Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Meo Oral Ans
Uploaded by
Kapil VermaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Meo Oral Ans
Uploaded by
Kapil VermaCopyright:
Available Formats
What all entries are entered in BDN (Bunker Delivery Note) ?
. Name of Barge/Port
b. Position of vessel.
c. Delivery date
d. IMO number
e. Gross tonnage of Vessel
f. Vessel name
g. Time of starting
h. Time of stopping
i. Product name & code
j. Viscosity at 50 Degree C
k. Density @ 15C
l. Water Content % V/V
m. Flash Point C
n. Sulphur Content % m/m
o. Pour Point C
p. Quantity taken @ 35C
What all equipments are carried in a Life boat of a ship?
1. Sufficient buoyant oars
2. 2 boat hook.
3. 2 Buckets
4. 6 Hand Flares
5. 2 Rocket parachutes
6. 2 smoke signals.
7. EPIRB
8. SART
9. Food Ration.
10. 1 knife and 3 tin opener.
11. Hand Pump
12. Tow line
13. Anti-sea sickness tablets
14. 1 set of fishing tackles.
15. Waterproof torch
16. Day light signalling lamp.
17. Radar reflector
18. First Aid Kit
19. Tools
20. Compass
21. Sea Anchor
22. 1 Whistle
23. Portable fire extinguisher
24. Thermal Protective aid
Procedure for lowering of a Life boat ?
1.
1. Minimum of 5 persons are required to lower the L/B.
2. One person goes inside the L/B and passes the end of toggle painter and plugs the drain.
3. Check all lifeline and falls are clear of L/B.
4. Make fast the other end of toggle painter on a strong point forward of the ship.
5. Remove forward and aft gripes and both person stand by for passing bowing tackle and tricing
pendant.
6. Remove harbour safety pin.
7. Make sure the ships side is free of everything, no water or garbage is there.
8. Now, one person lifts the dead mans handle slowly which releases the brake.
9. The boat along with cradle sides downward till it comes to the embarkation deck.
10. By pulling tricing pendant , bring it alongside the embarkation deck.
11. Persons embark inside the boat.
12. Now, tricing pendant is removed and the whole load comes on falls.
13. Now, boat is further lowered with deadmans handle.
14. As soon as the boat comes around 1meter above the sea-water, it can be released.
Explain Emergency fire Pump on board ship Location, Capacity and How to check its
performance
Location of Emergency Fire pump :- The space containing the pump should not
be contiguous to the boundaries of machinery space or those spaces containing main fire
pumps.
Normally located at : Steering Gear Compartment, Aft of Collision Bulkhead, Shaft Tunnel,
Forward part of ship.
Capacity:- Shall have capacity not less than 25 m3/hr & pump should be able to
deliver water at following pressure with two hydrants opens:
Passenger Ship above 4000 GRT :- 4 bar
Passenger ship below 4000 GRT :- 3 Bar
Cargo ship above 6000 GRT :- 2.7 Bar
Cargo ship below 6000 GRT :- 2.5 bar
The throw at the top most deck should not be less 12 meter.
Emergency Generator- Location & services or power supplied.
Location:- Should be on the uppermost continuous deck outside from the engine room but not
located at the forward collision bulkhead.
Services Supplied:-
(a) For a period of 3 Hrs at Emergency lighting at every muster & embarkation station.
(b) For a period of 18 hrs at:-
(i) In all service & accommodation alleyways, stairways & exits, personal lift cars &
personnel lift trunks.
(ii) In the machinery spaces & main generating stations including their control positions.
(iii) In all control stations, machinery control rooms, and at each main & emergency
switchboard.
(iv) At all stowage positions.
(v) At the steering gear.
(vi) At the fire pump & in all cargo pump rooms.
(vii) The navigational lights.
(viii) VHF & MF Radio installation.
(ix) The ship earth radio station.
(x) At all internal communication equipment
(xi) The fire detection & fire alarm system.
(xii) Intermittent operation of the daylight signalling lamp & all integral signals that are
required in an emergency.
Explain Regulations of Air pollution - NOx, SOx, ODS and Volatile substance
MARPOL Annex VI:- Regulation for the prevention of pollution by air from ships.
Regulation 12:- Ozone depleting Substance
Any deliberate emissions of Ozone depleting substance shall be prohibited. Deliberate
emissions include emissions occurring in the course of maintaining, servicing, repairing or
disposing of systems or equipments.
New installations which contain ozone depleting substance shall be prohibited on all ships,
except that new installations containing HCFCs are permitted until January 2020.
The substances & equipment containing such substances, shall be delivered to appropriate
reception facilities when removed from ships.
Regulation 13:- Nitrogen Oxide(NOx)
This regulation applies to the diesel engine with a power output of more than 130 KW which is
installed on a ship constructed on or after 1st January2000. & to diesel engines with a power
output of more than 130 KW which has undergone major conversion on or after 1st
January2000.
This regulation does not applies to emergency diesel engine, engines installed in lifeboats & any
device intended to be used solely in case of emergency.
Limits of NOx:-
a. 17.0 g/Kw-h when n less than 130 rpm.
b. 45.0 x n -0.2 g/Kw-h when is 130 or more but less than 2000 rpm
c. 9.8 g/Kw-h when n is 2000 rpm or more.
Regulation 14:- Sulphur Oxide (Sox)
The sulphur content of any fuel used on board ships shall not exceed 4.5% m/m.
In SECA Area the sulphur content should not exceed 1.5% m/m.
If in SECA area fuel used is having sulphur content more than 1.5% m/m , then exhaust gas
cleaning system to be provided to limit emission of Sox to 6.0g Sox /Kw-h or less.
Regulation 15:- Volatile Organic Compound
Regulation 16:- Shipboard Incineration
Alarms and trips of boiler and IG system
Alarms in IG System
a. Scrubber High Level
b. Scrubber low level
c. Deck seal High level
d. Deck seal low level
e. High O2 Content
f. High blower casing temp.
g. Low lube oil pressure alarm.
Trips in IG System
a. High Casing Temp. trip
b. Low lube oil pressure trip.
c. Low/ no flow scrubber water
d. Low / no flow deck seal water.
e. High boiler pressure trip.
f. Low boiler pressure trip.
