Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pedo Lab Case Presentation
Uploaded by
Rakan KhtoomCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pedo Lab Case Presentation
Uploaded by
Rakan KhtoomCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Pedo lab
Rakan Khtoum
Case Presentation
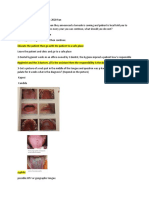
A child presenting with a permanent left central and lateral incisors and a primary
right central incisor. It is necessary in this case to take a radiograph.
The radiograph showed a presence of a supernumerary tooth that prevented the
eruption of the permanent incisor.
Writing a treatment plan
the information needed to draw a chart:
7s: unerupted.
16: amalgam restoration occlusally.
55: disto-occlusal cavity.
54: sound.
53: buccal caries.
11: Fractured mesially & incisally (due to trauma).
..
64: disto-occlusal cavity.
65: filling mesio-occlusally.
..
36: cavitated occlusally.
75: remaining root.
74: stainless steel crown (SSC).
..
LR primary 1
st
molar: extracted.
LR primary 2
nd
molar: mesial cavity.
46: recurrent caries.
85: mesial cavity.
2
The spaces between the teeth are closed.
Bitewings are needed to detect interproximal caries especially when spaces
between teeth are limited.
Periapical are needed for:
Tooth (74) to make sure that the tooth has received good treatment
(Pulpotomy + SSC) and it is still successful.
They are also needed for grossly carious teeth (Teeth 55, 64) to detect the
presence of any abscess, pulp necrosis and periapical radiolucency.
In case of extraction (LR primary 1
st
molar) to determine the need for space
maintainer.
Remaining root (tooth 75); to avoid complicated extraction.
Restored teeth.
Radiographic images showed the following results:
Tooth (55): interproximal caries in the mesial side extending to more than
thickness of enamel, while the distal carious lesion extends to more than
thickness of dentine.
Tooth (54): interproximal caries in the distal side extending to less than
thickness of enamel.
Tooth (65): interradicular lesion.
Tooth (75): interradicular lesion.
Tooth (64): distal carious lesion extending to less than thickness of
dentine.
Tooth (85): mesial carious lesion extending to less than thickness of
dentine.
3
Treatment plan
The first visit: Preventive OH instructions, Fluoride application & diet sheet.
Diet Sheet:
1
st
day 2
nd
day 3
rd
day
breakfast
In between
lunch
In between ) (
dinner
Dies sheet analysis:
1
st
2
nd
3
rd
Total
Solution Meal 0 0 1 1
In between 1 1 0 2
Retentive Meal 1 1 0 2
In between 1 0 2 3
We start treating the quadrant with the chief compliant. If there is no chief
compliant or emergent case, we usually start with the easiest quadrant.
The second visit: you give the patient OH instructions again and you do analysis
for the diet sheet you gave the patient in the first visit.
OH instructions are given in each visit.
Treatment plan for each quadrant
1
st
quadrant:
(53): Class V filling using glass ionomer or compomer.
(11): Class IV composite filling.
(55): pulpotomy + SSC.
4
2
nd
quadrant:
(64): Class II filling.
(65): Extraction.
Band selection for space maintainer.
3
rd
quadrant:
(75): Extraction.
Band selection for space maintainer.
4
st
quadrant
(46): repeat cavity preparation and restoration.
(85): class II filling.
Band selection on the (85) for band & loop space maintainer.
