Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digoxin
Uploaded by
Ivanne HisolerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digoxin
Uploaded by
Ivanne HisolerCopyright:
Available Formats
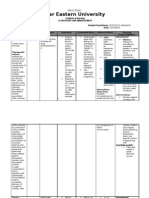
Drug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilities
Generic Name Pharmacologic General Indications Concentrations CNS: Headache, weakness, Before
Digoxin Class Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside which - Heart failure - Digitalis toxicity, drowsiness, visual disturbances, - Observe 15 rights in drug
Cardiac Glycoside has positive inotropic activity - Supraventricular - Ventricular mental status change administration.
Trade Name Cardiotonic characterized by an increase in the arrhythmias tachycardia/fibrillation, - Reduce dosage with hepatic or
Cardioxin, Lanox, force of myocardial contraction. It - Emergency heart failure - Obstructive CV: Arrhythmias renal failure.
Digitek, Lanoxicaps also reduces the conductivity of the cardiomyopathy. - Assess for allergy to digitalis
Therapeutic Class heart through the atrioventricular - Arrhythmias due to GI: GI upset, anorexia preparations.
Minimum Dose Antiarrhythmic, (AV) node. Digoxin also exerts accessory pathways (e.g. - Assess for other contraindications.
0.125 mg PO or Cardiac Drug direct action on vascular smooth Wolff-Parkinson-White - Follow diluting instructions
0.125 mg IV muscle and indirect effects syndrome). carefully, and use diluted solution
Pregnancy Risk mediated primarily by the promptly.
Maximum Dose Factor autonomic nervous system and an Precaution
1.25 mg PO or 0.25 C increase in vagal activity. - Pregnancy During
mg IV - Lactation - Monitor apical pulse for 1 minute
Pharmacokinetics before administering.
Contents Drug interaction - Administer as indicated. Check
Digoxin A: Absorption from the GI tract is Drug to drug dosage and preparation carefully.
variable. - Effectiveness reduced - Avoid IM injections, which may be
Availability and D: Widely distributed in tissues, by phenytoin, neomycin, very painful.
color including the heart, brain, sulphasalazine, kaolin, - Avoid giving with meals; this will
Lanoxicaps erythrocytes, and skeletal muscle. pectin, antacids and in delay absorption.
capsules: 0.05, 0.1, 20-30% bound to plasma proteins. patients receiving - Monitor for therapeutic drug levels:
0.2 mg; M: Digoxin is not extensively radiotherapy 0.5-2.0 ng/mL
Tablets: 0.125, 0.25 metabolized. - Metoclopramide may - Have emergency equipment ready.
mg; E: Excreted mainly unchanged. alter the absorption of
Elixir: 0.05 mg/mL; solid dosage forms of After
Injection: 0.25 Route Onset Peak Duration digoxin - Instruct patient not to stop taking
mg/mL - Blood levels increased drug without notifying physician.
Pediatric injection: Oral 30-120 2-6 6-8 days by calcium channel - Instruct to report slow or irregular
0.1 mg/mL min hr blockers, spironolactone, pulse, rapid weight gain, loss of
IV 5-30 1-5 4-5 days quinidine and calcium appetite, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting,
Routes of min hr salts. blurred or yellow vision, unusual
administration - Electrolyte imbalances tiredness or weakness, swelling of
Oral Drug Half Life such as hypokalaemia the ankles, legs or fingers, difficulty
Intravenous 30-40 hr and hypomagnesemia breathing.
(e.g. admin of potassium- - Weigh patient every other day.
losing diuretics, - Instruct to have regular medical
corticosteroids) can check-ups, which may include blood
increase the risk of tests, to evaluate effects of drug.
cardiac toxicity. - Do proper documentation.
Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009 http://mims.com.ph/ http://mims.com.ph/ http://mims.com.ph/ http://mims.com.ph/ Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug http://mims.com.ph/
Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Guide, pp. 384 Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug
Guide, pp. 384 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 384 Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 384 Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 384 Guide, pp. 384
Guide, pp. 384
You might also like
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AspirinDocument1 pageDrug Study AspirindaliaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Effects and Nursing Care for Clopidogrel (PlavixDocument3 pagesEffects and Nursing Care for Clopidogrel (PlavixTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- 4th Rot Drug StudyDocument3 pages4th Rot Drug StudyAaron GarciaNo ratings yet
- 10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateDocument2 pages10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateamitNo ratings yet
- Digitalis Dose Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDigitalis Dose Nursing ResponsibilitiesMaureen Campos-Pinera67% (3)
- Drug Study - DigoxinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DigoxinDanielle AglusolosNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetoprolol Drug Studykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesDopamine HydrochlorideNasrah N. MusaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLee JennyNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Clopidogrel - Drug StudyDocument1 pageClopidogrel - Drug StudyAcads useNo ratings yet
- Lourdes College Nursing Program Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLourdes College Nursing Program Drug Studypinksapphire929100% (2)
- MetoprololDocument1 pageMetoprololjchowking100% (1)
- CatapresDocument1 pageCatapres去約翰No ratings yet
- Morphine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMorphine Drug StudyNo Vem BerNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyMäc LäntinNo ratings yet
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug Study Mother TDocument14 pagesDrug Study Mother TEuzelle Jeena ArandaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LanoxinDocument2 pagesDrug Study LanoxinClariss Alota67% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyHanna Clarisse PataoNo ratings yet
- Drug Indication, Mode of Action, Dosage, Adverse Effects, and Nursing Responsibilities for HeparinDocument2 pagesDrug Indication, Mode of Action, Dosage, Adverse Effects, and Nursing Responsibilities for HeparinMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Reduce cholesterol and triglycerides with CRESTORDocument2 pagesReduce cholesterol and triglycerides with CRESTORSunny Mae T. PuigNo ratings yet
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document2 pagesNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Allopurinol Dosage, Classification, Indications, Adverse Reactions and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageAllopurinol Dosage, Classification, Indications, Adverse Reactions and Nursing ResponsibilitieskyawNo ratings yet
- Drug study on HydrochlorothiazideDocument2 pagesDrug study on Hydrochlorothiazidekuro hanabusa100% (1)
- 1 DrugsDocument2 pages1 DrugsPatricia Lucero100% (2)
- Ranitidine Drug Data for Erosive EsophagitisDocument3 pagesRanitidine Drug Data for Erosive EsophagitisArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- Levetiracetam Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLevetiracetam Drug Studykaycelyn jimenez50% (2)
- Lercanidipine Drug StudyDocument16 pagesLercanidipine Drug StudylenecarglbnNo ratings yet
- Digoxin Heart Failure TreatmentDocument2 pagesDigoxin Heart Failure TreatmentMaggie100% (20)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyROCHELLE DALIWAN100% (1)
- Calcium Channel Blocker AmlodipineDocument2 pagesCalcium Channel Blocker AmlodipineRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongNo ratings yet
- Tapazole and Calcium GluconateDocument3 pagesTapazole and Calcium Gluconatekuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- ZonisamideDocument2 pagesZonisamideRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- Warfarin SodiumDocument3 pagesWarfarin SodiumAndrea Huecas TriaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Contraindications: Before:: Diamox, Diamox SequelsDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Contraindications: Before:: Diamox, Diamox SequelsRomwella May AlgoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudygayskieNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezNo ratings yet
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineDocument10 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- Drug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN EtcDocument6 pagesDrug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN Etc'jmark FranciaNo ratings yet
- DexmedetomidineDocument2 pagesDexmedetomidineapt48 ukwmsNo ratings yet
- Epoetin Alfa Drug StudyDocument1 pageEpoetin Alfa Drug StudyAnni Barba100% (1)
- Medsurg Drug StudyDocument11 pagesMedsurg Drug StudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesLevetiracetamGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- Drug Study MCL or TechDocument7 pagesDrug Study MCL or TechKyra Lalaine Angub CervantesNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Forcadilla MedsudrugstudyDocument11 pagesForcadilla MedsudrugstudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Final Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesFinal Magnesium SulfateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (PR)Document6 pagesDrug Study (PR)Summer pickNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla-Medsurg Drug StudyDocument9 pagesForcadilla-Medsurg Drug StudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyDocument12 pagesForcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Doctor's Circumcision Procedure Damages Child's Urethra Leading to Civil LiabilityDocument2 pagesDoctor's Circumcision Procedure Damages Child's Urethra Leading to Civil LiabilityIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- LTD Finals Cases Batch 1Document29 pagesLTD Finals Cases Batch 1Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Case Digests For Canons 10-13Document6 pagesCase Digests For Canons 10-13Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- The Decriminalization of Vagrancy by Christian MonsodDocument17 pagesThe Decriminalization of Vagrancy by Christian MonsodIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Document31 pagesLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Loss - (SSS ID)Document1 pageAffidavit of Loss - (SSS ID)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS (Pre Finals)Document18 pagesCONTRACTS (Pre Finals)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- LTD Cases Batch 2 (6.24.14)Document18 pagesLTD Cases Batch 2 (6.24.