Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bernoulli Principle
Uploaded by
PrasillaPrisiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bernoulli Principle
Uploaded by
PrasillaPrisiCopyright:
Available Formats
1
[Chemical Engineering Lab Practice 1#]
SEGi UNIVERSITY
BERNOULLIS PRINCIPLE
Candidates name: Prasilla
Student ID: SCM 019310
Group members name: Edwin Cheong Zeng Tze
Loh Wei Neng
Shasonniaah Vjay Nair
Lecturer/Supervisor: Ms. Chan Yi Shee
Date of submission: 14/04/14
[SEGi University]
2
1) Abstract
The objective of this experiment is to investigate Bernoullis law and pressure
distribution along the venture tube. The Bernoullis principle experiment explores the
validity of the Bernoullis equation by applying it to the flow of water in a tapering
horizontal tube. This is done to determine if the total pressure head remains constant
along the length of the tube as predicted by the equation since the Bernoullis equation
states that variations in static pressure head along the tube can be calculated through the
equation. At the end of the experiment, graphs of flow velocity versus measurement
points and pressure distribution along venture tube is prepared for both set 1 and set 2.
2) Introduction
The Bernoullis equation simply states that pressure of the same liquid at the same level
is the same. This theory is applied onto a simple device to measure the pressure
distribution along the venture tube.
This equation also states that the pressure head, elevation head and velocity head are
constant along the venture tube. The friction along the tube is negligible. Since the tube is
horizontal and does not have any zero error, Z1=Z2 and the pressure head
can be measured through a simplified equation as below:
On the other hand, the mass flow rate, is also calculated in order to know the
velocity at point 1 and 2.
3
The calculated velocity
is obtained through this equation:
. The
dynamic pressure is calculated by subtracting static pressure from the total pressure head.
From the dynamic pressure,
was calculated
3) Procedure
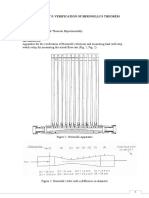
The apparatus used in the Bernoullis experiment are listed below
a) HM150.07
i) Assembly board
ii) Single water pressure gauge
iii) Discharge pipe
iv) Outlet valve
v) Venture tube with 6 measurement points
vi) Compression gland
vii) Probe for measuring overall pressure
viii) Hose connection(water supply)
ix) Valve at water inlet
x) 6-fold water pressure gauge(pressure distribution in venture tube)
4
A quick inspection was performed to ensure that the unit is in proper operating
condition. A hose connection was made and the unit was connected to the nearest
power supply. The discharge pipe was opened. The cap nut (1) of probe compression
gland was set such that the slight resistance is felt on moving probe. The inlet and
outlet valve was opened. The pump was switched on and main cock was slowly
opened. The vent valve (2) on water pressure gauge was opened and outlet cock was
carefully closed until the pressure gauges are flushed. The water level in pressure
gauges was regulated such that neither upper nor lower range limit (UL, LL) is
overshot or undershot, while the inlet and outlet cock was setting simultaneously. The
pressures at all measurement points were recorded. The overall pressure probe was
then moved to corresponding measurement level and the overall pressure was noted.
The volumetric flow rate was determined by using a stopwatch to establish the time
required for raising the level in the volumetric tank from 20 to 30 liters. The steps
were repeated for different flow rate.
5
4) Data and Analysis
h
1
(mmWs)
h
2
(mmWs)
h
3
(mmWs)
h
4
(mmWs)
h
5
(mmWs)
h
6
(mmWs)
Time, s
(10L)
.
V
(mm
3
/s)
h
stat.
265 255 135 210 225 230
92
109 000
h
total
305 307 308 293 285 282
h
dyn.
40 52 173 83 60 52
W
means
28.01 31.94 58.26 40.35 34.31 31.94
W
calc.
321.91 466.81 1288.4 640.42 427.12 321.91
h
stat.
280 270 98 210 228 235
131
71 300
h
total
305 307 310 297 277 266
h
dyn.
25 37 212 87 49 31
W
means
22.15 26.94 64.49 41.32 31.01 24.66
W
calc.
210.57 305.35 842.79 418.92 279.39 210.57
6
i) Set 1
Set 2
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
F
l
o
w
v
e
l
o
c
i
t
y
,
W
Measurement points
Flow velocity(W) versus measurement points
Wmeans
Wcalc
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
F
l
o
w
v
e
l
o
c
i
t
y
,
W
Measurement points
Flow velocity(W) versus measurement points
Wmeans
Wcalc
7
ii) Set 1
Set 2
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
d
i
s
t
r
i
b
u
t
i
o
n
Measurement points
Pressure distribution versus measurement
points
Hstat
Htotal
Hdynamic
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
d
i
s
t
r
i
b
u
t
i
o
n
Measurement points
Pressure distribution versus measurement
points
Hstat
Htotal
Hdynamic
8
5) Discussion
i) For both set 1 and 2, the
is more than the
. The graph shows that at
point 2, the velocity increases slightly. Between point 2 and point 3, there is a
significant change in the velocity. From point 3 to point 4, the velocity decreases
tremendously. From point 4 to point 5 and point 6, the velocity decreases slightly.
