Professional Documents
Culture Documents
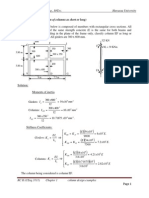
Pos.: Concrete Column With Bending Moment Without Buckling:: EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder: Beam
Uploaded by
agpsimoesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pos.: Concrete Column With Bending Moment Without Buckling:: EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder: Beam
Uploaded by
agpsimoesCopyright:
Available Formats
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Pos.: Concrete column with bending moment without buckling:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
N
b
h
M
Section properties:
Column width b = 25,00 cm
Column thick h = 75,00 cm
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 2,50 cm
nom_c = 3,50 cm
Design values:
N
Ed
= -1980 kN
M
Ed
= 563 kNm
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 20,00 N/mm
f
yd
=
f
yk
1,15
= 434,78 N/mm
Analysis:
d
1
= nom_c + d
s1
= 6,00 cm
d
1
/ h = 0,080 ~ 0,1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
v
Ed
=
* N
Ed
10
* b * h f
cd
= -0,528
Ed
=
* abs ( ) M
Ed
10
3
* b * h
2
f
cd
= 0,200
From the interactive diagram
tot
= 0,33
A
s,tot
= *
tot
* b * h
f
cd
f
yd
= 28,46 cm
A
s1
= A
s,tot
/2 = 14,23 cm
A
s2
= A
s,tot
/2 = 14,23 cm
Provide five 20 mm and five 20 mm bars
Longitudinal bars should have a diameter of not less than d
s,min
. The recommended value is:
d
s,min
= 8,00 mm
d
s1
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; d
s
d
s,min
) = 20 mm
A
s,sel1
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
=d
s1
;AsA
s1
) = 5 20
prov_A
s1
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel1
) = 15,71 cm
d
s2
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 20 mm
A
s,sel2
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
=d
s2
; AsA
s1
) = 5 20
prov_A
s2
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel2
) = 15,71 cm
prov_A
s
= prov_A
s1
+ prov_A
s2
= 31,42 cm
A
s,tot
/ prov_A
s
= 0,91 < 1
constuctive transverse reinforcement
min_d
sl
= MIN(d
s1
;d
s2
) = 20,00 mm
min_d
sw
= 6,00 mm
min_d
sw
= 0,25*min_d
sl
= 5,00 mm
min_d
sw
= 5,00 mm for mesh reinforceme
The spacing of the transverse reinforcement along the column should not exceed max_s
w
max_s
w
= MIN(20*min_dsl ; 400; MIN(b;h)*10 )*10
-1
= 25 cm
d
sw
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 10,00 mm
a
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea";Name;d
s
=d
sw
;e max_s
w
) = 10 / e = 20
prov_a
sw
= 2 * TAB("reinf/AsArea"; as; Name=a
s
) = 7,86 cm/m
Only closed links are recommended. Hooks are to be staggered.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Pos.: Concrete column without buckling:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
N
h
b
Section properties:
Column width b = 0,25 m
Column thick h = 0,75 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 2,50 cm
nom_c = 3,50 cm
Concrete cross-sectional area A
c
= b*h = 0,188 m
Design forces:
N
Ed
= -2800 kN
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;) = C20/25
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 20,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
f
tk,cal
= 525,00 N/mm
E
s
= 200000 N/mm
s
= 1,15
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 13,33 N/mm
f
td,cal
=
f
tk,cal
s
= 456,52 N/mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Analysis:
Value of stress
sd
of the bar with
s
=
c2
s
= -2,00 *10
-3
yd
=
f
yd
E
s
= 2,174*10
-3
su
= 25,00*10
-3
sd
= + f
yd
*
-
s
yd
-
su
yd
( ) - f
td,cal
f
yd
= 430,80 N/mm
A
s,tot
= *
+ * N
Ed
10
-3
* A
c
f
cd
sd
10
4
* (-1) = 6,82 cm
A
smin
= MAX( *
* 0,1 abs * ( ) N
Ed
10
-3
f
yd
10
4
;0,002 * A
c
*10
4
) = 6,44 cm
A
smin
/A
s,tot
= 0,94 1
A
s
= MAX(A
s,tot
;A
smin
) = 6,82 cm
Provide 4 20 mm bars
Longitudinal bars should have a diameter of not less than d
sl,min
. The recommended value is:
d
sl,min
= 8,00 mm
d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; d
s
d
sl,min
) = 20 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
=d
s
; AsA
s
) = 4 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 12,57 cm
A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,54 < 1
min_d
sw
= 6,00 mm
min_d
sw
= 0,25 * d
s
= 5,00 mm
min_d
sw
= 5,00 mm f. mesh reinforcement
The spacing of the transverse reinforcement along the column should not exceed max_s
w
max_s
w
= MIN(20*d
sl,min
; 400; (MIN(b;h))*10
3
)*10
-1
= 16 cm
d
sw
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 10,00 mm
a
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea";Name;d
s
=d
sw
;e max_s
w
) = 10 / e = 16
prov_a
sw
= 2 * TAB("reinf/AsArea"; as; Name=a
s
) = 9,82 cm/m
Only closed links are recommended. The hooks are to be curtailed.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Pos.: Single-span with cantilever^s:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
a
l
l
k
q
k
q
q
k
k
l
Centroid of Tension
reinforcement
Section properties:
Span l = 2,80 m
Length of cantilever l
cl
= 0,80 m
Length of cantilever l
cr
= 1,00 m
Width b = 0,24 m
Depth h = 0,55 m
Centroid of tension reinforcement a = 0,02 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 0,025 m
nom_c = 0,035 m
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 20,00 N/mm
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Actions on span:
from dead load: b * h * 25 = 3,30 kN/m
from nib: b * 1,35 * 25 = 8,10 kN/m
from Pos. 201: 48,50 kN/m
max q
gf
= 59,90 kN/m
live load from Pos1: 20,00 kN/m
live load from Pos2: 74,50 kN/m
max q
qf
= 94,50 kN/m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Actions on left cantilever:
from dead load: b * h * 25 = 3,30 kN/m
from nib: b * 1,35 * 25 = 8,10 kN/m
from Pos. 201: 48,50 kN/m
max q
gcl
= 59,90 kN/m
live load from Pos1: 40,00 kN/m
live load from Pos2: 70,50 kN/m
max q
qcl
= 110,50 kN/m
Actions on right cantilever:
from dead load: b * h * 25 = 3,30 kN/m
from nib: b * 1,35 * 25 = 8,10 kN/m
from Pos. 201: 48,50 kN/m
max q
gcr
= 59,90 kN/m
live load from Pos1: 40,00 kN/m
live load from Pos2: 70,50 kN/m
max q
qcr
= 110,50 kN/m
Design values and analysis:
M
gcl
=
* -q
gcl
l
cl
2
2
= -19,17 kNm
M
qcl
=
* -q
qcl
l
cl
2
2
= -35,36 kNm
M
gcr
=
* -q
gcr
l
cr
2
2
= -29,95 kNm
M
qcr
=
* -q
qcr
l
cr
2
2
= -55,25 kNm
M
gfield
=
* q
gf
l
2
8
= 58,70 kNm
M
qfield
=
* q
qf
l
2
8
= 92,61 kNm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Design values and analysis left cantilever:
M
Edcl
=
G
* M
gcl
+
Q
* M
qcl
= -78,92 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edc,s
= ABS(M
Edcl
) = 78,92 kNm
Edcl,s
=
* M
Edc,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,0708
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edcl,s
) = 0,075
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 3,99 cm
Provide three 16 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 16 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 3 16
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 6,03 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,66 < 1
Design values and analysis right cantilever:
M
Edcr
=
G
* M
gcr
+
Q
* M
qcr
= -123,31 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edcr,s
= ABS(M
Edcr
) = 123,31 kNm
Edcr,s
=
* M
Edcr,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,111
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edcr,s
) = 0,118
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 6,28 cm
Provide five 14 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 14 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 5 14
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 7,70 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,82 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Design values and analysis span:
M
Edf,min
= + M
gfield
+ M
Edcl
M
Edcr
2
= -42,41 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edf,min,s
= ABS(M
Edf,min
) = 42,41 kNm
Edf,min,s
=
* M
Edf,min,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,038
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edf,min,s
) = 0,039
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 2,08 cm
Provide two 14 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 14 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 2 14
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 3,08 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,68 < 1
M
Edf,max
= *
G
+ M
gfield
*
Q
+ M
qfield
+ M
gcl
M
gcr
2
= 193,60 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edf,max,s
= ABS(M
Edf,max
) = 193,60 kNm
Edf,max,s
=
* M
Edf,max,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,174
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edf,max,s
) = 0,193
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 10,27 cm
Provide four 20 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 20 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 4 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 12,57 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,82 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Pos.: Single-span with left cantilever:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
a
l
k
l
q
q
k
Cent roid of Tension
reinforcement
Section properties:
Span l = 2,80 m
Length of cantilever l
c
= 1,00 m
Width b = 0,25 m
Depth h = 0,55 m
Centroid of tension reinforcement a = 0,02 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 0,025 m
nom_c = 0,035 m
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 20,00 N/mm
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Actions on span:
from dead load: b * h * 25 = 3,44 kN/m
from nib: b * 1,35 * 25 = 8,44 kN/m
from Pos. 201: 48,50 kN/m
max q
g
= 60,38 kN/m
live load from Pos1: 20,00 kN/m
live load from Pos2: 74,50 kN/m
max q
p
= 94,50 kN/m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Actions on cantilever:
from dead load: b * h * 25 = 3,44 kN/m
from nib: b * 1,35 * 25 = 8,44 kN/m
from Pos. 201: 48,50 kN/m
max q
gc
= 60,38 kN/m
live load from Pos1: 40,00 kN/m
live load from Pos2: 70,50 kN/m
max q
pc
= 110,50 kN/m
Design values and analysis:
M
gcl
=
* -q
gc
l
c
2
2
= -30,19 kNm
M
pcl
=
* -q
pc
l
c
2
2
= -55,25 kNm
M
gfield
=
* q
g
l
2
8
= 59,17 kNm
M
pfield
=
* q
p
l
2
8
= 92,61 kNm
Design values and analysis cantilever:
M
Edc
=
G
* M
gcl
+
Q
* M
pcl
= -123,63 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edc,s
= ABS(M
Edc
) = 123,63 kNm
Edc,s
=
* M
Edc,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,1064
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edc,s
) = 0,113
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 6,26 cm
Provide four 25 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 25 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 4 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 19,63 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,32 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Design values and analysis span:
M
Edf,min
= + M
gfield
M
Edc
2
= -2,65 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edf,min,s
= ABS(M
Edf,min
) = 2,65 kNm
Edf,min,s
=
* M
Edf,min,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,0023
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edf,min,s
) = 0,002
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 0,11 cm
Provide two 16 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 16 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 2 16
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 4,02 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,03 < 1
M
Edf,max
= *
G
+ M
gfield
*
Q
+ M
pfield
M
gcl
2
= 203,70 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edf,max,s
= ABS(M
Edf,max
) = 203,70 kNm
Edf,max,s
=
* M
Edf,max,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,175
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edf,max,s
) = 0,194
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 10,75 cm
Provide four 20 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 20 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 4 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 12,57 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,86 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Pos.: Single-span with right cantilever:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
a
l
l
k
q
k
q
Centroi d of Tension
rei nforcement
Section properties:
Span l = 2,80 m
Length of cantilever l
c
= 1,60 m
Width b = 0,30 m
Depth h = 0,55 m
Centroid of tension reinforcement a = 0,02 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 0,025 m
nom_c = 0,035 m
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 20,00 N/mm
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Actions on span:
from dead load: b * h * 25 = 4,13 kN/m
from nib: b * 1,35 * 25 = 10,13 kN/m
from Pos. 201: 48,50 kN/m
max q
g
= 62,76 kN/m
live load from Pos1: 20,00 kN/m
live load from Pos2: 74,50 kN/m
max q
p
= 94,50 kN/m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Actions on cantilever:
from dead load: b * h * 25 = 4,13 kN/m
from nib: b * 1,35 * 25 = 10,13 kN/m
from Pos. 201: 48,50 kN/m
max q
gc
= 62,76 kN/m
live load from Pos1: 40,00 kN/m
live load from Pos2: 70,50 kN/m
max q
pc
= 110,50 kN/m
Design values and analysis:
M
gcr
=
* -q
gc
l
c
2
2
= -80,33 kNm
M
pcr
=
* -q
pc
l
c
2
2
= -141,44 kNm
M
gfield
=
* q
g
l
2
8
= 61,50 kNm
M
pfield
=
* q
p
l
2
8
= 92,61 kNm
Design values and analysis cantilever:
M
Edc
=
G
* M
gcr
+
Q
* M
pcr
= -320,61 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edc,s
= ABS(M
Edc
) = 320,61 kNm
Edc,s
=
* M
Edc,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,230
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edc,s
) = 0,267
req_A
s
=
* * d * b * 10
4
f
cd
f
yd
= 17,76 cm
Provide four 25 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 25 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 4 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 19,63 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,90 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Design values and analysis span:
M
Edf,min
= + M
gfield
M
Edc
2
= -98,81 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edf,min,s
= ABS(M
Edf,min
) = 98,81 kNm
Edf,min,s
=
* M
Edf,min,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,071
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edf,min,s
) = 0,075
req_A
s
=
* * d * b * 10
4
f
cd
f
yd
= 4,99 cm
Provide two 25 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 25 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 2 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 9,82 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,51 < 1
M
Edf,max
= *
G
+ M
gfield
*
Q
+ M
pfield
M
gcr
2
= 181,78 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,482 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,21 m
M
Edf,max,s
= ABS(M
Edf,max
) = 181,78 kNm
Edf,max,s
=
* M
Edf,max,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,130
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Edf,max,s
) = 0,140
req_A
s
=
* * d * b * 10
4
f
cd
f
yd
= 9,31 cm
Provide four 20 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 20 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 4 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 12,57 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,74 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Pos.: Single-beam
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
a
l
q
Centroid of Tension
reinforcement
Section properties:
Span L = 2,80 m
Width b = 0,24 m
Depth h = 0,58 m
Centroid of tension reinforcement a = 0,02 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 0,025 m
nom_c = 0,035 m
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 20,00 N/mm
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Actions on span:
from dead load: b * h * 25 = 3,48 kN/m
from nib: b * 1,35 * 25 = 8,10 kN/m
from Pos. 201: 48,50 kN/m
max q
g
= 60,08 kN/m
live load from Pos1: 20,00 kN/m
live load from Pos2: 37,50 kN/m
max q
q
= 57,50 kN/m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Beam
Design values and analysis:
M
G
=
* q
g
L
2
8
= 58,88 kNm
M
Q
=
* q
q
L
2
8
= 56,35 kNm
M
Ed
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 164,01 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,512 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,22 m
M
Ed,s
= ABS(M
Ed
) = 164,01 kNm
Ed,s
=
* M
Ed,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,130
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,140
req_A
s
=
* * d * b * 10
4
f
cd
f
yd
= 7,91 cm
Provide four 16 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 16 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 4 16
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 8,04 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,98 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Analysis for shearing without transverse reinforcement:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
b
w
h
d
t t
Section properties:
thickness t = 0,30 m
Rib width b
w
= 0,30 m
height h
= 0,42 m
effective depth of tension reinforcement
depth d = 0,375 m
Tension reinforcement A
s1
= 13,23 cm
length of span l = 3,00 m
Loads:
g = 20,20 kN/m
q
= 9,41 kN/m
V
G
= g * l/2 = 30,30 kN
V
Q
= q * l/2 = 14,12 kN
Materials, stresses and partial safety factors:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C20/25
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 20,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 13,33 N/mm
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
c
= 1,50
Shear Analysis:
max_V = V
G
*
G
+ V
Q
*
Q
= 62,09 kN
a
i
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t) = 0,15 m
Effective shearing force:
V
Ed
= max_V - (g
*
G
+ q
*
Q
) * (a
i
+ d) = 40,36 kN
k = MIN( + 1
200
* d 10
3
; 2) = 1,73
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
1
= MIN(
A
s1
* b
w
* d 10
4
; 0,02 ) = 0,012
k
1
= 0,15
C
Rd,c
= 0,18/
c
= 0,12
Acceptance:
Concrete compressive stress at the centroidal axis due to axial loading and/or presstressing
cp
=0;
cp
= 0,00 N/mm
V
Rd,c
= * ( ) * C
Rd,c
* k +
* 100 *
1
f
ck
3
* k
1
cp
* b
w
* d 10
3
= 67,37 kN
min
= * 0,035 *
k
3
f
ck
= 0,36 N/mm
V
Rd,c,min
= (
min
+ k
1
*
cp
) * b
w
* d*10
3
= 40,50 kN
V
Rd,c
= MAX(V
Rd,c
; V
Rd,c,min
) = 67,37 kN
V
Ed
/V
Rd,c
= 0,60 1
Shear reinforcement is not necessary, if proof is 1.
Constructive shearing reinforcement
w,min
= * 0,08
f
ck
f
yk
= 0,72*10
-3
s
t,max
= MIN(0,75*d; 0,60 ) = 0,28 m
= 90,00
a
sw,min
=
w,min
* 10
4
* b
w
* SIN(90) = 2,16 cm/m
Provide links of size 8 mm (double-shear)
d
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 8,00 mm
a
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea";Name;d
s
=d
s
;a
s
a
sw,min
/2) = 8 / e = 20
prov_a
sw
= 2 * TAB("reinf/AsArea"; as; Name=a
s
) = 5,02 cm/m
a
sw,min
/ prov_a
sw
= 0,43 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Concrete corbel, design with the strut and tie system:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
F
F
F
cd
td
H
a'
a
c
0
a
c
z
(d-z)
d h
H
d
d
Section properties:
Shear span a
c
= 20,00 cm
Depth of corbel h
c
= 60,00 cm
Thickness of bearing plate h
pl
= 4,00 cm
Center of reinforcement d
1
= 4,00 cm
Width of corbel b
w
= 50,00 cm
dimensions bearing in x direction b
x
= 120,00 mm
dimensions bearing in y direction b
y
= 350,00 mm
Materials, stresses and partial safety factors:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;) = C50/60
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 50,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
f
cd
= f
ck
/ 1,5 = 33,33 N/mm
cc
= 1,00
Design values:
F
d
= 250,00 kN
H
d
= 45,00 kN
Design values and analysis:
Distance a
H
= h
pl
+ d
1
= 8,00 cm
H
d
= MAX(0,2*F
d
; H
d
) = 50,00 kN
d = h
c
- d
1
= 56,00 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
v = * 0,6
( )
- 1
f
ck
250
= 0,48
Safe bearing stress
sb
= * 0,48 *
( )
- 1
f
ck
250
f
ck
= 19,20 N/mm
Actual bearing stress
ab
=
* F
d
10
3
* b
x
b
y
= 5,95 N/mm
Check the bearing stress
ab
sb
= 0,31 1
Concrete strut
effective depth d = h
c
- d
1
= 56,00 cm
Distance a' = (a
c
+ 0,2 * a
H
) = 21,60 cm
Therefore
1
=
a'
d
= 0,4
The design stress for the concrete strut
f
cd
= v*f
ck
/1,5 = 16,00 N/mm
Angle of inclination :
F
Ed
* f
cd
* d b
w
= *
( )
- 1 *
a'
d
tan( ) sin( ) * 2
This equation cannot be solved directly for but following table, which has been developed directly
from ecuation can be used.
Value f
1
=
* F
d
10
3
* f
cd
* d * b
w
10
2
= 0,056
= TAB("concrete/InclC"; Theta ;
1
; f = f
1
) = 39,00
z
0
= (a
c
+ 0,2 *a
H
)* TAN() = 17,49 cm
a
c
/ z
0
= 1,14 < 1 otherwise design as cantilever
Corbels (a
c
< z
0
) may be designed using strut-and-tie models
Main tension steel
The force in the main tension steel is
F'
td
= * F
d
( )
+
1
tan( )
0,2 = 358,72 kN
A
s,main
=
* F'
td
10
3
f
yd
* 10
-2
= 8,25 cm
Provide two loops H20 mm bars
d
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 20 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s,sel
; AsA
s,main
/2) = 2 20
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
prov_A
s,main
= 2*TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 12,56 cm
n = TAB("reinf/As"; n; Name=A
s,sel
) = 2
If a
c
0,5 * h
c
closed horizontal or inclined links with A
s,link
k
1
* A
s,main
should be provided in
addition to the main tension reinforcement.
a
c
* 0,5 h
c
= 0,67 1
Horizontal links ( A
s,lnk
A
s,main
)
A
s,lnk
= A
s,main
= 8,25 cm
Provide four H12 links
EN 1992-1-1 J.3.(2)
k
1
= 0,25
req_A
s,lnk
= k
1
* A
s,main
= 2,06 cm
d
slnk,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; A
s
0,5 * req_A
s,lnk
; n=1) = 12 mm
A
slnk,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
slnk,sel
; AsA
s,lnk
/2) = 4 12
prov_A
slnk
= 2* TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
slnk,sel
) = 9,04 cm
n = TAB("reinf/As"; n; Name=A
slnk,sel
) = 4
d
b
r
d
b
r
loops
horizontal link
assembly bar
2 O 20 loops
4 O 12
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Shear design of a rectangular section:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
b
w
h
d
t t
Section properties:
thickness t = 0,30 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
height h
= 0,42 m
effective depth d = 0,375 m
Actions:
Uniform load q
q
= 9,41 kN/m
Uniform load q
g
= 20,20 kN/m
Support reaction V
G
= 65,25 kN
Support reaction V
Q
= 30,39 kN
Materials, stresses and partial safety factors:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C20/25
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 20,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 13,33 N/mm
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Shear design:
max_V = V
G
*
G
+ V
Q
*
Q
= 133,67 kN
a
i
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t) = 0,15 m
Effective design shear force:
V
Ed
= max_V - (q
g
*
G
+ q
q
*
Q
) * (a
i
+ d) = 111,94 kN
v
1
= * 0,6
( )
- 1
f
ck
250
= 0,55
z
= 0,9 * d = 0,34 m
Limits EC2 for : 1 = cot = 2,5 (21,8 45)
provide cot x = 1,50
Consideration of the compressive strength of the diagonal concrete strut and its angle
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
= atan
( )
1
x
= 33,69
Is a coefficient taking account of the state of the stress in the compression chord.
For non-prestressed structures.
cw
= 1,00
The angle of the shearing reinforcement is = 90
V
Rd,max
= *
*
cw
* b
w
* z * f
cd
v
1
( )
+
1
tan( )
tan( )
10
3
= 345,14 kN
max_V/ V
Rd,max
= 0,39 < 1
f
ywd
= f
yd
= 434,78 N/mm
req_a
sw
=
* V
Ed
10
-3
* z * f
ywd
1
tan( )
*10
4
= 5,05 cm/m
Constructive shearing reinforcement
maximal spacing for links
s
t,max
= MIN(0,75*d; 0,60 ) = 0,28 m
w,min
= * 0,08
f
ck
f
yk
= 0,72*10
-3
= 90,00
a
sw,min
=
w,min
* 10
4
* b
w
* SIN(90) = 2,16 cm/m
req_a
sw
= MAX(req_a
sw
; a
sw,min
) = 5,05 cm/m
Provide links of size 8 mm (double-shear)
d
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 8,00 mm
a
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea";Name;d
s
=d
s
;a
s
req_a
sw
/2) = 8 / e = 15
prov_a
sw
= 2 * TAB("reinf/AsArea"; as; Name=a
s
) = 6,70 cm/m
req_a
sw
/ prov_a
sw
= 0,75 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Flexural design of a rectangular section with compression reinforcement using the
reinforcement ratio method
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
e
A
s2
A
s1
M
N
Centroid of Tensi on
reinforcement
Section properties:
Width b = 0,25 m
Depth h = 0,75 m
Concrete cover c
nom
= 0,035 m
Nominal axis distance a = 0,010 m
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds;) = 28,0 mm
Bar size d
s2
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds;) = 20,0 mm
Actions:
M
G
= 250,00 kNm
M
Q
= 240,00 kNm
N
G
= -80,00 kN
N
Q
= -60,00 kN
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
tk,cal
= 525,00 N/mm
Modulus of elasticity Steel E
s
= 200000 N/mm
Partial safety faktors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
s
= 1,15
c
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Design values and analysis:
f
yd
= f
yk
/
s
= 434,78 N/mm
yd
=
f
yd
E
s
= 2,174*10
-3
su
= 25,00*10
-3
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 20,00 N/mm
N
Ed
=
G
* N
G
+
Q
* N
Q
= -198,00 kN
M
Ed
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 697,50 kNm
d = - h - c
nom
-
d
s
* 2 10
3
a = 0,691 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,316 m
M
Ed,s
= ABS(M
Ed
) - N
Ed
* z
s1
= 760,07 kNm
Ed,s
=
* M
Ed,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,318
for C50/60
Ed,s,lim
= 0,296
Ed,s
Ed,s,lim
= 1,074 >1,0
compressive reinforcement is necessary!
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s,lim
) = 0,813
c2
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy";
c2
; =
Ed,s
)*10
-3
= -3,50*10
-3
s1
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy";
s1
; =
Ed,s
)*10
-3
= 3,58*10
-3
lim_M
Ed,s
=
Ed,s,lim
* b * d * f
cd
* 10 = 706,67 kNm
MEd,s
= M
Ed,s
- lim_M
Ed,s
= 53,40 kNm
d
2
= + c
nom
d
s2
* 2 10
3
= 0,045 m
z = * d = 0,562 m
req_A
s1
= *
1
f
yd
*
( )
+ +
lim_M
Ed,s
z
MEd,s
- d d
2
N
Ed
10 = 26,27 cm
Provide five 28 mm bars
A
s,prov
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s1
) = 5 28
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,prov
) = 30,79 cm
req_A
s1
/ prov_A
s
= 0,85 < 1
req_A
s2
= *
1
f
yd
*
MEd,s
- d d
2
10 = 1,90 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Provide two 12 mm bars
A
s,prov
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s2
; Asreq_A
s2
) = 2 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,prov
) = 6,28 cm
req_A
s2
/ prov_A
s
= 0,30 < 1
Check yield strength of tension reinforcement:
yd
= 2,17*10
-3
s2
= (ABS(
c2
) +
s1
) * (d - d
2
) / d -
s1
= 3,04*10
-3
s2
/
yd
= 1,40 > 1
The maximum yield strength was achieved!
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Flexural design of a rectangular section, K-method
to ENV 1992-1-1 !!!
N
M
a
Centroid of tension
reinforcement
Section properties:
Width b = 0,25 m
Depth h = 0,75 m
Concrete cover nom_c = 0,035 m
Nominal axis distance a = 0,020 m
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds;) = 25,0 mm
Actions:
M
G
= 250,00 kNm
M
Q
= 150,00 kNm
N
G
= 1,00 kN
N
Q
= 0,00 kN
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
Partial safety faktors:
s
= 1,15
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Design values and analysis:
f
yd
= f
yk
/
s
= 434,78 kN/cm
N
sd
=
G
* N
G
+
Q
* N
Q
= 1,35 kN
M
sd
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 562,50 kNm
d = h - nom_c - d
s
/10
- a = 0,670 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,295 m
M
sd,s
= ABS(M
sd
) - N
sd
* z
s1
= 562,10 kNm
k
d
= d * 100 / (M
sd,s
/ b) = 1,41
k
s
= TAB("reinf/kd"; ks1; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 2,830
= TAB("reinf/kd"; ; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 0,813
= TAB("reinf/kd"; ; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 0,450
c2
= TAB("reinf/kd";
c2
; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = -3,500*10
-3
s1
= TAB("reinf/kd";
s1
; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 4,270*10
-3
x= *d = 0,301 m
z= *d = 0,545 m
req_A
s
= M
sd,s
/(d*100)*k
s
+10*N
sd
/f
yd
= 23,77 cm
Provide five 25 mm bars
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 5 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 24,54 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,97 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Flexural design of a rectangular section
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
A
s1
M
N
a
reinf orcement
Cent roid of tension
Section properties:
Width b = 0,30 m
Depth h = 0,75 m
Concrete cover c
nom
= 0,035 m
Nominal axis distance a = 0,020 m
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds;) = 25,0 mm
Actions:
M
G
= 250,00 kNm
M
Q
= 150,00 kNm
N
G
= -80,00 kN
N
Q
= -60,00 kN
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
s
= 1,15
c
= 1,50
Design values and analysis:
f
yd
= f
yk
/
s
= 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 20,00 N/mm
N
Ed
=
G
* N
G
+
Q
* N
Q
= -198,00 kN
M
Ed
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 562,50 kNm
d = - h - c
nom
-
d
s
* 2 10
3
a = 0,683 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,308 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
M
Ed,s
= ABS(M
Ed
) - N
Ed
* z
s1
= 623,48 kNm
Ed,s
=
* M
Ed,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,223
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,868
z = * d = 0,593 m
req_A
s1
= *
1
f
yd
( )
+
M
Ed,s
z
N
Ed
*10 = 19,63 cm
Provide five 25 mm bars
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s1
) = 5 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 24,54 cm
req_A
s1
/ prov_A
s
= 0,80 < 1
n = TAB("reinf/As"; n; Name=A
s,sel
) = 5
Section width is appropriate!
CHECK = b-2*c
nom
- (n*d
s
+ MAX(d
s
; 20)*(n-1))*10
-3
= 0,00 0
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Punching shear analysis in a flat slap without punching shear reinforcement :
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
2d
c
d h
Section properties:
Slap thickness h = 24,00 cm
Effective depth d
x
= 19,00 cm
Effective depth d
y
= 19,00 cm
column width b
x
= 45,00 cm
column width b
y
= 45,00 cm
d
eff
=
+ d
x
d
y
2
= 19,00 cm
radial spacing of perimeters of shear reinforcement
s
r
= 0,75*d
eff
= 14,25 mm
s
t
= 1,5*d
eff
= 28,50 cm
Loads:
Shearing force for design:
V
Ed
= 600 kN
Materials and stresses:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
c
= 1,50
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
c
= 20,00 N/mm
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Top reinforcement in slab:
reinf
x
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; Name; ) = 20 / e = 8.5
a
sx
= TAB("reinf/AsArea"; a
s
; Name=reinf
x
) = 36,96 cm/m
reinf
y
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; Name; ) = 20 / e = 8.5
a
sy
= TAB("reinf/AsArea"; a
s
; Name=reinf
y
) = 36,96 cm/m
Design Calculation:
Punching shear analysis:
Critical perimeter:
u
1
=
* 2 ( )
+ b
x
+ b
y
* * 2 d
eff
100
= 4,19 m
distance =
- u
1
* ( )
+ b
x
b
y
* 2 10
-2
* 2
= 0,38 m
Shearing force per unit length along the critical perimeter:
for internal columns = 1,15
Ed
=
* * V
Ed
10
-3
* u
1
* d
eff
10
-2
= 0,867 MN/m
Maximum bearing capacity of slab per unit length without punching shear reinforcement:
k = MIN( + 1
200
* d
eff
10
; 2,0 ) = 2,0000
lx
=
a
sx
* b
x
d
x
= 0,0432
ly
=
a
sy
* b
y
d
y
= 0,0432
1
= MIN(
*
l x
l y
;0,02) = 0,0200
C
Rd,c
=
0,18
c
= 0,12
min
= * 0,035 *
k
3
f
ck
= 0,54
k
1
= 0,10
Acceptance:
Concrete compressive stress at the centroidal axis due to axial loading and/or presstressing
cp
=0;
cp
= 0,00 N/mm
Rd,c
= * C
Rd,c
* k +
( ) * 100 *
1
f
ck
3
* k
1
cp
= 0,940 MN/m
Rd,c,min
=
min
+ k
1
*
cp
= 0,540 MN/m
Rd,c
= MAX(
Rd,c
;
Rd,c,min
) = 0,940 MN/m
Ed
/
Rd,c
= 0,92 < 1 !!!
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
compressive reinforcement is not necessary, if
Ed
/
Rd,c
1,0
is a stregth reduction factor for concrete in shear
= 0,6 * (1- f
ck
/250) = 0,528 MN/m
for internal columns
u
0
= 2*(b
x
+ b
y
) * 10 = 1800 mm
Ed,0
=
* * V
Ed
10
3
* u
0
* d
eff
10
= 2,0175 N/mm
The maximum permissible shear force based on the face of the loaded area is given by the maximum
shear resistance
Rd,max
= 0,5 * * f
cd
= 5,280 N/mm
Ed,0
/
Rd,max
= 0,38 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Punching shear analysis in a flat slap:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
2d
c
d h
Section properties:
Slap thickness h = 24,00 cm
Effective depth d
x
= 19,00 cm
Effective depth d
y
= 19,00 cm
column width b
x
= 45,00 cm
column width b
y
= 45,00 cm
d
eff
=
+ d
x
d
y
2
= 19,00 cm
radial spacing of perimeters of shear reinforcement
s
r
= 0,75*d
eff
= 14,25 mm
s
t
= 1,5*d
eff
= 28,50 cm
Loads:
Shearing force for design:
V
Ed
= 809 kN
Materials and stresses:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
c
= 1,50
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
c
= 20,00 N/mm
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Top reinforcement in slab:
A
sx
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; Name; ) = 20 / e = 8.5
a
sx
= TAB("reinf/AsArea"; a
s
; Name=A
sx
) = 36,96 cm/m
A
sy
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; Name; ) = 20 / e = 8.5
a
sy
= TAB("reinf/AsArea"; a
s
; Name=A
sy
) = 36,96 cm/m
Design Calculation:
d
eff
= ( d
x
+ d
y
) / 2 = 19,00 cm
Punching shear analysis:
Critical perimeter:
u
1
=
* 2 ( )
+ b
x
+ b
y
* * 2 d
eff
100
= 4,19 m
distance =
- u
1
* ( )
+ b
x
b
y
* 2 10
-2
* 2
= 0,38 m
Shearing force per unit length along the critical perimeter:
for internal columns = 1,15
Ed
=
* * V
Ed
10
-3
* u
1
* d
eff
10
-2
= 1,169 MN/m
Maximum bearing capacity of slab per unit length without punching shear reinforcement:
k = MIN( + 1
200
* d
eff
10
; 2,0 ) = 2,0000
lx
=
a
sx
* b
x
d
x
= 0,0432
ly
=
a
sy
* b
y
d
y
= 0,0432
1
= MIN(
*
l x
l y
;0,02) = 0,0200
C
Rd,c
=
0,18
c
= 0,12
min
= * 0,035 *
k
3
f
ck
= 0,54
k
1
= 0,10
Acceptance:
Concrete compressive stress at the centroidal axis due to axial loading and/or presstressing
cp
=0;
cp
= 0,00 N/mm
Rd,c
= * C
Rd,c
* k +
( ) * 100 *
1
f
ck
3
* k
1
cp
= 0,940 MN/m
Rd,c,min
=
min
+ k
1
*
cp
= 0,540 MN/m
Rd,c
= MAX(
Rd,c
;
Rd,c,min
) = 0,940 MN/m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Ed
/
Rd,c
= 1,24 > 1 !!!
compressive reinforcement is necessary!
= 0,6 * (1- f
ck
/250) = 0,528 MN/m
for internal columns
u
0
= 2*(b
x
+ b
y
) * 10 = 1800 mm
Ed,0
=
* * V
Ed
10
3
* u
0
* d
eff
10
= 2,7203 N/mm
The maximum permissible shear force based on the face of the loaded area is given by the maximum
shear resistance
Rd,max
= 0,5 * * f
cd
= 5,280 N/mm
Ed,0
/
Rd,max
= 0,52 1
Reinforcement for punching shear:
f
ywd,ef
= 250 + 0,25 * d
eff
* 10 = 297,50 N/mm
< 0,75d
< kd
> 0,3 d
A B
B outer perimeter uout,ef at which reinforcement is not required.
A perimeter, at which reinforcement is required.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
<
2
d
<
1
,
5
d
2d
s
r
radial distance link of punching shear reinforcement
s
r
= 0,75*d
eff
* 10 = 142,50 mm
s
t
tangential distance link of punching shear reinforcement
s
t
= 1,5*d
eff
* 10 = 285,00 mm
first row:
distance a
1
= 0,5*d
eff
= 9,50 cm
u
cont,1
= * ( ) * ( )
+ b
x
b
y
+ 2 * * a
1
2 10
-2
= 2,40 m
Ed,1
=
* * V
Ed
10
-3
* u
cont,1
* d
eff
10
-2
= 2,04 N/mm
A
sw,1
=
-
Ed,1
* 0,75
Rd,c
* 1,5 *
( )
* d
eff
10
s
r
* f
ywd,ef
*
( )
1
* * u
1
10
3
* d
eff
10
sin( ) 90
* 10
-2
= 17,86 cm
A check must also be made the calculated reinforcement satisfies the minimum requirement that:
The angle of the Punching shear reinforcement is = 90
A
sw,min
= *
* 0,08
f
ck
f
yk
/ ( ) * 1,5 + sin( ) 90 cos ( ) 90
( ) * * s
r
10
-3
u
cont,1
10
4
= 2,00 cm
A
sw,1
= MAX(A
sw,1
; A
sw,min
) = 17,86 cm
Number of link-legs n
1
=
u
cont,1
* 1,5 * d
eff
10
-2
+ 0,5 = 9
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
d
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 14 mm
A
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; ds=d
s,sel
;nn
1
;A
s
A
sw,1
) = 12 14
prov_A
sw,1
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s
) = 18,47 cm
secand row:
distance a
2
= 0,75*d
eff
= 14,25 cm
u
cont,2
= * ( ) * ( )
+ b
x
b
y
+ 2 * * ( )
+ a
1
a
2
2 10
-2
= 3,29 m
Ed,2
=
* * V
Ed
10
-3
* u
cont,2
* d
eff
10
-2
= 1,49 N/mm
A
sw,2
=
-
Ed,2
* 0,75
Rd,c
* 1,5 *
( )
* d
eff
10
s
r
* f
ywd,ef
*
( )
1
* * u
1
10
3
* d
eff
10
sin( ) 90
* 10
-2
= 10,50 cm
A check must also be made the calculated reinforcement satisfies the minimum requirement that:
The angle of the Punching shear reinforcement is = 90
A
sw,min
= *
* 0,08
f
ck
f
yk
/ ( ) * 1,5 + sin( ) 90 cos ( ) 90
( ) * * s
r
10
-3
u
cont,2
10
4
= 2,74 cm
A
sw,2
= MAX(A
sw,2
; A
sw,min
) = 10,50 cm
Number of link-legs n
2
=
u
cont,2
* 1,5 * d
eff
10
-2
+ 0,5 = 12
d
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 14 mm
A
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; ds=d
s,sel
; A
s
A
sw,2
;nn
2
) = 12 14
prov_A
sw,2
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s
) = 18,47 cm
check
A
sw,1
/ prov_A
sw,1
= 0,97 < 1
A
sw,2
/ prov_A
sw,2
= 0,57 < 1
outer perimeter u
out ,ef
at which reinforcement is not required.
u
out,ef
=
* * V
Ed
10
-3
*
Rd,c
* d
eff
10
-2
= 5,21 m
Distance
out,ef
=
- u
out,ef
* ( )
+ b
x
b
y
* 2 10
-2
* 2
= 0,54 m
Factor k = 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
kd = k*d
eff
= 28,50 cm
remained distance = Distance
out,ef
-kd/100-(a
1
+ a
2
)/100 = 0,02 cm
Ed,a
=
* * V
Ed
10
-3
* u
out,ef
* d
eff
10
-2
= 0,94 N/mm
Ed,a
/
Rd,c
= 1,00 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Rectangular section with shear and torsion:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
e
h
b
reinforcement
centroi d of
System:
thickness t = 0,30 m
Beam width b= 0,40 m
Beam height h= 0,60 m
nom_c= 0,042 m
distance e = 0,032 m
From live load q
q
= 9,41 kN/m
From dead load q
g
= 20,20 kN/m
Support reaction V
G
= 150,00 kN
Support reaction V
Q
= 89,00 kN
Torsional moment T
Ed
= 45,00 kNm
Area A = h*b = 0,24 m
perimeter u = 2*(h+b) = 2,00 m
effective wall thickness t
ef,1
= A/u = 0,12 m
from flexural design prov_A
S,M
= 12,50 cm
Materials, stresses and partial safety factors:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;f
ck
50) = C25/30
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 25,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
ctm
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fctm; Name=Concrete) = 2,60 N/mm
f
ctk
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fctk05; Name=Concrete) = 1,80 N/mm
d = h-nom_c-e = 0,526 m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
ct = 1,00
cc = 1,00
f
ctd
=
* f
ctk
cc
1,5
= 1,20 N/mm
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 16,67 N/mm
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
c
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Shear design:
d = h-nom_c - e = 0,526 m
max_V = V
G
*
G
+ V
Q
*
Q
= 336 kN
a
i
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t) = 0,15 m
magebende Querkraft:
V
Ed
= max_V - (q
g
*
G
+ q
q
*
Q
) * (a
i
+ d) = 308,02 kN
z
= 0,9 * d = 0,47 m
Limits EC2 for : 1 = cot = 2,5 (21,8 45)
provide cot x = 1,00
Consideration of the compressive strength of the diagonal concrete strut and its angle
= atan
( )
1
x
= 45,00
smallest beam width b
w
= b = 0,40 m
b
k
= b-t
ef,1
= 0,28 m
h
k
= h-t
ef,1
= 0,48 m
A
k
Area enclosed by the centre lines of the connecting walls including the inner hollow areas
A
k
= h
k
*b
k
= 0,13 m
u
k
= 2*(b
k
+ h
k
) = 1,52 m
Normal Concrete v
1
= * 0,6
( )
- 1
f
ck
250
= 0,54
k = MIN( + 1
200
* d 10
3
; 2) = 1,62
1
= MIN(
prov_A
S,M
* b
w
* d 10
4
; 0,02 ) = 0,006
recommened Value
k
1
= 0,15
C
Rd,c
= 0,18/
c
= 0,12
Acceptance:
Concrete compressive stress at the centroidal axis due to axial loading and/or presstressing
cp
=0;
cp
= 0,00 N/mm
V
Rd,c
= * ( ) * C
Rd,c
* k +
* 100 *
1
f
ck
3
* k
1
cp
* b
w
* d 10
3
= 100,87 kN
for retangle ( l t )
l = MAX(b
k
;h
k
) = 0,480 m
t = MIN(b
k
;h
k
) = 0,280 m
l/t = 1,714 m
R = TAB("concrete/RFactor"; ; =l/t) = 0,210
R = TAB("concrete/RFactor"; ; =l/t) = 4,219
I
T
=
R
* l * t
3
= 2,213*10
-3
m
4
W
T
=
* l t
2
R
= 8,920*10
-3
m
3
T
Rd,c
= f
ctd
* W
T
* 10
3
= 10,70 kN/m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
It is only the minimum of reininforcement necessary, if the following proof are sucessfully
+
T
Ed
T
Rd,c
V
Ed
V
Rd,c
= 7,26 < 1
Is a coefficient taking account of the state of the stress in the compression chord.
