Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1
Uploaded by
jimmytanlimlongOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1
Uploaded by
jimmytanlimlongCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Let x, y and z be the number of adult, children and senior citizen tickets sold respectively.
x +y +z =500
7.50x +4.00y +3.50z =3025
x =2y
x +y +z =500
7.50x +4.00y +3.50z =3025
x 2y =0
Using GC, we get
i.e. x =300, y =150, z =50
Hence, 300 adult tickets, 150 children tickets and 50 senior citizen tickets were sold.
Alternative method:
Let the number of children tickets, adult tickets and senior citizen tickets sold be x, 2x and (500
3x) respectively.
2x(7.50) +x(4.00) +(500 3x)(3.50) =3025
15x +4x +1750 10.5x =3025
8.5x =1275
x =150
Hence, 150 children tickets, 300 adult tickets and 50 senior citizen tickets were sold.
2
d
d
1
d d
ln
,
kt C
x
kx
t
x k t
x
x kt C
x Ae A e
=
=
= +
= =
When 50 5371 t , x . = =
50
5.731 (1)
k
Ae =
Since it has a half-life of 16 days, when 34, 11.462 t x = =
34
11.462 (2)
k
Ae =
16
1 1 1
(1) (2) ln
2 16 2
k
e k = =
50 1
ln
16 2
5.731 50 Ae A = =
1 1
ln
16 2
50
t
x e =
When 0, 50 t x = =
3
Let
n
P be the proposition
2
2
1
(2 1) ( 1)
n
r
r
r n n
=
+ =
for 1 n
When n =1, LHS =
1 2 2 2
( 1) ( 1 ( ) ) (1) 3 2 + =
RHS =1(2(1) 1) 3 + = =LHS
Thus P
1
is true.
Assume P
k
is true for some k
+
i.e.
2
2
1
(2 1) ( 1)
k
r
r
r k k
=
+ =
When 1 n k = + ,
2( 1)
2 2 1 2 2 2 2
1
2 2
2 2 2
2
LHS (2 1) (
(2 1) ( 1)(2 1)
2
2 5 3
(2 3)( 1)
( 1)(2( 1) 1)
( 1) ( 1) 2 1) ( 1) (2 2)
(2 2)
4 4 1 4 8 4
RHS
k
r k k
r
r k k
k k k
k k
k
k
k k
k k
k
k k k k k
k
+
+ +
=
= = +
= + + +
=
= + +
= +
+ + + +
+ +
+ + +
+
= + + =
+
+
Thus P
k+1
is true.
Since P
1
is true and if P
k
is true implies P
k+1
is true, then by MI, P
n
is true for all n
+
.
92
2
5
92 4
2 2
1 1
8464
( 1)
( 1) ( 1)
46(92 1) 2(4 1) 42
25 36 49
68
r
r
r r
r r
r
r r
=
= =
+
=
=
= + + =
+ +
4 .(i) 0.15 d x =
[2 ( 1)0.15 ]
2
(2 0.15 0.15)
2
(1.85 0.15 )
2
(185 15 )
200
5
(37 3 )
200
(37 3 )
40
n
n
S x n x
nx
n
nx
n
nx
n
nx
n
nx
n
= +
= +
= +
= +
= +
= +
(ii) 1.1 r =
( 1)
1
[(1.1) 1]
1.1 1
[(1.1) 1]
1.1 1
[(1.1) 1]
0.1
10 [(1.1) 1]
n
n
n
n
n
n
a r
S
r
x
x
x
x
=
=
(iii)
(37 3 ) 10 [(1.1) 1]
40
(37 3 ) 400[(1.1) 1]
n
n
nx
n x
n n
+ <
+ <
Least 14 n =
5
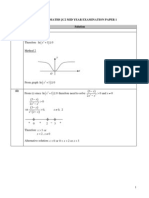
From Argand diagram, 2 2i z =
(i)
4 2
sin
4 6 2
w+
=
4 2 6 w+ =
(ii)
2
tan
5 2
= 0.19740 = or 11.310
Distance from point representing 4 2 to centre of circle =
( ) ( )
2 2
5 2 2 52 + =
2
sin
52
= 0.28103 = or 16.102
greatest possible value of
( )
arg 4 2 0.478 z + = + = (3 s.f.) or 27.4
(1 d.p.)
