Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5naomi Rahimi Levene
Uploaded by
denis_sp20101304Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5naomi Rahimi Levene
Uploaded by
denis_sp20101304Copyright:
Available Formats
TEG MONITORING & TREATING
BLEEDING PATIENTS
Naomi Rahimi-Levene MD, MHA
Director of the Blood Bank
Assaf Harofeh Medical Center
Zerifin, Israel
The Versailles wedding hall collapse
Jerusalem 2001
The Versailles wedding hall collapse
Jerusalem 2001
Wedding hall collapses
13 people killed
Hundreds injured
Injured were sent to distant hospitals as closer
ones were saturated
Sample Arrives
Blood Bank
TEG in the Blood Bank
TEG in the Blood Bank
TEG viewed in my office
TEG viewed at home
TEG viewed at home
TEG analyzer
Features
Two independent
channels
Temperature display &
control
Computerized data collection
& storage
The TEG analyzer
TEG Technology
How it works
Interactive
Coagulation Proteins
Hemostasis Components:
Virchows triad
Platelet function
Clot strength
Clotting
time
Clot
kinetics
Clot stability
Clot breakdown
TEG Technology
Hemostasis profile
Time (min)
P
i
n
R
o
t
a
t
i
o
n
A
m
p
l
i
t
u
d
e
(
m
m
)
Clot Parameters
Enzymatic pathways
(reaction time)
Platelets + fibrinogen (80/20)
(maximum amplitude)
Clot breakdown
Clot development (kinetics, rate)
CI = global coagulation index (linear expression of R, MA, K, angle)
Time (min)
A
m
p
l
i
t
u
d
e
(
m
m
)
LY30
LY30 measures the rate of amplitude reduction 30 minutes after MA. This
measurement gives an indication of the stability of the clot.
LY30
(EPL)
MA, or Maximum Amplitude, is a direct function of the maximum dynamic properties
of fibrin and platelet bonding and represents the ultimate strength of the fibrin clot.
MA
K time is a measure of the rapidity to reach a certain level of clot strength. K
The value measures the rapidity (kinetics) of fibrin build-up and cross-linking, that is,
the speed of clot strengthening.
R is the time of latency from the time that the blood was placed in the TEG analyzer
until the initial fibrin formation.
R
TEG value Clinical Cause Suggested
Treatment
R between 7 - 10 min clotting factors x 1 FFP or 4 ml/kg
R between 11-14 min clotting factors x 2 FFP or 8 ml/kg
R greater than 14 min clotting factors x 4 FFP or 16 ml/kg
MA between 49 -54 mm platelet function 0.3mcg/kg DDAVP
MA between 41 -48 mm platelet function x5 platelet units
MA at 40 mm or less platelet
function
x10 platelet units
less than 47 fibrinogen level .06 u/kg cryo
LY30 7.5% or greater, CI less than 3.0 Primary fibrinolysis antifibrinolytic of
choice
LY30 7.5% or greater, CI greater than 3.0 Secondary fibrinolysis anticoagulant of choice
LY30 less than 7.5%, C.I. greater than 3.0 Prothrombotic state anticoagulant of choice
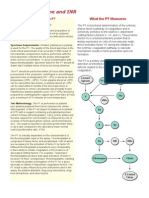
Treatment Protocol
Pattern Recognition
TEG decision tree
US Patent 6,787,363
Hemorrhagic
Thrombotic
Fibrinolytic
Developed from a number of clinical studies
33 years old women with epidural catheter after childbirth
67000 plts
63 years old patient with normal coagulation tests,
bleeding after prostatectomy
Bleeding patient with pathologic coagulation tests
prolonged INR & APTT coumadin overdose
The same patient after component treatment
received 7FFP and 2pc
Intensive care patient, massive bleeding, prolonged PT
and thrombocytopenia -
received 4pc+10FFP+10 cryo+10plts
Intensive care patient, massive bleeding,
prolonged PT and thrombocytopenia
Same patient after 12pc+14FFP+10cryo+15 plts
Patient with hematological malignancy all coagulation
tests pathological bleeding from stomach received
25pc+16FFP+25cryo+30plts
56 years old patient with acute on chronic renal failure,
Diabetes mellitus, Morbid obesity, Copd with acute
exacerbation, Mechanical ventilation
Same patient with heparinase
Same patient after component treatment
72 years old patient after TKR with bleeding in knee, PT
mildly prolonged and corrected with vit k, PTT,
fibrinogen normal, platelets normal
TEG (1)
In a catastrophic event many massively
bleeding patients will have to be treated
simultaneously, sharing available resources
Conventional blood tests will not provide a
swift enough answer to guide decision making
