Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Voltage Comperator3 LM397
Uploaded by
ΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views10 pageslm397
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlm397
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views10 pagesVoltage Comperator3 LM397
Uploaded by
ΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣlm397
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
LM397
Single General Purpose Voltage Comparator
General Description
The LM397 is a single voltage comparator with an input
common mode that includes ground. The LM397 is designed
to operate from a single 5V to 30V power supply or a split
power supply. Its low supply current is virtually independent
of the magnitude of the supply voltage.
The LM397 features an open collector output stage. This
allows the connection of an external resistor at the output.
The output can directly interface with TTL, CMOS and other
logic levels, by tying the resistor to different voltage levels
(level translator).
The LM397 is available in space saving SOT23-5 package
and pin compatible to TIs TL331, single differential com-
parator.
Features
(T
A
= 25C. Typical values unless otherwise specified).
n SOT23-5 package
n Industrial operating range 40C to +85C
n Single or dual power supplies
n Wide supply voltage range 5V to 30V
n Low supply current 300A
n Low input bias current 7nA
n Low input offset current 1nA
n Low input offset voltage 2mV
n Response time 440ns (50mV overdrive)
n Input common mode voltage 0 to V
S
- 1.5V
Applications
n A/D converters
n Pulse, square wave generators
n Peak detector
n Industrial applications
Connection Diagram
SOT23-5
20022108
Top View
Typical Circuit
Ordering Information
Package Part Number Package Marking Transport Media NSC Drawing
5-Pin SOT-23 LM397MF C397 1k Units Tape and Reel MF05A
LM397MFX 3k Units Tape and Reel
20022109
FIGURE 1. Inverting Comparator with Hysteresis
June 2001
L
M
3
9
7
S
i
n
g
l
e
G
e
n
e
r
a
l
P
u
r
p
o
s
e
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
C
o
m
p
a
r
a
t
o
r
2001 National Semiconductor Corporation DS200221 www.national.com
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
ESD Tolerance
Human Body Model 2KV (Note 2)
Machine Model 200V (Note 3)
V
IN
Differential 30V
Supply Voltages 30V or 15V
Voltage at Input Pins 0.3V to 30V
Storage Temperature Range 65C to +150C
Junction Temperature (Note 4) +150C
Soldering Information
Infrared or Convection (20 sec.) 235C
Wave Soldering (10 sec.) 260C
Operating Ratings (Note 1)
Supply Voltage, V
S
5V to 30V
Junction Temperature Range (Note 4) 40C to +85C
Package Thermal Resistance (Note 4)
SOT23-5 168C/W
Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for at T
J
= 25C, V
S
= 5V. Bold-
face limits apply at temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 6)
Typ
(Note 5)
Max
(Note 6)
Units
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage V
S
= 5V to 30V,
V
O
= 1.4V, V
CM
= 0V
2 7
10
mV
I
OS
Input Offset Current V
O
= 1.4V, V
CM
= 0V 1.6 50
250
nA
I
B
Input Bias Current V
O
= 1.4V, V
CM
= 0V 10 250
400
nA
I
S
Supply Current R
L
= Open, V
S
= 5V 0.25 0.7
mA
R
L
= Open, V
S
= 30V 0.30 2
I
O
Output Sink Current V
IN
+ = 1V,V
IN
= 0V, V
O
= 1.5V 6 13 mA
I
LEAKAGE
Output Leakage Current V
IN
+ = 1V,V
IN
= 0V, V
O
= 5V 0.1 nA
V
IN
+ = 1V,V
IN
= 0V, V
O
= 30V 1 A
V
OL
Output Voltage Low I
O
= 4mA, V
IN
+ = 0V,V
IN
= 1V 180 400
700
mV
V
CM
Common-Mode Input Voltage
Range
V
S
= 5V to 30V (Note 7) V
S
- 1.5V 0
V
V
S
- 2V 0
L
M
3
9
7
www.national.com 2
Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for at T
J
= 25C, V
S
= 5V.