Im
Re
2 2i C a = +
2 a =
locus of z
locus of w
3
4
2 2
4 2
6(a)
(b)
(i)
( ) ( )
2 2
3 3
2 2
2 2
1
2 5d 4 2 5d
4
1 2 1
2 5 2 5
4 3 6
x x x x x x
x C x C
=
= + = +
(ii)
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
3 2 2 2
3 3
2 2 2
2 2
3 3
2 2 2
2 2
3 5
2 2 2
2 2
3 5
2 2 2
2 2
2 5d 2 5 d
1 1
2 5 2 5 d
6 3
1 1 1
2 5 4 2 5 d
6 3 4
1 1 2
2 5 2 5
6 12 5
1 1
2 5 2 5
6 30
x x x x x x x
x x x x x
x x x x x
x x x C
x x x C
=
=
=
= +
= +
1 0.5 1
2 2 2
1 1 0.5
2 1 2 1 2 1
d d d
1 1 1
x x x
x x x
x x x x x x
| | | |
= +
| |
+ + + \ . \ .
0.5 1
2 2
1 0.5
ln 1 ln 1 x x x x
( (
= + + +
3 3
ln ln3 ln1 ln
4 4
( ( | | | |
= + +
| | ( (
\ . \ .
3
ln3 2ln
4
| |
=
|
\ .
3 16
ln ln
9
3
16
| |
| |
|
= =
|
|
\ .
\ .
( )
2 2
3
2
2
2 5
1
2 2 5
6
dv
u x x x
dx
du
x v x
dx
= =
= =
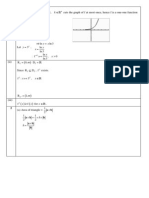
7 Equations of asymptotes: 0, y x a = =
2 2
3 3 4
( ) 4 ) 4 (2( )) 4 ( ) 8 4 4
) ( ) ( )
(
(
x a a ax x a a x a ax ax a
x a x a x a
dy
dx
= =
=
2
3
4 4
0
( )
ax a
x a
x a
= =
,
2
2 2
4 ( ) 4
1
( ) 4
a a a
y
a a a
= = =
Coords of turning point =( , 1) a
Axial intercepts: (0,0)
4 2 2 2 2
2 2
2 2 2
4 2
( ) (
4
) 16
1
( )
)
6
( ( )
x a x
ax
x a
x a x a
a a x
a x
= =
=
Thus we draw the graph
2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2
1 y x x a a
x y
y
a a
= = = (a
hyperbola)
No of real roots=2
x
y
x=a
(a, 1)
x
y
x=a
(a, 1)
2
4
( )
ax
y
x a
=
0 y =
8
(i)
(ii) Area of R =
0
3
d y x
When
2 2
3, 4 3 4 3 0 x t t t t = + = + + =
3(rejected) or 1 t t = =
When
2
0, 4 0 x t t = + =
4(rejected) or 0 t t = =
( )
2
4 d 2 4 d x t t x t t = + = +
Area of R
( )
( )
0
3 2
1
2 4 d t t t t
= + +
( )
0
4 3 2
1
2 6 4 d t t t t
= + +
0
5 4 3
1
2 3 4
5 2 3
t t t
(
= + +
(
7
30
= units
2
(iii) Volume of S rotated about x-axis
( ) ( )
12
2 2 2
5
12 12 2 5 d y x =
( )
( )
2 2
3 2
1
1728 20 2 4 d t t t t = + +
4302units
3
y
x
(12,12)
(4,4)
(0,0)
(3,0)
R
12
2
12 5
S
9 Solutions:
(i) perimeter p =3x +2y
3
2
p x
y
=
Area S =area of ABE +area of BCDE
=
2
1
sin60
2
x xy +
=
2
3 3
4 2
p x
x x
| |
+
|
\ .