Patient name:
Patient File#: 11816
You might also like
- Dissociative Identity DisorderDocument66 pagesDissociative Identity DisorderTemesgen Endalew100% (1)
- Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisDocument6 pagesCavernous Sinus ThrombosisSulabh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Plastic & Hand Surgery in Clinical Practice: Classifications and DefinitionsFrom EverandPlastic & Hand Surgery in Clinical Practice: Classifications and DefinitionsNo ratings yet
- Adl IadlDocument20 pagesAdl IadlKrisna Eka Yudha100% (1)
- Oxygen Therapies: Interview With Ed MccabeDocument5 pagesOxygen Therapies: Interview With Ed MccabeOrlando Gunther100% (1)
- Nbde Part 2 RQSDocument6 pagesNbde Part 2 RQScecy83100% (1)
- Impacted Max CaninesDocument6 pagesImpacted Max CaninesAnkur AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Inductia ElmanDocument3 pagesInductia ElmanAlice Suru100% (2)
- MFD Part2 Pastpapers According To SubjectsDocument255 pagesMFD Part2 Pastpapers According To SubjectsEnea Nastri100% (3)
- Nbde Part 2Document10 pagesNbde Part 2prasanti67% (3)
- Assignment5.1 - Comfort Theory CritiqueFinalDocument8 pagesAssignment5.1 - Comfort Theory CritiqueFinalRacheal100% (1)
- Fetal Macrosomia ArtDocument14 pagesFetal Macrosomia Artanyka2No ratings yet
- ABGD Written Study Questions 2007Document291 pagesABGD Written Study Questions 2007Almehey NaderNo ratings yet
- Admission of PatientsDocument4 pagesAdmission of Patientsmftaganas100% (2)
- Ahmed SLE Mcq-P2 - E2 - 80 - AB - E2 - 80 - AC PDFDocument172 pagesAhmed SLE Mcq-P2 - E2 - 80 - AB - E2 - 80 - AC PDFMohamed Kudaih100% (4)
- Vivas For The Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery FRCS-WDocument241 pagesVivas For The Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery FRCS-Warisnicole588% (8)
- DR - Ahmed Rafat - Prometric Exam PreparationDocument35 pagesDR - Ahmed Rafat - Prometric Exam PreparationMrunal Doiphode100% (2)
- MCQ Review For Saudi Licensing Exam (SLE)Document0 pagesMCQ Review For Saudi Licensing Exam (SLE)Rakesh Kumar83% (6)
- Fundamentals of Oral and Maxillofacial RadiologyFrom EverandFundamentals of Oral and Maxillofacial RadiologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 349 DR - Alyaa 3-2016Document55 pages349 DR - Alyaa 3-2016Kartik R. MorjariaNo ratings yet
- ABGD Written Study Questions 2007Document291 pagesABGD Written Study Questions 2007velangni100% (1)
- Hand OITE - 2012 2013 2014Document209 pagesHand OITE - 2012 2013 2014Sadiq AliNo ratings yet
- Saudi Licence Exam For General DentistDocument161 pagesSaudi Licence Exam For General Dentistsalman701275% (4)
- 3280 4.19MB Strabismus - A Decision Making ApproachDocument206 pages3280 4.19MB Strabismus - A Decision Making ApproachPaulEstrellaNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment: Patient Information LeafletDocument2 pagesOrthodontic Treatment: Patient Information LeafletRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp TherapyDocument56 pagesVital Pulp Therapyapi-37103310% (1)
- Dha LastDocument197 pagesDha LastCarlos Vidal Tudela89% (27)
- Prometric Exam 2018Document8 pagesPrometric Exam 2018Sara Ben Amara100% (1)
- ORE MCQsDocument268 pagesORE MCQspawi18No ratings yet
- Myopia APDF PDFDocument14 pagesMyopia APDF PDFRao Sab100% (1)
- Questions 1 - 100Document15 pagesQuestions 1 - 100Vicky Cezar Villanueva50% (2)
- Enamel GenesisDocument32 pagesEnamel GenesisRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- JOSECITO Always in My ALONDRADocument121 pagesJOSECITO Always in My ALONDRAРами КальматNo ratings yet
- Rosel-Comprehensive Review For Saudi Licence Exam For General DentistDocument8 pagesRosel-Comprehensive Review For Saudi Licence Exam For General DentistRosel Macalipas67% (3)
- Imm Toacs Feb 2023Document57 pagesImm Toacs Feb 2023rehan hayderNo ratings yet
- DR - Alyaa 3-2016Document62 pagesDR - Alyaa 3-2016Fatima SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Oral Surgery SEQDocument15 pagesOral Surgery SEQManaal Tahir100% (1)
- September SDLEDocument6 pagesSeptember SDLEQq qNo ratings yet