Boldface limits apply at temperature extremes. (Continued)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 6)
Typ
(Note 5)
Max
(Note 6)
Units
A
V
Voltage Gain V
S
= 15V, V
O
= 1.4V to 11.4V,
R
L
> = 15k connected to V
S
120 V/mV
t
PHL
Propagation Delay (High to Low) Input Overdrive = 5mV
R
L
= 5.1k connected to 5V,
C
L
= 15pF
900
ns
Input Overdrive = 50mV
R
L
= 5.1k connected to 5V,
C
L
= 15pF
250
t
PLH
Propagation Delay (Low to High) Input Overdrive = 5mV
R
L
= 5.1k connected to 5V,
C
L
= 15pF
940 s
Input Overdrive = 50mV
R
L
= 5.1k connected to 5V,
C
L
= 15pF
440 ns
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
intended to be functional, but specific performance is not guaranteed. For guaranteed specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics.
Note 2: Human body model, 1.5k in series with 100pF.
Note 3: Machine model, 0 in series with 200pF.
Note 4: The maximum power dissipation is a function of T
J(MAX)
,
JA
, and T
A
. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is
P
D
= (T
J(MAX)
- T
A
)/
JA
. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly onto a PC board.
Note 5: Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 6: All limits are guaranteed by testing or statistical analysis.
Note 7: The input common-mode voltage of either input should not be permitted to go below the negative rail by more than 0.3V. The upper end of the
common-mode voltage range is V
S
- 1.5V at 25C.
L
M
3
9
7
www.national.com 3
Typical Performance Characteristics T
A
= 25C. Unless otherwise specified.
Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage Input Bias Current vs. Supply Current
20022103 20022101
Output Saturation Voltage vs. Output Sink Current Input Offset Voltage vs. Supply Voltage
20022104 20022102
Response Time for Various Input Overdrives t
PHL
Response Time for Various Input Overdrives t
PLH
20022105 20022106
L
M
3
9
7
www.national.com 4
Application Notes
Basic Comparators
A comparator is quite often used to convert an analog signal
to a digital signal. The comparator compares an input volt-
age (V
IN
) at the non-inverting pin to the reference voltage
(V
REF
) at the inverting pin. If V
IN
is less than V
REF
the output
(V
O
) is low (V
OL
). However, if V
IN
is greater than V
REF
, the
output voltage (V
O
) is high (V
OH
). Refer to Figure 2.
Hysteresis
The basic comparator configuration may oscillate or produce
a noisy output if the applied differential input is near the
comparators input offset voltage. This tends to occur when
the voltage on the input is equal or very close to the other
input voltage. Adding hysteresis can prevent this problem.
Hysteresis creates two switching thresholds (one for the
rising input voltage and the other for the falling input volt-
age). Hysteresis is the voltage difference between the two
switching thresholds. When both inputs are nearly equal,
hysteresis causes one input to effectively move quickly pass
the other. Thus, effectively moving the input out of region that
oscillation may occur.
For an inverting configured comparator, hysteresis can be
added with a three resistor network and positive feedback.
When input voltage (V
IN
) at the inverting node is less than
non-inverting node (V
T
), the output is high. The equivalent
circuit for the three resistor network is R
1
in parallel with R
3
and in series with R
2
. The lower threshold voltage V
T1
is
calculated by:
V
T1
= ((V
S
R
2
) / (((R
1
R
3
) / (R
1
+ R
3
)) + R
2
))
When V
IN
is greater than V
T
, the output voltage is low. The
equivalent circuit for the three resistor network is R
2
in
parallel with R
3
and in series with R
1
. The upper threshold
voltage V
T2
is calculated by:
V
T2
= V
S
((R
2
R
3
) / (R
2
+ R
3
)) / (R
1
+ ((R
2
R
3
) / (R
2
+
R
3
)))
The hysteresis is defined as
V
IN
= V
T1
V
T2
20022110
20022111
FIGURE 2. Basic Comparator
20022112
20022113
FIGURE 3. Inverting Configured Comparator LM397
L
M
3
9
7
www.national.com 5
Application Notes (Continued)
Input Stage
The LM397 has a bipolar input stage. The input common
mode voltage range is from 0 to (V
S
1.5V).