as they can be lengthy and do not necessarily
represent the in vivo picture
TEG (2)
In our hospital TEG is performed in the blood
bank and can be viewed online in remote sites
(including the operating theater)
The anesthetists have been tutored in
interpreting the TEG and in a short time the
need for FFP, cryoprecipitate (fibrinogen) and
platelet concentrates can be assessed,
allowing prompt on time decision making
TEG (3)
In an event in which communication online is
cutoff the TEG can be transferred and setup in
the operating theater, allowing decision
making on the spot
The test can be repeated until the patient is
stabilized and has received proper
replacement therapy
TEG Blood Bank
TEG OR
TEG office
TEG home
Study Proposal
Trauma patients massively bleeding
TEG on entry OR
After receiving 1
st
pack - TEG
If bleeding continues reevaluate TEG
TEG when patient stabilizes
In parallel CBC, PT, APTT, fibrinogen
You might also like
- Managing Coagulopathy ICUDocument38 pagesManaging Coagulopathy ICUMirabela Colac100% (1)
- Thromboelastography (Teg) in TraumaDocument7 pagesThromboelastography (Teg) in TraumaJosueDanielDelgadoNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Renal Dialysis UnitDocument25 pagesPresented By: Renal Dialysis UnitGi Mendez DimzonNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion InstructionsDocument17 pagesBlood Transfusion InstructionsMuthuraj KasinathanNo ratings yet
- Roeloffzen 2010Document9 pagesRoeloffzen 2010Olivia Alexandra DavidNo ratings yet
- Use of Thromboelastography in Clinical Practice - VsDocument13 pagesUse of Thromboelastography in Clinical Practice - VsTactvisNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorder ChartsDocument25 pagesBleeding Disorder ChartsHiba MusthafaNo ratings yet
- Thromboelastogram (TEG) - LITFL - CCC Investigations PDFDocument13 pagesThromboelastogram (TEG) - LITFL - CCC Investigations PDFSiddharth Parmar100% (1)
- Thromboelastography: by Mike PoullisDocument28 pagesThromboelastography: by Mike PoullisDeepthi RamNo ratings yet
- Nefrología CríticaDocument10 pagesNefrología CríticaDobson Flores AparicioNo ratings yet
- JCDR 11 EC35Document3 pagesJCDR 11 EC35aulianmediansyahNo ratings yet
- Catheter Directed Thrombolysis: Gan Dunnington M.D. Stanford Vascular Conference 9/12/05Document25 pagesCatheter Directed Thrombolysis: Gan Dunnington M.D. Stanford Vascular Conference 9/12/05Pratik SahaNo ratings yet
- PT InrDocument3 pagesPT InrJeniah Lerios OcsioNo ratings yet
- Stationary Versus Agitated Storage of Whole Blood.6 PDFDocument5 pagesStationary Versus Agitated Storage of Whole Blood.6 PDFAngel CallesNo ratings yet
- 7 3 Transfusion Management of Major HaemorrhageDocument6 pages7 3 Transfusion Management of Major HaemorrhageKoas Neuro UnpattiNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Transfusion MedicineDocument96 pagesHandbook of Transfusion MedicineJoana Bessa83% (6)
- Grlinger ROTEM PPH DSMH Colombo 22-01-2019 ShortDocument86 pagesGrlinger ROTEM PPH DSMH Colombo 22-01-2019 ShortDobrila SimonovicNo ratings yet
- A Review of Thromboelastography PDFDocument5 pagesA Review of Thromboelastography PDFmarceloNo ratings yet
- Coagulopathy in Trauma: Rudy Alvarez, M.DDocument28 pagesCoagulopathy in Trauma: Rudy Alvarez, M.DRudy AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 4.massive HemorrhageDocument44 pages4.massive HemorrhageyeabsraNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Therapeutic Plasma ExchangeDocument65 pagesAn Overview of Therapeutic Plasma ExchangesayednourNo ratings yet
- Massive Transfusion Protocol 2017Document9 pagesMassive Transfusion Protocol 2017RosNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument5 pagesJournalJane De CastroNo ratings yet
- Massive TransfusionDocument17 pagesMassive TransfusiondenirojuniorNo ratings yet
- PBM (Autosaved)Document36 pagesPBM (Autosaved)dr AmitNo ratings yet
- Ajcp 2Document6 pagesAjcp 2margaruzzaNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Strategies For Minimizing Mortality in Major Blood LossDocument26 pagesHemostatic Strategies For Minimizing Mortality in Major Blood LossJonathan wiradinataNo ratings yet
