Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacological Drug Metabolised in Vivo Adme Bioavailability Gastrointestinal Tract
Uploaded by
Sindu Sai100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
79 views2 pagesdrugs
Original Title
Pro Drugs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdrugs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
79 views2 pagesPharmacological Drug Metabolised in Vivo Adme Bioavailability Gastrointestinal Tract
Uploaded by
Sindu Saidrugs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
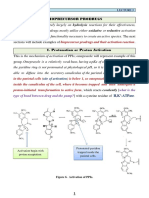
A prodrug is a pharmacological substance (drug) administered in an inactive
(or significantly less active) form. Once administered, the prodrug
is metabolised in vivo into an active metabolite. The rationale behind the use
of a prodrug is generally for absorption, distribution, metabolism, and
excretion (ADME) optimization. Prodrugs are usually designed to improve
oral bioavailability, with poor absorption from the gastrointestinal
tract usually being the limiting factor.
Typ
e
Convertin
g site
Subty
pe
Tissue
location of
conversion
Examples
Typ
e I
Intracellul
ar
Type
IA
Therapeutic
target
tissues/cells
Acyclovir, 5-Flurouracil, Cyclophosphamide, Diethylstilbestrol
diphosphate,
L-Dopa, 6-Mercaptopurine, Mitomycine C, Zidovudine
Typ
e I
Intracellul
ar
Type
IB
Metabolic
tissues
(liver, GI
mucosal
cell,lung
etc)
Cabamazepine, Captopril, Carisoprodol, Heroin, Molsidomine,
Paliperidone,
Phenacetin, Primidone, Psilocybin, Suldinac, Tetrahydrofurfury
l disulfide
Typ
e II
Extracellu
lar
Type
IIA
GI fluids
Lisdexamfetamine, Loperamide
oxide, Oxyphenisatin, Sulfasalazine
Typ
e II
Extracellu
lar
Type
IIB
Systemic
circulation
and Other
Extracellular
Fluid
Compartme
nts
Acetylsalicylate, Bacampicillin, Bambuterol, Chloramphenicol
succinate,
Dihydropyridine pralixoxime, Dipivefrin, Fosphenytoin
Typ
e II
Extracellu
lar
Type
IIC
Therapeutic
Target
Tissues/Cell
s
ADEPTs, GDEPs, VDEPs
Adapted from Pharmaceuticals (2:77-81, 2009) and Toxicology (236:1-6, 2007).
[edit]Examples
Carisoprodol is metabolized into meprobamate. Carisoprodol is not a controlled substance in
the United States, but meprobamate is classified as a potentially addictive controlled
substance that can produce dangerous and painful withdrawal symptoms upon
discontinuation of the drug.
Enalapril is converted by esterase to the active enalaprilat.
Valacyclovir is converted by esterase to the active acyclovir.
Fosamprenavir is hydrolysed to the active amprenavir.
Levodopa is converted by DOPA decarboxylase to the active dopamine.
Chloramphenicol succinate ester is used as an intravenous prodrug of chloramphenicol,
because pure chloramphenicol does not dissolve in water.
Psilocybin is dephosphorylated to the active psilocin.
Heroin is deacetylated by esterase to the active morphine.
Codeine is demethylated by the liver enzyme CYP2D6 to the active morphine, as well as
several other compounds that may be active in analgesia.
Molsidomine is metabolized into SIN-1 which decomposes into the active compound nitric
oxide.
Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic for schizophrenia. It is the active metabolite
of risperidone.
Prednisone, a synthetic cortico-steroid drug, is converted by the liver into the active
drug prednisolone, which is also a steroid.
Primidone is metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes into phenobarbital, which is major,
and phenylethylmalonamide, which is minor.
Dipivefrine, given topically as an anti-glaucoma drug, is converted to epinephrine.
Lisdexamfetamine is metabolized in the small intestine to produce dextroamphetamine at a
controlled (slow) rate for the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Diethylpropion is a diet pill that does not become active as a monoamine releaser or
reuptake inhibitor until it has been N-dealkylated to ethylpropion.
Fesoterodine is an antimuscarinic that is converted to tolterodine.
