Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vocabulary: Simplifying Radical Terms
Uploaded by
Bill LauloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vocabulary: Simplifying Radical Terms
Uploaded by
Bill LauloCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Vocabulary:
3 5
0.75 which can bewritten as aratio is called arational number
and 2 which can't bewritten as ratios arecalled irrational numbers
or or thesymbol is called aRADICAL
n thenumber beneath the
t
radical sign is theRADICAND
n is theprincipal or positivesquareroot of n
n is thenegativesquareroot of n
n isthepositiveor negativesquareroot of n
n is thepositiveor negativesquareroot of n
What is the approximate value of these radicals? Think about
how close they are to the square numbers 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49,64, 81
7 20
37
12 102
70 55 48
2.6 10.1 4.5 3.5
8.4 6.1 7.4 6.9
Simplifying radical terms.
1. look for factors that are square terms.
2. find the square root of that square term.
3. put that outside the radical.
45
9 5 =
9 5 =
8
4 2 =
4 2 =
75
25 3 =
25 3 =
48
16 3 =
16 3 =
3 5 =
2 2 =
5 3 =
4 3 =
700 100 7 = 10 7 = 100 7 =
16
x
8
x =
3
x
2
x x = x x =
7
m
6
m m =
3
m m =
23
y
22
y y =
11
y y =
7
8h
6
4h 2h =
3
2h 2h =
13
45p
12
9p 5p =
6
3p 5p =
Adding and subtracting radicals
Simplify the terms then gather like terms.
5 7 2 5 2 7 3 1 5 . + + 3 11 6 2 2. 2 11 8 2 +
3 7 5 5 = + 11 2 2 =
8 3 2 11 3 5 1 3. 1 + 6 7 3 5 . 6 4 3 +
7 3 3 11 = 4 6 6 3 =
5 1 5. 8 2 8 +
5 9 2 2 4 2 = +
5 3 2 2 2 2 = +
15 2 4 2 = +
19 2 =
2 75 6. 5 27
2 25 3 5 9 3 =
2 5 3 5 3 3 =
10 3 15 3 =
5 3 =
5 12 2 45 3 27 7. 5 4 00 + +
5 4 3 2 9 5 3 9 3 4 100 5 = + +
5 2 3 2 3 5 3 3 3 4 10 5 = + +
10 3 6 5 9 3 40 5 = + +
19 3 34 5 =
2 28 3 20 50 5 8 3 . 0 6
2 4 7 3 4 5 100 5 5 9 7 =
2 2 7 3 2 5 10 5 5 3 7 =
4 7 6 5 10 5 15 7 =
11 7 16 5 =
Simplifying Radicals with Fractions
Simplify the two parts of the radical and then simplify again if required.
99
100
99
100
=
9 11
10
=
3 11
10
=
50
27
25 2
9 3
=
5 2
3 3
=
300
3 8
10 3
6 2
=
5 3
3 2
=
50
10 49
25 2
10 7
=
5 2
10 7
=
2
14
=
100 3
3 4 2
=
2
Solving Equations with Radicals
2
there are actually two solutions.
Can you think of themboth?
x 4 =
which is written as 2 x 2 or 2 =
The rest of the steps in solving equations just use the
reverse operations that we have used before.
2
2x 3 9 =
2
add 3 on both 2x 12 sides =
2
divide 2 on both s 6 s x ide =
square root on both s x 6 ides =
2
3x
1 5
2
=
2
add 1 on both
3x
6
2
sides =
2
multiply by 2 on both 3x 12 s side =
22
divide by 3 on both s 4 s x ide =
square root on both s d s x i e 2 =
2
3x 1
5
4
=
2
multiply by 4 on bot 3x 1 2 h 0 es sid =
2
add 1 on both 3x 21 sides =
2
divide by 3 on both s 7 s x ide =
square root on both s x 7 ides = q
2
2x 4
5 11
7
+
+ =
2
minus 5 on bot
2x
h
4
6 s
7
s ide
+
=
2
7
2x
o
4 4
n .s
2
b
+ =
2
4 o
2x 3
.s
8
n b
=
2
2 on s
x 19
b.
=
x 19 =
2
4 .
2x
1
6
5
+
= x 7 =
2
3x
2 4
5
2. = x 10 =
2
3(m 1)
6 3.