- Physiology & ApplicationsDocument52 pagesPhysiology & ApplicationsYuliyanti YasinNo ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document2 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Yogi Agil MurdjitoNo ratings yet
- Approach To Bleeding Child: Moderator: Dr. Ayal (MD, Pediatrician) Presenters: Wubshet K. & Yihenew D. (C-I Students)Document92 pagesApproach To Bleeding Child: Moderator: Dr. Ayal (MD, Pediatrician) Presenters: Wubshet K. & Yihenew D. (C-I Students)woldemariamNo ratings yet
- Membrane Versus Centrifuge-Based Therapeutic Plasma Exchange, A Randomized Prospective Crossover StudyDocument6 pagesMembrane Versus Centrifuge-Based Therapeutic Plasma Exchange, A Randomized Prospective Crossover Studyalida romeroNo ratings yet
- Point of Care Coagulation Testing For P - 2022 - Best Practice - Research ClinicDocument16 pagesPoint of Care Coagulation Testing For P - 2022 - Best Practice - Research ClinicPaulHerreraNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Transfusion MedicineDocument83 pagesHemostasis and Transfusion MedicineJesserene Mangulad SorianoNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument6 pagesResearch Proposaldr.ahsanabid22No ratings yet
- Ribociclib Citratebased Liposomes With Regard To Successful Treating Rheumatismarcpp PDFDocument1 pageRibociclib Citratebased Liposomes With Regard To Successful Treating Rheumatismarcpp PDFpingun7No ratings yet
- Briggs2006 PDFDocument10 pagesBriggs2006 PDFRonal WinterNo ratings yet
- Use of Thromboelastography in Dogs With Immune-Mediated Hemolytic Anemia: 39 Cases (2000 2008)Document5 pagesUse of Thromboelastography in Dogs With Immune-Mediated Hemolytic Anemia: 39 Cases (2000 2008)soledadDC329No ratings yet
- Case Analysis Hemostasis and Coagulation PDFDocument5 pagesCase Analysis Hemostasis and Coagulation PDFGiannassablanNo ratings yet
- Thromboelastography (TEG) and Rotational Thromboelastometry (ROTEM) : Applications in AnesthesiaDocument25 pagesThromboelastography (TEG) and Rotational Thromboelastometry (ROTEM) : Applications in AnesthesiaDiana PredenciucNo ratings yet
- Massive Haemorrhage PPT en PDFDocument18 pagesMassive Haemorrhage PPT en PDFviaereaNo ratings yet
- DCR PresentationDocument34 pagesDCR PresentationHera YunataNo ratings yet
- Damage Control Resuscitation (DCR) : Respati Suryanto Dradjat Fkub/Rs Saiful Anwar MalangDocument34 pagesDamage Control Resuscitation (DCR) : Respati Suryanto Dradjat Fkub/Rs Saiful Anwar Malangbenny christantoNo ratings yet
- Pruebas de Coagulacion PDFDocument13 pagesPruebas de Coagulacion PDFmeds1313No ratings yet
- Hemostasis & Blood Coagulation: First Teaching Hospital Zhengzhou UnivDocument46 pagesHemostasis & Blood Coagulation: First Teaching Hospital Zhengzhou Univapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia 2009Document49 pagesHeparin Induced Thrombocytopenia 2009pannumdNo ratings yet
- Vein of Galen MalformationDocument69 pagesVein of Galen MalformationBhupendra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ecmo CoagulationDocument27 pagesEcmo CoagulationblakewilNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument22 pagesDisseminated Intravascular Coagulationanaeshkl100% (2)
- Laboratory Hemostatic DisordersDocument41 pagesLaboratory Hemostatic DisordersYohanna SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- PRP TechniqueDocument9 pagesPRP Techniquerandomaeiou7273No ratings yet
- BT CT PT PTTDocument31 pagesBT CT PT PTTCristineVillablancaNo ratings yet
- Exchange TransfusionDocument9 pagesExchange TransfusiondewpraNo ratings yet
- Thrombocytopenia Sarah WalterDocument49 pagesThrombocytopenia Sarah WalterSupicha VichaiditNo ratings yet
- Blood-Ordering For OtolaryngologyDocument5 pagesBlood-Ordering For OtolaryngologyDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Prothrombin TimeDocument8 pagesProthrombin Timeps piasNo ratings yet
- Liver Biopsy: Complications and Risk Factors: Pornpen Thampanitchawong and Teerha PiratvisuthDocument4 pagesLiver Biopsy: Complications and Risk Factors: Pornpen Thampanitchawong and Teerha PiratvisuthMauricio XimenesNo ratings yet
- Ying Li 2016Document8 pagesYing Li 2016Bogdan TrandafirNo ratings yet
