and distances, eg 13.5
cm is 13 centimetres and 5 millimetres 1a
recognise the equivalence of whole-number and decimal
representations of measurements of length, eg 165 cm
is the same as 1.65 m NS2.4
3a
investigate and compare perimeters of rectangles with
the same area WM in MS4.1
MAe-10MG MAe-10MG Area
describes and compares areas using
everyday language
MA1-10MG MA1-10MG Area 1
measures, records, compares and
estimates areas using uniform informal
units
MA1-10MG MA1-10MG Area 2
measures, records, compares and
estimates areas using uniform informal
units 1c
record comparisons of area informally using drawings,
numerals and words, and by referring to the uniform informal
unit used
MA2-10MG MA2-10MG Area 1
measures, records, compares and
estimates areas using square
centimetres and square metres 1c rectangles (including squares)
1e rectangles (including squares)
1i rectangles (including squares)
MA2-10MG MA2-10MG Area 2
measures, records, compares and
estimates areas using square
centimetres and square metres 1a ...of common two-dimensional shapes
1b measure the areas of irregular shapes
2a ..the larger of two or more
2b larger of two or more
MA3-10MG MA3-10MG Area 1
selects and uses the appropriate unit to
calculate areas, including areas of
squares, rectangles and triangles 2b
record, using words, the method for finding the area of any
rectangle, eg 'Area of rectangle
= length width 2e
apply measurement skills to solve problems involving
the areas of rectangles (including
squares) in everyday situations, eg determine the area
of a basketball court WM Stage 3
2d record
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
MA3-10MG MA3-10MG Area 2
selects and uses the appropriate unit to
calculate areas, including areas of
squares, rectangles and triangles 1a
investigate the area of a triangle by comparing the area of a
given triangle to the area of the rectangle of the same length
and perpendicular height, eg use a copy of the given triangle
with the given triangle to form a rectangle 1d
investigate and compare the areas of rectangles that
have the same perimeter, eg compare the areas of all
possible rectangles with whole-number dimensions and
a perimeter of 20 centimetres MS4.1
1c
record, using words, the method for finding the area of any
triangle
MAe-11MG
MAe-11MG Volume
and Capacity
describes and compares the capacities of
containers and the volumes of objects or
substances using everyday language 1f
establish that containers of different shapes may have
the same capacity, eg a tall narrow container may hold
the same amount as a short wide container WM Stage 1
MA1-11MG
MA1-11MG Volume
and Capacity 1
measures, records, compares and
estimates volumes and capacities using
uniform informal units
MA1-11MG
MA1-11MG Volume
and Capacity 2
measures, records, compares and
estimates volumes and capacities using
uniform informal units 1e
record volume and capacity comparisons informally using
drawings, numerals and words,
and by referring to the uniform informal unit used
MA2-11MG
MA2-11MG Volume
and Capacity 1
measures, records, compares and
estimates volumes and capacities using
litres, millilitres and cubic centimetres 1c record 2f
distinguish between mass and volume, eg 'This stone is
heavier than the ball but it takes up
less space WM Stage 2
1d and order
1e and check by measuring
2d record
2e
objects made from cubic-centimetre blocks by counting
blocks
MA2-11MG
MA2-11MG Volume
and Capacity 2
measures, records, compares and
estimates volumes and capacities using
litres, millilitres and cubic centimetres 1e record 1k
estimate the volume of a substance in a partially filled
container from the information on the
label detailing the contents of the container WM Stage 2
1g and order
1h and checking by measuring
MA3-11MG
MA3-11MG Volume
and Capacity 1
selects and uses the appropriate unit to
estimate, measure and calculate volumes
and capacities, and converts between
units of capacity 1d construct...
