Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10 Exercise 5 Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms
Uploaded by
Mohamed MostafaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10 Exercise 5 Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms
Uploaded by
Mohamed MostafaCopyright:
Available Formats
Prof. Dr. M. Helaly Eng. M.
Yakout Page 1 of 5
Alexandria University
Faculty of Engineering
Production Engineering Department
Second Year Production
2
nd
Semester (2013/2014)
Theory of Machines PE 253
4. Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms
Instantaneous Linear Acceleration
(1) Normal Component of Linear Acceleration
(2) Tangent Component of Linear Acceleration
Angular Acceleration
Coincident Point Acceleration (Coriolis Acceleration)
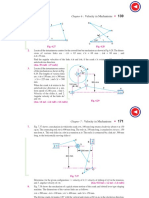
1. In the pin jointed four bar mechanism, shown below, AB = 300 mm, BC =
CD = 360 mm, and AD = 600 mm. The crank AB rotates at a constant
velocity of 100 rpm counterclockwise. Find the linear acceleration of joint
C and the angular acceleration of links BC and CD.
2. A mechanism, shown below, has the following dimensions: OA = 20 mm;
AB = 150 mm; BC = 60 mm; CD = 50 mm and BE = 40 mm. If crank
OA rotates uniformly at 120 rpm clockwise, find the linear acceleration of
B, C and D, then find the angular acceleration of links AB, BC and CD.
Prof. Dr. M. Helaly Eng. M. Yakout Page 2 of 5
3. The mechanism of a wrapping machine, shown below, has the following
dimensions: O
1
A = 100 mm; AC = 700 mm; BC = 200 mm; O
3
C = 200
mm; O
2
E = 400 mm; O
2
D = 200 mm and BD = 150 mm. The crank O
1
A
rotates at a uniform speed of 100 rad/s clockwise. Find the acceleration of
the point E of the bell crank lever and the point B and the angular
acceleration of links AC, EO
2
D, BD and O
3
C.
4. In the toggle mechanism, shown below, the slider D is constrained to
move on a horizontal path. The crank OA is rotating in the
counterclockwise direction at a speed of 180 rpm increasing at the rate of
50 rad/s
2
. The dimensions of various links are as follows: OA = 180 mm;
CB = 240 mm; AB = 360 mm and BD = 540 mm. For the given
configuration, find acceleration of slider D and angular acceleration of links
AB, CB and BD.
5. Find out the acceleration of the slider D and the angular acceleration of
links CD, CP and AB for the engine mechanism shown below. The crank
OA rotates uniformly at 180 rpm in clockwise direction. As shown below,
the various lengths are: OA = 150 mm; AB = 450 mm; PB = 240 mm; BC
= 210 mm and CD = 660 mm.
Prof. Dr. M. Helaly Eng. M. Yakout Page 3 of 5
6. A quick return mechanism of the crank and slotted lever type shaping
machine is shown below. The dimensions of the various links are as
follows: O
1
O
2
= 800 mm, O
1
B = 300 mm, O
2
D = 1300 mm and DR =
400 mm. The crank O
1
B makes an angle of 45 with the vertical and
rotates at 40 rpm in the counterclockwise direction. Find acceleration of
the ram R (the acceleration of the cutting tool) and the angular acceleration
of links O
2
D and RD. Describe the sliding acceleration of block C on O
2
D.
Homework Assignment (5): Acceleration Analysis
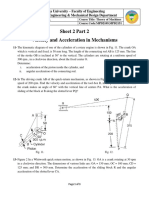
1. In the slider crank mechanism, shown below, the lengths of crank OB and
connecting rod AB are 100 mm and 400 mm respectively. If the crank
rotates uniformly clockwise with constant angular velocity of 10 rad/s, find
the linear acceleration of the slider A and the angular acceleration of the
connecting rod AB.
2. The offset slider-crank mechanism shown is driven by a slider (Link 4) at a
constant velocity of V
C
= 10 m/s to the left at the position shown.
