Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aspirin (Synthesis and Mechanism)
Uploaded by
Zubaydah Abdullah67%(3)67% found this document useful (3 votes)
4K views25 pagesAspirin
organic chemistry
salicylic acid acetic anhydride mechanism synthesis physical chemical properties
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAspirin
organic chemistry
salicylic acid acetic anhydride mechanism synthesis physical chemical properties
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
67%(3)67% found this document useful (3 votes)
4K views25 pagesAspirin (Synthesis and Mechanism)
Uploaded by
Zubaydah AbdullahAspirin
organic chemistry
salicylic acid acetic anhydride mechanism synthesis physical chemical properties
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Ministry of Higher Education
Taibah University
Aspirin
Faculty of Science
Chemistry Department
Supervised by : Dr. Laila Shakir
& Asst. Heba Alshareef
Presented by: Zubaydah Abdullah
Contents
! Some Background
! The Chemistry of Aspirin
! Physical properties
! Synthesis
! Mechanism
! IR and NMR Spectroscopy
!Biological activity
! Brand names
! Conclusion
! 1897 In Germany, Bayer's Felix
Ho!mann develops and patents a
process for synthesising acetyl salicylic
acid or aspirin. First clinical trials begin.
Some Background
[ 1 ][ 2 ]
It would later be marketed as aspirin a for
acetyl and spirin for Spirea, the genus
name of the source plant for salicylic acid, the
pain-relieving agent.
Some Background
[ 3 ]
Contents
! Some Background
! The Chemistry of Aspirin
! Physical properties
! Synthesis
! Mechanism
! IR and NMR Spectroscopy
! Biological activity
! Brand names
! Conclusion
Aspirin
IUPAC Name: 2!acetyloxybenzoic acid
Molecular Formula: C
9
H
8
O
4
Molecular Weight: 180.15742 g/mol
The chemical structure of aspirin:
also known as acetylsalicylic acid
The Chemistry of Aspirin
[ 4 ]
The Chemistry of Aspirin
Stability and Reactivity :
! Stability: Stable in dry air.
! Hazardous Decomposition Products: Decomposes to acetic
acid and salicylic acids in the presence of moist air. Carbon
dioxide and carbon monoxide may form when heated to
decomposition.
! Conditions to Avoid: Moisture.
[ 5 ]
Contents
! Some Background
! The Chemistry of Aspirin
! Physical properties
! Synthesis
! Mechanism
! IR and NMR Spectroscopy
! Biological activity
! Brand names
! Conclusion
Physical properties
[ 6 ]
Contents
! Some Background
! The Chemistry of Aspirin
! Physical properties
! Synthesis
! Mechanism
! IR and NMR Spectroscopy
! Biological activity
! Brand names
! Conclusion
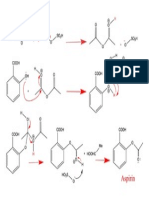
According to the above reaction, Salicylic acid is treated with acetic
anhydride causing the reaction that converts the hydroxyl group on
salicylic acid into and ester functionality.
The product of this reaction will be acetyl salicylic acid "aspirin# and
acetic acid. Sulphuric acid or phosphoric acid will be used as a
catalyst.
Reaction :
Synthesis
[ 7 ][ 8 ]
[ 9 ][ 10 ]
The production of aspirin
from raw materials can be
divided into four separate
reactions. These are shown:
Synthesis
[ 11 ]
Contents
! Some Background
! The Chemistry of Aspirin
! Physical properties
! Synthesis
! Mechanism
! IR and NMR Spectroscopy
! Biological activity
! Brand names
! Conclusion
Mechanism
[ 12 ]
Contents
! Some Background
! The Chemistry of Aspirin
! Physical properties
! Synthesis
! Mechanism
! IR and NMR Spectroscopy
! Biological activity
! Brand names
! Conclusion
IR Spectroscopy
[ 13 ]
NMR Spectroscopy
[ 14 ]
Contents
! Some Background
! The Chemistry of Aspirin
! Physical properties
! Synthesis
! Mechanism
! IR and NMR Spectroscopy
! Biological activity
! Brand names
! Conclusion
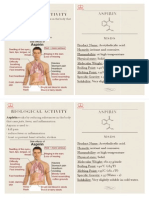
Aspirin works by reducing substances in the body that cause pain, fever,
and inammation.
Aspirin is used to :
! kill pain
! reduce fever or inammation
! treat or prevent heart attacks, strokes.
Biological activity
[ 15 ]
Contents
! Some Background
! The Chemistry of Aspirin
! Physical properties
! Synthesis
! Mechanism
! IR and NMR Spectroscopy
! Biological activity
! Brand names
! Conclusion
Brand names
Contents
! Some Background
! The Chemistry of Aspirin
! Physical properties
! Synthesis
! Mechanism
! IR and NMR Spectroscopy
! Biological activity
! Brand names
! Conclusion
Conclusion
! Aspirin is used for kill pain, reduce fever and prevent
hearts attack.
