Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sepam40 en
Uploaded by
Đức ThảoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sepam40 en
Uploaded by
Đức ThảoCopyright:
Available Formats
Building a New Electric World
TechnicaI data sheet
2003
Electrical network protection
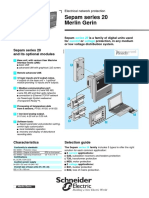
Sepam series 40
MerIin Gerin
Sepam series 40
and its optionaI moduIes
1 Base unit, with various User Machine
Interface levels (UMI):
b basic UMI
b advanced UMI with graphical LCD screen.
2 Remote advanced UMI.
3 10 logic inputs and 8 output relays,
4 outputs on the base unit + 1 optional
module providing 10 inputs and 4 outputs.
4 1 Modbus communication port:
b direct connection to 2-wire RS 485,
4-wire RS 485 and fiber optic networks
b connection to Ethernet TCP/IP network
via PowerLogic System webserver
(Transparent Ready').
5 Processing of temperature data
from 16 sensors, Pt100, Ni100, or Ni120.
6 1 low level analog output,
0-10 mA, 4-20 mA or 0-20 mA.
7 Software tools:
b Sepam parameter and protection setting,
control logic customization
b local installation operation
b recovery and display of disturbance
recording data.
Characteristics
Conformity to standards
IEC 60255 Protection relays
IEC 60529 Degree of protection IP52 on front panel
IEC 60068 Operating temperature -25 C to +70 C
Certifications
e, UL508, CSA C22.2
AuxiIiary power suppIy
24-250 V DC and 110-240 V AC
OveraII size of base units (H x W x D)
222 x 176 x 130 mm
Sepam series 40 is a famiIy of digitaI units used
for current and voltage protection, in any medium
or Iow voItage distribution system.
D
E
5
0
3
5
4
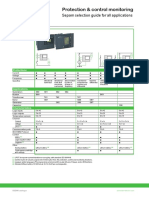
SeIection guide
The Sepam series 40 famiIy includes 7 types:
Specific
protections
avaiIabIe
AppIications
Substation Transformer Motor Generator
S40 T40 G40
Directional earth
fault
S41 M41
Directional earth
fault and phase
overcurrent
S42 T42
4
7
2
6
5
3
1
Schneider EIectric Industries SAS
Postal address:
Electrical Distribution Communication
38050 Grenoble cedex 9 - France
Tel : +33 (0)4 76 57 60 60
http://www.schneider-electric.com
http://www.sepamrelay.com
As standards, specifications and designs change from time to time, please ask for confirmation
of the information given in this publication.
This document has been printed
on ecological paper.
Design: Schneider Electric - Ameg
Publication: Schneider Electric
Printed: Imprimerie des Deux-Ponts
03-2003 ART.07900
P
C
R
E
D
3
0
1
0
0
2
E
N
/
3
2
0
0
3
S
c
h
n
e
i
d
e
r
E
l
e
c
t
r
i
c
-
A
l
l
r
i
g
h
t
r
e
s
e
r
v
e
d
7 types of Sepam series 40
b S40, S41, S42: substation incomers and
feeders protection
b T40, T42: transformer protection
b M41: motor protection
b G40: generator protection.
Protections ANSI code S40 S41 S42 T40 T42 M41 G40
Phase overcurrent 50/51 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
Voltage restrained overcurrent 50V/51V 1
Earth fault,
sensitive earth fault
50N/51N
50G/51G
4 4 4 4 4 4 4
Breaker failure 50BF 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Unbalance/negative sequence 46 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
D
E
5
0
3
5
2
Sepam series 40 connection scheme.