Determine the linear acceleration of points B and D and the angular
acceleration of links AB and BCD at the position shown (=45).
Prof. Dr. M. Helaly Eng. M. Yakout Page 4 of 5
3. In the mechanism, shown below, the constant angular velocity of the crank
OA is 600 rpm counterclockwise. The dimensions of various links are: OA
= 28 mm; AB = 44 mm; BC 49 mm and BD = 46 mm. The center
distance between the centers of rotation O and C is 65 mm. The path of
travel of the slider is 11 mm below the fixed point C. The slider moves
along a horizontal path and OC is vertical. Determine the linear
acceleration of the slider D and the angular acceleration of links AB, BC
and BD, when the crank is inclined at an angle of 75 to the vertical.
4. In the mechanism, shown below, the link A rotates clockwise at constant
velocity of 10 rad/s. The lengths of various links are as follows: Link A =
25 mm, Link B = Link C = 100 mm, and Link D = Link E = 50 mm. The
link D is hinged to link B at 25 mm from the left hand end of link B. Find
the angular acceleration of links B, C, D, and E.
5. In the mechanism, shown below, the crank OA is 100 mm long and rotates
uniformly clockwise about O at 120 rpm. The connecting rod AB is 400
mm long. At a point C on AB, 150 mm from A, the rod CE 350 mm long
is attached. This rod CE slides in a slot in a trunnion at D. The end E is
connected by a link EF, 300 mm long to the horizontally moving slider F.
For the mechanism in the position shown, find sliding acceleration of
sliders B and F, sliding acceleration of link CE in the trunnion, and angular
acceleration of links AB, CE, and EF.
Prof. Dr. M. Helaly Eng. M. Yakout Page 5 of 5
6. The driving crank AB of the quick return mechanism, shown below,
revolves at a uniform speed of 200 rpm. Find the velocity and acceleration
of the tool box R and the angular acceleration of links RQ and PQ, in the
position shown, when the crank makes an angle of 60 with the vertical
line of centres PA. Describe the acceleration of sliding of the block at B
along the slotted lever PQ.
Instructions:
All dimensions are required in mm.
All linear accelerations are required in m/sec
2
.
All angular accelerations are required in rad/sec
2
.
You are requested to hand-in your own homework assignment by the due
date of Monday 12 May 2014. NO LATE assignments will be accepted.
Good Luck
Monday 5 May 2014
You might also like
- Biophysics in Nursing (Sharma Suresh) (2011) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFDocument232 pagesBiophysics in Nursing (Sharma Suresh) (2011) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFNomathamsanqa Khumalo94% (18)
- Mechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetDocument4 pagesMechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetAgare Tube0% (1)
- Sheet5Document3 pagesSheet5Mahmoud salahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Vel and Accln PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Vel and Accln PDFSarvesh ArbattiNo ratings yet
- Relative Vel. and Accl. ProblemsDocument9 pagesRelative Vel. and Accl. ProblemsSanket KumbharNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceleration Diagram EXERCISESDocument2 pagesVelocity and Acceleration Diagram EXERCISESSpidyNo ratings yet
- Theory of MachineDocument2 pagesTheory of MachineRıshabhBhawarNo ratings yet
- ME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Document6 pagesME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Kumar RajeshNo ratings yet
- Question Bank KOMDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank KOMMudit MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- VelocitytutorialDocument4 pagesVelocitytutorialManoz Thapa KajiNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis Worksheet PDF FreeDocument4 pagesMechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis Worksheet PDF FreeHarsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Acceleration analysis tutorialDocument3 pagesAcceleration analysis tutorialdevraj subediNo ratings yet
