Professional Documents
Culture Documents
07 Childschd 6x4.5 1-Page PR
Uploaded by
Steluta Galbenus0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesinteresant
Original Title
07 Childschd 6x4.5 1-Page Pr
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentinteresant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pages07 Childschd 6x4.5 1-Page PR
Uploaded by
Steluta Galbenusinteresant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
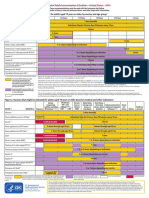
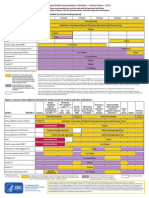
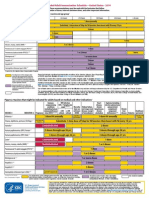
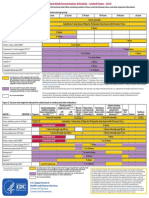
This schedule indicates the recommended ages for routine administration
of currently licensed childhood vaccines, as of December 1, 2006, for
children aged 06 years. Additional information is available at
http://www.cdc.gov/nip/recs/child-schedule.htm. Any dose not administered at the
recommended age should be administered at any subsequent visit, when indicated
and feasible. Additional vaccines may be licensed and recommended during the
year. Licensed combination vaccines may be used whenever any components of
the combination are indicated and other components of the vaccine are not
contraindicated and if approved by the Food and Drug Administration for that dose
of the series. Providers should consult the respective Advisory Committee on
Immunization Practices statement for detailed recommendations. Clinically
significant adverse events that follow immunization should be reported to the
Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Guidance about how to
obtain and complete a VAERS form is available at http://www.vaers.hhs.gov
or by telephone, 800-822-7967. FOOTNOTES ON REVERSE SIDE
Department of Health and Human Services
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Recommended Immunization Schedule for Persons Aged 06 YearsUNITED STATES 2007
Catch-up
immunization
Certain
high-risk
groups
Range of
recommended
ages
The Recommended Immunization Schedules for Persons Aged 018 Years
are approved by:
Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (http://www.cdc.gov/nip/acip)
American Academy of Pediatrics (http://www.aap.org)
American Academy of Family Physicians (http://www.aafp.org)
More information regarding
vaccine administration can be
obtained from the websites above
or the CDC-INFO contact center:
800-CDC-INFO
ENGLISH & ESPAOL 24/7
[800-232-4636]
Keep track of your
childs immunizations
with the
CDC Childhood
Immunization Scheduler
www.cdc.gov/nip/kidstuff/scheduler.htm
Vaccine
Age Birth
1
month
2
months
4
months
6
months
12
months
15
months
18
months
1923
months
23
years
46
years
Hepatitis B
1
Rotavirus
2
Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis
3
Haemophilus influenzae type b
4
Pneumococcal
5
Inactivated Poliovirus
Influenza
6
Measles, Mumps, Rubella
7
Varicella
8
Hepatitis A
9
Meningococcal
10
HepB Series HepB HepB HepB
see
footnote1
DTaP DTaP DTaP
Rota Rota Rota
DTaP DTaP
Hib Hib Hib
4
Hib
IPV IPV IPV IPV
MMR MMR
Varicella Varicella
PCV
Hib
PPV
PCV
PCV PCV PCV
Influenza (Yearly)
HepA (2 doses)
MPSV4
HepA Series
07childhoodschedule-0-6years_6x4.5.qxp 2/26/2007 2:33 PM Page 1
FOOTNOTES
1. Hepatitis B vaccine (HepB). (Minimum age: birth)
At birth:
Administer monovalent HepB to all newborns before hospital discharge.
If mother is hepatitis surface antigen (HBsAg)-positive, administer HepB
and 0.5 mL of hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) within 12 hours of birth.
If mothers HBsAg status is unknown, administer HepB within 12
hours of birth. Determine the HBsAg status as soon as possible and
if HBsAg-positive, administer HBIG (no later than age 1 week).
If mother is HBsAg-negative, the birth dose can only be delayed with
physicians order and mothers negative HBsAg laboratory report
documented in the infants medical record.