Output Stage
The LM397 has an open collector grounded-emitter NPN
output transistor for the output stage. This requires an exter-
nal pull-up resistor connected between the positive supply
voltage and the output. The external pull-up resistor should
be high enough resistance so to avoid excessive power
dissipation. In addition, the pull-up resistor should be low
enough resistance to enable the comparator to switch with
the load circuitry connected. Because it is an open collector
output stage, several comparator outputs can be connected
together to create an ORing function output. With an open
collector, the output can be used as a simple SPST switch to
ground.The amount of current which the output can sink is
approximately 10mA. When the maximum current limit is
reached, the output transistor will saturate and the output will
rise rapidly (Figure 4).
20022107
FIGURE 4. Output Saturation Voltage vs. Output Sink
Current
L
M
3
9
7
www.national.com 6
SOT23-5 Tape and Reel Specification
Tape Format
Tape Section # Cavities Cavity Status Cover Tape Status
Leader (Start End) 0 (min) Empty Sealed
75 (min) Empty Sealed
Carrier 3000 Filled Sealed
1000 Filled Sealed
Trailer (Hub End) 125 (min) Empty Sealed
0 (min) Empty Sealed
TAPE DIMENSIONS
20022115
8mm 0.130
(3.3)
0.124
(3.15)
0.130
(3.3)
0.126
(3.2)
0.138 0.002
(3.5 0.05)
0.055 0.004
(1.4 0.11)
0.157
(4)
0.315 0.012
(8 0.3)
Tape Size DIM A DIM Ao DIM B DIM Bo DIM F DIM Ko DIM P1 DIM W
L
M
3
9
7
www.national.com 7
SOT23-5 Tape and Reel Specification (Continued)
REEL DIMENSIONS
20022116
8mm 7.00
330.00
0.059
1.50
0.512
13.00
0.795
20.20
2.165
55.00
0.331 + 0.059/0.000
8.40 + 1.50/0.00
0.567
14.40
W1 + 0.078/0.039
W1 + 2.00/1.00
Tape Size A B C D N W1 W2 W3
L
M
3
9
7
www.national.com 8
Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
5-Pin SOT23
NS Package Number MF05A
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONALS PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Email: support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +44 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Franais Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
www.national.com
L
M
3
9
7
S
i
n
g
l
e
G
e
n
e
r
a
l
P
u
r
p
o
s
e
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
C
o
m
p
a
r
a
t
o
r
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
This datasheet has been download from:
www.datasheetcatalog.com
Datasheets for electronics components.