- Influence of Chlorhexidine Rinsing On The Healing of Oral Mucosa and Osseous LesionsDocument15 pagesInfluence of Chlorhexidine Rinsing On The Healing of Oral Mucosa and Osseous LesionsAna Maria Montoya GomezNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0266435604002372 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0266435604002372 MainmaxilohgugmNo ratings yet
- Isolation of The Operating Field in DentistryDocument87 pagesIsolation of The Operating Field in DentistryDr.HarshNo ratings yet
- Surgery BookDocument95 pagesSurgery BookKhaled Mahmud100% (1)
- Impacted CanineDocument16 pagesImpacted CaninePakistan Dental SocietyNo ratings yet
- Imp NotesDocument15 pagesImp NotesDR-RASHEED KHANNo ratings yet
- 2018 Article 1362 PDFDocument5 pages2018 Article 1362 PDFAuliaMahdaniatiNo ratings yet
- NileDocument5 pagesNileHarjotBrarNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Flap Design On Wound Healing After PDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Flap Design On Wound Healing After PGauri AroraNo ratings yet
- Cvek PulpotomyDocument6 pagesCvek PulpotomyMartyNo ratings yet
- Cerny Fixed RetainerDocument88 pagesCerny Fixed Retainerchinchiayeh5699No ratings yet
- CSDH ArticleDocument9 pagesCSDH ArticleAtharv SinghNo ratings yet
- Educate The Patient Then Go With The Patient To A Safe PlaceDocument30 pagesEducate The Patient Then Go With The Patient To A Safe PlaceghanimNo ratings yet
- #Prometric - 25 - 1 - 2015: Not Correct Bec Good Speech&masticationDocument6 pages#Prometric - 25 - 1 - 2015: Not Correct Bec Good Speech&masticationSubhajit SahaNo ratings yet
- Trauma Q&ADocument8 pagesTrauma Q&ANoor MaxeemNo ratings yet
- Exodontia Principles and Techniques: DR - BILLAL 49DDCH - 2017Document29 pagesExodontia Principles and Techniques: DR - BILLAL 49DDCH - 2017D YasIr MussaNo ratings yet
- Balanced Semi StaticDocument14 pagesBalanced Semi StaticRadhika SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- #Prometric - 25 - 1 - 2015: Not Correct Bec Good Speech&masticationDocument6 pages#Prometric - 25 - 1 - 2015: Not Correct Bec Good Speech&masticationSubhajit SahaNo ratings yet
- Dento - Alveolar InjuriesDocument34 pagesDento - Alveolar InjuriesdrelvNo ratings yet
- Clinical Study of Retraction Pockets in Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument4 pagesClinical Study of Retraction Pockets in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Mediavivy iskandarNo ratings yet
- Canine Impaction and Its ManagementDocument20 pagesCanine Impaction and Its Managementsidra.15656No ratings yet
- Lec 8 Cep Halo MetricDocument12 pagesLec 8 Cep Halo MetricHuda AljaderiNo ratings yet
- Management of Chylous LeakDocument5 pagesManagement of Chylous Leakdrnitinkaushik4931No ratings yet
- All April 2018Document32 pagesAll April 2018ravi guptaNo ratings yet
- Suleiman 2004Document16 pagesSuleiman 2004Cristián SanchezNo ratings yet
- 4 Suturas RinoplastiaDocument5 pages4 Suturas RinoplastianefimdNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of One Versus Two Appointment EndodonticDocument6 pagesA Comparison of One Versus Two Appointment EndodonticShurinam Zaidel Sinain MadariagaNo ratings yet
- 2003 ExamDocument10 pages2003 ExamBibek Raj100% (1)
- Preseptal Transconjunctival Approach in Orbital Rim FractureDocument4 pagesPreseptal Transconjunctival Approach in Orbital Rim FracturevonnyNo ratings yet
- 90 CasosDocument5 pages90 CasosroomaarlopezsalgadoNo ratings yet
- The Scrub's Bible: How to Assist at Cataract and Corneal Surgery with a Primer on the Anatomy of the Human Eye and Self AssessmentFrom EverandThe Scrub's Bible: How to Assist at Cataract and Corneal Surgery with a Primer on the Anatomy of the Human Eye and Self AssessmentNo ratings yet
- Local Flaps in Facial Reconstruction: A Defect Based ApproachFrom EverandLocal Flaps in Facial Reconstruction: A Defect Based ApproachNo ratings yet
- Osu 1331067181Document67 pagesOsu 1331067181Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- JP Journals 10021 1110Document4 pagesJP Journals 10021 1110Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- AndrewsDocument12 pagesAndrewsCarlitos LaizaNo ratings yet
