Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Microbiology
Uploaded by
Osama Bakheet100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
166 views35 pagesMicrobiology includes bacteriology, virology, mycology, immunology. Parasitology - it is the science to deal with the resistance of the body to any foreign substance.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMicrobiology includes bacteriology, virology, mycology, immunology. Parasitology - it is the science to deal with the resistance of the body to any foreign substance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
166 views35 pagesBasic Microbiology
Uploaded by
Osama BakheetMicrobiology includes bacteriology, virology, mycology, immunology. Parasitology - it is the science to deal with the resistance of the body to any foreign substance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 35
Basic Microbiology
Micro biology: It is science dealing with the study of
minute microorganism. Microbiology included bacteriology,
virology, Mycology, immunology.
Bacteriology:
It is science to deal with the study of the bacteria.
Virology:
It is science to deal with the study of the virus.
Mycology:
It is science to deal with the study of fungi.
Immunology:
It is the science to deal with the resistance of the body to
any foreign substance.
Parasitology It is the science to deal with Parasites.
Bacteriology:
Bacteria: It is unicellular microorganism capable of living
independently performing all the physiological function
essential for life as it contains all enzymes to perform vital
activity. It is proaryotes ! reproduce by binary fission what is
the type of cells depends on structure:
"# Proaryote.
$# %uaryote.
Proaryote cells %uaryote cells
&as primitive nucleus.
Multiply by binary
fission.
&as no nuclear
membrane.
'he ()* is one set of
single circular
&as true nucleus.
Multiply by mitosis.
&as nuclear membrane.
(ouble set of
chromosome inside the
"
chromosome of double
standard ()* in the
cytoplasm.
&as no organelles .
Include bacteria,
+icttsia, ,hlamydia !
Mycoplasma.
nuclear membrane.
&as organelles
-ungi ! protozoa.
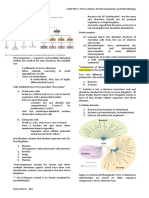
Morphology of bacteria
.hape arrangement size
/"0 .hape :
'he bacteria is characterized by different shape and size
/ Pleomorphism0 . .o to determine the shape of bacteria must be
during the lonarithmic phase of growth.
/a0 ,occi :
Means coccus i e spherical or oval or avoid.
%1ample :
.taphylococcus bacteria .
.treptococcus bacteria.
/b0 Bacilli or Bacillus :
Means stic lie . it2s length is more than breadth .
%1ample :
Bacillus bacteria.
,lostridium bacteria.
/c 0 ,occobacilli :
%1ample
,oryne bacteria, %scherichia coli.
/d0 .piral bacteria :
'he simplest form is coma shape:
$
%1ample
3ibreo cholea.
/e0 .pirullum:
)on fle1uous rod, spiral .
/f0 .pirocheates :
.piral but fle1uous move by a1ial filament.
/g0 long filamentous branched rod :.
%1ample:
*ctinomycetes
############################################################################
/B0 *rrangement / ,ell *ggregates 0 :
# 4hen the bacteria reproduce by binary fission without
separation form cell aggregates.
# 'he shape of cell aggregates or the arrangement depend on
o )o. of division
o Plane of division.
,occi
(iplococci
.ingle divistion ! single plane of
division e.g. )isseria ! pneumococci.
'efrad
5 group due to double division ! double
plane of division . e.g. Micrococcus.
.arcina
6 group dut to plane ! number of
division. .
.treptococci
chain
.ingle plane of division ! more than
one number of division from chain
77777
.taphylococci
More than ome division ! more than
plane of division.
8
Bacilli
(iplobacilli : e.g. Klebsiella, B. anthacoides.
.ingle or separately arranged . e.g. salmonella
.treptobacilli e.g. B. anthraces.
,hinese letter arrangement: v or 9 letter.
e.g. Corynebacteria diphtheriae .
#########################################################################
/, 0 .ize :
Bacteria is measured by micron.
Microne is the unite of measurement
: " millimeter
";;;
4hile nanometer / millimicron 0 : "
";;;
*ngestron : " millimicron # for virus
&ow to measure the bacterial size <
"# 7ccular and stage micrometry.
$# %lectron microscope.
8#Photographic method
# ,occi is " in bacilli vary =5> to =6> by " to ".? micron
5
Mesosome )ucleus
cytoplasm
+ibosomes metachromtic
@ranule /volatin0
.lime layer capsule cell membrane granules or
inclusion
cell wall
?
The bacterial structure is classified in to :
%ssential *ccessory
-ound in all bacteria may be found or not
# ,ell wall # ,apsule
# ,ell membrane # .lime layer.
# ,ytoplasm or protoplasm # .pores
# )ucleus of nuclear material # -lagella
/ ,hromatin material 0 # *1ial filament
# Pilli
# Metachromtic
granules.
Capsule :
.ome bacteria has capsule or not / called capsulated bacteria or
not 0.
7thers has capsule ! slime layer while others contain
capsules only.
It is gelatinous material compose of 9ipopolysaccharde or
protein as in B. anthraces or glycoprotein .
)ot stained e ordinary stain or appear as halos around the
organism but accept stain with capsular stain = Indian in >
and negative stain .
Function :
"# protection against phagocytosis /antiphagocytic function0
for virulence.
$# Protection from dryness / loss of water ! nutritive
substance0.
8# ,arry / capsular *g 0 / A 0 .
5# &elp in diagnosis because is high specific chemically !
immunologically ! thus allow for type differentiation as
B
in case of Macfadean reaction B. anthracis , Cuelling
reaction pneamococci .
Slime layer :
Is loose soluble layer chemical structure as capsule but the
water contents is high . 'his colloidal substance gives surface
colonies a mucoid appearance as in lebseilla.
.
Cell Wall :
Bacteria have well defined cell wall in compare with euaryote.
It is non living rigid consider as e1oseleton.
