Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L-1: Environment of Business: Ca (Becg)
Uploaded by
bazilsyedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L-1: Environment of Business: Ca (Becg)
Uploaded by
bazilsyedCopyright:
Available Formats
1
CA (BECG)
L-1: Environment of Business
This lesson deals with:-
1. Introduction to Business Environment
2. Internal Environment
3. External Environment
4. Issues in Management of Public Limited Company
1. Introduction to Business Environment:
The Business Environment (BE) is the environment of a
business organization, which is the aggregate of all
conditions, events and influences that surround and
affect it. Due to its complex, dynamic and multifaceted
nature, as well as its far-reaching impact, the BE
exhibits many characteristics. Consequently, dividing
the environment into (i) Internal and (ii) External
components enables its better understanding. Every
business enterprise has to cope with Internal Factors
(Controllable) as well External Factors (Uncontrollable).
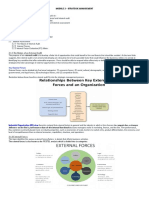
Corporate Environment (CE) comprises of (i) Players,
(ii) Issues, (iii) Responses, and (iv) Challenges. CE in
turn depends on Business Environment. All the relevant
environmental factors influence the CE.
There is a wide variation in environmental factors from
country to country and even region to region. The BE is
an extremely complex and dynamic phenomenon.
2
3
The two (2) major categories of BE:
(i) Economic Environment:
Fiscal Policy
Monetary Policy
Industrial Policy
The physical limits on Output, Price, Income.
Nature of Economic System
Pace of Economic Development
4
(ii) Non-Economic Environment:
Social Factor
Cultural Factor
Political Factor
Legal factor
Technological Factor
While the economic environment has non-economic
implications, the non-economic environment has
economic implications too. Considerable skill and
dexterity is required in adjusting, coping with and
managing the BE.
A study of the critical elements of the BE is essential to
facilitate the development of these skills. An
understanding of this turbulent and dynamic
environment also helps in effective decision making by
business managers.
Importance of BE:
Since the world of business today is ever changing
and dynamic, understanding of BE helps the
managers in right decision making.
BE helps the managers to understand the risk
associated with the business as well as corporates.
If the managers stay abreast of external
developments and react accordingly, it will help
them in solving their problems effectively and
running the firms efficiently.
5
2. Internal Environment:
The environment and its different sectors have to be
constantly monitored by business managers for
opportunities and threats that have or likely to have an
impact on their organization. Such monitoring is done
by means of environmental scanning.
The Internal Environment (IE) comprises of the
resources, synergy and distinctive competencies of a
firm. These together determine its organizational
capabilities in terms of its strengths and weaknesses
existing in the different functional areas marketing,
operations, personnel, financial, technical, etc.
Thus the firms capabilities in the above mentioned
functional areas in addition to the firms strategy and
structure make up the dynamics of its IE. However, IE
gets constantly influenced by the external environment
(EE).
Following are the Internal factors since the business
enterprise generally has control over these factors:-
(i) Strategy
(ii) Structure
(iii) Personnel Capability
(iv) Marketing Capability
(v) Operations capability
(vi) Financial capability
(vii) Technical capability
6
The above Internal factors can be altered or modified
by the organization with greater ease to suit the
environment. They are described below:-
(i) Strategy:
Strategy is a unified, comprehensive and integrated
plan relating to the strategic advantages of the firm to
the challenges of the environment. It is designed to
ensure that the basic objectives of the enterprise are
achieved.
Strategy involves establishing the proper organization-
environment matching the organizational factors with
the environmental factors. It involves an analysis of the
organizational factors (strengths and weaknesses) and
the environmental factors (opportunities and threats) in
the BE.