For non-prestressed structures.
cw
= 1,00
The angle of the shearing reinforcement is = 90
V
Rd,max
= *
*
cw
* b
w
* z * f
cd
v
1
( )
+
1
tan( )
tan( )
10
3
= 846,17 kN
max_V/ V
Rd,max
= 0,40 < 1
f
ywd
= f
yd
= 434,78 N/mm
req_a
sw,V
= *
V
Ed
* z * f
ywd
sin * ( ) 90
( )
+
1
tan( )
1
tan( ) 90
10 = 15,07 cm/m
Minimum shear reinforcement ratio
w,min
= * 0,08
f
ck
f
yk
= 0,80*10
-3
maximal spacing for links
s
t,max
= MIN(0,75*d; 0,60 ) = 0,39 m
a
sw,min
=
w,min
* 10
4
* b
w
* SIN(90) = 3,20 cm/m
req_a
sw,V
= MAX(req_a
sw,V
; a
sw,min
) = 15,07 cm/m
Design for torsion:
v = v
1
= 0,54
T
Rd,max
= v *
cw
* f
cd
* 2 * A
k
* t
ef,1
* SIN() * COS()*10
3
= 140,43 kN
T
Ed
/ T
Rd,max
= 0,32 < 1
tension reinforcement as a result of torsion
req_a
sl,T
=
* T
Ed
10
* 2 * A
k
* f
yd
tan( )
= 3,98 cm/m
links as a result of torsion
req_a
sw,T
=
* * T
Ed
10 tan( )
* 2 * A
k
f
yd
= 3,98 cm/m
T
Ed
/ T
Rd,max
+ V
Ed
/ V
Rd,max
= 0,68 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
reinforcement links:
req_a
sw
= 2* req_a
sw,T
+ req_a
sw,V
= 23,03 cm/m
Provide links of size 12 mm (double-shear)
d
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 12,00 mm
a
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea";Name;d
s
=d
s
;a
s
req_a
sw
/2) = 12 / e = 9.5
prov_a
sw
= 2*TAB("reinf/AsArea"; as; Name=a
s
) = 23,80 cm/m
req_a
sw
/ prov_a
sw
= 0,97 < 1
torsion reinforcement longitudinal bars:
req_A
Sl
= prov_A
S,M
+ req_a
sl,T
* u
k
/3 = 14,52 cm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; Asreq_A
Sl
) = 5 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 15,71 cm
provide five bars 20 mm
at the side:
req_A
Sl,T
= req_a
sl,T
* u
k
/3 = 2,02 cm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; Asreq_A
Sl,T
) = 2 14
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 3,08 cm
provide two bars 14 mm
side of compression
req_A
Sl,T
= req_a
sl,T
* u
k
/3 = 2,02 cm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; Asreq_A
Sl,T
) = 2 14
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 3,08 cm
provide two bars 14 mm
minimum reinforcement longitudinal bars :
A
Sl,min
= MAX( * 0,26 *
f
ctm
f
yk
* b d*10
4
; 0,0013 * b * d * 10
4
) = 2,84 cm
A
Sl,min
* req_a
sl,T
u
k
= 0,47 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Rectangular section using the kh-method
to ENV 1992-1-1 !!!
N
M
a
Centroid of tension
reinforcement
Section properties:
Width b = 0,25 m
Depth h = 0,75 m
Concrete cover nom_c = 0,035 m
Distance between centre of tension and lowest bar a = 0,020 m
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds;) = 25,0 mm
Loads:
M
G
= 250,00 kNm
M
Q
= 150,00 kNm
N
G
= 1,00 kN
N
Q
= 0,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
Partial safety faktors:
s
= 1,15
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Design Calculation:
f
yd
= f
yk
/
s
= 434,78 kN/cm
N
sd
=
G
* N
G
+
Q
* N
Q
= 1,35 kN
M
sd
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 562,50 kNm
d = h - nom_c - d
s
/10
- a = 0,670 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,295 m
M
sd,s
= ABS(M
sd
) - N
sd
* z
s1
= 562,10 kNm
k
d
= d * 100 / (M
sd,s
/ b) = 1,41
k
s
= TAB("reinf/kd"; ks1; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 2,830
= TAB("reinf/kd"; ; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 0,813
= TAB("reinf/kd"; ; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 0,450
c2
= TAB("reinf/kd";
c2
; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = -3,500*10
-3
s1
= TAB("reinf/kd";
s1
; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 4,270*10
-3
x= *d = 0,301 m
z= *d = 0,545 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
req_A
s
= M
sd,s
/(d*100)*k
s
+10*N
sd
/f
yd
= 23,77 cm
Provide five 25 mm bars
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 5 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 24,54 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,97 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Rectangular section with the Omega-method:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
A
s1
M
N
a
reinf orcement
Cent roid of tension
Section properties:
Width b = 0,30 m
Depth h = 0,75 m
Concrete cover c
nom
= 0,035 m
Distance between centre of tension and lowest bar a = 0,020 m
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds;) = 25,0 mm
Loads:
M
G
= 250,00 kNm
M
Q
= 150,00 kNm
N
G
= -80,00 kN
N
Q
= -60,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
cc = 1,00
Partial safety faktors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
s
= 1,15
c
= 1,50
Design Calculation:
f
yd
= f
yk
/
s
= 434,78 kN/cm
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
c
= 20,00 N/mm
N
Ed
=
G
* N
G
+
Q
* N
Q
= -198,00 kN
M
Ed
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 562,50 kNm
d = - h - c
nom
-
* d
s
10
-3
2
a = 0,683 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,308 m
M
Ed,s
= ABS(M
Ed
) - N
Ed
* z
s1
= 623,48 kNm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Ed,s
=
* M
Ed,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,223
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,257
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b + f
cd
* N
Ed
10
-3
f
yd
10
4
= 19,67 cm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 5 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 24,54 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,80 < 1
n = TAB("reinf/As"; n; Name=A
s,sel
) = 5
the width of the retangular is enough (add the legs of links, if exist)
CHECK = b-2*c
nom
- (n*d
s
+ MAX(d
s
; 20)*(n-1))*10
-3
= 0,00 0
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Rectangular section with compression reinforcement (omega-method)
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
A
s2
A
s1
M
N
reinforcement
a
Centroid of tension
Section properties:
Width b = 0,25 m
Depth h = 0,75 m
Concrete cover c
nom
= 0,035 m
Distance between centre of tension and lowest bar a = 0,010 m
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds;) = 28,0 mm
Bar size d
s2
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds;) = 20,0 mm
Loads:
M
G
= 250,00 kNm
M
Q
= 240,00 kNm
N
G
= -80,00 kN
N
Q
= -60,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
Modulus of elasticity Steel E
s
= 200000 N/mm
Partial safety faktors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
s
= 1,15
c
= 1,50
Design Calculation:
f
yd
= f
yk
/
s
= 434,78 N/mm
yd
=
f
yd
E
s
= 2,174*10
-3
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 20,00 N/mm
N
Ed
=
G
* N
G
+
Q
* N
Q
= -198,00 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
M
Ed
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 697,50 kNm
d = - h - c
nom
-
d
s
* 2 10
3
a = 0,691 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,316 m
M
Ed,s
= ABS(M
Ed
) - N
Ed
* z
s1
= 760,07 kNm
for C50/60
Ed,s,lim
= 0,296
Ed,s
=
* M
Ed,s
10
-3
* b * d
2
f
cd
= 0,318
Ed,s
Ed,s,lim
= 1,07 1
compressive reinforcement is necessary!
d
2
= + c
nom
d
s2
* 2 10
3
= 0,045 m
Difference
=
Ed,s
-
Ed,s,lim
= 0,022
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s,lim
) = 0,813
c2
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy";
c2
; =
Ed,s
)*10
-3
= -3,50*10
-3
s1
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy";
s1
; =
Ed,s
)*10
-3
= 3,58*10
-3
1,lim
=
Ed,s,lim
= 0,364
- 1
d
2
d
= 0,024
req_A
s1
= *
* ( )
+
1,lim
* d * b + f
cd
* N
Ed
10
-3
f
yd
10
4
= 26,28 cm
Provide five 28 mm bars
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s1
) = 5 28
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 30,79 cm
req_A
s1
/ prov_A
s
= 0,85 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Provide two 12 mm bars
2
=
= 0,024
req_A
s2
= *
*
2
* d * b f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 1,91 cm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s2
; Asreq_A
s2
) = 2 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 6,28 cm
req_A
s2
/ prov_A
s
= 0,30 < 1
Check tensile strain yield:
yd
= 2,17*10
-3
s2
= (ABS(
c2
) +
s1
) * (d - d
2
) / d -
s1
= 3,04*10
-3
s2
/
yd
= 1,40 > 1
Strain yield limit achieved!
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Rectangular section with shear and torsion:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
e
h
b
reinforcement
centroi d of
System:
thickness t = 0,30 m
Beam width b= 0,40 m
Beam height h= 0,60 m
nom_c= 0,042 m
distance e = 0,032 m
From live load q
q
= 9,41 kN/m
From dead load q
g
= 20,20 kN/m
Support reaction V
G
= 150,00 kN
Support reaction V
Q
= 89,00 kN
Torsional moment T
Ed
= 45,00 kNm
Area A = h*b = 0,24 m
perimeter u = 2*(h+b) = 2,00 m
effective wall thickness t
ef,1
= A/u = 0,12 m
from flexural design prov_A
S,M
= 12,50 cm
Materials, stresses and partial safety factors:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;f
ck
50) = C25/30
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 25,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
ctm
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fctm; Name=Concrete) = 2,60 N/mm
f
ctk
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fctk05; Name=Concrete) = 1,80 N/mm
d = h-nom_c-e = 0,526 m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
ct = 1,00
cc = 1,00
Is a coefficient taking account of the state of the stress in the compression chord.
For non-prestressed structures.
cw
= 1,00
f
ctd
=
* f
ctk
cc
1,5
= 1,20 N/mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 16,67 N/mm
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
c
= 1,50
Shear design:
d = h-nom_c - e = 0,526 m
max_V = V
G
*
G
+ V
Q
*
Q
= 336 kN
a
i
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t) = 0,15 m
magebende Querkraft:
V
Ed
= max_V - (q
g
*
G
+ q
q
*
Q
) * (a
i
+ d) = 308,02 kN
z
= 0,9 * d = 0,47 m
Limits EC2 for : 1 = cot = 2,5 (21,8 45)
provide cot x = 1,00
Consideration of the compressive strength of the diagonal concrete strut and its angle
= atan
( )
1
x
= 45,00
smallest beam width b
w
= b = 0,40 m
b
k
= b-t
ef,1
= 0,28 m
h
k
= h-t
ef,1
= 0,48 m
A
k
Area enclosed by the centre lines of the connecting walls including the inner hollow areas
A
k
= h
k
*b
k
= 0,13 m
u
k
= 2*(b
k
+ h
k
) = 1,52 m
Normal Concrete v
1
= * 0,6
( )
- 1
f
ck
250
= 0,54
k = MIN( + 1
200
* d 10
3
; 2) = 1,62
1
= MIN(
prov_A
S,M
* b
w
* d 10
4
; 0,02 ) = 0,006
recommened Value
k
1
= 0,15
C
Rd,c
= 0,18/
c
= 0,12
Acceptance:
Concrete compressive stress at the centroidal axis due to axial loading and/or presstressing
cp
=0;
cp
= 0,00 N/mm
V
Rd,c
= * ( ) * C
Rd,c
* k +
* 100 *
1
f
ck
3
* k
1
cp
* b
w
* d 10
3
= 100,87 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
for retangle ( l t )
l = MAX(b
k
;h
k
) = 0,480 m
t = MIN(b
k
;h
k
) = 0,280 m
l/t = 1,714
R = TAB("concrete/RFactor"; ; =l/t) = 0,210
R = TAB("concrete/RFactor"; ; =l/t) = 4,219
I
T
=
R
* l * t
3
= 2,213*10
-3
m
4
W
T
=
* l t
2
R
= 8,920*10
-3
m
3
T
Rd,c
= f
ctd
* W
T
* 10
3
= 10,70 kN/m
It is only the minimum of reininforcement necessary, if the following proof are sucessfully
+
T
Ed
T
Rd,c
V
Ed
V
Rd,c
= 7,26 < 1
The angle of the shearing reinforcement is = 90
V
Rd,max
= *
*
cw
* b
w
* z * f
cd
v
1
( )
+
1
tan( )
tan( )
10
3
= 846,17 kN
max_V/ V
Rd,max
= 0,40 < 1
f
ywd
= f
yd
= 434,78 N/mm
req_a
sw,V
= *
V
Ed
* z * f
ywd
sin * ( ) 90
( )
+
1
tan( )
1
tan( ) 90
10 = 15,07 cm/m
Minimum shear reinforcement ratio
w,min
= * 0,08
f
ck
f
yk
= 0,80*10
-3
maximal spacing for links
s
t,max
= MIN(0,75*d; 0,60 ) = 0,39 m
a
sw,min
=
w,min
* 10
4
* b
w
* SIN(90) = 3,20 cm/m
req_a
sw,V
= MAX(req_a
sw,V
; a
sw,min
) = 15,07 cm/m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Design Calculations
Design for torsion:
v = v
1
= 0,54
T
Rd,max
= v *
cw
* f
cd
* 2 * A
k
* t
ef,1
* SIN() * COS()*10
3
= 140,43 kN
T
Ed
/ T
Rd,max
= 0,32 < 1
tension reinforcement as a result of torsion
req_a
sl,T
=
* T
Ed
10
* 2 * A
k
* f
yd
tan( )
= 3,98 cm/m
links as a result of torsion
req_a
sw,T
=
* * T
Ed
10 tan( )
* 2 * A
k
f
yd
= 3,98 cm/m
T
Ed
/ T
Rd,max
+ V
Ed
/ V
Rd,max
= 0,68 < 1
reinforcement links:
req_a
sw
= 2* req_a
sw,T
+ req_a
sw,V
= 23,03 cm/m
Provide links of size 12 mm (double-shear)
d
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 12,00 mm
a
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea";Name;d
s
=d
s
;a
s
req_a
sw
/2) = 12 / e = 9.5
prov_a
sw
= 2*TAB("reinf/AsArea"; as; Name=a
s
) = 23,80 cm/m
req_a
sw
/ prov_a
sw
= 0,97 < 1
torsion reinforcement longitudinal bars:
req_A
Sl
= prov_A
S,M
+ req_a
sl,T
* u
k
/3 = 14,52 cm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; Asreq_A
Sl
) = 5 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 15,71 cm
provide five bars 20 mm
at the side:
req_A
Sl,T
= req_a
sl,T
* u
k
/3 = 2,02 cm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; Asreq_A
Sl,T
) = 2 14
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 3,08 cm
provide two bars 14 mm
side of compression
req_A
Sl,T
= req_a
sl,T
* u
k
/3 = 2,02 cm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; Asreq_A
Sl,T
) = 2 14
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 3,08 cm
provide two bars 14 mm
minimum reinforcement longitudinal bars :
A
Sl,min
= MAX( * 0,26 *
f
ctm
f
yk
* b d*10
4
; 0,0013 * b * d * 10
4
) = 2,84 cm
A
Sl,min
* req_a
sl,T
u
k
= 0,47 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Effective flange width of a single-span beam with cantilevers:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
Elevation:
l =0,85 * l
l
l l
0
l =0,7 * l
0 0
b
eff
eff,1 eff,2
1
b
1
b
b
2
2
bw
bw
b
b b
b
eff1 eff2 eff3
eff 1
l =0,15(l + l )
0 eff1 eff2
ef f2
l =0,15 * l + l
eff 2 eff 3
Load diagram:
L
q
q
kr
L
kr kl
L
q
kl
Section properties:
l
n
is the clear distance between the faces of supports
length l
n
= 6,26 m
bearing width t
1
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
2
= 0,30 m
height h= 0,50 m
a
1
and a
2
are the end distance at either end of the element.
a
1
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
1
) = 0,15 m
a
2
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
2
) = 0,15 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,75 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,37 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Single-span beam, top flange:
l
eff1
= l
n
+a
1
+a
2
= 6,56 m
l
0
= 0,7 * l
eff1
= 4,59 m
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 3,42 m
b
eff1
= MIN( 0,2 * b
1
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
1
) = 0,81 m
b
eff2
= MIN( 0,2 * b
2
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
2
) = 0,73 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff1
+ b
eff2
+ b
w
; b ) = 1,84 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Effective flange width at an internal column:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
Elevation:
l =0,85 * l
l
l l
0
l =0,7 * l
0 0
b
eff
eff,1 eff,2
1
b
1
b
b
2
2
bw
bw
b
b b
b
eff1 eff2 eff3
eff 1
l =0,15(l + l )
0 eff1 eff2
ef f2
l =0,15 * l + l
eff 2 eff 3
Section properties:
l
n
is the clear distance between the faces of supports
length l
n1
= 6,26 m
length l
n2
= 7,00 m
bearing width t
1
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
2
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
3
= 0,40 m
height h= 0,50 m
a
1
and a
2
are the end distance at either end of the element.
a
1
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
1
) = 0,15 m
a
2
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
2
) = 0,15 m
a
3
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
3
) = 0,20 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,75 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,37 m
Continuous flanged beam, bottom flange:
l
eff1
= l
n1
+a
1
+a
2
= 6,56 m
l
eff2
= l
n2
+a
2
+a
3
= 7,35 m
Innensttze l
0
= 0,15 * (l
eff1
+ l
eff2
) = 2,09 m
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 3,42 m
b
eff1
= MIN( 0,2 * b
1
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
1
) = 0,42 m
b
eff2
= MIN( 0,2 * b
2
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
2
) = 0,42 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff1
+ b
eff2
+ b
w
; b ) = 1,14 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Effective flange width of a cantilever beam:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
Elevation:
l =0,85 * l
l
l l
0
l =0,7 * l
0 0
b
eff
eff,1 eff,2
1
b
1
b
b
2
2
bw
bw
b
b b
b
eff1 eff2 eff3
eff 1
l =0,15(l + l )
0 eff1 eff2
ef f2
l =0,15 * l + l
eff 2 eff 3
Section properties:
The length of the cantilever l
3
should be less than half the adjacent span and the ratio of adjacent
spans should lie between 2/3 and 1,5.
length l
n2
= 6,26 m
length l
n3
= 2,80 m
bearing width t
2
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
3
= 0,30 m
height h= 0,50 m
a
1
and a
2
are the end distance at either end of the element.
a
2
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
2
) = 0,15 m
a
3
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
3
) = 0,15 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,75 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,37 m
Cantilever beam, bottom flange:
l
eff2
= l
n2
+a
2
+a
3
= 6,56 m
l
eff3
= l
n3
+a
3
= 2,95 m
l
0
= 0,15*l
n2
+ l
n3
= 3,74 m
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 3,42 m
b
eff1
= MIN( 0,2 * b
1
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
1
) = 0,72 m
b
eff2
= MIN( 0,2 * b
2
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
2
) = 0,65 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff1
+ b
eff2
+ b
w
; b ) = 1,67 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Single-span beam with shearing force:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
Elevation:
l =0,85 * l
l
l l
0
l =0,7 * l
0 0
b
eff
eff,1 eff,2
1
b
1
b
b
2
2
bw
bw
b
b b
b
eff1 eff2 eff3
eff 1
l =0,15(l + l )
0 eff1 eff2
ef f2
l =0,15 * l + l
eff 2 eff 3
Load diagram:
l
Section properties:
the depth of the stress block lies within the flange (s h
f
)
l
n
is the clear distance between the faces of supports
length l
n1
= 6,26 m
bearing width t
1
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
2
= 0,30 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,75 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,37 m
height h = 0,45 m
Slab thickness h
f
= 0,15 m
Axis of bending tension reinforcement a = 0,02 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 0,025 m
nom_c = 0,035 m
without alons stress influence
cp
= 0,00
a
1
and a
2
are the end distance at either end of the element.
a
1
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
1
) = 0,15 m
a
2
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
2
) = 0,15 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Single-span beam, top flange:
l
eff1
= l
n1
+a
1
+a
2
= 6,56 m
l
0
= l
eff1
= 6,56 m
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 3,42 m
b
eff1
= MIN( 0,2 * b
1
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
1
) = 1,01 m
b
eff2
= MIN( 0,2 * b
2
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
2
) = 0,93 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff1
+ b
eff2
+ b
w
; b ) = 2,24 m
L = l
eff1
= 6,56 m
Loads:
from dead load: (b * h
f
+ b
w
* (h - h
f
)) * 25 = 15,07 kN/m
From dead floor load: b * 1,50 = 5,13 kNm
max q
g
= 20,20 kNm
from live load: b * 1,50 = 5,13 kN/m
from partition surcharge: b * 1,25 = 4,28 kN/m
max q
q
= 9,41 kN/m
V
G
= q
g
* L / 2 = 66,26 kN
V
Q
= q
q
* L / 2 = 30,86 kN
M
G
= q
g
* L / 8 = 108,66 kNm
M
Q
= q
q
* L / 8 = 50,62 kNm
Bending design of retangular cross section:
Materials and stresses:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C20/25
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 20,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 13,33 N/mm
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Design Calculation:
M
Ed
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 222,62 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,383 m
M
Ed,s
= ABS(M
Ed
) = 222,62 kNm
Ed,s
=
* M
Ed,s
10
-3
* b
eff
* d
2
f
cd
= 0,051
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,053
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,971
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,077
x = * d = 0,029 m
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b
eff
f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 13,94 cm
Provide three 25 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 25 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 3 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 14,73 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,95 1
Whole compressed section is in flange:
x / h
f
= 0,19 < 1
Shear Analysis:
max_V = V
G
*
G
+ V
Q
*
Q
= 135,74 kN
Effective design shear force:
V
Ed
= max_V - (q
g
*
G
+ q
q
*
Q
) * (a
1
+ d) = 113,68 kN
v
1
= * 0,6
( )
- 1
f
ck
250
= 0,55
For flanged beams:
z
= d - h
f
/ 2 = 0,31 m
Limits EC2 for : 1 = cot = 2,5 (21,8 45)
provide cot x = 1,50
Consideration of the compressive strength of the diagonal concrete strut and its angle
= atan
( )
1
x
= 33,69
Is a coefficient taking account of the state of the stress in the compression chord.
For non-prestressed structures.
cw = 1,00
The angle of the shearing reinforcement is = 90
V
Rd,max
= *
*
cw
* b
w
* z * f
cd
v
1
( )
+
1
tan( )
tan( )
10
3
= 314,69 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
max_V/ V
Rd,max
= 0,43 < 1
f
ywd
= f
yd
= 434,78 N/mm
req_a
sw
=
* V
Ed
10
-3
* z * f
ywd
1
tan( )
*10
4
= 5,62 cm/m
Constructive shearing reinforcement
maximal spacing for links
s
t,max
= MIN(0,75*d; 0,60 ) = 0,29 m
w,min
= * 0,08
f
ck
f
yk
= 0,72*10
-3
= 90,00
a
sw,min
=
w,min
* 10
4
* b
w
* SIN(90) = 2,16 cm/m
req_a
sw
= MAX(req_a
sw
; a
sw,min
) = 5,62 cm/m
Provide links of size 8 mm (double-shear)
d
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 8,00 mm
a
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea";Name;d
s
=d
s
;a
s
req_a
sw
/2) = 8 / e = 15
prov_a
sw
= 2 * TAB("reinf/AsArea"; as; Name=a
s
) = 6,70 cm/m
req_a
sw
/ prov_a
sw
= 0,84 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Design of a single-span flanged beam with the reinforcement omega method:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
Elevation:
l =0,85 * l
l
l l
0
l =0,7 * l
0 0
b
eff
eff,1 eff,2
1
b
1
b
b
2
2
bw
bw
b
b b
b
eff1 eff2 eff3
eff 1
l =0,15(l + l )
0 eff1 eff2
ef f2
l =0,15 * l + l
eff 2 eff 3
Load diagram:
l
Section properties:
l
n
is the clear distance between the faces of supports
length l
n1
= 6,26 m
bearing width t
1
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
2
= 0,30 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,75 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,37 m
flanged beam height h = 0,50 m
Flange thickness h
f
= 0,15 m
Centroid of tension reinforcement a = 0,02 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 0,025 m
nom_c = 0,035 m
a
1
and a
2
are the end distance at either end of the element.
a
1
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
1
) = 0,15 m
a
2
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
2
) = 0,15 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Single-span beam, top flange:
l
eff1
= l
n1
+a
1
+a
2
= 6,56 m
l
0
= l
eff1
= 6,56 m
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 3,42 m
b
eff1
= MIN( 0,2 * b
1
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
1
) = 1,01 m
b
eff2
= MIN( 0,2 * b
2
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
2
) = 0,93 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff1
+ b
eff2
+ b
w
; b ) = 2,24 m
L = l
eff1
= 6,56 m
Loads:
from dead load: (b * h
f
+ b
w
* (h - h
f
)) * 25 = 15,45 kN/m
From dead floor load: b * 1,50 = 5,13 kNm
max q
g
= 20,58 kNm
from live load: b * 1,50 = 5,13 kN/m
from partition surcharge: b * 1,25 = 4,28 kN/m
max q
q
= 9,41 kN/m
V
G
= q
g
* L / 2 = 67,50 kN
V
Q
= q
q
* L / 2 = 30,86 kN
M
G
= q
g
* L / 8 = 110,70 kNm
M
Q
= q
q
* L / 8 = 50,62 kNm
Flexural design of the rectangular section:
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc
= 1,00
c
= 1,50
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
c
= 20,00 N/mm
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Design values and analysis:
M
Ed
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 225,38 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,433 m
M
Ed,s
= ABS(M
Ed
) = 225,38 kNm
Ed,s
=
* M
Ed,s
10
-3
* b
eff
* d
2
f
cd
= 0,027
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,028
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,982
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,052
x = * d = 0,023 m
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b
eff
f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 12,49 cm
Provide five 20 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 20 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 5 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 15,71 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,80 1
Whole compressed section is in flange:
x / h
f
= 0,15 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Effective flange width of a single-span beam:
to ENV 1992-1-1 !!!
Elevation:
h
f
h
b
w
b
w
b
w
b
b b b
b b
1 1 2 2
i a
b
w
b
w
b b
eff,1 eff,2 eff,2
b
Load diagram:
L
a
Centroid of tension
reinforcement
Section properties:
Span length l
1
= 6,26 m
Support width a
1
= 0,30 m
Support width a
2
= 0,30 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,75 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,37 m
Tee beams height h = 0,45 m
Slab height h
f
= 0,15 m
Axis of bending tension reinforcement a = 0,02 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 0,025 m
nom_c = 0,035 m
Single-span beam, top flange:
l
eff1
= l
1
+ a
1
/ 3 + a
2
/ 3 = 6,46 m
l
0
= l
eff1
= 6,46 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
w
+ l
0
/ 5; b
w
+ b
1
+ b
2
) = 1,59 m
L = l
eff1
= 6,46
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 3,42 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
from dead load: (b * h
f
+ b
w
* (h - h
f
)) * 25 = 15,07 kN/m
From dead floor load: b * 1,50 = 5,13 kNm
max q
g
= 20,20 kNm
from live load: b * 1,50 = 5,13 kN/m
from partition surcharge: b * 1,25 = 4,28 kN/m
max q
q
= 9,41 kN/m
V
G
= q
g
* L/2 = 65,25 kN
V
Q
= q
q
* L/2 = 30,39 kN
M
G
= q
g
* L / 8 = 105,37 kNm
M
Q
= q
q
* L / 8 = 49,09 kNm
Bending design of retangular cross section:
Materials and stresses:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name;) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Design Calculation:
M
sd
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
*
M
Q
= 215,88 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,383 m
z
s1
= d - h / 2 = 0,158 m
M
sd,s
= ABS(M
sd
) = 215,88 kNm
k
d
= d * 100 / (M
sd,s
/ b
eff
) = 3,29
k
s
= TAB("reinf/kd"; ks1; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 2,374
= TAB("reinf/kd"; ; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 0,969
= TAB("reinf/kd"; ; Name=Concrete; kd=k
d
) = 0,082
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
x = * d = 0,031 m
z = * d = 0,371 m
req_A
s
= M
sd,s
/(d*100)*k
s
= 13,38 cm
Provide three 25 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 25 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 4 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 19,63 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,68 1
Whole compressed section is in flange:
x = * d = 0,031 m
x / h
f
= 0,21 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Eff. Flange width Single-span:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
Elevation:
l =0,85 * l
l
l l
0
l =0,7 * l
0 0
b
eff
eff,1 eff,2
1
b
1
b
b
2
2
bw
bw
b
b b
b
eff1 eff2 eff3
eff 1
l =0,15(l + l )
0 eff1 eff2
ef f2
l =0,15 * l + l
eff 2 eff 3
Load diagram:
l
Section properties:
l
n
is the clear distance between the faces of supports
length l
n1
= 6,26 m
bearing width t
1
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
2
= 0,30 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,75 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,37 m
height h = 0,50 m
a
1
and a
2
are the end distance at either end of the element.
a
1
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
1
) = 0,15 m
a
2
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
2
) = 0,15 m
Single-span beam, top flange:
l
eff1
= l
n1
+a
1
+a
2
= 6,56 m
l
0
= l
eff1
= 6,56 m
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 3,42 m
b
eff1
= MIN( 0,2 * b
1
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
1
) = 1,01 m
b
eff2
= MIN( 0,2 * b
2
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
2
) = 0,93 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff1
+ b
eff2
+ b
w
; b ) = 2,24 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Single-span beam with shearing forces without transverse reinforcement:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
Elevation:
l =0,85 * l
l
l l
0
l =0,7 * l
0 0
b
eff
eff,1 eff,2
1
b
1
b
b
2
2
bw
bw
b
b b
b
eff1 eff2 eff3
eff 1
l =0,15(l + l )
0 eff1 eff2
ef f2
l =0,15 * l + l
eff 2 eff 3
Load diagram:
l
Section properties:
the depth of the stress block lies within the flange (s h
f
)
l
n
is the clear distance between the faces of supports
length l
n1
= 3,00 m
bearing width t
1
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
2
= 0,30 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,30 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,05 m
height h = 0,30 m
Slab thickness h
f
= 0,15 m
Axis of bending tension reinforcement a = 0,02 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 0,025 m
nom_c = 0,035 m
a
1
and a
2
are the end distance at either end of the element.
a
1
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
1
) = 0,15 m
a
2
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
2
) = 0,15 m
Single-span beam, top flange:
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
l
eff1
= l
n1
+a
1
+a
2
= 3,30 m
l
0
= l
eff1
= 3,30 m
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 2,65 m
b
eff1
= MIN( 0,2 * b
1
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
1
) = 0,59 m
b
eff2
= MIN( 0,2 * b
2
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
2
) = 0,54 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff1
+ b
eff2
+ b
w
; b ) = 1,43 m
L = l
eff1
= 3,30 m
Loads:
from dead load: (b * h
f
+ b
w
* (h - h
f
)) * 25 = 11,06 kN/m
From dead floor load: b * 1,50 = 3,98 kNm
max q
g
= 15,04 kNm
from live load: b * 1,50 = 3,98 kN/m
from partition surcharge: b * 1,25 = 3,31 kN/m
max q
q
= 7,29 kN/m
V
G
= q
g
* L / 2 = 24,82 kN
V
Q
= q
q
* L / 2 = 12,03 kN
M
G
= q
g
* L / 8 = 20,47 kNm
M
Q
= q
q
* L / 8 = 9,92 kNm
Bending design of retangular cross section:
Materials and stresses:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C20/25
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 20,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc = 1,00
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
1,5
= 13,33 N/mm
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
c
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Design Calculation:
M
Ed
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 42,51 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,233 m
M
Ed,s
= ABS(M
Ed
) = 42,51 kNm
Ed,s
=
* M
Ed,s
10
-3
* b
eff
* d
2
f
cd
= 0,041
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,042
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,976
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,067
x = * d = 0,016 m
req_A
s
= *
* * d * b
eff
f
cd
f
yd
10
4
= 4,29 cm
Provide three 25 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 25 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 3 25
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 14,73 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,29 1
Whole compressed section is in flange:
x / h
f
= 0,11 < 1
Shear Analysis:
max_V = V
G
*
G
+ V
Q
*
Q
= 51,55 kN
Effective shearing force:
V
Ed
= max_V - (q
g
*
G
+ q
q
*
Q
) * (a
1
+ d) = 39,59 kN
k = MIN( + 1
200
* d 10
3
; 2) = 1,93
1
= MIN(
prov_A
s
* b
w
* d 10
4
; 0,02 ) = 0,020
k
1
= 0,15
C
Rd,c
= 0,18/
c
= 0,12
Acceptance:
Concrete compressive stress at the centroidal axis due to axial loading and/or presstressing
cp
=0;
cp
= 0,00 N/mm
V
Rd,c
= * ( ) * C
Rd,c
* k +
* 100 *
1
f
ck
3
* k
1
cp
* b
w
* d 10
3
= 55,37 kN
min
= * 0,035 *
k
3
f
ck
= 0,42 N/mm
V
Rd,c,min
= (
min
+ k
1
*
cp
) * b
w
* d*10
3
= 29,36 kN
V
Rd,c
= MAX(V
Rd,c
; V
Rd,c,min
) = 55,37 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
V
Ed
/V
Rd,c
= 0,72 1
Shear reinforcement is not necessary, if proof is 1.
Constructive shearing reinforcement
w,min
= * 0,08
f
ck
f
yk
= 0,72*10
-3
s
t,max
= MIN(0,75*d; 0,60 ) = 0,17 m
= 90,00
a
sw,min
=
w,min
* 10
4
* b
w
* SIN(90) = 2,16 cm/m
Provide links of size 8 mm (double-shear)
d
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 8,00 mm
a
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea";Name;d
s
=d
s
;a
s
a
sw,min
/2) = 8 / e = 17
prov_a
sw
= 2 * TAB("reinf/AsArea"; as; Name=a
s
) = 5,92 cm/m
a
sw,min
/ prov_a
sw
= 0,36 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Design of a single-span flanged beam with the reinforcement ratio method:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
Elevation:
l =0,85 * l
l
l l
0
l =0,7 * l
0 0
b
eff
eff,1 eff,2
1
b
1
b
b
2
2
bw
bw
b
b b
b
eff1 eff2 eff3
eff 1
l =0,15(l + l )
0 eff1 eff2
ef f2
l =0,15 * l + l
eff 2 eff 3
Load diagram:
l
Section properties:
the depth of the stress block lies within the flange (s h
f
)
l
n
is the clear distance between the faces of supports
length l
n1
= 6,26 m
bearing width t
1
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
2
= 0,30 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,75 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,37 m
flanged beam height h = 0,50 m
Flange thickness h
f
= 0,15 m
Centroid of tension reinforcement a = 0,02 m
Assumed bar size d
s1
= 0,025 m
nom_c = 0,035 m
a
1
and a
2
are the end distance at either end of the element.
a
1
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
1
) = 0,15 m
a
2
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
2
) = 0,15 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Single-span beam, top flange:
l
eff1
= l
n1
+a
1
+a
2
= 6,56 m
l
0
= l
eff1
= 6,56 m
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 3,42 m
b
eff1
= MIN( 0,2 * b
1
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
1
) = 1,01 m
b
eff2
= MIN( 0,2 * b
2
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
2
) = 0,93 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff1
+ b
eff2
+ b
w
; b ) = 2,24 m
L = l
eff1
= 6,56 m
Loads:
from dead load: (b * h
f
+ b
w
* (h - h
f
)) * 25 = 15,45 kN/m
From dead floor load: b * 1,50 = 5,13 kNm
max q
g
= 20,58 kNm
from live load: b * 1,50 = 5,13 kN/m
from partition surcharge: b * 1,25 = 4,28 kN/m
max q
q
= 9,41 kN/m
V
G
= q
g
* L / 2 = 67,50 kN
V
Q
= q
q
* L / 2 = 30,86 kN
M
G
= q
g
* L / 8 = 110,70 kNm
M
Q
= q
q
* L / 8 = 50,62 kNm
Flexural design of the rectangular section:
Materials and characteristic strengths:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; f
ck
50) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("reinf/Steel"; Name;) = 500 S
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("reinf/Steel"; s; Name=Steel) = 500 MN/m
f
yd
= f
yk
/ 1,15 = 434,78 N/mm
cc
= 1,00
c
= 1,50
f
cd
=
* f
ck
cc
c
= 20,00 N/mm
Partial safety factors:
G
= 1,35
Q
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Design values and analysis:
M
Ed
=
G
* M
G
+
Q
* M
Q
= 225,38 kNm
d = h - nom_c - a - d
s1
/ 2 = 0,433 m
M
Ed,s
= ABS(M
Ed
) = 225,38 kNm
Ed,s
=
* M
Ed,s
10
-3
* b
eff
* d
2
f
cd
= 0,027
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,982
= TAB("reinf/Ecmy"; ; =
Ed,s
) = 0,052
x = * d = 0,023 m
z = * d = 0,425 m
req_A
s
= *
1
f
yd
( )
M
Ed,s
- d
h
f
2
*10 = 14,48 cm
Provide five 20 mm bars
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/As"; ds; ) = 20 mm
A
s,sel
= SEL("reinf/As"; Name; d
s
= d
s
; Asreq_A
s
) = 5 20
prov_A
s
= TAB("reinf/As"; As; Name=A
s,sel
) = 15,71 cm
req_A
s
/ prov_A
s
= 0,92 1
Whole compressed section is in flange:
x / h
f
= 0,15 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Flanged beams
Effective flange width of a single-span with a cantilever beam or endfield:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
Elevation:
l =0,85 * l
l
l l
0
l =0,7 * l
0 0
b
eff
eff,1 eff,2
1
b
1
b b
2
2
bw
bw
b
b b
b
eff1 eff2 eff3
ef f1
l =0,15(l + l )
0 e ff1 e ff2
e ff2
l =0,15 * l + l
eff2 ef f3
Section properties:
l
n
is the clear distance between the faces of supports
length l
n1
= 6,26 m
bearing width t
1
= 0,30 m
bearing width t
2
= 0,30 m
height h= 0,50 m
a
1
and a
2
are the end distance at either end of the element.
a
1
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
1
) = 0,15 m
a
2
= MIN(1/2*h ;1/2*t
2
) = 0,15 m
Beam width b
w
= 0,30 m
half slab width b
1
= 1,75 m
half slab width b
2
= 1,37 m
Continuous flanged beam, bottom flange:
l
eff1
= l
n1
+a
1
+a
2
= 6,56 m
Innensttze l
0
= 0,85 * l
eff1
= 5,58 m
b = b
1
+ b
2
+ b
w
= 3,42 m
b
eff1
= MIN( 0,2 * b
1
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
1
) = 0,91 m
b
eff2
= MIN( 0,2 * b
2
+ 0,1 * l
0
; 0,2 * l
0
; b
2
) = 0,83 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff1
+ b
eff2
+ b
w
; b ) = 2,04 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Reinforcement
General anchorage-bond length:
to EN 1992-1-1:2004
A A
A
A
h
a)
b)
250
h
300
c)
d)
a) 45 90
b) h 250 mm
c) h > 250 mm
d) h > 600 mm
A - direction of concreting
a) and b) Good bond conditions for all bars
c) and d) Good bond conditions in unhatched zone. Poor bond conditions in hatched zone.