From this pattern of flow velocity, it is known that the result is due to the error
occurred during the experiment.
ii) Both the set 1 and set 2 seem to be sharing the same pattern of pressure
distribution in which the static pressure is inconsistent whereby it increases till
point 3 then starts to decrease till point 6. For the dynamic pressure, it converge
upwards at point 3 whereas downwards for static pressure.
6) Conclusion
i) According to the theory proposed by the Bernoullis equation, the pressure should
be consistent throughout the experiment. Since the results are inconsistent, it is
understood that the pressure varies as the area changes. The smaller the area, the
higher the pressure and vice versa.
ii) The errors occurred during the experiment definitely affects the result. The error
found was the blockage of pitot tube, this error can be corrected by cleaning the
pitot tube using a strong and sharp pin. The outlet is too low due to this blockage.
7) References
i.) R.K. Bansal 1983, A Textbook of Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines, 1st
Edition, Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd, India.
ii.) Rama Durgaiah, 2002, Fluid Mechanics and Machinery, 1st Edition, New Age
International (P) Ltd, India.
You might also like
- Fluid Lab 2 - Bernoulli ExpDocument19 pagesFluid Lab 2 - Bernoulli ExpCik Tiem Ngagiman89% (65)
- Internship Report On Front End Compression (Qadirpur Gas Field, OGDCL)Document23 pagesInternship Report On Front End Compression (Qadirpur Gas Field, OGDCL)abbas_sohail11080% (5)
- Bernoulli S Theorem Demonstration Lab Report UitmDocument29 pagesBernoulli S Theorem Demonstration Lab Report UitmAbdallah AlhasanNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's PrincipleDocument8 pagesBernoulli's PrincipleMD Atiqur Rahman Faisal100% (1)
- 12 Experiment #2: Bernoulli'S Theorem DemonstrationDocument12 pages12 Experiment #2: Bernoulli'S Theorem DemonstrationYasir A. Al-ShataifNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli S Principle Demonstration Lab ReportDocument17 pagesBernoulli S Principle Demonstration Lab ReportpehweihaoNo ratings yet
- Line List Ammonia Urea P1 - RevisiDocument28 pagesLine List Ammonia Urea P1 - RevisiAbu Akhmad BusanaNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Theorem ExperimentDocument17 pagesBernoulli's Theorem ExperimentMimi Hashim95% (19)
- Bernoulli S Principle Demonstration Lab ReportDocument18 pagesBernoulli S Principle Demonstration Lab ReportHasan RabyNo ratings yet
- Investigate Validity of Bernoulli's TheoremDocument26 pagesInvestigate Validity of Bernoulli's TheoremSaber Minato Azrul100% (1)
- Process Description of Gambat South Gas Processing FacilityDocument13 pagesProcess Description of Gambat South Gas Processing FacilitywaheedNo ratings yet
- Lab ManuelDocument79 pagesLab ManuelMarty SmurdaNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Bernoulli S DemoDocument11 pagesLab 5 Bernoulli S DemoNando100% (1)
- Bernoulli's Principle Demonstration (Lab Report)Document17 pagesBernoulli's Principle Demonstration (Lab Report)Arey Ariena94% (110)
- Bernouli Lab ReportDocument18 pagesBernouli Lab ReportUgeswran Thamalinggam100% (3)
- Validates Bernoulli's Theorem in Tapered DuctDocument29 pagesValidates Bernoulli's Theorem in Tapered DuctAnonymous NyvKBWNo ratings yet
- Pure Substance LectureDocument43 pagesPure Substance LectureZesi Villamor Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Bernouli's Theorem DemonstrationDocument14 pagesBernouli's Theorem DemonstrationAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Distillation Tower DesignDocument65 pagesDistillation Tower DesignNicholaus ShawNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Bernoulli's EquationDocument12 pagesLab 2 Bernoulli's EquationDário Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- FM 24 ManualDocument18 pagesFM 24 ManualMohd Nor SollehanNo ratings yet
- Bournelli ExperimentDocument10 pagesBournelli ExperimentUsamaIjazNo ratings yet
- Demonstration On Bernoulli's TheoremDocument22 pagesDemonstration On Bernoulli's TheoremMahe RukhNo ratings yet
- Thermal Fluid Lab Semester 6 Bernoulli's Theorem DemoDocument22 pagesThermal Fluid Lab Semester 6 Bernoulli's Theorem DemoEason OngNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration Lab ReportDocument24 pagesBernoulli's Theorem Demonstration Lab ReportCendolz IssZul50% (2)
