Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Uploaded by
Dharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Uploaded by
Dharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaCopyright:
Available Formats
Pemphigus vulgaris
Reference: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1064187-overvie
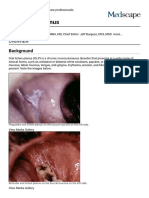
Pemphigus vulgaris is an autoimmune! intraepithelial! "listering disease affecting the s#in and mucous
mem"ranes. $t is mediated "% circulating autoanti"odies directed against #eratinoc%te cell surfaces. & potentiall%
life-threatening disease! it has a mortalit% rate of appro'imatel% (-1().[1]
Signs and symptoms
*ucous mem"ranes
*ucous mem"ranes of the oral cavit% are involved in almost all patients ith pemphigus vulgaris
Patients ma% have ill-defined! irregularl% shaped! gingival! "uccal! or palatine erosions! hich are painful and
slo to heal
$ntact "ullae are rare in the mouth
+rosions ma% "e seen on an% part of the oral cavit%! and the% ma% spread to involve the lar%n'! ith
su"se,uent hoarseness
$n -uvenile pemphigus vulgaris! stomatitis is the presenting complaint in more than (0) of cases
.ther mucosal surfaces ma% "e involved! including the con-unctiva![2]esophagus /causes od%nophagia
and/or d%sphagia0![3] la"ia! vagina! cervi'! vulva![4] penis! urethra! nasal mucosa! and anus
1#in
Primar% lesion of pemphigus vulgaris is a flaccid "lister filled ith clear fluid that arises on health% s#in or on
an er%thematous "ase
2listers are fragile and ma% rupture! producing painful erosions /the most common s#in presentation0
3ails
&cute or chronic paron%chia! su"ungual hematomas! and nail d%strophies affecting one or several fingers or toes
have "een reported ith pemphigus vulgaris.[5, 6]
4egetating pemphigus vulgaris
5esions in s#in folds readil% form vegetating granulations. $n some patients! erosions tend to develop e'cessive
granulation tissue and crusting6 these individuals displa% more vegetating lesions.
1ee Clinical Presentation for more detail.
Diagnosis
5a"orator% studies include the folloing:
7istopatholog%: 8emonstrates an intradermal "lister6 the earliest changes consist of intercellular edema ith
loss of intercellular attachments in the "asal la%er
8irect immunofluorescence /8$90: .n normal-appearing perilesional s#in[7] 6 demonstrates in vivo deposits of
anti"odies and other immunoreactants! such as complement
$ndirect immunofluorescence /$8$90: $f 8$9 results are positive6 circulating intercellular anti"odies are detected
using $8$9 in 80-:0) of patients ith pemphigus vulgaris
1ee Workup for more detail.
Management
;he aim of pharmacologic therap% for pemphigus vulgaris is to reduce inflammator% response and autoanti"od%
production. *edications used in the disease<s treatment include the folloing:
=orticosteroids: 8iscourage the inflammator% process "% inhi"iting specific c%to#ine production
$mmunosuppressants: 1hould "e considered earl% in the course of disease as steroid-sparing agents
You might also like
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Review On Its Etiopathogenesis: Title Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris - Report of A CaseDocument12 pagesReview On Its Etiopathogenesis: Title Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris - Report of A CaseNovita Cahya PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Arduino 2017Document8 pagesArduino 2017neetika guptaNo ratings yet
- Blistering Disorders: Diagnosis and Treatment: S. W. Y, B A, N S, & A. R ADocument10 pagesBlistering Disorders: Diagnosis and Treatment: S. W. Y, B A, N S, & A. R ARashmi KumariNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Periodontal Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesDocument13 pagesDiagnosis of Periodontal Manifestations of Systemic DiseaseskochikaghochiNo ratings yet
- Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Case Report With Review of The LiteratureDocument4 pagesOral Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Case Report With Review of The LiteratureDhilah Harfadhilah FakhirahNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology: Hyperplasia of Oral MucosaDocument7 pagesOral Pathology: Hyperplasia of Oral Mucosaعلي صادق جعفرNo ratings yet
