Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reducing ER-Diagrams To Tables: Tabular Representation of The ER - EER Diagram (EN94)
Uploaded by
Rajinder Sanwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pageslecture
Original Title
Lecture03_
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlecture
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pagesReducing ER-Diagrams To Tables: Tabular Representation of The ER - EER Diagram (EN94)
Uploaded by
Rajinder Sanwallecture
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
1
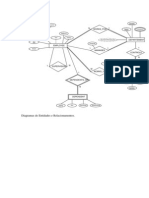
Reducing ER-Diagrams to Tables
Problem: Consider the entities of Project,
General Task and Employee in a project
management or job shop organization.
Specify the relations with typical attributes
to represent these entities and the
relationships between them. [MH91]
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
COMPANY DATABSE
DEPARTMENT
Number
Name
Location
Works_For
N
1
Manages
StartDate
1 1
Supervision
1
supervisee
supervisor
N
Dependents
EMP_DEP
Bdate
Name
Sex
Relationship
N
1
PROJECT
Name
Number
Location
Works_On
Hours
CONTROLS
N N
1
M
Dependents
Bdate
DeName
Sex
Relationship
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Dependents-Of
Works_On
Hours
N
M
N
1
N
Supervision
CONTROLS
Manages
StartDate
COMPANY DATABSE
1 N
1
1
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
DLocation
1
1
Tabular Representation of the
ER EER Diagram [EN94]
STEP 1:
For each regular entity type E in the ER schema,
create a relation R that includes all the simple
attributes of E.
Include only the simple component attributes of a
composite attribute.
Choose one of the key attributes of E as primary
key for R.
If the chosen key of E is composite, the set of simple
attributes that form it will together from the primary
key of R.
Dependents
Bdate
DeName
Sex
Relationship
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Dependents-Of
Works_On
Hours
N
M
N
1
N
Supervision
CONTROLS
Manages
StartDate
COMPANY DATABSE
1 N
1
1
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
DLocation
1
1
2
EMPLOYEE
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
FName
MI
LName
Manila 1950/02/02 12000 F Maria B. Santos 02
Makati 1960/01/01 10000 M Juan A. Cruz 01
Address Bdate Salary Sex LName MI FName SSN
Primary key
Dependents
Bdate
DeName
Sex
Relationship
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Dependents-Of
Works_On
Hours
N
M
N
1
N
Supervision
CONTROLS
Manages
StartDate
COMPANY DATABSE
1 N
1
1
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
DLocation
1
1
DEPARTMENT
DNo
Name
Location
Name DNo
Primary Key
Multi-valued attribute
Dependents
Bdate
DeName
Sex
Relationship
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Dependents-Of
Works_On
Hours
N
M
N
1
N
Supervision
CONTROLS
Manages
StartDate
COMPANY DATABSE
1 N
1
1
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
DLocation
1
1
Location Name PNo
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Primary Key
STEP 2:
For each weak entity type Win the ER schema with
owner entity type E, create a relation R and include all
simple attributes (or simple components of composite
attributes) of W as attributes of R.
In addition, include as foreign key attributes of R
the primary key attributes(s) of the relation(s) that
correspond to the owner entity type(s). This handles
the identifying relationship type of W.
The primary key of R is the combination of the
primary key(s) of the owner(s) and the partial key of
the weak entity type W, if any.
3
Dependents
Bdate
DeName
Sex
Relationship
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Dependents-Of
Works_On
Hours
N
M
N
1
N
Supervision
CONTROLS
Manages
StartDate
COMPANY DATABSE
1 N
1
1
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
DLocation
1
1
DEPENDENTS
Son 1990/04/04 M Jun Santos 02
Mother 1940/03/01 F Clara Cruz 01
Relationship Bdate Sex DeName ESSN
Foreign key
Dependents
Bdate
Sex
Relationship
DeName
Primary key
STEP 3:
For each binary 1:1 relationship type R in the
ER schema, identify the relations S and T that
correspond to the entity types participating in
R.
Choose one of the relations (let say S) and
include as foreign key in S the primary key
of T. It is better to choose an entity type with
total participation in R in the role of S.