Directional phase overcurrent 67 2 2
Directional earth fault 67N/67NC 2 2 2 2
Directional real overpower 32P 1 1 1 1
Directional reactive overpower 32Q/40 1 1
Thermal overload 49 RMS 2 2 2 2
Phase undercurrent 37 1
Locked rotor, excessive starting time /5 1
Starts per hour 66 1
Positive sequence undervoltage 27D 2
Remanent undervoltage 27R 1
Undervoltage 27/27S 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Overvoltage 59 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Neutral voltage displacement 59N 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Negative sequence overvoltage 47 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Overfrequency 81H 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Underfrequency 81L 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
Recloser (4 cycles) 79 v v v
Temperature monitoring
(8 or 16 RTDs, 2 set points per RTD)
38/49T v v v v
Thermostat / Buchholz v v
Metering
RMS phase current I1,I2,I3, residual current I0 b b b b b b b
Average current I1, I2, I3
Peak demand current IM1, IM2, IM3
b b b b b b b
Voltage U21, U32, U13, V1, V2, V3
Residual voltage V0
b b b b b b b
Positive sequence voltage Vd / rotation direction,
Negative sequence voltage Vi
b b b b b b b
Frequency b b b b b b b
Real / reactive / apparent power P, Q, S
Peak demand real/reactive power PM, QM
Power factor
b b b b b b b
Calculated real / reactive energy (W.h, var.h) b b b b b b b
D
E
5
0
4
7
2
Real/reactive energy impulse counter (W.h, var.h) v v v v v v v
Temperature measurement v v v v
Network and machine diagnosis
Tripping current TripI1, TripI2, TripI3, TripI0 b b b b b b b
Tripping context b b b b b b b
Unbalance ratio/negative sequence current b b b b b b b
Phase shift !0, !1, !2, !3 b b b b b b b
Disturbance recording b b b b b b b
Thermal capacity used b b b b
Remaining operating time before overload tripping b b b b
Waiting time after overload tripping b b b b
Running hours counter / operating time b b b b
Starting current and time b
Start inhibit time delay, number of starts
before inhibition
b
Switchgear diagnosis
Cumulative breaking current b b b b b b b
Trip circuit supervision v v v v v v v
Number of operations, operating time, charging time v v v v v v v
CT/VT supervision b b b b b b b
ControI and monitoring ANSI code
Circuit breaker / contactor control 94/69 b b b b b b b
Sepam series 40 rear face:
Base unit.
Main connector.
Input current connector.
Modbus communication port.
Link to remote optional modules.
Input voltage connector.
Optional digital inputs/outputs module.
Latching / acknowledgment 86 b b b b b b b
Logic discrimination 68 v v v v v v v
Switching of group of settings b b b b b b b
Logical equation editor b b b b b b b
Modbus communication
Measurement readout v v v v v v v
Remote indication and time tagging of event v v v v v v v
Remote control orders v v v v v v v
Remote setting of protections v v v v v v v
Transfer of disturbance recording data v v v v v v v
SeIf-diagnosis
Watchdog b b b b b b b
Output relay test v v v v v v v
b standard, v according to parameter settings and optional modules.
1
A
B
C
D
E
2
You might also like
- Short Moritz - LiverGB PDFDocument3 pagesShort Moritz - LiverGB PDFPetra JobovaNo ratings yet
- Dragons and Winged SerpentsDocument5 pagesDragons and Winged SerpentsYuna Raven100% (1)
- Beginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsFrom EverandBeginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CH Six Global Transportation Planning and ExecutionDocument41 pagesCH Six Global Transportation Planning and ExecutionDsh ShNo ratings yet
- AVEVA E3D Tutorial Equipment Modeling With Practical ExampleDocument8 pagesAVEVA E3D Tutorial Equipment Modeling With Practical ExampleRamon Alejandro Porras Hernandez100% (1)