- PemfigusDocument5 pagesPemfigusSherlyNo ratings yet
- Bullous-2018 TPDocument136 pagesBullous-2018 TPMary Dominique RomoNo ratings yet
- Epulis FissuratumDocument9 pagesEpulis FissuratumDilaC.FareshaNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations of SyphilisDocument7 pagesOral Manifestations of SyphilishunarsandhuNo ratings yet
- Renal Disease and MouthDocument6 pagesRenal Disease and MouthShantanu DixitNo ratings yet
- Ulcers and Vesicles2Document24 pagesUlcers and Vesicles2Kelly MayerNo ratings yet
- Painfulorallesions: Istvan A. HargitaiDocument13 pagesPainfulorallesions: Istvan A. HargitaiAlejandro Ln CNo ratings yet
- Parotitis - MedscapeDocument15 pagesParotitis - MedscapedrrianacsNo ratings yet
- PemphigusDocument32 pagesPemphigusAlondra CastilloNo ratings yet
- LabiopalatoschisisDocument21 pagesLabiopalatoschisisOna AkyuwenNo ratings yet
- Squamous Papilloma of The Tongue: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesSquamous Papilloma of The Tongue: A Case ReportAninda Wulan PradaniNo ratings yet
- SM1 3Document15 pagesSM1 3Smitha Kapani gowdaNo ratings yet
- Enfermedades InmunologicasDocument14 pagesEnfermedades InmunologicasKarina OjedaNo ratings yet
- Pemphigus Vulgaris Confined To The Gingiva: A Case ReportDocument16 pagesPemphigus Vulgaris Confined To The Gingiva: A Case ReportAlmasulah Al-akmaliyahNo ratings yet
- Australian Dental Journal - 2010 - Schifter - Oral Mucosal Diseases The Inflammatory DermatosesDocument16 pagesAustralian Dental Journal - 2010 - Schifter - Oral Mucosal Diseases The Inflammatory Dermatosesneetika guptaNo ratings yet
- Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid: by Student Dunya Adnan Khaled Supervision by Dr. LanaDocument13 pagesMucous Membrane Pemphigoid: by Student Dunya Adnan Khaled Supervision by Dr. LanaQueen LiveNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesDocument25 pagesOral Manifestations of Systemic Diseasesmicheal1960No ratings yet
- Lyon 2005Document21 pagesLyon 2005Renata StefaniNo ratings yet
- Pemfigus VulgarisDocument5 pagesPemfigus VulgarisAgus LarobuNo ratings yet
- Lom Mer 2013Document17 pagesLom Mer 2013M ElmanavieanNo ratings yet
- 02VBL PemphigusDocument48 pages02VBL PemphigusRaniya ZainNo ratings yet
- KalmarDocument8 pagesKalmarKING COMICNo ratings yet
- Oral Mucosal Changes Associated With FluDocument4 pagesOral Mucosal Changes Associated With FluManar AlsoltanNo ratings yet
- Orofacial Viral Infections An UpdateDocument6 pagesOrofacial Viral Infections An UpdateAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Papilloma Skuamosa: Laporan Kasus Dan Tinjauan PustakaDocument4 pagesPapilloma Skuamosa: Laporan Kasus Dan Tinjauan PustakarizkyayuarristaNo ratings yet
- Malignant Otitis ExternaDocument5 pagesMalignant Otitis Externasergeantchai068No ratings yet
- Condyloma Acuminatum: Some Aspects: Arūnas Rimkevičius, Alina Pūrienė, Mindaugas GaigalasDocument4 pagesCondyloma Acuminatum: Some Aspects: Arūnas Rimkevičius, Alina Pūrienė, Mindaugas GaigalasfaizawidiNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex VirusDocument9 pagesHerpes Simplex VirusFaerusNo ratings yet
- 005 - Additional MaterialDocument22 pages005 - Additional MaterialLucas Victor AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease: Autoimmune DiseasesDocument7 pagesOral Manifestations of Systemic Disease: Autoimmune DiseaseshussainNo ratings yet
- Nasal-Paranasal Sinus Complex: Xerostomia: A Continuing Challenge For Oral Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument3 pagesNasal-Paranasal Sinus Complex: Xerostomia: A Continuing Challenge For Oral Healthcare ProfessionalsDuong LeNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument33 pagesRheumatoid Arthritisdtpmaharaja100% (1)
- Atypical TuberculosisDocument3 pagesAtypical TuberculosisWilda Khairani DalimuntheNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument5 pages4 PDFLisda PraditaNo ratings yet