Section properties:
Transformed Value of moment in the level of tension reinforcement. M
Ed,s
=ABS(M
Ed
)- N
Ed
M
Eds
= 0,308 MN
N
Ed
= 0,100 MN
z = 0,552 m
prov_A
s1
= 25,00 cm
available condition AC= SEL("reinf/aTyps";AC;) = poor
When bond conditions are poor then the specified ultimate bond stress should be reduced by a factor
of 0,7
factor
1
= IF(AC="good";1,0;0,7) = 0,70
c
c
a
1
= min(a/2, c, c1) c
d
c
d
= c c
d
= min(a/2, c1)
a
c
1
c
a) Straight bars
b) Bent or hooked bars
c) Looped bars
concrete cover coefficent c
d
= 30 mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Reinforcement
A
s
A
st t, A
s
A
st t , A
s
A
st t,
Values of K for beams and slabs
K= 0,1 K= 0,05
K= 0
Value of K = 0,10
transverse pressure p= 0,00 N/mm
Value of (1 to 5)
Type of anchorange
VA = SEL("reinf/aTyps";Typ;) = other than straight
f
1
= TAB("reinf/aTyps";Val;Typ=VA) = 2
Construct CS = SEL("reinf/aTyps"; CS;) = beams
Material
Bar size d
s
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 20 mm
Concrete = SEL("reinf/al"; Name; ) = C35/45
Area of a single anchored bar with maximum bar diameter
Area A
s
= TAB("Bewehrung/As"; As ;n=1;ds=ds) = 3,14 cm
Bar Size transverse reinforcement along the design anchorage length
d
t
= SEL("reinf/AsArea"; ds; ) = 10,00 mm
quantity of transverse reinforcement along the design anchorage length
n
t
= 4
the cross-sectional area of the transverse reinforcement along the design anchorage length
A
st
= TAB("reinf/As"; As ;n=n
t
;ds=d
t
) = 3,14 cm
f
ctk_0,05
= TAB("concrete/EC";fctk05; Name=Concrete) = 2,20 N/mm
ct
= 1,00
c
= 1,50
f
yk
= 500,0 N/mm
s
= 1,15
E-Modul E
s
= 200000 N/mm
Berechnung
f
ctd
= *
ct
f
ctk_0,05
c
= 1,47 N/mm
The design value of the ultimate bond stress is also dependent on the bar size. For all sizes
greater than 32 mm the bond stress should additionally be multiplied by a faktor.
2
= IF(d
s
32; 1,0; (132-d
s
)/100) = 1,00
Design values of bond stresses f
bd
f
bd
= 2,25 *
1
*
2
* f
ctd
= 2,32 N/mm
Value of stress where the anchorange of the bar be calculated.
sd
= *
1
* prov_A
s1
10
-4
( )
+
M
Eds
z
N
Ed
= 263 N/mm
basic reqiured anchorage length to prevent pull out
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Reinforcement
l
b,rqd
= *
d
s
4
sd
f
bd
= 567 mm
the cross-sectional area of the minimum transverse reinforcement
A
st,min
= IF(CS
="beams"; 0,25*A
s
; 0) = 0,79 cm
anchorage-bond length for tension
1
for the effect of: The shape of the bars
1
= IF(f
1
=1;1;IF(c
d
>3*d
s
;0,7;1,0)) = 1,00
2
= for the effect of: Concrete cover to the reinforcement
2,1
= - 1 * 0,15
( )
- c
d
d
s
d
s
= 0,93
2,1
= IF(
2,1
< 0,7; 0,7;IF(
2,1
> 1,0; 1,0;
2,1
)) = 0,93
2,2
= - 1 * 0,15
( )
- c
d
* d
s
3
d
s
= 1,23
2,2
= IF(
2,2
< 0,7; 0,7;IF(
2,2
> 1,0; 1,0;
2,2
)) = 1,00
2
= IF(f
1
=1;
2,1
;
2,2
) = 1,00
2
= IF(f
1
=1;
2,1
;
2,2
) = 1,00
3
= for the effect of: Confinement of transverse reinforcement not welded to the main reinforcement
= (A
st
- A
st,min
)/A
s
= 0,75
3
= 1 - K * = 0,93
3
= IF(
3
< 0,7; 0,7;WENN(
3
> 1,0; 1,0;
3
)) = 0,93
4
= for the effect of: Confinement of transverse reinforcement welded to the main reinforcement
4
= 0,70
5
= for the effect of: Confinement by transverse pressure
5
= 1-0,04*p = 1,00
5
= IF(
5
< 0,7; 0,7; IF(
5
> 1,0; 1,0;
5
)) = 1,00
Design value of bond stresses l
bd
with transverse reinforcement but not welded transverse
reinforcement to the main reinforcement.
l
bd
=
1
*
2
*
3
*
5
*
l
b,rqd
= 527,31 mm
Design value of bond stresses l
bd
with welded transverse reinforcement to the main
reinforcement.
l
bd
=
1
*
2
*
4
*
5
*
l
b,rqd
= 396,90 mm
Design value of bond stresses l
bd
without transverse reinforcement and not welded
transverse reinforcement to the main reinforcement.
l
bd
=
1
*
2
*
5
*
l
b,rqd
= 567,00 mm
Design value of bond stresses l
bd
with all factors of
l
bd
=
1
*
2
*
3
*
4
*
5
*
l
b,rqd
= 369,12 mm
This minimum design length must not be less than:
for tension bars:
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
EN 1992-1-1:2004 Folder : Reinforcement
l
b,min,t
= MAX(0,3*l
b,rqd
; 10 * d
s
; 100 ) = 200,00 mm
Anchorage-bond length for compression
Design value of bond stresses l
bd
with welded transverse reinforcement to the main
reinforcement.
l
bd
=
4
*
l
b,rqd
= 396,90 mm
Design value of bond stresses l
bd
not welded transverse reinforcement to the main
reinforcement.
l
bd
= l
b,rqd
= 567,00 mm
This minimum design length must not be less than:
for compression bars:
l
b,min,d
= MAX(0,6*l
b,rqd
; 10 * d
s
; 100 ) = 340,20 mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Bolted angilar connection:
Ed
S
S
Ed
Ed
Ed
Dimensions of connection:
Plate thickness d = 15,00 mm
Bolt spacing e = 35,00 mm
Spacing of bolts e
o
= 30,00 mm
Spacing of bolts b = 70,00 mm
Spacing of bolts h = 220,00 mm
Angle of tension force = 45,00
Bolts:
Bolt = SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 20
SC = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 8.8
f
u,b
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC) = 800,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
l
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt) = 20,00 mm
Shaft diameter d
l l
= d
l
+2 = 22,00 mm
Cross-section areas A
s
= TAB("steel/bolt"; Asp; BS=Bolt) = 2,45 cm
Plate:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 510
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 355,00 N/mm
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 510,00 N/mm
M0
= 1,10
Mb
= 1,25
Loads:
S
Ed
= 424,26 kN
N
Ed
= COS() * S
Ed
= 300,00 kN
V
Ed
= SIN() * S
Ed
= 300,00 kN
Force per bolt:
F
t,Ed
=
N
Ed
4
= 75,00 kN
F
v,Ed
=
V
Ed
4
= 75,00 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Limit tension force of bolts:
F
t,Rd
= * 0,9
* f
u,b
A
s
*
Mb
10
= 141,12 kN
F
t,Ed
F
t,Rd
= 0,53 < 1
Check limit shear force for bolts:
F
v,Rd
= 0,6 *
* f
u,b
* d
l
2
* 4000
Mb
= 120,64 kN
F
v,Ed
F
v, Rd
= 0,62 < 1
Check combined:
+
F
t,Ed
* 1,4 F
t,Rd
F
v,Ed
F
v, Rd
= 1,00 1
Analysis of bearing strength:
as in 6.5.1.3: e
o
/ d
l l
= 1,36 > 1
as in 6.5.1.3: e
o
/ d
l l
= 1,36 < 1,5
as in 6.5.1.2(1): e / d
l l
= 1,59 > 1,2
as in 6.5.1.2(3): b / d
l l
= 3,18 > 3
= MIN(
e
* 3 d
l l
;
b
* 3 d
l l
- 0,25;
f
u,b
f
u
; 1) = 0,53
Tab.6.5.3 F
b1,Rd
= 2,5 * * d
l
* d *
f
u
*
Mb
10
3
= 162,18 kN
6.5.5.(10) F
b2,Rd
=
2
3
* F
b1,Rd
= 108,12 kN
F
b,Rd
= F
b2,Rd
+ (F
b1,Rd
- F
b2,Rd
) *
-
e
o
d
l
1,2
0,3
= 162,18 kN
F
v,Ed
F
b,Rd
= 0,46 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Bolted connection subject to bending
Dimensions of connection:
a = 80,00 mm
a
1
= 45,00 mm
e = 80,00 mm
e
1
= 45,00 mm
e
2
= 50,00 mm
e
3
= 90,00 mm
d
1
= 20,00 mm
d
2
= 8,00 mm
b
1
= 160,00 mm
h
2
= 2 * (e
2
+ e
3
) = 280,00 mm
Flange-Bolts:
Bolt
f
= SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 20
SC1 = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 4.6
f
u,bo
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC1) = 400,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
lo
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt
f
) = 20,00 mm
Shaft diameter d
l1o
= d
lo
+ 2 = 22,00 mm
Number of rows n
o
= 3
Steg-Bolts:
Bolt
S
= SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 16
SC2 = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 4.6
f
u,bs
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC2) = 400,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
ls
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt
S
) = 16,00 mm
Shaft diameter d
l1s
= d
ls
+ 2 = 18,00 mm
Number of rows n
s
= 3
Number of columns m
s
= 2
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Profil:
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = IPE 240
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 240,00 mm
Web thickness s = TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 6,20 mm
Flange thickness t = TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 9,80 mm
Cross-sectional area A = TAB("steel/"Typ; A; Name=Profil) = 39,10 cm
Moment of resistance W
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Wy; Name=Profil) = 324,00 cm
Moment of resistance W
pl
= 1,14 * W
y
= 369,36 cm
Material and Partial safety factors:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
M0
= 1,10
M2
= 1,25
Loads:
M
Ed
= 157,95 kNm
V
Ed
= 60,75 kN
Check beam-web strength without holes:
M
c,Rd
=
* W
pl
f
y
*
M0
10
3
= 78,91 kNm
M
Ed
M
c,Rd
= 2,00 < 1
A
v
= 1,04 *
* h s
100
= 15,48 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* *
3
M0
10
= 190,93 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,32 < 1
Check beam-web strength with holes:
A
z
= 0,5 * A = 19,55 cm
A
z,net
= - A
z
* 2 * d
l1o
+ t *
- n
s
1
2
* d
l1s
s
100
= 14,12 cm
*
f
y
f
u
M2
M0
* 0,9
A
z,net
A
z
= 1,14 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
W
pl,net
= W
pl
- 2 * d
l1o
* t *
- h t
2000
= 319,73 cm
M
c,Rd,C
=
* W
pl,net
f
y
*
M0
10
3
= 68,31 kNm
M
Ed
M
c,Rd,C
= 2,31 < 1
A
v,net
= A
v
- n
s
* d
l1s
*
s
100
= 12,13 cm
*
f
y
f
u
A
v
A
v,net
= 0,83 < 1
Area of holes will be neglected.
Analysis of bolts in flange:
I
w
=
* 2 * d
2
h
2
3
* 12 10
4
= 2926,93 cm
4
I
f
= 2 * b
1
* d
1
*
( )
+ h d
1
2
2
10
4
= 10816,00 cm
4
M
w
= M
Ed
*
I
w
+ I
w
I
f
= 33,64 kNm
M
f
= M
Ed
*
I
f
+ I
w
I
f
= 124,31 kNm
Effective tension force in flange:
N
Ed
=
M
f
+ h d
1
* 10 = 478,12 kN
Limit shear force
F
v,Rd
= n
o
* 2 * 0,6 *
* f
u,bo
*
4
d
lo
2
* 10
3
M2
= 361,91 kN
Limit bearing force:
= MIN(
a
1
* 3 d
l1o
;
a
* 3 d
l1o
- 0,25;
f
u,bo
f
u
; 1) = 0,682
F
b,Rd
= 2
* n
o
* 2,5 * * d
lo
* t *
f
u
*
M2
10
3
= 577,46 kN
MAX(
N
Ed
F
v,Rd
;
N
Ed
F
b,Rd
) = 1,32 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Analysis of bolts in web:
n
s1
=
- n
s
1
2
+ 0,49 = 1
n
s2
= n
s1
* 2 = 2
m
s1
=
- m
s
1
2
+ 0,49 = 1
m
s2
= m
s1
* 2 = 2
I
p
=
* n
s
* m
s2
+
( )
*
- m
s
1
2
e
2
* n
s2
* m
s
( )
*
- n
s
1
2
e
3
2
100
= 420,00 cm
M
Ew
= M
w
+
* V
Ed
e
3
10
3
= 39,11 kNm
R
Ed
=
+
( )
* 10 * M
Ew
e
3
I
p
2
( )
+
V
Ed
* m
s
n
s
* 10 * M
Ew
*
- m
s
1
2
e
I
p
2
= 96,27 kN
F
v,Rd
= m
s
* 0,6 * f
u,bs
*
4
*
d
ls
2
*
M2
10
3
= 77,21 kN
= MIN(
e
1
* 3 d
l1s
;
e
* 3 d
l1s
- 0,25;
f
u,bo
f
u
; 1) = 0,833
F
b,Rd
= 2,5 * * d
ls
* s *
f
u
*
M2
10
3
= 59,50 kN
MAX(
R
Ed
F
v,Rd
;
R
Ed
F
b,Rd
) = 1,62 < 1
Analysis of cover plates:
A =
* d
1
b
1
100
= 32,00 cm
A
net
= A -
* 2 * d
l1o
d
1
100
= 23,20 cm
Limit tension force:
N
t,Rd
= MIN(A *
f
y
*
M0
10
; 0,9 * A
net
*
f
u
*
M2
10
) = 601,34 kN
N
Ed
N
t,Rd
= 0,80 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Connection subject to moment load:
7
1 2 3
5 4
8 6
e
e
e
e
e
e
e e
2
2
3
3
1 1
Dimensions of connection:
Bolt spacing e = 50,00 mm
Edge distance e1
= 35,00 mm
Bolt spacing e3
= 70,00 mm
Plate thickness t = 6,00 mm
Number of bolts n = 8
Bolts:
Bolt1 = SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 30
SC1 = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 5.6
f
u,b1
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC1) = 500,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
l1
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt1) = 30,00 mm
Bolt2 = SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 12
SC2 = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 5.6
f
u,b2
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC2) = 500,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
s2
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt2) = 12,00 mm
Shaft diameter d
l2
= d
s2
+1 = 13,00 mm
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
u2
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
Mb
= 1,25
Mo
= 1,25
Loads:
V
Ed
= 58,70 kN
M
Ed
= 910,00 kNcm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Analysis of the right bolt:
Check limit shear force
F
v,Rd
= 0,6 * *
4
( )
d
l1
10
2
*
f
u,b1
* 10
Mo
= 169,65 kN
V
Ed
F
v, Rd
= 0,35 < 1
Limit bearing strength
F
b,Rd
= 1,5 * d
l1
* t *
f
u2
* 10
3
Mb
= 77,76 kN
V
Ed
F
b,Rd
= 0,75 < 1
Check bolts on left:
I
p
=
* 6
( )
+ e
2
e
3
2
100
= 444,00 cm
Maximum horizontal force in bolt due to moment:
F
h
= M
Ed
*
e
3
* I
p
10
= 14,35 kN
Maximum vertical force:
F
v
= * M
Ed
+
e
* I
p
10
V
Ed
n
= 17,59 kN
Resulting force
R
r
=
+ F
h
2
F
v
2
= 22,70 kN
F
v,Rd
= 0,6 * f
u,b2
* d
l2
*
* 4 *
Mb
10
3
= 31,86 kN
R
r
F
v, Rd
= 0,71 < 1
Analysis of bearing strength
= MIN(
e
1
* 3 d
l2
; 2 *
e
* 3 d
l2
- 0,25;
f
u,b2
f
u2
; 1) = 0,90
F
b,Rd
= 2,5 * * d
l2
* t *
f
u2
*
Mb
10
3
= 50,54 kN
F
h
F
b,Rd
= 0,28 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Bolted shear joint:
Dimensions of connection:
Spacing of bolts a = 45,00 mm
Spacing of bolts a
0
= 35,00 mm
Spacing of bolts a
1
= 30,00 mm
Spacing of bolts a
2
= 50,00 mm
Spacing of bolts a
3
= 90,00 mm
Depth of cope a
4
= 30,00 mm
Plate projection a
s
= 20,00 mm
Lever-arm x = 45,00 mm
Number of bolts n = 3
Bolts:
M16 4.6
Bolt = SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 16
SC = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 4.6
f
u,b
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC) = 400,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
l
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt) = 16,00 mm
Shaft diameter d
0
= d
l
+2 = 18,00 mm
Angle section P = SEL("steel/WG"; Name; ) = L 80x8
Angle thickness t = TAB("steel/WG"; s; Name=P) = 8,00 mm
Factor for group bolts as in 6.5.2..2(3):
k = 0,5 for 1 group bolts; =2,5 for 2 rows
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = IPE 270
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 270,00 mm
Web thickness s
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 6,60 mm
Mb
= 1,25
M2
= 1,25
M0
= 1,10
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Loads:
V
Ed
= 60,00 kN
Check bolt spacing as in 6.5.1:
1,2 * d
0
/ a
1
= 0,72 < 1
a
1
/ MAX(12 * t; 150) = 0,20 < 1
1,5 * d
0
/ a
0
= 0,77 < 1
a
0
/ MAX(12 * t; 150) = 0,23 < 1
2,2 * d
0
/ a
2
= 0,79 < 1
a
2
/ MIN(12 * s; 200) = 0,63 < 1
Check bolts strength:
Bolts in web of main beam F
v,Ed
=
V
Ed
* 2 n
= 10,00 kN
Bolts in web of connecting beam M
Ed
= *
x
10
V
Ed
= 270,00 kNcm
Horizontal force due to M
Ed
F
h,Ed
=
M
Ed
* ( ) - n 1
a
2
10
= 27,00 kN
Distributed shearing force on bolts F
v,Ed
=
V
Ed
n
= 20,00 kN
Maximum bolt strength F
Ed
=
+ F
h,Ed
2
F
v,Ed
2
= 33,60 kN
Limit strength and analysis of bolts:
Bolts in web of main beam:
Plain in the shear plane F
v,Rd
= 0,6 * f
u,b
* *
d
l
2
* 4 *
Mb
10
3
= 38,60 kN
Limit bearing strength
= MIN(
a
1
* 3 d
0
;
a
2
* 3 d
0
- 0,25;
f
u,b
f
u
; 1) = 0,556
F
b,Rd
= 2,5 * * d
l
* t *
f
u
*
M2
10
3
= 51,24 kN
Analysis:
F
Ed
F
b,Rd
= 0,66 < 1
Bolts in web of connecting beam:
F
v,Rd
= 2 * 0,6 * f
u,b
* *
d
l
2
* 4 *
Mb
10
3
= 77,21 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Limit bearing strength
= MIN(
a
1
* 3 d
0
;
a
2
* 3 d
0
- 0,25;
f
u,b
f
u
; 1) = 0,556
F
b,Rd
= 2,5 * * d
l
* s *
f
u
*
M2
10
3
= 42,27 kN
Analysis:
F
Ed
F
b,Rd
= 0,79 < 1
Check angle section strength
Design loads:
V
Edw
=
V
Ed
2
= 30,00 kN
M
Edw
=
M
Ed
2
= 135,00 kNm
A = (2 * a
2
+ 2 * a
1
) *
t
200
= 6,40 cm
A
net
= (2 * a
2
+ 2 * a
1
- n * d
0
) *
t
200
= 4,24 cm
*
f
y
f
u
M2
M0
* 0,9
A
net
A
= 1,24 > 1
Subtract bottom bolt holes.
A = A * 2 = 12,80 cm
A
net
= A
net
* 2 = 8,48 cm
*
f
y
f
u
A
A
net
= 0,99 < 1
Bolt holes should not be subtracted
W
pl
=
* t -
( ) * 2 + a
2
* 2 a
1
2
4
* d
0
* t a
2
1000
= 44,00 cm
M
pl,Rd
= * W
pl
f
y
*
M0
10
= 940,00 kNcm
M
Ed
M
pl,Rd
= 0,29 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
V
pl,Rd
= * A
f
y
*
M0
* 3 10
= 157,88 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,38 < 1
Also:
V
Ed
( )
V
pl,Rd
2
= 0,76 < 1
No interaction.
Check shear failure:
L
v
= (n - 1) * a
2
= 100,00 mm
L
1
= a
2
= 50,00 mm
L
1
* 5 d
0
= 0,56 < 1
L
2
= (a - k * d
0
) *
f
u
f
y
= 55,15 mm
L
3
= L
v
+ a
2
+ a
3
= 240,00 mm
L
v,eff
= L
v
+ L
1
+ L
2
= 205,15 mm
L
v, ef f
L
3
= 0,85 < 1
L
3
* ( )
+ L
v
+ a
2
- a
3
* n d
0
f
u
f
y
= 0,84 < 1
Effective shear area:
A
v,eff
= L
v,eff
* t / 100 = 16,41 cm
V
eff,Rd
= * A
v,eff
f
y
*
M0
* 3 10
= 202,41 kN
V
Ed
V
ef f , Rd
= 0,30 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Double shear joint with bolts:
Dimensions of connection:
Plate thickness d
1
= 6,00 mm
Number of plates n
1
= 2
Plate thickness d
2
= 7,10 mm
Number of plates n
2
= 1
Plate width b = 210,00 mm
Bolt spacing e = 40,00 mm
Edge distance e1
= 60,00 mm
Edge distance e2
= 40,00 mm
Bolt spacing e3
= 65,00 mm
Bolts:
Bolt = SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 20
SC = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 10.9
f
u,b
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC) = 1000,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
l
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt) = 20,00 mm
Cross-section areas A
s
= TAB("steel/bolt"; Asp; BS=Bolt) = 2,45 cm
Number of bolts n= 5
Plate :
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
M0
= 1,10
M2
= 1,25
Loads:
N
Ed
= 100,00 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Joint with tension and shear:
Limit tension force of plate links
A = b * d
1
*
n
1
100
= 25,20 cm
d = d
l
+ 2 = 22,00 mm
Cross-section area 1:
A
net,1
= A - 2 * d * d
1
*
n
1
100
= 19,92 cm
Cross-section area 2:
A
net,2
= A-3 *d *d
1
*
n
1
100
+ 2 * e / (4*e
3
) * d
1
*
n
1
100
= 18,76 cm
A
net
= MIN(A
net,1
; A
net,2
) = 18,76 cm
N
t,Rd1
= MIN(
* A
f
y
M0
; 0,9 * * A
net
f
u
M2
)/10 = 486,26 kN
Limit tension force of plate rechts
A = b * d
2
*
n
2
100
= 14,91 cm
d = d
l
+ 2 = 22,00 mm
A
net,1
= A - 2 * d * d
2
*
n
2
100
= 11,79 cm
A
net,2
= A - 3 * d * d
2
*
n
2
100
+ 2 * e / (4*e
3
) * d
2
*
n
2
100
= 11,10 cm
A
net
= MIN(A
net,1
; A
net,2
) = 11,10 cm
N
t,Rd2
= MIN(
* A
f
y
M0
; 0,9 * * A
net
f
u
M2
)/10 = 287,71 kN
N
t,Rd
= MIN(N
t,Rd2
; N
t,Rd1
) = 287,71 kN
Limit tension force of boltsn:
A
s
=
*
( )
d
l
10
2
4
= 3,14 cm
Thread in the shearing plane:
F
v,Rd
= 0,6 * n * (n
1
+ n
2
- 1) *
* f
u,b
A
s
* 10
M2
= 1507,20 kN
Limit bearing strength
= MIN(
e
1
* 3 d
; 2 *
e
* 3 d
- 0,25;
f
u,b
f
u
; 1) = 0,91
F
b,Rd1
= n
1
* n * 2,5 * * d
l
* d
1
*
f
u
*
M2
10
3
= 786,24 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
= MIN(
e
1
* 3 d
; 2 *
e
* 3 d
- 0,25;
f
u,b
f
u
; 1) = 0,91
F
b,Rd2
= n
2
* n * 2,5 * * d
l
* d
2
*
f
u
*
M2
10
3
= 465,19 kN
F
b,Rd
= MIN(F
b,Rd1
; F
b,Rd2
) = 465,19 kN
Maximum allowed force:
N
l,Rd
= MIN(N
t,Rd
; F
v,Rd
; F
b,Rd
) = 287,71 kN
Analysis:
N
Ed
/ N
l,Rd
= 0,35 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
High strength friction-grip bolt connection:
Dimensions of connection:
Plate thickness 1 d
1
= 10,00 mm
Plate thickness 2 d
2
= 8,00 mm
Bolt spacing e = 65,00 mm
Edge distance e1
= 55,00 mm
Edge distance e2
= 50,00 mm
Bolt spacing e3
= 70,00 mm
Plate width b= 240,00 mm
Bolts:
Bolt = SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 22
SC = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 10.9
f
u,b
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC) = 1000,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
l
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt) = 22,00 mm
Cross-section areas A
s
= TAB("steel/bolt"; Asp; BS=Bolt) = 3,03 cm
Number of bolts n= 5
normal holes with tolerance as K
s
= 1,00
Number of slip joints as in 6.5.8.1 (1) = 1,00
coefficient of friction as in 6.5.8.3 = 0,40
as in 6.5.8.1 (3)
Ms
= 1,25
Plate:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
M0
= 1,10
M2
= 1,25
Loads:
Tension force N
Ed
= 100,00 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Limit tension force of plate:
A = MIN(d
1
; d
2
) *
b
100
= 19,20 cm
as in 7.5.2 d = d
l
+ 2 = 24,00 mm
Cross-section area 1:
A
net,1
= A - 2 * MIN(d
1
; d
2
) *
d
100
= 15,36 cm
Cross-section area 2:
A
net,2
= A - 3 *
d
100
* MIN(d
1
;d
2
) + *
2
100
e
2
* 4 e
3
*MIN(d
1
;d
2
) = 15,85 cm
A
net
= MIN(A
net,1
; A
net,2
) = 15,36 cm
Friction-grip connection:
Plate
N
net,Rd
= A
net
*
f
y
*
M0
10
= 328,15 kN
Limit tension force of bolts
Limit shank tension F
p,cd
= 0,7 *
f
u,b
10
* A
s
= 212,10 kN
Limit slip resistance force F
s,Rd
= n * K
s
* * *
F
p,cd
Ms
= 339,36 kN
Limit bearing force:
= MIN(
e
1
* 3 d
; 2 *
e
* 3 d
- 0,25;
f
u,b
f
u
; 1) = 0,76
F
b,Rd
= n * 2,5 * * d
l
* MIN(d
1
; d
2
) *
f
u
*
M2
10
3
= 481,54 kN
Maximum allowed force:
N
g,Rd
= MIN(N
net,Rd
; F
b,Rd
; F
s,Rd
) = 328,15 kN
Analysis:
N
Ed
N
g,Rd
= 0,30 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Joint with tension and shear:
Dimensions of connection:
Plate thickness d
1
= 10,00 mm
Plate thickness d
2
= 8,00 mm
Bolt spacing e = 65,00 mm
Edge distance e1
= 55,00 mm
Edge distance e2
= 50,00 mm
Bolt spacing e3
= 70,00 mm
Plate width b = 240,00 mm
Bolts:
Bolt = SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 22
SC = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 4.6
f
u,b
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC) = 400,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
l
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt) = 22,00 mm
Cross-section areas A
s
= TAB("steel/bolt"; Asp; BS=Bolt) = 3,03 cm
Number of bolts n = 5
Plate:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
M0
= 1,10
M2
= 1,25
Loads:
N
Ed
= 100,00 kN
Joint with tension and shear:
Limit tension force of plate:
A = MIN(d
1
; d
2
)
*
b
100
= 19,20 cm
d = d
l
+ 2 = 24,00 mm
Cross-section area 1:
A
net,1
= A - 2 * MIN(d
1
; d
2
) *
d
100
= 15,36 cm
Cross-section area 2:
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
A
net,2
= A - 3 *
d
100
* MIN(d
1
;d
2
) + *
2
100
e
2
* 4 e
3
*MIN(d
1
;d
2
) = 15,85 cm
A
net
= MIN(A
net,1
; A
net,2
) = 15,36 cm
N
t,Rd
= MIN(
* A
f
y
M0
; 0,9 * * A
net
f
u
M2
)/10 = 398,13 kN
Limit tension force of boltsn:
A
s
=
*
( )
d
10
2
4
= 4,52 cm
Thread in the shearing plane:
F
v,Rd
= 0,6 * n *
* f
u,b
A
s
* 10
M2
= 433,92 kN
Limit bearing strength
= MIN(
e
1
* 3 d
; 2 *
e
* 3 d
- 0,25;
f
u,b
f
u
; 1) = 0,76
F
b,Rd
= n * 2,5 * * d * MIN(d
1
; d
2
) *
f
u
*
M2
10
3
= 525,31 kN
Maximum allowed force:
N
l,Rd
= MIN(N
t,Rd
; F
v,Rd
; F
b,Rd
) = 398,13 kN
Analysis:
N
Ed
/ N
l,Rd
= 0,25 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
Check shear failure:
VV
Ed
VV
V
V
V
V
Dimensions of connection:
Spacing of bolts a = 50,00 mm
Spacing of bolts a
1
= 43,00 mm
Spacing of bolts a
2
= 70,00 mm
Spacing of bolts a
3
= 75,00 mm
Number of bolts n = 4
Bolts:
Bolt = SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 20
SC = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 5.6
f
u,b
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC) = 500,00 N/mm
Hole diameter d
l
= TAB("steel/bolt"; d; BS=Bolt) = 20,00 mm
Shaft diameter d
l2
= d
l
+2 = 22,00 mm
k = 0,5 for 1 group bolts; =2,5 for 2 rows
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = IPE 360
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 360,00 mm
Web thickness s
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 8,00 mm
Mb
= 1,25
M0
= 1,10
Loads:
V
Ed
= 58,70 kN
Limit shear force of section:
A
v
= 1,04 *
* h s
100
= 29,95 cm
V
pl,Rdp
= * A
v
f
y
* 3 *
M0
10
= 369,41 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Bolted connections
A
v,net
= A
v
-
* n * s d
l2
100
= 22,91
*
f
y
f
u
A
v
A
v,net
= 0,85 < 1
Holes can be neglected.
Joint with shear failure as in Bild 6.5.5:
L
v
= (n - 1) * a
2
= 210,00 mm
L
1
= a
1
= 43,00 mm
L
1
* 5 d
l2
= 0,39 < 1
L
2
= (a - k * d
l2
) *
f
u
f
y
= 59,74 mm
L
3
= L
v
+ a
1
+ a
3
= 328,00 mm
L
v,eff
= L
v
+ L
1
+ L
2
= 312,74 mm
L
v, ef f
L
3
= 0,95 < 1
L
3
+ L
v
+ a
1
- a
3
+ n d
l2
= 0,95 < 1
Effective shear area:
A
v,eff
= L
v,eff
*
s
100
= 25,02 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v,eff
f
y
*
M0
* 3 10
= 308,60 kN
Maximum design force for shear:
V
Rd
= MIN(V
pl,Rdp
; V
pl,Rd
) = 308,60 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Column subject to compression force:
N
H
d
Column heigth H = 7,50 m
l
y
= H/2 = 3,75 m
l
z
= H/3 = 2,50 m
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 430
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 275,00 N/mm
E
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 0,92
Profil:
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = IPE 300
Cross-sectional area A = TAB("steel/"Typ; A; Name=Profil) = 53,80 cm
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 300,00 mm
Depth of web h
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ; h1; Name=Profil) = 248,00 mm
Web thickness s
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 7,10 mm
Flange width b = TAB("steel/"Typ; b; Name=Profil) = 150,00 mm
Flange thickness t = TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 10,70 mm
Radius of gyration i
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ; iy; Name=Profil) = 12,50 cm
Radius of gyration i
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ; iz; Name=Profil) = 3,35 cm
Section classification As in Table 5.3.1:
Web:
h
1
* s * 33
= 1,15 < 1
h
1
* s * 38
= 1,00 < 1
Section class 2.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Flange:
b
* 2 * t * 10
= 0,76 < 1
Section class 1.
Section will be classified as class 2.
Analysis:
nach 5.5.1.1 (1)
A
= 1,00 Cross-section class 2
nach 5.1.1 (2)
M1
= 1,10 Cross-section class 2
Check buckling In Y-Y Axis:
h / b = 2,00 > 1,2
t /10 = 1,07 cm < 4 cm
as in Tab 5.5.3 :
y
= l
y
*
100
i
y
= 30,00
1
= 93,9 * = 86,39
trans,y
= *
A
= 0,347
Apply strut curve a
As in Table 5.5.1 = 0,21
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,y
- 0,2) +
trans,y
) = 0,576
=
1
+
trans,y
2
= 0,9655
N
b,y,Rd
= *
A
* A *
f
y
* 10
M1
= 1298,60 kN
Check buckling In Z-Z Axis:
h / b = 2,00 > 1,2
t / 10 = 1,07 cm < 4cm
as in Tab 5.5.3 :
z
= l
z
* 100 / i
z
= 74,63
trans,z
= *
A
= 0,864
Apply strut curve b
As in Table 5.5.1 = 0,34
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,z
- 0,2) +
trans,z
) = 0,986
=
1
+
trans,z
2
= 0,6844
N
b,z,Rd
= *
A
* A *
f
y
* 10
M1
= 920,52 kN
max_N
d
= MIN(N
b,y,Rd
; N
b,z,Rd
) = 920,52 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Column of section class 4:
t
1
t
y
z
b
2
h
h
N
N
Load diagram:
Column heigth H = 4,00 kN
Flange width b = 20,00 cm
Depth of web h = 30,00 cm
Web thickness t
1
= 1,20 cm
Flange thickness t
2
= 1,20 cm
Loads:
N
d
= 700,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
E
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
Section classification As in Table 5.3.1:
b
* t
2
* 14
= 1,19 > 1
Section class 4
h
* t
1
* 33
= 0,76 > 1
Section class 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Effective web area:
Flangee:
As in Table 5.3.3:
= 1,00
k
= 0,43
as in 5.3.5(3)
trans,p
=
b
* t
2
* 28,4 *
k
= 0,89 >0,673
=
-
trans,p
0,22
trans,p
2
= 0,846
b
eff
= * b = 16,92 cm
A
eff
= 2 * (b
eff
* t
2
) + (h + 2 * t
2
) * t
1
= 79,49 cm
Location of shear centre:
y
s,eff
=
* b
ef f
* 2 * t
2
+ b
ef f
t
2
2
A
ef f
= 4,628 cm
I
z,eff
= *
b
eff
3
12
* 2 + t
2
* b
eff
* 2 * t
2
+
( )
-
+ b
eff
t
1
2
y
s,eff
2
* ( )
+ h * 2 t
2
( )
+
t
1
3
12
* t
1
y
s,eff
2
= 2604 cm
4
W
z,eff
=
I
z,eff
- ( )
+ b
eff
t
1
- y
s,eff
t
1
2
= 201,99 cm
Gross area:
A = b * 2 * t
2
+ (h + 2 * t
2
) * t
1
= 86,88 cm
Location of center of gravity:
y
s
=
* b * 2 * t
2
+ b t
1
2
A
= 5,856 cm
I
z
= *
b
3
12
* 2 + t
2
* b * 2 * t
2
+
( )
-
+ b t
1
2
y
s
2
* ( )
+ h * 2 t
2
( )
+
t
1
3
12
* t
1
y
s
2
= 4018 cm
4
e
Nz
= y
s
- y
s,eff
= 1,228 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Check buckling:
N
cr
= *
2
*
E
10
I
z
( ) * H 100
2
= 5204,85 kN
A
=
A
eff
A
= 0,915
trans,z
=
*
A
* A
f
y
* 10 N
cr
= 0,599
Apply strut curve c As in Table 5.5.3
= 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,z
- 0,2) +
trans,z
) = 0,777
=
1
+
trans,z
2
= 0,786
M
z,d
= N
d
*
e
Nz
100
= 8,60 kNm
= 1,00
M
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,10
z
=
trans,z
* (2 *
M
- 4) = -1,078 < 0,9
k
z1
= 1 -
*
z
N
d
* * A
eff
f
y
10
= 1,514 ~ 1,5
k
z2
= 1,500
k
z
= MIN(k
z1
; k
z2
) = 1,500
+
N
d
* * A
eff
f
y
*
M
10
* 100 * k
z
M
z,d
* W
z,eff
f
y
*
M
10
= 0,823 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Column with compression and moment:
H
N
M
d
d
Load diagram:
Column heigth H = 5,00 m
Loads:
N
d
= 200,00 kN
M
y,d
= 10,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
E
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G
= TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
= (235 / f
y
) = 1,00
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
g
= 1,35
platischer Formbeiwert
pl y
= 1,14
platischer Formbeiwert
pl z
= 1,25
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Profil:
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEA
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = HEA 160
Cross-sectional area A = TAB("steel/"Typ; A; Name=Profil) = 38,80 cm
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 152,00 mm
Depth of web h
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ; h1; Name=Profil) = 104,00 mm
Web thickness s
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 6,00 mm
Flange width b = TAB("steel/"Typ; b; Name=Profil) = 160,00 mm
Flange thickness t = TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 9,00 mm
Radius of gyration i
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ; iy; Name=Profil) = 6,57 cm
Radius of gyration i
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ; iz; Name=Profil) = 3,98 cm
W
el y
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Wy; Name=Profil) = 220,00 cm
W
pl y
=
pl y
* W
el y
= 250,80 cm
W
el z
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Wz; Name=Profil) = 76,90 cm
W
pl z
=
pl z
* W
el z
= 96,13 cm
Section classification As in Table5.3.1:
Web will be assumed as pressed in
h
1
* s * 33
= 0,53 < 1
Section class 1.
Flange:
b
* * 2 t * 10
= 0,89 < 1
Section class 1.
Check bending and buckling:
as in 5.5.1.1 (1)
A
= 1,00 Cross-section class 1
as in 5.1.1 (2)
M1
= 1,10 Cross-section class 1
y
= H *
100
i
y
= 76,10
1
= 93,9 * = 93,90
trans,y
= *
A
= 0,810
z
= H *
100
i
z
= 125,63
trans,z
=
z
*
E
f
y
= 1,34
As in Table 5.5.3
h / b = 0,95 < 1,2
t / 10 = 0,90 cm < 10cm
As in Table:5.5.1
Strut curve b for Y-Y axis
= 0,34
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,y
- 0,2) +
trans,y
) = 0,932
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
y
=
1
+
trans,y
2
= 0,7179
Apply strut curve c for z-Achse
= 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,z
- 0,2) +
trans,z
) = 1,677
z
=
1
+
trans,z
2
= 0,3724
= 0,00
My
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,80
y
=
trans,y
* (2 *
My
- 4) +
- W
ply
W
ely
W
ely
= -0,184 < 0,9
k
y
= 1 -
*
y
N
d
*
y
* A f
y
= 1,006 < 1,5
= MIN(
y
;
z
) = 0,372
+
N
d
* * A
f
y
*
M
10
* k
y
* 100
M
y,d
* W
pl y
f
y
*
M
10
= 0,836 < 1
Check torsional-flexural buckling:
w
= 1,00 Cross-section class 1
As in Table: F.1.1
= 0,00
k = 1,00
C
1
= 1,879
LT
= * 90
H
* i
z
( )
*
C
1
+ 1 *
1
20
( )
* 100
H
i
z
h
t
2
4
= 59,208
trans,LT
= *
LT
w
= 0,631
For rolled sections strut curve a
= 0,21
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,LT
- 0,2) +
trans,LT
) = 0,74
LT
=
1
+
trans,LT
2
= 0,89
M,LT
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,80
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
quer,z
= *
A
= 1,338
LT
= 0,15 *
quer,z
*
M,LT
- 0,15 = 0,211 < 0,9
h / b = 0,95 < 1,2
t / 10 = 0,90 cm < 10cm
Z-Z axis Strut curve c
= 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,z
- 0,2) +
trans,z
) = 1,677
z
=
1
+
trans,z
2
= 0,3724
k
LT
= 1 -
*
LT
N
d
*
z
* A f
y
= 0,988 < 1,5
+
N
d
*
z
* A
f
y
*
M
10
* k
LT
* 100
M
y,d
* *
LT
W
pl y
f
y
*
M
10
= 0,855 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Column subject to compression force:
N
H
d
Column base is pinned.
For buckling, column head is pinned about the Y-Y axis, and fixed about the Z-Z axis .
Load diagram:
Column heigth H = 8,00 m
Loads:
N
d
= 2000,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
E
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
Effective length factor:
k
y
= 1,00 For simply supported ends
k
z
= 0,70 fixed ends
Profil:
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEB
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = HEB 300
Cross-sectional area A = TAB("steel/"Typ; A; Name=Profil) = 149,00 cm
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 300,00 mm
Depth of web h
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ; h1; Name=Profil) = 208,00 mm
Web thickness s
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 11,00 mm
Flange width b = TAB("steel/"Typ; b; Name=Profil) = 300,00 mm
Flange thickness t = TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 19,00 mm
Moment of inertia I = TAB("steel/"Typ; Iy; Name=Profil) = 25170,00 cm
4
Radius of gyration i
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ; iy; Name=Profil) = 13,00 cm
Radius of gyration i
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ; iz; Name=Profil) = 7,58 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Section classification:
Web:
h
1
* s * 33
= 0,57 > 1
Flange:
b
* * 2 t * 10
= 0,79 > 1
Section class 1.