=
2 2
3 3
2 2 4
p
x x x + (shown)
(ii) Differentiate
2 2
3 3
2 2 4
p
S x x x = + wrt x:
d 3
3
d 2 2
S p
x x
x
= +
For stationary value,
d
0
d
S
x
= ,
3
3 0
2 2
3
3
2 2
p
x x
p
x x
+ =
=
3
2 3
2
6 3
p
x
| |
=
|
|
\ .
=
6 3
6
p
x
a
=
=
2
2
d 3
3 0( max area S)
2 d
S
x
= + <
(iii)
2 2
3 3
2 2 4
p
S x x x = +
( )
2
2
1 3 3
2 2 4
1 3 3
6 3
2 2 4 6 3
p
S x
x
p
(
| |
= +
(
|
\ .
(
| |
= +
( |
\ .
( )
( )
( )
2
2
2
2 6 3 6 3
4
6 3
4 6 3
p
p
(
+
(
=
(
10
.
sin 1 cos
cos sin
dx
x
dt
dy
y
dt
= =
= =
Equation of tangent at P
2
2 2
2 2
sin
cos ( sin 1)
cos
cos cos sin ( sin 1)
cos cos sin sin sin
cos cos sin sin sin
cos 1 sin sin
y x
y x
y x
y x
y x
= +
= +
= +
= +
=
Equation of normal at P
cos
cos ( sin 1)
sin
sin cos sin cos cos sin cos
sin cos cos
y x
y x
y x
= +
= +
= +
When y x =
sin cos cos
(sin cos ) cos
cos
(sin cos )
x x
x
x
= +
=
=
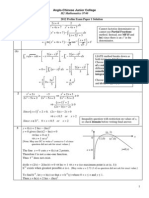
R
cos cos
( , )
sin cos sin cos
When y x =
sin cos cos
(cos sin ) cos
cos
cos sin
x x
x
x
= +
+ =
=
+
S
cos cos
( , )
cos sin cos sin
+ +
2 2
2 2
cos cos cos
OR ( ) ( ) 2( )
sin cos sin cos sin cos
cos cos cos
OS ( ) ( ) 2( )
cos sin cos sin cos sin
= + =
= + =
+ + +
2
2 2
1 cos cos
2( ) 2( )
2 cos sin sin cos
cos
sin cos
Area
=
+
=
R
S
O
2 2
2 2
sin 1 sin 1
cos
sin cos 1
( 1) 1
x x
y
x y
= = +
=
+ =
+ + =
11 (i) since line
1
l lie on plane
1
and is perpendicular to
3i + j +k
,
3 1 1
1 2 4
1 1 7
m
| | | | | |
| | |
= =
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
Eq of line
1
l :
3 1
1 4
2 7
r
| | | |
| |
= +
| |
| |
\ . \ .
(ii) distance between A and plane =
2 3
2 1
1 2
4
4 4 1
c
| | | |
| |
| |
| |
\ . \ .
=
+ +
6 2 2
4
3
6 12
6,18( )
c
c
c rejected
+
=
=
=
(iii) normal of the x-y plane =
0
0
1
| |
|
|
|
\ .
0 1
0 2
1 1
1
cos
1 1 4 1 6
65.9
| | | |
| |
| |
| |
\ . \ .
= =
+ +
=
(iv)
1
2
: 2 3
:2 2 6
x y z
x y z
+ + =
+ + =
Line of intersection is
3 0
3 1
0 2
| | | |
| |
= +
| |
| |
\ . \ .