! Preparation of aspirin by estercation of salicylic acid
and acetic anhydride
! The structure of aspirin has been proved by
Spectroscopic instruments as IR and NMR .
! The melting point = 135 !
References
1. aspirin!foundation.com/what/timeline.html
2. inventors.about.com/library/inventors/blaspirin.htm
3. mindhacks.com/2009/03/09/a!brief!history!of!aspirin
4. aspirin!foundation.com/what/chemistry.html
5. chem.uky.edu/courses/che554/0!SafetyIntro/AspirinMSDS.pdf
6. chemglue4u.com/lab!helper/organic!chem!lab!helpers/synthesis!of!acetylsalicylic!acid!aspirin/
7. The Organic Chemistry of Biological Pathways by John McMurry and Tadhg Begley $Roberts
and Company, 2005%
8. Organic Chemistry of Enzyme!Catalyzed Reactions by Richard Silverman $Academic Press,
2002%.
9. K. L. Williamson, Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments, 2nd Ed. 1994, Houghton
Mi&in, Boston. p379; revised 10/18/06
10. Palleros, Daniel R. $2000%. Experimental Organic Chemistry. New York: John Wiley & Sons. p.
11. aspirin!foundation.com/what/reactions.html
12. Carstensen, J.T.; F Attarchi and XP Hou $1985%. "Decomposition of aspirin in the solid state in
the presence of limited amounts of moisture". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 77
13. stonybrook.edu
14. biosite.dk/leksikon/acetylsalicylsyre.htm
15. drugs.com/aspirin.html
Thank you for your attention
You might also like
- Synthesis of Aspirin From Salicylic Acid and Acetic AnhydrideDocument6 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin From Salicylic Acid and Acetic AnhydrideChristine71% (7)
- Aspirin Synthesis Lab ReportDocument11 pagesAspirin Synthesis Lab ReportMuhammad Abdur RokhimNo ratings yet
- Aspirin - Lab ReportDocument13 pagesAspirin - Lab ReportRibka Kristania Hadhiwaluyo50% (4)
- Synthesis of Aspirin LabDocument5 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin LabSisilia Devi NNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Isoamyl AcetateDocument10 pagesSynthesis of Isoamyl AcetateMikaila Denise LoanzonNo ratings yet
- Precipitation Titration MethodsDocument3 pagesPrecipitation Titration MethodsBanana SenpaiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenDocument5 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenJason Raquin Roque100% (3)
- Ester of Carboxylic AcidsDocument6 pagesEster of Carboxylic Acidsmaryam_m_chemNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Synthesis of AspirinDocument4 pagesFormal Report Synthesis of AspirinEdrick Ramoran0% (1)
- Synthesis of Aspirin Lab ReportDocument12 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin Lab ReportJasmeetSingh63% (8)
- Synthesis of Acetanilide and Its Purification Through RecrystallizationDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Acetanilide and Its Purification Through RecrystallizationTeresa Saylo100% (1)
- Synthesis of Aspirin: 115% YieldDocument6 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin: 115% YieldStephanie ButedNo ratings yet
- The Synthesis of AspirinDocument4 pagesThe Synthesis of AspirinMarieya Elizabeth ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Salicylic AcidDocument2 pagesSynthesis of Salicylic AcidHarly Kabut100% (1)
- Production of Salicylic Acid via Kolbe-Schmitt ProcessDocument179 pagesProduction of Salicylic Acid via Kolbe-Schmitt ProcessHaiderAliJutt67% (3)
- Synthesis of Aspirin Results and DiscussionDocument9 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin Results and DiscussionGellie Dela Rosa Valencia33% (3)
- Experiment 9 Formal Laboratory ReportDocument5 pagesExperiment 9 Formal Laboratory ReportNathaniel Argelio Dimaano100% (1)
- Aspirin SythesisDocument4 pagesAspirin Sythesiskramnuj92% (12)
- Exercise 11 Synthesis of Aspirin (Aceylsalicylic Acid From Salicylic Acid)Document8 pagesExercise 11 Synthesis of Aspirin (Aceylsalicylic Acid From Salicylic Acid)MNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AspirinDocument6 pagesSynthesis of AspirinVanessaOlgaJ.Dagondon100% (1)
- Experiment #6Document11 pagesExperiment #6Tin-tin71% (7)
- Partially Miscible LiquidsDocument8 pagesPartially Miscible LiquidsRenz Roger Esteves Buendicho100% (1)
- Acyl Compunds: Soaps and DetergentsDocument4 pagesAcyl Compunds: Soaps and DetergentsLucile BronzalNo ratings yet
- Laredo Community College Science Department Qualitative Analysis GuideDocument12 pagesLaredo Community College Science Department Qualitative Analysis GuideRegina Morales0% (1)
- EXPERIMENT CalorimeterDocument15 pagesEXPERIMENT CalorimeterFath BondNo ratings yet