- Batch-B2 Acceleration AnalysisDocument2 pagesBatch-B2 Acceleration AnalysisAshutosh RautNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Velocity AnalysisDocument4 pagesTutorial 1 Velocity Analysisdevraj subediNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7b AccelerationDocument2 pagesTutorial 7b AccelerationGorkha EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Tom-Assignment 1Document2 pagesTom-Assignment 1jamunaa83No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 KDMDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 KDMvishalNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document4 pagesHW 4earn owinoNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 Part 2Document3 pagesSheet 2 Part 2Fouad MohamedNo ratings yet
- Unit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsDocument29 pagesUnit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Practical Relative Velocity & Acceleration PDFDocument2 pagesPractical Relative Velocity & Acceleration PDFKeshav PagarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Kamalesh DfcNo ratings yet
- Kom Assignment IDocument4 pagesKom Assignment IChadaram Jagadish JagadishNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Dynamics ProblemsDocument6 pagesMechanical Engineering Dynamics Problemsizel valerianoNo ratings yet
- Acceleration in MechanismsDocument38 pagesAcceleration in Mechanismsmurali_330No ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceleration AnalysisDocument6 pagesVelocity and Acceleration AnalysisPrithviNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machines Chapter Summary: Quick Return Mechanisms, Straight Line Motion, Intermittent MotionDocument80 pagesKinematics of Machines Chapter Summary: Quick Return Mechanisms, Straight Line Motion, Intermittent Motionteiborlin marngarNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion BankmunirajNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Kinematics TutorialDocument2 pagesMechanism Kinematics TutorialAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery Continuous Assessment TestDocument2 pagesKinematics of Machinery Continuous Assessment TestshiekziaNo ratings yet
- MEM 404 Mechanics of Machines Question BankDocument12 pagesMEM 404 Mechanics of Machines Question BankRohit DiwakarNo ratings yet
- CH7 Velocity in Mechanisms Relative Velocity MethoDocument32 pagesCH7 Velocity in Mechanisms Relative Velocity MethoAliNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Acceleration ExamplesDocument38 pagesMechanism Acceleration ExamplesApple VidalNo ratings yet
- KINEMATIC LINK MODEL QUESTIONSDocument4 pagesKINEMATIC LINK MODEL QUESTIONSNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Theory of MachinesDocument4 pagesExercises: Theory of Machinesgangadharan tharumarNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument2 pagesKinema TicsMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism and Theory of Machineries PDFDocument5 pagesMechanism and Theory of Machineries PDFJake AbrhamNo ratings yet
- Velocity and acceleration analysis of mechanismsDocument6 pagesVelocity and acceleration analysis of mechanismsAloysi DelouizaNo ratings yet
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3 Date of Submission: 07-01-2022Document2 pagesAssignment-3 Date of Submission: 07-01-2022Vasthadu Vasu Kannah DLNo ratings yet
- TOM Question BankDocument10 pagesTOM Question BankMadhan Kumar GovindarajuNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationDocument63 pagesVelocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationMPee Finance SumerpurNo ratings yet
- EJERCICIOS MECANISMOS - Javier Fuentes CDocument10 pagesEJERCICIOS MECANISMOS - Javier Fuentes CVictor MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 TranscriptDocument9 pagesLecture 4 TranscriptUD AthukoralaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Rigid BodyDocument4 pagesKinematics of Rigid BodyAbishek AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Mech IV Sem Question BankDocument59 pagesMech IV Sem Question BankSivaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument3 pagesKinematics of Machinessameer_m_daniNo ratings yet
- ME6401-Kinematics of MachineryDocument11 pagesME6401-Kinematics of Machineryappuanandh7811No ratings yet
- T4 - R1 - Kinematics of RB in 2D PDFDocument5 pagesT4 - R1 - Kinematics of RB in 2D PDFNurul AsyilahNo ratings yet
- Relative Velocity MethodDocument10 pagesRelative Velocity MethodOneplus entartainmentNo ratings yet
- Instantaneous Centre Velocity AnalysisDocument26 pagesInstantaneous Centre Velocity AnalysisSurya RSNo ratings yet