Include the entire simple attributes (or simple
components of composite attributes) of the 1:1
relationship type R as attributes of S.
Dependents
Bdate
DeName
Sex
Relationship
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Dependents-Of
Works_On
Hours
N
M
N
1
N
Supervision
CONTROLS
Manages
StartDate
COMPANY DATABSE
1 N
1
1
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
DLocation
1
1
MANAGES
Finance
Personnel
Name
02
01
MGRSSN
1992/06/06
1990/05/05
StartDate
D2
D3
DNo
Manages
StartDate
1 1
DEPARTMENT
DNo
Name
Location
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
Name DNo
Primary key
STEP 4:
For each regular (non-weak) binary 1:N
relationship type R, identify the relation S that
represents the participating entity type at the N-side of
the relationship type.
Include as foreign key in S the primary key of the
relation T that represents the other entity type
participating in R*.
Include any simple attributes (or simple components
of composite attributes) of the 1:N relationship type as
attributes of S.
*** The reason for this is that each entity instance on the N-side is
related to at most one entity instance on the 1-side of the
relationship type.
4
Dependents
Bdate
DeName
Sex
Relationship
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Dependents-Of
Works_On
Hours
N
M
N
1
N
Supervision
CONTROLS
Manages
StartDate
COMPANY DATABSE
1 N
1
1
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
DLocation
1
1
EMPLOYEE
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
Location
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
1
Manila
Makati
Address
D2 1950/02/02 12000 F Maria B. Santos 02
D1 1960/01/01 10000 M Juan A. Cruz 01
DNo Bdate Salary Sex LName M
I
FName SSN
Manila 1950/02/02 12000 F Maria B. Santos 02
Makati 1960/01/01 10000 M Juan A. Cruz 01
Address Bdate Salary Sex LName MI FName SSN
Primary key
STEP 5:
For each binary M:N relationship type R,
create a new relation S to represent R.
Include as foreign key attributes in S the
primary keys of the relations that represent the
participating entity types; their combination
will form the primary key of S.
Also include any simple attributes of the M:N
relationship (or simple components of
composite attributes) as attributes of S.
Dependents
Bdate
DeName
Sex
Relationship
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Dependents-Of
Works_On
Hours
N
M
N
1
N
Supervision
CONTROLS
Manages
StartDate
COMPANY DATABSE
1 N
1
1
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
DLocation
1
1
WORKS_ON
30 P1 02
20 P1 01
Hours PNo ESSN
Works_On
Hours
M
N
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
PROJECT
Name
PNo Location
Primary key
STEP 6:
For each multivalued attribute A, create a
new relation R that includes an attribute
corresponding to A.
Include the primary key attribute K (as a
foreign key in R) of the relation that represents
the entity type or relationship type that has A
as an attribute.
The primary key of R is the combination of A
and K. If the multivalued attribute is
composite, include its simple components.
5
Dependents
Bdate
DeName
Sex
Relationship
PROJECT
Name
PNo
Location
Dependents-Of
Works_On
Hours
N
M
N
1
N
Supervision
CONTROLS
Manages
StartDate
COMPANY DATABSE
1 N
1
1
Works_For
EMPLOYEE
SSN
Bdate
Name
Sex
Address
Salary
N
DEPARTMENT
DNo
DName
DLocation
1
1
DEPT_LOCATION
Loc2 D1
Loc1 D2
Loc3 D2
Loc1 D1
DLocation DNo
DEPARTMENT
DNo
Name
DLocation
Primary key
EMPLOYEE(SSN,FName,MI,Lname,Sex,
Salary,Bdate, Address, SUPERSSN,DNo)
DEPARTMENT(DNumber,DName,MGRSSN,
StartDate)
DEPT_LOCATION(DNo, Location)
PROJECT(PNo, PName, Plocation,DNum)
WORKS_ON(ESSN,PNo, Hours)
DEPENDENT(ESSN, DependentName, Sex,
Bdate, Relationship)
TABLES as RELATIONS STEP 7:
For each n-ary relationship type R, n>2, create a new
relation S to represent R.