- Digital Power Electronics and ApplicationsFrom EverandDigital Power Electronics and ApplicationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Type VHXM: Under / Over Voltage RelayDocument6 pagesType VHXM: Under / Over Voltage RelayAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Protection Features: Relay Design Features:: Local Keys As Well As Remote Setting by Communication PortDocument17 pagesProtection Features: Relay Design Features:: Local Keys As Well As Remote Setting by Communication PortNamrata ShettiNo ratings yet
- Macedonian KavalDocument1 pageMacedonian Kavalmikiszekely1362No ratings yet
- 7 Stages of NafsDocument7 pages7 Stages of NafsLilyNo ratings yet
- User Manual Sepam 20-1Document78 pagesUser Manual Sepam 20-1Ursula JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 2 Page S40 Data SheetDocument2 pages2 Page S40 Data SheetThinh DaoNo ratings yet
- Sepam Series 20 and Its Optional ModulesDocument2 pagesSepam Series 20 and Its Optional ModulesEphraem KalisNo ratings yet
- Sepam1000 20 Technical Short DataDocument2 pagesSepam1000 20 Technical Short DataGelu BordeaNo ratings yet
- Sepam Series 20 and Its Optional ModulesDocument2 pagesSepam Series 20 and Its Optional ModulesMohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Sepam1000 S40 letEN01Document2 pagesSepam1000 S40 letEN01Florin RageaNo ratings yet
- Sepam RelayDocument46 pagesSepam RelayLawrence AlexNo ratings yet
- Sepam Series 80 and Its Optional ModulesDocument4 pagesSepam Series 80 and Its Optional Modulesjellaso23No ratings yet
- Reakti̇f Güç Kontröl Rölesi̇ (RVT)Document8 pagesReakti̇f Güç Kontröl Rölesi̇ (RVT)iyilmaz1No ratings yet
- Argus 7SR22Document1 pageArgus 7SR22Arun dasNo ratings yet
- Em4 DinDocument8 pagesEm4 DinWilde RodriguezNo ratings yet
- De Thi AVCN1 - 7-2022Document7 pagesDe Thi AVCN1 - 7-2022vu965796No ratings yet
- Electric Amplifier Types VT-VRRA1 and VT-VRPA1: Series 2XDocument6 pagesElectric Amplifier Types VT-VRRA1 and VT-VRPA1: Series 2XАлександр БулдыгинNo ratings yet
- 042 MiCOM C434 (Compatibility Mode)Document27 pages042 MiCOM C434 (Compatibility Mode)penavicbNo ratings yet
- Presentation On BEAMEX MC5 CalibratorDocument29 pagesPresentation On BEAMEX MC5 Calibratoranu prakashNo ratings yet
- Italsea Manual 7BL00097Document25 pagesItalsea Manual 7BL00097Miguel GalindoNo ratings yet
- Wm4096deng270510 PDFDocument32 pagesWm4096deng270510 PDFFabián MedinaNo ratings yet
- LCD TV Service Manual: Konka Group Co, LTDDocument16 pagesLCD TV Service Manual: Konka Group Co, LTDpedroNo ratings yet
- Sepam Series 80-Sepd302058enDocument4 pagesSepam Series 80-Sepd302058enDiegoNo ratings yet
- Easergy Micom p14x - p143 M M LDocument3 pagesEasergy Micom p14x - p143 M M Lnur azizNo ratings yet
- WB7660QB-24Z Battery Inspection Unit User Operational ManualDocument12 pagesWB7660QB-24Z Battery Inspection Unit User Operational ManualKang UsmanNo ratings yet
- DVC700 Series Programmable System Controller DVC710 DVC710LC Programmed With HCT's Intella Software Suite™Document8 pagesDVC700 Series Programmable System Controller DVC710 DVC710LC Programmed With HCT's Intella Software Suite™Derik Carela DiazNo ratings yet
- ReleDocument4 pagesReledavidNo ratings yet
- MV CatalogueDocument28 pagesMV CatalogueAyman SaberNo ratings yet
- Compass B: Directional Short-Circuit and Directional Earth Fault IndicatorDocument2 pagesCompass B: Directional Short-Circuit and Directional Earth Fault Indicatormanskebe6121No ratings yet
- Easergy MiCOM P24x - P241 - B-M - JDocument2 pagesEasergy MiCOM P24x - P241 - B-M - Jخطاب الشاميNo ratings yet
- Bay Control and Breaker Management UnitDocument2 pagesBay Control and Breaker Management UnitabbastceNo ratings yet
- Solar-Log 10 (Bi-Directional Meter) : Installation ManualDocument36 pagesSolar-Log 10 (Bi-Directional Meter) : Installation ManualudhayNo ratings yet
- 7KM42120BA003AA0 Datasheet enDocument6 pages7KM42120BA003AA0 Datasheet ensantoNo ratings yet
- Temporizador Contador Tacómetro Multifunción ARRAY 482EDocument56 pagesTemporizador Contador Tacómetro Multifunción ARRAY 482EDiego CapezioNo ratings yet
- Easergy P3 Protection Relays - REL52018Document5 pagesEasergy P3 Protection Relays - REL52018gigiopicheli731No ratings yet