- Atlas of 3D Transesophageal Echocardiography in Structural Heart Disease Interventions: Cases and VideosFrom EverandAtlas of 3D Transesophageal Echocardiography in Structural Heart Disease Interventions: Cases and VideosNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Liver Intensive CareFrom EverandPediatric Liver Intensive CareNaresh ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis and Bleeding Disorders: Theory and MethodsFrom EverandThrombosis and Bleeding Disorders: Theory and MethodsNils U. BangRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Xyloglucan and Gelose For The Treatment of Acute Diarrhea in ChildrenDocument8 pagesRandomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Xyloglucan and Gelose For The Treatment of Acute Diarrhea in ChildrenvalenciaNo ratings yet
- Neurological AssessmentDocument47 pagesNeurological AssessmentRian TheredNo ratings yet
- Journal of The California Dental Association Oct 2007Document70 pagesJournal of The California Dental Association Oct 2007gerardo_ureñaNo ratings yet
- Quiz On ModifierDocument2 pagesQuiz On ModifierHemar5No ratings yet
- Daftar Isi Paediatrica IndonesianaDocument16 pagesDaftar Isi Paediatrica IndonesianaYURIS WIRDANo ratings yet
- List of Private Hospitals and Diagnostic Centers Approved by INSADocument16 pagesList of Private Hospitals and Diagnostic Centers Approved by INSAvijay sainiNo ratings yet
- Meckel DiverticulumDocument5 pagesMeckel DiverticulumYulianto Arifin DjieNo ratings yet
- Hemorragia Subaracnoidea AneurismaticaDocument30 pagesHemorragia Subaracnoidea AneurismaticajulianaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cerebral InfarctDocument11 pagesCase Study Cerebral InfarctRodel MorlaNo ratings yet
- Domingues-Montanari-2017-Journal of Paediatrics and Child HealthDocument6 pagesDomingues-Montanari-2017-Journal of Paediatrics and Child Healthmedicina ucnNo ratings yet
- Porcelain Fused To Metal CrownsDocument5 pagesPorcelain Fused To Metal CrownsCitra Dwi PrastiwieNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument24 pagesBloodapi-310193189No ratings yet
- Gates Sample Chapter Neurology PDFDocument50 pagesGates Sample Chapter Neurology PDFpartha9sarathi9ain100% (1)
- Low Cobalt Diet For Dyshidrotic Eczema PatientsDocument5 pagesLow Cobalt Diet For Dyshidrotic Eczema PatientsMaulidianaIndahNo ratings yet
- Prof DR Ali Ghufron MuktiDocument3 pagesProf DR Ali Ghufron MuktiKhalid Bin Tatang HarmaenNo ratings yet
- Cardiomegaly, RadiologyDocument20 pagesCardiomegaly, RadiologyJia LingNo ratings yet
- Auditory Function Screening Devices - NewbornDocument25 pagesAuditory Function Screening Devices - NewbornAdriana FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument12 pagesDaftar PustakaRenata YolandaNo ratings yet
- Organizing:, RN, Man ProfessorDocument68 pagesOrganizing:, RN, Man Professorailyn pinedaNo ratings yet
- Serial ExtractionDocument21 pagesSerial Extractionabhay_narayane34560% (1)
- Pediatric Parenteral NutritionDocument62 pagesPediatric Parenteral NutritionPetruNo ratings yet
- Notification No. SO (SC) 1-13317 Seniority List of Consultants (BS-18) 1-3-18Document51 pagesNotification No. SO (SC) 1-13317 Seniority List of Consultants (BS-18) 1-3-18IrfanNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide in Availing Your BenefitsDocument19 pagesStep by Step Guide in Availing Your BenefitsJohn Reyder Domingo CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Respiratory SystemKhrycys Olairez RNNo ratings yet
- 5d S - S - Hospital & College of NursinghDocument6 pages5d S - S - Hospital & College of NursinghManish pandeyNo ratings yet
- 7 - Respiratory Emergencies and Thoracic Trauma PDFDocument112 pages7 - Respiratory Emergencies and Thoracic Trauma PDFRere AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Doctor's DatabaseDocument9 pagesDoctor's DatabaseMãçåbrê MähíNo ratings yet
- IAEA - Quality Assurance For PET and PET-CT SystemsDocument158 pagesIAEA - Quality Assurance For PET and PET-CT SystemsErwin SchrodingerNo ratings yet
- CardiologistDocument72 pagesCardiologistArun Talluri100% (1)
- Ketamine Blow DartDocument3 pagesKetamine Blow Dartandrew herringNo ratings yet