r
(v) normal of plane
3
2 0 5
2 1 4
1 2 2
| | | | | |
| | |
= =
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
3
5 3 5
: 4 1 4 15
2 2 2
| | | | | |
| | |
= =
| | |
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
r
(vi) Right-angled triangular prism
You might also like
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document7 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document11 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document22 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math SolnDocument15 pages2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math Solnckhowh_23284524667% (3)
- HCI 2008 Promo W SolutionDocument12 pagesHCI 2008 Promo W SolutionMichael CheeNo ratings yet
- 2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsDocument11 pages2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsLionel Torres LeeNo ratings yet
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Document12 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Nyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionDocument10 pagesNyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chapter 13 AnswersDocument8 pagesUnit 2 Chapter 13 AnswersashtigosineNo ratings yet
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument10 pagesNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2Document15 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- TJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument12 pagesTJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document10 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2009 NYJC H2 Maths PromoDocument6 pages2009 NYJC H2 Maths PromoSapphireansNo ratings yet
- CJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesCJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1Document8 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- RI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument13 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2006 AJC H2 MY SolnDocument9 pages2006 AJC H2 MY Solnjunie9201No ratings yet
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document5 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- ACJC Maths Promos 2005Document3 pagesACJC Maths Promos 2005Suphadetch LeungNo ratings yet
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument6 pagesACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Ri h2 Math p2 SolutionsDocument11 pagesRi h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- IJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document8 pagesIJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsDocument21 pages2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsNicholas ChoyNo ratings yet
- Math 2009 Promos SolutionsDocument8 pagesMath 2009 Promos SolutionsMichael CheeNo ratings yet
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document3 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Acjc h2 Maths p1 QN PaperDocument6 pagesAcjc h2 Maths p1 QN Papervincesee85No ratings yet
- 2010 AJC H2 Math Promo With AnswersDocument8 pages2010 AJC H2 Math Promo With AnswersCindy KrisnadiNo ratings yet
- 2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 SolutionDocument13 pages2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 Solutioncherylhzy0% (4)
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2010 TJC SolDocument12 pages2010 TJC SolPooja KapurNo ratings yet
- Dhs Jc1 h2 Maths 2012 Promo SolutionsDocument13 pagesDhs Jc1 h2 Maths 2012 Promo SolutionsRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- 2014 - DHS - Prelim Paper 2Document7 pages2014 - DHS - Prelim Paper 2Ng Shu QingNo ratings yet
- 2012 SH1 H2 Math CT Revison Package SolutionsDocument89 pages2012 SH1 H2 Math CT Revison Package SolutionsAnnabel Seah0% (1)
- CJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesCJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2013 HCI C1 Block Test H2 Mathematics Revision Package SolutionsDocument80 pages2013 HCI C1 Block Test H2 Mathematics Revision Package SolutionsGabriel Francis ChuaNo ratings yet
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Ajc H2 Math P1Document6 pagesAjc H2 Math P1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1Document18 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 2006 AJC H2 Maths Promo - QuestionsDocument6 pages2006 AJC H2 Maths Promo - QuestionsniveumaNo ratings yet
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document5 pagesAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document7 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlong0% (1)
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- JC 1 H2 Maths Promo Practice Paper 1Document6 pagesJC 1 H2 Maths Promo Practice Paper 1brianfletcher182No ratings yet
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document10 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- TPJC Promo 2008Document11 pagesTPJC Promo 2008MathathleteNo ratings yet
- Dhs h2 Math p1 SolutionDocument11 pagesDhs h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- VJC 2015 H2 J1 Math Promos Questions Singapore JC VictoriaDocument5 pagesVJC 2015 H2 J1 Math Promos Questions Singapore JC VictoriaAlxNo ratings yet
- ACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)Document9 pagesACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)RaymondZhangNo ratings yet
- HCI H2 Maths 2012 Prelim P1 SolutionsDocument12 pagesHCI H2 Maths 2012 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695No ratings yet
- Mi h2 Math Solutions p1Document10 pagesMi h2 Math Solutions p1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- BT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)Document111 pagesBT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)gerwynngNo ratings yet
