Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DX 2
Uploaded by
Krizia R. PingkeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DX 2
Uploaded by
Krizia R. PingkeCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
The backflow gastric and duodenal contents into esophagus- GASTROESPHAGEAL REFLUX DSE
2. Portion of the stomach herniates thru the diaphragm and into thorax- HIATAL HERNIA
3. Inflammation of the stomach or gastric mucosa- GASTRITIS
4. Ulceration in the mucosal wall of the stomach, pyplorus, duodenum, or esophagus in the extend
thru the muscles- PEPTIC ULCER
5. Involves ulceration of the mucosal lining that extends to the submucosal layer of stomach
6. Gnawing sharp pain occurs 30-60mins after meals
7. Burning pain occurs after -3hrs after meals
8. Removal of stomach with attachment of esophagus to the jejunum or duodenum
9. Surgical division of vagus nerve to eliminate the vagal impulses
10. Removal of the lower half of the stomach
11. Partial gastrectomy with the remaining segment anastomosed to the duodenum.
12. Partial gastrectomy with the remaining segment anastomosed to the jejunum
13. Enlargmenet of the pylorus to prevent or decrease pyloric obstruction, thereby enhancing
gastric empyting
14. a break in the mucosal of the duodenum
15. The rapid emptying of the gastric contents into the small intestine that occurs following gastric
resection
16. Results from inadequate vitamin b12 intake or lack of absorption of ingestion of vitamin b12
from the gi tract
17. Results from the deficiency of the intrinsic factor necessary for intestinal absorption of vitamin
b12; gastric dse for intestinal absorption of the lack of instrinsic factor
18. Surgical reduction of gastric capacity that may be performed on the client with morbid obesity
to produce permanent weight loss
19. Allows the normal digestion without the risk of nutritional deficiency
20. The surgeon takes places a vertical line staples to create a small stomach pouch to which the
band is connected to provide an outlet to the small intestine
21. The inflatable band is placed around the stomach to limit stomach size able band is places
22. Dilated torturous veins in the submucousal of esophagus
23. The procedure involves the injection of sclerosing agent into around bleeding varices
24. The procedure involves ligation of varices with elastic rubber band
25. Shunt blood away from esophageal varice
26. Involves anastomosis of the splenic vein to the left renal vein.
27. Involves anastomosis of the portal vein to the inferior vena cava , diverting blood from the
portal system circulation
28. Involves a side anastomosis of the superior mesenteric vein to the proximal end of inferior vena
cava.
29. Ulcerative and inflammatory disease of the bowel that results in poor absorption of nutrients
30. Results in vascular congestion, hemorrhage, edema and ulceration of the bowel mucosa
31. Causes muscular hypertrophy, fat deposits and fibrous tissue with bowel thickening, shortening
and narrowing
32. Is the surgical creation of an opening into ileum or small intestine that allows for drainage of
fecal matter from ileum to the outside body
33. Surgical procedure of an opening into the colon that allows for drainage of fecal matter from the
colon to the outside of the body.
34. Curative and involves removal of entire colon
35. Intraabdominal pouch that stores the feces and is constructed from the terminal ileum
36. Is two-stage procedure that involves the excision of the rectal mucosa, abdominal colectomy,
construction of a reservoir to the anal canal and temporary loop ileostomy-
37. A 12 to 15 cm rectal stump is left after the colon is removed and small intestine is inserted into
this rectal sleeve and anastomosed.
38. Inflammatory dse that can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract but most often affect the
terminal ileum and leads to thickening and scarring, a narrowed lumen, fistulas, ulcer and
abcess. CROHNS DSE
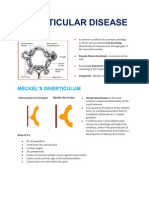
39. Outpunching or herniation of intestinal mucosa- DIVERTICULOSIS
40. Inflammation of one or more diverticula-
41. Dilated varicose veins of anal canal
42. Lie above the anal sphincter and cannot be seen on inspection of perianal area
43. Lie below anal sphincter and can be seen on inspection
44. Can become thrombosed or infammed
45. Simple resection of the hemorrhoids
46. Inflammation of appendix
47. Inflammation of peritonuim
48. Surgical removal of appendix
49. Chronic progressive dse of liver characterized by difuse degeneration and destruction of
hepatocytes
50. Alcohol induced , nutritional or portal
51. After massive liver necrosis
52. Develops from the chronic biliary obstruction , bile staisi and inflammation
53. Associated with sever risht sided CHF
54. A persistent in pressure in the portal vein that develops as resulst of obstructed flow
55. Accumulation of fluid in peritoneal cavity tha results from venous congestin of the hepatic
capillaries.