'he bacteria are classified into gram positive ! gram
negative bacteria . according to the structure of cell.
!" #ram positi$e bacteria :
* thic layer of peptidoglycan /?;#B;D0 of the cell wall
content0 E teichoic acid /acidic polysaccharide0. .o the bacteria
accept the crystal violet not decolorize by ethyl alcohol because
the stain in integrate in the cell.
%" #ram negati$e bacteria :
* thin layer of peptidoglycan /?#$;D0 of cell wall and
another membrane are made up of lipids, lipopolysaccharide
/9P.0 ! Protein lipopolysacharide is a harmful substance
classified as an endoto1in .
#ram&s stain : consist of :
"# ,rystal violet / primary#"ry stain 0 gram positive tae
violet
$# @ram iodine/mordant0.
8# %thyl alcohol . / decolourization 0
5# ,arbol fuschin / counter stain 0 gram negative tae pin
color .
F
Function of cell 'all :
"# *ct as e1oseleton.
$# (etermines the shape.
8# *llow the classification of bacteria into gram positive and
gram negative.
5# Protection to the cell from rupture e g. due to change in
pressure /rigidity0.
?# ,arry somatic /7 *g0 which is importance in virulence.
Flagella :
(efinition: whip lie process, mae of flagellin protein
/contractile protein0 resemble to myosin protein in muscle,
originates from the cytoplasm.
# 4hen it beats bacward, the bacteria move forward.
# It can be seen e electron microscope.
Function:
"# It is responsible for motility.
$# It is carry & antigen.
8# I. m in identification.
-lagella are of great practical I . m to bacteriology since specific
antisera can be prepared ! used for serological differentiation.
6
(istribution and number of flagella:
Bacteria
Motility:
)on motile bacteria motile bacteria
Brownian Movement 'rue movement
/ -alse movement 0
Method of detection of motility:
G
*trichate
no flagella
e.g. B. anthracis
,orynebacteria.
Monotrichate
7ne flagella at " pole
e.g3ibrio cholera
9ophotrichate
tuft of flagella
In both pole or one pole
%1. Pseudomonas
aeruginosa
*mphitrichate
'wo flagella at both
Pole
e.g. 3. parahemolytica
Peritrichate
%scherichia coli
%.coli
'richate
)ot true , due to molecules in
the liCuid stricing an obHect !
causing obHect to be vibrate at
about the same rates !
maintain their relative position.
'he body contraction or
a1ial filament .
%.g. spirachaetes.
-lagella
)B : Move from one position to another
"#(ar field microscope.
$#Phase contrast microscope.
8#4et mount method.
5#&anging drop techniCue.
Pilli or fimbria:
(efine: short hair lie structure arising from cytoplasm
made up of protein, shorter than flagella.
# Present in some gram negative bacteria e.g. %.coli or
)eisseria gonorrhoea.
-unction :
a0 *ttachment to each other, or attachment to host cells.
b0 -or transfer of genetic material from one cell to
another where they are able to be specialized pilli
called se1 pilli. /-.pilli0.
#############################################################################
Spores not in all bacteria "
4hen conditions for vegtative growth are not favourable,
bacteria of the genera Bacillus and ,lostridium are able to
survive by forming resistance endospore.
'hese spores are able to with stand cold, heat dehydration,
or the action of disinfectants . * spore is unable to
multiply , but when condition for vegetative growth
return , it is able to produce bacterial cell which is capable
of reproducing.
.pore is not stained e ordinary stains as it appear as halos
around the organism. It tae special stain called schaeffer
fulton / malchite green 0 or (orner method.
";
Malchite green E heat the spore/ green 0 ! the bacteria /Pin0
*lso modified Iiehl )eelsen stain in to we decolourize e ;.?D
&
$
.7
5
spore appear pin ! the body of bacilli blue.
Type and position of spores :
.hape Position bulged or
.pherical central non bulged
7val or ovoid subterminal
'erminal
e.g. clostridium tetani drumstic spore / .pherical , terminal
and proHected 0.
-unction :
"# Protection of the bacteria from unfavorable condition.
$# I.m in identification of bacteria .
e.g. B . subtilis with stand radiation , J3 light , boiling at
"$;, for "? minute.
Formation of spore :
'he cell is divided by septum into two uneCual cell. 'he larger
one is called Kmother cellK and the daughter cell. *nd the
mother cell is surrounded the spore.
""
*1ial filament : rotates giving a twisting and fle1ing movement
Cell membrane :
Formation :
# It is formed due to condensation of cytoplasm toward
outside.
# It is formed of a lipid bilayer with protein embedded in
between.
(efine :
It is semi permeable membrane found in all bacteria formed of
phospholipids and protein.
Function :
"# It is the active part of bacterial cell function for
proaryotes instead of organelles in euaryotes.
$# It is the place of metabolic ! enzymatic activities e.g.
respiration /transport energy e transport system 0.
8# ,ontrol the entry electrolytes , water ! transport of
nutrients into the cell via carrier protein / transport protein
permease 0 .
5# %1it of wastes out of the cell.
Mesosomes: are folding up of cell membrane into finger lie
protrusions or pocets that e1tend to cytoplasm. * place where
chromosome is a attached during replication.
Cytoplasm or protoplasm :
"$
Internal content of cell gelatin lie solution made up of
mainly water E nutrient / sugar , a a , salt L.0 .
4ithin cytoplasm :
Chromatin )ucleod":
@enetic material is made up of a single circular strand of
()* called the chromatin and no nuclear membrane / no true
nucleus 0. 'he area in which ()* concentrated is called
nucleoid.
Function :
,arry information for function and survival of cell.
*ibosomes :
-unction : Place for protein synthesis .
Made up of $ unit protein E r +)*
It give the cytoplasm of bacteria a granular appear .
#ranules Inclusions " :
-unction : to store different types of nutrient and consume them
when nutrients are not available in the environment .