Analysis:
A
= 1,00 Cross-section class 1
M1
= 1,10 Cross-section class 1
Check buckling In Y-Y Axis:
h / b = 1,00 < 1,2
t / 10 = 1,90 cm < 10cm
y
= k
y
* H *
100
i
y
= 61,54
1
= 93,9 * = 93,90
trans,y
= *
A
= 0,655
Apply strut curve b
As in Table 5.5.1 = 0,34
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,y
- 0,2) +
trans,y
) = 0,792
=
1
+
trans,y
2
= 0,8083
N
b,Rd
= *
A
* A
*
f
y
* 10
M1
= 2572,966 kN
N
d
N
b,Rd
= 0,78 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Check buckling In Z-Z Axis:
h / b = 1,00 < 1,2
t / 10 = 1,90 cm < 10cm
z
= k
z
* H *
100
i
z
= 73,88 m
trans,z
= *
A
= 0,787
Apply strut curve c
As in Table 5.5.1 = 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,z
- 0,2) +
trans,z
) = 0,953
=
1
+
trans,z
2
= 0,6709
N
b,Rd
= *
A
* A
*
f
y
* 10
M1
= 2135,60 kN
N
d
N
b,Rd
= 0,94 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Column of channel section with compression and transverse loads:
H
d
d
q
t
1
t
y
z
b
2
h
N
Load diagram:
Column height H = 4,00 m
Beam width b = 9,50 cm
Depth of web h = 29,40 cm
Web thickness t
1
= 1,00 cm
Flange width t
2
= 0,60 cm
Loads:
q
d
= 15,00 kN/m
N
d
= 90,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
E
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Section classification:
As in Table 5.3.1
b
* t
2
* 14
= 1,13 > 1
Section class 4
As in Table 5.3.2
h
* t
1
* 33
= 0,89 > 1
Section class 1
A = b * 2 * t
2
+ (h + 2 * t
2
) * t
1
= 42,00 cm
Location of center of gravity:
y
s
=
* b * 2 * t
2
+ b t
1
2
A
= 1,425 cm
I
z
= *
b
3
12
* 2 + t
2
* b * 2 * t
2
+
( )
-
+ b t
1
2
y
s
2
* ( )
+ h * 2 t
2
( )
+
t
1
3
12
* t
1
y
s
2
= 317,21 cm
4
I
y
= *
h
3
12
+ t
1
* 2 * b
( )
+
t
2
3
12
* t
2
( )
+ h t
2
2
2
= 4683,02 cm
4
W
el,z
=
I
z
+ b -
t
1
2
y
s
= 36,99 cm
W
el,y
=
I
y
( )
+ h t
1
2
= 308,09 cm
Effective web area:
Flangee:
As in Table 5.3.3:
= 1,00
k
= 0,43
as in 5.3.5(3)
trans,p
=
b
* t
2
* 28,4 *
k
= 0,85 >0,673
=
-
trans,p
0,22
trans,p
2
= 0,872
b
eff
= * b = 8,28 cm
A
eff
= 2 * (b
eff
* t
2
) + (h + 2 * t
2
) * t
1
= 40,54 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Location of shear centre:
y
s,eff
=
* b
ef f
* 2 * t
2
+ b
ef f
t
2
2
A
ef f
= 1,088 cm
e
Nz
= y
s
- y
s,eff
= 0,337 cm
A
=
A
eff
A
= 0,965
Slenderness and reductions:
In Z-Z Axis:
N
cr,z
= *
2
* E
I
z
( ) * H 100
2
= 4109,09 kN
trans,z
=
*
A
* A
f
y
N
cr,z
= 1,52
Apply strut curve c
= 0,49
= 0,5 *(1 + * (
trans,z
- 0,2) +
trans,z
) = 1,979
z
=
1
+
trans,z
2
= 0,308
In Y-Y Axis:
N
cr,y
= *
2
* E
I
y
( ) * H 100
2
= 60663,06 kN
trans,y
=
*
A
* A
f
y
N
cr,y
= 0,40
Apply strut curve c
= 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,y
- 0,2) +
trans,y
) = 0,629
y
=
1
+
trans,y
2
= 0,897
= MIN(
z
;
y
) = 0,3080
N
b,Rd
= * * A
ef f
f
y
M
= 2667,53 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Limit bending moment about the Y-Y axis:
Cross-section class 4
z'
s
=
* -b
ef f
* t
2
+
+ h t
2
2
*
( )
+ b
t
1
2
* t
2
+ h t
2
2
A
ef f
= 0,382 cm
*
( )
+ h t
2
3
12
+ t
1
* ( )
+ h t
2
* t
1
z'
s
= 2261,46 cm
4
* b
eff
* t
2
+
( )
+
+ h t
2
2
z'
s
2
*
( )
+ b
t
1
2
* t
2
( )
-
+ h t
2
2
z'
s
2
= 2457,57 cm
4
I
eff,y =
4719,03 cm
4
W
eff,y
=
I
eff,y
+
+ h t
2
2
z'
s
= 306,79 cm
M
c,Rd,y
= * W
ef f , y
f
y
M
= 65541,50 kNm
Limit bending moment about the Z-Z axis:
Cross-section class 4 Tab 5.3.3
=
-y
s
+ b -
t
1
2
y
s
= -0,17
k
= 0,57 - 0,21 * + 0,07 * = 0,61
+ b
t
1
2
* t
2
* 21 *
k
= 1,02 > 1
As in Table:5.3.5 (3)
trans,p
=
+ b
t
1
2
* t
2
* 28,4 *
k
= 0,75 >0,673
=
-
trans,p
0,22
trans,p
2
= 0,942
b
eff
= *
+ b
t
1
2
- 1
= 8,05 cm
b
t
= -1 * *
( )
+ b
t
1
2
- 1
= 1,45 cm
c
eff
= b
eff
+ b
t
= 9,50 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
A
eff
= (h + t
2
) * t
1
+ 2 * c
eff
* t
2
= 41,40 cm
y' = * 2 * c
ef f
2
t
2
* 2 A
ef f
= 1,31 cm
I
eff,z
= (h + t
2
) * t
1
* y' + 2 *
c
eff
3
12
* t
2
+ 2 * c
eff
* t
2
*
( )
-
c
eff
2
y'
2
= 272,12 cm
4
W
eff,z
=
I
eff,z
-
c
eff
2
y'
= 79,10 cm
M
c,Rd,z
= * W
ef f , z
f
y
M
= 16898,64 kNm
Check buckling:
N
Ed
= N
d
= 90,00 kN
M
y,Ed
= q
d
*
H
2
8
= 30,00 kNm
M
z,Ed
= N
d
*
e
Nz
100
= 0,30 kNm
My
= 1,30
y
=
trans,y
* (2 *
My
- 4) = -0,560 < 0,9
k
y
= 1 -
*
y
N
Ed
*
y
* A
eff
f
y
= 1,006 < 1,5
= 1,000
M
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,10 < 1,5
z
=
trans,z
* (2 *
M
- 4) = -2,736 < 0,9
k
z1
= 1 -
*
z
N
Ed
* * A
eff
f
y
= 1,082
k
z2
= 1,500
k
z
= MIN(k
z1
; k
z2
) = 1,082
+
N
Ed
* * A
eff
f
y
M
* k
y
* 100 +
M
y,Ed
* W
eff,y
f
y
M
* k
z
* 100
M
z,Ed
* W
eff,z
f
y
M
= 0,081 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Laced column made up of channel and angle sections:
l
l
y
N
d
b
h
H
sd
Loads:
N
d
= 300,00 kN
H
d
= 45,00 kN
Plan and elevation values:
Span length l
y
= 69,20 cm
Column height l = 10*l
y
/100 = 6,92 m
Width b = 40,00 cm
Winkel
1
= 45,00
U-Profil U = SEL("steel/U"; Name; ) = U 300
A
f
= TAB("steel/U"; A; Name=U) = 58,80 cm
e
z
= TAB("steel/U"; ez; Name=U) = 2,70 cm
i
z
= TAB("steel/U"; iz; Name=U) = 2,90 cm
Winkel W = SEL("steel/WG"; Name; ) = L 50x5
Angle thickness A
D
= TAB("steel/WG"; A; Name=W) = 4,80 cm
Angle thickness i
= TAB("steel/WG"; i; Name=W) = 0,98 cm
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
E
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Maximal tension force in chord:
Effective length ratio k = 2,00
Imperfection:
w
o
=
* 2 l
5
= 2,77 cm
Effective moment of inertia:
h
o
= b - 2 * e
z
= 34,60 cm
I
eff
= 0,5 * h
o
* A
f
= 35196,50 cm
4
Shear strength:
S
v
= 2 *
E
10
* A
D
* l
y
*
h
o
2
* 2
* 2 h
o
2 2
3
= 71276,36 kN
N
cr
=
1
* 4 +
( ) * 100 l
2
*
2
*
E
10
I
eff
1
S
v
= 3615,26 kN
max_M
E
= H
d
* l +
N
d
- 1
N
d
N
cr
*
w
o
100
= 320,46 kNm
N
f,Ed
= 0,5 * N
d
+ 100 *
max_M
E
h
o
= 1076,18 kN
Analysis of channels:
=
l
y
i
z
= 23,86
trans
=
*
1
= 0,254
Apply strut curve c
= 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans
- 0,2) +
trans
) = 0,545
=
1
+
trans
2
= 0,9735
N
b,Rd
= * A
f
*
f
y
*
M
10
= 1222,89 kN
N
f,Ed
N
b,Rd
= 0,880 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Analysis of lacing angles:
max_V
E
= H
d
+ *
N
d
- 1
N
d
N
cr
* w
o
* 200 l
= 47,06 kN
Design force for a diagonal:
N
Ed
=
max_V
E
* 2 cos ( )
1
= 33,28 kN
=
* 2 h
o
2
i
= 49,93
trans
=
*
1
= 0,532
Apply strut curve c
= 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans
- 0,2) +
trans
) = 0,723
=
1
+
trans
2
= 0,8247
N
b,Rd
= * A
D
*
f
y
*
M
10
= 84,57 kN
N
Ed
N
b,Rd
= 0,39 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Column of section class 4:
h
t
t
b
C D
B
A
2
1
h
N
N
Load diagram:
Column height H = 6,50 m
Beam width b = 50,00 cm
Column height h = 100,00 cm
Web thickness t
1
= 1,00 cm
Flange thickness t
2
= 1,00 cm
Loads:
N
d
= 3500,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
E
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
g
= 1,35
Section classification:
As in Table 5.3.1
b' = b - 2 * t
1
= 48,00 cm
b'
* t
2
* 42
= 1,14 > 1
Section class 4
h' = h - 2 * t
2
= 98,00 cm
h'
* t
1
* 42
= 2,33 > 1
Section class 4
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Effective web area:
Part A-B; C-D As in Table 5.3.2:
= 1,00
k
= 4,00
as in 5.3.5(3)
quer,p
=
b'
* t
2
* 28,4 *
= 0,85 >0,673
=
-
quer,p
0,22
quer,p
2
= 0,872
b
eff
= * b' = 41,86 cm
Part A-C; B-D As in Table 5.3.2:
= 1,00 cm
k
= 4,00
as in 5.3.5(3)
quer,p
=
h'
* t
1
* 28,4 *
= 1,73 >0,673
=
-
quer,p
0,22
quer,p
2
= 0,505
h
eff
= * h' = 49,49 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Columns
Check buckling:
A
eff
= 2 * (h
eff
* t
1
+ b
eff
* t
2
) + 4 * t
1
* t
2
= 186,70 cm
A = b * h - (b - 2 * t
1
) * (h - 2 * t
2
) = 296,00 cm
A
=
A
eff
A
= 0,631
I
b
=
* b - h
3
* ( )
- b * 2 t
1
( )
- h * 2 t
2
3
12
= 401898,67 cm
4
I
h
=
* b
3
- h * ( )
- b * 2 t
1
3
( )
- h * 2 t
2
12
= 138498,67 cm
4
I = MIN(I
b
; I
h
) = 138498,67 cm
4
N
cr
= *
2 * E I
* H
2
10
5
= 67941,82 kN
transv
=
*
A
* A
f
y
* 10 N
cr
= 0,25
Apply strut curve b
= 0,34
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
transv
- 0,2) +
transv
) = 0,540
=
1
+
transv
2
= 0,9817
N
b,Rd
= *
A
* A
*
f
y
*
M
10
= 3917,19 kN
N
d
N
b,Rd
= 0,893 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Continuous Beam
Purlin / Strut with biaxial bending and torsional-flexural buckling:
q
d
q
d
Plan and elevation values:
Span length l= 720,00 cm
Angle of slope = 10,00
Spacing of purlin l'= 4,00 m
platischer Formbeiwert
pl y
= 1,14
platischer Formbeiwert
pl z
= 1,25
Loads:
From dead load g= 0,20 kN/m
From snow load s= 0,40 kN/m
Section classification for: IPE 200
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = IPE 200
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 200,00 mm
Flange width b
f
= TAB("steel/"Typ; b; Name=Profil) = 100,00 mm
Flange thickness t
f
= TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 8,50 mm
Flange thickness t
w
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 5,60 mm
Moment of inertia I
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Iy; Name=Profil) = 1940,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Iz; Name=Profil) = 142,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ; IT; Name=Profil) = 6,98 cm
4
I
= t
f
* b
f
* (h - t
f
) / (24*10
6
) = 12988,09 cm
6
i
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ; iz; Name=Profil) = 2,24 cm
W
el y
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Wy; Name=Profil) = 194,00 cm
W
pl y
=
pl y
* W
el y
= 221,16 cm
W
el z
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Wz; Name=Profil) = 28,50 cm
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G = TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
g
= 1,35
p
= 1,50
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Continuous Beam
Design calculations:
Factored load
p
d
=
g
* g +
p
* s = 0,87 kN/m
Effective load
q
d
= p
d
* 4 = 3,48 kN/m
Vertical load component q
zd
= q
d
* COS() = 3,43 kN/m
Horizontal load component q
yd
= q
d
* SIN() = 0,60 kN/m
Forces at 2nd support:
M
byEd
= 0,105 * q
zd
*
( )
l
100
2
= 18,67 kNm
M
bzEd
= 0,105 * q
yd
*
( )
l
100
2
= 3,27 kNm
V
bzEd
= 0,606 * q
zd
*
l
100
= 14,97 kN
V
byEd
= 0,606 * q
yd
*
l
100
= 2,62 kN
Check biaxial bending strength:
About Y-Y axis
A
v
= 1,04 * h * t
w
/ 10 = 11,65 cm
V
pl,z,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* *
3
M
10
= 143,69 kN
V
bzEd
V
pl,z,Rd
= 0,10 < 1
V
bzEd
V
pl,z,Rd
= 0,10 < 0,5
No reduction in moment strength necessary due to shear.
M
pl,y,Rd
=
* W
ply
f
y
*
M
10
= 4724,78 kNcm
About Z-Z axis
A
v
= 2 * b
f
* t
f
/ 10 = 17,00 cm
V
pl,y,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* *
3
M
10
= 209,68 kN
V
byEd
V
pl,y,Rd
= 0,01 < 1
V
byEd
V
pl,y,Rd
= 0,01 < 0,5
No reduction in moment strength necessary due to shear
M
pl,z,Rd
= 1,5 *
* W
elz
f
y
*
M
10
= 913,30 kNcm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Continuous Beam
Analysis:
as in 5.35: for I- and H- sections:
= 2,00
= 1,00
Or else: 5.4.8.1 (11)
abs
( )
+
( )
* M
byEd
10
2
M
pl,y,Rd
( )
* M
bzEd
10
2
M
pl,z,Rd
= 0,514 < 1
Check flexural-torsional buckling strength:
i
LT
=
* I
z
I
W
pl y
2
4
= 2,48 cm
Load is applied in top flange.
z
a
= 10,00 cm
z
s
= 0,00 cm
z
g
= z
a
- z
s
= 10,00 cm
As in Table F.1.2, interpolated.
C
1
= 1,00
C
2
= 0,80
C
3
= 0,70
For simply supported ends fixed ends k = 0,70
No measures taken toward bending k
w
= 1,00
h
s
=
- h t
f
10
= 19,15 cm
5.5.2; Section class 1+2
w
= 1,00
1
= *
E
s
f
y
= 93,91
LT
=
* k / l i
LT
*
C
1
+
( )
k
k
w
2
*
1
20
+
( )
* k / l i
LT
h
t
f
2
( )
* 2 * C
2
z
g
h
s
2
* 2 * C
2
z
g
h
s
= 172,86
trans,LT
= *
LT
w
= 1,841
Apply strut curve a:
As in Table 5.5.1 = 0,21
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,LT
-0,2) +
trans,LT
) = 2,37
LT
=
1
+
trans,LT
2
= 0,26
No longitudinal forces k
z
= 1,00
No longitudinal forces k
LT
= 1,00
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Continuous Beam
* k
LT
+
M
byEd
*
LT
M
pl,y,Rd
100
* k
z
M
bzEd
M
pl,z,Rd
100
= 1,88 < 1
Section is not adequate: Restrain section in quarterly points:
l = l / 4 = 180,00 cm
LT
=
* k / l i
LT
*
C
1
+
( )
k
k
w
2
*
1
20
+
( )
* k / l i
LT
h
t
f
2
( )
* 2 * C
2
z
g
h
s
2
* 2 * C
2
z
g
h
s
= 85,08
trans,LT
= *
LT
w
= 0,906
Apply strut curve a:
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,LT
-0,2) +
trans,LT
) = 0,98
LT
=
1
+
trans,LT
2
= 0,74
* k
LT
+
M
byEd
*
LT
M
pl,y,Rd
100
* k
z
M
bzEd
M
pl,z,Rd
100
= 0,89 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : foot and support
Concentrated point load of a beam in another beam:
Design loads and properties
P
d
= 68,00 kN
M
Ed1
= 70,00 kNm
M
Ed2
= -22,00 kNm
Top beam (IPE180)
Profil TypO = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected ProfilO = SEL("steel/"TypO; Name; ) = IPE 180
Web thickness s
o
= TAB("steel/"TypO; s; Name=ProfilO) = 5,30 mm
Flange thickness t
o
= TAB("steel/"TypO; t; Name=ProfilO) = 8,00 mm
Radius r
o
= TAB("steel/"TypO; r; Name=ProfilO) = 9,00 mm
Flange width b
o
= TAB("steel/"TypO; b; Name=ProfilO) = 91,00 mm
Web depth h
o
= TAB("steel/"TypO; h; Name=ProfilO) = 180,00 mm
Web depth h
1o
= TAB("steel/"TypO; h1; Name=ProfilO) = 146,00 mm
W
elo
= TAB("steel/"TypO; W
y
; Name=ProfilO) = 146,00 cm
W
plo
= 1,14 * W
elo
= 166,44 cm
3
I
yo
= TAB("steel/"TypO; Iy; Name=ProfilO) = 1320,00 cm
4
Bottom beam (HEA200)
Profil TypO = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEA
Selected ProfilO = SEL("steel/"TypO; Name; ) = HEA 200
Web thickness of beam s
u
= TAB("steel/"TypO; s; Name=ProfilO) = 6,50 mm
Flange thickness t
u
= TAB("steel/"TypO; t; Name=ProfilO) = 10,00 mm
Radius r
u
= TAB("steel/"TypO; r; Name=ProfilO) = 18,00 mm
Flange width bu = TAB("steel/"TypO; b; Name=ProfilO) = 200,00 mm
Web depth h
u
= TAB("steel/"TypO; h; Name=ProfilO) = 190,00 mm
Web depth h
1u
= TAB("steel/"TypO; h1; Name=ProfilO) = 134,00 mm
W
elu
= TAB("steel/"TypO; W
y
; Name=ProfilO) = 389,00 cm
W
plu
= 1,14 * W
elu
= 443,46 cm
3
I
yu
= TAB("steel/"TypO; Iy; Name=ProfilO) = 3690,00 cm
4
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : foot and support
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G
= TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
= (235 / f
y
) = 1,00
M
= 1,10
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
f
yd
= f
y
/
M
= 213,64 kN/cm
Limit plastic bearing:
Stiff bearing length of top, bottom beam:
s
s1
= s
o
+ 2 * t
o
+ 4 * r
o
* (1 -
2
2
) = 31,84 mm
f,Ed1
= 100 *
M
Ed1
W
elu
= 17,99 kN/cm
b
f1
= t
u
* 25 = 250,00 mm
b
f1
= MIN(b
f1
; b
u
) = 200,00 mm
s
y1
= 2 * t
u
*
b
u
s
u
*
- 1
( )
*
M
*
f,Ed1
10
f
y
2
= 59,83 mm
R
y,Rd1
= (s
s1
+ s
y1
) * s
u
*
f
y d
10
3
= 127,30 kN
P
d
R
y,Rd1
= 0,53 < 1
Stiff bearing length of bottom beam:
s
s2
= s
u
+ 2 * t
u
+ 4 * r
u
* (1 -
2
2
) = 47,59 mm
f,Ed2
= 100 *
M
Ed2
W
elo
= -15,07 kN/cm
b
f
= t
o
* 25 = 200,00 mm
b
f2
= MIN(b
f
; b
o
) = 91,00 mm
s
y2
= 2 * t
o
*
b
o
s
o
*
- 1
( )
*
M
*
f,Ed2
10
f
y
2
= 46,99 mm
R
y,Rd2
= (s
s2
+ s
y2
) * s
o
*
f
y d
10
3
= 107,09 kN
P
d
R
y,Rd2
= 0,63 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : foot and support
Check web crushing:
Bottom beam:
m
1
=
s
s1
h
1u
= 0,238
m
2
= 0,200
m
u
= MIN(m
1
; m
2
) = 0,200
R
a,Rd1
= * 0,5 * s
u
2
*
* E
s
f
y
+
t
u
s
u
* 3 *
s
u
t
u
m
u
*
M
10
3
= 219,95 kN
P
d
R
a,Rd1
= 0,31 < 1
M
c,Rd1
= W
plu
*
f
y d
10
3
= 94,74 kNm
M
Ed1
M
c,Rd1
= 0,74 < 1
Top beam:
m
1
=
s
s2
h
1o
= 0,326
m
2
= 0,200
m
o
= MIN(m
1
; m
2
) = 0,200
R
a,Rd2
= * 0,5 * s
o
2
*
* E
s
f
y
+
t
o
s
o
* 3 *
s
o
t
o
m
o
*
M
10
3
= 145,85 kN
P
d
R
a,Rd2
= 0,47 < 1
M
c,Rd2
= W
plo
*
f
y d
10
3
= 35,56 kNm
abs ( ) M
Ed2
M
c,Rd2
= 0,62 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : foot and support
Check web buckling for whole web:
Bottom beam:
Effective web width b
eff2
=
+ h
u
2
s
s1
2
= 192,65 mm
Effective web area A
2
= b
eff2
*
s
u
100
= 12,52 cm
Moment of inertia I
2
=
*
b
eff2
10
( )
s
u
10
3
12
= 0,441 cm
4
Radius of gyration i
2
=
I
2
A
2
= 0,188 cm
Effective slenderness
trans2
=
h
u
* i
2
*
1
10
= 1,076
Apply strut curve c:
= 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans2
- 0,2) +
trans2
) = 1,294
2
=
1
+
trans2
2
= 0,4968
R
b,Rd2
=
2
* A
2
*
f
y d
10
= 132,88 kN
P
d
R
b,Rd2
= 0,51 < 1
Top beam:
Effective web width b
eff1
=
+ h
o
2
s
s1
2
= 182,79 mm
Effective web area A
1
= b
eff1
*
s
o
100
= 9,69 cm
Moment of inertia I
1
=
*
b
eff1
10
( )
s
o
10
3
12
= 0,227 cm
4
Radius of gyration i
1
=
I
1
A
1
= 0,153 cm
Effective slenderness
trans1
=
h
o
* i
1
*
1
10
= 1,253
Apply strut curve c:
= 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans1
- 0,2) +
trans1
) = 1,543
1
=
1
+
trans1
2
= 0,4093
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : foot and support
R
b,Rd1
=
1
* A
1
*
f
y d
10
= 84,73 kN
P
d
R
b,Rd1
= 0,80 < 1
Check web yield at load points:
Bottom beam:
x,Ed2
= M
Ed1
* 10 *
-
h
u
2
t
u
I
y u
= 161,25 kN/cm
z,Ed2
=
* 10
3
P
d
* ( )
+ s
s1
* 2 t
u
s
u
= 201,80 kN/cm
+
( )
x,Ed2
f
yd
2
-
( )
z,Ed2
f
yd
2
*
x,Ed2
f
yd
z,Ed2
f
yd
= 0,75 < 1
Top beam:
x,Ed1
= -M
Ed2
* 10 *
-
h
o
2
t
o
I
y o
= 136,67 kN/cm
z,Ed1
=
* 10
3
P
d
* ( )
+ s
s2
* 2 t
o
s
o
= 201,76 kN/cm
+
( )
x,Ed1
f
yd
2
-
( )
z,Ed1
f
yd
2
*
x,Ed1
f
yd
z,Ed1
f
yd
= 0,70 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : foot and support
Column base subject to compression und bending:
l
Msd
Nsd
a
b
e1
e1
p
e
d
Ed
Ed
Plan and elevation values:
Distance to edge of baseplate e = 45,00 mm
Distance to edge of baseplate e
1
= 100,00 mm
Spacing of bolts p = 300,00 mm
Width of baseplate b = 500,00 mm
Length of baseplate a = 500,00 mm
Plate thickness d = 30,00 mm
Projection of plate l = 100,00 mm
Weld thickness a
w
= 10,00 mm
Projection of pad footing a
r
= 1000,00 mm
Depth of pad footing h = 1400,00 mm
as in L.3 (idR) Bearing plane factor
j
= 2/3 = 0,67
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEB
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = HEB 300
Moment of inertia I
y1
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Iy; Name=Profil) = 25170,00 cm
4
Flange width b
f
= TAB("steel/"Typ; b; Name=Profil) = 300,00 mm
Flange thickness t
f
= TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 19,00 mm
Column height h
t
= TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 300,00 mm
M
pl,y,Rd
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Mplyd; Name=Profil) = 418,00 kNm
N
pl,Rd
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Npld; Name=Profil) = 3250,00 kN
Loads:
N
Ed
= 1000,00 kN
M
Ed
= 221,75 kNm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : foot and support
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 430
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 275,00 N/mm
Concrete = SEL("Concrete/EC"; Name; ) = C30/37
f
ck
= TAB("Concrete/EC"; f
ck
; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
SC = SEL("steel/bolt"; SC; ) = 4.6
Bolt = SEL("steel/bolt"; BS; ) = M 24
f
u
= TAB("steel/bolt"; fubk; SC=SC) = 400,00 N/mm
A
s
= TAB("steel/bolt"; Asp; BS=Bolt) = 3,53 cm
Mb
= 1,25
c
= 1,50
M0
= 1,10
Design:
m = l - e - 0,8 * a
w
*
2 = 43,69 mm
l
eff1a
= MIN(4 * m + 1,25 * e; 2 * m + 0,625 * e + e
1
) = 215,51 mm
l
eff1b
= MIN(2 * m + 0,625 * e + 0,5 * p; e
1
+ 0,5 * p; b / 2) = 250,00 mm
l
eff1
= MIN(l
eff1a
; l
eff1b
) = 215,51 mm
l
eff2a
= MIN( * 2 * m; * m + 2 * e
1
) = 274,51 mm
l
eff2b
= MIN( * m + p; p + 2 * e
1
) = 437,26 mm
l
eff
= MIN(l
eff2a
; l
eff2b
; l
eff1
) = 215,51 mm
Beanspruchbarkeit der Lagerplatte auf der Seite der Zugstangen:
M
pl,1,Rd
= *
1
4
* l
eff
*
( )
d
10
2
f
y
*
M0
10
= 12,12*10
3
kNmm
n = e = 45,00 mm
n
* 1,25 m
= 0,82 < 1
B
t,Rd
= 0,9 * f
u
*
A
s
*
Mb
10
= 101,66 kN
Full flange yield:
F
T,Rd1
= 4 *
M
pl,1,Rd
m
= 1109,64 kN
Bolt failure with flange yielding:
F
T,Rd2
=
* 2 + M
pl,1,Rd
* n * 2 B
t,Rd
+ m n
= 376,47 kN
Bolt failure without flange yielding:
F
T,Rd3
= 2 * B
t,Rd
= 203,32 kN
F
T,Rd
= MIN(F
T,Rd1
; F
T,Rd2
; F
T,Rd3
) = 203,32 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : foot and support
Effective compression area:
Limit pressure in the base plate:
a
1
= MIN(a + 2 * a
r
; 5 * a; a + h) = 1900,00 mm
k
j
=
a
1
2
* a b
= 3,80
f
j
=
j
* k
j
*
f
ck
c
= 50,92 N/mm
A
eff
= * 10
+ N
Ed
F
T,Rd
f
j
= 236,32 cm
c = * d
* f
y
10
* 3 * f
j
M0
= 121,36 mm
x
0
= 100 *
A
eff
* 2 + c b
f
= 43,54 mm
x
0
+ t
f
* 2 c
= 0,17 < 1
Limit moment at column base:
r
c
= +
h
t
2
- c
x
0
2
= 249,59 mm
M
Rd
=
* F
T,Rd
* 10
3
+
( )
+
h
t
2
- 100 e * A
ef f
* 100 * f
j
r
c
10
6
= 342,02 kNm
Check permissible strength of column to bending and compression.:
M
Ny,Rd
= 1,1 * M
pl,y,Rd
* (1-
N
Ed
N
pl,Rd
) = 318,32 kNm
Analysis:
MAX(
M
Ed
M
Ny,Rd
;
M
Ed
M
Rd
) = 0,70 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Sway frame with bracing out of plane of frame, plastic theory:
d
q
d
H
A
B D
C
h
l
Plan and elevation values:
Frame width l = 8,00 m
Frame depth h = 6,00 m
Number of column n
c
= 2
Number of storeys n
s
= 1
Beam:
Profil Typ1 = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil1= SEL("steel/"Typ1; Name; ) = IPE 240
Column height h
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; h; Name=Profil1) = 240,00 mm
Web thickness s
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; s; Name=Profil1) = 6,20 mm
Moment of inertia I
y1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; Iy; Name=Profil1) = 3890,00 cm
4
Cross-sectional area A
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; A; Name=Profil1) = 39,10 cm
Moment of resistance W
y1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; Wy; Name=Profil1) = 324,00 cm
Moment of resistance Wpl
y1
= 1,14 * W
y1
= 369,36 cm
Column section:
Profil Typ2 = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEB
Selected Profil2 = SEL("steel/"Typ2; Name; ) = HEB 240
Flange width b
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; b; Name=Profil2) = 240,00 mm
Column height h
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; h; Name=Profil2) = 240,00 mm
Web thickness s
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; s; Name=Profil2) = 10,00 mm
Moment of inertia I
y2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; Iy; Name=Profil2) = 11260,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
z2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; Iz; Name=Profil2) = 3920,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
t2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; IT; Name=Profil2) = 103,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
= 10*TAB("steel/"Typ2; I; Name=Profil2) = 486900,00 cm
6
Cross-sectional area A
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; A; Name=Profil2) = 106,000 cm
i
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; iy; Name=Profil2) = 10,30 cm
i
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; iz; Name=Profil2) = 6,08 cm
Moment of resistance W
ely2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2;Wy; Name=Profil2) = 938,00 cm
Moment of resistance W
ply2
= 1,25 * W
ely2
= 1172,50 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Loads:
H
d
= 9,00 kN
q
d
= 9,00 kN/m
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G
= TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
= (235 / f
y
) = 1,00
M
= 1,10
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
Frame classification as in 5.2.5.2.:
Frame sways
k = *
I
y 1
I
y 2
h
l
= 0,259
Deflection at top of frame due to horizontal load:
H = 1,00 kN
= *
* ( ) * 100 h
3
10
* 12 * E
s
I
y2
* 2 + k 1
* k H
= 0,446 cm
Sumtotal of vertical loads:
V = q
d
* l = 72,00 kN
Bracing is restrained out of plane of frame
*
* h 100
V
H
= 0,054 < 0,1
Sway frame, plastic theory, restrained from moving out of plane.
Design with plastic theory
Imperfection:
0
=
1
200
= 0,005
k
c
= MIN(
+ 0,5
1
n
c
; 1) = 1,00
k
s
= MIN(
+ 0,2
1
n
s
; 1) = 1,00
=
0
* k
c
* k
s
= 0,0050
H
d
= * V = 0,36 kN
H
Ed
= H
d
+ H
d
= 9,36 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Design calculations:
Reactions at column bases:
H
l
=
* q
d
l
2
* 4 * h ( ) * 2 + k 3
= 6,82 kN
V
l
= q
d
*
l
2
= 36,00 kN
M
Bl
= -H
l
* h = -40,92 kNm
H
2
= H
Ed
/ 2 = 4,68 kN
V
2
= H
Ed
*
h
l
= 7,02 kN
M
B2
= H
2
* h = 28,08 kNm
Analysis of column
N
Ed
= V
l
+ V
2
= 43,02 kN
V
Ed
= H
l
+ H
2
= 11,50 kN
M
D
= M
Bl
- M
B2
= -69,00 kNm
M
C
= 0,00 kNm
Buckling in the plane of frame as in section E:
k
c
=
I
y2
* h 100
= 18,77 cm
k
1
= 1,5 *
I
y1
* l 100
= 7,29 cm
k
2
= 0,0
2
= 1 (Hinge)
1
=
k
c
+ k
c
+ k
1
k
2
= 0,72
Slenderness ratio as in Fig. E.2.1.:
l = 3,2 * h = 19,20 m
y
= * 100
l
i
y
= 186,41
trans,y
=
y
*
1
= 1,99
h
2
b
2
= 1,00 < 1,2
Apply strut curve b:
= 0,34
A =
1,000
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,y
- 0,2) +
trans,y
) = 2,784
y
=
1
+
trans,y
2
= 0,2114
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Buckling outside the plane of frame
z
= 100 *
h
i
z
= 98,68
trans,z
=
z
*
1
= 1,05
Apply strut curve c:
= 0,49
A
=
1,000
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,z
- 0,2) +
trans,z
) = 1,260
z
=
1
+
trans,z
2
= 0,5111
min
= MIN(
y
;
z)
= 0,2114
Check bending and buckling:
= 0,00
My
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,80
y
=
trans,y
* (2 *
My
- 4) +
- W
pl y2
W
el y2
W
el y2
= -0,546 < 0,9
k
y
= 1 -
*
y
N
Ed
*
y
* A
2
f
y
= 1,004 < 1,5
+
N
Ed
*
min
* A
2
f
y
*
M
10
* 100 * k
y
abs ( ) M
D
* W
ply2
f
y
*
M
10
= 0,37 < 1
Check torsional-flexural buckling:
C
1
= 1,879
M
cr
= * C
1
*
*
2
* E
s
I
z2
* ( ) * h 100
2
10
+
I
I
z2
* ( ) * h 100
2
* G I
t2
*
2
* E
s
I
z2
= 94241,31 kNm
As in Table: F.1.1
= 0,00
w
= 1,00
k = 1,00
LT
=
*
2
*
E
s
10
W
ply2
M
cr
= 50,78
trans,LT
= *
LT
w
= 0,541
Apply strut curve a
= 0,21
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,LT
- 0,2) +
trans,LT
) = 0,682
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
LT
=
1
+
trans,LT
2
= 0,911
M,LT
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,80
LT
= 0,15 *
trans,z
*
M,LT
- 0,15 = 0,134 < 0,9
k
LT
= 1 -
*
LT
N
Ed
*
LT
* A
2
f
y
= 1,000 < 1,5
+
N
Ed
*
z
* A
2
f
y
*
M
10
* 100 * k
LT
abs ( ) M
D
* *
LT
W
ply2
f
y
*
M
10
= 0,340 < 1
Section analysis at D:
Column:
A
v
= 1,04 * h
2
* s
2
/ 10 = 24,96 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* 3 *
M
10
= 307,86 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,037 < 0,5
No interaction
N
pl,Rd
= * A
2
f
y
*
M
10
= 2264,55 kN
n =
N
Ed
N
pl,Rd
= 0,02
M
pl,y,Rd
= * W
ply2
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 250,49 kNm
M
Ny,Rd
= 1,11 * M
pl,y,Rd
* (1 - n) = 272,48 kNm
MAX(
abs ( ) M
D
M
pl,y,Rd
;
abs ( ) M
D
M
Ny,Rd
) = 0,28 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Beam:
A
v
= 1,04 * h
1
* s
1
/ 10 = 15,48 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* 3 *
M
10
= 190,93 kN
N
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,225 < 0,5
No interaction
N
pl,Rd
= A
1
* f
y
/ 10 /
M
= 835,32 kN
n = V
Ed
/ N
pl,Rd
= 0,014
M
pl,y,Rd
= * W
ply1
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 78,91 kNm
M
Ny,Rd
= 1,11 * M
pl,y,Rd
* (1 - n) = 86,36 kNm
MAX(
abs ( ) M
D
M
pl,y,Rd
;
abs ( ) M
D
M
Ny,Rd
) = 0,87 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Frame, plastic with magnifying factor
d
P
d
P
d
q
d
H
A
B D
C
h
l
Plan and elevation values:
Frame width l= 8,00 m
Frame depth h= 6,00 m
Number of column n
c
= 2
Number of storeys n
s
= 1
Beam:
Profil Typ1 = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil1= SEL("steel/"Typ1; Name; ) = IPE 240
Column height h
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; h; Name=Profil1) = 240,00 mm
Flange thickness s
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; s; Name=Profil1) = 6,20 mm
Moment of inertia I
y1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; Iy; Name=Profil1) = 3890,00 cm
4
Cross-sectional area A
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; A; Name=Profil1) = 39,10 cm
Moment of resistance W
y1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; Wy; Name=Profil1) = 324,00 cm
Moment of resistance Wpl
y1
= 1,14 * W
y1
= 369,36 cm
Column section:
Profil Typ2 = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEB
Selected Profil2 = SEL("steel/"Typ2; Name; ) = HEB 240
Flange width b
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; b; Name=Profil2) = 240,00 mm
Column height h
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; h; Name=Profil2) = 240,00 mm
Flange thickness s
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; s; Name=Profil2) = 10,00 mm
Moment of inertia I
y2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; Iy; Name=Profil2) = 11260,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
z2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; Iz; Name=Profil2) = 3920,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
t2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; IT; Name=Profil2) = 103,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
= 10*TAB("steel/"Typ2; I; Name=Profil2) = 486900,00 cm
6
Cross-sectional area A
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; A; Name=Profil2) = 106,000 cm
i
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; iy; Name=Profil2) = 10,30 cm
i
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; iz; Name=Profil2) = 6,08 cm
Moment of resistance W
ely2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2;Wy; Name=Profil2) = 938,00 cm
Moment of resistance W
ply2
= 1,25 * W
ely2
= 1172,50 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Loads:
H
d
= 9,00 kN
q
d
= 8,00 kN/m
P
d
= 100,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G
= TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
M
= 1,10
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
Frame classification as in 5.2.5.2.:
Frame sways
Classification of stiffness:
k = *
I
y 1
I
y 2
h
l
= 0,259
Deflection at top of frame due to horizontal load:
H = 1,00 kN
= *
* ( ) * 100 h
3
10
* 12 * E
s
I
y2
* 2 + k 1
* k H
= 0,446 cm
Sumtotal of vertical loads:
V = P
d
* 2 + q
d
* l = 264,00 kN
*
* h 100
V
H
= 0,1962 < 0,1
Frame, laterally unrestrained!;restrained from moving out of plane. mit Vergrerungsfaktor!