56. End tage hepatic failure
57. Progressive renal failure associated hepatic failure
58. Coarse tremors characterized by rapid nonrhytminc and flexions on wrist of fingers
59. Fruity musty breath odor of severe chronic liver dse
60. Inflammation of gallbladder
61. Associated with gallstones
62. Results whe insufficient bile emptying and gallbladder muscles wall dse cause fibrotic and
contracted gallbladder
63. Occurs in the absence of gallstones and is caused by bacterial invasion via lymphatic or vascular
system.
64. Cannot take deep breath if examiners fingers are passed below the heaptic margin
65. Removal of gallbladder
66. Inciosion into the common bile duct to remove the stone
67. Acute or chronic inflame of the pancreas with associated escape of pancreatic enzymes into
surrounding tissue
68. Occurs suddenly as one attack
69. Continual inflammation
70. Discoloration of abdomen and periumbilical area
71. Bluish discoloration of the flanks
72.
You might also like
- Diverticulitis Cure: The Ultimate Diverticulitis Diet: Diverticulitis Recipes: Your Ultimate Diverticulitis CookbookFrom EverandDiverticulitis Cure: The Ultimate Diverticulitis Diet: Diverticulitis Recipes: Your Ultimate Diverticulitis CookbookNo ratings yet
- Mouth and oral cavity conditionsDocument5 pagesMouth and oral cavity conditionsFan EliNo ratings yet
- DIVERTIKULOSISDocument28 pagesDIVERTIKULOSISAndrie WigunaNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic PseudocystDocument3 pagesPancreatic PseudocystViorel BudacNo ratings yet
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- GastrotomyDocument23 pagesGastrotomyMr. AlphaNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder HydropsDocument6 pagesGallbladder HydropsSaifulAnamNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-26 at 5.15.31 PMDocument39 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-26 at 5.15.31 PMgauravsingh708284No ratings yet
- Diverticular Diseases of ColonDocument22 pagesDiverticular Diseases of ColonGyan Prakash BhartiNo ratings yet
- Victoria-Intestinal ObstructionsDocument45 pagesVictoria-Intestinal ObstructionsVictoria &BeautifulPeopleNo ratings yet
- Hepatico JDocument4 pagesHepatico Jcharie2No ratings yet
- Rectovaginal Fistula RepairDocument3 pagesRectovaginal Fistula Repairnaftalina7No ratings yet
- Surgery of PancreasDocument30 pagesSurgery of PancreasmackieccNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy and Partial Cholecystectomy TechniquesDocument16 pagesCholecystectomy and Partial Cholecystectomy Techniquesmutmainnah_kamil100% (1)
- Surgical Management of Biliary Diseases Jamie R. Bellah, DVM, Diplomate ACVSDocument2 pagesSurgical Management of Biliary Diseases Jamie R. Bellah, DVM, Diplomate ACVSArokiya Anand KumarNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The GallbladderDocument67 pagesDisorders of The GallbladderGeofry OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- Cystotomy 37 LDocument19 pagesCystotomy 37 LDr Anais AsimNo ratings yet
- Colon, Rectum and Anus: Dentate or Pectinate LineDocument4 pagesColon, Rectum and Anus: Dentate or Pectinate LineAzria John DemetriNo ratings yet
- 2 Acute CholecystitisDocument21 pages2 Acute CholecystitisEtteh MaryNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology ExplainedDocument3 pagesGastroenterology ExplainedDeepthi VallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynDocument29 pagesCholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynCams BonoanNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Pseudocysts: Made By: Roll No 31-40 Aarushi Agarwal Batch Group Leader: Roll No. 32 Sajangiri GoswamiDocument23 pagesPancreatic Pseudocysts: Made By: Roll No 31-40 Aarushi Agarwal Batch Group Leader: Roll No. 32 Sajangiri GoswamizainNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic PseudocystDocument16 pagesPancreatic PseudocystSpandan KadamNo ratings yet