MA3-11MG
MA3-11MG Volume
and Capacity 2
selects and uses the appropriate unit to
estimate, measure and calculate volumes
and capacities, and converts between
units of capacity 2b interpret 2a
recognise the equivalence of whole-number and decimal
representations of measurements of capacities, eg 375
mL is the same as 0.375 L NS2.4
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
4a
describe the 'length', 'width' and 'height' of a rectangular prism
as the 'dimensions' of the
prism
4c
use repeated addition to find the volumes of rectangular
prisms, eg 'My rectangle has3 layers of 6 cubes, so the total
number of cubes is 6 plus 6 plus 6, or 18'
4d
establish the relationship between the number of cubes in one
layer, the number of layers,
and the volume of a rectangular prism
4e
record, using words, the method for finding the volumes of
rectangular prisms, eg 'Volume of rectangular prism = number
of cubes in one layer number of layers'
MAe-12MG MAe-12MG Mass
describes and compares the masses of
objects using everyday language
MA1-12MG MA1-12MG Mass 1
measures, records, compares and
estimates the masses of objects using
uniform informal units 1a identify materials that are light or heavy 1c use a pan balance to compare the masses of two objects MES1.4
1b pan balance 1d sort objects on the basis of their mass MES1.4
1f
use drawings to record findings from using a pan
balance MES1.4
MA1-12MG MA1-12MG Mass 2
measures, records, compares and
estimates the masses of objects using
uniform informal units 1f
record comparisons of mass informally using drawings,
numerals and words, and by referring to the uniform informal
units used 1b
recognise that mass is conserved, eg the mass of a lump
of plasticine remains constant regardless of the shape it
is moulded into or whether it is divided up into smaller
pieces WM Stage 1
1d
record masses by referring to the number and type of
uniform informal unit used
Split from
existing dot
point
MA2-12MG MA2-12MG Mass 1
measures, records, compares and
estimates the masses of objects using
kilograms and grams 1c record
1e
compare and order two or more objects by mass measured to
the nearest kilogram
MA2-12MG MA2-12MG Mass 2
measures, records, compares and
estimates the masses of objects using
kilograms and grams 1c a scaled instrument
1d record
1e ..or more objects
1g record
MA3-12MG MA3-12MG Mass 1
selects and uses the appropriate unit and
device to measure the masses of objects,
and converts between units of mass 1d
distinguish between the gross mass and the net mass of
containers holding substances,
eg cans of soup
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
1f
find the approximate mass of a small object by establishing the
mass of a number of that
object, eg 'The stated weight of a box of chocolates is 250 g. If
there are 20 identical
chocolates in the box, what does each chocolate weigh?'
MA3-12MG MA3-12MG Mass 2
selects and uses the appropriate unit and
device to measure the masses of objects,
and converts between units of mass 1b interpret 1a
recognise the equivalence of whole-number and decimal
representations of measurements of mass, eg 3 kg 250 g
is the same as 3.25 kg WM in NS2.4
2b
solve problems involving different units of mass, eg find
the total mass of three items weighing 50 g, 750 g and
2.5 kg WM Stage 3
MAe-13MG MAe-13MG Time
sequences events, uses everyday
language to describe the durations of
events, and reads hour time on clocks
MA1-13MG MA1-13MG Time 1
describes, compares and orders
durations of events, and reads half- and
quarter-hour time 3b
describe the position of the hands on a clock for the half-
hour WM Stage 1
MA1-13MG MA1-13MG Time 2
describes, compares and orders
durations of events, and reads half- and
quarter-hour time 1a
use a calendar to calculate the number of months, weeks or
days until an upcoming event 2c
identify which hour has just passed when the hour hand
is not pointing to a numeral MS2.5
2a to the quarter hour 2a using the term 'past' and 'to' MS2.5
2b
describe the position of the hands on a clock for quarter past
and quarter to
2d
record quarter-past and quarter-to time on analog and digital
clocks
MA2-13MG MA2-13MG Time 1
reads and records time in one-minute
intervals and converts between hours,
minutes and seconds 1c
record in words various times shown on analog and
digital clocks WM Stage 2