- Determining Surface Tension of Solutions Using Capillary Rise MethodDocument12 pagesDetermining Surface Tension of Solutions Using Capillary Rise MethodGel Garcia67% (3)
- Phase diagram of phenol water systemDocument5 pagesPhase diagram of phenol water systemPaulraj Mosae SelvakumarNo ratings yet
- NaBH4 Reduction of Cyclohexanone to CyclohexanolDocument8 pagesNaBH4 Reduction of Cyclohexanone to CyclohexanolAmar SafwanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsDocument16 pagesExperiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsLuisGabito100% (1)
- Experiment: Gravimetric AnalysisDocument9 pagesExperiment: Gravimetric Analysisadda84% (25)
- Ester Synthesis LabDocument6 pagesEster Synthesis LabMuhammad Abdur RokhimNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis Nelson's AssayDocument4 pagesQuantitative Analysis Nelson's AssayJenelle Jane Quilaneta25% (4)
- Syntheses of Soap and DetergentDocument4 pagesSyntheses of Soap and DetergentChin Castro Zabat100% (2)
- Synthesis of AspirinDocument13 pagesSynthesis of AspirinTriza AndradeNo ratings yet
- Determining Order of Reaction with Sodium ThiosulfateDocument12 pagesDetermining Order of Reaction with Sodium ThiosulfateAdrian WongNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document12 pagesExperiment 6Keo De Leon100% (3)
- Experiment 1Document9 pagesExperiment 1Anonymous Osp8BbYEyNo ratings yet
- Chem 26.1 Formal Report Experiment 3 Iodine Clock ReactionDocument5 pagesChem 26.1 Formal Report Experiment 3 Iodine Clock ReactionromiYAY71% (7)
- Lab Report Food Chem Exp 1 FullDocument8 pagesLab Report Food Chem Exp 1 FullNur AsiahNo ratings yet
- Dissolved oxygen estimation by redox titrationDocument2 pagesDissolved oxygen estimation by redox titrationSuet Wan GohNo ratings yet
- CHEM 22161 Lab 1 :synthesis of Medicinal Agent: Synthesis of AspirinDocument8 pagesCHEM 22161 Lab 1 :synthesis of Medicinal Agent: Synthesis of AspirinKasun WekasingheNo ratings yet
- Adsorption of Acetic Acid with Activated CarbonDocument8 pagesAdsorption of Acetic Acid with Activated CarbonHayden Chappelear-RobbinsNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - & Carbonyl-Containing CompoundsDocument8 pagesExperiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - & Carbonyl-Containing CompoundsPatricia Isabel Tayag100% (7)
- Chapter 10Document18 pagesChapter 10Nini KhanNo ratings yet
- Activation Energy Lab Report GroupDocument2 pagesActivation Energy Lab Report GroupSyazwani Abdullah100% (1)
- Separation and Identification of Amino Acids by Paper ChromatographyDocument4 pagesSeparation and Identification of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatographyroxannediana86% (14)
- Formal Report Distillation of ALcoholic BeveragesDocument12 pagesFormal Report Distillation of ALcoholic Beveragespatricia_moran_4No ratings yet
- AP01 Measurement of Reaction Kinetics by UV Visible Spectroscopy.Document22 pagesAP01 Measurement of Reaction Kinetics by UV Visible Spectroscopy.Hui SanNo ratings yet
- Crystallization PDFDocument28 pagesCrystallization PDFAS LAM100% (1)
- Experiment 3 Lab ReportDocument10 pagesExperiment 3 Lab ReportVanessa Denise AguilarNo ratings yet
- Group compares acidities of carboxylic acids and phenolsDocument4 pagesGroup compares acidities of carboxylic acids and phenolsEmmanuel PlazaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report OneDocument8 pagesLab Report OneMirandaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives: Nucleophilic Addition-EliminationDocument45 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Derivatives: Nucleophilic Addition-EliminationAtirahSakinahNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Determination of ChlorideDocument8 pagesGravimetric Determination of Chloridejess100% (1)
- ChemDocument16 pagesChemgersonkevin025No ratings yet
- The Aspirin ProjectDocument9 pagesThe Aspirin ProjectShabaz SaysNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory Report - EditedDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Laboratory Report - EditedIsaac NgugiNo ratings yet
- Aspirin NewDocument26 pagesAspirin NewsanasharNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Aspirină: "Asprin" Redirecţionează Aici. For The Author, See - Pentru Autor, A Se VedeaDocument30 pagesAspirin Aspirină: "Asprin" Redirecţionează Aici. For The Author, See - Pentru Autor, A Se VedeaIonela IordacheNo ratings yet