- Abdomen-Clinicals - PDF Version 1Document11 pagesAbdomen-Clinicals - PDF Version 1hamzabhayatNo ratings yet
- Aetiology, Pathology and Management of Enterocutaneous FistulaDocument34 pagesAetiology, Pathology and Management of Enterocutaneous Fistularoselinekhadija100% (1)
- Anatomy Atresia, Volvulus, Meckel's Diverticulum: BowelDocument45 pagesAnatomy Atresia, Volvulus, Meckel's Diverticulum: BowelkedokterankeluargaNo ratings yet
- Anorectal DisorderDocument31 pagesAnorectal DisorderSaid SalimNo ratings yet
- Small Nowel Emergency SurgeryDocument8 pagesSmall Nowel Emergency SurgerySurya Nirmala DewiNo ratings yet
- Sabiston Biliary System NotesDocument5 pagesSabiston Biliary System NotessvidrillionNo ratings yet
- Cirugía y Cirujanos: Gallstone Ileus After Endoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyDocument4 pagesCirugía y Cirujanos: Gallstone Ileus After Endoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyMuhammad Fuad MahfudNo ratings yet
- Dimatingcal, Warda M. BSN14D Group 24 (Laparoscopic Feeding Jejunostomy)Document18 pagesDimatingcal, Warda M. BSN14D Group 24 (Laparoscopic Feeding Jejunostomy)WARDA DIMATINGCALNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls of GastrectomyDocument23 pagesPitfalls of Gastrectomyshita febrianaNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Intestinal and RectaldisordersDocument16 pagesManagement of Patients With Intestinal and RectaldisordersintotheunknownNo ratings yet
- Bladder Diverticulum HinmanDocument6 pagesBladder Diverticulum HinmanGilberto ChafrinaNo ratings yet
- Aetiology, Pathology and Management of Enterocutaneous FistulaDocument34 pagesAetiology, Pathology and Management of Enterocutaneous Fistulabashiruaminu100% (4)
- Whipple ComplicationDocument34 pagesWhipple ComplicationMike Hugh100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal ImagingDocument134 pagesGastrointestinal ImagingAnonymous RTSL19BmiNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Insertion - OriginalDocument11 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis Catheter Insertion - OriginalZul HazmiNo ratings yet
- 54.the Gallbladder and Bile DuctsDocument19 pages54.the Gallbladder and Bile DuctsAdenegan Adesola RaymondNo ratings yet
- Diverticular DiseaseDocument8 pagesDiverticular Diseasenurizzah_885541100% (1)
- Total Pelvic ExenterationDocument13 pagesTotal Pelvic ExenterationRirin Wahyuni100% (1)
- CPP 301Document35 pagesCPP 301Ogwuche AndrewNo ratings yet
- Colostomy & Colostomy CareDocument56 pagesColostomy & Colostomy Careapi-3722454100% (31)
- Surgical Treatment: Shany Schwarzwald s1711 DR Cojocaru CristinaDocument12 pagesSurgical Treatment: Shany Schwarzwald s1711 DR Cojocaru CristinaShany SchwarzwaldNo ratings yet
- Common Surgical Procedures TerminologyDocument10 pagesCommon Surgical Procedures TerminologySara Tongcua TacsagonNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument25 pagesAppendicitisshahadelkanzi56No ratings yet
- Obstractive SymptomDocument43 pagesObstractive Symptomfairuz saadahNo ratings yet
- Open CystojejunostomyDocument5 pagesOpen CystojejunostomyDimas AdhiatmaNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlserDocument8 pagesPeptic UlserSubhanshu DadwalNo ratings yet
- Stoma Care BasicsDocument83 pagesStoma Care BasicsTeoh HsNo ratings yet
- Lect 3 Disorder of Mouth and EsophagusDocument42 pagesLect 3 Disorder of Mouth and EsophagusShayan ShayanNo ratings yet
- Ileus MeconiumDocument27 pagesIleus MeconiumDebby TamaraNo ratings yet
- Acute Suppurative PeritonitisDocument47 pagesAcute Suppurative PeritonitissanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Cudia, Mary Jesrel Cruz, Alyzza Gean Mempin, Allyssa Mae BSN 1-ADocument17 pagesCudia, Mary Jesrel Cruz, Alyzza Gean Mempin, Allyssa Mae BSN 1-ARomelyn CudiaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pancriatis Special HDocument9 pagesAcute Pancriatis Special HInga CeagleiNo ratings yet