.tored nutrient as : %nergy rich organic compound .
e.g. glycogen / .tored glucose 0
sulfur granules phosphate.
Metachromatic granule $olatin "
-ound due to abnormal metabolic or it is stored nutrient. It
is scattered in cytoplasm as in case of ,orynbacterium diphteria
or in both poles of cell / Bipolarity0 Pasteurella. .tained e
special stain -unction identification.
Main Protoplasmic compounds+
Carbohydrates ,ipids Proteins )ucleic
Composition
building
bloc-"
Simple sugars
. amino group
found as
Triglycerides
of F+/
phosphors in
a+ a+ )ucleotides
comple0
combination
"8
*ol+c in the cell
#lycogen
Stored
glucose"
Cell 'all
synthesis
1ssential
energy source
phospholipids
Cell membrane
1nergy source
2 1n3ymes
2 Synthesis of
organelles .
other cell
structures
'ith protein
)ucleoproteins"
2 ()/ :
Code for cell
function .
structure
20
Bacterial Cell &
Nucleiod DNA Ring
DNA replication
Cell wall synthesis
Cell separation
'ransverse Binary -ission
a0 Parental cell .
"5
b0 ,ell elongation size enlarged walls chromosome.
(uplication E attached to mesosomes.
c0,ell wall septum grow inwards , chromosomes move to
opposite ends. .eptum formation E chromosome separate from
mesosomes.
d0 'wo identical daughter cells.
Phases of #ro'th :
5 Phases :
"# 9ag phase
$# 9og phase .
8# .tationary phase .
5# (eath phase.
!2,ag phase :
Bacteria are first introduced into an environment or media.
Bacteria are checing out their surrounding.
,ell are v . active metabolically.
)o of cells changes v. little / does not increase 0.
I hr to several days according to type of bacteria media and
accommodation of the bacteria.
%2 ,og phase :
"?
+apid cell growth / e1ponential growth 0 .
Population doubles every generation.
Microbes are sensitive to adverse condition . eg. *ntibiotic
! antimicrobial agents.
42 Stationary phase :
(eath rate : rate of reproduction .
,ells begin to encounter environmental stress .
9ac of nutrient ! &
$
7 , metabolic wastes ! spore form
now.
(eath phase
1SS1)TI/, 1,1M1)TS
)11(1( F5* B/CT1*I/, #*5WT6
%9%M%)'. +79%
I 0 %lements needed
for synthesis of
structural components.
II0 %lements needed
for cellular function
/mineral salts 0
III 0 'race elements
/ needed in minute
Cuantities.0
,
"
&
$
7
$
)itrogen phosphorus.
A
"
Mg
"
-e
,a
,opper ,obalt
Maganize In
.ynthesis of : sugars
amino acids , lipids,
nucleic acid.
a.a. E nucleic acid *'P
nucleic acid
phospholipids.
*ctivation and
function of certain
enzymes.
%nzyme activity spore
formation.
*ctivation of enzymes.
"B
I30 @rowth factors
/ earn it be synthesized
by the cell 0
3itamines purine
pyrimidine
Precursors of nucleic
acid / ()* 0
Factors affecting microbial gro'th :
1n$ironmental Conditions :
!2 Temperature :
'emperature affect microbial growth and structure , especially it
affects enzymes. 'here groups of M.7 according to temperature
reCuirements.
a. Psychrophiles : # ?, $?, .
b. Mesophiles : between $? 5?,
c. 'hermophiles between 5?, F; "";,
%2 #ases :
a 71ygen gas /7
$
0
-our groups according to 7
$
. reCuirements :
i0 .trict anaerobes : 7
$
is to1ic .
7rganism die in presence of 7
$
. not contain catalase nor
supreo1ide mismutase
ii0 .trict aerobes : 7
$
is a must if 7
$
is absent organisms
die$;D, contain catalase.
iii0 -acultative anaerobes: ,an live in the presence or absence of
7
$
.contain catalase ! supero1ide dismutase.
iv0 Microaerophilic: +eCuire little amounts of 7
$
to grow /$#
";D0 contain supero1ide dismutase.
b# ,arbon dio1ide gas : ,7
$
*ll bacteria need little amounts of
,7
$
to grow . Bacteria produce the ,7
$
as end product of
"F
metabolisms / carbo1yphilic organism can live in presence of
carbon dio1ide 0 .
42 6ydrogen Ion concentration p60 :
p& affects the reproduction of M.7 maHority lives at neutral
p&:F neutrophiles .
# .ome grow at low p& 8#? M.7 . are called
*,I(7P&I9%.. 9actobacilli.
# .ome grow at high p&: 6#G M M.7 are called *9A*97
P&I9%..
72 5somotic pressure :
'he pressure e1erted on cell membranes due to flow of water
/ from less solute concentrated to more concentrated solute0
across a concentration gradient.
Microorganisms prefer a slight hypotonic or isotonic
solution, concentration of ;.6?D )a,l K)ormal .alineK .
In hypertonic solution: the bacteria shrinage and dryness.
In hypotonic solution :the bacteria rupture and burst.
T1*MI)5,5#8 :
.terilization :
'he complete illing of all forms of living organisms
including bacterial spores.
(isinfection :
'he Ailling of pathogenic microorganisms from obHects.
(isinfectant :
* chemical agent used to destroy pathogens on non living
obHects. .
*ntiseptic:
"6
* chemical substance / disinfectant 0 used to destroy m.o
that is safe to use on living tissues.
*sepsis:
*bsence of pathogenic m.o on living tissues.
.anitization:
+educe the )o of M.7 on obects and from environment to
a safe level accepted by public health organization / .anitary
condition 0 .
.uffi1es : *dded at the end of words.
,idal : is added when a illing action is meat e1:
Bactericidal.
.tatic : Is added when the organism is inhibiled from
multiplication . %1. Bacteriostatic .