Alarms in Boiler
a. Low water level Alarm
b. Too low water level alarm.
c. High water level alarm
d. High fuel oil temp. alarm.
e. Low fuel oil temp. alarm
f. Low boiler pressure alarm.
Trips in Boiler
a. Low Low level water trip
b. High boiler pressure trip.
c. Flame failure
d. Low fuel oil pressure trip.
What are the entries in a Oil record Book? (MARPOL Annex 1. Regulation 17)
As per MARPOL Annex 1. Regulation 17. Regulation for the prevention of pollution by oil.
Enteries done in Oil Record book are:-
a. Ballasting or cleaning of fuel oil tanks.
b. Discharge of dirty ballast or cleaning water from fuel oil tanks.
c. Collection & disposal of oil residues, sludge & bilge oil.
d. Bunkering of fuel or bulk lubricating oil.
e. Any failure of the Oil Filtering Equipment.
f. Date & time of the operation.
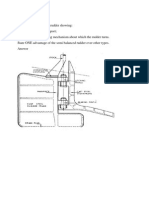
What is Rudder wear Down, Rudder Drop, Jumping Clearence. What is its purpose and
how it is measured?
Rudder wear down refers to the measurements taken generally during a docking period to
indicate excessive wear in the steering gear system particularly the rudder carrier. This wear
down or rudder drop is measured using a special L shaped instrument called Tramel. When the
vessel is built a distinct centrepunch mark is placed onto the ruder stock and onto a suitable
location on the vessels structure, here given as a girder which is typical. The trammel is
manufactured to suit these marks As the carrier wears the upper pointer will fall below the
centrepunch mark by an amount equal to the wear down.
Rudder Clearance
Pads are welded to the hull and rudder. A clearance is given ( sometimes refered to as the
jumping clearance). As the carrier wears this clearance will increase
(Join this site to get all updated oral and important questions)
What is CAS (Condition Assessment Scheme)?
CAS- Condition Assessment Scheme
Tanker type 1:- Oil Tankers above 20000 DWT, not having segregated ballast tank(SBT)
Tanker Type 2:- Oil tankers above 20000 DWT having SBT.
Type 1 tankers have already been phased out by 2005.
CAS Applies to only Type 2 tankers. Which are to be phased out in segregated manner by April
2015.
CAS is a method of checking structural integrity of ship, & its certification by regular inspection
by authority. The said inspections are carried on annually by authorities.
ISM Code, It's Purpose and certificates issued for ISM code
ISM Code:- As per SOLAS Chapter IX. Management for the Safe Operation of Ship.
ISM is International Safety Management Code for safe operation of ships & for pollution
prevention as adopted.
Purpose of this code is to provide an international standard for safe management and operation
of ships and for pollution prevention.
The objective is to ensure safety at sea, prevention of human injury or loss of life & avoidance of
damage to the environment , in particular to marine environment and to property.
certificate issued for ISM code.
DOC- Document of Compliance . Valid for 5 years
SMC- Safety Management Certificate. Valid for 5 Years
Interim DOC- Valid for 12 months.
Interim SMC- Valid for 6 months
Safety system in a fire line or Why fire line fitted with relief valve and drain valve
Relief valve:- Relief valve is provided if pumps are capable of developing the pressure
exceeding the design pressure of water service pipes, hydrants & hoses. It assists to avoid any
overpressure to develop in any part of the fire main.
The fire line is fitted with relief valve to prevent the damage to pipe in case , the V/L is fighting
fire with the help of shore while in dry-dock.
Drain Valve :- Drain valve is fitted to drain the fire line when not in use & also prevent the
damage to pipe due to icing, while V/L is operating in Sub-zero temperature area.
Maintenance on a CO2 fire fighting system onboard a ship
1. Check the hinges of the CO2 Room door & grease it.
2. Check the pressure gauge.
3. Check the condition of the blower.
4. Check all lightings are properly working.
5. If Manual pull cables operate the remote release controls, they should be checked to verify the
cables & corner pulleys are in good condition and freely move and do not require an excessive
amount of travel to activate the system.
6. Check the weight of the CO2 Bottles.
7. The discharge piping & nozzles should be tested to verify that they are not blocked. The test
should be performed by isolating the discharge piping from the system & flowing dry air or
nitrogen from test cylinder or through any other suitable means.
8. The hydrostatic test of all the cylinders should be done once in 10 years atleast.
9. The alarm to be tested.
10. The CO2 Lines should be blown through with service air.
Testing procedure
a. Close the section isolating valve, this will raise an alarm indicating zone isolation.
b. Now, open the test valve, if no water comes out, then it means the NR valve placed after the
section isolating valve is not leaking.
c. Since, the section after the NR valve remains pressurized, opening of the drain valve will
cause the water pressure in the section line to decrease. A pressure switch sensor senses the
decreased pressure & raises an alarm.
d. Now, close the drain valve, open the section isolating stop valve. To check the flow switch,
open the flow test switch to activate an alarm.
e. All the above alarms will be indicated on the navigation bridge, E/room as well as in the Fire
Control Room. The alarm will also indicate the particular zone from where it has risen.
f. If all the alarm conditions are satisfied, close all the testing valves, open the section isolating
valve, purge the sprinkler line by air and again keep the line pressurized. Check from the
pressure gauge, that proper pressure has been maintained or not.
Markings on Life boat and life raft of a ship as per LSA Code book chapter 4
As per LSA Code book Chapter 4.
Marking on Lifeboat.
a. Name of Ship
b. Port of Registry
c. IMO Number
d. Lifeboat dimension
e. Carrying Capacity
f. Maker Name
g. Serial number
Marking on Liferaft:
a. Name of Ship.
b. Port of Registry
c. IMO Number
d. Carrying Capacity
e. Maker Name
f. Serial Number
g. Date of last servicing.
Garbage Disposal regulation as per MARPOL Annex V from ship
As per MARPOL Annex V, Regulation for the prevention of pollution by Garbage from
ship.
1. The disposal into the sea of all plastics, plastic garbage bags and incinerator ashes from
plastic products which may contain toxic or heavy metal residues is prohibited.