- Lab Report 3Document14 pagesLab Report 3Siti Syuhadah0% (1)
- Bernoulli PrincipleDocument18 pagesBernoulli PrincipleMAC DARREL MICHAEL MAC DARREL MICHAELNo ratings yet
- Formal ReportxDocument7 pagesFormal ReportxDarshan ShaarmaNo ratings yet
- Mapua Institute of Technology Experiment Validates Bernoulli's TheoremDocument16 pagesMapua Institute of Technology Experiment Validates Bernoulli's TheoremNadine Pascual100% (2)
- (UNISIM (BEHAS) - Introduction To Aerospace) EAS105 - Lab2Document29 pages(UNISIM (BEHAS) - Introduction To Aerospace) EAS105 - Lab2Mohd Ashraf Mohd IsmailNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Theorem DemonstrationDocument27 pagesBernoulli Theorem DemonstrationmanzahuhuNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment BernoulliDocument13 pagesLab Experiment BernoulliAmoluck BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Verify Bernoulli's Theorem LabDocument5 pagesVerify Bernoulli's Theorem LabismailNo ratings yet
- E3 BernoulliDocument16 pagesE3 BernoullikishoreNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Theorem DemonstrationDocument16 pagesBernoulli's Theorem Demonstrationamirahabidin100% (1)
- 220s15 ExpB LabManualDocument5 pages220s15 ExpB LabManualMetu Ncc HaberlerNo ratings yet
- Validating Bernoulli's TheoremDocument26 pagesValidating Bernoulli's TheoremNurul AinNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli EquationDocument6 pagesBernoulli EquationMohanadAlrofuNo ratings yet
- University of Basrah Fluid Lab Experiment on Bernoulli's TheoremDocument17 pagesUniversity of Basrah Fluid Lab Experiment on Bernoulli's Theoremمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Bernaulli's Theorem FullDocument17 pagesBernaulli's Theorem FullBart KwanNo ratings yet
- Verification of Bernoulli's Theorem Using a Venturi TubeDocument7 pagesVerification of Bernoulli's Theorem Using a Venturi Tubevj kumarNo ratings yet
- Adarsh Institute of Technology and Research Centre, VitaDocument44 pagesAdarsh Institute of Technology and Research Centre, VitaPushkar FegadeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics-I Lab (MEEN 2217)Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics-I Lab (MEEN 2217)waqarNo ratings yet
- Bernoullis TheiremDocument7 pagesBernoullis TheiremAli M. ChehadehNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Equation Full ReportDocument6 pagesBernoulli Equation Full ReportChala1989No ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Measurement Lab ReportDocument16 pagesFluid Flow Measurement Lab Reportقاسمي عندامNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1.1Document7 pagesLab Report 1.1vj kumarNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Principle's LabDocument6 pagesBernoulli Principle's LabDusty SpearsNo ratings yet
- Calibrating a Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument47 pagesCalibrating a Bourdon Pressure Gaugeزياد الحربيNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.: 04 Experiment Name: Experimental Verification of Bernoulli's Equation. ObjectivesDocument9 pagesExperiment No.: 04 Experiment Name: Experimental Verification of Bernoulli's Equation. ObjectivesMd Afif AbrarNo ratings yet
- Verify Bernoulli's Theorem for a Viscous FluidDocument5 pagesVerify Bernoulli's Theorem for a Viscous FluidBasant Sharma100% (1)
- Calbaration of Pressure GaugeDocument12 pagesCalbaration of Pressure Gaugehamza19792005No ratings yet
- Problem A1Document8 pagesProblem A1Heidy CruzNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 Bernoullis Energy - 20240223 - 050049 - 0000Document11 pagesLab Report 2 Bernoullis Energy - 20240223 - 050049 - 0000ack awnsNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi MeterDocument8 pagesConservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi Meterdist2235No ratings yet
- Bernoulli's EquationDocument12 pagesBernoulli's Equationasfand12345100% (1)
- Lab1 - Verification of Bernoullis PrincipleDocument20 pagesLab1 - Verification of Bernoullis PrincipleAbenezer Tasew0% (1)