2
+
= m 3 =
2
1 .5y 4 11 = y 2 =
2
4g
2 10
3
5. = g 3 =
2
5(h 1) 1 6. 9 = h 3 =
2
7y 1 + 7y 1
. 2 7 3
3
+
= y 2 =
2 2
5n 1 13 8 2n . + = n 2 =
2
3z
2 8 9.
5
+ = z 10 =
2
5 3b 1 10. 2 + = b no solution =
2
3(5z
1
4
11.
2)
7
+ = z 2 =
2
5 2(4t 1 1 12 1 . ) + = t 1 =
Finding the Area of Complex Shapes see Looking For Pythagoras. Investigation 2
1. Make a rectangle
around the shape.
2. Make triangles and
rectangles in the outside.
Findtheareaof therectangle 3 4 12
A
B
C
D
E
Find the area of the rectangle. 3 4 12 =
Find the area of the outside shapes.
1 2
B 1
2
= = 11
A 0.5
2
= =
C 2 1 2 = =
2 2
D 2
2
= =
3 1
E 1.5
2
= =
Find the total outside area 7 =
Subtract the area of the outside from
the rectangle area to get the inside area.
5 =
Find the area of the rectangle. 5 4 20 =
B
C
A
D
E
Find the area of the outside shapes.
B 2 1 2 = =
3 2
A 3
2
= =
1 2
C 1
2
= =
4 1
E 2
2
= =
Find the total outside area 14 =
Subtract the area of the outside from
the rectangle area to get the inside area.
6 =
3 4
D 6
2
= =
3
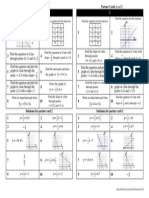
Finding the Length of Segments see Looking For Pythagoras. Page20
Makea square
around thesegment.
Counting thenumber of
dots on each side makes it easy.
Findtheareaof theoutsidesquare 6 6 36 Find the area of the outside square. 6 6 36 = =
Find the area of the outside triangles. )
5 1
4( 10
2
= =
Find the area of the inside square. 36 10 26 = =
Therefore the length of one side
of the square is
26
Findtheareaof theoutsidesquare 5 5 25 Find the area of the outside square. 5 5 25 = =
Find the area of the outside triangles. )
3 2
4( 12
2
= =
Find the area of the inside square. 25 12 13 = =
Therefore the length of one side
of the square is
13
Pythagorean Theorem. See page 482 in the textbook.
In a right triangle the area of a square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the area
of the squares on the other two sides.
Note: The hypotenuse is the long side of the triangle. It is opposite the right angle.
2 2 2
a b c + =
The sum of the areas gives the equation:
When the hypotenuse is the unknown.
2 2 2
a b c + =
2 2 2
3 5 x + =
22
34 x =
x 34 =
When a leg is the unknown.
2 2 2
a b c + =
2 2 2
5 x 11 + =
2 2 2
x 11 5 =
2
x 96 =
x 96 =
x 4 6 =
4
When the side lengths include variables.
2 2 2
a b c + =
2 2 2
(2x) (3x) 8 + =
2 2
4x 9x 64 + =
2x
8
3x
2
13x 64 =
64
x
13
=
8
13
=
2 2 2
a b c + =
( ) ( )
2 2
2
5p 6 7p + =
2 2 2
25p 6 49p + =
2 2
6 24p =
3
2
3
p
2
=
3
p
2
=
When there is more than one triangle in the diagram.
2 2 2
9 8 y + =
Choose the triangle where you know two sides.
Label the third side with a variable.
2
145 y =
Note: We dont need to know what y is.
Solve the other triangle.
2 2 2
y x 13 + =
2 2 2
weknow y 145 so 145 x 13 = + =
2 2
x 13 145 =
2
x 24 =
x 24 =
x 2 6 =
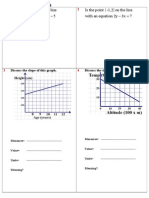
Dot Paper Problems:
Find the perimeter of this shape.
Construct right triangles and then solve using Pythagoras.
2 2
x 3 2 13 + x 3 2 13 = + =
2 2
y 5 2 29 = + =
perimeter 4 13 29 2 5 = + + +
2 2
z 4 2 20 2 5 = + = =
Find the perimeter for
these shapes.
2 10 6 2 5 1 2 + + + =
8 1 2 5 2 0 = + +
3 3 3 5 3 2 = + +
3 10 5 2 4 5 + = + +
2 13 2 10 3 5 2 82 2 13 2 10 3 5 2 82 = + + +
6 2 13 10 = +
5 13 2 7 65 7 5 1 + + + + =
Questions Involving Recognising Pythagorean Relationships:
1. Recognising right triangles:
Are the following triangles right triangles?