2. The disposal of garbage i.e., dunnage, lining & packing materials to be made 25 Nautical
miles away from the nearest land.
3. Disposal of food wastes and all other garbage including paper products, rags, glass, metal to
be made 12 Nautical miles away from the nearest land.
4. Disposal of food wastes can be permitted if it has passed through a comminuter or grinder ,
distance is more than 3 Nautical miles from the nearest land. Such comminuted or ground
garbage shall be capable of passing through a screen with openings no greater than 25mm.
What is SOPEP and its purpose - Shipboard Oil Pollution Emergency Plan (As per
MARPOL Annex 1, Regulation 37)
SOPEP :- Shipboard Oil Pollution Emergency Plan
As per MARPOL Annex 1, Regulation 37.
Every oil tanker of 150GRT and above and every ship other than oil tanker of 400GRT & above
shall carry onboard a SOPEP approved by the administration.
The SOPEP consists of:-
1. The procedure to be followed by Master & other person having charge of the ship to report an
Oil Pollution incident.
2. The list of authorities or persons to be contacted in event of Oil Pollution incident.
3. A detailed description of the action to be taken immediately by persons onboard to reduce or
control the discharge of oil.
4. The procedures & point of contact on the ship for co-ordinating ship board action with national
& local authorities.
Explain the procedure to pump out Engine Room Bilge step by step.
a. Inform Chief Engineer.
b. Note down the V/L Position from the bridge.
c. Take the sounding of the bilge tank.
d. Check the 15ppm alarm for its proper working.
e. Open the overboard valve , open sea water valve & bilge pump inlet and outlet valve.
f. Note down the time of starting.
g. Start the bilge pump & fill the OWS with sea water. Let the OWS run on sea water for 10-15
mins.
h. Slowly close the sea water inlet valve & start opening the outlet valve of the bilge tank.
Regulations for pumping out ER bilges in Special areas and outside special areas
Pumping out ER Bilges outside special area:
As per Marpol Annex I, Regulation 15.
Any discharge into the sea of oily or oily mixtures from ships of 400 GRT & above shall be
prohibited except when all the following conditions are satisfied:-
1. The ship should be proceeding enroute from Point A to point B.
2. The oily mixture is processed through an oil filtering equipment.
3. The oily content of the effluent without dilution does not exceeds more than 15ppm.
4. The oily mixture does not originate from cargo pump room bilges on oil tankers.
5. The oily mixture, in case of oil tankers, is not mixed with oil cargo residues.
Pumping out ER Bilges inside special area.
1. The ship should be proceeding enroute from Point A to Point B.
2. The oily mixture is processed through an Oil filtering Equipment approved by the
Administration.
3. The oil content of the effluent without dilution does not exceeds more than 15ppm.
4. The oily mixture does not originate from Cargo pump room bilges on oil tankers.
5. The oily mixture in case of oil tankers, is not mixed with oil cargo residues.
Collision Bulkhead in a ship - Purpose, location and Regulations
Purpose:-
Avoids flooding of ship in case of damage to bows.
Location
Location is such that it is not so much forward as to get damaged on impact , Neither it should
be too far aft so that compartment flooded forward causes extensive trim by head. As a rule
located at minimum distance to get maximum space for cargo.
Minimum at 1/20 of ships length from forward perpendicular
The collision bulkhead is continuous to upper most continuous deck
The collision bulkhead is 20% stronger than other bulkheads
Collision bulkhead is 5 to 8 percent of ships length from forward.
what is tender and stiff ship
Tender Ship:- The ship with a small Metacentric height has a small righting lever at any angle
& will roll easily is said to be tender ship. In tender ship, In it the centre of gravity lies below
the transverse metacentre. The GM is more than GZ. & these kind of ship are more stable.
Stiff Ship:- The ship with a large Metacentric height has a large righting lever at any angle &
has considerable resistance to rolling. A stiff ship is very uncomfortable. In it the Centre of
Gravity lies above the transverse metacentre.
what is tender and stiff ship.
Tender Ship:- The ship with a small Metacentric height has a small righting lever at any angle
& will roll easily is said to be tender ship. In tender ship, In it the centre of gravity lies below
the transverse metacentre. The GM is more than GZ. & these kind of ship are more stable.
Stiff Ship:- The ship with a large Metacentric height has a large righting lever at any angle &
has considerable resistance to rolling. A stiff ship is very uncomfortable. In it the Centre of
Gravity lies above the transverse metacentre.
TUESDAY, APRIL 3, 2012
Boiler Gauge Glass Drill or Daily Maintenece
Procedure:
1. Make sure drain line is clear
2. Close the steam outlet valve.
3. Close the water outlet valve.
4. Open the drain valve.
5. Open the water out valve & let water flow thru it and close the valve after blowing down with
water.
6. Open the steam out valve and blow thru with steam.
7. Close steam valve.
8. Close the drain valve.
9. Now, open the water side valve.
10. Let water fill up 3/4th gauge glass.
11. Open the steam valve slowly.
SATURDAY, MAY 5, 2012
What is SOPEP and its purpose onboard a ship?
SOPEP: - Shipboard Oil Pollution Emergency Plan
As per MARPOL Annex 1, Regulation 37:
Every oil tanker of 150GRT and above and every ship other than oil tanker of 400GRT & above
shall carry onboard a SOPEP approved by the administration.
The SOPEP consists of: -
1. The procedure to be followed by Master & other person having charge of the ship to report
an Oil Pollution incident.
2. The list of authorities or persons to be contacted in event of Oil Pollution incident.
3. A detailed description of the action to be taken immediately by persons onboard to reduce or
control the discharge of oil.
4. The procedures & point of contact on the ship for coordinating ship board action with
national & local authorities.
Checks to be done for Purifier over flowing
* Size of gravity disc.
* High throughput.
* Temperature of the oil.
* Operating water level in tank.
* Sealing water is not present in purifier.
* Bowl is not closed properly.
* Seal ring is damaged.
* By mistake if bowl opening water is feeded.
* Increasing the specific gravity of the oil will tend to push the interface outlet and cause
overflow from the heavy phase outlet until the equilibrium is restored.
Methods for measuring tappet clearance in an engine
Dial Gauge Method: -
In this method the fuel injector is taken out and from the opening a dial gauge is put inside.