MA2-13MG MA2-13MG Time 2
reads and records time in one-minute
intervals and converts between hours,
minutes and seconds 2c
solve simple time problems using appropriate strategies, eg
calculate the time spent on
particular activities during the school day
MA3-13MG MA3-13MG Time 1
uses 24-hour time and am and pm
notation in real-life situations, and
constructs timelines 2a
select an appropriate unit to measure a particular
period of time WM Stage 3
2c
order a series of events according to the time taken to
complete each one WM Stage 3
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
MA3-13MG MA3-13MG Time 2
uses 24-hour time and am and pm
notation in real-life situations, and
constructs timelines 1b
use bus, train, ferry and airline timetables, including
those accessed on the internet, to prepare simple travel
itineraries WM Stage 3
MAe-14MG
MAe-14MG Three-
Dimensional Space
manipulates, sorts and represents three-
dimensional objects and describes them
using everyday language
MA1-14MG
MA1-14MG Three-
Dimensional Space 1
sorts, describes, represents and
recognises familiar three-dimensional
objects, including cones, cubes,
cylinders, spheres and prisms 1c
use the terms 'surface', 'flat surface' and 'curved surface' in
describing familiar threedimensional objects 1f
select and name a familiar three-dimensional object
from a description of its features, eg find an object with
six square faces WM Stage 1
1g vantage points
MA1-14MG
MA1-14MG Three-
Dimensional Space 2
sorts, describes, represents and
recognises familiar three-dimensional
objects, including cones, cubes,
cylinders, spheres and prisms 1a 'flat surface', 'curved surface' 'vertex'
1b
distinguish between objects, which are 'three-dimensional'
(3D), and shapes, which are 'two-dimensional' (2D), and
describe the differences informally, eg 'This is a
twodimensional
shape because it is flat'
MA2-14MG
MA2-14MG Three-
Dimensional Space 1
makes, compares, sketches and names
three-dimensional objects, including
prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones and
spheres, and describes their features 1b
describe and compare curved surfaces and flat surfaces of
cylinders, cones and spheres,
and faces, edges and vertices of prisms (including cubes) and
pyramids
1c use a variety of materials
MA2-14MG
MA2-14MG Three-
Dimensional Space 2
makes, compares, sketches and names
three-dimensional objects, including
prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones and
spheres, and describes their features 1e
interpret given isometric drawings to make models of three-
dimensional objects using connecting cubes 1d
draw different views of an object constructed from
connecting cubes on isometric grid paper SGS4.1
MA3-14MG
MA3-14MG Three-
Dimensional Space 1
identifies three-dimensional objects,
including prisms and pyramids, on the
basis of their properties, and visualises,
sketches and constructs them given
drawings of different views 1b identify the 'base' of prisms and pyramids 1a
identify and determine the number of pairs of parallel
faces of three-dimensional objects, eg 'A rectangular
prism has three pairs of parallel faces' SGS4.1
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
1h
use the term 'apex' to describe the highest point above the
base of a pyramid or cone 1d
visualise and draw the resulting cut face (plane section)
when a three-dimensional object receives a straight cut SGS2.1
2b
examine a diagram to determine whether it is or is not the net
of a closed three-dimensional
object 1e
recognise that prisms have a 'uniform cross-section'
when the section is parallel to the base SGS2.1
2d
visualise and name prisms and pyramids, given diagrams of
their nets 1f
recognise that pyramids do not have a uniform cross-
section when the section is parallel to the base SGS2.1
MA3-14MG
MA3-14MG Three-
Dimensional Space 2
identifies three-dimensional objects,
including prisms and pyramids, on the
basis of their properties, and visualises,
sketches and constructs them given
drawings of different views 1a
create prisms and pyramids using a variety of materials, eg
plasticine, paper or cardboard
nets, connecting cubes
1b
create skeletal models of prisms and pyramids, eg using
toothpicks and modelling clay or
straws and tape
1c and sketch the front, side and top views
MAe-15MG
MAe-15MG Two-
Dimensional Space
manipulates, sorts and describes
