Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cat-D Physics Paper B
Uploaded by
Anshul Jindal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesphysics sample paper
Original Title
Cat-d Physics Paper b
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentphysics sample paper
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesCat-D Physics Paper B
Uploaded by
Anshul Jindalphysics sample paper
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
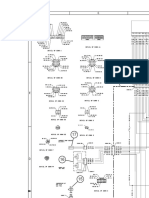
FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi - 110016. Ph: 46106000/10/13/15 Fax : 26513942.
FACULTY RECRUITMENT TEST
CATEGORY-D
Formal School Education/IX, X / NSEJS/NTSE/ Foundation
for KVPY, Senior Olympiads, JEE Main & JEE Advanced
PHYSICS
PAPER B
Time: 1 Hour Maximum Marks: 40
Name:.................................................................................
Subject:...........................................
Marks:
Instructions
* Attempt all questions.
* Paper A has Two Parts I and II. Each question of Part I carries 2 marks and each
question of part II caries 4 marks.
* Calculators and log tables are not permitted.
PART I
1. A 2kg ball drops on floor from a height of 20 m and rebounds with 20% of the initial speed. Find the
impulse received by the ball.
2. A uniform chain of length L and mass M is lying on a smooth table and one-third of its length is
hanging vertically down over the edge of the table. If g is acceleration due to gravity, calculate the
work required to pull the hanging part on to the table.
3. Find the value of current i in the circuit shown in the figure.
15 A
i A 5 A
8 A
3 A
4. A ray of light falling at an angle of 50
o
is refracted through a prism in minimum deviation position. The
angle of the prism is 60
o
. Calculate the refractive index of the prism. Given that sin 50
o
= 0.766.
5. A block of mass 3 kg is resting on a horizontal plane
(coefficient of static friction = 1 2 3 ). A force F is applied to
the block as shown in the figure. Find the minimum magnitude
of F for which the block begins to slide. (g =
2
10 m/s )
m=3kg
F
60
6. A current of 2 A enters at the corner d of a square frame abcd of side 20
cm and leaves at the opposite corner b. A magnetic field B = 0.1 T exists
in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the frame as
shown in the figure Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic
forces on the four sides of the frame.
a b
c d
FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi - 110016. Ph: 46106000/10/13/15 Fax : 26513942.
P2-FACREC-PH-2
7. Gravitational force between point masses m and M separated by a distance F. Now if a point mass
2m is placed next to m, what will be the (a) force on M due to m. (b) total force on M
8. In the figure shows the graph of the x-coordinate of a
particle going along the X-axis as a function of time. Find
(a) the average velocity during 0 to 10 s. (b) instantaneous
velocity at 2 sec
2.5
50
0
100
5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5
X (m)
Time (second)
(m)
15.0
9. A block of mass m is kept on a frictionless inclined wedge of mass
M with angle of inclination . The wedge is given an acceleration a
to keep the block stationary. Find the acceleration a.
a
10. A ball is dropped on a floor from a height of 2.0 m. After the collision it rises upto a height of 1.5m.
Assuming that 40% of mechanical energy lost goes as thermal energy into the ball. Calculate the rise
in temperature of the ball in the collision. Specific heat capacity of the ball is 800 J/K.
(Take g = 10m/s
2
)
PART II
11. A ball is thrown vertically upward with a velocity 20 m/s. Find the distance covered by the ball is 3 sec.
12. A point source of light B is placed at a distance L in front of the
centre of a mirror of width d hung vertically on a wall. A man
walks in front of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror at a
distance 2L from it as shown. Find the greatest distance over
which he can see the image of the light source in the mirror.
L
2L
B d
13. A liquid of density is filled in a beaker of cross section A to a
height H and then a cylinder of mass M and cross-section a is
made to float in it as shown in figure. If the atmospheric pressure
is P
0
, find the pressure (a) at the top face B of the cylinder (b) at
the bottom face C of the cylinder and (c) at the base D of the
beaker (d) can ever these pressures be equal?
B
C
D
H
B
14. A small charged particle of mass m and charge q is suspended by an
insulated thread in front of a very large sheet of charge density . Find the
angle made by the thread with the vertical in equilibrium.