Then the turning gear is engaged and the engine turned over. The pointer of the dial gauge will
move in one direction and then stop and start in opposite direction. The moment the pointer of
the dial gauge stops and changes its direction of movement is the TDC of the unit. This method
is not normally used in day-to-day practice, but may be used in the calibration of the flywheel if
it is not calibrated, or after some repairs
Camshaft Method: -
The camshaft window of the engine can be opened up and the camshaft inspected. The cam of
the engine has a base circle, and acceleration and dwell periods. If the roller of the follower is
at the base circle, then the particular valve is closed by spring action. When both the exhaust
valve and the inlet valve follower are on the base circle, then the unit is also at TDC. It must be
remembered that as a four-stroke engine has two rotations of the crankshaft there is one
injection TDC where the injection and the combustion take place. The second time the piston is
at TDC is when the exhausting of the flue gases takes place. It is very important to identify the
combustion TDC, as tappets have to be adjusted at that point.
Cam Profile
Crankcase Method: -
In this method the crankcase doors are opened up and the piston is visually checked whether is
going up or down. This is the surest method, but a bit cumbersome. It should be used when
you have a strong doubt about the other methods.
Valve Spring Method: -
This is not an independent method but is used in conjunction with the flywheel method. In this
method if the flywheel is indicating two units, you can check the springs of both the units. The
unit in which the springs are loose is the one at TDC. The caution is that this method is useful
for an engine in use. If you have removed the rocker arms during the overhaul and thereafter
you want to use this method then it can cause errors.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
What is the effect of less and more tappet clearances in an engine
If tappet clearance is less:
I. Valve will open early & close late
ii. Air induced through inlet valve may leak out. So less air for combustion.
iii. Power will be reduced.
iv. Fuel consumption will increase, engine may become unbalanced, exhaust temp. will be very
high.
v. In worst condition, valve may remain open, resulting in loss of compression pressure,
burning of exhaust valve, T/C fouling will increase.
If tappet clearance is more:
I. Valve will open late & close early.
ii. Lesser heat energy to T/C, so reduction in scavenge air & hence power.
iii. No proper removal of gases.
iv. Hammering of valve stem-may cause damage to valve stem.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
How aft peak tank is sealed from stern tube?
The propeller enters the shaft outside from the ship, acting as its barrier. In case of water-
cooled Stern Tube, Gland packing is used to prevent water ingress inside. But incase of Lignum
vitae bearing, some water is allowed to go.
In case of Oil cooled Stern tube, the rubber seals fitted with springs are used.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
Importance and precautions during fuel oil bunkering ?
1) Sawdust is a great absorbent and hence ample amount of sawdust should be kept in sacks
on deck so that if any leakage takes place during the bunkering procedure, it can be easily
controlled by putting sawdust on it.
2) Proper means of communication with the use of hand held radio sets or other means should
be established between the ships crew and the staff at the bunkering installation to avoid
misunderstandings.
3) The scuppers should be closed to make sure that no oil goes overboard.
4) Drips trays should be closed off.
5) The bunkering lines should be properly checked and fuel tank valves should be carefully
checked before commencing bunkering.
6) Valves not in operation should be effectively sealed off.
7) A sounding of all the ship tanks should be done before starting the bunkering operation.
8) Sounding equipment should be checked properly before the bunkering starts.
9) A marker to indicate the filling up of a particular tank should be used.
10) Port authorities should be immediately contacted in case of a major oil spill.
11) There should be no damage to the hose and it should be of a sufficient length. The
couplings should also be checked for any damage.
12) High level alarms of bunker tanks should be properly checked for their functioning.
13) The SOPEP lockers should be checked whether they have sufficient supplies.
14) Oil absorbing apparatus like oil absorbing pads should be kept at important areas to reduce
any oil leaks.
15) Make sure the bunkering plans are agreed upon by all officers onboard the ship.
16) Discuss the procedures to be undertaken in case of an emergency with the supplier.
17) A proper system of signals for communication should be established between the shipboard
crew and suppliers.
18) Fire extinguishers and other fire fighting apparatus should be readily available.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
Action in case of Purifier room fire
A purifier room is one of the most probable places in the engine room to catch fire. Purifier
room fire has been the reason for several major accidents on various ships in the past. In this
article we will learn about everything related to purifier room fires.
As we all know, for a fire to happen, three things are needed and in the purifier room all these
things are present. These three things are fuel oil which is present in abundant (lubricating oil
in lube oil separator and fuel oil or diesel oil in fuel oil separator), air for combustion, and a heat
source such as extremely hot oil, electrical short circuit etc.
When all these things are present together and lie within the flammable limit, a fire can take
place.Therefore, if a spray of oil takes place through a leaking pipe over a hot surface or over
an electrical point, a fire can immediately take place.
Prevention of Purifier Fire
The following points are to be followed in order to prevent purifier room fire:
1) All the pipes leading to the separator are to be double sheathed; the reason for this is that if
inner pipe leaks, then it will not spray all over the place but instead it will leak into outer pipe.
2) Drip trays should be provided below the purifier or separator, so that in case of oil spill the
oil will not flow and spread in the purifier room and contact with any hot material and catch
fire.
3) All the pipes with flanges or connections are to be covered with anti spill tapes which can
prevent spill from the flanges in case of a leakage.
4) Fire fighting system such as water mist and CO2 system should be installed.
5) Quick closing valves and remote stopping of pumps and purifier should be provided.
6) Fire detection and alarm system are to be provided so that quick action can be taken.
How to fight purifier room fire
A small purifier fire can be easily stopped with the help of small fire extinguisher. In case of a
bigger fire, the following steps should be taken:
1) As soon as fire alarm is sounded, call the chief engineer and locate the fire.
2) Close the quick closing valves from which the oil is leaking.
3) Stop the transfer pump.
4) Both transfer and quick closing valves can be closed from remote location like ship control
center or from the engine control room.
5) Stop all the motors and electrical equipments, which can be stopped from emergency stop
button outside the purifier room.
6) The fire can be stopped with the help of fire extinguisher.
7) In case of a big fire, close the air supply pump and exhaust from the purifier room.