P68SIC/, M1T65(S 5F C5)T*5,
Method 7bHect sterilized
(ry &eat :
a0 &ot *ir oven
"B;, for " "N$ hours "6;,
b0 Incineration :
-ire temperature O 8;;, .
c0 -laming
@lass ware , metals, intruments.
(estroy not need obHects as dead
bodies and turn them to ashes.
"G
d0 +ed hot method
Most &eat :
*bove ";;,
a0 *utoclave :
"$", for "?min pressure "?
pound Ninch
$
Below ";;, vaccine
B;,N" hr.
b0 Pasteurization :
B8, for 8;min / 9'&'0
F$, for "? .ec /&'.'0
68, mommentery
/ flash 0
# metal /scissor scalpel !
mouth of test tube ! -las0.
platinum loop platinum wire.
.urgical dressing, metallic
instruments, gowns any articles
not heat sensitive, fluids .
Media not contain /mil
gelatin sugar0
3accine
Aill pathogens in mil and other
fluids as Huices.
*t ";;, :
# boiling.
# 'yndallization : ";;, intermittent for 8 successive .
# .teaming days for sterilization of media /.ugar , mil
gelatin0.
%2 Filtration :
,ellulose acetate membrane filter heat sensate pore size : ;.$M /
for bacteria 0
uses: liCuids as : .erum , sugar sol protein
-iltration :
Physical removal of microorganisms from liCuids and air.
It does not ill microorganism.
$;
-luid / *ir or liCuid 0 are allowed to pass through fine
filters with pores that permit ant passage of fluid but traps M.7
filters include cellulose acetate membrane filters.
,ellulose acetate membrane filters made of various pore sizes
ranging from 6mm E; ;.$? m. Pore size of ;.$$m is effective
for removing bacteria, however some viruses and mycoplasma
can pass through it.
*pplications:
.terilize heat sensitive liCuids as serum sugars , drugs and
proteins.
.eparate drugs and proteins.
-ilter air to remove airborne contaminants .
.artorius membrane filter syringe filter .eitz.
Jltrasonic cleaners : Mechanical cleaning very high freCuency
sound waves super and ultra sonic . It creates strong .
*adiation :
%nergy in the form of electromagnetic waves and particles
that are transmitted though space.
P Mode of action :
(amage to ()* causing damage death or mutation.
*lso can from free radicals / 7&
#
E &7
$
0 which are to1ic to
cells.
'wo types of +adiation :
Ionizing radiation 6#rays , Q#rays with short /0 wave length ,
high energy strong penetration power. Jsed to sterilize heat
sensitive items.
$"
*s: *ntibiotics , drugs , tissue grafts , vaccines , +ubber gloves,
plastic products as petri#dishes, syringes, catheters .. ,anned
food, -resh meat , poultry.
)onionizing : J. 3 . light :
&as moderate /0 , low penetration power used for disinfection
of smooth surfaces , air ..
+eduction of M.7 of air in clinics hospitals , industry ,
food catering areas. -ood storage areas.
%1. @ermicidal 9amp
Chemical /gents used
To control microorganisms+
*ntiseptic and disinfectants :
"# *lcohols .
$# &alogens
8# &eavy metal ions K Mercuric compounds silver nitrate eye
dropsK.
5# Phenolic compounds .
?# (etergents . surface active agents.
B# *lylating agents.
F# (yes.
6# 71idizing agents . &ydrogen pero1ide / &
$
7
$
0.
G# *cid ! *lalies.
!2 /lcohols : / )ot effective in presence of organic matter0 :
%thanol E Isopropyl alcohol not effective against bacterial
endospore . Mainly used against vegetative bacteria, fungi and
most viruses .
Mode of action : ,ytoto1ic to morobial cell.
(isruption of cell membrane.
Jses :
# *ntiseptic at a concentration F;#F?D to disinfect the sin.
$$
# (isinfection of thermometers.
# (isinfection certain surgical instruments.
# )eedles and syringes by soaing but not much reliable.
$# &alogens : / 71idizing agents 0 :
,hlorine / cl0 , -luorine / - 0 , Bromine / Br0 Iodine /I0 not
effective in presence of 7.M.
Mode of action : Inactivate enzymes . 71idize cellular
components.
,hlorine :
Jsed as a disinfectant of water / ;.?#"ppm 0 swimming
pools. Jsed as a gas or liCuid from.
,&
$
E &
$
7 &ypochlorous acid .
# Bleaching agent in form of hypochlorite / ,l7
#
0 in ?;D
solution ac chloro1.
# (isinfecting hemodialysis material at a concentration soop
against hepatitis B virus.
(isadvantages : ,orrosive to metals E sin.
Iodine :
?D solution , used as an antiseptic for wounds.
# 'incture iodine / iodine E F;D alcohol 0 .
# Betadine / providine or iodophore0 where surface active
agents. *re added . very effective .
(isinfect : Patient2s sin before surgery . cleaning of wounds.
Bromine . Flourine: 'o1ic to humans used in little amount to
event dental caries.
42Phenolic Compounds : Bactericidal or bacteriostatic
depending on the concentration . But to1ic of corrosive to sin
gives brown stain.
*ction : ,oagulate proteins.
$8
%nzyme inactivation.
(isruption of cell membrane.
%ffective against vegetative bacteria including M. tuberculosis,
fungi and enveloped viruses.
(isinfectant of walls E floors .. / 9ysol , gresol 0 .
,hlorohe1idine : phenol derivative effective against gram
/Eve0 E /#ve0 bacteria added to soaps for hand washing
before surger.
&e1achlorophene effective against ..aureus but to1ic
Brain damage.
%ffective in presence of 7.M.
(etergents Surface acti$e agents " :
7rganic molecules which dissociate in water into anionic
or cationic molecules and these are germicidal. But some are
non ionic and these are not germicidal.
*ction : # (isrupt cell membrane activity .