After the birth dose:
The HepB series should be completed with either monovalent HepB
or a combination vaccine containing HepB. The second dose should
be administered at age 12 months. The final dose should be admin-
istered at age 24 weeks. Infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers
should be tested for HBsAg and antibody to HBsAg after completion
of 3 doses of a licensed HepB series, at age 918 months (generally
at the next well-child visit).
4-month dose:
It is permissible to administer 4 doses of HepB when combination
vaccines are administered after the birth dose. If monovalent HepB is
used for doses after the birth dose, a dose at age 4 months is not needed.
2. Rotavirus vaccine (Rota). (Minimum age: 6 weeks)
Administer the first dose at age 612 weeks. Do not start the series
later than age 12 weeks.
Administer the final dose in the series by age 32 weeks. Do not
administer a dose later than age 32 weeks.
Data on safety and efficacy outside of these age ranges are insufficient.
3. Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine
(DTaP). (Minimum age: 6 weeks)
The fourth dose of DTaP may be administered as early as age 12 months,
provided 6 months have elapsed since the third dose.
Administer the final dose in the series at age 46 years.
4. Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine (Hib).
(Minimum age: 6 weeks)
If PRP-OMP (PedvaxHIB
or ComVax
[Merck]) is administered at ages
2 and 4 months, a dose at age 6 months is not required.
TriHiBit
(DTaP/Hib) combination products should not be used for
primary immunization but can be used as boosters following any Hib
vaccine in children aged 12 months.
5. Pneumococcal vaccine. (Minimum age: 6 weeks for pneumococcal conjugate
vaccine [PCV]; 2 years for pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine [PPV])
Administer PCV at ages 2459 months in certain high-risk groups.
Administer PPV to children aged 2 years in certain high-risk groups.
See MMWR 2000;49(No. RR-9):135.
6. Influenza vaccine. (Minimum age: 6 months for trivalent inactivated influenza
vaccine [TIV]; 5 years for live, attenuated influenza vaccine [LAIV])
All children aged 659 months and close contacts of all children aged
059 months are recommended to receive influenza vaccine.
Influenza vaccine is recommended annually for children aged 59
months with certain risk factors, health-care workers, and other
persons (including household members) in close contact with persons
in groups at high risk. See MMWR 2006;55(No. RR-10):141.
For healthy persons aged 549 years, LAIV may be used as an
alternative to TIV.
Children receiving TIV should receive 0.25 mL if aged 635 months or
0.5 mL if aged 3 years.
Children aged <9 years who are receiving influenza vaccine for the
first time should receive 2 doses (separated by 4 weeks for TIV and
6 weeks for LAIV).
7. Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR). (Minimum age: 12 months)
Administer the second dose of MMR at age 46 years. MMR may be
administered before age 46 years, provided 4 weeks have elapsed
since the first dose and both doses are administered at age 12 months.
8. Varicella vaccine. (Minimum age: 12 months)
Administer the second dose of varicella vaccine at age 46 years.
Varicella vaccine may be administered before age 46 years, provided
that 3 months have elapsed since the first dose and both doses are
administered at age 12 months. If second dose was administered 28
days following the first dose, the second dose does not need to be repeated.
9. Hepatitis A vaccine (HepA). (Minimum age: 12 months)
HepA is recommended for all children aged 1 year (i.e., aged 1223 months).
The 2 doses in the series should be administered at least 6 months apart.
Children not fully vaccinated by age 2 years can be vaccinated at
subsequent visits.
HepA is recommended for certain other groups of children, including
in areas where vaccination programs target older children. See
MMWR 2006;55(No. RR-7):123.
10. Meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine (MPSV4). (Minimum age: 2 years)
Administer MPSV4 to children aged 210 years with terminal complement
deficiencies or anatomic or functional asplenia and certain other
high-risk groups. See MMWR 2005;54(No. RR-7):121.