representations of two-dimensional
shapes, including circles, triangles,
squares and rectangles, using everyday
language 1h draw closed two-dimensional shapes without tracing
MA1-15MG
MA1-15MG Two-
Dimensional Space 1
manipulates, sorts, represents, describes
and explores two-dimensional shapes,
including quadrilaterals, pentagons,
hexagons and octagons 1c quadrilaterals 1g
identify and name shapes embedded in pictures, designs
and the environment,
eg in Aboriginal art WM Stage 1
1c_i vertex
1e quadrilateral
1e_i e.g. a shape turned on its vertex is still a square
1f recognise that rectangles and squares are quadrilaterals
MA1-15MG
MA1-15MG Two-
Dimensional Space 2
manipulates, sorts, represents, describes
and explores two-dimensional shapes,
including quadrilaterals, pentagons,
hexagons and octagons 1a use the term 'two-dimensional' to describe plane (flat) shapes 2a ...describe the movement of the shape WM Stage 1
1c draw
2a
identify a one-step slide or flip of a single shape and use the
terms 'slide' and 'flip'
2b perform a one-step slide or flip with a single shape
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
2c
record the result of performing one-step slides and flips, with
and without the use of digital
technologies
3a
identify full-, half- and quarter-turns of a single shape and use
the terms 'turn', 'full-turn',
'half-turn' and 'quarter-turn'
3b
identify and describe amounts of turn using the terms
'clockwise' and 'anti-clockwise
3c perform full-, half- and quarter-turns with a single shape
3d
record the result of performing full-, half- and quarter-turns of
a shape, with and without the use of digital technologies
3e
determine the number of half-turns required for a full-turn and
the number of quarter-turns required for a full-turn
MA2-15MG
MA2-15MG Two-
Dimensional Space 1
manipulates, identifies and sketches two-
dimensional shapes, including special
quadrilaterals, and describes their
features 1a special quadrilaterals kites 1g
identify and describe two-dimensional shapes as either
'regular' or 'irregular', eg 'This shape is a regular
pentagon because it has five equal sides and five equal
angles SGS3.2a
1d
recognise the vertices of two-dimensional shapes as the
vertices of angles that have the sides of the shape as their arms 2a
identify lines of symmetry in pictures, artefacts, designs
and the environment, eg Aboriginal rock carvings or
Asian lotus designs SGS1.2
1e identify right angles in squares and rectangles 2b identify SGS1.2
1h drawand irregular two-dimensional shapes
1i and irregular two-dimensional shapes
2b drawand irregular shapes
MA2-15MG
MA2-15MG Two-
Dimensional Space 2
manipulates, identifies and sketches two-
dimensional shapes, including special
quadrilaterals, and describes their
features 1a
combine common two-dimensional shapes, including special
quadrilaterals, to form other
common shapes or designs, eg combine a rhombus and a
triangle to form a trapezium 2c identify shapes that do and do not tessellate SGS1.2
1b
split a given shape into two or more common shapes and
describe the result, eg 'I split the parallelogram into a rectangle
and two equal-sized triangles'
1c
record the arrangements of common shapes used to create
other shapes, and the arrangement of shapes formed after
splitting a shape, in diagrammatic form, with and without the
use of digital technologies
2a create symmetrical patterns
2b and record
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
2d
draw the reflection (mirror image) to complete symmetrical
pictures and shapes, given a line
of symmetry, with and without the use of digital technologies
MA2-16MG MA2-16MG Angles 1
identifies, describes, compares and
classifies angles 1c
describe informally an angle as the 'amount of turning'
between two arms 1a
identify 'angles' with two arms in practical situations, eg
the angle between the arms of a
clock SGS1.2
1b identify the 'arms' and 'vertex' of an angle SGS1.2
1d
compare angles directly by placing one angle on top of
another and aligning one arm SGS1.2
MA2-16MG MA2-16MG Angles 2
identifies, describes, compares and
classifies angles 1b
recognise and describe angles as 'less than', 'equal to', 'about
the same as' or 'greater than'
a right angle 1c
classify angles as acute, right, obtuse, straight, reflex or
a revolution SGS3.2b
1e createand classify...