The sides of a right triangle will make the
Pythagoras equation true. Try it for this
triangle
6
9
7
2 2 2
6 7 9 + =
36 49 81 + =
85 81 =
Not true so not a right triangle.
15
20
16
72
90
54
2 2 2
15 16 20 + =
481 400 =
Not trueso not
aright triangle.
2 2 2
12 16 20 + =
400 400 =
Trueso it is
aright triangle.
16
20
12
2 2 2
54 72 90 + =
8100 8100 =
True so it is
aright triangle.
5
Questions Involving Recognising Pythagorean Relationships:
2. Recognising pythagoras triples:
These are a set of three numbers that fit the pythagorean relationship?
Are these sets of numbers pythagoras triples?
35,12,37
2 2 2
35 12 37 + =
1369 1369 =
23,11,25
2 2 2
23 11 25 + =
650 625 =
It is a pythagorean triple Not a pythagorean triple
9,40,41
2 2 2
9 40 41 + =
1681 1681 =
It is a pythagorean triple
17,24,29
865 841 =
Not a pythagorean triple
2 2 2
17 24 29 + =
If you recognise the common pythagoras triples 3,4,5 and 5,12,13 it can make
solving questions much quicker.
12 4
16 4
3
4
=
24 2
26 2
x 2 1
12
13
5 0
=
=
= =
16
12
x
24
26
x
25
16
x 4 2 5
4 4
0
=
= =
40
x
50
60
x
5
12
2
13
5 5
60 5
x 5 65
=
=
= =
4
5
3
40 10
50 10
x 10 30
=
=
= =
Special Right Triangles. See page 493 in the textbook.
We will use two special triangles that are derived using Pythagoras.
1. The 45-90-45 triangle.
Using this triangle and proportions we can solve any other
45-90-45 triangle.
Use the angles to match up the sides in the two triangles
13
M
90
45 45
Use the angles to match up the sides in the two triangles.
put the unknown on the top for the proportion.
M 2
13 1
=
2
M 13
1
=
M 13 2 =
2. The 30-60-90 triangle.
Using this triangle and proportions we can solve any other 30-60-90 triangle.
11
N
60
30
Use the angles to match up the sides in the two triangles.
put the unknown on the top for the proportion.
N 3
11 2
=
11 3
N
2
=
K
F
12
45
45 90
M
12
60
30
90
F 1
12 2
=
12
F
2
=
M 2
12 3
=
24
F
3
=
Use special triangles to solve these questions:
5
14
H
60
K 2
5 1
=
F 5 2 =
H 1
14 2
=
H 7 =
You might also like
- Unit 1. Algebraic Reasoning.: See Pages 8 - 12 of Your Textbook For VocabularyDocument6 pagesUnit 1. Algebraic Reasoning.: See Pages 8 - 12 of Your Textbook For VocabularyBill Laulo100% (1)
- Completing the Square Solves Quadratic EquationsDocument14 pagesCompleting the Square Solves Quadratic Equationsnmahmud75No ratings yet
- MaANVCO08Unit+Three+Algebraic+MethodsCh6 7-8-11Document56 pagesMaANVCO08Unit+Three+Algebraic+MethodsCh6 7-8-11Epic WinNo ratings yet
- FORMULAS AND FACTORINGDocument25 pagesFORMULAS AND FACTORINGitsankurzNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - ExponentsDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 3 - ExponentsLen Alair0% (1)
- New Century Maths Year 8 Chapter 1Document34 pagesNew Century Maths Year 8 Chapter 1vivian25% (4)
- PptsDocument88 pagesPptsXavNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers and OperationsDocument16 pagesReal Numbers and OperationsMuskaan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Find All The Points On The Graph of 100 Where The Slope of The Tangent Line 3 4Document3 pagesFind All The Points On The Graph of 100 Where The Slope of The Tangent Line 3 4etome05No ratings yet
- MAT1581 Tutorial SolutionsDocument20 pagesMAT1581 Tutorial SolutionsmatshonaNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic MaterialDocument163 pagesArithmetic MaterialKoteswara Rao Challa50% (4)
- In Term Compte NcyDocument7 pagesIn Term Compte Ncyjasming1No ratings yet
- X/÷ Numbers Multiples, Factors, Primes, Squares, Cubes and BracketsDocument86 pagesX/÷ Numbers Multiples, Factors, Primes, Squares, Cubes and Bracketsayu dayueNo ratings yet
- Math and arithmetic rules for engineersDocument7 pagesMath and arithmetic rules for engineersMubasair MubeNo ratings yet
- Answers Are You Ready For CalculusDocument6 pagesAnswers Are You Ready For CalculusKevin HsiehNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 POLYNOMIALSDocument69 pagesTopic 1 POLYNOMIALSNorlianah Mohd ShahNo ratings yet