Strategy serves as a blue print indicating the courses of
action to achieve the desired objectives. The influence of
strategy on IE of an enterprise can be understood from
the following points: -
Strategy determines organizational tasks
Strategy influences the choice of technology
Strategy defines a BE and gets defined by the latter
(ii) Structure:
Some of the important factors influencing the
business decisions are the organization structure, the
7
composition of the Board, the extent of
professionalization of management, etc. The
organization structure is affected by the size, nature
and diversity of the business; the characteristics of
the market; the future business plans; etc. Changes in
the strategy of a business may necessitate changes in
the structure. Organization structure needs to be
flexible to respond to changes in the market.
Similarly, decision-making is delayed if there is a long
hierarchy or more layers in the administrative
system.
(iii) Personnel Capability (PC):
PC factors are those that are related to existence and
use of human resources and skills related aspects that
have a bearing on the ability of an organization to
implement strategies to attract and retain human
resources. Some of the important PC factors are: -
Personnel System (manpower planning,
selection, development, compensation,
communication, appraisal, etc)
Employees Characteristics (corporate image,
quality of managers, staff and workers,
employee promotion opportunities, working
conditions, etc.)
Industrial Relations (relationship between
union and employees, collective bargaining,
safety, welfare and security, employee
satisfaction, employee morale, etc.)
8
(iv) Marketing Capability (MC):
MC factors are those related to pricing, promotion and
distribution of products or services and all aspects
relating to the ability of the firm to market its products
and services. The factors which influence the MC are: -
Product related factors (variety, differentiation,
positioning, packaging, etc.)
Price-related factors (pricing objective, policies,
changes, protection, advantages etc.)
Promotion related factors (promotional tools, sales
promotion, advertising, public relations, etc.)
Integrative and systematic factors (marketing mix,
distribution system, company image, marketing
organization, system and management, information
system, etc.)
(v) Operaions Capability (OC):
OC factors are those related to production of products
or services, use of material resources, all related aspects
that have a bearing on the capacity and ability of the
organization to implement its strategies to produce
products and services. Some of the OC factors are:-
Factors related to production system (capacity,
location, layout, product/service design,
automation, vertical integration, etc.)
Factors related to operation and control system
(aggregate production, planning, material supply,
9
inventory, cost and quality control, maintenance
system and procedure, etc.)
Factors related to R&D (product development,
patent right, level of technology, technical
collaboration and support, etc.)
(vi) Financial Capability (FC):
FC factors include those related to the availability,
usage and management of funds and all related aspects
having bearing on the capacity and ability of the
organization to implement its strategies to procure and
disburse funds. Such FC factors are:-
Those related to the sources of funds (capital
structure, procurement of capital, financing
pattern, availability of working capital,
borrowings, capital and credit availability, reserves
and surpluses, relationship with banks, lenders and
FIs, etc.)
Those related to the use of funds (capital
investment, fixed assets acquisition, current assets,
loans and advances, dividend distribution, and
relationship with shareholders).
Factors related to management of funds (financial
accounting, budgeting, management control
system, state of financial health, cash, inflation,
credit, return and risk management, cost reduction
& control, and tax planning and control).
10
(vii) Technical Capability (TC):
TC implies strategy for organizational fitness. Most
product development organizations recognize that the
capability of their technical staff is critical to improving
their productivity and quality in achieving their
business goals. (Example: BMW for elegance and
design which speaks for its technical capability; BHEL
for its designing of steel turbines).
3. External Environment:
All the factors that provide opportunities or pose
threats to an organization make up the external
environment of the organization. The external
environment, in a broader sense encompasses a variety
of factors like international, national and local
economy. The environment is made up of social
changes, demographic variables, political system,
technology, government or public attitude towards
business, energy sources, availability of raw materials
and other resources, and several other macro level
factors. The immediate concern of an organization
would be to concentrate on those external factors that
are intimately related to its very existence and
profitable performance.
Following are the individual factors of the external
environment: -
11
(i) Demographic Environment:
Demand for goods and services is affected by
demographic factors such as population size,
growth rate, gender composition, life expectancy,
family size, spatial dispersal, occupational status,
employment pattern, etc. which have implications
for business. Heterogeneity of labor in terms of
language, caste, religion and ethnicity, etc. is likely
to make personal management a more complex
task.