CS108190
07childhoodschedule-0-6years_6x4.5.qxp 2/26/2007 2:33 PM Page 2
You might also like
- Kidney Diet DelightsDocument20 pagesKidney Diet DelightsArturo Treviño MedinaNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsFrom EverandUSMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- The Theory of Motivation in Dog Training: By: Ed FrawleyDocument30 pagesThe Theory of Motivation in Dog Training: By: Ed Frawleyrodrigue angbohNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2021Document11 pagesChildhood Immunization Schedule 2021Paula QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 1: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3From EverandClinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 1: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Immunisation ScheduleDocument3 pagesImmunisation SchedulejegathesmsjsNo ratings yet
- DENSO Diagnostic TipsDocument1 pageDENSO Diagnostic TipsVerona MamaiaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Vac + NotesDocument36 pagesPediatric Vac + NotesTrang VuNo ratings yet
- Cruz v. CA - G.R. No. 122445 - November 18, 1997 - DIGESTDocument2 pagesCruz v. CA - G.R. No. 122445 - November 18, 1997 - DIGESTAaron Ariston80% (5)
- General Leasing and Managing AuthorityDocument14 pagesGeneral Leasing and Managing AuthorityKatharina SumantriNo ratings yet
- 200 State Council Members 2010Document21 pages200 State Council Members 2010madhu kanna100% (1)
- Ear CandlingDocument2 pagesEar CandlingpowerleaderNo ratings yet
- Recommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0-6 YearsDocument3 pagesRecommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0-6 YearsAlvaro FloresNo ratings yet
- IZSchedule0 6yrsDocument1 pageIZSchedule0 6yrsKaty ForemanNo ratings yet
- 0 6yrs Schedule BWDocument1 page0 6yrs Schedule BWRyan ArdyantoNo ratings yet
- Catchup Schedule PRDocument1 pageCatchup Schedule PRJesus A. Pineda GarciaNo ratings yet
- IZSchedule0 6yrsDocument1 pageIZSchedule0 6yrsgeany2911No ratings yet
- Hepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at BirthDocument5 pagesHepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at Birthannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Figure 2. Catch-Up Immunization Schedule For Persons Ages 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More Than 1 Month Behind, U. S., 2013Document1 pageFigure 2. Catch-Up Immunization Schedule For Persons Ages 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More Than 1 Month Behind, U. S., 2013Alvaro FloresNo ratings yet
- Summary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Document5 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Annie AnnaNo ratings yet
- WHO Immunization Schedule ChildrenDocument9 pagesWHO Immunization Schedule Childrenashchua21No ratings yet
- Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Recommended Immunization Schedule For Children Aged 0 Through 18 Years - India, 2014 and Updates On ImmunizationDocument16 pagesIndian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Recommended Immunization Schedule For Children Aged 0 Through 18 Years - India, 2014 and Updates On Immunizationkrishna615No ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument4 pagesVaccinesSam smithNo ratings yet
- Highlghts in Pediatric Infectious DiseasesDocument37 pagesHighlghts in Pediatric Infectious DiseasesLibay Villamor IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Over-All Goal: To Reduce The Morbidity and Mortality Among Children Against The Most Common Vaccine-Preventable Specific GoalDocument9 pagesOver-All Goal: To Reduce The Morbidity and Mortality Among Children Against The Most Common Vaccine-Preventable Specific GoalRetiza EllaNo ratings yet
- (MMUNISATIONDocument54 pages(MMUNISATIONatharva sawantNo ratings yet
- Adult ScheduleDocument3 pagesAdult ScheduledrmanojvimalNo ratings yet
- Recommended Immunization - Canadian Immunization Guide - Seventh Edition - 2006Document2 pagesRecommended Immunization - Canadian Immunization Guide - Seventh Edition - 2006Maja MudriNo ratings yet
- Table 2: Summary of WHO Position Papers - Recommended Routine Immunizations For ChildrenDocument8 pagesTable 2: Summary of WHO Position Papers - Recommended Routine Immunizations For Childrenfadityo1No ratings yet