- Student Version Solutions 2 SEMESTER 2 1Document4 pagesStudent Version Solutions 2 SEMESTER 2 1Lovingmore LavasNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Solution Set 1Document31 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Solution Set 1TEJA SINGHNo ratings yet
- ACP Algebra 2 Final Exam Review 2023Document7 pagesACP Algebra 2 Final Exam Review 2023middletown njNo ratings yet
- SurdsDocument27 pagesSurdsSha Mercs100% (1)
- Chreso University Maths AssignmentDocument5 pagesChreso University Maths AssignmentJoe KundaNo ratings yet
- Sol Mat Haeussler ByPriale PDFDocument719 pagesSol Mat Haeussler ByPriale PDFKarem Herrera FeriaNo ratings yet
- Sol Mat HaeusslerDocument719 pagesSol Mat Haeusslerm1228m1228No ratings yet
- 20210605-Class - 8 Ls. No. 4. Cubes and Cube Roots SolutionDocument13 pages20210605-Class - 8 Ls. No. 4. Cubes and Cube Roots SolutionHardik KarelNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: All Problems (Q1-Q66) Except DerivationsDocument89 pagesAnswer Key: All Problems (Q1-Q66) Except DerivationsAnish Anand kumar100% (1)
- Lesson Factoring PolynomialsDocument18 pagesLesson Factoring PolynomialsNathalieNo ratings yet
- Simultanous Equations Chapter 4 PDFDocument10 pagesSimultanous Equations Chapter 4 PDFSyazwan AkidNo ratings yet
- N A A N Aa A A: Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesN A A N Aa A A: Practice QuestionsAnonymous vBe1sOVVOpNo ratings yet
- Decimal LsDocument55 pagesDecimal LsZerihun IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Sample Mathtest4Document2 pagesSample Mathtest4Vu LuongNo ratings yet
- Algebra Taller 6Document2 pagesAlgebra Taller 6Juan LuqueNo ratings yet
- Sistem Persamaan Linier Tiga VariabelDocument3 pagesSistem Persamaan Linier Tiga Variabeltasya kaylaNo ratings yet
- Sia3e SSM 01Document97 pagesSia3e SSM 01brian_pena8997No ratings yet
- Transposing FormuleaDocument10 pagesTransposing FormuleaMick RoganNo ratings yet
- More Trigonometric SubstitutionDocument35 pagesMore Trigonometric SubstitutionArsalan JumaniNo ratings yet
- 3472-2 MT Trial SPM 2013 SoalanDocument19 pages3472-2 MT Trial SPM 2013 SoalanRohaya MoratNo ratings yet
- Sri Kdu - Mid Year 2011Document15 pagesSri Kdu - Mid Year 2011arcp49No ratings yet
- MODULE 0 SPECIAL PRODUCTS AND FACTORINGDocument19 pagesMODULE 0 SPECIAL PRODUCTS AND FACTORINGKarla YasaNo ratings yet
- Mathcounts Toolbox: Facts, Formulas and TricksDocument9 pagesMathcounts Toolbox: Facts, Formulas and TricksSridhar NamaNo ratings yet
- M9 - Q1 W3 - Equations Transformable To Quadratic Equations PDFDocument32 pagesM9 - Q1 W3 - Equations Transformable To Quadratic Equations PDFmark hernandezNo ratings yet
- GCD Sep 2022Document5 pagesGCD Sep 2022trad.cecal9No ratings yet
- Synthetic Division GuideDocument5 pagesSynthetic Division GuideMabz Bell Amiscosa100% (2)
- Pset 2 MMWDocument12 pagesPset 2 MMWMark UlitNo ratings yet
- 2018 Metrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge National Finals Grade 10 Individual Oral Competition QuestionsDocument5 pages2018 Metrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge National Finals Grade 10 Individual Oral Competition QuestionsHarris Lee50% (2)
- Presentation5 3Document23 pagesPresentation5 3412137No ratings yet
- Algebra 2.final Exam - SolutionsDocument15 pagesAlgebra 2.final Exam - Solutionsdr.saidongargaonkaNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics 1Document16 pagesBusiness Mathematics 1Alfiano VivazNo ratings yet
- Basic AlgebraDocument6 pagesBasic AlgebraMayank Ajugia100% (1)
- BAB 2 TrigonometriDocument84 pagesBAB 2 TrigonometriR I Wijaya100% (5)
- 18 Quadratic EquationsDocument28 pages18 Quadratic Equationsapi-259236539No ratings yet
- Blue Print: Class Xii Maths: Model Question PaperDocument14 pagesBlue Print: Class Xii Maths: Model Question Paperapi-243565143No ratings yet