- Syndromes and Periodontal Disease-An Insight!: Dr. Grishmi NiswadeDocument6 pagesSyndromes and Periodontal Disease-An Insight!: Dr. Grishmi NiswadeTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Acute LeukemiaDocument16 pagesAcute Leukemianouval_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Benign Migratory Glossitis: A Review: KeywordsDocument11 pagesBenign Migratory Glossitis: A Review: KeywordsDita Merry Diah VanonyNo ratings yet
- 01 AidsDocument6 pages01 AidsJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINo ratings yet
- Behçet's SyndromeDocument7 pagesBehçet's Syndromeson gokuNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology, Histopathology, Sequelae and Pathogenesis of Oral Mucosal LesionsDocument24 pagesBacteriology, Histopathology, Sequelae and Pathogenesis of Oral Mucosal LesionsVijetha RaiNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus AND Acquired Immunodeficiency SyndromeDocument59 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus AND Acquired Immunodeficiency SyndromeJose Joy IdicullaNo ratings yet
- Nonneoplastic Diseases of The Salivay Glands October 2001Document12 pagesNonneoplastic Diseases of The Salivay Glands October 2001Cholida RachmatiaNo ratings yet
- Mac411 Lecture 4 Microbiology of Peridiontal DiseasesDocument17 pagesMac411 Lecture 4 Microbiology of Peridiontal Diseasesفاطمة الجش.No ratings yet
- Printer Friendly Breno Rocha Lima, M.D.: ObjectiveDocument21 pagesPrinter Friendly Breno Rocha Lima, M.D.: ObjectiveKartikaEkaWulandariNo ratings yet
- Transformasi Ganas Lichen Planus F, Rosif Mukosamulut: IJD 2006 Edisi Khusus KppkgxiyDocument3 pagesTransformasi Ganas Lichen Planus F, Rosif Mukosamulut: IJD 2006 Edisi Khusus KppkgxiyMuhammadNaufalNo ratings yet
- Cumming - Otolaryngology - EpistaxisDocument9 pagesCumming - Otolaryngology - EpistaxisPro fatherNo ratings yet
- 10.a Lump On The GingivaDocument4 pages10.a Lump On The Gingivamirfanulhaq100% (1)
- Pemphigus - Current Therapy (Pages 90-98)Document9 pagesPemphigus - Current Therapy (Pages 90-98)jenNo ratings yet
- Liquen Plano OralDocument44 pagesLiquen Plano OralJoana MartinsNo ratings yet
- Journal 2.Document5 pagesJournal 2.Dha Dina SevofrationNo ratings yet
- Handbook of SepsisFrom EverandHandbook of SepsisW. Joost WiersingaNo ratings yet
- Clinically Relevant Mycoses: A Practical ApproachFrom EverandClinically Relevant Mycoses: A Practical ApproachElisabeth PresterlNo ratings yet
- Business Proposal Ilocos NorteDocument4 pagesBusiness Proposal Ilocos NorteDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- CHN&CDDocument7 pagesCHN&CDDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis ActivityDocument2 pagesMitosis ActivityDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- At PreboardDocument12 pagesAt PreboardKevin Ryan EscobarNo ratings yet
- Oncologic NursingDocument16 pagesOncologic NursingDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Without Advance Notice To The BorrowerDocument2 pagesWithout Advance Notice To The BorrowerDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis ActivityDocument2 pagesMitosis ActivityDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Notes - Nurse's Clinical Pocket Guide (FA Davis, 2007)Document242 pagesMedSurg Notes - Nurse's Clinical Pocket Guide (FA Davis, 2007)Keron Hou97% (62)
- Ifrs For SmesDocument130 pagesIfrs For SmesDharren Rojan Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Grandparent 2Document20 pagesGrandparent 2Dharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- December2012nletips Funda 121005040112 Phpapp02 PDFDocument6 pagesDecember2012nletips Funda 121005040112 Phpapp02 PDFJessamine Rochelle Reyes EsbertoNo ratings yet
- GrandparentDocument4 pagesGrandparentDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- CHN&CDDocument7 pagesCHN&CDDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing PharmacologyDocument22 pagesNursing PharmacologyDharren Rojan Garvida Agullana100% (2)
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesMyocardial InfarctionDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPDharline Abbygale Garvida Agullana100% (2)