(ii) Social Environment:
Buying and consuming pattern of people, their
beliefs and values, languages, customs and
traditions, tastes and preferences, education etc.
are some important factors and influences
operating the firm in the social environment.
(iii) Cultural Environment:
Cultural forces play a major role in shaping a
companys marketing mix program. The cultural
elements are: language; aesthetics like art, drama,
music, folklore and architecture present in a
society; education; and religion.
12
(iv) Political Environment (PE):
PE refers to management of public affairs and
their impact on business. PE is closely related to
the economic system and economic policy. Some
governments specify certain standards for the
products, including packaging, while others
prohibit marketing of certain products.
Promotional activities are subject to various types
of controls in most nations. Indian government
plays an active role as a planner, promoter and
regulator of economic activity and India has a
stable political system.
(v) Economic Environment (EE):
EE is made up of macro level factors relating to
production and distribution of wealth that affects
an organization. Some of the factors influencing EE
are: (i) Economic Structure e.g. capitalistic,
socialistic or mixed economy; (ii) Economic
Planning such as 5-year plans, budgets, etc;
Economic Policies like monetary, industrial and
fiscal policies; (iii) Economic Indices like national
income, per capita income, disposable personal
income, GNP growth rate, distribution of income,
saving rate, imports and exports, balance of
payments, etc.; and (iv) Infrastructural Factors
such as Financial Institutions (FIs), banks,
communication facilities, modes of transport,
energy source, etc.
13
(vi) Financial Environment (FE):
The financial system constitutes an integral part of
the economic system covering (i) flow of savings to
provide funds for investments in industry, trade
and service organizations; (ii) financial
intermediaries like banks, NBFCs and FIs to
service them; and (iii) financial instruments and
securities that facilitate transfer of funds. Money
and capital markets contribute greatly to the
development of business and industry and are
integral part of business environment.
(vii) Trade Environment (TE):
Economic reforms worldwide have led to global
trade which is the universal rule of business to-day.
Globalization refers to the integration of the world
into one huge market. There were many efforts to
reduce the trade barriers like import-export duties
and non-trade barriers like import quotas, export
subsidies, countervailing duties, dumping, etc. and
also reduce the gap between the domestic prices
and world prices, thus liberalizing the trade gap.
WTO has been established and General Agreement
on Trade and Services (GATS), Trade-Related
Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPs), Trade-
Related Investment Measures (TRIMs) have been
brought under its purview for establishing a better
trade environment.
14
(viii) Technological Environment (TE):
TE comprises of the factors which are related to the
applied knowledge and the materials and machines
used in the production of goods and services. The
main factors and influences operating in the
technological environment are:
Sources of Technology (Company sources,
external sources and foreign sources; cost of
acquisition of technology; and collaboration in
and transfer of technology)
Technological development, stages of
development change, rate of change of
technology, and research and development.
Impact of technology on human beings, the
man-machine system, and the effects of
technology on environment.
Communication and infrastructural
technology and technology in management.
In Indian context, there is variation in the state of
technological development among different sectors of
the industry.
(ix) Legal Environment:
A unique system of law prevails in every country to
regulate their corporate entities. This makes a
multinational corporation to cope up with widely
different legal systems of varied complexity and
15
dimensions. In some countries, the laws do not specify
every detail and their interpretations are left to the
courts. Hence a foreign enterprise has to be
scrupulously careful to abide by the local laws and
regulations. Since there is no international body to
make rules and oversee the fulfillment of rules by
different parties, the jurisdiction of laws gains
importance when disputes arise. To control foreign
businesses in their economies, host countries enact
laws, which take several forms such as tariffs,
antidumping laws, export/import licensing investment
regulations, legal incentives, and restrictive trading
laws.