MA3-15MG
MA3-15MG Two-
Dimensional Space 1
manipulates, classifies and draws two-
dimensional shapes, including
equilateral, isosceles and scalene
triangles, and describes their properties 2b
describe the effect when a two-dimensional shape is
translated, reflected or rotated, eg when a vertical arrow is
rotated 90, the resulting arrow is horizontal 1e
select and classify a two-dimensional shape from a
description of its features WM Stage 3
3a
identify and quantify the total number of lines (axes) of
symmetry (if any exist) of twodimensional shapes,
including the special quadrilaterals and triangles SGS2.2a
MA3-15MG
MA3-15MG Two-
Dimensional Space 2
manipulates, classifies and draws two-
dimensional shapes, including
equilateral, isosceles and scalene
triangles, and describes their properties 1a convex
1b all the diagonals
3a
identify whether a two-dimensional shape has been translated,
reflected or rotated, or has
undergone a number of transformations, eg 'The parallelogram
has been rotated clockwise
through 90 once and then reflected once'
3b
construct patterns of two-dimensional shapes that involve
translations, reflections and
rotations using computer software
3c
predict the next translation, reflection or rotation in a pattern,
eg 'The arrow is being rotated
90 anti-clockwise each time'
MA3-16MG MA3-16MG Angles 1
measures and constructs angles, and
applies angle relationships to find
unknown angles
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
MA3-16MG MA3-16MG Angles 2
measures and constructs angles, and
applies angle relationships to find
unknown angles 1b investigate, with and without the use of digital technologies 1b
...adjacent angles that form a
right angle and establish that they add to 90 SGS24.2
1c investigate, with and without the use of digital technologies 1c
adjacent angles on a straight
line and establish that they form a straight angle and
add to 180 SGS4.2
1d investigate, with and without the use of digital technologies 1d
angles at a point and establish
that they form an angle of revolution and add to 360 SGS4.2
1e use the results established 1e
for adjacent angles that form right angles, straight
angles and
angles of revolution to find the size of unknown angles
in diagrams SGS4.2
1f
investigate, with and without the use of digital
technologies, vertically opposite angles and establish
that they are equal in size WM in SGS4.2
1g
use the equality of vertically opposite angles to find the
size of unknown angles in diagrams WM in SGS4.2
MAe-16MG MAe-16MG Position
describes position and gives and follows
simple directions using everyday
language
MA1-16MG MA1-16MG Position 1
represents and describes the positions of
objects in everyday situations and on
maps 1b
give and follow directions, including directions involving turns
to the left and right, to move
between familiar locations, eg within the classroom or school 1c
give and follow instructions to position objects in
models and drawings, eg 'Draw the bird between the
two trees WM Stage 1
MA1-16MG MA1-16MG Position 2
represents and describes the positions of
objects in everyday situations and on
maps 1a
interpret simple maps by identifying objects in different
locations, eg find a classroom on a school plan map WM Stage 2
MA2-17MG MA2-17MG Position 1
uses simple maps and grids to represent
position and follow routes, including
using compass directions 1c ..grid references 1e draw and label a grid on a given map SGS3.3
1f
draw simple maps and plans from an aerial view, with
and without labelling a grid, eg create a map of the
classroom SGS3.3
1h
interpret and use simple maps found in factual texts and
in the media WM Stage 2
MA2-17MG MA2-17MG Position 2
uses simple maps and grids to represent
position and follow routes, including
using compass directions 1g
use NE, SE, SW and NW to indicate north-east, south-east,
south-west and north-west,
respectively, on a compass rose 1j
calculate the distance between two points on a map
using a simple given scale SGS3.3
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
1k
use scales involving multiples of 10 to calculate the distance
between two points on maps
and plans 1l
recognise that the same location can be represented by
maps or plans using different scales SGS3.3
MA3-17MG MA3-17MG Position
locates and describes position on maps