- Planning and Organizing LecturesDocument3 pagesPlanning and Organizing LecturesDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Tallest ManDocument1 pageTallest ManDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Industry BackgroundDocument1 pageIndustry BackgroundDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TriviasDocument1 pageChemistry TriviasDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry JokesDocument3 pagesChemistry JokesDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument7 pagesHypertensionDharren Rojan Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- KorsakoffDocument4 pagesKorsakoffDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument4 pagesCancerDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Head Nursing Evaluation ToolDocument2 pagesHead Nursing Evaluation ToolDharline Abbygale Garvida Agullana100% (5)
- Bone DiseasesDocument9 pagesBone DiseasesDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing/ Non-Modifialbe Precipitating/ Modifiable: HepaticDocument2 pagesPredisposing/ Non-Modifialbe Precipitating/ Modifiable: HepaticDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Meat Processing IndustryDocument36 pagesMeat Processing IndustryDharline Abbygale Garvida Agullana100% (1)
- ScoliosisDocument4 pagesScoliosisDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Echzema DermatitisDocument7 pagesEchzema DermatitisAiman TymerNo ratings yet
- LedesmaDocument6 pagesLedesmaAngela Dimaano SaladaNo ratings yet
- Resume Format For Doctors PDFDocument3 pagesResume Format For Doctors PDFANIL PATELNo ratings yet
- UrticariaDocument16 pagesUrticariaIvan HoNo ratings yet
- Abdi LatifDocument2 pagesAbdi LatifEdward MutegekiNo ratings yet
- Qualis Novo 2020Document430 pagesQualis Novo 2020Anelise Gregis EstivaletNo ratings yet
- Produk 2023-01-13 19 - 00 - 38Document2 pagesProduk 2023-01-13 19 - 00 - 38Dwi Sheva30No ratings yet
- Joy N. Saquibal, M.DDocument78 pagesJoy N. Saquibal, M.DJoy AlmondsNo ratings yet
- Approach To Oral LesionsDocument53 pagesApproach To Oral LesionsUmut YücelNo ratings yet
- Inventory Override Report 02.14.2023 12.25 PMDocument14 pagesInventory Override Report 02.14.2023 12.25 PMFlorenciaNo ratings yet
- Molluscum Contagiosum: Dermatology Patient EducationDocument3 pagesMolluscum Contagiosum: Dermatology Patient EducationOrang KalonganNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Word ListDocument3 pagesCH 12 Word ListtigertiaNo ratings yet
- HH 7Document2 pagesHH 7CHENNAM PRAVEENNo ratings yet
- Organic Lotion CMODocument12 pagesOrganic Lotion CMOAishani LakamsaniNo ratings yet
- Not Copy: Studying in Dermatology ResidencyDocument5 pagesNot Copy: Studying in Dermatology ResidencyHemkerovner Keresztszegh von Kolowrat-KrakowskyNo ratings yet
- Photodermatologic Disorders (Photodermatoses) : Mikias Woldetensay Dermatology & Venereology Oct 2021Document59 pagesPhotodermatologic Disorders (Photodermatoses) : Mikias Woldetensay Dermatology & Venereology Oct 2021CHALIE MEQUNo ratings yet
- Complicaciones DermatologicasDocument219 pagesComplicaciones DermatologicasVanessaVillaMayta100% (1)
- The Chronicle of Cosmetic Medicine+Surgery Q4 2011Document24 pagesThe Chronicle of Cosmetic Medicine+Surgery Q4 2011Nino Avanti100% (1)
- New Client Prod Revival 2023 1st QTRDocument14 pagesNew Client Prod Revival 2023 1st QTRstephanie alvaranNo ratings yet
- AVEENO Daily Moisturizing Lotion Benefits Fact SheetDocument1 pageAVEENO Daily Moisturizing Lotion Benefits Fact SheetMari PerezNo ratings yet
- Infectious DermatologyDocument206 pagesInfectious DermatologyAaron Christian Earl VillosoNo ratings yet
- 1 Jyothi Sanjeevini Full DetailsDocument161 pages1 Jyothi Sanjeevini Full DetailsPramodNo ratings yet
- د. هالة Dermatitis-1 (Muhadharaty)Document7 pagesد. هالة Dermatitis-1 (Muhadharaty)adwNo ratings yet
- Specialist Doctors PDFDocument28 pagesSpecialist Doctors PDFvivek adNo ratings yet
- Aad Body Mole MapDocument2 pagesAad Body Mole Mapapi-265745737No ratings yet
- ImpetigoDocument5 pagesImpetigoInges PSNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris - Overview of ManagementDocument39 pagesAcne Vulgaris - Overview of ManagementDaulet AmangeldyNo ratings yet
- PemphigusDocument8 pagesPemphiguszuqiri ChanelNo ratings yet
- Acne VulgarisDocument58 pagesAcne VulgarisNargisNo ratings yet
- K7 Jamur Superficial 2020Document51 pagesK7 Jamur Superficial 2020Jimmy Fran IINo ratings yet