- Comon Mistakes: Maths Problem Can Be An Illusion !!Document5 pagesComon Mistakes: Maths Problem Can Be An Illusion !!Nor Aishah AsimNo ratings yet
- Maths Quest 9 - Chapter 1Document42 pagesMaths Quest 9 - Chapter 1Bella Carr100% (1)
- Q1W2 M9 - Solving Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square RootsDocument15 pagesQ1W2 M9 - Solving Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square RootsMarjorie PeralesNo ratings yet
- My First Padded Board Books of Times Tables: Multiplication Tables From 1-20From EverandMy First Padded Board Books of Times Tables: Multiplication Tables From 1-20No ratings yet
- Multiplication Tables and Flashcards: Times Tables for ChildrenFrom EverandMultiplication Tables and Flashcards: Times Tables for ChildrenRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- GCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseFrom EverandGCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseNo ratings yet
- A Mother's Guide to Multiplication: For 7-11 Year OldsFrom EverandA Mother's Guide to Multiplication: For 7-11 Year OldsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AFC Outline Part 2Document2 pagesAFC Outline Part 2Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- Sources For PovertyDocument2 pagesSources For PovertyBill LauloNo ratings yet
- Resources From EBSCO - WATERDocument1 pageResources From EBSCO - WATERBill LauloNo ratings yet
- AFC OutlineDocument2 pagesAFC OutlineBill LauloNo ratings yet
- AFC Outline IIDocument2 pagesAFC Outline IIBill LauloNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument1 pageWater ResourcesBill LauloNo ratings yet
- AFC Outline Part 2Document2 pagesAFC Outline Part 2Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- ReviewCubes BasicSkills3Document4 pagesReviewCubes BasicSkills3Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- ReviewCubes Ma8IntroToFunctions2Document1 pageReviewCubes Ma8IntroToFunctions2Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- Review Partner Cards Functions Part 2Document1 pageReview Partner Cards Functions Part 2Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- Understanding Radicals HomeworkDocument1 pageUnderstanding Radicals HomeworkBill LauloNo ratings yet
- Basic Skills 3 Review 1Document2 pagesBasic Skills 3 Review 1Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- Political Brief Sentence Frames 2014Document2 pagesPolitical Brief Sentence Frames 2014Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- Propaganda Poster Paragraph Organizer ExampleDocument4 pagesPropaganda Poster Paragraph Organizer ExampleBill LauloNo ratings yet
- Political Propaganda Poster 2014Document1 pagePolitical Propaganda Poster 2014Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- Energy CalculationsDocument18 pagesEnergy CalculationsBill LauloNo ratings yet
- Propaganda Poster Paragraph Organizer ExampleDocument4 pagesPropaganda Poster Paragraph Organizer ExampleBill LauloNo ratings yet
- PPR ConclusionDocument1 pagePPR ConclusionBill LauloNo ratings yet
- Who Done It - Performance TaskDocument2 pagesWho Done It - Performance TaskBill LauloNo ratings yet
- Sample People Power Revolution EssayDocument3 pagesSample People Power Revolution EssayBill Laulo85% (13)
- PPR Body P1Document1 pagePPR Body P1Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- Intorduction Paragraph OrganizerDocument5 pagesIntorduction Paragraph OrganizerBill LauloNo ratings yet
- PPR Essay OrganizerDocument5 pagesPPR Essay OrganizerBill LauloNo ratings yet
- PPR IntroDocument1 pagePPR IntroBill LauloNo ratings yet
- Review Partner Cards 1-Intro To Functions Part 1Document6 pagesReview Partner Cards 1-Intro To Functions Part 1Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Transitional Words Transitional PhrasesDocument1 pageVocabulary Transitional Words Transitional PhrasesBill LauloNo ratings yet