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is an anti-HIV drug (NtRTI class) that is converted
to tenofovir (PMPA).
You might also like
- Drug Metabolism: JKKMMRF'S College of PharmacyDocument20 pagesDrug Metabolism: JKKMMRF'S College of PharmacyManmeet Kohli IyerNo ratings yet
- Prodrug: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesProdrug: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaArvind SinghNo ratings yet
- 4) Conversion of An Active Compound To Another Equally Active Compound (No Change in Activity)Document5 pages4) Conversion of An Active Compound To Another Equally Active Compound (No Change in Activity)Surjeet ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Medicinal Organic Chemistry: International School of Asia and The Pacific - KalingaDocument3 pagesPharmaceutical Medicinal Organic Chemistry: International School of Asia and The Pacific - KalingaJunimy GamonganNo ratings yet
- Prodrugsseminar 150815053204 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument48 pagesProdrugsseminar 150815053204 Lva1 App6892 PDFNuwaira BalochNo ratings yet
- Prodrugs (Pharmaceutical Importance)Document4 pagesProdrugs (Pharmaceutical Importance)Mugendi100% (1)
- Metabolism BhramankarDocument48 pagesMetabolism Bhramankarnavneetkumar00709No ratings yet
- BiotransformationDocument2 pagesBiotransformationEftakharul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 BPDocument80 pagesUnit-2 BPsrinusmart192No ratings yet
- B.pharm. Class NotesDocument817 pagesB.pharm. Class NotesMukesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Drug Design Metabolism 3Document19 pagesDrug Design Metabolism 3Hanaa HashemNo ratings yet
- A. Principles of Drug MetabolismDocument4 pagesA. Principles of Drug MetabolismLynette EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- 2 Pharmacokinetics MetabolismDocument2 pages2 Pharmacokinetics MetabolismLloyd Selorio ArboledaNo ratings yet
- عضوية٤Document8 pagesعضوية٤مصطفى ابراهيم سعيدNo ratings yet
- Pro-Drugs and Optimization of Drug AbsorptionDocument14 pagesPro-Drugs and Optimization of Drug AbsorptionMussa MwaitolageNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics:: MetabolismDocument34 pagesPharmacokinetics:: Metabolismarquam464No ratings yet
- Metabolism of XenobioticsDocument30 pagesMetabolism of XenobioticsCzarina RiveraNo ratings yet
- Metabolism 2017Document96 pagesMetabolism 2017aimaNo ratings yet
- 5-BScN BIOTRANSFORMATIONDocument25 pages5-BScN BIOTRANSFORMATIONIshaq ArshadNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 4 AntiDocument55 pages11 - Chapter 4 AntilichenresearchNo ratings yet
- Drug Metabolism FinalDocument78 pagesDrug Metabolism FinalPrasanna DNo ratings yet
- Drug Metabolism - Chapter 8Document44 pagesDrug Metabolism - Chapter 8Shaun李好No ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Drug MetabolismDocument17 pagesPharmacokinetics Drug MetabolismChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Pharma 4Document11 pagesPharma 4Ibrahim dhainyNo ratings yet
- Elimination of DrugsDocument39 pagesElimination of Drugsdeepshah6068No ratings yet
- Biotransformation - Mbbs PPT - DR Anoosha BhandarkarDocument40 pagesBiotransformation - Mbbs PPT - DR Anoosha BhandarkaranooshabhandarkarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rathnakar U.P.: Department of Pharmacology Kasturba Medical College, MangaloreDocument27 pagesDr. Rathnakar U.P.: Department of Pharmacology Kasturba Medical College, MangaloreDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Drug MetabolismDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Drug MetabolismNicole AguilarNo ratings yet
- Wk7 FunMed - 4. PK (ADME2) DR MalekigorjiDocument44 pagesWk7 FunMed - 4. PK (ADME2) DR MalekigorjiziaduddinNo ratings yet
- Drug EliminationDocument18 pagesDrug EliminationBriana NdayisabaNo ratings yet