- 2013 NJC H2 Econs Paper 2 (Answers)Document34 pages2013 NJC H2 Econs Paper 2 (Answers)jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- J1 Lecture - Technology Part 1 - 2aDocument8 pagesJ1 Lecture - Technology Part 1 - 2ajimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Equations Is Correct? (A) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/s (B) 8 J 2 KG × (2 M/S) (C) 8 J 2 KG × 2 (M/S) (D) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/sDocument1 pageWhich of The Following Equations Is Correct? (A) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/s (B) 8 J 2 KG × (2 M/S) (C) 8 J 2 KG × 2 (M/S) (D) 8 J 2 KG × 4 M/sjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument13 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- TPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesTPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Section B AnsDocument7 pagesSection B AnsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- VJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesVJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- RI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesRI JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1Document18 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- TJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument12 pagesTJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- SRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2Document15 pagesSRJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument10 pagesNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document7 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlong0% (1)
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Document10 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1Document5 pagesNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1Document8 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- PJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2Document6 pagesPJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Question Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- CJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesCJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document10 pagesMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- IJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2Document8 pagesIJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Questions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- CJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesCJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam QuestionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- MGFDocument3 pagesMGFJuhi Taqwa Famala IINo ratings yet
- MATH7MELC8Document2 pagesMATH7MELC8Donabel CariosNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Natural Logarithm of Complex NumbersDocument5 pages1.5 Natural Logarithm of Complex NumbersTyrone PaulinoNo ratings yet
- 19MT1201 Mathematics For Engineers PDFDocument2 pages19MT1201 Mathematics For Engineers PDFChaitanya CheyNo ratings yet
- Slide Rule UsageDocument17 pagesSlide Rule UsageschmurtzNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus ReviewDocument75 pagesAP Calculus ReviewJuliaNo ratings yet
- 1145 Tut 1 SolutionDocument4 pages1145 Tut 1 SolutionGulbanu KarimovaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Límites Propuestos en BiDocument3 pagesEjercicios de Límites Propuestos en BiLara SánchezNo ratings yet
- O'level MATHEMATICS TRIGONOMETRY REVISIONDocument9 pagesO'level MATHEMATICS TRIGONOMETRY REVISIONelishabagalwNo ratings yet
- Texr Func. Trascendentales PurcellDocument122 pagesTexr Func. Trascendentales PurcellAdriana MonteroNo ratings yet
- Claret College of IsabelaDocument5 pagesClaret College of IsabelaEmamMsHome-hyhyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Singular PointsDocument4 pagesClassification of Singular PointsBala BalajiNo ratings yet
- AsaynmentDocument4 pagesAsaynmentMarlou BenemeritoNo ratings yet
- MSC MathematicsDocument21 pagesMSC MathematicsshivaiahvNo ratings yet
- Calculsu 7 - 3 Practice PDFDocument2 pagesCalculsu 7 - 3 Practice PDFspeterlee6253No ratings yet
- Differentiation: and It'S ApplicationsDocument25 pagesDifferentiation: and It'S ApplicationsShoxan AliNo ratings yet
- w8 q1 l17 Rational and Irrational NumbersDocument22 pagesw8 q1 l17 Rational and Irrational NumbersRiana Margaret S. IngresoNo ratings yet
- Revit Basic FormulaDocument3 pagesRevit Basic FormulaDadii CrisNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric GraphsDocument1 pageTrigonometric GraphsBlaine RogalskiNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers and The Complex Exponential: Figure 1. A Complex NumberDocument19 pagesComplex Numbers and The Complex Exponential: Figure 1. A Complex NumberHimraj BachooNo ratings yet
- The Algebra of Complex NumbersDocument2 pagesThe Algebra of Complex NumbersAdnan NajemNo ratings yet
- Analytic Functions MCQ +notesDocument20 pagesAnalytic Functions MCQ +notesECE A SRM VDP81% (192)
- Renault Clio Gearbox DiagramDocument3 pagesRenault Clio Gearbox DiagramWawan SatiawanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics HSSC I Annual 2017 FbiseDocument15 pagesMathematics HSSC I Annual 2017 FbiseimtiazNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 Laplace Transform TablesDocument5 pagesModule 3.1 Laplace Transform TablesrupinsgmNo ratings yet
- Generating Functions: 1 From Recurrences To Closed FormDocument9 pagesGenerating Functions: 1 From Recurrences To Closed FormvarunNo ratings yet
- Concise Selina Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 22 Trigonometrical RatiosDocument28 pagesConcise Selina Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 22 Trigonometrical RatiosredNo ratings yet
- Centurion University of Technology & Management:: Paralakhemundi OdishaDocument15 pagesCenturion University of Technology & Management:: Paralakhemundi OdishaSadhan PadhiNo ratings yet
- Integration by PartsDocument5 pagesIntegration by PartsJoeSchmoe99999No ratings yet