Design with plastic theory and magnifying factor
Imperfection:
0
=
1
200
= 0,005
k
c
= MIN(
+ 0,5
1
n
c
; 1) = 1,00
k
s
= MIN(
+ 0,2
1
n
s
; 1) = 1,00
=
0
* k
c
* k
s
= 0,0050
H
d
= * V = 1,32 kN
H
Ed
= H
d
+ H
d
= 10,32 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Design calculations:
Reactions at column bases:
H
l
=
* q
d
l
2
* 4 * h ( ) * 2 + k 3
= 6,06 kN
V
l
= q
d
*
l
2
= 32,00 kN
M
Bl
= -H
l
* h = -36,36 kNm
H
2
= H
Ed
/ 2 = 5,16 kN
V
2
= H
Ed
*
h
l
= 7,74 kN
M
B2
= H
2
* h = 30,96 kNm
Analysis of column
Dischinger factor:
D =
1
- 1 *
* h 100
V
H
= 1,244
M
D
= M
Bl
- D * M
B2
= -74,87 kNm
N
Ed
= V
l
+ D * V
2
+ P
d
= 141,63 kN
V
Ed
= H
l
+ D * H
2
= 12,48 kN
Buckling in the plane of frame:
k
c
=
I
y2
* h 100
= 18,77 cm
k
1
=
I
y1
* l 100
= 4,86 cm
k
2
= 0,0
2
= 1 (Hinge)
1
=
k
c
+ k
c
+ k
1
k
2
= 0,79
Slenderness ratio as in Fig. E.2.1.:
l = 0,92 * h = 5,52 m
y
= * 100
l
i
y
= 53,59
trans,y
=
y
*
1
= 0,57
h
2
b
2
= 1,00 < 1,2
Apply strut curve b:
= 0,34
A =
1,000
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,y
- 0,2) +
trans,y
) = 0,725
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
y
=
1
+
trans,y
2
= 0,8525
Buckling outside the plane of frame
z
= 100 *
h
i
z
= 98,68
trans,z
=
z
*
1
= 1,05
Apply strut curve c:
= 0,49
A =
1,000
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,z
- 0,2) +
trans,z
) = 1,260
z
=
1
+
trans,z
2
= 0,5111
min
= MIN(
y;
z)
= 0,5111
Check bending and buckling:
= 0,00
My
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,80
y
=
trans,y
* (2 *
My
- 4) +
- W
pl y2
W
el y2
W
el y2
= 0,022 < 0,9
k
y
= 1 -
*
y
N
Ed
*
y
* A
2
f
y
= 1,000 < 1,5
+
N
Ed
*
min
* A
2
f
y
*
M
10
* 100 * k
y
abs ( ) M
D
* W
ply2
f
y
*
M
10
= 0,42 < 1
Check torsional-flexural buckling:
C
1
= 1,879
M
cr
= * C
1
*
*
2
* E
s
I
z2
* ( ) * h 100
2
10
+
I
I
z2
* ( ) * h 100
2
* G I
t2
*
2
* E
s
I
z2
= 94241,31 kNm
As in Table: F.1.1
= 0,00
w
= 1,00
k = 1,00
LT
=
*
2
*
E
s
10
W
ply2
M
cr
= 50,78
trans,LT
= *
LT
w
= 0,541
Apply strut curve a
= 0,21
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,LT
- 0,2) +
trans,LT
) = 0,682
LT
=
1
+
trans,LT
2
= 0,911
M,LT
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,80
LT
= 0,15 *
trans,z
*
M,LT
- 0,15 = 0,134 < 0,9
k
LT
= 1 -
*
LT
N
Ed
*
LT
* A
2
f
y
= 0,999 < 1,5
+
N
Ed
*
z
* A
2
f
y
*
M
10
* 100 * k
LT
abs ( ) M
D
* *
LT
W
ply2
f
y
*
M
10
= 0,450 < 1
Section analysis at D:
Column:
A
v
= 1,04 * h
2
* s
2
/ 10 = 24,96 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* 3 *
M
10
= 307,86 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,041 < 0,5
No interaction
N
pl,Rd
= * A
2
f
y
*
M
10
= 2264,55 kN
n =
N
Ed
N
pl,Rd
= 0,063
M
pl,y,Rd
= * W
ply2
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 250,49 kNm
M
Ny,Rd
= 1,11 * M
pl,y,Rd
* (1 - n) = 260,53 kNm
MAX(
abs ( ) M
D
M
pl,y,Rd
;
abs ( ) M
D
M
Ny,Rd
) = 0,30 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Beam:
A
v
= 1,04 * h
1
* s
1
/ 10 = 15,48 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* 3 *
M
10
= 190,93 kN
N
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,742 < 0,5
No interaction
N
pl,Rd
= A
1
* f
y
/ 10 /
M
= 835,32 kN
n = V
Ed
/ N
pl,Rd
= 0,015
M
pl,y,Rd
= * W
ply1
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 78,91 kNm
M
Ny,Rd
= 1,11 * M
pl,y,Rd
* (1 - n) = 86,28 kNm
MAX(
abs ( ) M
D
M
pl,y,Rd
;
abs ( ) M
D
M
Ny,Rd
) = 0,95 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Sway frame with bracing out of plane of frame, plastic theory:
d
q
d
H
A
B D
C
h
l
Plan and elevation values:
Frame width l= 8,00 m
Frame depth h= 6,00 m
Number of column n
c
= 2
Number of storeys n
s
= 1
Beam:
Profil Typ1 = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil1= SEL("steel/"Typ1; Name; ) = IPE 240
Column height h
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; h; Name=Profil1) = 240,00 mm
Web thickness s
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; s; Name=Profil1) = 6,20 mm
Moment of inertia I
y1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; Iy; Name=Profil1) = 3890,00 cm
4
Cross-sectional area A
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; A; Name=Profil1) = 39,10 cm
Moment of resistance W
y1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; Wy; Name=Profil1) = 324,00 cm
Moment of resistance Wpl
y1
= 1,14 * W
y1
= 369,36 cm
Column section:
Profil Typ2 = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEB
Selected Profil2 = SEL("steel/"Typ2; Name; ) = HEB 240
Flange width b
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; b; Name=Profil2) = 240,00 mm
Column height h
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; h; Name=Profil2) = 240,00 mm
Web thickness s
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; s; Name=Profil2) = 10,00 mm
Moment of inertia I
y2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; Iy; Name=Profil2) = 11260,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
z2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; Iz; Name=Profil2) = 3920,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
t2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; IT; Name=Profil2) = 103,00 cm
4
Moment of inertia I
= 10*TAB("steel/"Typ2; I; Name=Profil2) = 486900,00 cm
6
Cross-sectional area A
2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; A; Name=Profil2) = 106,000 cm
i
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; iy; Name=Profil2) = 10,30 cm
i
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; iz; Name=Profil2) = 6,08 cm
Moment of resistance W
ely2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2;Wy; Name=Profil2) = 938,00 cm
Moment of resistance W
ply2
= 1,25 * W
ely2
= 1172,50 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Loads:
H
d
= 9,00 kN
q
d
= 9,00 kN/m
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G
= TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
M
= 1,10
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
Frame classification as in 5.2.5.2.:
Frame sways
k = *
I
y 1
I
y 2
h
l
= 0,259
Deflection at top of frame due to horizontal load:
H = 1,00 kN
= *
* ( ) * 100 h
3
10
* 12 * E
s
I
y2
* 2 + k 1
* k H
= 0,446 cm
Sumtotal of vertical loads:
V = q
d
* l = 72,00 kN
Bracing is restrained out of plane of frame
*
* h 100
V
H
= 0,0535 < 0,1
Sway frame, plastic theory;restrained from moving out of plane.
Design with plastic theory and magnifying factor
Imperfection:
0
=
1
200
= 0,005
k
c
= MIN(
+ 0,5
1
n
c
; 1) = 1,00
k
s
= MIN(
+ 0,2
1
n
s
; 1) = 1,00
=
0
* k
c
* k
s
= 0,0050
H
d
= * V = 0,36 kN
H
Ed
= H
d
+ H
d
= 9,36 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Design calculations:
Reactions at column bases:
H
l
=
* q
d
l
2
* 4 * h ( ) * 2 + k 3
= 6,82 kN
V
l
= q
d
*
l
2
= 36,00 kN
M
Bl
= -H
l
* h = -40,92 kNm
H
2
= H
Ed
/ 2 = 4,68 kN
V
2
= H
Ed
*
h
l
= 7,02 kN
M
B2
= H
2
* h = 28,08 kNm
Analysis of column
N
Ed
= V
l
+ V
2
= 43,02 kN
V
Ed
= H
l
+ H
2
= 11,50 kN
Dischingerfaktor:
D =
1
- 1 *
* h 100
V
H
= 1,057
M
D
= M
Bl
- D * M
B2
= -70,60 kNm
Buckling in the plane of frame:
k
c
=
I
y2
* h 100
= 18,77 cm
k
1
=
I
y1
* l 100
= 4,86 cm
k
2
= 0,0
2
= 1 (Hinge)
1
=
k
c
+ k
c
+ k
1
k
2
= 0,79
Slenderness ratio as in Fig. E.2.1.:
l = 0,92 * h = 5,52 m
y
= * 100
l
i
y
= 53,59
trans,y
=
y
*
1
= 0,57
h
2
b
2
= 1,00 < 1,2
Apply strut curve b:
= 0,34
A =
1,000
= 0,5*(1+*(
trans,y
-0,2)+
trans,y
) = 0,725
y
=
1
+
trans,y
2
= 0,8525
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Buckling outside the plane of frame
z
= 100 *
h
i
z
= 98,68
trans,z
=
z
*
1
= 1,05
Apply strut curve c:
= 0,49
A
=
1,000
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,z
- 0,2) +
trans,z
) = 1,260
z
=
1
+
trans,z
2
= 0,5111
min
= MIN(
y
;
z
) = 0,5111
Check bending and buckling:
= 0,00
My
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,80
y
=
trans,y
* (2 *
My
- 4) +
- W
ply2
W
ely2
W
ely2
= 0,022 < 0,9
k
y
= 1 -
*
y
N
Ed
*
y
* A
2
f
y
= 1,000 < 1,5
+
N
Ed
*
min
* A
2
f
y
*
M
10
* 100 * k
y
abs ( ) M
D
* W
ply2
f
y
*
M
10
= 0,32 < 1
Check torsional-flexural buckling:
C
1
= 1,879
M
cr
= * C
1
*
*
2
* E
s
I
z2
* ( ) * h 100
2
10
+
I
I
z2
* ( ) * h 100
2
* G I
t2
*
2
* E
s
I
z2
= 94241,31 kNm
As in Table: F.1.1
= 0,00
w
= 1,00
k = 1,00
LT
=
*
2
*
E
s
10
W
ply2
M
cr
= 50,78
trans,LT
= *
LT
w
= 0,541
Apply strut curve a
= 0,21
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,LT
- 0,2) +
trans,LT
) = 0,682
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
LT
=
1
+
trans,LT
2
= 0,911
M,LT
= 1,8 - 0,7 * = 1,80
LT
= 0,15 *
trans,z
*
M,LT
- 0,15 = 0,134 < 0,9
k
LT
= 1 -
*
LT
N
Ed
*
LT
* A
2
f
y
= 1,000 < 1,5
+
N
Ed
*
z
* A
2
f
y
*
M
10
* 100 * k
LT
abs ( ) M
D
* *
LT
W
ply2
f
y
*
M
10
= 0,347 < 1
Section analysis at D:
Column:
A
v
= 1,04 * h
2
* s
2
/ 10 = 24,96 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* 3 *
M
10
= 307,86 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,037 < 0,5
No interaction
N
pl,Rd
= * A
2
f
y
*
M
10
= 2264,55 kN
n =
N
Ed
N
pl,Rd
= 0,02
M
pl,y,Rd
= * W
ply2
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 250,49 kNm
M
Ny,Rd
= 1,11 * M
pl,y,Rd
* (1 - n) = 272,48 kNm
MAX(
abs ( ) M
D
M
pl,y,Rd
;
abs ( ) M
D
M
Ny,Rd
) = 0,28 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Frames
Beam:
A
v
= 1,04 * h
1
* s
1
/ 10 = 15,48 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* 3 *
M
10
= 190,93 kN
N
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,225 < 0,5
No interaction
N
pl,Rd
= A
1
* f
y
/ 10
/
M
= 835,32 kN
n = V
Ed
/ N
pl,Rd
= 0,014
M
pl,y,Rd
= * W
ply1
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 78,91 kNm
M
Ny,Rd
= 1,11 * M
pl,y,Rd
* (1 - n) = 86,36 kNm
MAX(
abs ( ) M
D
M
pl,y,Rd
;
abs ( ) M
D
M
Ny,Rd
) = 0,89 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Pos.: Flexural-torsional buckling of a single-span beam:
End supports are laterally fixed.
s
b
h
b
t
t
o
o
u
u
t
s
q
d
Load diagram:
Span length l = 24,00 m
top width b
o
= 40,00 cm
bottom width b
u
= 50,00 cm
Depth of web h= 100,00 cm
top Flange thickness t
o
= 3,50 cm
bottom Flange thickness t
u
= 3,50 cm
Web thickness s= 2,00 cm
Weld thickness t
s
= 1,00 cm
Loads:
q = 4,04 kN/m
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 510
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G= TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 355,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 0,81
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
g
= 1,35
Section classification as in Table 5.3.1:
A = (b
o
* t
o
+ b
u
* t
u
+ h * s) = 515,00 cm
Plastic neutral axis:
x =
-
A
2
* b
o
t
o
s
= 58,75 cm
x
s
= h - x = 41,25 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Flange:
c =
-
- b
o
s
2
* t
s
2
t
o
= 5,02 cm
c
* 9
= 0,69 < 1
Section class 1
Web:
=
x
h
= 0,59 cm
h
* s * 456
* 13 -
1
= 0,90 < 1
h
* s * 396
* 13 -
1
= 1,04 > 1
Section class 2
Check bending moment strength:
M
Ed
=
g
*
* q l
2
8
= 392,69 kNm
Critical torsional-buckling moment:
I
z
= * t
o
+
b
o
3
12
* t
u
b
u
3
12
= 55125,00 cm
4
As in Table: F.1.2(2)
k= 1,00
As in Table: F.1.1(4)
k
w
= 1,00
As in Table: F.1.2
C
1
= 1,132
C
2
= 0,459
C
3
= 0,525
Location of center of gravity:
e=
* b
u
* t
u
+ ( )
+ h t
o
* h * s
( )
+ h t
o
2
A
= 55,27 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Location of shear centre:
s
s
= *
( )
+ h
+ t
o
t
u
2
b
u
3
+ b
o
3
b
u
3
= 68,45 cm
z
s
= -(s
s
- e) = -13,18 cm
I
t
=
1
3
* (b
u
* t
u
+ b
o
* t
o
+ h * s) = 1552,92 cm
4
z
a
= 0,00 cm
z
g
= z
a
-z
s
= 13,18 cm
as in F 1.4:
f
=
b
o
3
+ b
o
3
b
u
3
= 0,339 < 0,5
z
j
= (2 *
f
- 1) *
+ h
+ t
o
t
u
2
2
= -16,66 cm
I
w
=
f
* (1 -
f
) * I
z
*
( )
+ h
+ t
o
t
u
2
2
= 132,32*10
6
cm
6
P
1
= * C
1
* *
2
E
s
I
z
( ) * k * l 100
2
= 22453,85
P
2
=
*
( )
k
k
w
2
+
I
w
I
z
+
* ( ) * k * l 100
2
* G I
t
*
2
* E
s
I
z
( ) * C
2
- z
g
* C
3
z
j
2
= 94,66
P
3
= C
2
* z
g
- C
3
* z
j
= 14,80
M
cr
= * P
1
- P
2
P
3
10
3
= 1793,16 kNm
W
pl
= b
u
* t
u
* (x
s
+
t
u
2
) + x
s
*
s
2
+ b
o
* t
o
* (x +
t
o
2
) + x *
s
2
= 21148,13 cm
Section class 2
w
= 1,00
trans,LT
=
*
w
* W
pl
f
y
* 10
3
M
cr
= 2,046
As in Table 5.5.1 = 0,49
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans,LT
-0,2) +
trans,LT
) = 3,05
LT
=
1
+
trans,LT
2
= 0,1883
M
b,Rd
= *
w
*
LT
* W
pl
f
y
*
M
2
10
3
= 1168,33 kNm
M
Ed
M
b,Rd
= 0,34 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Pos.: Single-span beam with biaxial bending:
N
q
d
t,d
q
d
Span length l = 5,80 m
Angle of slope = 8,53
Loads:
q
d
= 7,00 kN/m
N
t,d
= 100,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
platischer Formbeiwert
pl y
= 1,14
platischer Formbeiwert
pl z
= 1,25
M
= 1,10
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEA
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = HEA 140
Section classification:
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 133,00 mm
Depth of web h
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ; h1; Name=Profil) = 92,00 mm
Web thickness s
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 5,50 mm
Flange width b = TAB("steel/"Typ; b; Name=Profil) = 140,00 mm
Flange thickness t = TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 8,50 mm
Moment of inertia I = TAB("steel/"Typ; Iy; Name=Profil) = 1030,00 cm
4
Cross-sectional area A= TAB("steel/"Typ; A; Name=Profil) = 31,40 cm
W
el y
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Wy; Name=Profil) = 155,00 cm
W
pl y
=
pl y
* W
el y
= 176,70 cm
W
el z
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Wz; Name=Profil) = 55,60 cm
W
pl z
=
pl z
* W
el z
= 69,50 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Design loads:
Plastic limit force:
N
pl,Rd
= * A
f
y
*
M
10
= 670,82 kN
Limit force that plasticizes the web
N
pl,w,Rd
= (h - 2 * t) * s *
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 136,30 kN
MAX(
N
t,d
* 0,5 N
pl,w,Rd
;
N
t,d
* 0,25 N
pl,Rd
) = 1,47 > 1
Reduce plastic limit force as in 5.4.8.1:
=
- A * 2 * b
t
100
A
= 0,242 < 0,5
=
N
t,d
N
pl,Rd
= 0,149
M
Ny,Rd
= * W
pl y
*
f
y
*
M
10
3
- 1
- 1 * 0,5
= 36,55 kNm
= 0,62 < 1
M
Nz,Rd
= W
plz
*
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 14,85 kNm
Design momente:
q
dy
= q
d
* COS() = 6,92 kN/m
q
dz
= q
d
* SIN() = 1,04 kN/m
M
y,Ed
= q
dy
*
l
2
8
= 29,10 kNm
M
z,Ed
= q
dz
*
l
2
8
= 4,37 kNm
Check section strength:
for I-Profile gilt = 2,00
1
= 5 * = 0,75 < 1
2
= 1,00
= MAX(
1
;
2
) = 1,00
+
( )
M
y,Ed
M
Ny,Rd
( )
M
z,Ed
M
Nz,Rd
= 0,93 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Pos.: flexural-torsional buckling:
End supports are laterally fixed, load is applied in the middle of the bottom flange.
s
b
h
t
t
t
s
q
d
Load diagram:
Span length l = 8,00 m
Beam width b= 20,00 cm
Column height h= 50,00 cm
Flange thickness t= 2,50 cm
Web thickness s= 1,20 cm
Weld thickness t
s
= 0,50 cm
Loads:
q
d
= 50,00 kN/m
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 510
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G= TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 355,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 0,81
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
Section classification:
Flange:
c =
-
b
2
* t
s
2
t
= 3,72 cm
c
* 9
= 0,51 < 1
Section class 1
Web:
d= - h * 2 * t
s
2 = 48,59 cm
d
* s * 72
= 0,69 < 1
Section class 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Check bending moment strength:
W
pl
= *
( )
* b * t +
+ h t
2
*
h
2
* s
h
4
2 = 3375,00 cm
M
c,Rd
=
* W
pl
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 1089,20 kNm
M
Ed
=
* q
d
l
2
8
= 400,00 kNm
M
Ed
M
c,Rd
= 0,37 < 1
Check shear strength:
A
v
= h * s = 60,00 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* *
3
M
10
= 1117,96 kN
V
Ed
= * q
d
l
2
= 200,00 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,18 < 1
Check torsional buckling strength:
I
z
= 2 * t *
b
3
12
= 3333,33 cm
4
I
w
= * I
z
( ) + h t
2
4
= 2,297*10
6
cm
6
I
t
=
1
3
* (2 * b * t + h * s) = 237,13 cm
4
As in Table F.1.2(2) k= 1,00
As in Table F.1.1(4) k
w
= 1,00
As in Table F.1.2 C
1
= 1,13
As in Table F.1.2 C
2
= 0,46
As in Table F.1.2 C
3
= 0,53
Load is applied in centroid of section z
a
= -27,50 cm
Centroid of section and shear centre are identical z
s
= 0,00 cm
Section is symmetrical z
j
= 0,00 cm
z
g
= z
a
-z
s
= -27,50 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Critical torsional-buckling moment
P
1
= * C
1
* *
2
E
s
I
z
( ) * k * l 100
2
= 12198,18
P
2
=
*
( )
k
k
w
2
+
I
w
I
z
+
* ( ) * k * l 100
2
* G I
t
*
2
* E
s
I
z
( ) * C
2
- z
g
* C
3
z
j
2
= 51,27
P
3
= C
2
* z
g
- C
3
* z
j
= -12,65
M
cr
= * P
1
- P
2
P
3
10
3
= 779,71 kNm
Cross-section class 1
w
= 1,00
trans,LT
=
*
w
* W
pl
f
y
* 10
3
M
cr
= 1,240
Apply strut curve c:
LT
= 0,49
LT
= 0,5*(1+
LT
*(
trans,LT
-0,2)+
trans,LT
) = 1,524
LT
=
1
+
LT -
LT
2
trans,LT
2
= 0,415
M
b,Rd
= *
w
*
LT
* W
pl
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 452,02 kNm
M
Ed
M
b,Rd
= 0,88 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Pos.: Flexural-torsional buckling of a single-span beam:
End supports are laterally fixed, Load is applied in centroid of section.
s
b
h
t
t
t
s
q
d
Load diagram:
Span length l = 8,00 m
Beam width b= 20,00 cm
Column height h= 50,00 cm
Flange thickness t= 2,50 cm
Web thickness s= 1,20 cm
Weld thickness t
s
= 0,50 cm
Loads:
q
d
= 45,00 kN/m
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 510
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G= TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 355,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 0,81
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Section classification As in Table 5.3.1:
Flange:
c =
-
b
2
* t
s
2
t
= 3,72 cm
c
* 9
= 0,51 < 1
Section class 1
Web:
d= - h * 2 * t
s
2 = 48,59 cm
d
* s * 72
= 0,69 < 1
Section class 1
Check bending moment strength:
W
pl
= *
( )
* b * t +
+ h t
2
*
h
2
* s
h
4
2 = 3375,00 cm
M
c,Rd
=
* W
pl
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 1089,20 kNm
M
Ed
=
* q
d
l
2
8
= 360,00 kNm
M
Ed
M
c,Rd
= 0,33 < 1
Check shear strength:
A
v
= h * s = 60,00 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* *
3
M
10
= 1117,96 kN
V
Ed
= * q
d
l
2
= 180,00 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,16 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Check torsional buckling strength:
I
z
= 2 * t *
b
3
12
= 3333,33 cm
4
I
w
= * I
z
( ) + h t
2
4
= 2,297*10
6
cm
6
I
t
=
1
3
* (2 * b * t + h * s) = 237,13 cm
4
As in Table F.1.2(2) k= 1,00
As in Table F.1.1(4) k
w
= 1,00
As in Table F.1.2 C
1
= 1,13
As in Table F.1.2 C
2
= 0,46
As in Table F.1.2 C
3
= 0,53
Load in centroid z
a
= 0,00 cm
Centroid of section and shear centre are identical z
s
= 0,00 cm
Section is symmetrical z
j
= 0,00 cm
Critical torsional-buckling moment
M
cr
= * C
1
*
*
2
* E
s
I
z
( )
* k * l 10
2
2
*
( )
k
k
w
2
+
I
w
I
z
* ( )
* k * l 10
2
2
* G I
t
*
2
* E
s
I
z
10
3
= 606,05 kNm
Cross-section class 1
w
= 1,00
trans,LT
=
*
w
* W
pl
f
y
* M
cr
10
3
= 1,406
Apply strut curve c:
LT
= 0,49
LT
= 0,5*(1+
LT
*(
trans,LT
-0,2)+
trans,LT
) = 1,784
LT
=
1
+
LT -
LT
2
trans,LT
2
= 0,347
M
b,Rd
= *
w
*
LT
* W
pl
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 377,95 kNm
M
Ed
M
b,Rd
= 0,95 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Pos.: Flexural-torsional buckling of a single-span beam:
End supports are laterally fixed, Load is applied in centroid of section.
s
b
h
t
t
t
s
q
d
Load diagram:
Span length l = 8,00 m
Beam width b= 20,00 cm
Column height h= 50,00 cm
Flange thickness t= 2,50 cm
Web thickness s= 1,20 cm
Weld thickness t
s
= 0,50 cm
Loads:
q
d
= 36,00 kN/m
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 510
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G= TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 355,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 0,81
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Section classification As in Table 5.3.1:
Flange:
c =
-
b
2
* t
s
2
t
= 3,72 cm
c
* 9
= 0,51 < 1
Section class 1
Web:
d= - h * 2 * t
s
2 = 48,59 cm
d
* s * 72
= 0,69 < 1
Section class 1
Check bending moment strength:
W
pl
= *
( )
* b * t +
+ h t
2
*
h
2
* s
h
4
2 = 3375,00 cm
M
c,Rd
=
* W
pl
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 1089,20 kNm
M
Ed
=
* q
d
l
2
8
= 288,00 kNm
M
Ed
M
c,Rd
= 0,26 < 1
Check shear strength:
A
v
= h*s = 60,00 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* *
3
M
10
= 1117,96 kN
V
Ed
= * q
d
l
2
= 144,00 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,13 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Check torsional buckling strength:
I
z
= 2 * t *
b
3
12
= 3333,33 cm
4
I
w
= * I
z
( ) + h t
2
4
= 2,297*10
6
cm
6
I
t
=
1
3
* (2 * b * t + h * s) = 237,13 cm
4
As in Table F.1.2(2) k= 1,00
As in Table F.1.1(4) k
w
= 1,00
As in Table F.1.2 C
1
= 1,13
As in Table F.1.2 C
2
= 0,46
As in Table F.1.2 C
3
= 0,53
Load in centroid z
a
= 27,50 cm
Centroid of section and shear centre are identical z
s
= 0,00 cm
Section is symmetrical z
j
= 0,00 cm
z
g
= z
a
-z
s
= 27,50 cm
Critical torsional-buckling moment
P
1
= * C
1
* *
2
E
s
I
z
( ) * k * l 100
2
= 12198,18
P
2
=
*
( )
k
k
w
2
+
I
w
I
z
+
* ( ) * k * l 100
2
* G I
t
*
2
* E
s
I
z
( ) * C
2
- z
g
* C
3
z
j
2
= 51,27
P
3
= C
2
*z
g
-C
3
*z
j
= 12,65
M
cr
= * P
1
- P
2
P
3
10
3
= 471,09 kNm
Cross-section class 1
w
= 1,00
trans,LT
=
*
w
* W
pl
f
y
* 10
3
M
cr
= 1,595
Apply strut curve c:
LT
= 0,49
LT
= 0,5*(1+
LT
*(
trans,LT
-0,2)+
trans,LT
) = 2,114
LT
=
1
+
LT -
LT
2
trans,LT
2
= 0,286
M
b,Rd
= *
w
*
LT
* W
pl
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 311,51 kNm
M
Ed
M
b,Rd
= 0,92 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Pos.: Single-span beam subject to flexural-torsional buckling with uniform load and
compression:
End supports are laterally fixed.
N
t,d
q
d
Load diagram:
Span length l = 24,00 m
top Flange width b
o
= 40,00 cm
bottom Flange width b
u
= 50,00 cm
Depth of web h= 100,00 cm
top Flange thickness t
o
= 3,50 cm
bottom Flange thickness t
u
= 3,50 cm
Web thickness s= 2,00 cm
Weld thickness t
s
= 1,00 cm
Loads:
q
d
= 18,00 kN/m
N
t,d
= 500,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 510
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
G = TAB("steel/EC"; G; Name=steel) = 81000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 355,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 0,81
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
g
= 1,35
A = (b
o
* t
o
+ b
u
* t
u
+ h * s) = 515,00 cm
Location of center of gravity:
e=
* b
u
* t
u
+ ( )
+ h t
o
* h * s
( )
+ h t
o
2
A
= 55,27 cm
Location of shear centre:
s
s
= *
( )
+ h
+ t
o
t
u
2
b
u
3
+ b
o
3
b
u
3
= 68,45 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Plastic neutral axis:
x =
-
A
2
( ) * b
o
t
o
s
= 58,75 cm
Section classification As in Table 5.3.1:
Flange:
c =
-
- b
o
s
2
* t
s
2
t
o
= 5,02 cm
c
* 9
= 0,69 < 1
Section class 1
Web:
=
x
h
= 0,59 cm
h
* s * 456
* 13 -
1
= 0,90 < 1
h
* s * 396
* 13 -
1
= 1,04 > 1
Section class 2
Check bending moment strength:
M
Ed
=
* q
d
l
2
8
= 1296,00 kNm
I
z
= * t
o
+
b
o
3
12
* t
u
b
u
3
12
= 55125,00 cm
4
I
y
= b
o
*t
o
*e+b
u
*t
u
*(h+t
u
-e)+s*h/12+h*s*(e-(h/2+t
u
/2)) = 1003886,210 cm
4
I
y
= b
o
*t
o
*e+b
u
*t
u
*(h+t
u
-e)+s*
h
3
12
+h*s*
( )
- e
( )
+
h
2
t
u
2
2
= 1003886,210 cm
4
W
com
= I
y
/ (e + t
o
/ 2) = 17605,86 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Effective bending moment:
M
Ed
=
* q
d
l
2
8
= 1296,00 kNm
Assumption as in 5.5.3
vec
= 0,80
com,Ed
= -
* M
Ed
100
W
com
*
vec
N
t,d
A
= 6,58 kN/cm
M
eff,Ed
=
* W
com
com,Ed
100
= 1158,47 kNm
As in TableF.1.2(2) k = 1,00
As in TableF.1.1(4) k
w
= 1,00
As in Table: F.1.2
C
1
= 1,132
C
2
= 0,459
C
3
= 0,525
z
s
= -(s
s
- e) = -13,18 cm
I
t
=
1
3
* (b
u
* t
u
+ b
o
* t
o
+ h * s) = 1552,92 cm
4
z
a
= 0,00 cm
z
g
= z
a
- z
s
= 13,18 cm
f
=
b
o
3
+ b
o
3
b
u
3
= 0,339 < 0,5
z
j
= (2 *
f
- 1) *
+ h
+ t
o
t
u
2
2
= -16,66 cm
I
w
=
f
* (1 -
f
) * I
z
*
( )
+ h
+ t
o
t
u
2
2
= 132,32*10
6
cm
6
P
1
= * C
1
* *
2
E
s
I
z
( ) * k * l 100
2
= 22453,85
P
2
=
*
( )
k
k
w
2
+
I
w
I
z
+
* ( ) * k * l 100
2
* G I
t
*
2
* E
s
I
z
( ) * C
2
- z
g
* C
3
z
j
2
= 94,66
P
3
= C
2
* z
g
- C
3
* z
j
= 14,80
M
cr
= * P
1
- P
2
P
3
10
3
= 1793,16 kNm
W
pl
= b
u
* t
u
* (x
+
t
u
2
) + x *
s
2
+ b
o
* t
o
* (h-x +
t
o
2
) + (h-x) *
s
2
= 21760,63 cm
Section class 2
w
= 1,00
trans,LT
=
*
w
* W
pl
f
y
* 10
3
M
cr
= 2,076
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
As in Table 5.5.1 = 0,49
= 0,5*(1+*(
trans,LT
-0,2)+
trans,LT
) = 3,11
LT
=
1
+
trans,LT
2
= 0,1843
M
b,Rd
= *
w
*
LT
* W
pl
f
y
*
M
2
10
3
= 1176,63 kNm
M
eff,Ed
M
b,Rd
= 0,98 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Pos.: Single-span beam with cantilever, asymmetric section:
s
b
h
b
t
t
o
o
u
u
t
s
q
d
Span length l = 10,50 m
Cantilever length l
k
= 5,00 m
top Flange width b
o
= 50,00 cm
bottom Flange width b
u
= 30,00 cm
top Flange thickness t
o
= 2,00 cm
bottom Flange thickness
tu
= 2,00 cm
Depth of web h = 60,00 cm
Web thickness s = 1,50 cm
Weld thickness t
s
= 0,80 cm
Loads:
Dead weight g = 26,00 kN/m
Live load q = 37,70 kN/m
Snow load s
0
= 7,00 kN/m
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
Partial safety factors:
fg
= 1,35
fq
= 1,50
= 0,90
M
= 1,10
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Design loads:
q
d1
=
fg
* g +
fq
* q = 91,65 kN/m
q
d2
=
fg
* g + *
fq
* (q + s
0
) = 95,44 kN/m
q
d
= MAX(q
d1
; q
d2
) = 95,44 kN/m
M
Edk
= * -q
d
l
k
2
2
= -1193,00 kNm
B
v
= *
( )
+ l l
k
2
2
q
d
l
= 1091,88 kN
B
r
= q
d
* l
k
= 477,20 kN
B
l
= B
v
- B
r
= 614,68 kN
A
v
= (l + l
k
) * q
d
- B
v
= 387,44 kN
M
Edfield=
* A
v
A
v
* q
d
2
= 786,41 kNm
Plastic neutral axis:
A = (b
o
* t
o
+ b
u
* t
u
+ h * s) = 250,00 cm
x =
-
A
2
* b
o
t
o
s
= 16,67 cm
W
pl
= (b
o
*t
o
*(x+
t
o
2
)+0,5*s*x+b
u
*t
u
*(
t
u
2
+(h-x))+0,5*s*(h-x)) = 6043,33 cm
M
pl
= * W
pl
f
y
10
3
= 1420,18 kNm
Section classification Kragarm As in Table 5.3.1:
Bottom Flange:
c = -
- b
u
s
2
* t
s
2 = 13,12 cm
c
* * 9 t
u
= 0,73 < 1
Web:
=
- h x
h
= 0,72
( )
- h * 2 * t
s
2
s
( )
* 396
* 13 -
1
= 0,81 < 1
Section class 1.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Check shear strength:
A
V
= h * s = 90,00 cm
V
pl,Rd
=
* A
V
f
y
* 10 *
3
M
= 1110,09 kN
V
Ed
= MAX(B
l
; B
r
;A
v
) = 614,68 kN
V
Ed
* V
pl,Rd
0,5
= 1,11 > 1
Mpl, reduced.
Check bending moment strength:
=
( )
* 2 -
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
1
2
= 0,012
M
V,Rd
= (1 - ) *
M
pl
M
= 1275,58 kNm
abs
( )
M
Edk
M
V,Rd
= 0,94 < 1
Section classification Feld As in Table 5.3.1:
top Flange:
c = 0,5 * (b
o
- s) - t
s
*
2 = 23,12 cm
c / t
o
/ (10 * ) = 1,16 > 1
c
* t
o
* 10
= 1,16 > 1
c
* t
o
* 14
= 0,83 < 1
Section class 3.
Web:
=
x
h
= 0,28 < 1
( )
- h * 2 * t
s
2
s
( )
* 396
* 13 -
1
= 0,26 < 1
Section class 1.
Check section strength:
abs ( ) M
Edfield
M
pl
M
= 0,61 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Pos.: Analysis single-span beam:
End supports are laterally fixed.
N
q
d
d
P
d
Load diagram:
Span length l = 6,00 m
Loads:
q
d
= 10,00 kN/m
N
d
= 273,00 kN
P
d
= 15,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
Plastic shape factor
pll
= 1,14
Section classification:
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = IPE 300
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 300,00 mm
Depth of web h
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ; h1; Name=Profil) = 248,00 mm
Web thickness s
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 7,10 mm
Flange width b = TAB("steel/"Typ; b; Name=Profil) = 150,00 mm
Flange thickness t = TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 10,70 mm
Moment of inertia I = TAB("steel/"Typ; Iy; Name=Profil) = 8360,00 cm
4
Cross-sectional area A= TAB("steel/"Typ; A; Name=Profil) = 53,800 cm
iy= TAB("steel/"Typ; iy; Name=Profil) = 12,50 cm
i
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ; iz; Name=Profil) = 3,35 cm
W
el
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Wy; Name=Profil) = 557,00 cm
W
pl
=
pll
* W
el
= 634,98 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Section classification As in Table 5.3.1:
Web:
h
1
* s * 33
= 1,06 ~ 1
Section class 1.
Flange:
b
* 2 * t * 10
= 0,70 < 1
Section class 1.
Check bending moment strength:
M
Ed
= q
d
*
l
2
8
+ P
d
*
l
4
= 67,50 kNm
M
pl,y,Rd
= * W
pl
f
y
*
M
10
3
= 135,65 kNm
N
pl,Rd
= * A
f
y
*
M
10
= 1149,36 kN
n =
N
d
N
pl,Rd
= 0,238
=
- A * 2 * b
t
10
2
A
= 0,403 < 0,5
Reduced limit moment due to tension force:
M
N,y,Rd
= * M
pl,y,Rd
- 1 n
- 1 * 0,5
= 129,45 kNm
M
Ed
M
N,y,Rd
= 0,52 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Check shear strength:
V
Ed
=
+ P
d
* q
d
l
2
= 37,50 kN
A
v
= 1,04 * h *
s
10
2
= 22,15 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* *
3
M
10
= 273,20 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,14 < 1
Where max M occurs::
V
S
=
P
d
2
= 7,50 kN
V
S
* 0,5 V
pl,Rd
= 0,05 1
No interaction!
Check buckling strength:
y
= 100 *
l
i
y
= 48,00 < 1
trans,y
=
y
*
E
s
f
y
= 0,511
z
= 100 *
l
i
z
= 179,10
trans,z
=
z
*
E
s
f
y
= 1,91
h/b = 2,00 > 1,2
t/10 = 1,07 < 4
Apply strut curve:
line = SEL("steel/buck"; line; ) = a
= TAB("steel/buck"; ; line=line) = 0,210
y
= TAB("steel/buck"; ; =; q=
trans,y
) = 0,9205
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Auxilliary values:
M
= 1,30 Picture 5,5,3
y
=
trans,y
* (2 *
M
- 4) +
- W
pl
W
el
W
el
= -0,575 < 0,9
k
y
= - 1
*
y
N
d
*
y
* A f
y
= 1,013 < 1,5
+
N
d
*
y
* A
f
y
M
* 100 * k
y
M
Ed
* W
pl
f
y
M
= 0,076 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Pos.: Single-span beam:
q
d
Span length l = 7,50 m
Loads:
Dead weight g = 3,00 kN/m
Live load q = 5,00 kN/m
Snow load s
0
= 2,00 kN/m
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
Partial safety factors:
fg
= 1,35
fq
= 1,50
= 0,90
Mo
= 1,10
Design loads:
q
d1
=
fg
*g+
fq*
q = 11,55 kN/m
q
d2
=
fg
*g+*
fq
*(q+s
0
) = 13,50 kN/m
q
d
= MAX(q
d1
;q
d2
) = 13,50 kN/m
Design moment:
M
Ed
=
* q
d
l
2
8
= 94,92 kNm
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; MplydM
Ed
) = IPE 270
with M
pl,yd
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Mplyd; Name=Profil) = 107,00 kNm
M
Ed
M
pl,yd
= 0,89 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Single-span beam
Section classification:
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 270,00 mm
Depth of web h
1
= TAB("steel/"Typ; h1; Name=Profil) = 219,00 mm
Web thickness s
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 6,60 mm
Flange width b = TAB("steel/"Typ; b; Name=Profil) = 135,00 mm
Flange thickness t = TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 10,20 mm
Moment of inertia I = TAB("steel/"Typ; Iy; Name=Profil) = 5790,00 cm
4
Section classification as in Table 5.3.1:
Web:
h
1
s
* 72
= 0,46 < 1
Flange:
b
* 2 t
* 10
= 0,66 < 1
Section class 1.