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Astm-A707 CS As LTS PDFDocument5 pagesAstm-A707 CS As LTS PDFGoutam Kumar DebNo ratings yet
- f094 PDFDocument4 pagesf094 PDFAnshuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Sound AttenuatorsDocument24 pagesSound Attenuatorsadeel_akhtarNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- Coiled Tubing For Downhole ProcessDocument10 pagesCoiled Tubing For Downhole ProcessCristian BarbuceanuNo ratings yet
- L Uk SulphDocument24 pagesL Uk SulphypyeeNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Part Ii - Particular Technical Specifications Chapter 13 - Permanent Access Bridge 13. PERMANENT ACCESS BRIDGE........................................................ 13-1Document11 pagesPart Ii - Particular Technical Specifications Chapter 13 - Permanent Access Bridge 13. PERMANENT ACCESS BRIDGE........................................................ 13-1Anonymous KHIyWRIWmaNo ratings yet
- LM2907 LM2917 Conversor F - VDocument18 pagesLM2907 LM2917 Conversor F - VAlejandra Vasquez GiraldoNo ratings yet
- NOx Control of Kiln and Preheater Complete AnalysisDocument129 pagesNOx Control of Kiln and Preheater Complete AnalysisAnonymous sfY8T3q0100% (2)
- LM397MF Comparador 6 Pines PDFDocument8 pagesLM397MF Comparador 6 Pines PDFAndres AlegriaNo ratings yet
- LM311Document23 pagesLM311Brzata PticaNo ratings yet
- LM392Document6 pagesLM392Brzata PticaNo ratings yet
- LM111-N/LM211-N/LM311-N Voltage Comparator: FeaturesDocument30 pagesLM111-N/LM211-N/LM311-N Voltage Comparator: FeaturesJuan GomezNo ratings yet
- Adjustable Voltage and Current Regulator: DescriptionDocument12 pagesAdjustable Voltage and Current Regulator: DescriptionAnghelescu CristinaNo ratings yet
- LM324 OpampDocument9 pagesLM324 OpampYuvarajaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet L298 PDFDocument13 pagesData Sheet L298 PDFbaymax love spideyNo ratings yet
- LM1117Document12 pagesLM1117George ArambuloNo ratings yet
- Low Dropout Positive Regulator DatasheetDocument9 pagesLow Dropout Positive Regulator DatasheetiammiaNo ratings yet
- TSM 101Document15 pagesTSM 101thiemncNo ratings yet
- OpAmp - LF451Document8 pagesOpAmp - LF451Ludwig SchmidtNo ratings yet
- LM2586 Simple Switcher 3A Flyback Regulator With Shutdown: General Description FeaturesDocument29 pagesLM2586 Simple Switcher 3A Flyback Regulator With Shutdown: General Description FeaturesJonny JohnNo ratings yet
- Low Power Quad Voltage Comparators: LM139, A LM239, A - LM339, ADocument11 pagesLow Power Quad Voltage Comparators: LM139, A LM239, A - LM339, Alinguyen1No ratings yet
- LMD18201 3A, 55V H-Bridge: General DescriptionDocument8 pagesLMD18201 3A, 55V H-Bridge: General DescriptionNairo FilhoNo ratings yet
- Application Note AN4121: Design of Power Factor Correction Circuit Using FAN7527BDocument22 pagesApplication Note AN4121: Design of Power Factor Correction Circuit Using FAN7527BRicardo VieiraNo ratings yet
- Variatore Di TensioneDocument12 pagesVariatore Di Tensioneconti51No ratings yet
- L298 Dual Full-Bridge Driver IC for Motors and RelaysDocument12 pagesL298 Dual Full-Bridge Driver IC for Motors and RelaysBastian RamadhanNo ratings yet
- LM338KDocument14 pagesLM338KBernardo Gomez JuarezNo ratings yet
- LM139, A LM239, A-LM339, A: Low Power Quad Voltage ComparatorsDocument9 pagesLM139, A LM239, A-LM339, A: Low Power Quad Voltage ComparatorsRicardo Teixeira de AbreuNo ratings yet
- LM78S40 Universal Switching Regulator Subsystem: General Description FeaturesDocument9 pagesLM78S40 Universal Switching Regulator Subsystem: General Description FeaturesgusguicorNo ratings yet
- 2.5A Power Switching Regulator: DescriptionDocument16 pages2.5A Power Switching Regulator: Descriptionbikram9830No ratings yet
- Low Power Energy Harvester IC From Linear Technologies - LTC3108Document22 pagesLow Power Energy Harvester IC From Linear Technologies - LTC3108shawnleegabrielNo ratings yet