- SI Organizing Sheet For PPR EssayDocument2 pagesSI Organizing Sheet For PPR EssayBill LauloNo ratings yet
- Adapted Ma8ConceptCheck#28Document2 pagesAdapted Ma8ConceptCheck#28Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Functions Review Questions For Assessment Part 1Document7 pagesIntroduction To Functions Review Questions For Assessment Part 1Bill LauloNo ratings yet
- The One and Only by Emily GiffinDocument12 pagesThe One and Only by Emily GiffinRandom House of Canada50% (2)
- TerroirDocument11 pagesTerroirPaulie Salgado DelaParraNo ratings yet
- Calculate rook arrangementsDocument7 pagesCalculate rook arrangementsDanielValadãoBastosNo ratings yet
- EXPORTDocument530 pagesEXPORTJan LhesterNo ratings yet
- Spare Part CatalogueDocument178 pagesSpare Part Cataloguethinewill_bedone8055No ratings yet
- Manual Kholer 2000reozddDocument4 pagesManual Kholer 2000reozddVictorNo ratings yet
- Fluids Long ReportDocument23 pagesFluids Long ReportjameswattNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis ReportDocument34 pagesBronchitis ReportRolinette DaneNo ratings yet
- Design of Irrigation CanalsDocument6 pagesDesign of Irrigation CanalsSaad ShauketNo ratings yet
- Rasff Annual Report 2018Document53 pagesRasff Annual Report 2018juliusjimNo ratings yet
- X-Plane FMS Manual PDFDocument24 pagesX-Plane FMS Manual PDFAnish ShakyaNo ratings yet
- DR Khaled Final Exam MCQ 2012 - 2013Document89 pagesDR Khaled Final Exam MCQ 2012 - 2013ﻣﻠﻚ عيسى100% (2)
- Full Download Introduction To Statistical Methods and Data Analysis 6th Edition Ott Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Introduction To Statistical Methods and Data Analysis 6th Edition Ott Solutions Manualrucaizatax98% (45)
- Arthropod Diversity Lab ReportDocument3 pagesArthropod Diversity Lab ReportJudge Michael GarzaNo ratings yet
- Existential TheoryDocument12 pagesExistential Theorymanuelana100% (1)
- Requiem Concert ProgramDocument4 pagesRequiem Concert ProgramAdam KuriharaNo ratings yet
- Design of Rocker-Bogie MechanismDocument27 pagesDesign of Rocker-Bogie MechanismInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology86% (7)
- Sample CollectionDocument41 pagesSample Collectionsoumen100% (1)
- Once Upon A TimeDocument2 pagesOnce Upon A TimeAnup Kumar TiwaryNo ratings yet
- Cleaner Production, Project Management and Strategic DriversDocument10 pagesCleaner Production, Project Management and Strategic DriversAlexandre CosteiraNo ratings yet
- List of Items - SiemensDocument4 pagesList of Items - Siemensriyadh al kamalNo ratings yet
- Passion PRO Feb 2017Document262 pagesPassion PRO Feb 2017sudhirNo ratings yet
- Chirality (mathematics) : (enantíos), meaning "opposite", and μέρος (méros), meaning "part"), also known asDocument2 pagesChirality (mathematics) : (enantíos), meaning "opposite", and μέρος (méros), meaning "part"), also known asHyperionNo ratings yet
- Hilti Crane Support Frame BaseDocument6 pagesHilti Crane Support Frame BaseDhina karanNo ratings yet
- Signet Products Pvt. Ltd. - ProfileDocument18 pagesSignet Products Pvt. Ltd. - ProfileGirish NimbhorkarNo ratings yet
- Sedgwick, Shame, TheatricalityDocument34 pagesSedgwick, Shame, TheatricalityMarcia MichniakNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Section 1-Open-Ended Questions: (2 Marks)Document6 pagesHomework 1 Section 1-Open-Ended Questions: (2 Marks)jabirNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Transportation Sampling: International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA)Document10 pagesFertilizer Transportation Sampling: International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA)lamvanthongNo ratings yet
- Configurations & Parts Identification: Trailer Suspension SeriesDocument26 pagesConfigurations & Parts Identification: Trailer Suspension SeriesleosignareNo ratings yet