Check shear strength:
V
Ed
= 0,5 * q
d
* l = 50,63 kN
A
v
= 1,04 * h * s / 100 = 18,53 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* *
3
Mo
10
= 228,55 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,22 1
Analysis working / servicing capacity as in Table 4.1:
q
ser
= g + * ( q + s
0
) = 9,30 kN/m
max
= *
5
384
* q
ser
( ) * l 100
4
* E
s
* I 10
= 3,15 cm
max
* l
100
250
= 1,05 1
2
= *
5
384
* ( )
+ q s
0
( ) * l 100
4
* E
s
* I 10
= 2,37 cm
2
* l
100
300
= 0,95 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Lattice girder with circular hollow sectionsn:
e
Profil 1
Profil 2
g
1
2
h
l
0
D
U
U
V
2
2
2
3
Plan and elevation values:
Span length l
0
= 250,00 cm
1
= 30,96
2
= 90,00
h = 150,00 cm
g = 2,00 cm
e = 0,81 cm
Weld thickness a = 3,00 mm
Profil1: SEL("steel/CHS"; Name; ) = CHS 114.3x5
d
U
= TAB("steel/CHS"; d; Name=Profil1) = 114,30 mm
t
U
= TAB("steel/CHS"; t; Name=Profil1) = 5,00 mm
A
U
= TAB("steel/CHS"; A; Name=Profil1) = 17,20 cm
Profil2: SEL("steel/CHS"; Name; ) = CHS 60.3x3
d
2
= TAB("steel/CHS"; d; Name=Profil2) = 60,30 mm
t
2
= TAB("steel/CHS"; t; Name=Profil2) = 3,00 mm
A
2
= TAB("steel/CHS"; A; Name=Profil2) = 5,40 cm
i
2
= TAB("steel/CHS"; i; Name=Profil2) = 2,03 cm
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
M
= 1,10
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
Member forces:
U
2
= 116,67 kN
U
3
= 200,00 kN
D
2
= 97,18 kN
V
2
= 50,00 kN
* l
0
10
d
U
= 21,87 > 6
* h 10
d
2
= 24,88 > 6
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Section classification:
Member V2:
d
2
* t
2
* 50
2
= 0,40 < 1
Section class 1
Analysis of the members:
Member V
2
:
Section class 1
A
= 1,00
= 0,75*h/i
2
= 55,42
trans
=
*
1
= 0,590
Apply strut curve a
= 0,21
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans
- 0,2) +
trans
) = 0,715
=
1
+
trans
2
= 0,8937
N
b,Rd
= *
A
* A
2
*
f
y
*
M
10
= 103,10 kN
V
2
N
b,Rd
= 0,485 < 1
Member D2:
N
Rd
= A
2
*
f
y
*
M
10
= 115,36 kN
D
2
N
Rd
= 0,842 < 1
Member U2;U3
N
Rd
= A
U
*
f
y
*
M
10
= 367,45 kN
U
3
N
Rd
= 0,544 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Analysis of joint:
Check permissible stress As in Table: K.5
d
2
/ d
U
= 0,528 < 1
d
2
/ d
U
= 0,528 > 1
d
U
/ t
U
= 22,860 > 10
d
U
/ t
U
= 22,860 < 50
d
2
/ t
2
= 20,100 > 10
d
2
/ t
2
= 20,100 < 50
(t
U
+ t
2
) / g = 4,000 < 1
Analysis as given in Table. K.6:
t
2
/ 2,5 = 1,200 > 1
t
U
/ 25 = 0,200 < 1
= MIN(
1
;
2
) = 30,960
30 / = 0,969 < 1
e / (d
U
/ 4) = 0,028 < 1
Eccentricities can be neglected.
a / (MIN(t
U
; t
2
) ) = 1,000 > 0,84
Calculate maximum stress As in Table K.6
Collapse of top chord:
=
d
U
* 2 t
U
= 11,43
10 *
g
t
U
= 4,00
k
g
= *
0,2
( )
+ 1 * 0,024
1,2
+ 1 2,7183
( )
* 0,5 * 10 -
g
t
U
1,33
= 1,874
k
p
= 1,00 (tension)
=
d
2
d
U
= 0,528
N
1,Rd
= *
* k
g
* k
p
* f
y
t
U
2
* ( ) - 1 sin( )
1
*
( )
+ 1,8 * 10,2
d
2
d
U
1,1
*
M
10
3
= 325,61 kN
N
2,Rd
=
sin( )
1
sin( )
2
* N
1,Rd
= 167,51 kN
V
2
N
2,Rd
= 0,30 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Collapse due to punching shear:aus Pos. :
d
2
- d
U
* 2 t
U
= 0,58 < 1
N
i1,Rd
= *
f
y
3
* t
2
* * d
2
*
+ 1 sin( )
1
* 2 sin( )
1
2
1,1
*
M
10
3
= 220,62 kN
D
2
/ N
i1,Rd
= 0,44 < 1
N
i1,Rd
= *
f
y
3
* t
2
* * d
2
*
+ 1 sin( )
2
* 2 sin( )
2
2
1,1
*
M
10
3
= 77,11 kN
V
2
/ N
i1,Rd
= 0,65 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Truss joint with rectangular hollow sections:
Profil 1
Profil 2
1
2
e
d
d d
t
t
t
1
1
2
2
2
2
Plan and elevation values:
Span length l
2
= 200,00 cm
Projection length
ov
= 40,00 %
1
= 50,00
2
= 50,00
e = -2,00 cm
Weld thickness a = 3,50 mm
Profil1: SEL("steel/SHS"; Name; ) = SHS 100x4
d
1
= TAB("steel/SHS"; a; Name=Profil1) = 100,00 mm
t
1
= TAB("steel/SHS"; t; Name=Profil1) = 4,00 mm
A
1
= TAB("steel/SHS"; A; Name=Profil1) = 15,20 cm
Profil2: SEL("steel/SHS"; Name; ) = SHS 60x4
d
2
= TAB("steel/SHS"; a; Name=Profil2) = 60,00 mm
t
2
= TAB("steel/SHS"; t; Name=Profil2) = 4,00 mm
A
2
= TAB("steel/SHS"; A; Name=Profil2) = 8,79 cm
i
2
= TAB("steel/SHS"; i; Name=Profil2) = 2,27 cm
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
M
= 1,10
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
Member forces:
U
l
= 250,00 kN
U
r
= 150,00 kN
D
l
= 77,80 kN (compression)
D
r
= 77,80 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Section classification:
Member Dl:
d
2
* t
2
* 33
2
= 0,45 < 1
Section class 1
Analysis of the members:
Member V2:
= 0,75 *
l
2
i
2
= 66,08
section class 1
A
= 1,00
trans
= *
A
= 0,70
Knickspannungslinie a
= 0,21
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans
- 0,2) +
trans
) = 0,797
=
1
+
trans
2
= 0,8489
N
b,Rd
= *
A
* A
2
*
f
y
* 10
M
= 159,412 kN
D
l
N
b,Rd
= 0,488 < 1
Member Dr:
N
Rd
= A
2
*
f
y
* 10
M
= 187,786 kN
D
r
N
Rd
= 0,414 < 1
Member U2;U3
N
Rd
= A
1
*
f
y
* 10
M
= 324,727 kN
U
l
N
Rd
= 0,770 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Analysis of joint:
Check permissible stress as in Table: K.14
d
2
d
1
= 0,60 > 0,25
d
2
* t
2
* 1,1
E
s
f
y
= 0,456 < 1 (compression)
d
2
t
2
= 15,000 < 35 (tension)
d
1
t
1
= 25,000 < 35 (tension)
ov
100
= 0,400 < 1
25
ov
= 0,625 < 1
Analysis as given in Table. K.12:
t
2
/ 2,5 = 1,600 > 1
t
2
/ 25 = 0,160 < 1
= MIN(
1
;
2
) = 50,000
30 / = 0,600 < 1
e
* -d
1
0,55
= 0,036 < 1
Eccentricities can be neglected.
a / MIN(t
1
; t
2
) = 0,875 > 0,84
Calculate maximum stress As in Table K.14
Only the overlapping diagonals will be analysed:
b
eff
= *
t
1
d
1
*
t
2
t
1
d
2
= 2,40 cm
b
eff
/ (MIN(d
1
; d
2
)/10) = 0,40 < 1
b
e,ov
= *
t
2
d
2
*
t
1
t
2
d
2
= 4,00 cm
b
e,ov
/ (MIN(d
1
; d
2
)/10) = 0,67 < 1
k
n
= 1,00 (tension)
so da
ov
50
= 0,800 < 1
25
ov
= 0,625 < 1
N
2,Rd
= *
f
y
10
2
* t
2
( )
*
ov
50
+
* 2 - d
2
* 4 t
2
10
+ b
eff
b
e,ov
= 138,368 kN
D
r
N
2,Rd
= 0,562 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Roof truss:
A A
v
sd
x
l
x
a * l
y
l
y
b * l
h
w
sd
Plan and elevation values:
Span width l
x
= 3,00 m
Span length l
y
= 5,00 m
Number of spans in X a = 10
Number of spans in Y b = 10
Truss depth h = 2,00 m
section for chords:
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEA
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = HEA 140
Cross-sectional area A = TAB("steel/"Typ; A; Name=Profil) = 31,40 cm
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
Loads:
w
Ed
= 2,00 kN/m
v
Ed
= 5,00 kN/m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Design loads:
M
Ed
= * v
Ed
( ) * a l
x
2
8
= 562,50 kNm
Compression force in the top chord:
N =
M
Ed
h
= 281,25 kN
Total compression force / Stabiilising force:
N
ges
= *
+ a 1
2
N = 1546,88 kN
Imperfection:
k
r1
=
+ 0,2
1
( )
+ a 1
2
= 0,62
k
r2
= 1,00
k
r
= MIN(k
r1
; k
r2
) = 0,62 < 1
e
0
= k
r
* a *
l
x
5
= 3,72 cm
Equivalent load instead of buckling:
q
= a *
l
x
25
= 1,20 cm
q =
N
ges
* 60 * a l
x
* (k
r
+ 0,2) = 0,70 kN/m
h
Ed
= w
Ed
+ q = 2,70 kN/m
Check deformation q:
E'
Ieff
= 10 * E
s
* 0,5 * A
* l
y
= 8,24*10
10
kNcm
Deformation in the middle of truss:
q1
= *
5
384
* h
Ed
( ) * a l
x
4
* E'I
ef f
10
-6
= 0,35 cm
q1
q
= 0,29 < 1
With it the acceptance, that
q
l / 2500 properly.
It can be calculated with h
sd
.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Vertical bracing Non sway frame:
H
P
d
d
P
d
P
d
P
d
y
l
y
b * l
A
B C
D
Plan and elevation values:
Frame width l
y
= 6,00 m
Number of frames b = 5
Frame depth h = 5,00 m
Angle of bracing = atan
( )
h
l
y
= 39,81
Number of bracings n = 1
Number of storeys n
s
= 1
Number of column n
c
= b+1 = 6
Diagonalen wirken auf Zug und auf Druck, Or else sd=1
s
d
= 2
Profil Typ1 = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil1 = SEL("steel/"Typ1; Name; ) = IPE 200
Moment of inertia I
y1
= TAB("steel/"Typ1; Iy; Name=Profil1) = 1940,00 cm
4
Profil Typ2 = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = HEA
Selected Profil2 = SEL("steel/"Typ2; Name; ) = HEA 180
Flange width b
t
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; b; Name=Profil2) = 180,00 mm
Column height h
t
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; h; Name=Profil2) = 171,00 mm
Flange thickness t = TAB("steel/"Typ2; t; Name=Profil2) = 9,50 mm
Moment of inertia I
y2
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; Iy; Name=Profil2) = 2510,00 cm
4
Cross-sectional area A
t
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; A; Name=Profil2) = 45,300 cm
i
y
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; iy; Name=Profil2) = 7,45 cm
i
z
= TAB("steel/"Typ2; iz; Name=Profil2) = 4,52 cm
ProfilR: SEL("steel/CHS"; Name; ) = CHS 168.3x6
d = TAB("steel/CHS"; d; Name=ProfilR) = 168,30 mm
t
r
= TAB("steel/CHS"; t; Name=ProfilR) = 6,00 mm
A
r
= TAB("steel/CHS"; A; Name=ProfilR) = 30,60 cm
i
r
= TAB("steel/CHS"; i; Name=ProfilR) = 5,74 cm
Span length l
r
=
+ h
2
l
y
2
= 7,81 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Loads:
H
d
= 80,00 kN
P
d
= 300,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
E
s
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; Name=steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
M
= 1,10
1
= 93,90 * = 93,90
Check swaying:
k = *
I
y 1
I
y 2
h
l
y
= 0,644
Deflection at top of frame due to horizontal load:
H = 1,00 kN
F
= *
* ( ) * 100 h
3
10
* 12 * E
s
I
y2
*
* 2 + k 1
k
H = 0,702 cm
Shear strength:
S
v
= *
2
10
* n * E
s
* A
r
* h
l
y
2
l
r
3
= 485,6*10
3
kN
w
= H *
h
S
v
* 100 = 1,03*10
-3
cm
Deflection at top of frame:
H = 1,00 kN
tot
=
1
+
1
F
1
w
= 1,028*10
-3
cm
Reduction due to bracing:
( )
- 1
tot
F
* 100 = 99,85 % > 80
Non sway frame.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Analysis of vertical bracing
Imperfection to 5.2.4.3:
0
=
1
200
= 0,005
k
c1
=
+ 0,5
1
n
c
= 0,82
k
c2 =
1,00
k
c
= MIN(k
c1
; k
c2
) = 0,82
k
s1
=
+ 0,2
1
n
s
= 1,10
k
s2
=
1,00
k
s
= MIN(k
s1
; k
s2
) = 1,00
=
0
* k
c
* k
s
= 0,0041
H
d
= * P
d
* (b + 1) = 7,38 kN
H
Ed
= H
d
+ H
d
= 87,38 kN
Bracing is restrained out of plane of frame
*
w
* h 100
* ( ) + b 1 P
d
H
= 0,004 < 0,1
restrained from moving out of plane.
Analysis of lacing angles:
Design compression load:
N
Ed
=
H
Ed
* 2 cos( )
= 56,88 kN
Slenderness:
= 100 *
l
r
i
r
= 136,06
Effective slenderness:
trans
=
*
1
= 1,45
Apply strut curve a:
= 0,21
A
= 1,000
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans
- 0,2) +
trans
) = 1,683
=
1
+
trans
2
= 0,3941
N
Rd
= *
A
* A
r
*
f
y
*
M
10
= 257,63 kN
N
Ed
N
Rd
= 0,221 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Analysis of frame:
Column CD:
N
Ed
= P
d
+
H
Ed
2
*
h
l
y
= 336,41 kN
Buckling in the plane of frame:
k
c
=
I
y2
* h 100
= 5,02 cm
k
1
= 1,0 *
I
y1
* l
y
100
= 3,23 cm
k
2
= 0,0
2
= 1,0
1
=
k
c
+ k
c
+ k
1
k
2
= 0,61
Slenderness ratio as in Fig. E.2.1.:
l = h * 0,85 = 4,25 m
y
= 100 *
l
i
y
= 57,05
trans
=
y
*
1
= 0,61
h
t
b
t
= 0,95 < 1,2
Apply strut curve b:
= 0,34
A
= 1,000
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans
- 0,2) +
trans
) = 0,756
y
=
1
+
trans
2
= 0,8315
Buckling outside the plane of frame
y
= 100 *
h
i
z
= 110,62
trans
=
y
*
1
= 1,18
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Trusses and lattice girders
Apply strut curve c:
= 0,49
A
= 1,000
= 0,5 * (1 + * (
trans
- 0,2) +
trans
) = 1,436
z
=
1
+
trans
2
= 0,4436
min
= MIN(
y;
z
) = 0,4436
N
Rd
=
min
*
A
* A
t
*
f
y
*
M
10
= 429,30 kN
N
Ed
N
Rd
= 0,784 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Welded connections
Angle gusset joint:
Dimensions of connection:
As demanded from EC3 6.6.2.2. b = 12,00 mm
Weld length l = 100,00 mm
Joint plate thickness d = 10,00 mm
Weld thickness a
w
= 4,00 mm
Angle section P = SEL("steel/WG"; Name; ) = L 60x6
Area of angle A = TAB("steel/WG"; A; Name=P) = 6,91 cm
Width of angle h = TAB("steel/WG"; a; Name=P) = 60,00 mm
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
w
= TAB("steel/EC"; w; Name=steel) = 0,80
M0
= 1,10
Mw
= 1,25
Plastic tension force:
N
Rdp
= 2 * A *
f
y
*
M0
10
= 295,25 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Welded connections
Maximum strength of weld:
as in 6.6.5.2(2)
3 / a
w
= 0,75 < 1
MIN(40; 6 * a
w
) / l = 0,24 < 1
l / (150 * a
w
) = 0,17 < 1
12 / b = 1,00 < 1
Reduction factor
wl1
= 1,2 - 0,2 *
l
* 150 a
w
= 1,17
w
= MIN(1;
wl1
) = 1,00
l =
w
* l = 100,00 mm
N
w,Rd
= 4 * l *a
w
*
f
u
*
3 *
w
*
Mw
10
3
= 266,04 kN
Maximum strength of gusset:
Assumption: Stress spreads at 30angle in gusset:
A = (2 * l * TAN(30) + h) *
d
100
= 17,55 cm
N
Rd
= A *
f
y
*
M0
10
= 374,93 kN
Limit design force for tension :
MIN(N
Rd
; N
w,Rd
; N
Rdp
) = 266,04 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Welded connections
Welded beam splice
Dimensions of connection:
Plate thickness d
1
= 20,00 mm
Plate thickness d
2
= 8,00 mm
Plate width b
1
= 160,00 mm
Plate thickness h
2
= 280,00 mm
Weld length l
1
= 240,00 mm
Weld length l
2
= 200,00 mm
Welds
Weld thickness Flange a
wf
= 6,00 mm
Weld thickness Web a
ws
= 4,00 mm
l
wf
= 2 * l
1
= 480,00 mm
l
ws
= 2 * l
2
+ h
2
= 680,00 mm
Profil: IPE 400
Profil Typ = SEL("steel/Profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Selected Profil = SEL("steel/"Typ; Name; ) = IPE 400
Column height h = TAB("steel/"Typ; h; Name=Profil) = 400,00 mm
Web thickness s
= TAB("steel/"Typ; s; Name=Profil) = 8,60 mm
Flange width b = TAB("steel/"Typ; b; Name=Profil) = 180,00 mm
Flange thickness t = TAB("steel/"Typ; t; Name=Profil) = 13,50 mm
Cross-sectional area A
= TAB("steel/"Typ; A; Name=Profil) = 84,50 mm
W
el
= TAB("steel/"Typ; Wy; Name=Profil) = 1160,00 cm
W
pl
= 1,14* W
el
= 1322,40 cm
Material and Partial safety factors:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
w
= TAB("steel/EC"; w; Name=steel) = 0,80
M0
= 1,10
M2
= 1,25
Mw
= 1,25
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Welded connections
Loads :
M
Ed
= 157,95 kNm
V
Ed
= 60,75 kN
Check beam:
M
c,Rd
=
* W
pl
f
y
*
M0
10
3
= 282,51 kNm
M
Ed
M
c,Rd
= 0,56 < 1
A
v
= 1,04 *
* h s
100
= 35,78 cm
V
pl,Rd
= * A
v
f
y
* *
3
M0
10
= 441,32 kN
V
Ed
V
pl,Rd
= 0,14 < 1
Check welds in flanges:
I
w
= *
2
12
* d
2
h
2
3
10
4
= 2926,93 cm
4
I
f
=
* 2 * b
1
* d
1
( )
+ h d
1
2
2
10
4
= 28224,00 cm
4
M
w
= M
Ed
*
I
w
+ I
w
I
f
= 14,84 kNm
M
f
= M
Ed
*
I
f
+ I
w
I
f
= 143,11 kNm
Effective tension force in flange
N
Ed
=
M
f
+ h d
1
* 10 = 340,74 kN
Limit shear stress of flange plates:
f
v,wd
=
f
u
*
3 *
w
*
Mw
10
= 20,78 kN/cm
Design stress:
f
Ed
=
N
Ed
* l
wf
a
wf
* 10 = 11,83 kN/cm
f
Ed
f
v ,wd
= 0,57 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Welded connections
Change welds in web:
Centre of gravity
e =
* 2 * l
2
*
l
2
2
a
ws
* l
ws
a
ws
= 58,82 mm
I
x
=
* a
ws
+
h
2
3
12
* 2 * l
2
*
( )
h
2
2
2
a
ws
10
4
= 3867,73 cm
4
I
y
=
* h
2
* a
ws
+ e
2
*
2
12
* a
ws
+ l
2
3
* 2 * l
2
* a
ws
( )
-
l
2
2
e
2
10
4
= 1192,16 cm
4
Design moment
M
Ew
= M
w
+ * V
Ed
- l
2
e
10
3
= 23,42 kNm
Maximum shear stress
f
Ex
= 10 * M
Ew
*
h
2
* 4 ( )
+ I
x
I
y
= 3,24 kN/cm
f
Ey
=
+
V
Ed
* l
ws
a
ws
100
* 100 * M
Ew
- l
2
e
10
* 2 ( )
+ I
x
I
y
= 5,50 kN/cm
f
E
=
+ f
Ex
2
f
Ey
2
= 6,38 kN/cm
f
E
f
v ,wd
= 0,31 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Welded connections
Beam with cover plates on flange:
b
s
t
t
h
ts
tb
bn
e2 l
Plan and elevation values:
Flange width b = 16,00 cm
Flange thickness t = 1,20 cm
Depth of web h = 34,00 cm
Web thickness s = 0,80 cm
Plate thickness t
b
= 0,80 cm
Weld thickness a = 0,30 cm
Weld distance l = 9,50 cm
Loads:
M
Ed
= 241,90 kNm
V
Ed
= 97,50 kN
Materials and stresses
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
y
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; Name=steel) = 235,00 N/mm
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
w
= TAB("steel/EC"; w; Name=steel) = 0,80
=
235
f
y
= 1,00
Partial safety factors:
M
= 1,10
Mw
= 1,25
Design:
W
pl
= *
( )
* b * t +
+ h t
2
*
h
2
* s
h
4
2 = 907,04 cm
M
pl
= 0,001 * W
pl
*
f
y
M
= 193,78 kNm
V
pl,Rd
= h * s *
f
y
*
3 *
M
10
= 335,49 kN
Distance between cover plates:
b
n
=
*
M
* 10 -
M
Ed
f
y
W
pl
* 2 * t
b
( )
+
h
2
+ t
t
b
2
= -30,10 cm
gew b
n
= 7,60 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Welded connections
W
pl
= + *
( )
* b * t +
+ h t
2
*
h
2
* s
h
4
2 * 2 * t
b
*
( )
+
h
2
+ t
t
b
2
b
n
= 1133,22 cm
M
pl,Rd
= 0,001 * W
pl
*
f
y
M
= 242,10 kNm
Analysis:
M
Ed
M
pl,Rd
= 1,00 1
V
Ed
*
1
2
V
pl ,Rd
= 0,58 1
Length e2 of weld:
I
y
=
+
* b -
( )
+ h * 2 t
3
* ( )
- b s h
3
12
* 2 * t
b
* b
n
( )
+
h
2
+ t
t
b
2
2
= 18726,53 cm
4
T' = * V
Ed
* t
b
* b
n
( )
+
h
2
+ t
t
b
2
I
y
= 0,59 kN/cm
f
v,wd
=
f
u
*
3 *
w
*
Mw
10
= 20,78 kN/cm
F
w,Rd
= 0,2 * a * f
v,wd
= 1,25 kN/cm
e
2
=
T'
F
w,Rd
= 0,47 cm
sel e2 = 40,00 mm (Minimum allowed length)
T = T' * (e
2
+ l) = 29,20 kN
F
w,Rd
= 0,2*a*e
2
*f
v,wd
= 49,87 kN
Analysis:
T
F
w,Rd
= 0,59 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Welded connections
Welded connection
Sd Sd
l b
h
Plan and elevation values:
Span length l = 200,00 mm
Width b = 80,00 mm
Web depth h = 140,00 mm
Weld thickness a
w
= 6,00 mm
Loads:
S
d
= 100,00 kN
Materials and stresses:
steel = SEL("steel/EC"; Name; ) = Fe 360
f
u
= TAB("steel/EC"; fu; Name=steel) = 360,00 N/mm
w
= TAB("steel/EC"; w; Name=steel) = 0,80
Mw
= 1,25
Design:
Weld properties:
A = 0,02 * a
w
* ( b+h ) = 26,40 cm
I
y
=
* 2 * b * a
w
+
( )
h
2
2
* 2 * a
w
h
3
12
10
4
= 744,80 cm
4
I
z
=
* 2 * h * a
w
+
( )
b
2
2
* 2 * a
w
b
3
12
10
4
= 320,00 cm
4
I
p
= I
y
+I
z
= 1064,80 cm
4
Design load in relation to the centroid of weld:
S
dz
= S
d
= 100,00 kN
M
y,Ed
= S
d
*
l
10
= 2000,00 kNcm
M
t,Ed
= S
d
*
b
20
= 400,00 kNcm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 3 Folder : Welded connections
Check stress at weakest point:
A
= *
M
y,Ed
I
y
h
20
= 18,80 kN/cm
1
= *
M
t,Ed
I
p
h
20
= 2,63 kN/cm
2
= *
M
t,Ed
I
p
b
20
+
S
dz
A
= 5,29 kN/cm
res
=
+
A
2
+
1
2
2
2
= 19,71 kN/cm
Check weld strength:
Limit shear stress
f
w,Rd
=
f
u
*
3 *
w
*
Mw
10
= 20,78 kN/cm
res
f
w,Rd
= 0,95 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Columns
Concrete encasement composite column with eccentric force application:
e
h
F
H
H
F
System:
Height h = 8,00 m
Eccentricity e = 0,15 m
Beam type = SEL("steel/profils"; Name; ) = HEB
Nominal height NH = SEL("steel/"type; NH; ) = 340
A
a
= TAB("steel/"type; A; NH=NH) = 171,00 cm
h
p
= TAB("steel/"type; h; NH=NH) = 340,00 mm
s = TAB("steel/"type; s; NH=NH) = 12,00 mm
t = TAB("steel/"type; t; NH=NH) = 21,50 mm
b = TAB("steel/"type; b; NH=NH) = 300,00 mm
I
ya
= TAB("steel/"type; I
y
; NH=NH) = 36660,00 cm
4
W
pa
= 1.14*TAB("steel/"type; W
y
; NH=NH) = 2462,40 cm
W
pa
= 2408,00 cm
Materials:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; ) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("steel/EC"; NameEN; ) = S235
E
cm
= TAB("concrete/EC"; E
cm
; Name=Concrete) = 32000,00 N/mm
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 30,00 N/mm
The value for for use in a contry should lie between 0,8 - 1,0 and me be found in a National Annex.
The Recommended Value for is 1,0
= 1,00
E
a
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; NameEN=Steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; NameEN=Steel) = 235,00 N/mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Columns
Partial safety factors:
Dead load
G
= 1,35
Imposed Load
Q
= 1,50
Concrete
c
= 1,50
Construction steel
a
= 1,10
Profile steel sheeting
ap
= 1,10
Longitudinal shear
vs
= 1,25
Elastic modulus = 1,35
Load:
g
k
= 450,00 kN
q
k
= 1000,00 kN
Calculation:
N
Ed
= g
k
*
G
+ q
k
*
Q
= 2107,50 kN
M
Ed
= N
Ed
* e = 316,13 kNm
V
Ed
= M
Ed
/ h = 39,52 kN
f
cd
= * f
ck
/
c
= 20,00 N/mm
f
yd
= f
yk
/
a
= 213,64 N/mm
E
cd
= E
cm
/ = 23703,70 N/mm
A
c
= ( h
p
* b ) *10
-2
-A
a
= 849,00 cm
I
yc
= ( h
p
* b / 120000 ) - I
ya
= 61600,00 cm
4
Local buckling of parts of the steel section:
=
235
f
yk
= 1,00
/ b t
* 44
= 0,32 < 1
Load-bearing capacity of the column under centric pressure with buckling risk:
N
pl,Rd
=
* A
a
+ f
yd
* A
c
f
cd
10
= 5351,24 kN
Structural verification procudure applicable?
=
* A
a
f
yd
* 10 N
pl,Rd
= 0,68
0.2 / = 0,29 < 1
/ 0.9 = 0,76 < 1
Structural verification procudure applicable.
On the effect of lateral shear:
A
v
= ( 1.04 * h
p
* s ) * 10
-2
= 42,43 cm
V
pl,Rd
=
* A
v
f
yd
* 3 10
= 523,35 kN
V
Ed
/ V
pl,Rd
= 0,08 < 0,5
The lateral shear force has no effect on the load-bearing capacity.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Columns
Cross section bearing capacity under pressure and single-axis bending:
Plastic limit moment at point D:
W
pc
= -
* b h
p
2
4000
W
pa
= 6262,00 cm
M
max,Rd
= ( W
pa
*f
yd
+ 1/2 * W
pc
* f
cd
) * 10
-3
= 577,07 kNm
N
D
= 1/20 * A
c
* f
cd
= 849,00 kN
Plastic limit moment in points B and C:
N
pm,Rd
= ( A
c
* f
cd
) * 10
-1
= 1698,00 kN
h
N
=
N
pm,Rd
* 0,2 * b * 10
-1
+ f
cd
* 2 * s * 10
-2
( ) * 2 - f
yd
f
cd
= 7,80 cm
h
N
* ( ) - / b 2 t 10
-1
= 0,61 1
Plastic neutral axis is in the rib!
W
pan
= s/10 * h
N
= 73,01 cm
W
pcn
= ( b * h
N
) * 10
-1
- W
pan
= 1752,19 cm
M
N,Rd
= (W
pan
* f
yd
+ 1/2 * W
pcn
* f
cd
)*10
-3
= 33,12 kNm
The plastic limit moment in points B and C is:
M
pl,Rd
= M
max,Rd
- M
N,Rd
= 543,95 kNm
N
B
= 0,00 kN
N
C
= 2 * N
D
= 1698,00 kN
Load-bearing capacity of a composite column under pressure and single-axis bending:
N
pl,Rk
= (A
a
* f
yk
+ A
c
* * f
ck
)*10
-1
= 6565,50 kN
Effective elastic bending rigidity:
EI
e
= (E
a
* I
ya
+ 0.8 * E
cd
* I
yc
) * 10
-5
= 88667,18 kN/m
Reference degree of slenderness:
N
cr
=
*
2
EI
e
h
2
= 13673,57 kN
' =
N
pl,Rk
N
cr
= 0,69
Long-term behaviour (creep and shrinkage) may be disregarded.
Strut curve b:
Type = SEL("comp/buck"; Desc; ) = concrete-encased profile strong axis
line = TAB("comp/buck"; line; Desc=Type) = b
= TAB("comp/buck"; ; line=line; lat=') = 0,789
d
= N
Ed
/ N
pl,Rd
= 0,394
Proportion of edge moments r = 0,00
N
= * ( ( 1 - r ) / 4 ) = 0,197
The resulting values for point C are:
c
= N
C
/ N
pl,Rd
= 0,317
c
= 1,00
k
= *
- 1
- 1
c
c
= 0,309
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Columns
d
= *
- 1
d
- 1
k
= 0,887
The length is:
=
d
-
k
* (
d
-
N
) / ( -
N
) = 0,784
Structural verification of load-bearing capacity:
N
Ed
* N
pl,Rd
= 0,50 1
M
Ed
* 0,9 * M
pl,Rd
= 0,82 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Columns
Concrete-filled hollow section:
F
F
h
t
t
d
System:
Column height h = 7,00 m
Outside pipe diameter d = 273,00 mm
Pipe thickness t = 6,30 mm
Load:
g
k
= 500,00 kN
q
k
= 600,00 kN
Materials:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; ) = C30/37
Steel = SEL("steel/EC"; NameEN; ) = S355
E
cm
= TAB("concrete/EC"; E
cm
; Name=Concrete) = 32800,00 N/mm
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete)| = 30,00 N/mm
E
a
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; NameEN=Steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; NameEN=Steel) = 355,00 N/mm
The value for for use in a contry should lie between 0,8 - 1,0 and me be found in a National Annex.
The Recommended Value for is 1,0
= 1,00
Partial safety factors:
Dead load
G
= 1,35
Imposed Load
Q
= 1,50
Concrete
c
= 1,50
Construction steel
a
= 1,10
Profile steel sheeting
ap
= 1,10
Longitudinal shear
vs
= 1,25
Concrete elastic modulus = 1,35
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Columns
Calculation:
f
yd
= f
yk
/
a
= 322,73 N/mm
f
cd
= * f
ck
/
c
= 20,00 N/mm
N
Ed
=
G
* g
k
+
Q
* q
k
= 1575,00 kN
f
yd
= f
yk
/
a
= 322,73 N/mm
A
a
= *
400
( )
- d
2
( ) - d * 2 t
2
= 52,79 cm
I
a
= *
640000
( )
- d
4
( ) - d * 2 t
4
= 4695,82 cm
4
E
cd
= E
cm
/ = 24296,30 N/mm
A
c
=
* ( ) - d * 2 t
2
400
= 532,56 cm
I
c
=
* ( ) - d * 2 t
4
640000
= 22570,10 cm
4
Local buckling of parts of the steel section:
=
235
f
yk
= 0,81
/
( )
d
t
( )
* 90
2
= 0,73 1
Structural verification of the column's load-bearing capacity:
N
pl,Rd
= ( A
a
* f
yd
+ A
c
* f
cd
) * 10
-1
= 2768,81 kN
Structural verification procudure applicable?
=
( )
* A
a
f
yk
a
* N
pl,Rd
10
= 0,62
0.2 / = 0,32 < 1
/ 0.9 = 0,69 < 1
Structural verification procudure applicable
N
pl,Rk
= (A
a
* f
yk
+ A
c
* * f
ck
)*10
-1
= 3471,72 kN
Effective elastic bending rigidity:
EI
e
= (E
a
* I
a
+ 0,8 * E
cd
* I
c
)*10
-5
= 14248,18 kNm
Reference degree of slenderness:
N
cr
= * EI
e
/ h = 2869,87 kN
' =
N
pl,Rk
N
cr
= 1,10
'
g
=
0,8
( ) - 1
= 2,11
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Columns
' / '
g
= 0,52 < 1
Long-term behaviour (creep and shrinkage) may be disregarded.
Concrete-filled hollow section, therefore strut curve a
Type = SEL("comp/buck"; Desc; ) = concrete-filled hollow section
line = TAB("comp/buck"; line; Desc=Type) = a
= TAB("comp/buck"; ; line=line; lat=') = 0,596
N
Rd
= * N
pl,Rd
= 1650,21 kN
Structural verification:
N
Ed
/ N
Rd
= 0,95 < 1
The ultimate load bearing capacity is almost completely exploited.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Composite beams - Ultimate load bearing capacity:
q
l
System:
Beam length L = 12,00 m
Beam distance s = 3,60 m
Materials:
Beam type = SEL("steel/profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Nominal height NH = SEL("steel/"type; NH; ) = 450
A = TAB("steel/"type; A; NH=NH) = 98,80 cm
h = TAB("steel/"type; h; NH=NH)/10 = 45,00 mm
I
y
= TAB("steel/"type; I
y
; NH=NH) = 33740,00 cm4
Shear connectors 22
h
b
= 100,00 mm
d = 22,00 mm
Distance of shear connectors e
L
= 15,00 cm
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; ) = C25/30
Steel = SEL("steel/EC"; NameEN; ) = S355
Load:
g
1k
= 15,28 kN/m
g
2k
= 7,74 kN/m (after removal of temporary props)
q
k
= 18,00 kN/m
b
h
h
eff
pb
d
Floor thickness h
d
= 16,00 cm
Thickness of profile steel sheeting h
pb
= 5,10 cm
Material properties:
E
cm
= TAB("concrete/EC"; E
cm
; Name=Concrete) = 31500,00 N/mm
E
a
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; NameEN=Steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
Cross section load bearing capacity at full shear connection:
b
eff
= 2 * L / 8 = 3,00 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff
;s) = 3,00 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Working state analysis of composite beams:
Form factors:
Short term load at point of time t =0:
n
0
= E
a
/ E
cm
= 6,67
Effective component thickness:
Beam width in air u = 360,00 cm
h
o
= 2 * h
d
* u / u = 32,00 cm
Final creep value t
0
=14 days
according to EC2 Appendix1 = 2,70
constant continuous load
A,B
= 1,10
Shrinkage
A,S
= 0,55
Creep under continuous load n = n
0
* ( 1+
A,B
* ) = 26,48
Shrinkage n
S
= n
0
* ( 1+
A,S
* ) = 16,57
A
c
= 100 * b
eff
* ( h
d
- h
pb
) = 3270,00 cm
I
c
= 100 * b
eff
* ( h
d
- h
pb
) / 12 = 32375,72 cmm
z'
s0
=
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
*
A
c
n
0
( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
+ A
A
c
n
0
= 10,99 cm
*
( )
+ I
y
I
c
n
0
+ 10
-4
*
( )
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
2
*
A
c
n
0
( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
2
10
-4
= 19,96 cmm
*
( ) * z'
s0
10
-2
2
*
( )
+ A
A
c
n
0
( ) -1 = -7,11 cmm
I
i0 =
12,85 cmm
z'
s
=
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
*
A
c
n
/ ( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
+ A / A
c
n
= 20,14 cm
*
( )
+ I
y
I
c
n
+ 10
-4
*
( )
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
2
*
A
c
n
( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
2
10
-4
= 18,51 cmm
*
( ) * z's
10
-2
2
*
( )
+ A
A
c
n
( ) -1 = -9,02 cmm
I
iphi
= 9,49 cmm
I
i
= I
iphi
= 9,49 cmm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
z'
sS
=
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
*
A
c
n
S
/ ( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
+ A / A
c
n
S
= 16,48 cm
*
( )
+ I
y
I
c
n
S
+ 10
-4
*
( )
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
2
*
A
c
n
S
( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
2
10
-4
= 18,80 cmm
*
( ) * z'
sS
10
-2
2
*
( )
+ A
A
c
n
S
( ) -1 = -8,04 cmm
I
iS =
10,76 cmm
Calculation of midspan deflection:
Release of temporary prop at point of time t =0
B = g
1k
* 1.25 * L/2 = 114,60 kN
f
B0
= 100 * B * L / ( 48 * E
a
/10 * I
i0
) = 1,53 cm
Assumption: 40% of the live load as a permanent load at point of time t =0:
Ratio= 0,40
f
g2,0
= 100 * 5/384 *(g
2k
+ Ratio* q
k
) * L
4
/ ( E
a
/10 * I
i0
) = 1,49 cm
from imposed load (short term ratio):
Ratio2 = 1 - Ratio = 0,60
f
q
= 100 * 5/384 * Ratio2 * q
k
* L
4
/ ( E
a
/10
*
I
i0
) = 1,08 cm
From removal of temporary prop at point of time t =:
f
B
= f
B0
* I
i0
/ I
i
= 2,07 cm
From g
k2
+ q
permanent
at point of time t =:
f
g2
= f
g2,0
* I
i0
/ I
i
= 2,02 cm
From shrinkage at point of time t =:
Final shrinkage value
cS
= 325*10
-6
N
sch
= (A
c
* E
a
/ n
S
*
cS
) / 10 = 1346,88 kN
z
sch
= z'
sS
- (h
d
-h
pb
)/2 = 11,03 cm
M
sch
= N
sch
* z
sch
/ 100 = 148,56 kN
f
sch
= 100 * 1/8 * M
sch
* L / ( E
a
/10 * I
iS
) = 1,18 cm
Maximum deflection:
max_f = f
B
+ f
g2
+ f
sch
+ f
q
= 6,35 cm
Recommended camber:
f
0
= f
B0
+ f
g2,0
= 3,02 cm
Maximum deflection in final state:
f = max_f - f
0
= 3,33 cm
Structural verification:
f/100 / ( L / 300 ) = 0,83 < 1
The deflection in the working state meets the required standard!
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Composite floor in the final state:
q
l
System:
Steel profile with lugs; values according to manufacturer's specifications (approval )
m = 166,00
k = 0,15
Sheet thickness t = 0,86 mm
e = 17,00 mm
Beam length L = 4,80 m
Stability f
yp
= 350,00 N/mm
Cross section area A
p
= 1562,00 N/mm
u,Rd
= 280,00 kN/m
minimum width of concrete ribs b
0
= 750,00 mm/m
Concrete:
Floor thickness h
t
= 14,00 cm
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; ) = C25/30
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 25,00 N/mm
f
ctk005
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fctk05; Name=Concrete)| = 1,80 N/mm
Influences:
Final state:
Permanent load of composite floor G
1
= 3,30 kN/m
Permanent load of design loads G
2
= 1,20 kN/m
Imposed load Q = 5,00 kN/m
Partial safety factors:
Dead load
G
= 1,35
Imposed Load
Q
= 1,50
Concrete
c
= 1,50
Profile steel sheeting
ap
= 1,10
Longitudinal shear
vs
= 1,25
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Structural verification of the composite floor in the final state:
b = 1000,00 mm
Deflection:
M
Ed
= (
G
* ( G
1
+G
2
)+
Q
* Q) * L / 8 = 39,10 kNm/m
Design resistance:
N
cf
= (A
p
* f
yp
/
ap
)/1000 = 497,00 kN
The value for for use in a contry should lie between 0,8 - 1,0 and me be found in a National Annex.
The Recommended Value for is 1,0
= 1,00
=
* N
cf
10
3
* b
( )
*
f
ck
c
= 29,82
d
p
= 10*h
t
- e = 123,00 mm
M
p,Rd
= * N
cf
- d
p
* 0,5
10
3
= 53,72 kNm/m
Structural verification:
M
Ed
/ M
p,Rd
= 0,73 < 1
Longitudinal shear, m + k - method:
Design shear force at the footing point:
V
Ed
= (
G
*(G
1
+G
2
) +
Q
* Q ) * L / 2 = 32,58 kN/m
Longitudinal shear resistance:
Shear length L
s
= 1000 * L / 4 = 1200,00 mm
V
l,Rd
= *
* b * d
p
( )
* m +
A
p
* b L
s
k
vs
10
-3
= 36,02 kN/m
Structural verification:
V
Ed
/ V
l,Rd
= 0,90 < 1
Longitudinal shear, partial shear connection ( EC4, Appendix E ):
Design value of the bond strength according to manufacturer's information:
Shear length at full shear connection = 1,00
L
sf
=
N
cf
* b * 10
-3
u,Rd
= 1,77 m
Design resistance:
Rd
= * 0,09
f
ck
3
= 0,26 N/mm
k
v
= 1.6 - d
p
/1000 = 1,48 > 1
A
p
= b
0
* t = 645,00 mm
=
A
p
* b
0
d
p
= 0,007
V
v,Rd
= (b
0
* d
p
*
Rd
* k
v
* ( 1.2 + 40 * ))/1000 = 52,54 kN/m
Structural verification:
V
Ed
/ V
v,Rd
= 0,62 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Composite beams - Ultimate load bearing capacity:
q
l
System:
Beam length L = 12,00 m
Number of temporary props a = 1,00
Beam distance s = 3,60 m
Flange width b
0
= 12,60 cm
Load:
g
1k
= 14,50 kN/m
g
2k
= 7,74 kN/m (Hilfsuntersttzung entfernt)
q
k
= 18,00 kN/m
Materials:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; ) = C25/30
Steel = SEL("steel/EC"; NameEN; ) = S355
Beam type = SEL("steel/profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Nominal height NH = SEL("steel/"type; NH; ) = 400
A = TAB("steel/"type; A; NH=NH) = 84,50 cm
h = TAB("steel/"type; h; NH=NH)/10 = 40,00 cm
t = TAB("steel/"type; s; NH=NH)/10 = 0,86 cm
I
y
= TAB("steel/"type; I
y
; NH=NH) = 23130,00 cm
4
M
pl
= TAB("steel/"type; M
plyd
; NH=NH) = 289,00 kNm
M
pl
= IF(Steel="S355";1,5;1)*M
pl
= 433,50 kNm
Shear connectors 22
h
b
= 100,00 mm
d = 19,00 mm
Distance of shear connectors e
L
= 15,00 cm
Ultimate strength f
u
= 450,00 N/mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Partial safety factors:
Dead load
G
= 1,35
Imposed Load
Q
= 1,50
Concrete
c
= 1,50
Construction steel
a
= 1,10
Profile steel sheeting
ap
= 1,10
Longitudinal shear
vs
= 1,25
b
h
h
eff
pb
d
Floor thickness h
d
= 16,00 cm
Thickness of profile steel sheeting h
pb
= 5,10 cm
Cross-sectional area of plate A
p
= 15,62 kN/m
Material properties:
E
cm
= TAB("concrete/EC"; E
cm
; Name=Concrete) = 30500,00 N/mm
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 25,00 N/mm
f
ctk005
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fctk05; Name=Concrete) = 1,80 N/mm
f
cd
= f
ck
/
c
= 16,67 N/mm
E
a
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; NameEN=Steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; NameEN=Steel) = 355,00 N/mm
f
yd
= f
yk
/
a
= 322,73 N/mm
Holorib sheeting in accordance with building regulations approval:
f
yp
= 280,00 N/mm
Conformation of fitness for purpose:
Stress resultants in ultimate state analysis of fitness for purpose:
r
d
=
G
* (g
1k
+ g
2k
) +
Q
* q
k
= 57,02 kN/m
M
Ed
= r
d
* L / 8 = 1026,36 kNm
V
Ed
= r
d
*L / 2 = 342,12 kN
Cross section load bearing capacity with full shear connection:
b
eff
= 2 * L / 8 = 3,00 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff
; s) = 3,00 m
A
v
= 1.04 * h * t = 35,78 cm
N
pl,a,Rd
= A * f
yd
/ 10 = 2727,07 kN
N
cd
= 0,85 * f
cd
* 100 * b
eff
* ( h
d
- h
pb
) = 46334,26 kN
The value for for use in a contry should lie between 0,8 - 1,0 and me be found in a National Annex.