# Bind to organic materials.
Main function is cleaning of surfaces by removing
microorganism and organic materials.
# Bactericidal against vegetative bacteria fungi E some
viruses / Ruternary ammoning compounds 0.
/l-ylating agents :
.terilizing agents :
*ction : *dd methyl or ethyl group to cellular molecules.
%specially alylating proteins and ()* )on functional .
%thlene o1ide : @as or liCuid or B propriolacton.
&igh penetration power.
3ery to1ic to human.
$5
Jsed as a chemosterilant for heat sensitive wrapped items :
+espiratory tubes
Plastics , heart pumps.
+ubber , I.3 catheters.
Instruments / delicate ones 0.
.terilization is done in a special chamber at B;, for "#"; hours .
-ollowed by deto1ification i.e. aeration for 565.
ii0 -ormaldehyde gas /8FD0
iii0 @lutaraldehyde gas /$D0
9ow penetration power , effective to :
disinfect rooms in hospitals / -umigation0.
.terilize inantmate obHects.
.terilize surgical instruments , tubing which are not
wrapped by glutaraldehyde which is more effective and
less to1ic than formaldehyde.
.terilization is run by seeing unwrapped items for ";#"$ hours.
/F0 (yes :
%.g. @entian violet .
,rystal violet.
@entian violet.
Brilliant green
Methylene blue.
# 'hey are slowly bactericidal .
# 'hey are used alone or incompination with other agents as
sin antiseptics.
9" 50idi3ing agents : e.g. &
$
7
$
A Mn7
5
/ Pot . Permenganate0.
M.7.* : o1idation of m.o
Jse antiseptic .
)ot act well in the presence of 7.M.
$?
:" /cid ; /l <alies :
M.7 . * : *ffect the hydrogen iron conc.
).B. Mycobacterium is e1treme resistant to p&
change.
e.g.
*cetic acid Benzoic acid / Preservative 0 9actic acid
.our mil.
Boric acid ! picric acid *ntiseptic of wound.
.odium hydro1ide ! Potassium hydro1ide use in soaps.
Salts of hea$y metals :
M.7.* : ,oagulate protein :
e.g.
.ilver nitrate
Mercurochrome *ntiseptic for sin ! mucous
mebrans.
Merthiolate Preservation of serum.
Iinc o1ide sin antiseptic .
*rsenical preparation for treatment of spirochaetosis !
syphoilis.
$B
/)TIMIC*5BI/, /#1)TS
Terminology ..
1 - Chemotheraputic agent: is any chemical substance
used to treat diseases .
2 - Antimicrobial agent: a chemical that inhibits the growth
or kills microorganisms .
3 - Antibiotic: a compound produced by certain bacteria or
molds to inhibit the growth or kills microorganisms .
4 - Bactericidal: an antimicrobial drug that kills bacteria .
5 - Bacteriostatic: an antimicrobial drug that inhibits the
growth of bacteria .
6 - Broad-spectrum antimicrobial: an antimicrobial agent
that is effective against a wide range of microorganisms ,
often against gram positive and gram negative organisms .
7 - Narrow spectrum antimicrobial: an anti microbial agent
that effective against a limited number of organisms .
e. ! gram "ve or gram #ve $ bacteria .
$F
Site of action of antibiotics on bacterial cell .
Side effects ( adverse effects (
1 - Allergic reaction : some people develop allergy or
hypersensitivity to certain antimicrobials .
they will have symptoms of fever rash and most serious
ANA%&'(AC)*C +&,C-. e... penicillin.s .
2 - )oic effects : some cause toic effects to certain parts
of body when used at high concentrations .
e...a- amino glycosides: can damage kidney , anemia ,
deafness .
$6
Sulfonamide : inhibit folic acid synthesis .
metabolism
Protein synthesis : !2 amino glycosides
2 - tetracycline&s .
3 - chloramphenicol .
Cell 'all synthesis :
1 - penicillins .
2 - cephalosporines .
3 - bacitracin .
Inhibit
peptidoglycan
synthesis
Cell membrane permeability
1 - polymixin-B
)ucleic acid
rifamycin
b- tetracycline.s : deposit in certain body tissues as
* /.I tract colitis, gastro intestine tract
diarrhea .
* liver damage to
hepatocytes .
* teeth " bones Broun discoloration to teeth among
children ! from birth 0 years .(
3 - suppression to the normal flora: normal flora might be
inhabit or kill the normal flora so specific bacteria will over
grow and cause disease e... antibiotic associated colitis .
Examples of antimicrobials
1 - %enicillins: produced from the mould called
) penicillium $. an antibiotic very effective against gram
positive bacteria and some gram negative bacteria .
+ome organisms especially +.aureus produce en1yme
penicinillase that become resistant to the antibiotic .
2erivatives include :
* penicillin /- effective against streptococci .
* penicillin v
* ampicillin .
* amoicillin .
* methicillin .
+ide effects: anaphylactic shock due to allergy , which
could be fatal within feus hours .
$G
) Haundice , fatty liver (
Broad spectrum
2 - cephalosporins: produced from the fungus
cephalosporium .
+everal derivatives eist called
e. .. cephradine . cephaclor. Cefiine ..
later generation :
bacteria .
3 - aminoglycosides : produced from bacteria
streptomyces .
+everal derivatives as. gentamycin streptomycin to
bramycin. +ide effects . very toic to kidney, and liver "
hearting lass .
3ffective against gram negative rods and some gram
positive bacteria .
Control of antibiotic resistance
1 - 2evelopment of new antibiotic so that there is a large
and epanding number of diverse antibacterial drugs .
2 - Antibacterial drugs should be administered at
therapeutic doses only for stable time .
3 - 2rugs combinations may over come the development
of chromosomal mutation to resistance or to plasmid #
mediated resistance e.g ..! clavulanic acid or sulbactum
resistance beta # lactamases (
4 - 2rugs use should be guided by antimicrobial
susceptibility test ! antibiotic sensitive test ( .