- Applsci 11 06439 v3Document17 pagesApplsci 11 06439 v3Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- 14985-Article Text-29120-1-10-20210409Document6 pages14985-Article Text-29120-1-10-20210409Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Molecules: Ffect of Partial Corticotomy On The Rate ofDocument11 pagesMolecules: Ffect of Partial Corticotomy On The Rate ofRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Teeth and Brace Friendly Food and Drink PDFDocument2 pagesTeeth and Brace Friendly Food and Drink PDFRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Your First VisitDocument2 pagesYour First VisitRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Teeth and Brace Friendly Food and Drink PDFDocument2 pagesTeeth and Brace Friendly Food and Drink PDFRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Pink Esthetic ScoreDocument6 pagesPink Esthetic ScoreEstefania Beltran TatesNo ratings yet
- How To Keep Your Teeth and Gums HealthyDocument2 pagesHow To Keep Your Teeth and Gums HealthyRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Impacted Canines: Patient Information LeafletDocument2 pagesImpacted Canines: Patient Information LeafletRakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- Local Analgesia10.5.11Document14 pagesLocal Analgesia10.5.11Rakan KhtoomNo ratings yet
- FY 1 Antimicrobial PrescriptionDocument10 pagesFY 1 Antimicrobial Prescriptiongus_lionsNo ratings yet
- Secondary SurveyDocument2 pagesSecondary SurveySakta SuryagunaNo ratings yet
- Ob2rle Sas 1Document13 pagesOb2rle Sas 1Meow MeowNo ratings yet
- Retropharyngeal AbscessDocument1 pageRetropharyngeal AbscessJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- Dfd-Example-ContextdiagramDocument3 pagesDfd-Example-ContextdiagramعديلسليمNo ratings yet
- 2017-4-12 7.59.10-Main Catalogue Neuro 2015 Roboz TechDocument256 pages2017-4-12 7.59.10-Main Catalogue Neuro 2015 Roboz TechRoboz TechNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument18 pagesChronic Renal FailureJoan Carla BocoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Patient Centred Communication 20-21Document16 pagesIntroduction To Patient Centred Communication 20-21Ngetwa TzDe TheWirymanNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue CalcificationDocument13 pagesSoft Tissue CalcificationReuben Abraham JacobNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) Sanglah General Hospital 2012Document28 pagesFailure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) Sanglah General Hospital 2012ferekonstantinusNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP Risk For Electrolyte ImbalanceLouie ParillaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam: Theory of Nursing SystemsDocument2 pagesFinal Exam: Theory of Nursing SystemsXeian Calamba RafaelNo ratings yet
- Flap HemisoleusDocument6 pagesFlap HemisoleuscweetblueNo ratings yet
- Agreement, Compliance or Permission Given Voluntarily Without CompulsionDocument8 pagesAgreement, Compliance or Permission Given Voluntarily Without CompulsionRaihana RafiNo ratings yet
- Ect BrochureDocument2 pagesEct Brochureapi-283706202No ratings yet
- NCP Proper TahbsoDocument3 pagesNCP Proper TahbsoMiriam EstradaNo ratings yet
- Final Past Papers With Common MCQS: MedicineDocument17 pagesFinal Past Papers With Common MCQS: MedicineKasun PereraNo ratings yet
- Medical AbbreviationDocument76 pagesMedical AbbreviationNajwa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Professional Services, Inc. vs. NatividadDocument13 pagesProfessional Services, Inc. vs. NatividadEarleen Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Service Delivary Organization Realignment: A Message From Karen Herd, Deputy Minister of Manitoba Health, Seniors and Active LivingDocument4 pagesService Delivary Organization Realignment: A Message From Karen Herd, Deputy Minister of Manitoba Health, Seniors and Active LivingmatthewtrevithickNo ratings yet