8 )The fire can be stopped by releasing water mist system if present on the ship.
9) Entry in the purifier room is made putting on the fire fighter suit, along with self contained
breathing apparatus (SCBA) and fire hose.
10) The fire can be extinguished with the help of spraying water.
11) In case the fire is still not extinguished then the chief engineer will decide about using the
carbon dioxide bottles for fighting fire.
12) When these bottles are to be used, there should not be any person present inside the
Purifier space as Co2 can cause suffocation due to displacement of air and the person involved
may die.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
Safety features in marine air compressor
Every Air compressor on a ship is fitted with several safety features to avoid abnormal and
dangerous operational errors of the equipment. If safety, alarms and trips are not present on
the air compressor, abnormal operation may lead to breakdown of the compressor and may
also injure a person working on or around it.
Relief valve: Fitted after every stage to release excess pressure developed inside it. The setting
of the lifting pressure increases after every ascending stage.
Bursting disc: A bursting disc is a copper disc provided at the airside of the compressor. It is a
safety disc, which bursts when the pressure exceeds over the pre-determined value.
Fusible plug: Generally located on the discharge side of the compressor, it fuses if the air
temperature is higher than the operational temperature. The fusible plug is made up of
material, which melts at high temperature.
Lube Oil low-pressure alarm and trip: If the lube oil pressure goes lower than the normal, the
alarm is sounded followed by a cut out trip signal to avoid damage to bearings and crank shaft.
Water high temperature trip: If the intercoolers are choked or the flow of water is less, then the
air compressor will get over heated. To avoid this situation high water temperature trip is
activated which cut offs the compressor.
Water no-flow trip: If the attached pump is not working or the flow of water inside the
intercooler is not enough to cool the compressor then moving part inside the compressor will
get seized due to overheating. A no flow trip is provided which continuously monitor the flow of
water and trips the compressor when there is none.
Motor Overload trip: If the current taken by motor during running or starting is very high then
there is a possibility of damage to the motor. An overload trip is thus fitted to avoid such
situation.
High Air Temperature Trip
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
How mud and water removed from ship chain locker ?
The chain moves through the chain pipe and the hawse pipe as the anchor is raised or lowered.
The chain pipe connects the chain locker to the deck and the hawse pipe runs from the deck
through the hull of the ship. When recovering the anchor, the anchor and chain are washed off
with a fire hose to remove mud, marine organisms, and other debris picked up during
anchoring. Seawater from the fire hose is directed either through the hawse pipe or directly
over the side onto the chain while recovering the anchor.
The top of the chain pipe has a canvas sleeve to keep water from entering the chain locker
through the chain pipe. Under rare circumstances, like heavy weather, rain or green water
(seawater that comes over the bow during heavy weather) gets under the chain pipe canvas
cover and into the chain locker. A diagram of a typical chain locker is provided in Figure 2.
Any fluid that accumulates in the chain locker sump is removed by either drainage eductor for
discharge directly overboard or by draining the chain locker effluent into the bilge.
As the fluid in the chain locker sump is being drained for overboard discharge, the locker is
sprayed with firemain water to flush out sediment, mud, or silt. An eductor is a pumping device
that uses a high velocity jet of seawater from the firemain system to create a suction to remove
the accumulated liquids and solids.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
Maintenance carried out on a portable fire fighting extinguishers
* Portable fire extinguishers are to be examined by a competent person annually.
* Each portable fire extinguisher is to be provided with a label indicating that it has been
examined and the date of the examination, or the date of next examination.
* Containers of permanently pressurized portable fire extinguishers and propellant bottles /
containers of non-pressurized portable fire extinguishers shall be hydraulically pressure tested
as follows:
a. Powder extinguishers every 10 years
b. CO2 extinguishers every 10 years
c. Other extinguishers every 10 years
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
What all maintenance are carried out on CO2 fixed fire fighting installations
* CO2 bottles of fixed CO2 fire extinguishing installation shall be hydraulically tested 20 years
after the date on which the bottles were put into use, and every 5 years thereafter.
* The quantity of the medium in the CO2 bottles should be checked once every 4 years. This
may be carried out in batches of 25% of the CO2 bottles annually, or 50% of the CO2 bottles
biennially or in accordance with the ships maintenance so long as every CO2 bottle is checked
once every 4 years.
* All stop valves should be checked monthly to ensure that they are in their proper open or
closed position.
* The installation should be checked monthly for leakage.
* All CO2 bottle connections for cable operating clips should be checked for tightness every 3
months.
* All control valves should be inspected annually, and internally inspected every
5 years.
Air should be blown through the piping of the installation annually.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
Requirements for the storage of CO2 storage room?
Carbon dioxide storage rooms
The following requirements are applicable only for the storage rooms for fire-extinguishing
media of fixed gas fire-extinguishing systems:
1) The storage room should be used for no other purposes;
2) If the storage space is located below deck, it should be located no more than one deck
below the open deck and should be directly accessible by a stairway or ladder from the open
deck;
3) Spaces which are located below deck or spaces where access from the open deck is not
provided, should be fitted with a mechanical ventilation system designed to take exhaust air
from the bottom of the space and should be sized to provide at least 6 air changes per hour;
and
4) Access doors should open outwards, and bulkheads and decks including doors and other
means of closing any opening therein, which form the boundaries between such rooms and
adjacent enclosed spaces, should be gas tight.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
What are the main components of a Ship's hull?
The main components are the framing or skeleton to which the platting or skin is attached. The
backbone of the skeleton is the keel to which the frames or ribs are connected. Deck beams are
fitted between the side frames across or athwart the hull and are fastened to it by brackets.
The frames are shaped to the hull lines and the deck beams are given a slight curve or beam
round.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
Checks during a Marine Main Engine crankcase inspection
The crankcase inspection is done every month whenever the ship is in port and there is
sufficient time for inspection. Thorough inspection is required during this to analyze the
condition inside and damage to the bearings.
Before inspection following procedures has to be followed: -
Permission has to be taken before reaching port to make sure that the authority is not having
any problem with this. This is called Immobilization permission of the main engine.
After the permission is received the checklist has to be filled.
Safety issues have to be discussed with the people taking part in the inspection.