The Recommended Value for is 1,0
c
= 1,00
z
pl
= N
pl,a,Rd
/ ( 10 *
c
* f
cd
* b
eff
) = 5,45 cm
The plastic neutral axis is in the concrete chord above the profile steel sheeting.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Distance to centre of gravity:
a = h / 2 + h
d
- z
pl
/ 2 = 33,27 cm
M
pl,Rd
= N
pl,a,Rd
* a / 100 = 907,30 kNm
V
pl,Rd
= A
v
* f
yk
/ ( 10 * (3) *
a
) = 666,68 kN
Structural verifications:
M
Ed
/ M
pl,Rd
= 1,13 < 1
V
Ed
/ V
pl,Rd
= 0,51 < 1
Longitudinal shear load capacity and shear connection:
h
b
/ d = 5,26 > 4 -> shear connectors are ductile
= IF(h
b
/d>4; 1; 0.2 * ((h
b
/d)+1)) = 1,00
Marginal force of a shear connector:
P
Rd1
=
* 0,8 * f
u
* d
2
* 4 *
vs
10
3
= 81,66 kN
P
Rd2
= *
( )
* 0,29 * * d
2
* f
ck
E
cm
vs
10
-3
= 73,13 kN
P
Rd
= MIN( P
Rd1
; P
Rd2
) = 73,13 kN
single-row:
N
r
= 1,00 (one row of shear connectors)
k
t1
= *
0,7
N
r
*
b
0
h
pb
( )
-
* h
b
10
-1
h
pb
1
= 1,66
k
t2
= 0,85
k
t
= MIN ( k
t1
; k
t2
) = 0,85
P
Rd1
= k
t
* P
Rd
= 62,16 kN
double-row:
N
r
= 2,00 (two rows of shear connectors)
k
t1
= *
0,7
N
r
*
b
0
h
pb
( )
-
* h
b
10
-1
h
pb
1
= 1,17
k
t2
= 0,70
k
t
= MIN ( k
t1
; k
t2
) = 0,70
P
Rd2
= k
t
* P
Rd
= 51,19 kN
Possible shear connector configurations:
7 pairs of shear connectors at the end of the beam Anzp = 7,00
33 individual shear connectors in the span Anze = 33,00
aufn_V = Anze * P
Rd1
+ 2 * Anzp * P
Rd2
= 2767,94 kN
Structural verification:
N
pl,a,Rd
/ aufn_V = 0,99 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Structural verification against diagonal strut failure according to NAD for Germany:
A
cv
= 100 * ( h
d
- h
pb
) = 1090,00 N/m
Normal concrete = 1,00
Rd,2
=
* 0,2 * A
cv
* f
ck
*
c
10
= 363,33 kN/m
Ed
=
P
Rd1
* e
L
10
-2
= 414,40 kN/m
Ed,li
=
Ed
*1/2 = 207,20 kN/m
Ed,li
/
Rd,2
= 0,57 < 1
This calculation disregards the input from profile steel sheeting!
Cross reinforcement necessary:
NAD
Rd
= * 0,09
f
ck
3
= 0,26 MN/mm
pd
=
* A
p
f
yp
*
ap
10
= 397,60 kN/m
Rd,3
= 2.5 * A
cv
* * (
Rd
/ 10 ) +
pd
= 468,45 kN/m
Structural verification of diagonal strut:
Ed,li
/
Rd,3
= 0,44 < 1
Working state analysis of composite beams:
Form factors:
Short term load at point of time t =0:
n
0
= E
a
/ E
cm
= 6,89
Effective component thickness:
Beam width in air u = 360,00 cm
h
o
= 2 * h
d
*u / u = 32,00 cm
Final creep value t
0
=14 days
according to EC2 Appendix1 = 2,70
Creep under continuous load n = n
0
* 3 = 20,67
Shrinkage and creep n
S
= n
0
* 2 = 13,78
A
c
= 100 * b
eff
* ( h
d
- h
pb
) = 3270,00 cm
I
c
= 100 * b
eff
* ( h
d
- h
pb
) / 12 = 32375,72 cmm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
z'
s0
=
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
*
A
c
n
0
( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
+ A
A
c
n
0
= 10,07 cm
*
( )
+ I
y
I
c
n
0
+ 10
-4
*
( )
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
2
*
A
c
n
0
( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
2
10
-4
= 15,14 cmm
*
( ) * z'
s0
10
-2
2
*
( )
+ A
A
c
n
0
( ) -1 = -5,67 cmm
I
i0 =
9,47 cmm
z'
s
=
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
*
A
c
n
/ ( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
+ A / A
c
n
= 16,09 cm
*
( )
+ I
y
I
c
n
+ 10
-4
*
( )
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
2
*
A
c
n
( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
2
10
-4
= 13,89 cmm
*
( ) * z's
10
-2
2
*
( )
+ A
A
c
n
( ) -1 = -6,28 cmm
I
iphi
= 7,61 cmm
I
i
= I
iphi
= 7,61 cmm
z'
sS
=
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
*
A
c
n
S
/ ( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
+ A / A
c
n
S
= 13,47 cm
*
( )
+ I
y
I
c
n
S
+ 10
-4
*
( )
* A +
( )
+
h
2
h
d
2
*
A
c
n
S
( )
- h
d
h
pb
2
2
10
-4
= 14,20 cmm
*
( ) * z'
sS
10
-2
2
*
( )
+ A
A
c
n
S
( ) -1 = -5,84 cmm
I
iS =
8,36 cmm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Calculation of midspan deflection:
Release of temporary prop at point of time t =0
B = g
1k
* 1,25 * L/2 = 108,75 kN
f
B0
=
* 10
2
* B L
3
* 48 * E
a
* 10
-1
I
i0
= 1,97 cm
Assumption: 40% of the live load as a permanent load at point of time t =0:
Ratio= 0,40
f
g2,0
=
*
5
384
* 10
2
* ( )
+ g
2k
* Ratio q
k
L
4
* E
a
* 10
-1
I
i0
= 2,03 cm
f
0
= f
B0
+ f
g2,0
= 4,00 cm
from imposed load (short term ratio):
Ratio2 = 1 - Ratio = 0,60
f
q
=
*
5
384
* 10
2
* ( ) * Ratio2 q
k
L
4
* E
a
* 10
-1
I
i0
= 1,47 cm
From removal of temporary prop at point of time t =:
f
B
= f
B0
* I
i0
/ I
i
= 2,45 cm
From g
k2
+ q
permanent
at point of time t =:
f
g2
= f
g2,0
* I
i0
/ I
i
= 2,53 cm
f
d
= f
B
+ f
g2
= 4,98 cm
Creep under continuous load only:
f
k
= f
d
- f
0
= 0,98 cm
From shrinkage at point of time t =:
Final shrinkage value
cS
= 325*10
-6
N
sch
= (A
c
* E
a
/ n
S
*
cS
) / 10 = 1619,58 kN
z
sch
= z'
sS
- (h
d
-h
pb
)/2 = 8,02 cm
M
sch
= N
sch
* z
sch
/ 100 = 129,89 kN
f
sch
=
*
1
8
* M
sch
* 10
2
L
2
* E
a
* 10
-1
I
iS
= 1,33 cm
Maximum deflection:
max_f = f
B
+ f
g2
+ f
sch
+ f
q
= 7,78 cm
Recommended camber:
f
0
= f
B0
+ f
g2,0
= 4,00 cm
Maximum deflection in final state:
f = max_f - f
0
= 3,78 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Structural verification:
/
f
100
L
250
= 0,79 1
The deflection in the working state meets the required standard!
Vibration behaviour:
= *
* 10
2
L
2
* E
a
I
i0
* ( )
+ g
1k
g
2k
* 10 9,81
= 20,69 (1/s)
f =
* 2
= 3,29 Hz
The natural frequency should be no less than 3 Hz.
For sports or dance halls, it should be no less than 5 Hz.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
POS.: Composite beams - Ultimate load bearing capacity:
q
l
System:
Beam length L = 12,00 m
Number of temporary props a = 1,00
Beam distance s = 3,60 m
Flange width b
0
= 12,60 cm
Materials:
Concrete = SEL("concrete/EC"; Name; ) = C25/30
Steel = SEL("steel/EC"; NameEN; ) = S355
Beam type = SEL("steel/profils"; Name; ) = IPE
Nominal height NH = SEL("steel/"type; NH; ) = 450
A = TAB("steel/"type; A; NH=NH) = 98,80 cm
h = TAB("steel/"type; h; NH=NH)/10 = 45,00 cm
t = TAB("steel/"type; s; NH=NH)/10 = 0,94 cm
I
y
= TAB("steel/"type; I
y
; NH=NH) = 33740,00 cm4
M
pl
= TAB("steel/"type; M
plyd
; NH=NH) = 373,00 kNm
M
pl
= IF(Steel="S355";1,5;1)*M
pl
= 559,50 kNm
Shear connectors 22
h
b
= 100,00 mm
d = 22,00 mm
Distance of shear connectors e
L
= 15,00 cm
Ultimate strength f
u
= 450,00 N/mm
Load:
g
k1
= 15,28 kN/m
g
k2
= 7,74 kN/m (after removal of temporary props)
q
k
= 18,00 kN/m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Partial safety factors:
Dead load
G
= 1,35
Imposed Load
Q
= 1,50
Concrete
c
= 1,50
Construction steel
a
= 1,10
Profile steel sheeting
ap
= 1,10
Longitudinal shear
vs
= 1,25
b
h
h
eff
pb
d
Floor thickness h
d
= 16,00 cm
Thickness of profile steel sheeting h
pb
= 5,10 cm
Cross-sectional area of plate A
p
= 15,62 kN/m
Material properties:
E
cm
= TAB("concrete/EC"; E
cm
; Name=Concrete) = 30500,00 N/mm
f
ck
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fck; Name=Concrete) = 25,00 N/mm
f
ctk005
= TAB("concrete/EC"; fctk05; Name=Concrete) = 1,80 N/mm
f
cd
= f
ck
/
c
= 16,67 N/mm
E
a
= TAB("steel/EC"; E; NameEN=Steel) = 210000,00 N/mm
f
yk
= TAB("steel/EC"; fy; NameEN=Steel) = 355,00 N/mm
f
yd
= f
yk
/
a
= 322,73 N/mm
Holorib sheeting in accordance with building regulations approval:
f
yp
= 280,00 N/mm
Conformation of fitness for purpose:
Stress resultants in ultimate state analysis of fitness for purpose:
r
d
=
G
* ( g
k1
+ g
k2
) +
Q
* q
k
= 58,08 kN/m
M
Ed
= r
d
* L / 8 = 1045,44 kNm
V
Ed
= r
d
*L / 2 = 348,48 kN
Cross section load bearing capacity with full shear connection:
b
eff
= 2 * L / 8 = 3,00 m
b
eff
= MIN(b
eff
; s) = 3,00 m
A
v
= 1.04 * h * t = 43,99 cm
N
pl,a,Rd
= A * f
yd
/ 10 = 3188,57 kN
N
cd
= 0.85 * f
cd
* 10 * b
eff
* ( h
d
- h
pb
) = 4633,43 kN
The value for for use in a contry should lie between 0,8 - 1,0 and me be found in a National Annex.
The Recommended Value for is 1,0
c
= 1,00
z
pl
= N
pl,a,Rd
/ ( 10 *
c
* f
cd
* b
eff
) = 6,38 cm
The plastic neutral axis is in the concrete chord above the profile steel sheeting.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Distance to centre of gravity:
a = h / 2 + h
d
- z
pl
/ 2 = 35,31 cm
M
pl,Rd
= N
pl,a,Rd
* a / 100 = 1125,88 kNm
V
pl,Rd
=
* A
v
f
yk
* 10 * 3
a
= 819,65 kN
Structural verifications:
M
Ed
/ M
pl,Rd
= 0,93 < 1
V
Ed
/ V
pl,Rd
= 0,43 < 1
Longitudinal shear capacity and shear connection:
h
b
/ d = 4,55 > 4 -> shear connectors are ductile
= IF(h
b
/d>4; 1; 0.2 * ((h
b
/d)+1)) = 1,00
Marginal force of a shear connector:
P
Rd1
=
* 0,8 * f
u
* d
2
* 4 *
vs
10
3
= 109,48 kN
P
Rd2
= *
( )
* 0,29 * * d
2
* f
ck
E
cm
vs
10
-3
= 98,05 kN
P
Rd
= MIN( P
Rd1
; P
Rd2
) = 98,05 kN
Number of rows of shear connectors N
r
= 1,00
k
t1
= *
0,7
N
r
*
b
0
h
pb
( )
-
* h
b
10
-1
h
pb
1
= 1,66
k
t2
= 0,75
k
t
= MIN ( k
t1
; k
t2
) = 0,75
P
Rd
= k
t
* P
Rd
= 73,54 kN
Required number of shear connectors for full shear connection:
req_n = N
pl,a,Rd
/ P
Rd
+ 0.49 = 44
prov_n = 100*L/2/e
L
+0.49 = 40
because: req_n / prov_n = 1,10 is a partial connection
The maximum transferrable concrete compression force is:
N
c
= prov_n * P
Rd
= 2941,60 kN
Degree of shear connection = N
c
/ N
pl,a,Rd
= 0,92 < 1
Reduced plastic bending moment, calculated with linear interpolation:
M
Rd
= M
pl
+ * ( M
pl,Rd
- M
pl
) = 1080,57 kNm
Structural verification:
M
Ed
/ M
Rd
= 0,97 < 1
Note: No reduction in interaction, because maximum moment and maximum lateral shear force do
not occur in the same place.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 4 Folder : Floors
Shear connector configurations permissible?
a) Cross section class 1 or 2 OK
b) req_ = 0.25 + 0.03 * L = 0,61
req_/ = 0,66 < 1
c)
M
pl,Rd
/ ( 2.5 * M
pl
) = 0,80 < 1
All conditions a-c have to be met!
Connection of lateral concrete chord:
Lateral shear::
Ed
= P
Rd
/ ( e
L
/ 100 ) = 490,27 kN/m
Relevant:
Ed,li
=
Ed
* 1 / 2 = 245,13 kN/m
A
cv
= ( h
d
- h
pb
) * 100 = 1090,00 cm/m
Normal concrete = 1,00
Rd,2
= 0.2 * A
cv
* * f
ck
/ (
c
*10 ) = 363,33 kN/m
Structural verification against diagonal strut failure:
Ed,li
/
Rd,2
= 0,67 < 1
This calculation disregards the input from profile steel sheeting!
EC4
Rd1
= 0.25 * f
ctk005
/
c
= 0,30 MN/mm
NAD
Rd2
= * 0,09
f
ck
3
= 0,26 MN/mm
Rd
= MIN (
Rd1
;
Rd2
) = 0,26 MN/mm
pd
= A
p
* f
yp
/(
ap
* 10 ) = 397,60 kN/m
Rd,3
= 2.5 * A
cv
* * (
Rd
/ 10 ) +
pd
= 468,45 kN/m
Structural verification of diagonal strut:
Ed,li
/
Rd,3
= 0,52 < 1
The cross reinforcement has been ignored in this calculation.
In the construction, provision should be made for 0.2% or the relevant cross section area A
cv
that
may also be taken into account as part of the bending reinforcement to absorb the negative moment
(moment at support) of the transversal continuous composite floor.
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Beams
Half-span roof:
rd
a
b
l
System:
Beam length l = 7,00 m
Beam width b = 14,00 cm
Beam height an a h
a
= 26,00 cm
Pitch = 6,00
Support length t = 10,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS14h
f
m,g,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fm.k; SG=SG) = 28,00 N/mm
f
v,g,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fv.k; SG=SG) = 2,70 N/mm
f
t,90,g,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; ft,90.k; SG=SG) = 0,45 N/mm
f
c,90,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc,90.k; SG=SG) = 5,50 N/mm
E
0,mean
= TAB("wood/EC"; E0.mean; SG=SG) = 12500,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Load:
r
d
= 12,50 kN/m
Calculation:
f
m,g,d
= f
m,g,k
*
k
mod
M
= 19,38 N/mm
f
v,g,d
= f
v,g,k
*
k
mod
M
= 1,87 N/mm
f
c,90,d
= f
c,90,k
*
k
mod
M
= 3,81 N/mm
f
t,90,g,d
= f
t,90,g,k
*
k
mod
M
= 0,31 N/mm
Stress resultants for analysis of load bearing capacity:
M
d
= r
d
*
l
2
8
= 76,56 kNm
V
d
=
l
2
* r
d
= 43,75 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Beams
h
s,req
= * 150
V
d
* b f
v,g,d
= 250,67 mm
h
s,req
* 10 h
a
= 0,96 < 1
h
b
= h
a
+ l * 100 * TAN() = 99,57 cm
Point of maximum stress:
x =
l
+ 1
h
b
h
a
= 1,45 m
M
x,d
= V
d
* x - r
d
* x * 0,5 = 50,30 kNm
W
x,req
= 1100 *
M
x,d
f
m,g,d
= 2855,01 cm
h
x
= h
a
+ x * 100 * TAN() = 41,24 cm
W
x
= b *
h
x
2
6
= 3968,39 cm
W
x,req
W
x
= 0,72 < 1
Required area moment of second degree at a deflection of l/300:
I
req
= 3130000 * *
M
d
1,4
l
E
0,mean
= 95853,12 cm
4
h
m,req
= 0,1 *
* 12000
I
req
b
3
= 43,47 cm
h
m
=
- h
b
h
a
2
+ h
a
= 62,78 cm
h
m,req
h
m
= 0,69 < 1
Analysis of load-bearing capacity:
Shearing stress at footing a:
a,d
= 15 *
V
d
* b h
a
= 1,80 N/cm
a,d
f
v,g,d
= 0,96 < 1
Stresses in the edge parallel to the grain:
m,0,d
= 0,001 * (1 + 4 * (TAN())) * 6 * 10
6
*
M
x,d
* b h
x
2
= 13,24 N/mm
m,0,d
f
m,g,d
= 0,68 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Beams
Stresses in the edge with grains at an angle:
m,,d
= 0,001 * (1 - 4 * (TAN())) * 6 * 10
6
*
M
x,d
* b h
x
2
= 12,12 N/mm
f
m,,d
=
f
m,g,d
*
f
m,g,d
f
c,90,d
+ sin( )
2
cos ( )
2
= 18,55 N/mm
m,,d
/ f
m,,d
= 0,65 < 1
Bearing pressure:
Assumption: l < 150 mm;l
1
> 150 mm
; k
c,90
according to Tab. 5.1.5
k
c,90
= 1,0
req_A = 10 *
V
d
* f
c,90,d
k
c,90
= 114,83 cm
req_t =
req_A
b
= 8,20 cm
req_t
t
= 0,82 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Buck
Buckling lengths:
Euler's crippling load:
l = 5,00 m
l
l
ef
= 2*l = 10,00 m
l
l
ef
= l = 5,00 m
l
l
ef
= 0,7*l = 3,50 m
l
l
ef
= 0,5*l = 2,50 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Buck
l
Kr
Sorting grade SG = SEL("Wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
E
0,mean
= TAB("Wood/EC"; E
0.mean
; SG=SG) = 11000,00 N/mm
K
r
= 100000,00 1/N
l
ef
= * l
+ 4
*
2
E
0,mean
* l K
r
= 10,27 m
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Buck
Roof post:
h
System:
Post height h = 3,40 m
Cross-sectional width b = 14,00 cm
Cross-sectional thickness d = 14,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
f
c,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc,0,k; SG=SG) = 21,00 N/mm
f
c,90,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc,90,k; SG=SG) = 5,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load at the head:
V
c,d
= 50,40 kN
Calculation:
Buckling length l
ef
= h = 3,40 m
A = b *d = 196,00 cm
i =
1
12
*MIN(b;d) = 4,04 cm
Degree of slenderness
min
= 100 *
l
ef
i
= 84,16 > 30
Buckling proof required!
k
c
= TAB("wood/ECbuckl"; kc; SG=SG; =
min
) = 0,427
c,0,d
= 10 *
V
c,d
A
= 2,57 N/mm
f
c,0,d
= f
c,0,k
*
k
mod
M
= 14,54 N/mm
f
c,90,d
= f
c,90,k
*
k
mod
M
= 3,46 N/mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Buck
Structural verifications:
Buckling:
c,0,d
* k
c
f
c,0,d
= 0,41 1
Lateral pressure:
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
= 0,74 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Dowel
Beam connection:
b
a1 a1 a1
h
e
3
e
2
e
1
F
d
t2 t2 t1
System:
Distance a
1
= 4,00 cm
Width b = 3*a
1
= 12,00 cm
Distance e
1
= 4,00 cm
Distance e
2
= 8,50 cm
Distance e
3
= 5,50 cm
Thickness t
1
= 6,00 cm
Thickness t
2
= 8,00 cm
Load:
F
d
= 40,00 kN
Material:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
Dowel: S235
Dowel diameter d = SEL("wood/DPin"; d; )/10 = 1,20 cm
f
u,k
= 360,00 N/mm
S
= 1,10 N/mm
Calculation:
M
y,d
= 0,8 * f
u,k
*
d
3
* 6
S
* 10
3
= 75403,6 Nmm
Post:
f
h,1,d
= 0,082 *
k
* (1-0,1*d) *
k
mod
M
= 16,87 N/mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Dowel
Support:
k
90
= 1.35 + 0.15 * d = 1,53
f
h,2,d
= 0,082 *
k
* (1-0,1*d) *
k
mod
*
M
k
90
= 11,03 N/mm
=
f
h,2,d
f
h,1,d
= 0,654
R
D1
= f
h,1,d
* t
1
* d
* 100 = 12146 N
R
D2
= 0,5 * f
h,1,d
* t
2
* d * * 100 = 5296 N
R
D3
= 1,1*f
h,1,d
*10*t
1
* *
d
+ 2 ( )
-
* 2 * + ( ) + 1
* 4 * * ( ) + 2 M
y,d
* f
h,1,d
* 10
3
* d t
1
2
= 5254 N
R
D4
= 1,1 *
* 2
+ 1
*
* 2 * M
y,d
* f
h,1,d
* d 10 = 5405 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 5,25 kN
n =
F
d
* 2 R
D
= 3,8
selected: 4 PIN 12mm S 235 l = 20 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Dowel
Tensile splice Design of strut
d
N
t
1
t
1
t
2
System:
Timber thickness t
1
= 8,00 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 12,00 cm
Load:
F
d
= 116,00 kN
Materials: NH S 10
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Dowel: DPin 16mm S 275
Dowel diameter d = SEL("wood/DPin"; d; )/10 = 0,80 cm
f
u,k
= 360,00 N/mm
Calculation:
Minimum distances according to Tab.6.6a:
a
1
= 7* d = 5,60 cm
a
2
= 3 * d = 2,40 cm
a
3,t
= 7* d = 5,60 cm
a
4,t
= 3 * d = 2,40 cm
Design value of bearing stress resistance:
f
h,0,d
= 0,082 *
k
* (1-0,1*d) *
k
mod
M
= 17,64 N/mm
M
y,d
= 1000 * 0,8 *
* f
u,k
d
3
* 6
S
= 22341,8 Nmm
k
M
= * 10
t
1
M
y,d
* f
h,0,d
* d 10
= 6,36
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Dowel
R
D1
= 100 * f
h,0,d
* t
1
* d = 11289,60 N
R
D2
= 100 * 0,5 * f
h,0,d
* t
2
* d = 8467,20 N
R
D3
= 100 * 0,367 * f
h,0,d
* t
1
* d *
( )
* 2 -
+ 1
3
k
M
2
1 = 4445,08 N
R
D4
= 155,6 * f
h,0,d
* t
1
*
d
k
M
= 2762,05 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 2,76 kN
required number of dowels n =
F
d
* 2 R
D
= 21,0
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Dowel
Tension diagonal:
1
2
Ft
slot plate
System:
Rod 1 : 1 * 160mm * 160mm Glulam
Rod 2 : 1 * 160mm * 180mm Glulam
System angle = 60,0
Timber thickness t
1
= 16,00 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 16,00 cm
Thickness of slotted plate t
3
= 0,80 cm
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS11
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 410,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Dowel: DPin 16mm S 275
Dowel diameter d = SEL("wood/DPin"; d; )/10 = 1,60 cm
f
u,k
= 430,00 N/mm
F
t,d
= 80,79 kN
Calculation:
Minimum distances of Rod1 according to Tab.6.6a:
a
1
= 7* d = 11,20 cm
a
2
= 3 * d = 4,80 cm
a
3,t
= 7* d = 11,20 cm
a
4,t
= 3 * d = 4,80 cm
Minimum distances Rod2 according to Tab.6.6a:
a
1
= ( 3 + 4 * ABS(COS( )))* d = 8,00 cm
a
2
= 3 * d = 4,80 cm
a
3,t
continuous top chord
a
4,t
= ( 2 + 2 * ABS(SIN())) * d = 5,97 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Dowel
Rod 1 :
f
h,1,d
= 0,082 *
k
* (1-0,1*d) *
k
mod
M
= 17,38 N/mm
Rod 2 :
f
h,0,d
= 0,082 *
k
* (1-0,1*d) *
k
mod
M
= 17,38 N/mm
k
90
= 1,35 + 0,15 * d = 1,59
f
h,2,d
=
f
h,0,d
* k
90
+ sin( )
2
cos( )
2
= 12,05 N/mm
M
y,d
= * 10
3
* 0,8 * f
u,k
d
3
* 6
S
= 213488,5 Nmm
Design value of drift pins in Rod 1:
R
D1
= 100* f
h,1,d
*(
t
1
2
- t
3
) * d = 20022 N
R
D2
= * 110 * f
h,1,d
*
( )
-
t
1
2
t
3
* d
( )
-
+ 2
* 4 M
y,d
* f
h,1,d
* 10
3
* d
( )
-
t
1
2
t
3
2
1 = 13437 N
R
D3
= * 1,5
* 20 * M
y,d
* f
h,1,d
d = 16345 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
) = 13,44 kN
n =
F
t,d
* 2 R
D
= 3,0
selected: 4 DPin 16 S 275 l = 16cm
Design value of drift pins in Rod 2:
R
D1
= 100* f
h,2,d
*(
t
1
2
- t
3
) * d = 13882 N
R
D2
= * 110 * f
h,2,d
*
( )
-
t
1
2
t
3
* d
( )
-
+ 2
* 4 M
y,d
* f
h,2,d
* 10
3
* d
( )
-
t
1
2
t
3
2
1 = 10528 N
R
D3
= * 1,5
* 20 * M
y,d
* f
h,2,d
d = 13610 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
) = 10,53 kN
n =
F
t,d
* 2 R
D
= 3,8
selected: 4 DPin 16 S 275 l = 16cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Dowel
Tension diagonal:
1
2
Ft
System:
Rod 1 : 2 * 60mm * 140mm
Rod 2 : 1 * 100mm * 180mm
System angle = 60,00
Timber thickness t
1
= 6,00 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 10,00 cm
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S7
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 350,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Dowel: DPin 12mm
Dowel diameter d = SEL("wood/DPin"; d; )/10 = 1,20 cm
f
u,k
= 360,00 N/mm
Load:
F
t,d
= 40,00 kN
Calculation:
Minimum distances of Rod1 according to Tab.6.6a:
a
1
= 7* d = 8,40 cm
a
2
= 3 * d = 3,60 cm
a
3,t
= 7* d = 8,40 cm
a
4,t
= 3 * d = 3,60 cm
Minimum distances Rod2 according to Tab.6.6a:
a
1
= ( 3 + 4 * ABS(COS()))* d = 6,00 cm
a
2
= 3 * d = 3,60 cm
a
3,t
continuous top chord
a
4,t
= ( 2 + 2 * ABS(SIN( ))) * d = 4,48 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Dowel
Rod 1 :
f
h,1,d
= 0,082 *
k
* (1-0,1*d) *
k
mod
M
= 15,54 N/mm
Rod 2 :
f
h,0,d
= 0,082 *
k
* (1-0,1*d) *
k
mod
M
= 15,54 N/mm
k
90
= 1,35 + 0,15 * d = 1,53
f
h,2,d
=
f
h,0,d
* k
90
+ sin( )
2
cos ( )
2
= 11,12 N/mm
=
f
h,2,d
f
h,1,d
= 0,716
M
y,d
= * 10
3
* 0,8 * f
u,k
d
3
* 6
S
= 75403,6 Nmm
R
D1
= f
h,1,d
* t
1
* d
* 100 = 11189 N
R
D2
= 0,5 * f
h,1,d
* t
2
* d * * 100 = 6676 N
R
D3
= 1,1*f
h,1,d
*10*t
1
* *
d
+ 2 ( )
-
* 2 * + ( ) + 1
* 4 * * ( ) + 2 M
y,d
* f
h,1,d
* 10
3
* d t
1
2
= 5026 N
R
D4
= 1,1 *
* 2
+ 1
*
* 2 * M
y,d
* f
h,1,d
* d 10 = 5329 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 5,03 kN
n =
F
t,d
* 2 R
D
= 4,0
selected: 4 DPin 12 S 235 l = 22cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Nail calculation for each shear joint, thin outside plate:
Thin outside plate
d
N
t
1
t
1
t
2
System:
Sheet thickness t
1
= 0,15 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 4,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 38x100
Nail length l
N
= 10,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,38 cm
t
1
/ d
N
= 0,39 < 0,5
otherwise a different calculation applies
Calculation:
pre-drilled:
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,98 N/mm
not pre-drilled::
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,88 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 7896,02 Nmm
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 5264,02 Nmm
f
h,d
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k
= 14,46 N/mm
R
D1
= 100*0,5* f
h,d
* t
2
* d
N
= 1098,96 N
R
D2
= * 1,1
* 20 * M
y,d
* f
h,d
d
N
= 836,65 N
R
D
= 0.001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
) = 0,84 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Design of a shear connection:
b
l
h
h
h
h
h
e
r
1
2
i
n
2
l l
b b b2
System:
Thickness of outer wood d
2
= 4,00 cm
Nail distance l
r
= 6,00 cm
Nail distance b
e
= 16,00 cm
Cross beam width b = 16,00 cm
Cross beam height h = 40,00 cm
Height h
1
= 24,00 cm
Height h
2
= 28,00 cm
Height h
3
= 32,00 cm
Height h
4
= 36,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS11
Shear and torsion f
v,g,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fv,k; SG=SG) = 2,70 N/mm
Rectangular shear f
t,90,g,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; ft,90.k; SG=SG) = 0,45 N/mm
MH
= 1,30
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
Rectangular shear f
t,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; ft,0,k; SG=SG) = 14,00 N/mm
Nails 38x100:
Nail diameter d = 0,38 cm
Nail length l
N
= 10,00 cm
Nail strength R
D
= 6000*d = 866,40 N
F
= 1,50
f
v,g,d
= * f
v,g,k
k
mod
MH
= 1,869 N/mm
f
t,90,g,d
= * f
t,90,g,k
k
mod
MH
= 0,312 N/mm
f
t,0,d
= * f
t,0,k
k
mod
MH
= 9,692 N/mm
l
eff
= 10*MIN(d
2
;12*d;l
N
-d
2
) = 40,00 mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Calculation of maximum design value:
from nail analysis F
90,d,N
= 0.002 * 16 * R
D
= 27,72 kN
from tension bar F
90,d,Z
= 0.2 /
F
* d
2
*l
N
* f
t,0,d
= 51,69 kN
detailed structural verification:
b
e
h
= 0,40 < 0,5
detailed structural verification required
b
ef
= 2 * l
eff
= 80,00 mm
c = *
4
3
*
b
e
h
( )
- 1
b
e
h
3
= 0,392
l
r,ef
= * 10
+ l
r
2
( ) * c h
2
= 167,89 mm
A
ef
= l
r,ef
*b
ef
= 13431,20 mm
k
r
= 0,25 *(1 +
( )
h
1
h
2
2
+
( )
h
1
h
3
2
+
( )
h
1
h
4
2
) = 0,685
= 1 - 3 *
( )
b
e
h
2
+ 2 *
( )
b
e
h
3
= 0,648
F
90,d
= *
0,001
* k
r
* 13 * A
ef
0,8
f
t,90,g,d
= 18,34 kN
Decisive F
90,d,max
= MIN(F
90,d
;F
90,d,N
;F
90,d,Z
) = 18,34 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Nail calculation for each shear joint for two different kinds of wood:
two unequal kinds of wood
d
N
t
1
t
1
t
2
System:
Timber thickness t
1
= 4,00 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 4,00 cm
t
1
< t
2
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG1= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
k1
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG1) = 380,00 kg/m
Strength grade SG2= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = MS13
k2
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG2) = 400,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 38x100
Nail length l
N
= 10,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,38 cm
Calculation:
pre-drilled:
f
h,k1
= 0.082 *
k1
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,98 N/mm
not pre-drilled::
f
h,k1
= 0.082 *
k1
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,88 N/mm
pre-drilled:
f
h,k2
= 0.082 *
k2
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 31,55 N/mm
not pre-drilled::
f
h,k2
= 0.082 *
k2
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 21,98 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 7896,02 Nmm
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 5264,02 Nmm
f
h,d1
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k1
= 14,46 N/mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
f
h,d2
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k2
= 15,22 N/mm
=
f
h,d1
f
h,d2
= 0,95
R
D1
= 100* f
h,d1
* t
1
* d
N
= 2198 N
R
D2
= 100* 0,5 * f
h,d1
* t
2
* d
N
* = 1044 kN
R
D3
= 110*f
h,d1
*t
1
* *
d
N
+ 2 ( )
-
* 2 * + ( ) + 1
* 4 * * ( ) + 2 M
y,d
* f
h,d1
* 10
3
* d
N
t
1
2
= 936 N
R
D4
= 1,1 *
* 2
+ 1
*
* 2 * M
y,d
* f
h,d1
* d
N
10 = 826 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 0,83 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Nail calculation for each shear joint:
Thick outside plate
d
N
t
1
t
1
t
2
System:
Sheet thickness t
1
= 0,50 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 4,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 38x100
Nail length l
N
= 10,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,38 cm
otherwise a different calculation applies
Calculation:
pre-drilled:
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,98 N/mm
not pre-drilled::
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,88 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 7896,02 Nmm
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 5264,02 Nmm
f
h,d
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k
= 14,46 N/mm
R
D1
= 100*0,5* f
h,d
* t
2
* d
N
= 1098,96 N
R
D2
= * 1,5
* 20 * M
y,d
* f
h,d
d
N
= 1140,88 N
R
D
= 0.001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
) = 1,10 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Nail calculation for each shear joint, plate inside:
Plate inside
d
N
t
1
t
1
t
2
System:
Timber thickness t
1
= 4,00 cm
Sheet thickness t
2
= 1,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 38x100
Nail length l
N
= 10,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,38 cm
Calculation:
pre-drilled:
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,98 N/mm
not pre-drilled::
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,88 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 7896,02 Nmm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 5264,02 Nmm
f
h,d
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k
= 14,46 N/mm
R
D1
= 100* f
h,d
* t
1
* d
N
= 2198 N
R
D2
= * 110 * f
h,d
* t
1
* d
N
( )
-
+ 2
* 4 M
y,d
* f
h,d
* 10
3
* d
N
t
1
2
1 = 1200 N
R
D3
= * 1,5
* 20 * M
y,d
* f
h,d
d
N
= 1141 N
R
D
= 0.001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
) = 1,14 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Nail calculation for each shear joint:
d
N
t
1
t
1
t
2
System:
Timber thickness t
1
= 4,00 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 4,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 38x100
Nail length l
N
= 10,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,38 cm
Calculation:
pre-drilled:
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,98 N/mm
not pre-drilled::
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,88 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 7896,02 Nmm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 5264,02 Nmm
f
h,d
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k
= 14,46 N/mm
k
M
= MIN(t
1
;t
2
) *
10
M
y,d
* f
h,d
* 10 d
N
= 4,09
R
D1
= 100* f
h,d
* t
1
* d
N
= 2197,92 N
R
D2
= 100* 0,5 * f
h,d
* t
2
* d
N
= 1098,96 N
R
D3
= 100 * 0,367 * f
h,d
* t
1
* d
N
*
( )
* 2 -
+ 1
3
k
M
2
1 = 945,34 N
R
D4
= 155,6 * f
h,d
* t
1
*
d
N
k
M
= 836,18 N
R
D
= 0.001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 0,84 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Determination of required number of nails
t
2
t
1
t
1
System:
Timber thickness t
1
= 4,00 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 4,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM = SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD = SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = permanent
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,60
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 42x110
Nail length l
N
= 12,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,42 cm
Load:
F
sd
= 16,00 kN
Calculation:
Minimum timber thickness adhered to according to 6.3.1.2(11):
(MAX(7*d
N
;(13*d
N
-30)*
k
/400))/(MIN(t
1
;t
2
)) = 0,73 < 1
Minimum driving depth according to 6.3.1.2(4):
(8*d
N
)/MIN(t
1
;t
2
) = 0,84 < 1
Minimum nail distances according to Tab.6.3.1.2:
a
1
= 10* d
N
= 4,20 cm
a
2
= 5 * d
N
= 2,10 cm
a
3,t
= 15* d
N
= 6,30 cm
a
4,t
= 5 * d
N
= 2,10 cm
pre-drilled f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,85 N/mm
not pre-drilled f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,26 N/mm
f
h,d
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k
= 9,35 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 10242,81 Nmm
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 6828,54 Nmm
k
M
= MIN(t
1
;t
2
) *
10
M
y,d
* f
h,d
* 10 d
N
= 3,03
R
D1
= 100* f
h,d
* t
1
* d
N
= 1570,80 N
R
D2
= 100* 0,5 * f
h,d
* t
2
* d
N
= 785,40 N
R
D3
= 36,7 * f
h,d
* t
1
* d
N
*
( )
* 2 -
+ 1
3
k
M
2
1 = 751,57 N
R
D4
= 155,6 * f
h,d
* t
1
*
d
N
k
M
= 806,66 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 0,75 kN
required number of nails n = F
sd
/(2*R
D
) = 10,7
selected: 2x6 nails 42x120 DIN 1151
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Determination of required number of nails
t
2
t
1
t
1
System:
Timber thickness t
1
= 4,00 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 4,00 cm
Timber width b = 8,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM = SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD = SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = permanent
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,60
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 42x110
Nail length l
N
= 6,50 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,28 cm
Load:
F
sd
= 16,00 kN
Calculation:
t
3
= (l
N
- t
1
) = 2,50 cm
Checking the lapped joint length according to 6.3.1.2(10):
4 * d
N
/ (t
2
- t
3
) = 0,75 < 1
Minimum timber thickness adhered to according to 6.3.1.2(11):
(MAX(7*d
N
;(13*d
N
-30)*
k
/400))/(MIN(t
1
;t
2
)) = 0,49 < 1
Minimum driving depth according to 6.3.1.2(4):
(8*d
N
)/MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) = 0,90 < 1
Minimum nail distances according to Tab.6.3.1.2:
a
1
= 10* d
N
= 2,80 cm
a
2
= 5 * d
N
= 1,40 cm
a
3,t
= 15* d
N
= 4,20 cm
a
4,t
= 5 * d
N
= 1,40 cm
pre-drilled f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 30,29 N/mm
not pre-drilled f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 22,88 N/mm
f
h,d
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k
= 10,56 N/mm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 3569,29 Nmm
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 2379,53 Nmm
k
t
= MAX(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
)/MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) = 1,60
k
M
= MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) *
10
M
y,d
* f
h,d
* 10 d
N
= 2,79
R
D1
= 100* f
h,d
* MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) * d
N
= 739,20 N
R
D2
= 100*0,5*f
h,d
*MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
)*d
N
*(( 3 * k
t
+ 2 * k
t
+ 3 ) - k
t
-1 ) = 416,02 N
R
D3
= 36,7 * f
h,d
* MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) * d
N
*
( )
* 2 -
+ 1
3
k
M
2
1 = 367,34 N
R
D4
= 155,6 * f
h,d
* MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) *
d
N
k
M
= 412,26 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 0,37 kN
required number of nails n = F
sd
/R
D
= 43,2
selected: 2x3x8=48 nails 28x65 DIN 1151
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Attachment of roof boarding/sheathing
F
F
t
t
ax,d
ld,d
1
2
System:
Timber thickness t
1
= 2,80 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 38x100
Nail length l
N
= 7,50 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,40 cm
Load:
Wind suction F
ax,d
= 0,55 kN CLD: short term
Roof shear Load scheme g F
la,d1
= 0,25 kN CLD: permanent
Roof shear Load scheme g+s F
la,d2
= 0,45 kN CLD: short term
Calculation:
Load-bearing capacity under shear load:
pre-drilled f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,91 N/mm
not pre-drilled f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,56 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 9022,50 Nmm
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 6015,00 Nmm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
decisive load scheme:
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = permanent
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod1
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,60
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod2
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
* F
la,d1
k
mod2
* F
la,d2
k
mod1
= 0,83 < 1
Load scheme g+s decisive
f
h,d
=
k
mod2
M
* f
h,k
= 14,23 N/mm
t
2
= (l
N
- t
1
) = 4,70 mm
k
t
= MAX(t
1
;t
2
)/MIN(t
1
;t
2
) = 1,68
k
M
= MIN(t
1
;t
2
) *
10
M
y,d
* f
h,d
* 10 d
N
= 2,72
R
D1
= 100* f
h,d
* t
1
* d
N
= 1593,76 N
R
D2
= 100* 0,5 * f
h,d
* t
2
* d
N
= 1337,62 N
R
D3
= 100 * 0,367 * f
h,d
* t
1
* d
N
*
( )
* 2 -
+ 1
3
k
M
2
1 = 801,95 N
R
D4
= 155,6 * f
h,d
* t
1
*
d
N
k
M
= 911,72 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 0,80 kN
F
la,d2
R
D
= 0,56 < 1
Pullout capacity:
according to DIN 1052-2 Section 6.3.1
f
1,d
= 40 * 10
-6
*
k
*
k
mod2
M
= 4,00 N/mm
f
2,d
= 600 * 10
-6
*
k
*
k
mod2
M
= 59,98 N/mm
R
d1
= 100* f
1,d
* d
N
* t
2
= 752,00 N
R
d2
= 100* f
2,d
* d
N
= 959,68 N
R
d
= MIN(R
d1
;R
d2
)/1000 = 0,75 kN
F
ax,d
R
d
= 0,73 < 1
Combined loads:
+
( )
F
ax,d
R
d
2
( )
F
la,d2
R
D
2
= 0,85 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Nail calculation for a shear joint (thick plate)
Wood-metal connection with plate t
1
> 0.5 d
d
N
t
1
t
2
System:
Sheet thickness t
1
= 0,50 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 4,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 38x100
Nail length l
N
= 10,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,38 cm
Calculation:
pre-drilled:
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,98 N/mm
not pre-drilled::
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,88 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 7896,02 Nmm
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 5264,02 Nmm
f
h,d
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k
= 14,46 N/mm
R
D1
= * 110 * f
h,d
* t
2
* d
N
( )
-
+ 2
* 4 M
y,d
* f
h,d
* 10
3
* d
N
t
2
2
1 = 1200 N
R
D2
= * 1,5
* 20 * M
y,d
* f
h,d
d
N
= 1141 N
R
D3
= 100 * f
h,d
* t
2
* d
N
= 2198 N
R
D
= 0.001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
) = 1,14 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Nail calculation for a shear joint (thin plate) :
Wood-metal connection with plate t
1
< 0.5 d
d
N
t
1
t
2
System:
Sheet thickness t
1
= 0,15 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 4,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 38x100
Nail length l
N
= 10,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,38 cm
t
1
/ d
N
= 0,39 < 0,5
otherwise a different calculation applies
Calculation:
pre-drilled:
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,98 N/mm
not pre-drilled::
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,88 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 7896,02 Nmm
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 5264,02 Nmm
f
h,d
= k
mod
/
M
* f
h,k
= 14,46 N/mm
R
D1
= 100* (2 -1)*f
h,d
* t
2
* d
N
= 910,41 N
R
D2
= * 1,1
* 20 * M
y,d
* f
h,d
d
N
= 836,65 N
R
D
= 0.001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
) = 0,84 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Nail calculation for a shear joint:
d
N
t
1
t
2
System:
Timber thickness t
1
= 4,00 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 4,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 38x100
Nail length l
N
= 10,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,38 cm
Calculation:
pre-drilled:
f
h,k
= 0.08 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,24 N/mm
not pre-drilled::
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,88 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 * (10*d
N
)
2.6
/
S
= 7896,02 Nmm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 * (d
N
*10)
2.6
/
S
= 5264,02 Nmm
f
h,d
= k
mod
/
M
* f
h,k
= 14,46 N/mm
k
t
= MAX(t
1
;t
2
)/MIN(t
1
;t
2
) = 1,00
k
M
= MIN(t
1
;t
2
) *
10
M
y,d
* f
h,d
* 10 d
N
= 4,09
R
D1
= 100* f
h,d
* MIN(t
1
;t
2
) * d
N
= 2197,92 N
R
D2
= 100* 0,5*f
h,d
*MIN(t
1
;t
2
)*d
N
*
( )
-
* 3 + k
t
2
* 2 + k
t
3
- k
t
1 = 910,41 N
R
D3
= 100 * 0,367 * f
h,d
* t
1
* d
N
*
( )
* 2 -
+ 1
3
k
M
2
1 = 945,34 N
R
D4
= 155,6 * f
h,d
* t
1
*
d
N
k
M
= 836,18 N
R
D
= 0.001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 0,84 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Tie rod connection
s
h
b
h
F
d
t
1
t
2 t1
1
2
System:
Timber thickness t
1
= 3,80 cm
Timber thickness t
2
= 3,80 cm
Timber height h
1
= 14,00 cm
Timber height h
2
= 10,00 cm
Nail distance s = 3,50 cm
Nail distance b = 2,50 cm
Nail rows a = 3
Nail columns v = 3
Load:
F
d
= 15 kN
Materials:
Construction material CM = SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD = SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Nails: 42x110
Nail length l
N
= 11,00 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,42 cm
Calculation:
t
3
= (l
N
- t
1
- t
2
) = 3,40 cm
pre-drilled:
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (1-0.1*d
N
) = 29,85 N/mm
not pre-drilled::Imposed Load:
f
h,k
= 0.082 *
k
* (10*d
N
)
-0.3
= 20,26 N/mm
Characteristic value for yield moment of square nails
M
y,d
= 270 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 10242,81 Nmm
Characteristic value for yield moment of round nails
M
y,d
= 180 *
( ) * 10 d
N
2,6
S
= 6828,54 Nmm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
f
h,d
=
k
mod
M
* f
h,k
= 12,47 N/mm
k
t
= MAX(t
1
;t
2
)/MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) = 1,12
k
M
= MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) *
10
M
y,d
* f
h,d
* 10 d
N
= 2,98
R
D1
= 100* f
h,d
* MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) * d
N
= 1780,72 N
R
D2
= 100* 0,5 * f
h,d
* MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
)
* d
N
= 890,36 N
R
D3
= 36,7 * f
h,d
* MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) * d
N
*
( )
* 2 -
+ 1
3
k
M
2
1 = 858,26 N
R
D4
= 155,6 * f
h,d
* MIN(t
1
;t
2
;t
3
) *
d
N
k
M
= 929,80 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
;R
D4
) = 0,86 kN
required number of nails n = F
d
/(2*R
D
) = 8,7
selected: 3x3=9 nails 42x110 DIN 1151
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
Wind brace connection:
t
s
F
h
h
a4 a4
b
a2
System:
Beam thickness h = 16,00 cm
Driving depth t = 11,40 cm
Sheet thickness s = 0,60 cm
Angle of tensile force = 45,00
Tensile force F
d
= 23,54 kN
Materials: Post
Construction material CM = SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD = SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS14h
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 410,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
Screws: 4 Sr 12*120 DIN 571
Screw diameter d = 1,20 cm
f
u,k
= 300,00 N/mm
S
= 1,10
Minimum distances Rod1 according to Tab.6.23:
a
1
= 7* d = 8,40 cm
a
2
= 4 * d = 4,80 cm
a
4,t
= 3 * d = 3,60 cm
Design value of bearing stress resistance:
f
h,d
= 0,082 *
k
* (1-0,1*d) *
k
mod
M
= 20,48 N/mm
0.8/d = 0,67 < 1
calculation as for pins:
* 0,6 + ( ) + t s * 4 d
t
= 1,05 > 1,0
d
ef
= 9 *d = 10,80 mm
M
y,d
= 0,8 * f
u,k
*
d
ef
3
* 6
S
= 45807,7 N/mm
s/(d/2) = 1,00 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Nail
thin plate
R
D1
= (2 -1)*f
h,d
*(t-1,5*d)*d*100 = 9772,52 N
R
D2
= 1,1 *
* 20 * M
y,d
* f
h,d
d = 5219,54 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
) = 5,22 kN
Design value for pullout:
f
3,d
=
k
mod
M
* (1,5 + 6*d) *
k
= 121,96 N/mm
R
d
= f
3,d
* (0,6*(t+s)-d)*0,01 = 7,32 kN
Combined loads:
+
( )
* F
d
sin( )
* 4 R
d
2
( )
* F
d
cos ( )
* 4 R
D
2
= 0,96 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Shrinkage
Shrinkage and swelling of wood:
b
h
System:
The only appreciable stress is generated to the fibre.