using a grid-reference system 1a grid references
2c
follow a sequence of two or more directions, including compass
directions, to find and
identify a particular location on a map
SP Statistics and Probability
Mae-17SP MAe-17SP Data
represents data and interprets data
displays made from objects
MA1-17SP MA1-17SP Data 1
gathers and organises data, displays data
in lists, tables and picture graphs, and
interprets the results 1a
investigate a matter of interest by choosing suitable
questions to obtain appropriate data WM Stage 1
MA1-17SP MA1-17SP Data 2
gathers and organises data, displays data
in lists, tables and picture graphs, and
interprets the results 2b
identify categories of data and use them to sort data, eg sort
data collected on attendance
by day of the week and into boys and girls present 1a
pose suitable questions that will elicit categorical
answers and gather the data, WM Stage 1
3d
record observations based on tables and picture graphs
developed from collected data 3b display data using lists and tables DS2.1
3c in lists, tables DS2.1
MA2-18SP MA2-18SP Data 1
selects appropriate methods to collect
data, and constructs, compares,
interprets and evaluates data displays,
including tables, picture graphs and
column graphs 1a
recognise that data can be collected either by the user or by
others 1c
pose questions about a matter of interest to obtain
information WM Stage 2
1b
identify possible sources of data collected by others, eg
newspapers, government data collection agencies, sporting
agencies, environmental groups
1c recorded in categories
1d
predict and create a list of categories for efficient data
collection in relation to a matter of interest
3a describe and
MA2-18SP MA2-18SP Data 2
selects appropriate methods to collect
data, and constructs, compares,
interprets and evaluates data displays,
including tables, picture graphs and
column graphs 1a
related recording sheet, organisation of categories for data
collection 1d
compare the effectiveness of different methods
recording data WM Stage 2
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
1b refine survey questions as necessary after a small trial 3a
interpret... the effectiveness of various data displays
found in media and in factual texts, where displays
represent data using a scale of many-to-one
correspondence WM Stage 2
1c categorical
1d of collecting and
2a categorical
3a and evaluate the
MA3-18SP MA3-18SP Data 1
uses appropriate methods to collect data
and constructs, interprets and evaluates
data displays, including dot plots, line
graphs and two-way tables 1a
pose and refine questions to construct a survey to obtain
categorical and numerical data about a matter of interest
1b
collect categorical and numerical data through observation or
by conducting surveys, eg observe the number of a particular
type of insect in one square metre of the playground over time
2a including numerical data 2a tabulate collected data WM Stage 3
2c
construct dot plots for numerical data, eg the number of
siblings of each student in the class DS4.1
2d
consider the data type to determine and draw the most
appropriate display(s), such as column graphs, dot plots
and line graphs DS4.1
3b dot plots DS4.1
MA3-18SP MA3-18SP Data 2
uses appropriate methods to collect data
and constructs, interprets and evaluates
data displays, including dot plots, line
graphs and two-way tables 1c
interpret side-by-side column graphs for two categorical
variables, eg favourite television
show of students in Year 1 compared to that of students in Year
6 1c interpret data presented in two-way tables DS2.1
1d
interpret and compare different displays of the same data set
to determine the most
appropriate display for the data set
create a two-way table to organise data involving two
categorical variables DS2.1
1c categorical variables DS4.1
2a
interpret data representations found in digital media
and in factual texts WM Stage 3
2b
critically evaluate data representations found in digital
media and related claims WM in DS4.1
MA1-18SP MA1-18SP Chance 1
recognises and describes the element of
chance in everyday events 1a
identify possible outcomes of familiar activities and
events, WM Stage 1
MA1-18SP MA1-18SP Chance 2
recognises and describes the element of
chance in everyday events 2a
describe possible outcomes in everyday activities and