8;
@eneration cephalosporin2s .
*re more effective against gram negative
5 - )he development of wholly synthetic antimicrobial drugs
as fluoro4uinolones may also make naturally occurring
resistant populations less population .
5ethods for evaluation of antibiotic sensitivity ..
1 ( antibiotic sensitivity test !-irby-Bauer method (
a-tube dilution method .
b-agar diffusion test .
=Muller 6inton agar+
"0 *ntibiotic sensitivity test / Airby bauer Method 0
a0 'ube diluation method .
b0 *gar diffusion test.
a2Tube dilution :to determine minimal inhibitory conc MI,
.uitable to determine *b. level in body fluids.
b2/gar diffusion :
8"
synergism
*utonomy antagonist
*
*
*
*
B
B
B
B
'he media used : Mueller &inton agar which allows the
chemotherapeutic agent to diffuse freely.
Procedure:
". *septically cover the plate e the desired show swab
in three directions to ensure complete plate coverage.
$. .terilize forceps by dipping in alcohol ! burn off the
alcohol. 'hen obtain the discs ! place into the
surface of the agar. @ently tap the dis to ensure
better contact e the agar. Placing ?#B disc the same
distance apart.
8. Incubation at 8F, "6#$5 hours . Measure the zone
of inhibition in mm. using ruler according to the
clearance of the zone of inhibit and the diameter
indicate whether the m.o is sensitive, intermediate or
resistance.
T1*MI)5,5#8
,hemotheraputic agent: it any chemical substance used to
treat diseases.
*ntimicrobial agent: * chemical that inhibits the growth
or ills microorganisms .
*ntibiotic : * compound produced by ceria bacteria or
molds to inhibit the growth or ills microorganisms.
Bactericidal : *n antimicrobial drug that ills bacteria.
Bacteriostatic : *n antimicrobial drug that inhibits the
growth of bacher .
Broad spectrum antimicrobial : *n antimicro agent that
is effective against a wide range of microorganisms , often
against gram positive and gram negative organisms.
)arrow spectrum antimicrobial *n anti microbial agent
that is effective against a limited number of organism. %1.
@ram Eve or gram /#ve0 bacteria.
8$
+esistant an terminal.
side effects /d$erse effects " :
"# *llergic reactions : .ome people develop allergy or
hypersensitivity to certain antimicrobials. 'hey will have
symptoms of fever , rash and most serious
*)*P&S9*,'I, .&7,A . %1. Penicillins.
$# 'o1ic effects some cause to1ic effects to certain parts of
body when used at high concentrations.
*minogycosides : can damage idney anemia , deafness.
'etracyclines: deposite in certain body tissue as
o @ I'ract colitis, diarthoea.
o 9iver damage to hepatocytes.
o 'eeth E bones brown discoloration to teeth among
children from birth 6 years.
8# .uppression to the normal flora : )ormal flora might be
inhibit or ill the normal flora so specific bacteria will
over grow and cause disease e1. *ntibiotic accociCted
colities
%Q*MP9%. 7- *)'IMI,+7BI*9.
"# Penicillins : Produced from the mold P%),I99IJM . *n
antibiotic very effective against gram positive bacteria,
and some gram negative bacteria.
.ome organisms especially .. aureus produce enzyme
penicinillase that breas the structure of penicillin and become
resistant to the antibiotic.
(erivative include :
Penicillin @ %ffective against streptococci.
Penicillin 3
88
*mpicillin
*mo1icillin Broad spectrum
Methicillin
.ide %ffects : /*naphylactic shoc 0 due to allergy which could
be fatal within few hours.
$# ,ephalosporins: Produced from the fungus
cephalosporium several derivatives e1ist called ", $ , 8 ,
5 generation ,ephalosporins .
%1. ,ephradine, cephaclor, cefi1ine later generations /8 ,
5 0 are more effective against gram negative bacteria.
8# *MI)7@9S,7.I(%.: Produced from bacteria
.treptomyces. .everal derivatives as @entamycin
.treptomycin, tobramycin .
.ide %ffects : very to1ic to idney and liver E hearing loss.
%ffective against gram negative rods and some gram positive
bacteria.
Control of /ntibiotic resistance :
"# (evelopment of new antibiotics so that the is a large and
e1panding number of diverse antibacterial drugs.
$# *ntibacterial drugs should be administered at therapeutic
doses only for suitable time.
8# (rugs combinations many over come the development of
chromosomal mutations to resistance or to plasmid
mediated resistance e.g. / clavulanic acid or sulbactum
resistance to beta lactamases 0.
5# (rugs use should be guided by antimicrobial susceptibility
test.
'he development of wholly synthetic antimicron drugs as
fluoruCrinolones, many also mae naturally occurring resistant
populations less population
85
8?