- Gastrostomy: Berry Erida HasbiDocument11 pagesGastrostomy: Berry Erida HasbiMukhizalNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology Batch Cinereum Compilation 1Document3 pagesClinical Pathology Batch Cinereum Compilation 1RjDNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder Disorders: Group 3Document51 pagesGallbladder Disorders: Group 3Mae GabrielNo ratings yet
- Patient Instructions After Axillary Surgery PDFDocument25 pagesPatient Instructions After Axillary Surgery PDFKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Pedia Table of ContentsDocument2 pagesPedia Table of Contentsɹǝʍdןnos100% (4)
- Hepa e Hepatitis-A-Antibody MetDocument19 pagesHepa e Hepatitis-A-Antibody MetKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Haematomas Management and TreatmentDocument4 pagesHaematomas Management and TreatmentKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Asses PregnancyDocument15 pagesAsses PregnancyKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineers November 2013Document64 pagesCivil Engineers November 2013zoomscanner0% (1)
- Nursing Practice IVDocument11 pagesNursing Practice IVapi-3718174100% (1)
- Patient Instructions After Axillary Surgery PDFDocument25 pagesPatient Instructions After Axillary Surgery PDFKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- And Standards of Practice EmphasizesDocument15 pagesAnd Standards of Practice EmphasizesKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Table of ContentsDocument2 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Table of Contentsɹǝʍdןnos0% (1)
- Calculating IV Rates - Drops Per Minute (DPM) Calculating IV RatesDocument2 pagesCalculating IV Rates - Drops Per Minute (DPM) Calculating IV RatestakethatthisNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineers November 2013Document64 pagesCivil Engineers November 2013zoomscanner0% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing Assessment TechniquesDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Assessment TechniquesKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Pedia Table of ContentsDocument2 pagesPedia Table of Contentsɹǝʍdןnos100% (4)
- Maternal & Child Care Nursing Table of ContentsDocument2 pagesMaternal & Child Care Nursing Table of Contentsɹǝʍdןnos100% (4)
- Risk Factors and Nursing Care for Neurological ConditionsDocument4 pagesRisk Factors and Nursing Care for Neurological ConditionsKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Kidney StonesDocument10 pagesKidney StonesKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Case Study On The Concept ofDocument5 pagesCase Study On The Concept ofKrizia R. Pingke100% (1)
- Med Surg - Endocrine System QuestionsDocument7 pagesMed Surg - Endocrine System QuestionsKrizia R. Pingke100% (8)
- Ambulatory Care Information SystemDocument3 pagesAmbulatory Care Information SystemKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- DX 2Document3 pagesDX 2Krizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Groups Count Sum Average VarianceDocument1 pageGroups Count Sum Average VarianceKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Ni ReportDocument53 pagesNi ReportKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- 10 Leopold's ManeuverDocument5 pages10 Leopold's ManeuverKrizia R. Pingke83% (6)
- Learning Objectives Chapter One: Overview of Education in HealthDocument8 pagesLearning Objectives Chapter One: Overview of Education in HealthKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- A Rationale For Performance Examinations.3Document1 pageA Rationale For Performance Examinations.3Krizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Internal Credit Risk Rating Model by Badar-E-MunirDocument53 pagesInternal Credit Risk Rating Model by Badar-E-Munirsimone333No ratings yet