When the engine is in stopped condition, the lubricating oil pump and cross-head oil pump
have to be stopped and the breaker taken out so that it doesnt start on its own or by any other
person by mistake.
Proper sign and placards to be displayed regarding men at work.
Since engine crankcase is an enclosed space, an enclosed space checklist is also to be filled.
After stopping the engine and the pumps the crankcase doors have to be opened and sufficient
time is to be given to cool and ventilate the space as the temperature inside is very hot and
deprived of air.
After the cooling and ventilating the space, the person entering the space should be with proper
personnel protective equipments like boiler suit, safety harness, and anti slipping pads for
shoes.
Make sure there are no tools, pen etc in your pockets which might drop inside and cause
damage to bearing and machinery parts
Before entering, the person has to be detailed as what needs be checked inside. Special
attention is also given if technical department specifies any other issue or any major problem
found on other ships.
Inside Crankcase Following Checks are to be made: -
1. Check the overall quality of oil whether it is clean or dirty with carbon particles.
2. Check for any distinguished smell, if found, this could be because of bacterial contamination
of oil. The smell is generally of rotten eggs.
3. Check for any metal particles near the grating in the crankcase.
4. Check the condition and damage to the gratings.
5. Check the slip marks on the web; they should be in the same line. If slip is found then report
is to be made to the company and classification society regarding this.
6. Check for any bluish dark patches, this indicates that hot spots are caused by friction of
insufficient lubrication.
7. Check crosshead for any damages.
8. Check crosshead guides for damages and marks.
9. Check the bedplate for any welding cracks etc.
10. Check any metal seen near the bearings coming out due to wiping.
11. Check for piping and any loose connections between them.
12. Check the locking wires and locking washers on bolts of stuffing box.
13. Make any other checks specified by technical department.
14. Before coming out make sure there is nothing left inside.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
Difference between a Clarifier and a Purifier and how to change a purifier to clarifier?
The main difference between a clarifier and a purifier is the presence of a dam ring in the latter.
In a purifier, the interface or the line of separation between the oil and water is created using a
dam ring. The position of the dam ring plays an important role in the generation of interface
and thus in the clarifying process. For example, if the diameter of dam ring is large, the
interface moves out towards the periphery and as a result some oil is discharged with water
from the water outlet. Also, if the diameter is small, the interface formed will be more inwards
and water will be discharged with the oil from the oil outlet.
The diameter of holes in the dam rings also plays an important role in the creation of interface
and purification process. If the diameter of the holes is more, the interface is formed towards
the periphery and oil globules are found with water and sludge. If the diameter is less the oil-
water interface moves inwards and water is released with the clean oil discharged.
However, clarifiers do not have a dam ring but have a sealing ring which seals the water outlet.
This prevents the impurities and water to remain inside the bowl unless opening the cleansing
bowl discharges them automatically or manually. Also, the conical discs in a clarifier usually
dont have feed holes in them but if they do, then a disc without any holes is fitted at the
bottom of the stack.
Another difference between a clarifier and purifier is that a purifier needs to be filled completely
with water for the generation of a seal that prevents the oil to leave from the water outlet.
Whereas a clarifier doesnt needs to be filled up with water. Purifiers are used for filtering
lubricating oil whereas clarifiers are not used for the same unless the oil is completely devoid of
water.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
Precautions before starting Auxiliary engine after overhaul
* Turn engine through flywheel for checking any restrictions.
*Water tightness to be checked.
* Air to be removed from jacket water outlet line.
* Priming lube oil pump to run before starting the engine.
* Check the lube oil level.
* Check the flow of lube oil.
* Blow through the engine before starting.
0 comments
Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to Facebook
What all safety trips are present in Marine Auxiliary Engine ?
The various trips and alarms are mentioned as follows
Alternator bearing low oil level alarm & trip
Alternator bearing high temperature lube oil alarm &trip
Low sump oil level alarm and trip
Lube low oil pressure alarm and trip
Reverse current trip
Over speed trip
Over load trip
High and low frequency trip
Jacket cooling water low-pressure alarm
0 comments
You might also like
- MEO CLASS IV OralsDocument25 pagesMEO CLASS IV OralsAnoop Vijayakumar0% (1)
- Safety MEO Class 4 Part B - For OralsDocument11 pagesSafety MEO Class 4 Part B - For Oralslazyreaderr100% (2)
- Marine Notes - MMD Exams India and Baiscs - MEO Class 4 Oral QuestionsDocument6 pagesMarine Notes - MMD Exams India and Baiscs - MEO Class 4 Oral QuestionsPuloma PramanickNo ratings yet
- MEO Class 2 Orals Function 6 Q & ADocument7 pagesMEO Class 2 Orals Function 6 Q & Aneeraj11850% (1)
- Class 4 EoowDocument74 pagesClass 4 EoowRyan Cardoza0% (1)
- MEO Class 2 Orals Safety Q & ADocument9 pagesMEO Class 2 Orals Safety Q & Aneeraj118593% (14)
- All in One Class4 OralsDocument33 pagesAll in One Class4 OralsSantharam Mariner100% (2)
- 200 OralDocument295 pages200 OralSamarendu Tiwari100% (7)
- Oral Candy Meo Class 4Document32 pagesOral Candy Meo Class 4deepanck0% (2)
- Class4 Question & Answers Ship ConstDocument48 pagesClass4 Question & Answers Ship ConstNarine100% (2)