- Catchup Schedule PR 1Document1 pageCatchup Schedule PR 1MichelleNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. Recommended Immunization Schedule For Adults Aged 19 Years or Older, by Vaccine and Age GroupDocument2 pagesFigure 1. Recommended Immunization Schedule For Adults Aged 19 Years or Older, by Vaccine and Age GroupmsarasNo ratings yet
- Hep BDocument47 pagesHep BMia Mia MiaNo ratings yet
- Immunization Child2005 EnglDocument4 pagesImmunization Child2005 EnglGanesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Immunization Routine Table1Document9 pagesImmunization Routine Table1MeeKo VideñaNo ratings yet
- Adult Immunization ScheduleDocument3 pagesAdult Immunization ScheduleBryan Mae H. DegorioNo ratings yet
- ScheduleDocument2 pagesScheduleapi-286634335No ratings yet
- Expanded Program On ImmunuzationDocument37 pagesExpanded Program On ImmunuzationRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Adult Combined ScheduleDocument5 pagesAdult Combined ScheduleAwal Safar MNo ratings yet
- Summary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years and Older)Document5 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years and Older)Hannah Caburian RemoNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedDocument11 pagesChildhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedPatricia Bernadette PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Immunization ScheduleDocument2 pagesImmunization ScheduleTracy100% (1)
- Binational Schedule Immunization USA MEXICODocument2 pagesBinational Schedule Immunization USA MEXICOfernando_morales_15No ratings yet
- Correctedtable4 PDFDocument1 pageCorrectedtable4 PDFWiwin R UtamiNo ratings yet
- Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Recommended Immunization Schedule 2013Document14 pagesIndian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Recommended Immunization Schedule 2013Mahesh ShankarNo ratings yet
- What's New On The Child and Adolescent Immunization SchedulesDocument30 pagesWhat's New On The Child and Adolescent Immunization SchedulesMark ReinhardtNo ratings yet
- Acip 2020 21 Summary of RecommendationsDocument4 pagesAcip 2020 21 Summary of RecommendationsGroup12IrvinAndy AnchetaNo ratings yet
- CHN1 Lec Session #17 SASDocument9 pagesCHN1 Lec Session #17 SASJhanna Mae BalbonNo ratings yet
- Table 2: Summary of WHO Position Papers - Recommended Routine Immunizations For ChildrenDocument7 pagesTable 2: Summary of WHO Position Papers - Recommended Routine Immunizations For ChildrenKrishnendu PramanikNo ratings yet
- World Immunization Week 2023 PPA EPIDocument42 pagesWorld Immunization Week 2023 PPA EPIMuhammad ShafiNo ratings yet
- The Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument26 pagesThe Expanded Program On ImmunizationJudee Marie MalubayNo ratings yet
- Jawaban B InggrisDocument4 pagesJawaban B InggrisMhd SholehNo ratings yet
- Updates in Iraq National Program of Immunization 2012Document36 pagesUpdates in Iraq National Program of Immunization 2012Husain TamimieNo ratings yet
- Vaccinations For NJ SchoolsDocument2 pagesVaccinations For NJ SchoolskimtranpatchNo ratings yet
- Immunizations: Policies and Procedures: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualDocument2 pagesImmunizations: Policies and Procedures: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualSedaka DonaldsonNo ratings yet
- CPG On Immunization For WomenDocument28 pagesCPG On Immunization For WomenYnoli DiosomitoNo ratings yet
- Immreqpk15 16Document4 pagesImmreqpk15 16api-234991765No ratings yet
- Adult ScheduleDocument3 pagesAdult SchedulelcmurilloNo ratings yet
- Recommended Doses of Hepatitis B Vaccine: Vaccine Age Group Formulation Dosage ScheduleDocument1 pageRecommended Doses of Hepatitis B Vaccine: Vaccine Age Group Formulation Dosage ScheduledhityasagitaNo ratings yet
- Adult Pocafeket SizeDocument2 pagesAdult Pocafeket SizedadfNo ratings yet
- Summary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years & Older)Document4 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years & Older)gyna_2002No ratings yet
- Splenectomy: DisclaimerDocument5 pagesSplenectomy: DisclaimerMimi FatinNo ratings yet
- Table I-IAP Immunization Schedule 2016-FinalDocument6 pagesTable I-IAP Immunization Schedule 2016-Finalsheb2004No ratings yet