(x) Regulatory Environment:
Regulatory environment comprises factors related to
the planning, promotion, and regulation, by the
government, of those economic activities that affect the
business of the organization. Such factors are:-
The constitutional framework, directive principles
of state policy, fundamental rights, and division of
legislative power between central and state
governments.
Policies relating to licensing monopolies, foreign
investment and financing of industries.
Policies related to distribution and pricing and
their control.
Policies related to imports and exports.
16
Other policies related to the public sector, small-
scale industries, sick industries, development of
backward areas, control of environment pollution
and customer protection.
Since the Indian economy is by and large centrally
planned and controlled, the economic activities are
regulated by public authorities in the larger interest.
Business and industry operate within a regulatory
environment. A two-way relationship exists between
the industry and the regulatory environment. The
policies, procedures and rules according to which
industry functions are laid down by the government.
(xi) Tax Environment:
Governments design tax systems to raise revenues
and promote economic and social goals. While at
times government attempts to stimulate overall
national economic activity through tax reduction, at
other times, they attempt to retard excessive growth
through tax hikes. To stimulate productive activity,
the government may extend tax concessions to certain
industries. The Indian government has been
promoting infrastructure and IT sectors through
attractive tax incentives.
Similarly tariffs may be imposed by government on
imported manufactured goods to discourage the
outflow of FE reserves or to shelter a domestic
17
industry from the onslaught of foreign competition
(Example: Automobile Industry).
(xii) Ethical Environment (ETE):
In every society, there will be some dos and donts.
The principle of morality or rules of conduct are
referred to ethics. Ethics deals with identification of
rules that should govern the behavior of people. A
situation, problem or opportunity in which an
individual must choose among several actions that
must be evaluated as right or wrong is what
comprises an ethical issue. Likewise the moral
principles and the standards that guide behavior in
the world of business comprise business ethics and
corporate governance.
Due to the highly publicized unethical activities by
businesses, the demand for ethical behavior has
increased. Decision made on the basis of what is
right and what is wrong constitutes the ethical
environment of an organization. Increasingly,
managers are realizing the importance of
separation of management from ownership of a
company to ensure the observance of a code of
conduct.
4. Issues in Management of Public Limited Company:
This chapter is covered in a separate lesson (L_I A)
*********
You might also like
- The SWOT Analysis: A key tool for developing your business strategyFrom EverandThe SWOT Analysis: A key tool for developing your business strategyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- B E (Unit-1)Document20 pagesB E (Unit-1)SHIVAMNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument30 pagesBusiness EnvironmentDr. Khem ChandNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial Planning Is Subject To The Various Macro and Micro Environmental Factors'. Elucidate.Document4 pagesStrategic Financial Planning Is Subject To The Various Macro and Micro Environmental Factors'. Elucidate.DivyaDesai100% (1)
- Introduction To Business EnvironmentDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Business Environment401 KALAVALA SAI NAVEENNo ratings yet
- Govind Singh Commerce Stream Full BookDocument539 pagesGovind Singh Commerce Stream Full Bookyashsharma2837No ratings yet