- MEK - QuestionsDocument5 pagesMEK - QuestionsManeesh100% (2)
- IAMI EKES Marine Engineering Exam PapersDocument7 pagesIAMI EKES Marine Engineering Exam PapersAshwin YadavNo ratings yet
- MEO Class 4 Oral QuestionsDocument33 pagesMEO Class 4 Oral QuestionsAnkit Batra50% (2)
- MotorDocument84 pagesMotorSarath Raghav100% (1)
- Thermal Expansion and Heat Transfer Study GuideDocument123 pagesThermal Expansion and Heat Transfer Study GuidekamaalNo ratings yet
- PURIFIERSDocument7 pagesPURIFIERSjames dogelioNo ratings yet
- IMP Main Engine and Aux EngineDocument37 pagesIMP Main Engine and Aux EngineLOKINo ratings yet
- MEO Class 2 Orals FN 3 6 Q ADocument15 pagesMEO Class 2 Orals FN 3 6 Q AAnkit BatraNo ratings yet
- MEO Class 4 Oral and Written Questions Part 4Document43 pagesMEO Class 4 Oral and Written Questions Part 4amitt.rulezz80% (5)
- MEO Class 2 QuestionDocument2 pagesMEO Class 2 Questionsumitsinha8950% (2)
- MEO Class I OralsDocument2 pagesMEO Class I OralsGurvindarNo ratings yet
- EKM Question Bank (COC Written) - 1Document15 pagesEKM Question Bank (COC Written) - 1Tarek AzizNo ratings yet
- Class IV oral questions on ship construction and safety equipmentDocument18 pagesClass IV oral questions on ship construction and safety equipmentdeepanck100% (2)
- MEO Class 2 Orals Function 4 & 6 Q & ADocument8 pagesMEO Class 2 Orals Function 4 & 6 Q & Aneeraj118578% (9)
- EOOW - Orals Questions & AnswersDocument54 pagesEOOW - Orals Questions & Answersnkosithandile Vuke100% (1)
- IAMI MocK TestDocument6 pagesIAMI MocK TestAshwin YadavNo ratings yet
- MEO Question and AnsDocument221 pagesMEO Question and AnsVikram Singh100% (1)
- 200 Oral Question and AnswersDocument198 pages200 Oral Question and AnswersRejoGevargheseRajan50% (4)
- Latest Oral Questions MEO Class 4 - Mumbai MMDDocument23 pagesLatest Oral Questions MEO Class 4 - Mumbai MMDGaurav Ranjan100% (3)
- Eoow Orals QuestionaireDocument10 pagesEoow Orals QuestionaireHemachandren Subramani100% (3)
- UK MCA 4th Class OralDocument33 pagesUK MCA 4th Class OralRicky Chua Snr100% (3)
- Met Class 4 Electrical WrittenDocument83 pagesMet Class 4 Electrical WrittenAjeet Jha86% (7)
- Class 2 OralsDocument39 pagesClass 2 OralsDhawal Tandon100% (1)
- Safety-Overall MEO Class 4 Part BDocument21 pagesSafety-Overall MEO Class 4 Part Blazyreaderr100% (1)
- MEO Class 4 Oral Questions With Answers PDFDocument46 pagesMEO Class 4 Oral Questions With Answers PDFArvind Sugumaran85% (13)
- Iami Section A - Motor EkDocument9 pagesIami Section A - Motor Ekstelios0% (1)
- Regulations, diagrams, and safety discussed in marine engineering oral examsDocument18 pagesRegulations, diagrams, and safety discussed in marine engineering oral examsStewardGriffindorNo ratings yet
- All About Marine Enginnering OralsDocument76 pagesAll About Marine Enginnering OralsUdana Hettiarachchi100% (3)
- Elec Oral Ques MMD KolkataDocument7 pagesElec Oral Ques MMD KolkataAkshay Ankit100% (2)
- EOOW Oral QuestionsDocument134 pagesEOOW Oral QuestionsMitch Rea71% (7)
- MEO Class 4B Motor Orals Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesMEO Class 4B Motor Orals Exam QuestionsInzaHopeNo ratings yet
- Hfo To Mdo Change Over ProcedureDocument3 pagesHfo To Mdo Change Over ProcedureJanell Prince50% (2)
- Recent MMD QuestionsDocument49 pagesRecent MMD QuestionsAkash Nair100% (1)
- Class 4 Safety Oral Solas & Marpol FileDocument106 pagesClass 4 Safety Oral Solas & Marpol FileAkash Vimal100% (3)
- MEO Class 4 Oral Questions April-August 11 Kolkata MMDDocument12 pagesMEO Class 4 Oral Questions April-August 11 Kolkata MMDSatpal YadavNo ratings yet
- Oily Water Separator Safety DevicesDocument15 pagesOily Water Separator Safety DevicesMohammad Jahid Alam100% (6)
- Orals For Marine EnggDocument82 pagesOrals For Marine EnggRegin100% (1)
- Meo cl2 MMDDocument38 pagesMeo cl2 MMDAurvin SinghNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Oral Preparation Watch Keeper Deck Mates: Question and Answer GuidelinesFrom EverandOral Preparation Watch Keeper Deck Mates: Question and Answer GuidelinesNo ratings yet
- Function 3Document12 pagesFunction 3Pandiya RajanNo ratings yet
- Control Valve FunctionDocument1 pageControl Valve FunctionKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Management: Prepared By-Ms. Anshu M.Sc. Nursing 2 Year KGMU Institute of NursingDocument35 pagesManagement: Prepared By-Ms. Anshu M.Sc. Nursing 2 Year KGMU Institute of NursingKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- History of Community Health and Community Health Nursing: Uma J Deaver Asst Professor MM College of NursingDocument46 pagesHistory of Community Health and Community Health Nursing: Uma J Deaver Asst Professor MM College of NursingKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Bench Marking: Meenakshi Soni Lecturer College of Nursing, JaipurDocument11 pagesBench Marking: Meenakshi Soni Lecturer College of Nursing, JaipurKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Material ManagementDocument16 pagesMaterial ManagementKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Meenakshi Soni Lecturer College of Nursing, JaipurDocument18 pagesHuman Resource Management: Meenakshi Soni Lecturer College of Nursing, JaipurKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Nursing AuditDocument26 pagesNursing AuditKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Nursing AuditDocument29 pagesNursing AuditKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Pert Gantt Chart & MBO: Presesnted By: Navaneeta Kusum M.Sc. NSG 2 YRDocument31 pagesPert Gantt Chart & MBO: Presesnted By: Navaneeta Kusum M.Sc. NSG 2 YRKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Principlesofbudgetinginnursingadmin 140215014709 Phpapp02Document27 pagesPrinciplesofbudgetinginnursingadmin 140215014709 Phpapp02SrideviRaviNo ratings yet
- BUDGETING ESSENTIALS FOR NURSING SCHOOLSDocument46 pagesBUDGETING ESSENTIALS FOR NURSING SCHOOLSashraf100% (1)
- Meo 1 - Question BankDocument81 pagesMeo 1 - Question BankVijai Abraham80% (5)