- A.R Engineering College: Villupuram Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesA.R Engineering College: Villupuram Department of Mechanical EngineeringVENKATESHNo ratings yet
- Mechanism WorksheetDocument8 pagesMechanism Worksheetnatnaelzelalem03No ratings yet
- Kinematic Inversions of MechanismsDocument6 pagesKinematic Inversions of MechanismsMECH HODNo ratings yet
- MCQ MechanismsDocument22 pagesMCQ Mechanismstvkbhanuprakash100% (1)
- E Are Free To Rotate On The Axis P. The Compound Gear B and C Rotate Together On TheDocument2 pagesE Are Free To Rotate On The Axis P. The Compound Gear B and C Rotate Together On ThekookoNo ratings yet
- STUCOR_ME8492-WQDocument13 pagesSTUCOR_ME8492-WQsk.bashaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Document11 pagesKinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- MENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 2 Kinematics ProblemsDocument3 pagesMENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 2 Kinematics ProblemsMidnight_dreamerNo ratings yet
- Journal of Applied Polymer Science Volume 103 Issue 5 2007 (Doi 10.1002/app.25468) Sergul Acikalin Gulmus Ulku Yilmazer - Effect of The Surface Roughness and Construction Material On Wall Slip inDocument7 pagesJournal of Applied Polymer Science Volume 103 Issue 5 2007 (Doi 10.1002/app.25468) Sergul Acikalin Gulmus Ulku Yilmazer - Effect of The Surface Roughness and Construction Material On Wall Slip inMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Design 101 Course Week 1Document19 pagesDesign 101 Course Week 1Mohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Survey ProcedureDocument1 pageSurvey ProcedureMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- MicropittingDocument8 pagesMicropittingMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering 2 Year Production Sheet 3 Math 4 Spring 2014Document2 pagesAlexandria University Faculty of Engineering 2 Year Production Sheet 3 Math 4 Spring 2014Mohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design: (Perspective of A Mechanical Engineer Working in Vibration Related Problems)Document49 pagesEngineering Design: (Perspective of A Mechanical Engineer Working in Vibration Related Problems)Mohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- KamalDocument2 pagesKamalMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Surface Texture DoohaDocument5 pagesSurface Texture DoohaMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- TableDocument1 pageTableMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Restraint SystemsDocument25 pagesSupplemental Restraint SystemsMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- VIP ProblemsDocument1 pageVIP ProblemsMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis TutorialDocument2 pagesVector Analysis TutorialMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Mostafa AdamDocument3 pagesMohamed Mostafa AdamMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Fault Diagnostics - Report-2Document12 pagesFault Diagnostics - Report-2Mohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Restraint SystemsDocument25 pagesSupplemental Restraint SystemsMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Alexandria University Production Engineering Course SyllabusDocument1 pageAlexandria University Production Engineering Course SyllabusMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Saylor StudentHandbookDocument14 pagesSaylor StudentHandbookMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Eccentric Loading in Welding Joint TutorialDocument2 pagesEccentric Loading in Welding Joint TutorialMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- 02) MechanismsDocument21 pages02) MechanismsMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Algebera LecDocument9 pagesAlgebera LecMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Material Technology Mini Project - RegistrationDocument1 pageMaterial Technology Mini Project - RegistrationMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Velocity in MechanismsDocument41 pagesVelocity in MechanismsMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics Section 5 PDFDocument6 pagesSolid Mechanics Section 5 PDFMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics PDFDocument1 pageSolid Mechanics PDFMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 3 PDFDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture 3 PDFMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Outlines PDFDocument1 pageSeminar Outlines PDFMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- 7 Essential Skills For Teamwork PDFDocument2 pages7 Essential Skills For Teamwork PDFMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Supporting Student Success Through Education ReformDocument2 pagesSupporting Student Success Through Education ReformMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Amr Adel Abd El-Slam El-masrY ResumeDocument2 pagesAmr Adel Abd El-Slam El-masrY ResumeMohamed Mostafa100% (1)