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Document31 pagesLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Daily Assignment PlanDocument2 pagesDaily Assignment PlanIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Freedom of Expression, Assembly and Petition Case DigestsDocument22 pagesFreedom of Expression, Assembly and Petition Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Procedural Due Process Case DigestsDocument8 pagesProcedural Due Process Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Case Digest (QC v. Ericta)Document1 pageCase Digest (QC v. Ericta)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Digests (Canons 21-22 of CPR)Document1 pageDigests (Canons 21-22 of CPR)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Republic vs. Castellvi DigestDocument1 pageRepublic vs. Castellvi DigestIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law I NotesDocument59 pagesConstitutional Law I NotesIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Eminent Domain Case DigestsDocument18 pagesEminent Domain Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Legal Ethics Codals (Rules 135-143)Document34 pagesLegal Ethics Codals (Rules 135-143)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Contract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Document3 pagesContract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Ivanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Persons - Midterms NotesDocument23 pagesPersons - Midterms NotesEvina Michaela LupangoNo ratings yet
- Cases 1 15Document11 pagesCases 1 15Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Persons - Notes For MidtermsDocument10 pagesPersons - Notes For MidtermsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Penicillin G BenzathineDocument1 pagePenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Affidavit of Loss - CabrerosDocument1 pageAffidavit of Loss - CabrerosIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument1 pageTerbutaline SulfateIvanne Hisoler100% (2)
- MethotrexateDocument2 pagesMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- Rgaleon Consti1 - Cases 3rd BatchDocument40 pagesRgaleon Consti1 - Cases 3rd BatchIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (27)
- Chap 4 eDocument22 pagesChap 4 eHira AmeenNo ratings yet
- Speed of Sound and its Relationship with TemperatureDocument2 pagesSpeed of Sound and its Relationship with TemperatureBENNY CALLONo ratings yet
- Havighurst ThePirenneThesis (BW)Document133 pagesHavighurst ThePirenneThesis (BW)tmarr014100% (1)
- Pin Block Formats Explained in DetailDocument3 pagesPin Block Formats Explained in DetailJinay SanganiNo ratings yet
- Onsemi ATX PSU DesignDocument37 pagesOnsemi ATX PSU Designusuariojuan100% (1)
- 1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Document10 pages1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Zuber RokhmanNo ratings yet
- Scent of Apples: Does The Author Make Us Think Seriously of Life? Why Do You Say So?Document2 pagesScent of Apples: Does The Author Make Us Think Seriously of Life? Why Do You Say So?carl tom BondiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Econ - Advanced Economic Theory (Eng)Document1 page5 - Econ - Advanced Economic Theory (Eng)David JackNo ratings yet
- MF 04Document21 pagesMF 04Carlos De la CruzNo ratings yet
- People vs. LorenzoDocument8 pagesPeople vs. LorenzoMRose SerranoNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument25 pagesFoundation of Special and Inclusive Educationmarjory empredoNo ratings yet
- 2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidenceDocument16 pages2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidencebaridinoNo ratings yet
- Software Security Engineering: A Guide for Project ManagersDocument6 pagesSoftware Security Engineering: A Guide for Project ManagersVikram AwotarNo ratings yet
- Fuzzys CodesDocument39 pagesFuzzys CodesJak JakNo ratings yet
- Jolly Phonics Teaching Reading and WritingDocument6 pagesJolly Phonics Teaching Reading and Writingmarcela33j5086100% (1)
- Why Research Is Important in The BusinessDocument2 pagesWhy Research Is Important in The BusinessBricx BalerosNo ratings yet
- Japanese Tea Cups LessonDocument3 pagesJapanese Tea Cups Lessonapi-525048974No ratings yet
- Sexual Self PDFDocument23 pagesSexual Self PDFEden Faith Aggalao100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENTDocument5 pagesASSIGNMENTPanchdev KumarNo ratings yet
- PIC16 F 1619Document594 pagesPIC16 F 1619Francisco Martinez AlemanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Amanda CeresaDocument2 pagesWeek 1 Amanda CeresaAmanda CeresaNo ratings yet
- 4th Singapore Open Pencak Silat Championship 2018-1Document20 pages4th Singapore Open Pencak Silat Championship 2018-1kandi ari zonaNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications For The: LAMBDA 950 UV/Vis/NIR and LAMBDA 850 UV/Vis SpectrophotometersDocument4 pagesTechnical Specifications For The: LAMBDA 950 UV/Vis/NIR and LAMBDA 850 UV/Vis SpectrophotometersDiogo GálicoNo ratings yet
- LAWS1150 Principles of Private LawDocument102 pagesLAWS1150 Principles of Private Lawelpatron87100% (2)
- Javier Couso, Alexandra Huneeus, Rachel Sieder Cultures of Legality Judicialization and Political Activism in Latin America Cambridge Studies in Law and SocietyDocument290 pagesJavier Couso, Alexandra Huneeus, Rachel Sieder Cultures of Legality Judicialization and Political Activism in Latin America Cambridge Studies in Law and SocietyLívia de SouzaNo ratings yet
- 3B Adverbial PhrasesDocument1 page3B Adverbial PhrasesSarah INo ratings yet
- The Forty Nine StepsDocument312 pagesThe Forty Nine Stepsoldnic67% (3)
- Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS) : Fiona Li Pharm D Candidate University of Saint Joseph School of PharmacyDocument22 pagesEhlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS) : Fiona Li Pharm D Candidate University of Saint Joseph School of PharmacyDiogo CapellaNo ratings yet
- Dreams and Destiny Adventure HookDocument5 pagesDreams and Destiny Adventure HookgravediggeresNo ratings yet