- 3 Pharmacokinetics 2Document15 pages3 Pharmacokinetics 2aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Analgetik Opioid, Nonopioid & AntagonisDocument29 pagesAnalgetik Opioid, Nonopioid & AntagonisHadiyogaNo ratings yet
- BiotransformationDocument18 pagesBiotransformationRajesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Drug Metabolism: Enzymatic Activity Generally Highest inDocument4 pagesDrug Metabolism: Enzymatic Activity Generally Highest inAntonio BorgiaNo ratings yet
- BiotransformationDocument33 pagesBiotransformationAlphaRaj Mekapogu67% (3)
- Enzyme Inducers and Inhibitors TransDocument6 pagesEnzyme Inducers and Inhibitors TransLeonallee MayorNo ratings yet
- Biotransfermation of XenobioticsDocument34 pagesBiotransfermation of XenobioticsМохіт Кумар ЯмпатіNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Biochemistry Assignment 1Document6 pagesRunning Head: Biochemistry Assignment 1Fredrick LiyengaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: Metabolism and Excretion of Drugs, Kinetics of EliminationDocument46 pagesPharmacokinetics: Metabolism and Excretion of Drugs, Kinetics of EliminationShubhank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole PDFDocument8 pagesOmeprazole PDFRafael SyfuNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Phase I & Phase IIDocument16 pagesMetabolism: Phase I & Phase IIMerlin DineshNo ratings yet
- Drug Metabolism and EliminationDocument62 pagesDrug Metabolism and EliminationAshmita DhakalNo ratings yet
- 4.drug Metabolism (Biotransformation)Document33 pages4.drug Metabolism (Biotransformation)Osama KhanNo ratings yet
- Drug Metabolism and Excretion by AsadDocument19 pagesDrug Metabolism and Excretion by AsadAsadullah ghalibNo ratings yet
- Dr. M. Azhar Chishti Dept. Medical BiochemistryDocument46 pagesDr. M. Azhar Chishti Dept. Medical Biochemistryvarsha CRNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: The Dynamics of Drug Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, EliminationDocument108 pagesPharmacokinetics: The Dynamics of Drug Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, EliminationTazkiyatan IsriaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: - What The Body Does To The Drug - Movement and Reaction - Adme!Document8 pagesPharmacokinetics: - What The Body Does To The Drug - Movement and Reaction - Adme!Yana QisNo ratings yet
- Anti ConvulsantsDocument23 pagesAnti ConvulsantsRaman Kumar0% (1)
- Metabolism & ExcretionDocument6 pagesMetabolism & ExcretionAnant KhotNo ratings yet
- LoperamideDocument4 pagesLoperamideMazen MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Changes of DrugsDocument103 pagesMetabolic Changes of DrugsDaniel Wang100% (2)
- Prodrug MyDocument7 pagesProdrug Myshortsmotivation87No ratings yet
- By Ashutosh Gupta From BIT Mesra RanchiDocument31 pagesBy Ashutosh Gupta From BIT Mesra Ranchiexcel pro100% (1)
- عضوية٣Document7 pagesعضوية٣مصطفى ابراهيم سعيدNo ratings yet
- Water-Soluble Vitamins: Intestinal Absorption For Selected VitaminsDocument58 pagesWater-Soluble Vitamins: Intestinal Absorption For Selected VitaminsRoxanna LevineNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHARMACOLOGY (Metabolism)Document37 pagesGENERAL PHARMACOLOGY (Metabolism)rexef82757No ratings yet
- Drug Metabolism ADME PrincipalDocument38 pagesDrug Metabolism ADME PrincipalA. Kumar Soni100% (1)
- Clinical Pharmacokinetics (Biotransformation)Document49 pagesClinical Pharmacokinetics (Biotransformation)kamalNo ratings yet
- Pro DrugsDocument25 pagesPro DrugsMankaran Singh100% (1)