Include as foreign key attributes in S the primary keys
of the relations that represent the participating entity
types.
Also, include any simple attributes of the n-ary
relationship type (or simple components of composite
attributes) as attributes of S.
The primary key of S is usually a combination of all
the foreign keys that reference the relations
representing the participating entity types.
However if the participation is constraint (min,
max) of one of the entity types E participating
in R has max = 1, then the primary key of S
can be the single foreign key attribute that
references the relation E corresponding to E.
This is because in this case, each entity e in E
will participate in at most one relationship
instance of R and hence can uniquely identify
that relationship instance.
SUPPLY
Part2
Part1
PartNo
30
20
Quantity
P1 B
P1 A
PNo SName
SUPPLY
Quantity
SUPPLIER
SName
PROJECT
PNo
PART
PartNo
Primary key
M
M
M
You might also like
- 304 9 ER To Relational By6Document6 pages304 9 ER To Relational By6Behin SamNo ratings yet
- Expt No 1Document74 pagesExpt No 1SuryaShibuNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Design: IS311 Enterprise Systems Divine Word UniversityDocument31 pagesRelational Database Design: IS311 Enterprise Systems Divine Word UniversityNewman LekeNo ratings yet
- ER-and-EER-to-Relational Mapping: - For Each Regular Entity Type E in The ER SchemaDocument7 pagesER-and-EER-to-Relational Mapping: - For Each Regular Entity Type E in The ER SchemagtgnomeNo ratings yet
- Dbms ManualDocument23 pagesDbms ManualmeetmeifucanNo ratings yet
- Dbms-Module-2 SolutionsDocument13 pagesDbms-Module-2 SolutionsneelagundNo ratings yet
- ER To Relational MappingDocument30 pagesER To Relational MappingMohith RajNo ratings yet
- Logical DB Design: Mapping An ER Model To The Relational ModelDocument15 pagesLogical DB Design: Mapping An ER Model To The Relational ModelDrsamah AlmotairyNo ratings yet
- ER & EER To Relational MappingDocument34 pagesER & EER To Relational MappingragucmbNo ratings yet
- Chapter9-ER and EER MappingsDocument28 pagesChapter9-ER and EER MappingsalizaNo ratings yet
- L5-1 - DatabaseDocument31 pagesL5-1 - DatabaseElisante DavidNo ratings yet
- Relational Data ModelDocument21 pagesRelational Data ModelChemistry Jee AdvNo ratings yet
- 4 Relational - ModelDocument44 pages4 Relational - ModelHono LuluNo ratings yet
- St. Francis Institute of Technology: Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesSt. Francis Institute of Technology: Experiment No. 2JESSICA GONSALVES202053No ratings yet
- 4 1 Logical Database Design ER and EERR To Relational MappingDocument58 pages4 1 Logical Database Design ER and EERR To Relational MappingMisgana ShewangizawNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Design - : Mapping ERD To RelationalDocument61 pagesRelational Database Design - : Mapping ERD To RelationalMonkey dragon10No ratings yet
- ER Relational MappingDocument52 pagesER Relational MappingNikhilesh PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Reduction of ER Model To Relational ModelDocument18 pagesReduction of ER Model To Relational ModelNamanNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document17 pagesWeek 6ابتهاج عبدالسلامNo ratings yet
- How To Draw An ER DiagramDocument96 pagesHow To Draw An ER DiagramTech_MX100% (1)
- Scala Quiz NotesDocument144 pagesScala Quiz NotesRitika PapnejaNo ratings yet
- Er & RMDocument26 pagesEr & RMEftekher Ahmed AqibNo ratings yet
- Convert NormalizationDocument42 pagesConvert NormalizationSanduniNo ratings yet
- DBMS LAB Assign. 1Document5 pagesDBMS LAB Assign. 1Deep PatoliyaNo ratings yet
- 5 ER - and EER-to-Relational MappingDocument20 pages5 ER - and EER-to-Relational MappingTala alammNo ratings yet
- MappingDocument8 pagesMappingLakshit PardeshiNo ratings yet