Width b = 32,00 cm
Height h = 12,00 cm
Coefficient for the degree of shrinkage and swelling
90
= 0,24 %
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
E
90,mean
= TAB("wood/EC"; E
90.mean
; SG=SG) = 370,00 N/mm
Timber moisture before w
1
= 10,00 %
Timber moisture after w
2
= 15,00 %
Stress:
c,90
= E
90,mean
*
90
*(w
2
-w
1
)/200 = 2,22 N/mm
Total force:
F
,90
=
c,90
* b * h = 852,48 N
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : spec dowel
Tensile splice with special dowels:
a a a
a
1
a
1
t
1
t
2
t
1
System:
Distance a = 22,00 cm
Distance a
1
= 6,00 cm
Thickness t
1
= 8,00 cm
Thickness t
2
= 10,00 cm
Cut surfaces n
z
= 2
Tensile force F
t,d
= 95,00 kN
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Transition to DIN 1052-2
F
d
= F
t,d
/1.35 = 70,37 kN
Selection of dowel: Split ring connector Type A according to DIN 1052-2, Table 4, 6 or 7
Dowel 95 - A with 2 * M12 + 4 * washers 58/6
Number of dowels selected per cut n = 3
zul.N
c
= 17,00 kN
b
min
= 12,00 cm
a
min
= 22,00 cm
a
min4
= b
min
/2 = 6,00 cm
a/a
min
= 1,00 < 1
a
1
/a
min4
= 1,00 < 1
n
ef
= MIN(2 + ( 1-
n
20
) * ( n - 2 );6) = 2,85
Structural verification:
F
d
* n
z
* n
ef
zul.N
c
= 0,73 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : spec dowel
Diagonal tie connection with special dowels:
a
a2
a2
h
h
1
d1 d d1
System:
Distance a = 8,00 cm
Distance a
2
= 9,00 cm
System angle = 40,00
Beam height h = 30,00 cm
Beam thickness d = 16,00 cm
Strut height h
1
= 18,00 cm
Strut thickness d
1
= 8,00 cm
Number of rows n
z
= 2
Tensile force F
t,d
= 165,00 kN
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Transition to DIN 1052-2
F
d
= F
t,d
/1.35 = 122,22 kN
Selection of dowel: Split ring connector Type D according to DIN 1052-2, Table 4, 6 or 7 and 8
Dowel 65 - A with 6 * M12 + 12 * washers 58/6
Number of dowels selected per cut n = 6
per.N
c
= 11,00 kN
Dowel height h
c
= 2,70 cm
Dowel diameter d
c
= 6,50 cm
Minimum wood dimensions of the beam from b/a = 110/40
Minimum wood dimensions of the strut from b/a = 100/40
Distance a
1
= 14,00 cm
a
2,1
= d
c
+
h
c
2
= 7,85 cm
a
3,t
= 14,00 cm
a
4,strut
= 10/2 = 5,00 cm
a
4,beam
= 11/2 = 5,50 cm
l =
a
2
sin( )
= 14,00 cm
a
1
/l = 1,00 < 1
a
2,1
/a
2
= 0,87 < 1
a
4,beam
-
h
2
a
2
= 0,92 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : spec dowel
a
4,strut
- h
1
a
2
= 1,00 < 1
n
ef
= MIN( 2 + ( 1-
n
n
z
/ 20) * (
n
n
z
- 2 );6) = 2,85
Structural verification:
F
d
* 2 * n
z
* n
ef
per.N
c
= 0,97 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
Arched beam:
d
t
Fd
System:
Cutting depth t = 12,00 cm
Support length d = 24,00 cm
Beam width b = 16,00 cm
Support angle = 55,00
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS14k
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 410,00 kg/m
Rectangular shear f
c,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc,0.k; SG=SG) = 27,50 N/mm
Rectangular shear f
c,90,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc,90.k; SG=SG) = 5,50 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
F
d
= 300,00 kN
Calculation:
f
c,0,d
= f
c,0,k
*
k
mod
M
= 16,92 N/mm
f
c,90,d
= f
c,90,k
*
k
mod
M
= 3,38 N/mm
Vertical supporting force:
= 90 - = 35,00
k
c,
=
1
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
+ sin( )
2
cos ( )
2
= 0,431
V
d,max
= 100 * b * d * k
c,
* f
c,0,d
* 0,001 = 280,03 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
Horizontal supporting force:
k
c,
=
1
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
+ sin( )
2
cos ( )
2
= 0,271
H
d,max
= 100* b*d*k
c,
*f
c,0,d
*0.001 = 176,08 kN
F
d,h
= F
d
* COS() = 172,07 kN
F
d,v
= F
d
* SIN() = 245,75 kN
Structural verifications:
F
d,h
H
d,max
= 0,98 < 1
F
d,v
V
d,max
= 0,88 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
Centre purlin with 2-axis deflection:
b
h
Fd
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
f
m,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fm.k; SG=SG) = 24,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
Loading moments as a result of the sloping load
M
y,d
= 20,00 kNm
M
z,d
= 5,00 kNm
Calculation:
f
m,d
= f
m,k
* k
mod
/
M
= 16,62 N/mm
Approximation W
y,req
= 1000 *
+ M
y, d
M
z,d
f
m,d
= 1504,21 cm
selected: Cross section:
b = 16,00 cm
h = 24,00 cm
W
y
= b *
h
2
6
= 1536,00 cm
W
z
= h *
b
2
6
= 1024,00 cm
Structural verification:
k
m
= 0,70 for rectangular cross section
otherwise k
m
= 1.0
*
( )
+
M
y,d
W
y
* k
m
M
z,d
W
z
1000
f
m,d
= 0,99 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
Compression member connection
1 1
Fd
System:
Cross-sectional width in cut 1-1 b = 8,00 cm
Cross-sectional in cut 1-1 h = 16,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
Rectangular shear f
c,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc,0.k; SG=SG) = 21,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
F
d
= 112,00 kN
Calculation:
A = b*h = 128,00 cm
f
c,0,d
= f
c,0,k
*
k
mod
M
= 12,92 N/mm
c,0,d
=
F
d
A
* 10 = 8,75 N/mm
Structural verification:
c,0,d
f
c,0,d
= 0,68 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
Structural analysis of deflection in two directions and pressure:
q
d
d
N
q
d
b
h
System:
Beam width b = 18,00 cm
Beam height h = 24,00 cm
Beam length l = 3,50 m
Load angle = 75,00
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
Rectangular shear f
c,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc,0.k; SG=SG) = 21,00 N/mm
f
m,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fm.k; SG=SG) = 24,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
q
d
= 13,21 kN/m
N
d
= 94,50 kN
Calculation:
q
d,y
= q
d
* SIN() = 12,76 kN/m
q
d,z
= q
d
* COS() = 3,42 kN/m
M
y,d
= q
d,y
*
l
2
8
= 19,54 N/mm
M
z,d
= q
d,z
*
l
2
8
= 5,24 N/mm
f
c,0,d
= f
c,0,k
*
k
mod
M
= 12,92 N/mm
f
m,d
= f
m,k
*
k
mod
M
= 14,77 N/mm
W
y
= b *
h
2
6
= 1728,00 cm
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
W
z
= h *
b
2
6
= 1296,00 cm
A = b * h / 1 = 432,00 cm
k
m
= 0,70 for rectangular cross section
otherwise k
m
= 1.0
c,0,d
= 10 * N
d
/ A = 2,19 N/mm
Structural verifications:
+
( )
c,0,d
f
c,0,d
2
*
( )
+
M
y,d
W
y
* k
m
M
z,d
W
z
1000
f
m,d
= 0,99 < 1
+
( )
c,0,d
f
c,0,d
2
*
( )
+ * k
m
M
y,d
W
y
M
z,d
W
z
1000
f
m,d
= 0,84 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
Structural analysis of deflection in two directions and tension:
q
d
d
N
q
d
b
h
System:
Beam width b = 18,00 cm
Beam height h = 24,00 cm
Beam length l = 3,50 m
Load angle = 75,00 m
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
f
t,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; ft.0.k; SG=SG) = 14,00 N/mm
f
m,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fm.k; SG=SG) = 24,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
q
d
= 10,21 kN/m
N
d
= 47,50 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
Calculation:
q
d,y
= q
d
* SIN() = 9,86 kN/m
q
d,z
= q
d
* COS() = 2,64 kN/m
M
y,d
= q
d,y
*
l
2
8
= 15,10 N/mm
M
z,d
= q
d,z
*
l
2
8
= 4,04 N/mm
f
t,0,d
= f
t,0,k
*
k
mod
M
= 8,62 N/mm
f
m,d
= f
m,k
*
k
mod
M
= 14,77 N/mm
W
y
= b *
h
2
6
= 1728,00 cm
W
z
= h *
b
2
6
= 1296,00 cm
A = b * h = 432,00 cm
k
m
= 0,70 for rectangular cross section
otherwise k
m
= 1.0
Structural verification:
+
* 10 N
d
* A f
t,0,d
*
( )
+
M
y,d
W
y
* k
m
M
z,d
W
z
1000
f
m,d
= 0,87 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
End support of a laminated timber beam
V
d
h
d
System:
Width of laminated timber beam b = 18,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS11
Rectangular shear f
c,90,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc,90.k; SG=SG) = 5,50 N/mm
f
m,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fm.k; SG=SG) = 24,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
V
d
= 98,00 kN
Calculation:
f
c,90,d
= f
c,90,k
* k
mod
/
M
= 3,38 N/mm
Assumption: l > 150 mm otherwise k
c,90
according to Tab. 5.1.5
k
c,90
= 1,00
erf_A = * 10
V
d
* f
c,90,d
k
c,90
= 289,94 cm
erf_d =
erf_A
b
= 16,11 cm
sel. d = 17,00 cm
Structural verification:
erf_d / d = 0,95 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
Stress analysis of shear force and torsion:
b
h
d
T
d
V
System:
Support width b = 30,00 cm
Support depth h = 14,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS16k
f
v,g,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fv.k; SG=SG) = 2,70 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
relevant shear force V
d
= 18,00 kN
relevant torsional moment T
d
= 1,74 kNm
Calculation:
A = b*h = 420,00 cm
= 1 + * 0,6
h
b
= 1,28
tor,d
= 3000 * T
d
*
* b h
2
= 1,14 N/mm
v,d
= 30 *
V
d
* 2 A
= 0,64 N/mm
f
v,d
= k
mod
*
f
v,g,k
M
= 1,87 N/mm
Structural verifications:
Shear:
v,d
f
v,d
= 0,34 < 1
Torsion:
tor,d
f
v,d
= 0,61 < 1
Combination:
tor,d
f
v,d
+
( )
v,d
f
v,d
2
= 0,73 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : Stress analysis
Stud:
a l l1 l
h
Fc,d Fc,d
System:
Length of wood beam projection a = 6,00 cm
Support length l = 6,00 cm
Support depth d = 12,00 cm
clear distance between studs l
1
= 34,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S10
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
f
c,90,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc.90.k; SG=SG) = 5,00 N/mm
f
m,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fm.k; SG=SG) = 24,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
F
c,d
= 20,00 kN
Calculation:
f
c,90,d
= * k
mod
f
c,90,k
M
= 3,46 N/mm
fr: 15 / l
1
= 0,44 < 1
und: l / 15 = 0,40 < 1
according to Tab. 5.1.5 k
c,90
= 1 + a *
- 150 * 10 l
1700
= 1,32
A = l * d = 72,00 cm
c,90,d
= * 10
F
c,d
A
= 2,78 N/mm
Structural verification:
c,90,d
* k
c,90
f
c,90,d
= 0,61 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
Acceptable force of a double shoulder joint:
h
t
l
v1
v2
N
N
2
/2
/2
N
1
tv2
1
l
v1
System:
Beam height h = 22,00 cm
Beam width b = 14,00 cm
Length of wood beam projection l
v1
= 22,00 cm
Length of wood beam projection l
v2
= 30,00 cm
Shoulder depth t
v1
= 3,50 cm
Shoulder depth t
v
= 4,50 cm
Angle = 45,00
Comply with structural rules for shoulder depth and length of wood beam projection.
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 380,00 kg/m
f
v,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fv.k; SG=SG) = 2,50 N/mm
f
c,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc,0.k; SG=SG) = 23,00 N/mm
f
c,90,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc.90.k; SG=SG) = 5,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
N
d
= 86,00 kN
Calculation:
f
v,d
= f
v,k
*
k
mod
M
= 1,54 N/mm
f
c,0,d
= f
c,0,k
*
k
mod
M
= 14,15 N/mm
f
c,90,d
= f
c,90,k
*
k
mod
M
= 3,08 N/mm
with approximation:
k
F
=
1
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
+ * sin( )
2
cos ( ) cos ( )
3
= 0,51
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
k
s
=
4
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
* + sin( )
2
+ cos ( )
2
2 + cos ( ) 1
= 0,77
l
v1,min
= * 10 *
N
d
2
cos ( )
* b f
v,d
= 14,10 cm
l
v1,1
= 8* t
v
= 36,00 cm
l
v1,min
/ l
v1,1
= 0,39 < 1
l
v1,min
/ l
v1
= 0,64 < 1
l
v2,min
= * 10 *
N
d
2
cos ( )
* b f
v,d
= 14,10 cm
l
v2,1
= 8* t
v
= 36,00 cm
l
v2,min
l
v2,1
= 0,39 < 1
l
v2,min
l
v 2
= 0,47 < 1
R
F,d
= b * t
v
* f
c,0,d
* k
F
/ 10 = 45,46 kN
R
S,d
= b * t
v
* f
c,0,d
* k
s
/ 10 = 68,64 kN
detailed calculation:
k
c,
=
1
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
+ sin( )
2
cos ( )
2
= 0,358
R
F,d
= k
c,
* f
c,0,d
* b *
t
v
* cos ( ) 10
= 45,13 kN
k
c,
=
1
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
+ sin
( )
2
2
cos
( )
2
2
= 0,655
f
c,0,5,d
= k
c,
* f
c,0,d
= 9,27 N/mm
R
S,d
= f
c,0,5,d
* *
b
* cos
( )
2
2
100
= 68,42 kN
Structural verification:
N
d
+ R
F,d
R
S,d
= 0,76 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
Acceptable force of a face staggered joint:
h
t
l
/2
/2
v
v
N
1
N
System:
Beam height h = 22,00 cm
Beam width b = 14,00 cm
Length of wood beam projection l
v
= 22,00 cm
Shoulder depth t
v
= 4,50 cm
Angle = 45,00
Comply with structural rules for shoulder depth and length of wood beam projection.
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
f
v,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fv.k; SG=SG) = 2,50 N/mm
f
c,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc.0.k; SG=SG) = 23,00 N/mm
f
c,90,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc.90.k; SG=SG) = 5,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
N
d
= 63,00 kN
Calculation:
f
v,d
= f
v,k
*
k
mod
M
= 1,54 N/mm
f
c,0,d
= f
c,0,k
*
k
mod
M
= 14,15 N/mm
f
c,90,d
= f
c,90,k
*
k
mod
M
= 3,08 N/mm
with approximation:
k
s
=
4
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
* + sin( )
2
+ cos ( )
2
2 + cos ( ) 1
= 0,77
l
v,min
= * 10 * N
d
cos ( )
* b f
v,d
= 20,66 cm
l
v,1
= 8* t
v
= 36,00 cm
l
v,min
/ l
v,1
= 0,57 < 1
l
v,min
/ l
v
= 0,94 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
R
S,d
= b * t
v
* f
c,0,d
* k
s
/ 10 = 68,64 kN
detailed calculation:
k
c,
=
1
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
+ sin
( )
2
2
cos
( )
2
2
= 0,655
f
c,0,5,d
= k
c,
* f
c,0,d
= 9,27 N/mm
R
S,d
= f
c,0,5,d
* *
b
* cos
( )
2
2
100
= 68,42 kN
Structural verification:
N
d
R
S,d
= 0,92 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
Acceptable force of a heel staggered joint:
h
t
l
v
v
N
N
2
System:
Beam height h = 22,00 cm
Beam width b = 14,00 cm
Length of wood beam projection l
v
= 22,00 cm
Shoulder depth t
v
= 4,50 cm
Angle = 45,00
Comply with structural rules for shoulder depth and length of wood beam projection.
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
f
v,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fv.k; SG=SG) = 2,50 N/mm
f
c,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc.0.k; SG=SG) = 23,00 N/mm
f
c,90,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc.90.k; SG=SG) = 5,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Load:
N
d
= 43,00 kN
Calculation:
f
v,d
= f
v,k
*
k
mod
M
= 1,54 N/mm
f
c,0,d
= f
c,0,k
*
k
mod
M
= 14,15 N/mm
f
c,90,d
= f
c,90,k
*
k
mod
M
= 3,08 N/mm
with approximation:
k
F
=
1
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
+ * sin( )
2
cos ( ) cos ( )
3
= 0,51
l
v,min
= * 10 * N
d
cos ( )
* b f
v,d
= 14,10 cm
l
v,1
= 8* t
v
= 36,00 cm
l
v,min
/ l
v,1
= 0,39 < 1
l
v,min
/ l
v
= 0,64 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
R
F,d
= b * t
v
* f
c,0,d
* k
F
/ 10 = 45,46 kN
detailed calculation:
k
c,
=
1
*
f
c,0,d
f
c,90,d
+ sin( )
2
cos ( )
2
= 0,358
R
d
= k
c,
* f
c,0,d
* b *
t
v
* cos ( ) 10
= 45,13 kN
Structural verification:
N
d
R
d
= 0,95 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
Connection of a binding joist to a support:
c
h
s1 s
c
b1b1
h
1
h
1
h
1
Schlitzblech
System:
Centroidal distance s = 16,00 cm
Centroidal distance s
1
= 5,00 cm
Dowel distance b
1
= 5,00 cm
Dowel distance h
1
= 8,00 cm
Thickness of slotted plate m = 1,00 cm
Width of binding joist b = 16,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS11
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 410,00 kg/m
M
= 1,30
S
= 1,10
Load at tie point:
V
c,d
= 34,60 kN
M
c,d
= 0,01*V
c,d
* (s
1
+s) = 7,27 kNm
Geometric values:
r
1
=
+ b
1
2
( )
h
1
2
2
= 6,4 cm
r
2
=
+ b
1
2
( ) * h
1
1,5
2
= 13,0 cm
M
= atan
( )
b
1
* h
1
1,5
= 22,62
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
Calculation:
Drift pin forces:
as the result of shear force F
V,d
=
V
c,d
8
= 4,33 kN
as the result of moment F
M,d
= * 100
* M
c,d
r
2
* 4
( )
+ r
1
2
r
2
2
= 11,25 kN
Components:
F
M2,d,V
= F
M,d
* SIN(
M
) = 4,33 kN
F
M2,d,H
= F
M,d
* COS(
M
) = 10,38 kN
F
d,max
=
+ ( )
+ F
M2,d,V
F
V,d
2
F
M2,d,H
2
= 13,52 kN
= atan
( )
+ F
M2,d,V
F
V,d
F
M2,d,H
= 39,84
selected: Dowel DPin 16mm
d = 1,60 cm
f
u,k
= 360,0 N/mm
M
y,d
= 0,8 * f
u,k
*
d
3
* 6
S
= 178,7 kNmm
f
h,0,d
= 0,082 *
k
* (1-0,1*d) *
k
mod
M
= 17,38 N/mm
k
90
= 1,35 + 0,15 * d = 1,59
f
h,1,d
=
f
h,0,d
* k
90
+ sin( )
2
cos ( )
2
= 13,99 N/mm
t
1
=
- b m
2
= 7,50 cm
R
D1
= 100 * f
h,1,d
* t
1
* d = 16788 N
R
D2
= * 110 * f
h,1,d
* t
1
* d
( )
-
+ 2
* 4 M
y,d
* f
h,1,d
* d t
1
2
1 = 11125 N
R
D3
= * 150
* 2 * M
y,d
* f
h,1,d
d = 13416 N
R
D
= 0,001 * MIN(R
D1
;R
D2
;R
D3
) = 11,13 kN
Structural verification:
F
d,max
* 2 R
D
= 0,61 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
Joist hanger:
b
h
1
h
s
h
1
B'
N
H'
h
H
F
1,d
System:
Height of principal beam h
H
= 32,00 cm
Height of short-tie beam h
N
= 24,00 cm
Joist hanger distance h
1
= 6,00 cm
Nail distance s = 15,20 cm
Load:
F
1,d
= 12,00 kN
Materials:
Principal beam: 120mm*380mm
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS11
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 410,00 kg/m
f
t,90,g,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; ft.90.k; SG=SG) = 0,45 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Short-tie beam: 140mm*240mm NH S 10
selected: GH joist hanger 04 140*160 with 14 RN 4.0x60
Horizontal distance between centroidal axis of nails B' = 18,60 cm
Vertical Nail distance H' = 12,00 cm
Joist hanger thickness d
b
= 0,20 cm
Nail diameter d
N
= 0,40 cm
Nail length l
N
= 6,00 cm
Number of nails n
N
= 14
According to manufacturer's table R
0,d
= 16,40 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
f=
1
- 1 * 0,93
+ s h
1
h
H
= 2,61
t
ef
= MIN(12*d
N
;l
N
-d
b
) = 4,80 cm
f
t,90,d
= f
t,90,g,k
*
k
mod
M
= 0,28 N/mm
R
t,90,d
= * 0,0055 * f * ( ) * 10 t
ef
0,8
* ( ) * 10 + h
H
* 4 * 100 * B' H'
0,8
f
t,90,d
= 20,86 kN
R
d
= MIN(R
t,90,d
;R
0,d
) = 16,40 kN
Structural verification:
F
1,d
R
d
= 0,73 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
Notch joist
h
he
x
Fd
l
qd
d
System:
Cross-sectional width b = 14,00 cm
Support length d = 18,00 cm
Cross sectional height h = 88,00 cm
Cross sectional height at footing h
e
= 78,00 cm
Notch distance x = 13,00 cm
Notch length l = 20,00 cm
Beam length l
1
= 850,00 cm
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 2
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS14k
k
= TAB("wood/EC"; k; SG=SG) = 410,00 kg/m
f
v,g,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fv.k; SG=SG) = 2,70 N/mm
f
c,90,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; fc.90.k; SG=SG) = 5,50 N/mm
for solid wood k
n
= IF(CM="Glulam";6,5;5) = 6,50
M
= 1,30
Load:
Supporting force F
d
= 95,30 kN
Line load q
d
= 2,80 kN/m
Calculation for splintering:
Maximum design shear force:
for uniformly distributed load k
r
= 1 - 2 *
h
l
1
= 0,79
F
d,b
= k
r
* F
d
= 75,29 kN
for individual load k
F
=(0.5-h/l
1
)*e/h with e the distance of the force from footing k
and F
b,d
=k
F
* F
d
f
v,d
= f
v,g,k
*
k
mod
M
= 1,87 N/mm
l=MAX(l;0.01)
= atan
( )
- h h
e
l
= 26,57
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
k
= + 1
* 1,1 tan( )
-1,5
* h 10
= 1,105
=
h
e
h
= 0,886
k
90
=
k
n
* * h 10
( )
+
* ( ) - 1 * 0,8 *
x
h
-
1
2
= 0,566
k
v
= MIN(1;k
90
*k
) = 0,63
Structural verification:
* 15
F
d,b
* b h
e
* k
v
f
v,d
= 0,88 < 1
Calculation of bearing pressure:
f
c,90,d
= f
c,90,k
*
k
mod
M
= 3,81 N/mm
Assumption: Support length t > 150 mm otherwise k
c,90
according to Tab. 5.1.5
k
c,90
= 1,0
erf_A = 10 *
F
d
* f
c,90,d
k
c,90
= 250,13 N/mm
erf_d =
erf_A
b
= 17,87 mm
Structural verification:
erf_d
d
= 0,99 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
Rail post:
h
H
d
h
h
h
1
2
3
System:
Post distance l = 1,70 m
Rail height h
1
= 100,00 cm
Dowel distance h
2
= 5,00 cm
Dowel distance h
3
= 23,00 cm
Q
= 1,50
Load: according to DIN 1055-3
H' = 1,00 kN/m
H
d
=
Q
* l * H' = 2,55 kN/m
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = Glulam
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = short term
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,90
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = BS11
f
t,90.g,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; ft,90.k; SG=SG) = 0,45 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Calculation:
M
c,d
= 0,01 * H
d
* (h
1
+ h
2
+
h
3
2
) = 2,97 kNm
F
1,d
= +
H
d
2
M
c,d
* h
3
0,01
= 14,19 kN
F
2,d
= -
M
c,d
* h
3
0,01
H
d
2
= 11,64 kN
Transition to DIN 1052-2:
F
1
= MAX(F
1,d
;F
2,d
)/1,4 = 10,14 kN
selected: 2 DPin 85 - D
mit zul_N
c
= 14,50 kN
Structural verification:
F
1
zul_N
c
= 0,70 < 1
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
Eurocode 5 Folder : System
Suspender:
t t
Fc,d Fc,d
Ft,d
a
System:
Height of diagonal brace h = 14,00 cm
Width of diagonal brace b = 14,00 cm
Height of suspender h
H
= 18,00 cm
Width of suspender b
H
= 14,00 cm
Shoulder depth t
v
= 3,00 cm
Diameter of pin d = 1,20 cm
Angle = 45,00
Comply with structural rules for shoulder depth and length of wood beam projection.
Materials:
Construction material CM= SEL("wood/kmod"; CM; ) = solid wood
Class of load duration CLD= SEL("wood/kmod"; CLD; ) = normal
Utility class UC= SEL("wood/kmod"; UC; ) = 1
k
mod
= TAB("wood/kmod"; kmod; CM=CM; CLD=CLD; UC=UC) = 0,80
Strength grade SG= SEL("wood/EC"; SG; ) = S13
f
t,0,k
= TAB("wood/EC"; ft.0.k; SG=SG) = 18,00 N/mm
M
= 1,30
Calculation:
A
w,v
= 2*b*t
v
= 84,00 cm
A
w,bo
= (d+1)*(h
H
-2*t
v
) = 26,40 cm
A
w
= b
H
*h
H
-MAX(A
w,bo
;A
w,v
) = 168,00 cm
f
t,0,d
= f
t,0,k
*
k
mod
M
= 11,08 N/mm
Maximum force to be accepted by the construction:
F
t,d,max
= f
t,0,d
*A
w
*0,1 = 186,14 kN
Pdf-Overview: Templates for Structural Engineering
You might also like
- Exercise EC4Document23 pagesExercise EC4babel_stanNo ratings yet
- Euro-Code 4: ColumnDocument19 pagesEuro-Code 4: ColumnMr PolashNo ratings yet
- EC2 Design CalculationsDocument81 pagesEC2 Design Calculationscollins unankaNo ratings yet
- Column LRFDshear (SI)Document12 pagesColumn LRFDshear (SI)donnybtampubolonNo ratings yet
- DG Consulting Engineers: Job NoDocument52 pagesDG Consulting Engineers: Job NosthakshyNo ratings yet
- Design ProjectDocument36 pagesDesign Projectveenabalu20No ratings yet
- En Column Base Plate 1.0Document7 pagesEn Column Base Plate 1.0Ali AlomyNo ratings yet
- 03 1 Weynand Moment Resistant JointsDocument71 pages03 1 Weynand Moment Resistant Jointsdeepak_dce_meNo ratings yet
- TCC11 Element DesignDocument9 pagesTCC11 Element DesignMario Sajulga Dela CuadraNo ratings yet
- RC BeamDocument77 pagesRC BeamJvv GudboyNo ratings yet
- Primeri Ec3Document0 pagesPrimeri Ec3jelenavukojeNo ratings yet
- RC04 Bending2Document40 pagesRC04 Bending2Cristhianares Lonjawon OboLightNo ratings yet
- Budynas SM Ch08Document35 pagesBudynas SM Ch08John Supelano GarciaNo ratings yet
- Column DesignDocument28 pagesColumn DesignHayman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Column Base Plate (Eurocode)Document4 pagesColumn Base Plate (Eurocode)_at_to_No ratings yet
- Staircase Design 1Document365 pagesStaircase Design 1Vanu VamalaiNo ratings yet
- Slab On GradeDocument105 pagesSlab On Gradevijaystructural100% (6)
- Culvert (Excel)Document97 pagesCulvert (Excel)Dwi Ist56% (9)
- RCC Design SheetsDocument40 pagesRCC Design SheetsIbrahim El SharNo ratings yet
- RCC Design SheetsDocument40 pagesRCC Design SheetsAnonymous 9iK0i8h0dPNo ratings yet
- RCC Design SheetsDocument40 pagesRCC Design Sheetsashuswara84% (25)
- Example Isolated FootingDocument4 pagesExample Isolated FootingDan TamiruNo ratings yet
- RCC Design SheetsDocument40 pagesRCC Design SheetsAnonymous nwByj9L100% (2)
- Calculation of Column Reinforcement Area According To en 1992Document6 pagesCalculation of Column Reinforcement Area According To en 1992Florian EsnaultNo ratings yet
- CorbelDocument6 pagesCorbelAsraf MuidinNo ratings yet
- Column Design Examples EBCSDocument7 pagesColumn Design Examples EBCSMesfin Derbew89% (28)
- Sloped FootingDocument19 pagesSloped FootingBala ChandarNo ratings yet
- Design Calc Sheet - Septic Tank Rev1 15-03-09 - 200Document12 pagesDesign Calc Sheet - Septic Tank Rev1 15-03-09 - 200Bok MortegaNo ratings yet
- Design of Rectangular Water TankDocument268 pagesDesign of Rectangular Water Tankchetanmale89% (28)
- Assignment 4: Question 1 REF Output Calculations: MSC - Str/Ecs 762/seismic DesignDocument11 pagesAssignment 4: Question 1 REF Output Calculations: MSC - Str/Ecs 762/seismic DesignMai OthmanNo ratings yet
- EC4 English PDFDocument23 pagesEC4 English PDFSever KawaNo ratings yet
- 2 Design of Beam Ledges 23052014Document2 pages2 Design of Beam Ledges 23052014Ahmad Badsha QuadriNo ratings yet
- Example Flange Beam PDFDocument17 pagesExample Flange Beam PDFFarhana HussinNo ratings yet
- Soal No.1: A B C DDocument21 pagesSoal No.1: A B C DLis Theeii YaaNo ratings yet
- 14a. Check Shear - B400x800dDocument8 pages14a. Check Shear - B400x800dYoukhanna ZayiaNo ratings yet
- RC07 TBeam PDFDocument14 pagesRC07 TBeam PDFchin daroNo ratings yet
- RCCe11 Element DesignDocument8 pagesRCCe11 Element DesignLam TranNo ratings yet
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- VLF Radio Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Electromagnetic WavesFrom EverandVLF Radio Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Electromagnetic WavesNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignFrom EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsFrom EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Abloy Mechanical Lock Cases Technical DescriptionsDocument56 pagesAbloy Mechanical Lock Cases Technical DescriptionsKristjan IgastaNo ratings yet
- NSC1506 Feature 08Document4 pagesNSC1506 Feature 08bijukoottalaNo ratings yet
- CIDECT Design Guide 3Document156 pagesCIDECT Design Guide 3paris062100% (1)
- SBS Design GuideDocument28 pagesSBS Design GuideKristjan IgastaNo ratings yet
- Wall Calculation Example EC2Document15 pagesWall Calculation Example EC2Kristjan Igasta88% (8)