- Electrostatics: Coulomb's Law and ApplicationsDocument19 pagesElectrostatics: Coulomb's Law and ApplicationsArielle Emperador De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lect Acceleration Analysis - GraphicalDocument63 pagesLect Acceleration Analysis - GraphicalRayan IsranNo ratings yet
- Boundless Lecture Slides: Available On The Boundless Teaching PlatformDocument63 pagesBoundless Lecture Slides: Available On The Boundless Teaching PlatformAvirup RayNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Work Energy PowerDocument17 pagesAP Physics Work Energy Powernetsam_flixsamNo ratings yet
- Sizing Criteria For Cylinders and Servocylinders: F (P A - P A) 10 (N) F (P A - P A) 10 (N) F (P - P) A 10 (N)Document5 pagesSizing Criteria For Cylinders and Servocylinders: F (P A - P A) 10 (N) F (P A - P A) 10 (N) F (P - P) A 10 (N)Mohammed bakrimNo ratings yet
- Name: - Form: - Date: - Lesson 1 - Linear Motion A) IntroductionDocument26 pagesName: - Form: - Date: - Lesson 1 - Linear Motion A) Introductionpallz007No ratings yet
- Physics formulas cheat sheetDocument2 pagesPhysics formulas cheat sheetBOT NigmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Study Guide Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesChapter 12 Study Guide Physical Sciencekso20No ratings yet
- Part 1 - Mechanics: Useful WeblinksDocument2 pagesPart 1 - Mechanics: Useful WeblinksSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Newtons LawsDocument8 pagesNewtons LawsdenunderligeranNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document75 pagesWeek 1Tengmantz TVNo ratings yet
- Understanding Motion in Rotating and Accelerating FramesDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Motion in Rotating and Accelerating Frameskevinchu021195No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Checkpoint 1 (P. 192)Document14 pagesElectromagnetism: Checkpoint 1 (P. 192)ftg72395No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Q1 Pre-TestDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Science Q1 Pre-TestFlora May PacatangNo ratings yet
- Ce6006 Traffic Engineering and Management: Page 1 of 34Document37 pagesCe6006 Traffic Engineering and Management: Page 1 of 34KarthickNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Week 7 - Module 7Document16 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Week 7 - Module 7Carl Gabriel GravilezNo ratings yet
- YTU Mechanical Engineering Department Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesYTU Mechanical Engineering Department Exam ReviewAsniah HADJISALAMNo ratings yet
- AP PhysicsDocument78 pagesAP Physicsaprileverlasting100% (1)
- NEET-1 PHYSICS - PMD PDFDocument11 pagesNEET-1 PHYSICS - PMD PDFRameshbabu GellepoguNo ratings yet
- ME301 Dynamics and Vibration Lecture 05Document59 pagesME301 Dynamics and Vibration Lecture 05崔大炮No ratings yet
- Position Analysis IntroductionDocument5 pagesPosition Analysis Introductionmuddassir razzaqNo ratings yet
- Complete Solutions To The Physics GRE: PGRE0177Document123 pagesComplete Solutions To The Physics GRE: PGRE0177Taylor Faucett100% (4)
- DADF3 D 01Document255 pagesDADF3 D 01Raja BalaNo ratings yet
- U4 ReviewDocument5 pagesU4 ReviewmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitledMessias Martins - JUBANo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Class 9thDocument18 pagesChapter Two Class 9thAliNo ratings yet
- Physics EoS1 1819 V2Document12 pagesPhysics EoS1 1819 V2farid oluwasegun SHITTUNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Iceskaters-Coseriu BogdanDocument4 pagesThe Physics of Iceskaters-Coseriu Bogdancosbog94No ratings yet
- Jun 20 Paper 2P (QP)Document24 pagesJun 20 Paper 2P (QP)AishaNo ratings yet