- LM-339 Data SheetDocument11 pagesLM-339 Data SheetThorik AchsanNo ratings yet
- 1.5A Power Switching Regulator: DescriptionDocument16 pages1.5A Power Switching Regulator: DescriptionPravin MevadaNo ratings yet
- LTC1073fa DatasheetDocument16 pagesLTC1073fa DatasheetKushal KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Boost Controller With Power Factor CorrectionDocument14 pagesBoost Controller With Power Factor CorrectionChiseledPrawnNo ratings yet
- LM393, LM393E, LM293, LM2903, LM2903E, LM2903V, NCV2903 Low Offset Voltage Dual ComparatorsDocument10 pagesLM393, LM393E, LM293, LM2903, LM2903E, LM2903V, NCV2903 Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparatorssam2No ratings yet
- Motor Controller Data SheetDocument13 pagesMotor Controller Data Sheetapi-284769767No ratings yet
- LM331 VFCDocument15 pagesLM331 VFCfmsanturioNo ratings yet
- LM10 Operational Amplifier and Voltage Reference: General DescriptionDocument19 pagesLM10 Operational Amplifier and Voltage Reference: General DescriptionMario SbampatoNo ratings yet
- UC3842 current mode controller application noteDocument7 pagesUC3842 current mode controller application noteCui BapNo ratings yet
- 1A Step-Down LED Driver Data SheetDocument12 pages1A Step-Down LED Driver Data SheetselocaNo ratings yet
- l200 AppDocument13 pagesl200 AppZoran TesinovicNo ratings yet
- LM 200Document13 pagesLM 200dulocoNo ratings yet
- H1000e I Ema-Emc PDFDocument4 pagesH1000e I Ema-Emc PDFNguyen Van ChungNo ratings yet
- lm2907 PDFDocument20 pageslm2907 PDFArieNo ratings yet
- LM3914 Dot Bar Display Driver GuideDocument16 pagesLM3914 Dot Bar Display Driver GuideHelton AmorimNo ratings yet
- lm331 PDFDocument21 pageslm331 PDFOsvaldo Dominguez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- LM2907Document21 pagesLM2907leorio88No ratings yet
- Datasheet l298bDocument14 pagesDatasheet l298bgioganNo ratings yet
- LM393 DDocument10 pagesLM393 DPardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Tda 2593Document6 pagesTda 2593Luis Arturo Leiva MonjarasNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument8 pagesData SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument16 pagesData SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- 3.3 V Ecl/Pecl/Hstl/Lvds: ÷2/4, ÷4/5/6 Clock Generation ChipDocument12 pages3.3 V Ecl/Pecl/Hstl/Lvds: ÷2/4, ÷4/5/6 Clock Generation ChipΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument19 pagesData SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Datasheet TL082 PDFDocument11 pagesDatasheet TL082 PDFJavier RenanNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 1Document17 pagesData Sheet 1ΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Types MC and MCN Multilayer RF Capacitors High-Frequency OptionsDocument9 pagesTypes MC and MCN Multilayer RF Capacitors High-Frequency OptionsΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Types MC and MCN Multilayer RF Capacitors High-Frequency OptionsDocument9 pagesTypes MC and MCN Multilayer RF Capacitors High-Frequency OptionsΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Axial Leads/Spinguard: General DescriptionDocument6 pagesAxial Leads/Spinguard: General DescriptionΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument9 pagesData SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- LM1117Document21 pagesLM1117dipankaborahNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument4 pagesData SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- TC1072 50ma Cmos Ldo With Shutdown, Error Output and V BypassDocument12 pagesTC1072 50ma Cmos Ldo With Shutdown, Error Output and V BypassΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- CD 4023Document12 pagesCD 4023giorgio19741No ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument12 pagesData SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument6 pagesData SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Patented : SM6S10 Thru