- F1 - Frequently Asked Questions On Immunization DVLMDocument25 pagesF1 - Frequently Asked Questions On Immunization DVLMMAHAMMAD ANWAR ALINo ratings yet
- Raymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM, MAN UNP-College of NursingDocument32 pagesRaymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM, MAN UNP-College of NursingrnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Cdi 2106 CDocument2 pagesCdi 2106 CVerdi LeonardoNo ratings yet
- States, 2011 United Recommended Childhood and Adolescent Immunization SchedulesDocument7 pagesStates, 2011 United Recommended Childhood and Adolescent Immunization SchedulesDolores KilpatrickNo ratings yet
- Health Advice and Immunizations for TravelersFrom EverandHealth Advice and Immunizations for TravelersNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studysnowyfingers100% (1)
- To Be or Not To Be Healthy 4144Document3 pagesTo Be or Not To Be Healthy 4144Vesna Milosavljevic100% (1)
- EMI Course CatalogDocument645 pagesEMI Course CatalogFarouk OthmaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Front SheetDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 Front SheetBách PhạmNo ratings yet
- Imperial SpeechDocument2 pagesImperial SpeechROJE DANNELL GALVANNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet HFE-7000 Prod SpecDocument6 pagesData Sheet HFE-7000 Prod Specsshaffer_9No ratings yet
- How Condensing Boilers WorkDocument1 pageHow Condensing Boilers WorkBrianNo ratings yet
- Arcelor Mittal Operations: Operational Area Is Sub-Divided Into 4 PartsDocument5 pagesArcelor Mittal Operations: Operational Area Is Sub-Divided Into 4 Partsarpit agrawalNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension MaterialsDocument6 pagesReading Comprehension MaterialsDiana PundavelaNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathic Treatment of Complicated Sebaceous Cyst - A Case StudyDocument5 pagesHomoeopathic Treatment of Complicated Sebaceous Cyst - A Case StudyDr deepakNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Comparison of Highly Soluble Sodium Stearyl Fumarate With Other Lubricants in VitroDocument8 pagesEvaluation and Comparison of Highly Soluble Sodium Stearyl Fumarate With Other Lubricants in VitroSvirskaitė LaurynaNo ratings yet
- KQ2H M1 InchDocument5 pagesKQ2H M1 Inch林林爸爸No ratings yet
- TNEB Thermal Power PlantDocument107 pagesTNEB Thermal Power Plantvicky_hyd_130% (1)
- Jose de Villa National School: Home Visitation FormDocument3 pagesJose de Villa National School: Home Visitation FormNoli AsuroNo ratings yet
- Aqa Food Technology Coursework Mark SchemeDocument7 pagesAqa Food Technology Coursework Mark Schemeafjwdbaekycbaa100% (2)
- 3.0.2 3.0.2 Thermax Inc.: Pressure Building Ambient Vaporizers For Bulk Storage TanksDocument2 pages3.0.2 3.0.2 Thermax Inc.: Pressure Building Ambient Vaporizers For Bulk Storage TanksSiDdu KalashettiNo ratings yet
- Brief Psychological Interventions For Borderline Personality Disorder. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled TrialsDocument9 pagesBrief Psychological Interventions For Borderline Personality Disorder. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled TrialsFELIPE ROJAS TRAVERSONo ratings yet
- Comparison of Microsurgical and Conventional Open Flap DebridementDocument9 pagesComparison of Microsurgical and Conventional Open Flap DebridementNoemi LukacsNo ratings yet
- The Necessity of Using Neurophysiological Methods For Diagnosing Communication Disorders. by Akhsaful To Tawhida Jahan MamDocument11 pagesThe Necessity of Using Neurophysiological Methods For Diagnosing Communication Disorders. by Akhsaful To Tawhida Jahan MamAkhsaful ImamNo ratings yet
- اطلع علي زتونة 3 ع مراجعة الترم الثاني 2024Document60 pagesاطلع علي زتونة 3 ع مراجعة الترم الثاني 2024ahmad sholokNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP BUỔI SỐ 2 - VIẾT UNIT 1Document7 pagesBÀI TẬP BUỔI SỐ 2 - VIẾT UNIT 1Huy Trương GiaNo ratings yet
- Affidavit Format FOR ART LEVEL 1 CLINIC RegistrationDocument2 pagesAffidavit Format FOR ART LEVEL 1 CLINIC Registrationward fiveNo ratings yet
- Materials Today: Proceedings: Ashish Malik, Shivam KohliDocument7 pagesMaterials Today: Proceedings: Ashish Malik, Shivam KohliSenthil KumarNo ratings yet