- Unit-2: Marketing Environment (Macro & Micro)Document11 pagesUnit-2: Marketing Environment (Macro & Micro)danny antonyNo ratings yet
- WORK SHEET - Business Environment: 1.SWOT AnalysisDocument4 pagesWORK SHEET - Business Environment: 1.SWOT AnalysisMukesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument5 pagesStrategic ManagementRanjeet singhNo ratings yet
- DLA 212 - Topic 1Document16 pagesDLA 212 - Topic 1kobus7532No ratings yet
- SM Module 1Document10 pagesSM Module 1Jeevan ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Business EnviromentDocument40 pagesBusiness EnviromentMalav NanavatiNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 The Firm and Its EnvironmentDocument3 pagesChap 2 The Firm and Its EnvironmentJonathan Miergas CayabyabNo ratings yet
- MBA 205 Legal Unit 7Document13 pagesMBA 205 Legal Unit 7Soumen SahuNo ratings yet
- Bus. Env. NotesDocument12 pagesBus. Env. Notesmohak vilechaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Meaning of Business Environment: Senior SecondaryDocument10 pages3.1 Meaning of Business Environment: Senior SecondarysrinivasaNo ratings yet
- Business Environment Unit 1Document7 pagesBusiness Environment Unit 1Bawa GamerNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Concepts of Business EnvironmentDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Concepts of Business EnvironmentMohd AqdasNo ratings yet
- Ed Unit 2Document49 pagesEd Unit 2pecmba23No ratings yet
- PESTLE - IntroDocument57 pagesPESTLE - IntroSuraj GawandeNo ratings yet
- Topic Three Business Environment: Page 1 of 19Document19 pagesTopic Three Business Environment: Page 1 of 19Collins AbereNo ratings yet
- MBA-SEM-1 EAM (Envrionmental Analysis and Management)Document56 pagesMBA-SEM-1 EAM (Envrionmental Analysis and Management)Vijayshri NairNo ratings yet
- Etop and Swot AnalysisDocument6 pagesEtop and Swot AnalysisAnonymous btU0rk0pN75% (4)
- Business Environment, Introduction To Business Environment, Environmental Scanning, JNTU KakinadaDocument14 pagesBusiness Environment, Introduction To Business Environment, Environmental Scanning, JNTU KakinadaP Manoj BabuNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Principles of Management Topic: PESTEL AnalysisDocument29 pagesModule-1 Principles of Management Topic: PESTEL AnalysisnandhiniNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument29 pagesBusiness EnvironmentRahul Paliya100% (1)
- Ugc Net Commerce: Unit SnapshotDocument59 pagesUgc Net Commerce: Unit SnapshotPeer SheebaNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScanningDocument18 pagesEnvironmental ScanningShivangi DhamijaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 The Role of Business in The Environment & How The Environment Affects The FirmDocument13 pagesLesson 5 The Role of Business in The Environment & How The Environment Affects The FirmRonalyn CabonceNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Business EnvironmentDocument3 pagesModule 8 - Business EnvironmentDivine NgeneNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Tools For Case Analysis PDFDocument21 pagesModule 3 Tools For Case Analysis PDFMahua Adak MandalNo ratings yet
- The Term Business Environment' Means The Sum Total of All Individuals, Institutions and Other Forces That Are Outside The Control of A Business Enterprise But That May Affect Its PerformanceDocument9 pagesThe Term Business Environment' Means The Sum Total of All Individuals, Institutions and Other Forces That Are Outside The Control of A Business Enterprise But That May Affect Its PerformanceChandana MNo ratings yet
- The Business EnvironmentDocument24 pagesThe Business EnvironmentjujNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Environmental Context of ManagementDocument9 pagesChapter 4 Environmental Context of ManagementBinodBasnet100% (3)