- Entity-Relationship (ER) Data ModelDocument42 pagesEntity-Relationship (ER) Data ModelChemistry Jee AdvNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Refining The ER, Design For Company DataBase and Relational ModelDocument59 pagesUnit 2 Refining The ER, Design For Company DataBase and Relational Modelprathameshm.cs21No ratings yet
- 04 ER To TableDocument43 pages04 ER To TableSyeda Areeba RashidNo ratings yet
- Relational Schema DesignDocument5 pagesRelational Schema DesignsishidNo ratings yet
- Week 5 ER To Relation Mapping - 1Document14 pagesWeek 5 ER To Relation Mapping - 1Marco CartagenaNo ratings yet
- Ders # 2: Veri Tabani Ders Notlari Data Modeling With ER References Addison Wesley"Document31 pagesDers # 2: Veri Tabani Ders Notlari Data Modeling With ER References Addison Wesley"Hi11eTNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Design by ER-to-Relational MappingDocument11 pagesRelational Database Design by ER-to-Relational MappingHARDIK PANPALIYANo ratings yet
- Ch5 MappingDocument66 pagesCh5 MappingAditya Kharisma WicaksanaNo ratings yet
- The Entity-Relationship ModelDocument34 pagesThe Entity-Relationship ModelFarah FazalNo ratings yet
- Unit-2-ER-Relational-Mapping and Relational-ModelDocument59 pagesUnit-2-ER-Relational-Mapping and Relational-ModelSAKSHAM PRASADNo ratings yet
- CSE - 220 Database Management Systems: Subrat K Dash LnmiitDocument45 pagesCSE - 220 Database Management Systems: Subrat K Dash LnmiitRishiGuptaNo ratings yet
- Mapping Relational Model - Er: Database TechnologyDocument28 pagesMapping Relational Model - Er: Database TechnologyVineet MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: ER-and-EER-to-Relational Mapping: OutlineDocument11 pagesChapter 5: ER-and-EER-to-Relational Mapping: OutlineKadi AlhammadiNo ratings yet
- Normalization SDocument13 pagesNormalization SAvani GadhaviNo ratings yet
- The ER and EER ModelDocument62 pagesThe ER and EER ModelbijaysubediNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument603 pagesFinalMuhammad Sultan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Entity RelationshipDocument28 pagesEntity RelationshipabrahamzagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 ERDDocument44 pagesChapter 03 ERDNguyễn Thanh PhátNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Design: S. Nandagopalan, BIT 1Document42 pagesIntroduction To Database Design: S. Nandagopalan, BIT 1thinkinghat2050No ratings yet
- Praktikum: Nabilah ShofianiDocument8 pagesPraktikum: Nabilah Shofianiofi_ns140No ratings yet
- Reading NormalizationFormsDocument8 pagesReading NormalizationFormsCatarina Lopes GarcezNo ratings yet
- ER To Relational MappingDocument17 pagesER To Relational MappingMohammad DiabNo ratings yet
- DB Unit2Document44 pagesDB Unit2Druthi GsNo ratings yet
- (E) ER Mapping To RelationalSchemaDocument23 pages(E) ER Mapping To RelationalSchemaKayan SamiNo ratings yet
- The Entity-Relationship (Er) Model: CHAPTER 7 (6/E) CHAPTER 3 (5/E)Document25 pagesThe Entity-Relationship (Er) Model: CHAPTER 7 (6/E) CHAPTER 3 (5/E)mamasita25No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Database Management System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument16 pagesUnit 2 - Database Management System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inGourav CHOUDHURYNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Design by ER - To-Relational MappingDocument16 pagesRelational Database Design by ER - To-Relational Mappingلو شئت ان تغادر الارض قليلاNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design and The Entity-Relationship ModelDocument44 pagesConceptual Design and The Entity-Relationship ModelSimran KaurNo ratings yet
- Diagramas de Entidades e Relacionamentos.: Works - For 1 NDocument3 pagesDiagramas de Entidades e Relacionamentos.: Works - For 1 NTiago SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05-2 ER-EER To Relational MappingDocument27 pagesChapter 05-2 ER-EER To Relational MappingFantasypie 888No ratings yet