events as being 'likely' or 'unlikely' to happen WM Stage 1
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
2d
identify and distinguish between 'certain' and
'uncertain' events DS2.1
MA2-19SP MA2-19SP Chance 1
describes and compares chance events in
social and experimental contexts 1a
use the term 'outcome' to describe any possible result of a
chance experiment
1d
predict the number of times each outcome should occur in a
chance experiment involving a set number of trials, carry out
the experiment, and compare the predicted and actual results
MA2-19SP MA2-19SP Chance 2
describes and compares chance events in
social and experimental contexts 1a 'equally likely... 1b
compare the chance of familiar events occurring and
describe the events as being 'more likely' or 'less likely'
to occur than each other WM Stage 2
2a
identify and discuss everyday events occurring that cannot
occur at the same time, eg the
sun rising and the sun setting
3a
identify and discuss events where the chance of one event
occurring will not be affected by
the occurrence of the other, eg obtaining a 'head' when tossing
a coin does not affect the
chance of obtaining a 'head' on the next toss
3b
compare events where the chance of one event occurring is not
affected by the occurrence of the other, with events where the
chance of one event occurring is affected by the occurrence of
the other, eg decide whether taking five red lollies out of a
packet containing 10 red and 10 green lollies affects the chance
of the next lolly taken out being red, and compare this to what
happens if the first five lollies taken out are put back in the jar
before
the sixth lolly is selected
MA3-19SP MA3-19SP Chance 1
conducts chance experiments and
assigns probabilities as values between 0
and 1 to describe their outcomes 1a
use the term 'probability' to describe the numerical value that
represents the likelihood of an
outcome of a chance experiment 1b
recognise that outcomes are described as 'equally likely'
when any one outcome has the same chance of
occurring as any other outcome NS4.4
1c
list all outcomes in chance experiments where each
outcome is equally likely to occur NS4.4
1d
represent probabilities of outcomes of chance
experiments using fractions, eg for one throw of a
standard six-sided die or for one spin of an eight-sector
spinner NS4.4
2a
establish that the sum of the probabilities of the
outcomes of any chance experiment is equal to 1 NS4.4
Sub strand 2013 NSW syllabus outcome description
Dot point
ID new content for this outcome
Dot
point ID content moved to this outcome From
MA3-19SP MA3-19SP Chance 2
conducts chance experiments and
assigns probabilities as values between 0
and 1 to describe their outcomes 1a
use the term 'frequency' to describe the number of times a
particular outcome occurs in a chance experiment
1b
compare the expected frequencies of outcomes of chance
experiments with observed
frequencies, including where the outcomes are not equally
likely
2a
list the outcomes for chance experiments where the outcomes
are not equally likely to occur
and assign probabilities to the outcomes using fractions
3a
assign expected probabilities to outcomes...
including digital simulators, and compare the expected
probabilities with the observed
probabilities after both small and large numbers of trials 3a ... in chance experiments with random generators NS2.5
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Edward The Emu S2Document25 pagesEdward The Emu S2S TANCRED100% (3)
- I'm Sorry S1Document24 pagesI'm Sorry S1S TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Electrical Machines IIDocument180 pagesLecture Notes On Electrical Machines IILidef Sellenrof100% (1)
- Tops and Bottoms UnitDocument45 pagesTops and Bottoms UnitS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Geography Scope and SequenceDocument6 pagesGeography Scope and SequenceS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus ExamDocument37 pagesPre Calculus Exammoncarla lagon100% (1)