- Unit - I Lesson 1 Introduction of Business EnvironmentDocument32 pagesUnit - I Lesson 1 Introduction of Business EnvironmentVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Threat and Opportunity Profile (Etop) : G.Dileep 1Document4 pagesEnvironmental Threat and Opportunity Profile (Etop) : G.Dileep 1Irin I.gNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Management DefinitionsDocument11 pagesContemporary Management DefinitionsMahmoud AfifiNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Business EnvironmentDocument52 pages1-Introduction To Business EnvironmentRavitej Philkhana100% (1)
- NOTES-Business Env.Document8 pagesNOTES-Business Env.Chitra MukimNo ratings yet
- 2021 2022 TLED 210 Module 2Document29 pages2021 2022 TLED 210 Module 2balanivalshcaNo ratings yet
- Open Book-9Document26 pagesOpen Book-9Anitha NNo ratings yet
- Indian Business Enironment: SyllabusDocument68 pagesIndian Business Enironment: SyllabusNarayanan BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management, Alliances and International Trade: Professional Programme ExaminationDocument23 pagesStrategic Management, Alliances and International Trade: Professional Programme ExaminationJayachandra JcNo ratings yet
- Business Environment Refers To Different Forces or Surroundings That Affect Business OperationsDocument9 pagesBusiness Environment Refers To Different Forces or Surroundings That Affect Business Operationsmldc2011No ratings yet
- CH 2Document6 pagesCH 2DARSHAN GONDALIYANo ratings yet
- Business Environment Unit 1: 1.1 Concepts of Business Environment 1.1.1 Defination of BEDocument12 pagesBusiness Environment Unit 1: 1.1 Concepts of Business Environment 1.1.1 Defination of BEVamshi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Module2 Businessenvironment 150627035534 Lva1 App6892Document53 pagesModule2 Businessenvironment 150627035534 Lva1 App6892zm7485689No ratings yet
- Bel NotesDocument20 pagesBel Notesg8r88v8rdh888r8dd88kNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Unit I Introduction of Strategic ManagementDocument11 pagesStrategic Management Unit I Introduction of Strategic ManagementsatyachandrasarmaNo ratings yet
- 1456919520com P12 M10 EtextDocument12 pages1456919520com P12 M10 EtextGunavanth GNo ratings yet
- M1 and M2 SentDocument11 pagesM1 and M2 Sentdivya86kNo ratings yet
- 814 AssignmentDocument5 pages814 AssignmentRahma Abdulkadir ArahNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 & 4 StrategicDocument19 pagesTopic 3 & 4 StrategicMAURICE KIOKONo ratings yet
- Business Environment For MBA.Document18 pagesBusiness Environment For MBA.keneyenanalioNo ratings yet
- Factors That Shape The Company's Strategy: (I) Internal Environment FactorsDocument6 pagesFactors That Shape The Company's Strategy: (I) Internal Environment Factorsmba departmentNo ratings yet
- Usiness Environment Encompasses The Climate or Set of ConditionsDocument90 pagesUsiness Environment Encompasses The Climate or Set of ConditionsHarsh RajNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Strat ManDocument4 pagesModule 2 - Strat ManElla MaeNo ratings yet
- Business Environment 2nd SemsterDocument23 pagesBusiness Environment 2nd SemsterChuadhary kumarNo ratings yet
- MMPC 003Document23 pagesMMPC 003skatyal28No ratings yet
- Theories of EthicsDocument31 pagesTheories of EthicsbazilsyedNo ratings yet
- Ethical LeadershipDocument13 pagesEthical LeadershipbazilsyedNo ratings yet
- L-10F.becg - JJ Irani CommitteeDocument14 pagesL-10F.becg - JJ Irani CommitteebazilsyedNo ratings yet
- Ganguly CommitteeDocument16 pagesGanguly Committeebazilsyed0% (1)
- AGMDocument21 pagesAGMPriyanka AgarwalNo ratings yet
- BC Cross CulturalDocument14 pagesBC Cross CulturalbazilsyedNo ratings yet
- Ed 407 Course OutlineDocument3 pagesEd 407 Course OutlineEdwin SamisNo ratings yet
- Form GSTR 2aDocument2 pagesForm GSTR 2aparam.ginniNo ratings yet
- PHCUOR Scorecard 6Document154 pagesPHCUOR Scorecard 6Iyiola Daniel100% (1)