You might also like
- FAQ in MicrobiologyDocument117 pagesFAQ in MicrobiologyVenkatesh Arumugam100% (1)
- Microbiology NotesDocument14 pagesMicrobiology Notesapi-264004571No ratings yet
- Microbiology MasterDocument13 pagesMicrobiology MasterDelixae Phoinix100% (6)
- Safe Blood: Purifying the Nations Blood Supply in the Age of AFrom EverandSafe Blood: Purifying the Nations Blood Supply in the Age of ANo ratings yet
- Man Meets Microbes: An Introduction to Medical MicrobiologyFrom EverandMan Meets Microbes: An Introduction to Medical MicrobiologyNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY, CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandBIOCHEMISTRY, CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Microbiology for NursesFrom EverandAn Introduction to Microbiology for NursesN. A. SimmonsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Microbiology ReviewDocument6 pagesMicrobiology ReviewStarlet Rhonadez Bito-onon OrielNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Outline of Microbiology, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Microbiology, Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pathology, Vector Studies, and CultureFrom EverandPathology, Vector Studies, and CultureJulius P. KreierRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesFrom EverandPractical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesNo ratings yet
- The Diverse Faces of Bacillus CereusFrom EverandThe Diverse Faces of Bacillus CereusVincenzo SaviniNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandMedical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Medical VirologyFrom EverandTextbook of Medical VirologyErik LyckeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in the Environment: Volume 1 in the Advances in Environmental Pollution Research seriesFrom EverandAntibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in the Environment: Volume 1 in the Advances in Environmental Pollution Research seriesMuhammad Zaffar HashmiNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument17 pagesMicrobiologyMompati Letsweletse100% (3)
- Microbiology NotesDocument3 pagesMicrobiology NotesAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Microbiology Lecture NotesDocument95 pagesMicrobiology Lecture NotesRabia Haider67% (3)
- Microbiology SummaryDocument9 pagesMicrobiology SummaryMargaretha IreneNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument108 pagesMicrobiologyHampson Malekano100% (1)
- Microbiology Exam II Fall 2001 Name: - Multiple Choice: Circle The Most Correct Answer For Each of The Following Questions. (2 Points Each)Document8 pagesMicrobiology Exam II Fall 2001 Name: - Multiple Choice: Circle The Most Correct Answer For Each of The Following Questions. (2 Points Each)Jini Luckie0% (1)
- MicrobiologyDocument57 pagesMicrobiologyAswin KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab Manual and GuideDocument117 pagesMicrobiology Lab Manual and GuideSelvaraju Parthibhan100% (1)
- MicrobiologyDocument45 pagesMicrobiologyStephen Niroshan Xavier67% (3)
- Chpater 1 MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesChpater 1 MicrobiologyRoma Blaise G FloresNo ratings yet
- Microbiology NotesDocument177 pagesMicrobiology NotesMarichu Rogas91% (11)
- Medical LaboratoryDocument5 pagesMedical LaboratoryvictorasaurasNo ratings yet
- Medical MicrobiologyDocument82 pagesMedical MicrobiologyAdithya100% (2)
- Morphology of Bacteria & Its CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesMorphology of Bacteria & Its CharacteristicsMonika Kshetri100% (2)
- Microbiology Mnemonics: Study Online atDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Mnemonics: Study Online atKriselda May Torio100% (1)
- MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesMicrobiologyWenxinn JCFNo ratings yet
- Micro Zoubi PDFDocument73 pagesMicro Zoubi PDFVims BatchNo ratings yet
- Basic MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesBasic Microbiologyslimann100% (4)
- Bacterial Flash Cards (Part 1 of 4)Document25 pagesBacterial Flash Cards (Part 1 of 4)Nafis Shamsid-DeenNo ratings yet
- Microbiology OPDocument1,309 pagesMicrobiology OPThư Phạm100% (2)
- PathologyDocument31 pagesPathologyStudy Usmle100% (1)
- MicroParaReviewer PDFDocument12 pagesMicroParaReviewer PDFEinah EinahNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument44 pagesMicrobiologyBonnie Hardy100% (1)
- Gram StainDocument5 pagesGram Stainادم PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Higher Secondary-First YearDocument140 pagesMicrobiology: Higher Secondary-First Yearwiranchana-na3014100% (3)
- Microbiology Exam 1Document10 pagesMicrobiology Exam 1Ryan67% (3)
- 116 - Disorders of HemostasisDocument13 pages116 - Disorders of HemostasisMuliyamanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lecture NotesDocument116 pagesMicrobiology Lecture NotesDodge StuffNo ratings yet
- Immunology NotesDocument26 pagesImmunology Notesmildred alidonNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids (Post Lab)Document56 pagesBody Fluids (Post Lab)Dorothy Silva-JameroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Microbiology 101Document14 pagesChapter 1 Microbiology 101Roma Blaise G FloresNo ratings yet
- How The Immune System WorksDocument13 pagesHow The Immune System Worksnishant nagyan100% (2)
- Reviewer in MicrobiologyDocument25 pagesReviewer in MicrobiologyMicole Manahan100% (1)
- Complete MicroBiology NOTESDocument55 pagesComplete MicroBiology NOTESrida100% (4)
- MicrobiologyDocument16 pagesMicrobiologymassom100% (1)
- Immunology NotesDocument27 pagesImmunology Notescomputerlois88% (8)
- Sterilization and DisinfectionDocument10 pagesSterilization and DisinfectiondrugdrugNo ratings yet
- 9Document13 pages9Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- New England Journal Medicine: The ofDocument12 pagesNew England Journal Medicine: The ofOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- 1Document11 pages1Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- 7Document11 pages7OSAMANo ratings yet
- Pembrolizumab Versus Docetaxel For Previously Treated, PD-L1-positive, Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (KEYNOTE-010) : A Randomised Controlled TrialDocument12 pagesPembrolizumab Versus Docetaxel For Previously Treated, PD-L1-positive, Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (KEYNOTE-010) : A Randomised Controlled TrialOSAMANo ratings yet