- ERD To Relational ModelDocument11 pagesERD To Relational ModelSaadNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2: Data Modeling Using The Entity-Relationship (ER) ModelDocument71 pagesUnit - 2: Data Modeling Using The Entity-Relationship (ER) ModelEAKEHEH HNo ratings yet
- ER To Relational MappingsDocument36 pagesER To Relational MappingsAyele NugusieNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Parallelism Is UbiquitousDocument3 pages1.1 Parallelism Is UbiquitousRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- IT 606L05 Parallel ComputingDocument2 pagesIT 606L05 Parallel ComputingRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Parallel Algorithm TutorialDocument53 pagesParallel Algorithm TutorialRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Padma Awards 2016 - The Complete Winners ListDocument6 pagesPadma Awards 2016 - The Complete Winners ListVikramaSimhaNo ratings yet
- CS627Document1 pageCS627Rajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- NBA Evaluation GuidelinesDocument23 pagesNBA Evaluation Guidelinesgantasrinivas_bell1160No ratings yet
- UKPSC Haridwar Official Answer SheetDocument4 pagesUKPSC Haridwar Official Answer Sheetvj4249No ratings yet
- List of Dams and Reservoirs On Rivers in India (State Wise)Document9 pagesList of Dams and Reservoirs On Rivers in India (State Wise)Gaurav Pareta100% (2)
- Foc PaperDocument1 pageFoc PaperRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Latancy Solution-Pipeline Reservation TableDocument14 pagesLatancy Solution-Pipeline Reservation TableBhavendra Raghuwanshi60% (10)
- Syllabus For Written Examination For PGT (Biology) : Diversity of Living WorldDocument34 pagesSyllabus For Written Examination For PGT (Biology) : Diversity of Living WorldRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Important AnswersDocument14 pagesImportant Answersvjay2003No ratings yet
- Fofhkuu Inksa Ds Fy, Vko" DRKDocument2 pagesFofhkuu Inksa Ds Fy, Vko" DRKRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- CS627Document1 pageCS627Rajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Ble 93Document26 pagesBle 93Pushkar PandeNo ratings yet
- Jacobi Method PDFDocument57 pagesJacobi Method PDFRajinder Sanwal100% (1)
- Unit 4 OpenmpDocument8 pagesUnit 4 OpenmpRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Parallel Algo TechniquesDocument2 pagesParallel Algo TechniquesRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Parallel Reduction in CUDADocument38 pagesOptimizing Parallel Reduction in CUDARajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument104 pagesClass NotesRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- AJAX: Creating Web Pages With A Synchronous Javascript and XMLDocument408 pagesAJAX: Creating Web Pages With A Synchronous Javascript and XMLmary100% (2)
- Himachal Pradesh 2016 (Jan-Aug) by AffairsCloudDocument7 pagesHimachal Pradesh 2016 (Jan-Aug) by AffairsCloudRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- NBA Evaluation GuidelinesDocument23 pagesNBA Evaluation Guidelinesgantasrinivas_bell1160No ratings yet
- Central Board of Secondary Education H-149, Sector - 63, Noida - 201309 (U.P.)Document1 pageCentral Board of Secondary Education H-149, Sector - 63, Noida - 201309 (U.P.)Rajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- The Screening Test(s) Will Be Objective Type of One Paper Carrying 100 Questions Having Duration of 02 HoursDocument1 pageThe Screening Test(s) Will Be Objective Type of One Paper Carrying 100 Questions Having Duration of 02 HoursRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Brochure GATE2017Document62 pagesBrochure GATE2017mohitNo ratings yet
- 2012 - 2 - Syllabus Lect Tech Edu PDFDocument1 page2012 - 2 - Syllabus Lect Tech Edu PDFRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument70 pagesPDFRajinder Sanwal100% (1)