- Sangalang v. IACDocument12 pagesSangalang v. IACJoanne CamacamNo ratings yet
- Role of Judiciary With Respect To Health Insurance Laws in IndiaDocument15 pagesRole of Judiciary With Respect To Health Insurance Laws in IndiaBharat RkNo ratings yet
- The Comprehensive Refugee Response Framework: Progress in KenyaDocument25 pagesThe Comprehensive Refugee Response Framework: Progress in Kenyah3493061No ratings yet
- IB Economics Notes - Chapter 12Document37 pagesIB Economics Notes - Chapter 12Anindya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Ttl1 ModuleDocument50 pagesTtl1 ModuleNeisha Kwane PuglayNo ratings yet
- Pfeffer (2005) Producing Sustainable PDFDocument15 pagesPfeffer (2005) Producing Sustainable PDFdoncupidNo ratings yet
- Sample (Term Paper)Document8 pagesSample (Term Paper)hassan99No ratings yet
- Asas Lex Specialis Systematis Dan Hukum Pidana Pajak (Principle of Lex Specialist Systematic and Tax Criminal Law)Document12 pagesAsas Lex Specialis Systematis Dan Hukum Pidana Pajak (Principle of Lex Specialist Systematic and Tax Criminal Law)Leony ArinataliNo ratings yet
- Records Retention and ManagementDocument56 pagesRecords Retention and ManagementMaine Trust For Local NewsNo ratings yet
- RICS Official Definition: Isurv Recommended Reading and ServicesDocument3 pagesRICS Official Definition: Isurv Recommended Reading and Serviceslinga2014No ratings yet
- Form Vat-27: (See Rule 46)Document2 pagesForm Vat-27: (See Rule 46)vishnu kumarNo ratings yet
- BSBDIV501 Assessor Workbook V1.1Document25 pagesBSBDIV501 Assessor Workbook V1.1Çrox Rmg PunkNo ratings yet
- Compliance Manager ResumeDocument7 pagesCompliance Manager Resumeonguiqekg100% (1)
- Savani - A Choice Mind-Set Increases The Acceptance and Maintenance of Wealth InequalityDocument10 pagesSavani - A Choice Mind-Set Increases The Acceptance and Maintenance of Wealth Inequalityselena pNo ratings yet
- Violation Against Women: Our Topic For DiscussuionDocument9 pagesViolation Against Women: Our Topic For DiscussuionAyesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- Effective Risk Management PlanDocument4 pagesEffective Risk Management PlanJhuliane RalphNo ratings yet
- Internship Report - AdsellsDocument149 pagesInternship Report - AdsellsM Abrar RasoolNo ratings yet
- Strategic Policy and Planning DepartmentDocument3 pagesStrategic Policy and Planning Departmentraja mohanNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesCorporate Social ResponsibilityJohanne LariosaNo ratings yet
- Kampala Boda-Bodas Regulation ProposalDocument16 pagesKampala Boda-Bodas Regulation ProposalMukiibi DuncanNo ratings yet
- Component of Economic Law Group 2Document12 pagesComponent of Economic Law Group 2kudaNo ratings yet
- واقع الجهاز المصرفي الجزائري بين متطلبات لجنة بازل - 2 - وتحديات تطبيق بازل - 3 -Document15 pagesواقع الجهاز المصرفي الجزائري بين متطلبات لجنة بازل - 2 - وتحديات تطبيق بازل - 3 -Nada NadaNo ratings yet
- Gri 413 Local Communities 2016Document14 pagesGri 413 Local Communities 2016RizkyAufaSNo ratings yet
- Janaagraha - Urban Governance - Challenges and Solutions - Planning Commission - ppt250107Document22 pagesJanaagraha - Urban Governance - Challenges and Solutions - Planning Commission - ppt250107Nazeeha NazneenNo ratings yet
- On The President's Order Governing Through Killing: The War On Drugs in The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesOn The President's Order Governing Through Killing: The War On Drugs in The PhilippinesRolando E. CaserNo ratings yet
- Environmental Policy and Law: The Ethiopian Context: - IntroductionDocument35 pagesEnvironmental Policy and Law: The Ethiopian Context: - Introductionf212No ratings yet
- Concepts of Constitution, Constitutional Law, and ConstitutionalismDocument6 pagesConcepts of Constitution, Constitutional Law, and Constitutionalismكاشفة أنصاريNo ratings yet