- Srvastava SirDocument2 pagesSrvastava SirKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Motor Capcitor SelectionDocument10 pagesMotor Capcitor SelectionKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Meo 1 - Question BankDocument81 pagesMeo 1 - Question BankVijai Abraham80% (5)
- Propeller Cap TurbineDocument4 pagesPropeller Cap TurbineKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Development of COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING in IndiaDocument12 pagesDevelopment of COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING in IndiaKapil Verma100% (3)
- Address LionDocument16 pagesAddress LionKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Amendments To The MARPOL Convention From 01 January 2013.: 1. BackgroundDocument10 pagesAmendments To The MARPOL Convention From 01 January 2013.: 1. BackgroundKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- MKDWX PTKFK G6HTV 2G2GJ R23Q7Document1 pageMKDWX PTKFK G6HTV 2G2GJ R23Q7Kapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Marine Engineering PracticeDocument13 pagesMarine Engineering PracticeKapil Verma100% (1)
- Arduino Playground - ProcessingDocument3 pagesArduino Playground - ProcessingKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Clodiuno - Processing ADXL335 AccelerometerDocument3 pagesClodiuno - Processing ADXL335 AccelerometerKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Environmental ProjectDocument14 pagesEnvironmental ProjectKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- 3-Axis Accelerometer and Processing - Robot Is HappyDocument4 pages3-Axis Accelerometer and Processing - Robot Is HappyKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No:: ToolsDocument3 pagesAssignment No:: ToolsKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Dicrectorate of PanamaDocument9 pagesDicrectorate of PanamaKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Pujangga Piping - The Meaning of Valves - Only The BasicDocument21 pagesPujangga Piping - The Meaning of Valves - Only The BasicKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Meo NotesDocument2 pagesMeo NotesKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- AllDocument112 pagesAllKapil VermaNo ratings yet
- Rha GGBS 27 4Document12 pagesRha GGBS 27 4KhaDeja MawraNo ratings yet
- MARCOMDocument35 pagesMARCOMDrei SalNo ratings yet
- Predictive Analytics: QM901.1x Prof U Dinesh Kumar, IIMBDocument36 pagesPredictive Analytics: QM901.1x Prof U Dinesh Kumar, IIMBVenkata Nelluri PmpNo ratings yet
- Hearing God Through Biblical Meditation - 1 PDFDocument20 pagesHearing God Through Biblical Meditation - 1 PDFAlexander PeñaNo ratings yet
- PanimulaDocument4 pagesPanimulaCharmayne DatorNo ratings yet
- Otis Brochure Gen2life 191001-BELGIUM SmallDocument20 pagesOtis Brochure Gen2life 191001-BELGIUM SmallveersainikNo ratings yet
- LP IV Lab Zdvzmanual Sem II fbsccAY 2019-20z 20-ConvxvzzertedDocument96 pagesLP IV Lab Zdvzmanual Sem II fbsccAY 2019-20z 20-ConvxvzzertedVikas GuptaNo ratings yet
- Component 2 Learner Statement Y2Document6 pagesComponent 2 Learner Statement Y2api-426152133No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Tech-1Document6 pagesManufacturing Tech-1Vikram Rao0% (1)
- Enterprise Architecture A General OverviewDocument45 pagesEnterprise Architecture A General OverviewraducooNo ratings yet
- Marikina Development Corporation vs. FiojoDocument8 pagesMarikina Development Corporation vs. FiojoJoshua CuentoNo ratings yet
- EA Flora 1Document3 pagesEA Flora 1A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- EDUC 5 - QuestionairesDocument7 pagesEDUC 5 - QuestionairesWilliam RanaraNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Soal UN Bahasa Inggris SMP 2012 (Paket Soal C29) PDFDocument15 pagesPembahasan Soal UN Bahasa Inggris SMP 2012 (Paket Soal C29) PDFArdi Ansyah YusufNo ratings yet
- 4900 DatasheetDocument2 pages4900 DatasheetMakam Raghu100% (1)
- Gabriel Nobre de Souza - Groningen Mini-MetropolisDocument9 pagesGabriel Nobre de Souza - Groningen Mini-MetropolisGabrielNobredeSouzaNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Blooming GroveDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Blooming GroveHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Laser Engrave Co2 System BJ-1390Document5 pagesLaser Engrave Co2 System BJ-1390Sasa TodorovicNo ratings yet
- RFID Receiver Antenna Project For 13.56 MHZ BandDocument5 pagesRFID Receiver Antenna Project For 13.56 MHZ BandJay KhandharNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Aptitude-More Exercise Questions Updated On Jul 2019Document4 pagesQuantitative Aptitude-More Exercise Questions Updated On Jul 2019SANAMGI BHAVYANo ratings yet
- Scientific Passage English TestDocument57 pagesScientific Passage English TestAb HadiNo ratings yet
- STR File Varun 3Document61 pagesSTR File Varun 3Varun mendirattaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Endurance Exercise Training in the Fasted State on Muscle Metabolism and Insulin SensitivityDocument14 pagesImpact of Endurance Exercise Training in the Fasted State on Muscle Metabolism and Insulin SensitivityYo Vivo Fit Pablo y KarlaNo ratings yet
- Ethics Book of TAMIL NADU HSC 11th Standard Tamil MediumDocument140 pagesEthics Book of TAMIL NADU HSC 11th Standard Tamil MediumkumardjayaNo ratings yet
- CH 22 Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesCH 22 Solutions Manuallmbrn0415No ratings yet
- Hong Kong A-Level Chemistry Book 3ADocument69 pagesHong Kong A-Level Chemistry Book 3AMARENG BERNABENo ratings yet
- HYBT Series: Assembling Terminal BlockDocument8 pagesHYBT Series: Assembling Terminal Blockanon_670965762No ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Accounting Canadian 5th Edition Brewer Solutions ManualMaryJohnsonsmni100% (57)
- Finding My Voice in ChinatownDocument5 pagesFinding My Voice in ChinatownMagalí MainumbyNo ratings yet
- The Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsDocument28 pagesThe Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsAngela FigueroaNo ratings yet