- Bernouli S Theorem DemonstrationDocument14 pagesBernouli S Theorem DemonstrationHarris ImranNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 6 Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration Apparatus: LABORATORY MANUAL For ENGR2860U-Fluid MechanicsDocument11 pagesExperiment # 6 Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration Apparatus: LABORATORY MANUAL For ENGR2860U-Fluid MechanicsAbdullah AlshihriNo ratings yet
- Session 11Document21 pagesSession 11Kais Garchi CasalNo ratings yet
- Lab3 HidrauDocument16 pagesLab3 HidrauNurul Abdul JalilNo ratings yet
- Demonstrating Bernoulli's TheoremDocument5 pagesDemonstrating Bernoulli's Theorempravishek maniNo ratings yet
- Continuity and Energy EquationsDocument53 pagesContinuity and Energy Equationssushil.vgiNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Wind Tunnel and Boundary LayerDocument9 pagesLab 3 - Wind Tunnel and Boundary LayerameershamiehNo ratings yet
- For 2 Inch Intalox Saddle Ceramic: Name: Abu Bakkar Siddique REG #: 2014-CH-215Document5 pagesFor 2 Inch Intalox Saddle Ceramic: Name: Abu Bakkar Siddique REG #: 2014-CH-215Atif MehfoozNo ratings yet
- Zanzibar Oswams WastewaterDocument31 pagesZanzibar Oswams Wastewatersalum abasiNo ratings yet
- Visio - Water Balance - Woodlark IslandDocument1 pageVisio - Water Balance - Woodlark IslandCraftychemistNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle Informational TextDocument3 pagesWater Cycle Informational Textapi-233611431100% (2)
- Water Cycle Lesson 3Document5 pagesWater Cycle Lesson 3api-247794398No ratings yet
- LED and induction street lights cut energy bills 87Document11 pagesLED and induction street lights cut energy bills 87Zain NadeemNo ratings yet
- Complementary Aspects of Fog, Rain and Dew CollectionDocument7 pagesComplementary Aspects of Fog, Rain and Dew CollectionGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Kezia Gloria A.RDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Kezia Gloria A.RQinthara MahdaniNo ratings yet
- Pump installation diagrams and total dynamic head explainedDocument3 pagesPump installation diagrams and total dynamic head explainedMichaelNo ratings yet
- How RO Booster Pumps WorkDocument3 pagesHow RO Booster Pumps WorkNix Darwin L. TobingNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Multiple Choice ReviewDocument3 pagesGas Laws Multiple Choice ReviewRolina Ruiz-LabaoNo ratings yet
- CR 0701 CH 10Document13 pagesCR 0701 CH 10Rıfat BingülNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 Molar Mass of A Volatile LiquidDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 2 Molar Mass of A Volatile LiquidJericho MaganaNo ratings yet
- Earth SpheresDocument18 pagesEarth Spheresdani_0227No ratings yet
- KLM Restriction Orifice Plate ProgramDocument37 pagesKLM Restriction Orifice Plate ProgramSiddharth BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- AIGA 075 - 11 Cal Method For Prevention of Overpress - Cryogenic Tanks - Reformated Jan 12 PDFDocument57 pagesAIGA 075 - 11 Cal Method For Prevention of Overpress - Cryogenic Tanks - Reformated Jan 12 PDFdaimon_pNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Exploration and ProductionDocument34 pagesFundamental of Exploration and ProductionVelya Galyani Pasila Galla100% (1)
- Solved Problems Ref SystemDocument5 pagesSolved Problems Ref SystemArchie Gil DelamidaNo ratings yet
- Lecture I - Classification of Fluid Machines - MCE 506 - Fluid Machinery by Professor WaheedDocument22 pagesLecture I - Classification of Fluid Machines - MCE 506 - Fluid Machinery by Professor WaheedTemidayo DavidNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Evaporation From Sample Cups, and Assessment of Their Effect On Analytical ErrorDocument11 pagesFactors Influencing Evaporation From Sample Cups, and Assessment of Their Effect On Analytical ErrorFerliemNo ratings yet
- Indian Maritime University: 4) Gas Sampling EquipmentDocument11 pagesIndian Maritime University: 4) Gas Sampling EquipmentMohd AkifNo ratings yet
- Kimia - BuferDocument12 pagesKimia - BuferHaryo Anggoro Permadi100% (1)
- Hydraulics Chapter 2 Problem SetDocument6 pagesHydraulics Chapter 2 Problem SetjosephussucoNo ratings yet
- Storm Water ManagementDocument19 pagesStorm Water Managementvarsha mataliNo ratings yet
- Chatoyer KRO1500 ManualDocument20 pagesChatoyer KRO1500 Manualrazaq athabNo ratings yet