- Questions: Every Climate Activist Hears and What To SayDocument22 pagesQuestions: Every Climate Activist Hears and What To SaySindu SaiNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 390 9497 PDFDocument44 pages10 1 1 390 9497 PDFSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy For Mastery of Open Operations: A Multimedia Curriculum For Training Surgery ResidentsDocument1 pageSurgical Anatomy For Mastery of Open Operations: A Multimedia Curriculum For Training Surgery ResidentsSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Infestations Requiring Surgical InterventionsDocument9 pagesParasitic Infestations Requiring Surgical InterventionsSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- The M.D. Anderson Surgical Oncology Handbook-2011 PDFDocument920 pagesThe M.D. Anderson Surgical Oncology Handbook-2011 PDFjimdioNo ratings yet
- 2016 ASCO - ONS Chemo Standards PDFDocument13 pages2016 ASCO - ONS Chemo Standards PDFSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- 2 222214KQ PDFDocument19 pages2 222214KQ PDFSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Buddha and KalingaDocument20 pagesBuddha and Kalingaalokmukh100% (1)
- The Language of Medicine in EnglishDocument125 pagesThe Language of Medicine in EnglishSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Epartment of Urgery Andbook: General Surgery Residency ProgramDocument34 pagesEpartment of Urgery Andbook: General Surgery Residency ProgramSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- SatelliteDocument47 pagesSatelliteSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- MCH Theory ExamDocument1 pageMCH Theory ExamSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Scientific Research: AstrologyDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Scientific Research: AstrologySindu Sai100% (1)
- The Biography of The Lord BuddhaDocument30 pagesThe Biography of The Lord Buddhaprajya100% (1)
- Gautam BuddhaDocument64 pagesGautam BuddhasharathVEMNo ratings yet
- YasodharaDocument4 pagesYasodharaSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Tales From The BagavathamDocument148 pagesTales From The Bagavathamom srisairam100% (2)
- Respirology: Dr. C. Chan and Dr. N. Lazar Adrienne Chan and Gloria Rambaldini, Editors Deborah Cheng, Associate EditorDocument44 pagesRespirology: Dr. C. Chan and Dr. N. Lazar Adrienne Chan and Gloria Rambaldini, Editors Deborah Cheng, Associate EditorSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Alina Gonzalez-Mayo, MD: Psychiatry Highlights For USMLE Step 2 Somatoform Disorders Somatoform DisordersDocument2 pagesAlina Gonzalez-Mayo, MD: Psychiatry Highlights For USMLE Step 2 Somatoform Disorders Somatoform DisordersSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Usmle Comlex Most CommonDocument3 pagesUsmle Comlex Most Commonsooryarao100% (1)
- Sathyabama University B.E CSE - 2011-2015 BATCH: University Theory Examinations Schedule, AugDocument1 pageSathyabama University B.E CSE - 2011-2015 BATCH: University Theory Examinations Schedule, AugSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Highlights For USMLE Step 2 Substance Disorders Buzz WordsDocument1 pagePsychiatry Highlights For USMLE Step 2 Substance Disorders Buzz WordsSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Genetic DisordersDocument10 pagesGenetic Disordersphantomspb100% (2)
- Anatomy: "I Love Going Places in My Very Own Underwear"Document7 pagesAnatomy: "I Love Going Places in My Very Own Underwear"Sindu SaiNo ratings yet
- r4f Pastest MnemonicsDocument23 pagesr4f Pastest MnemonicsplayuhzNo ratings yet
- The Hub of MetabolismDocument1 pageThe Hub of MetabolismDr. SHIVA AITHALNo ratings yet
- 2014 First Aid Step 1 ErrataDocument4 pages2014 First Aid Step 1 Erratawecan12345No ratings yet
- Common Medical Problems For Clinical Year Examination: FundosDocument2 pagesCommon Medical Problems For Clinical Year Examination: FundosSindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Medical MnemonicsDocument256 pagesMedical MnemonicssitalcoolkNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics 1Document149 pagesMnemonics 1Sindu SaiNo ratings yet