- 9Document13 pages9Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Eua Biocerna Sars Euasum 0Document7 pagesEua Biocerna Sars Euasum 0Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Lipids MetabolismDocument19 pagesLipids MetabolismOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- كيفية الحصول على شهادة البورد الامريكى للجمعية الأمريكية للكلينيكال باثولوجيDocument11 pagesكيفية الحصول على شهادة البورد الامريكى للجمعية الأمريكية للكلينيكال باثولوجيOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- كيفية الحصول على شهادة البورد الامريكى للجمعية الأمريكية للكلينيكال باثولوجيDocument11 pagesكيفية الحصول على شهادة البورد الامريكى للجمعية الأمريكية للكلينيكال باثولوجيOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- 182+سؤال+Document27 pages182+سؤال+Mohsen HaleemNo ratings yet
- كيفية الحصول على شهادة البورد الامريكى للجمعية الأمريكية للكلينيكال باثولوجيDocument11 pagesكيفية الحصول على شهادة البورد الامريكى للجمعية الأمريكية للكلينيكال باثولوجيOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Aborashad 2010 - Edit by Bosha11-4Document96 pagesAborashad 2010 - Edit by Bosha11-4Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Practical Ielts Strategies 5 Test Practice Book 2015 An Insanely Dangerous Activities 5Document3 pagesPractical Ielts Strategies 5 Test Practice Book 2015 An Insanely Dangerous Activities 5Osama Bakheet100% (1)
- Cross Matching (Compatibility Test)Document2 pagesCross Matching (Compatibility Test)Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- 1grammar For IeltsDocument71 pages1grammar For IeltsPaul Stato88% (8)
- Install Acrobatupd11021 First Install Acrobatupd11022 AfterDocument1 pageInstall Acrobatupd11021 First Install Acrobatupd11022 AfterOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Isolation of NeisseriaDocument2 pagesIsolation of NeisseriaOsama Bakheet100% (1)
- MCB101 Introductory Microbiology LabDocument8 pagesMCB101 Introductory Microbiology LabOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Mrsa in Latin AmericaDocument12 pagesMrsa in Latin AmericaOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- 2001 Pathology MCQDocument11 pages2001 Pathology MCQOsama Bakheet100% (2)
- Neisseria - Denise PDFDocument2 pagesNeisseria - Denise PDFOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Microbiology MR - VP Flashcards - QuizletDocument4 pagesMicrobiology MR - VP Flashcards - QuizletOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis SlidesDocument10 pagesUrinalysis SlidesOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology BOC.Document12 pagesMolecular Biology BOC.Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- User Manual Ed 6 July 09Document34 pagesUser Manual Ed 6 July 09Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Microbiology Immunology Questions and Answers With ExplanationDocument4 pagesMCQ in Microbiology Immunology Questions and Answers With ExplanationOsama Bakheet50% (2)
- BacteDocument13 pagesBacteAdriana GarciaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Microbes Manual of Molecular Biology TechniquesDocument367 pagesAnalyzing Microbes Manual of Molecular Biology TechniquesOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- StoolDocument1 pageStoolAhmed J AlhindaweNo ratings yet
- Arts6,4, Week2, Module 2V4Document24 pagesArts6,4, Week2, Module 2V4Loreen Pearl MarlaNo ratings yet
- Physics 101Document21 pagesPhysics 101Kuna KunavathiNo ratings yet
- JHS 182Document137 pagesJHS 182harbhajan singhNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument61 pagesCase StudyA GNo ratings yet
- Manufacuring EngineeringDocument3 pagesManufacuring Engineeringapi-79207659No ratings yet
- Natural Disasters Vocabulary Exercises Fun Activities Games Icebreakers Oneonone Activiti 42747Document2 pagesNatural Disasters Vocabulary Exercises Fun Activities Games Icebreakers Oneonone Activiti 42747Andrea Tercero VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LidocaineDocument15 pagesDrug Study LidocaineFrancym R. BatengaNo ratings yet
- SAT Biochar Ethylene Poster 10 - 10b PDFDocument1 pageSAT Biochar Ethylene Poster 10 - 10b PDFsherifalharamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power System Device Function NumberDocument2 pagesElectrical Power System Device Function Numberdan_teegardenNo ratings yet
- 1ST SUMMATIVE TEST FOR G10finalDocument2 pages1ST SUMMATIVE TEST FOR G10finalcherish austriaNo ratings yet
- Serial Analysis of Gene Expression (SAGE)Document34 pagesSerial Analysis of Gene Expression (SAGE)Rohit PhalakNo ratings yet
- SPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 BerjawapanDocument18 pagesSPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 Berjawapanpss smk selandar71% (7)
- Hot Topic 02 Good Light Magazine 56smDocument24 pagesHot Topic 02 Good Light Magazine 56smForos IscNo ratings yet
- RhythmDocument10 pagesRhythmSalcedo NoelNo ratings yet
- Upaam 1135891 202105060749199700Document18 pagesUpaam 1135891 202105060749199700Kartik KapoorNo ratings yet
- Maths All FormulasDocument5 pagesMaths All FormulasVishnuNo ratings yet
- Eliminating Oscillation Between Parallel MnosfetsDocument6 pagesEliminating Oscillation Between Parallel MnosfetsCiprian BirisNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 English As Grade 4Document28 pagesQuarter 4 English As Grade 4rubyneil cabuangNo ratings yet
- Final TestDocument10 pagesFinal TestbennyNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Manufacturing Companies NoidaDocument9 pagesSheet Metal Manufacturing Companies NoidaAmanda HoldenNo ratings yet
- Ge Fairchild Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesGe Fairchild Brochure PDFDharmesh patelNo ratings yet
- Ask A Monk EnlightenmentDocument16 pagesAsk A Monk EnlightenmentPetruoka EdmundasNo ratings yet
- GLP BmsDocument18 pagesGLP BmsDr.Subhashish TripathyNo ratings yet
- RUKUS April 2011Document40 pagesRUKUS April 2011RUKUS Magazine100% (2)
- ChipmunkDocument19 pagesChipmunkema.nemec13No ratings yet
- Superposition and Statically Indetermina - GDLCDocument25 pagesSuperposition and Statically Indetermina - GDLCAnonymous frFFmeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - The Mature ErythrocyteDocument55 pagesChapter 10 - The Mature ErythrocyteSultan AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Fama Fraternitatis Rosae Crucis PDFDocument2 pagesFama Fraternitatis Rosae Crucis PDFJudy50% (2)
- Earth Science (Metamorphic Rocks)Document8 pagesEarth Science (Metamorphic Rocks)MA. ALEXIS LAURENNo ratings yet
- Reloved - October 2015Document116 pagesReloved - October 2015Barron Fields67% (3)