+ + +
+ + +
+ + +
+ + +
q
m
15. An artificial satellite of mass 100 kg is in circular orbit at 500 km above the earths surface. Take the
radius of the earth as 6.5 10
6
m.
(a) Find the acceleration due to gravity at any point along the satellite path.
(b) What is the centripetal acceleration of the satellite?
* * * * *
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Reversible ProcessDocument37 pagesReversible ProcessTushar Kant SwainNo ratings yet
- Wadada Hydel Techgeneral 2021Document36 pagesWadada Hydel Techgeneral 2021Hamza IzharNo ratings yet
- Conductive Polymer Based On Polyaniline-Eggshell Powder (PANI-ESP) CompositesDocument17 pagesConductive Polymer Based On Polyaniline-Eggshell Powder (PANI-ESP) CompositesSergioNo ratings yet
- Refacciones Cems ACF5000Document1 pageRefacciones Cems ACF5000Mauro Portugal LagardaNo ratings yet
- H Physics All 2009Document24 pagesH Physics All 2009Duncan McClementsNo ratings yet
- 108 Weldox 900 Uk Data SheetDocument2 pages108 Weldox 900 Uk Data SheetjodakiNo ratings yet
- Markflow Grout 2 PDFDocument3 pagesMarkflow Grout 2 PDFBharat PaintsNo ratings yet
- Schaeffler Diagram PDFDocument16 pagesSchaeffler Diagram PDFrajesh_14No ratings yet
- DNV Rudder, Steering Gear, Anchoring, Mooring PDFDocument50 pagesDNV Rudder, Steering Gear, Anchoring, Mooring PDFDian Arina100% (1)
- Science 6 Quarter 3 Module 4 Week 4 Heat Ang Light Energy: Let's UnderstandDocument4 pagesScience 6 Quarter 3 Module 4 Week 4 Heat Ang Light Energy: Let's UnderstandALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry 4 Spectroscopy - 1Document43 pagesAnalytical Chemistry 4 Spectroscopy - 1PERPETUAL TAKYINo ratings yet
- Smart Fibres Technology Introduction PDFDocument5 pagesSmart Fibres Technology Introduction PDFKavya ShivakumarNo ratings yet
- Methods of Heat Transfer: ConductionDocument54 pagesMethods of Heat Transfer: Conductionmuhammed badushaNo ratings yet
- Thermoflex Webinar 1Document52 pagesThermoflex Webinar 1sizmaruNo ratings yet
- Codul TempDocument6 pagesCodul TempGeorge TsavdNo ratings yet
- AC SchematicDocument6 pagesAC SchematicsuwarjitechnicNo ratings yet
- ISO Standards Handbook Paints 2Document3 pagesISO Standards Handbook Paints 2Luis Gustavo Pacheco0% (1)
- Modelos Atómicos InglésDocument8 pagesModelos Atómicos InglésManuel GordilloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document31 pagesLecture 01nghaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment: (Single Correct Choice Type) Q.1Document3 pagesChemistry Assignment: (Single Correct Choice Type) Q.1Samridh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 7 HT6M 34 Atmospheric Lapse RatesDocument8 pages7 HT6M 34 Atmospheric Lapse RatesNewton WestNo ratings yet
- Corrosion 9.5 and 9.6Document13 pagesCorrosion 9.5 and 9.6Adam AriffNo ratings yet
- Turcite T51 Engineering DataDocument1 pageTurcite T51 Engineering DataAntonio Rivera VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Truss-EC3 DesignDocument57 pagesTruss-EC3 Designshaff85No ratings yet
- Siegbahn Lecture 1Document30 pagesSiegbahn Lecture 1Edgar PerezNo ratings yet
- 2a - Precision-Interferometer-Experiment 1Document27 pages2a - Precision-Interferometer-Experiment 1Brenda CruzNo ratings yet
- ES Q2 Layers of The EarthDocument45 pagesES Q2 Layers of The Earthsab lightningNo ratings yet
- Engineering Room Data SheetDocument1 pageEngineering Room Data SheetquycoctuNo ratings yet
- Mini CE Board SimulationDocument17 pagesMini CE Board SimulationRamjie JoveroNo ratings yet