- Sample File: Official Game AccessoryDocument6 pagesSample File: Official Game AccessoryJose L GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Yuri LotmanDocument3 pagesYuri LotmanNHNo ratings yet
- Photojournale - Connections Across A Human PlanetDocument75 pagesPhotojournale - Connections Across A Human PlanetjohnhorniblowNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Success FactorsDocument147 pagesOperations Management Success Factorsabishakekoul100% (1)
- Assignment Chemical Bonding JH Sir-4163 PDFDocument70 pagesAssignment Chemical Bonding JH Sir-4163 PDFAkhilesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Econometrics IntroductionDocument41 pagesEconometrics IntroductionRay Vega LugoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Project Cost ManagementDocument48 pagesChapter 7 Project Cost Managementafifah suyadiNo ratings yet
- Araminta Spook My Haunted House ExtractDocument14 pagesAraminta Spook My Haunted House Extractsenuthmi dihansaNo ratings yet
- Cartha Worth SharingDocument27 pagesCartha Worth SharingtereAC85No ratings yet
- English Vocabulary For MedicineDocument5 pagesEnglish Vocabulary For MedicineDentistryuv 2020100% (1)
- Report of Physical ExaminationDocument6 pagesReport of Physical ExaminationJerome Paul De VeneciaNo ratings yet
- Simon Baumberg - Prokaryotic Gene ExpressionDocument348 pagesSimon Baumberg - Prokaryotic Gene ExpressionBodhi Dharma0% (1)
- Dryer User ManualDocument118 pagesDryer User ManualAyman Alhassny100% (1)
- Grammar activities and exercisesDocument29 pagesGrammar activities and exercisesElena NicolauNo ratings yet
- 1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQsDocument467 pages1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQskibrom atsbha67% (3)
- Business Policy FormulationDocument21 pagesBusiness Policy FormulationWachee Mbugua50% (2)
- Personal Branding dan Positioning Mempengaruhi Perilaku Pemilih di Kabupaten Bone BolangoDocument17 pagesPersonal Branding dan Positioning Mempengaruhi Perilaku Pemilih di Kabupaten Bone BolangoMuhammad Irfan BasriNo ratings yet
- Hannah Money Resume 2Document2 pagesHannah Money Resume 2api-289276737No ratings yet
- Touratsoglou, Coin Production and Circulation in Roman Peloponesus PDFDocument23 pagesTouratsoglou, Coin Production and Circulation in Roman Peloponesus PDFCromwellNo ratings yet
- Revolute-Input Delta Robot DescriptionDocument43 pagesRevolute-Input Delta Robot DescriptionIbrahim EssamNo ratings yet
- Commonlit The Cask of AmontilladoDocument10 pagesCommonlit The Cask of Amontilladoapi-506044294No ratings yet
- Module 1-PRELIM: Southern Baptist College M'lang, CotabatoDocument11 pagesModule 1-PRELIM: Southern Baptist College M'lang, CotabatoVen TvNo ratings yet
- Exodus Post Apocalyptic PDF 10Document2 pagesExodus Post Apocalyptic PDF 10RushabhNo ratings yet
- Second Periodic Test - 2018-2019Document21 pagesSecond Periodic Test - 2018-2019JUVELYN BELLITANo ratings yet
- SOW Form 4 2017Document8 pagesSOW Form 4 2017ismarizalNo ratings yet
- 15Document74 pages15physicsdocs60% (25)
- QHSE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM DOCUMENTATIONDocument25 pagesQHSE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM DOCUMENTATIONherisb100% (1)
- Proposal For Funding of Computer Programme (NASS)Document6 pagesProposal For Funding of Computer Programme (NASS)Foster Boateng67% (3)
- Bonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Document4 pagesBonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Mel Patricia M. CabreraNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Secure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeFrom EverandSecure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (16)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)