- 2012 - 11 - Syllabus For The Post of Lecturer Computer EngineeringDocument1 page2012 - 11 - Syllabus For The Post of Lecturer Computer EngineeringRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- CS-PHD Shortlisted CandidatesDocument1 pageCS-PHD Shortlisted CandidatesRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Business AnalyticsDocument42 pagesBusiness AnalyticsDakshkohli31 KohliNo ratings yet
- Daily Support Status 20-24feb2023Document3 pagesDaily Support Status 20-24feb2023zaheer ahmedNo ratings yet
- Legal Research MethodologyDocument37 pagesLegal Research MethodologyVinayak BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Common Administrative Commands in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5, 6, and 7Document30 pagesCommon Administrative Commands in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5, 6, and 7Shailendra MathurNo ratings yet
- Reverse EngineeringDocument183 pagesReverse Engineeringssimorgh100% (2)
- Oracle Cache Buffer InternalsDocument67 pagesOracle Cache Buffer InternalsSaeed MeethalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5: Research MethodologyDocument17 pagesChapter-5: Research MethodologyShilpa SulekhNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4. Data CollectionDocument7 pagesLESSON 4. Data CollectionRose MaeNo ratings yet
- ALLAMA IQBAL OPEN UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD (Department of Home & Health Sciences)Document4 pagesALLAMA IQBAL OPEN UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD (Department of Home & Health Sciences)Anonymous EIjnKecu0JNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms in JavaDocument44 pagesData Structures and Algorithms in JavanafygeeNo ratings yet
- Guide To Scaling Web Databases With MySQL ClusterDocument20 pagesGuide To Scaling Web Databases With MySQL ClustersergengNo ratings yet
- CNIL - Referentiel Training Program enDocument10 pagesCNIL - Referentiel Training Program enmbeatrizsaboyaNo ratings yet
- File Formats in Big DataDocument13 pagesFile Formats in Big DataMeghna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PR 1Document28 pagesModule 1 PR 1Alehxis Gglc Fonts RnlptNo ratings yet
- Big Data Tools-An Overview: ArticleDocument16 pagesBig Data Tools-An Overview: ArticleAdzan YogaNo ratings yet
- The History of Touch-Based System and Development of Braille Writing System in MalaysiaDocument11 pagesThe History of Touch-Based System and Development of Braille Writing System in MalaysiahifzhanNo ratings yet
- AyushiPatra ResumeDocument1 pageAyushiPatra ResumePrasannaNo ratings yet
- Useful Oracle Queries For SAP Basis AdminisDocument10 pagesUseful Oracle Queries For SAP Basis AdminisKalyanNo ratings yet
- LVM Version 2.0 Volume Groups in HP-UX 11i v3Document31 pagesLVM Version 2.0 Volume Groups in HP-UX 11i v3robinNo ratings yet
- Spark Kafkaintegration PDFDocument71 pagesSpark Kafkaintegration PDFehenry100% (1)
- Autopsy Installation & UseDocument8 pagesAutopsy Installation & UseMohammed BasheeruddinNo ratings yet
- CP3 Sept 2022 NotesDocument49 pagesCP3 Sept 2022 Notesharihfam0% (1)
- Impact of Dietary Patterns On Academic Performance of Zimbabwean College StudentsDocument15 pagesImpact of Dietary Patterns On Academic Performance of Zimbabwean College StudentsEvelyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- PRBDocument3 pagesPRBPK DasNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management. (Project) ShilpaDocument58 pagesWorking Capital Management. (Project) ShilpaPraveen KambleNo ratings yet
- Mulugeta DassaDocument77 pagesMulugeta DassaamogneNo ratings yet
- Learning Microsoft Access 2007 - InvoicesDocument14 pagesLearning Microsoft Access 2007 - InvoicesGuided Computer Tutorials60% (5)
- Data Engineering 6 Months PlanDocument3 pagesData Engineering 6 Months PlanitiNo ratings yet
- Mindtools AssessmentDocument4 pagesMindtools Assessmentapi-272993959No ratings yet
- 11G PLSQLDocument86 pages11G PLSQLprasanna ghareNo ratings yet