- Read The Biography To Answer These Questions.: Born in What Year October 25 1891Document2 pagesRead The Biography To Answer These Questions.: Born in What Year October 25 1891S TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Numeracy Tracking Group C O'DONNELLDocument15 pagesNumeracy Tracking Group C O'DONNELLS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Milk EjDocument2 pagesMilk EjS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Literacy - Tracking - Group - C O'DonnellDocument46 pagesLiteracy - Tracking - Group - C O'DonnellS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Text Type Features Based On Qsa Documents 3Document2 pagesText Type Features Based On Qsa Documents 3S TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Working Mathematically: First Give Me An Interesting ProblemDocument2 pagesWorking Mathematically: First Give Me An Interesting ProblemS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Ac Year Level Icu Scope and Sequence Term 4 FinalDocument16 pagesAc Year Level Icu Scope and Sequence Term 4 FinalS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Geography AcDocument11 pagesGeography AcS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- English Planning TemplateDocument1 pageEnglish Planning TemplateS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- AchStnd Geog With ConceptDocument1 pageAchStnd Geog With ConceptS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Infer Rubric 2Document1 pageInfer Rubric 2S TANCREDNo ratings yet
- English Planning Template-D Cherry-Cabramurrah PSDocument1 pageEnglish Planning Template-D Cherry-Cabramurrah PSS TANCRED100% (1)
- Detergents (Anionic Surfactants, MBAS)Document1 pageDetergents (Anionic Surfactants, MBAS)Anggun SaputriNo ratings yet
- 3D ShapesDocument5 pages3D Shapesdeez000No ratings yet
- INOI 2012 Question PaperDocument6 pagesINOI 2012 Question PaperShourya BoseNo ratings yet
- ACUCOBOL-GT Users Guide v8 Tcm21-18390Document587 pagesACUCOBOL-GT Users Guide v8 Tcm21-18390Miquel CerezuelaNo ratings yet
- MT882 User ManualDocument61 pagesMT882 User ManualMarius HîrsescuNo ratings yet
- Flight Inspection of GAST D Approach and Taxi Guidance Systems - v1Document10 pagesFlight Inspection of GAST D Approach and Taxi Guidance Systems - v1Olivier LaylyNo ratings yet
- SMAC Actuators User ManualDocument52 pagesSMAC Actuators User ManualGabo DuarNo ratings yet
- Exploit Writing Tutorial Part 1 - Stack Based Overflows - Corelan TeamDocument54 pagesExploit Writing Tutorial Part 1 - Stack Based Overflows - Corelan Teamdamir_krstanovicNo ratings yet
- 03 Traversing Gear SlaveDocument69 pages03 Traversing Gear SlaveDeMen NguyenNo ratings yet
- OneTen-Frontend Web Development FundamentalsDocument5 pagesOneTen-Frontend Web Development FundamentalsOkpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- Hot-Forged 6082 Suspension PartsDocument13 pagesHot-Forged 6082 Suspension Partsfkaram1965No ratings yet
- BDU Konfrans 2022 Tezis JurnaliDocument395 pagesBDU Konfrans 2022 Tezis JurnalinarminpashabayliNo ratings yet
- Sequencing Problems 1Document24 pagesSequencing Problems 1Div SavaliyaNo ratings yet
- Knitting GSM Calculations PDFDocument11 pagesKnitting GSM Calculations PDFHifza khalidNo ratings yet
- LYNQ 2020 Installation GuideDocument16 pagesLYNQ 2020 Installation GuideasdfsadfasdfNo ratings yet
- Structural Evaluation TechniquesDocument6 pagesStructural Evaluation TechniquesMohan NaikNo ratings yet
- SDH To EthernetDocument23 pagesSDH To Ethernetpulkit_khNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Digital ForensicsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Digital ForensicsAbhinav GadekarNo ratings yet
- A Presentation OF Vocational Training On Combined Cycle Power PlantDocument20 pagesA Presentation OF Vocational Training On Combined Cycle Power PlantramezhosnyNo ratings yet
- TYBTech Syllabus MechanicalDocument49 pagesTYBTech Syllabus MechanicalswapnillkNo ratings yet
- Latex ProjectDocument3 pagesLatex ProjectPrincess MiroNo ratings yet
- Tafl KCS 402 Cia-I 2019-20Document2 pagesTafl KCS 402 Cia-I 2019-20vikNo ratings yet
- Fairwell TestDocument16 pagesFairwell TestSsekyanzi CalvinNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 10 ATP 2024Document19 pagesLife Sciences Grade 10 ATP 2024olwe149No ratings yet
- Topic 4Document23 pagesTopic 4Joe HanNo ratings yet
- Compliance Statement - FormDocument16 pagesCompliance Statement - Formaqil khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - SkullDocument10 pagesChapter 11 - Skullwamaithamargaret257No ratings yet
- L05 - DumitriuDocument9 pagesL05 - DumitriuLouisaMjjNo ratings yet