- Prakruti: Products PVT LTDDocument5 pagesPrakruti: Products PVT LTDडा. सत्यदेव त्यागी आर्यNo ratings yet
- Licensing Agreements in The Pharmaceutical Industry: Reasons For PartneringDocument13 pagesLicensing Agreements in The Pharmaceutical Industry: Reasons For Partneringmodava-2No ratings yet
- Pitocin: (Oxytocin Injection, USP) Synthetic DescriptionDocument7 pagesPitocin: (Oxytocin Injection, USP) Synthetic Descriptionrevathidadam55555No ratings yet
- SymptomAssessmentRevised Sept09Document2 pagesSymptomAssessmentRevised Sept09Nicole Lopez DaquiadoNo ratings yet
- Application For Wholesale MedicineDocument8 pagesApplication For Wholesale Medicinesashi debsarmaNo ratings yet
- Formulation DevelopmentDocument1 pageFormulation DevelopmentbilcareNo ratings yet
- 3 - Muran & Lutz, 2015Document6 pages3 - Muran & Lutz, 2015mariluNo ratings yet
- Consumer Health in PeruDocument18 pagesConsumer Health in PeruMiguel DaneriNo ratings yet
- Dibis Conseil PresentationDocument23 pagesDibis Conseil Presentationupadhyay.jalpan1994No ratings yet
- Unit1 DrRakhiMishra (2) CNPDocument107 pagesUnit1 DrRakhiMishra (2) CNPAnkit Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical QBD (Final)Document41 pagesPharmaceutical QBD (Final)Tahsin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Malaria Treatment Guidelines WHO 2010Document211 pagesMalaria Treatment Guidelines WHO 2010emc27No ratings yet
- Weakness and Its Homeopathic Self Treatment Scheme - Bashir Mahmud ElliasDocument4 pagesWeakness and Its Homeopathic Self Treatment Scheme - Bashir Mahmud ElliasBashir Mahmud ElliasNo ratings yet
- Analyzing OSCE PDFDocument15 pagesAnalyzing OSCE PDFWaleed Mostafa100% (1)
- Soal BING Kelas 12Document3 pagesSoal BING Kelas 12Nino SalemNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Evaluation of Liposphere Based Topical Drug Delivery System Containing Nsaid DrugDocument113 pagesPreparation and Evaluation of Liposphere Based Topical Drug Delivery System Containing Nsaid Drugakedia1100% (5)
- RESUME (M.Pharm-Pharmaceutics) : Ashishkumar N. PanchalDocument3 pagesRESUME (M.Pharm-Pharmaceutics) : Ashishkumar N. PanchalAshish100% (1)
- Job Search-1Document2 pagesJob Search-1Prashanth RajuNo ratings yet
- Stock 2023 10 31Document16 pagesStock 2023 10 31Farmacias San IsidroNo ratings yet
- Date Sheet For The Doctor of Pharmacy PharmD Annual Examination 2023 t8008Document2 pagesDate Sheet For The Doctor of Pharmacy PharmD Annual Examination 2023 t8008Haniya RajpootNo ratings yet
- March 2021Document36 pagesMarch 2021rammvr05No ratings yet
- Mesna PM ENG v4.0 011218Document23 pagesMesna PM ENG v4.0 011218Vimal NishadNo ratings yet
- ###Questions Model PDFDocument2 pages###Questions Model PDFDave DMNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Deep Dive PDFDocument1 pageDexamethasone Deep Dive PDFRizky TiensNo ratings yet
- 6 135Document6 pages6 135Ashok LenkaNo ratings yet
- A Herbal Plant Cassia AngustifoliaDocument5 pagesA Herbal Plant Cassia Angustifoliabalakrishna GolusuNo ratings yet
- Joe Vialls: 30 January 2004 From Website Recov Ered Through WebsiteDocument18 pagesJoe Vialls: 30 January 2004 From Website Recov Ered Through WebsiteMaria ShipkaNo ratings yet
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) Guidelines: Visit For More Ppt's & MaterialDocument40 pagesGood Manufacturing Practices (GMP) Guidelines: Visit For More Ppt's & Materialmohammed50% (4)
- Proceasep. Congreso Interncional Procesamiento Aséptico en La Industria Biotecnológica y FarmacéuticaDocument1 pageProceasep. Congreso Interncional Procesamiento Aséptico en La Industria Biotecnológica y FarmacéuticaClaudioRMNo ratings yet
- The Client With Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesThe Client With Urinary Tract InfectionMarisol Jane JomayaNo ratings yet