- CollagenDocument27 pagesCollagenZubaydah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Fossil FuelsDocument33 pagesFossil FuelsZubaydah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Aspirin MSDS and Biological Activity CardDocument1 pageAspirin MSDS and Biological Activity CardZubaydah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Simple Separation MethodsDocument1 pageSimple Separation MethodsZubaydah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Separation and Chromatographic TechniquesDocument1 pageSeparation and Chromatographic TechniquesZubaydah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of AspirinDocument1 pageMechanism of AspirinZubaydah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Electrophoresis: Created byDocument11 pagesElectrophoresis: Created byZubaydah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Acidity, Basicity and PkaDocument39 pagesAcidity, Basicity and PkaZubaydah Abdullah100% (1)
- Timoshchuk1995 PDFDocument30 pagesTimoshchuk1995 PDFPhan NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Pyridones PDFDocument5 pagesPyridones PDFJuanAmayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Protecting Groups PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 3 Protecting Groups PDFGilbert OfeiNo ratings yet
- Study of Adulterants in Food StuffDocument17 pagesStudy of Adulterants in Food StuffKuldeep Sharma64% (55)
- Tennessee Eastman Acetic Anhydride Process LL Organometallic ChemistryDocument2 pagesTennessee Eastman Acetic Anhydride Process LL Organometallic ChemistryfarshidNo ratings yet
- US8461377 Aspirin 2013Document10 pagesUS8461377 Aspirin 2013Haruo YamashitaNo ratings yet
- Chemical NPFA CodesDocument930 pagesChemical NPFA CodesKomsan Buntengsuk100% (2)
- Synthesize Aspirin from Salicylic AcidDocument23 pagesSynthesize Aspirin from Salicylic AcidCyrene MBolañosNo ratings yet
- FRITZLER, 2014. Acetic Anhydryde Hydrolysis at High Acetic Anhydride To Water RatiosDocument10 pagesFRITZLER, 2014. Acetic Anhydryde Hydrolysis at High Acetic Anhydride To Water RatiosAnonymous DMjWxgNo ratings yet
- Full Report: Synthesis of AspirinDocument3 pagesFull Report: Synthesis of AspirinNor Ashikin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Protecting Groups in Carbohydrate ChemistryDocument10 pagesProtecting Groups in Carbohydrate ChemistryJános CsernákNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance ChartDocument20 pagesChemical Resistance Chartharsh shah100% (1)
- tmp5B78 TMPDocument18 pagestmp5B78 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1. ReagentsDocument106 pages4.1.1. ReagentsJjangyiNo ratings yet
- Sinpro Tugas Bab 5 6 7Document13 pagesSinpro Tugas Bab 5 6 7Ariqoh RizqyNo ratings yet
- Chemical ManufactureDocument18 pagesChemical ManufactureChellam Siva Chellam Siva100% (1)
- Tamilnadu 12 Chemistry Shortcuts EMDocument18 pagesTamilnadu 12 Chemistry Shortcuts EMthom_atjNo ratings yet
- SIMSCI Component Data Input Manual PDFDocument164 pagesSIMSCI Component Data Input Manual PDFDrakzNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument4 pagesAspiringenelleestremos100% (1)
- StoichiometryDocument48 pagesStoichiometryUmmu JuraijNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenDocument3 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenAnonymous orNHXM0f0No ratings yet
- Ethyl AlcoholDocument3 pagesEthyl AlcoholRoseanne Legaspi CasayuranNo ratings yet
- Acetic AnhydrideDocument60 pagesAcetic Anhydridecyper zoonNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry (Assignment 3) PDFDocument4 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry (Assignment 3) PDFCRSFZNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems with Solutions for Metric System, Density, and Significant FiguresDocument34 pagesPractice Problems with Solutions for Metric System, Density, and Significant Figures신재호No ratings yet
- Methods of Synthesis & Properties of HexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitaneDocument8 pagesMethods of Synthesis & Properties of HexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitanefranklynNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compatibility Guide Colder Products CommonDocument26 pagesChemical Compatibility Guide Colder Products CommonManual SourceNo ratings yet
- Chem 1310 Lab Report 2Document5 pagesChem 1310 Lab Report 2Umar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Acetic Anhydride Production ProcessDocument10 pagesAcetic Anhydride Production ProcessChellam Siva Chellam SivaNo ratings yet