SM6S36ADocument5 pagesPatented : SM6S10 Thru SM6S36AΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument4 pagesData SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- DMTH6004SPS: 60V 175°C N-Channel Enhancement Mode Mosfet PowerdiDocument7 pagesDMTH6004SPS: 60V 175°C N-Channel Enhancement Mode Mosfet PowerdiΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- VN0610LL FET Transistor: N Channel - EnhancementDocument4 pagesVN0610LL FET Transistor: N Channel - EnhancementΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- AX97 Series: SMD Power InductorsDocument3 pagesAX97 Series: SMD Power InductorsΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument16 pagesData SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- 54ACT283 4-Bit Binary Full Adder With Fast Carry: General Description FeaturesDocument8 pages54ACT283 4-Bit Binary Full Adder With Fast Carry: General Description FeaturesΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
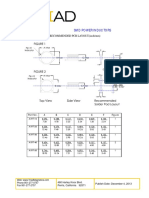
- Wall Plug Ins Electrical SpecsDocument1 pageWall Plug Ins Electrical SpecsΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNo ratings yet
- 8K Microwire Compatible Serial EEPROM: 93AA76A/B/C, 93LC76A/B/C, 93C76A/B/CDocument26 pages8K Microwire Compatible Serial EEPROM: 93AA76A/B/C, 93LC76A/B/C, 93C76A/B/CΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣ100% (1)
- DB2 WebSphere BestPracticeDocument53 pagesDB2 WebSphere BestPracticeSpeedyKazamaNo ratings yet
- Categoria ApiDocument61 pagesCategoria ApiHector MARTINEZ DEL ANGELNo ratings yet
- Cava v6 1x Install enDocument29 pagesCava v6 1x Install enWael SalahNo ratings yet
- Notice No.8: Rules and Regulations For TheDocument40 pagesNotice No.8: Rules and Regulations For TherickNo ratings yet
- IEEE Modeling of Generator Controls For Coordinating Generator Relays Draft 4.0Document65 pagesIEEE Modeling of Generator Controls For Coordinating Generator Relays Draft 4.0Alex PANo ratings yet
- Cable Memebres ProfiledirectoryDocument5 pagesCable Memebres ProfiledirectoryMigration Solution100% (1)
- University Institute of Information Technology: Ouick Learn - MCQDocument53 pagesUniversity Institute of Information Technology: Ouick Learn - MCQvimalNo ratings yet
- Acetylated Castor Oil - Preparation and Thermal DecompositionDocument7 pagesAcetylated Castor Oil - Preparation and Thermal DecompositionPee Hai NingNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 - Questioning - Written Assessment: Satisfactory or Not YetsatisfactoryDocument38 pagesAssessment 1 - Questioning - Written Assessment: Satisfactory or Not YetsatisfactoryAbhishek Kumar0% (1)
- Netsys NVF-200EKIT User Guide 1.0.6Document19 pagesNetsys NVF-200EKIT User Guide 1.0.6pkramellaNo ratings yet
- USBN Bahasa Inggris 2021Document6 pagesUSBN Bahasa Inggris 2021Indah timorentiNo ratings yet
- VELUXDocument16 pagesVELUXEko SalamunNo ratings yet
- Hdpe Alathon H5520 EquistarDocument2 pagesHdpe Alathon H5520 EquistarEric Mahonri PereidaNo ratings yet
- 02 - Heat ExchangersDocument88 pages02 - Heat ExchangerssanjaysyNo ratings yet
- Tivizen Iplug Greek GuideDocument13 pagesTivizen Iplug Greek GuideDenexoNo ratings yet
- Mount EFS Across VPCs and Availability ZonesDocument12 pagesMount EFS Across VPCs and Availability Zonesbiswajit patrasecNo ratings yet
- Active Front EndDocument5 pagesActive Front EndDaleel LillaNo ratings yet
- Manual Akaso V50 XDocument44 pagesManual Akaso V50 XLucas T. CavalcantiNo ratings yet
- VP R&D/VP QualityDocument3 pagesVP R&D/VP Qualityapi-79326007No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 XXXDocument8 pagesChapter 1 XXXChristelle Mary Sabile SabanalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Solution All Year First Part Ioe NotesDocument31 pagesEngineering Drawing Solution All Year First Part Ioe Notesई. सन्तोष शर्माNo ratings yet
- Maximo Sandbox SettingsDocument6 pagesMaximo Sandbox SettingsChandra SekharNo ratings yet