- Puassembly Instructions & General Information: 23006 - 611 User ManualDocument3 pagesPuassembly Instructions & General Information: 23006 - 611 User Manualfreddy brigstoneNo ratings yet
- Ipr-A GBBR 180315Document4 pagesIpr-A GBBR 180315Victor Hugo González BaezaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6FE1242-6TM20-0BB1: General InformationDocument4 pagesData Sheet 6FE1242-6TM20-0BB1: General InformationAndreyPovoroznyukNo ratings yet
- Dual Plug-In Valve Controller, Canopen®Document5 pagesDual Plug-In Valve Controller, Canopen®Simen EllingsenNo ratings yet
- SBS V1.1-Compliant Gas Gauge IC: FeaturesDocument61 pagesSBS V1.1-Compliant Gas Gauge IC: Featuressoft4gsmNo ratings yet
- CLC5957 12-Bit, 70 MSPS Broadband Monolithic A/D Converter: General Description FeaturesDocument16 pagesCLC5957 12-Bit, 70 MSPS Broadband Monolithic A/D Converter: General Description FeaturesPeter SolyomNo ratings yet
- ADR245BDocument19 pagesADR245BNamrata ShettiNo ratings yet
- GE Fanuc IC695ALG728: Analog Output HART Module, 8 Channels, That Is Configurable IC695A IC695AL IC695ALGDocument46 pagesGE Fanuc IC695ALG728: Analog Output HART Module, 8 Channels, That Is Configurable IC695A IC695AL IC695ALGJosé EduardoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Generator Set AccessoriesDocument4 pagesIndustrial Generator Set Accessoriesyannick.ziboNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electronics Automotive Electronics Product Information Evaluation Circuit For Sensor Impedance Ratios - CC215Document2 pagesAutomotive Electronics Automotive Electronics Product Information Evaluation Circuit For Sensor Impedance Ratios - CC215X'mix ĐreamerNo ratings yet
- Reyrolle 7SR51: Overcurrent ProtectionDocument2 pagesReyrolle 7SR51: Overcurrent ProtectionFelipe FrancoNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Komponen 74vhc14Document16 pagesDatasheet Komponen 74vhc14Mang Asep BuhoyNo ratings yet
- EN FANOX DATA SILS FeederCurrentVoltageFrequency ProtectionRelays R03Document11 pagesEN FANOX DATA SILS FeederCurrentVoltageFrequency ProtectionRelays R03kais abdaouiNo ratings yet
- ADDAD-5 Preliminary DatasheetDocument16 pagesADDAD-5 Preliminary Datasheetbhuvan16No ratings yet
- Cop310 410 411Document20 pagesCop310 410 411Riadalg RiadNo ratings yet
- Protection & Control Monitoring: Sepam Selection Guide For All ApplicationsDocument1 pageProtection & Control Monitoring: Sepam Selection Guide For All ApplicationsHany ShaltootNo ratings yet
- X200X English.Document84 pagesX200X English.Jevgeni SakajevNo ratings yet
- Installation, Testing &integration of New Remote Telemetry Unit (RTU) For Water SCADA System Requirements & SpecificationsDocument35 pagesInstallation, Testing &integration of New Remote Telemetry Unit (RTU) For Water SCADA System Requirements & Specificationshussam aldragmaNo ratings yet
- Easergy P3 - REL52034Document6 pagesEasergy P3 - REL52034usefiNo ratings yet
- GFlow KUF810 Ultrasonic FlowmeterTechnical Specification RevCDocument9 pagesGFlow KUF810 Ultrasonic FlowmeterTechnical Specification RevCadi michaelNo ratings yet
- MM74C926Document9 pagesMM74C926Marco NochebuenaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - HK Es51922 4700752Document35 pagesDatasheet - HK Es51922 4700752Wagner MirandaNo ratings yet
- Genie NX1Document2 pagesGenie NX1Singam SridharNo ratings yet
- PRen GB000092 02 AS3500 DatasheetDocument2 pagesPRen GB000092 02 AS3500 Datasheet8acanosNo ratings yet
- Hypomineralised Second Primary Molars May Be Indicative of Future Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation PDFDocument6 pagesHypomineralised Second Primary Molars May Be Indicative of Future Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation PDFnha khoa NHƯ NGỌCNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument300 pagesUntitledUnbox itNo ratings yet
- DRS Rev.0 GTP-TR1!01!002 Condensate RecyclingDocument4 pagesDRS Rev.0 GTP-TR1!01!002 Condensate RecyclingBalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Oertel - Extracts From The Jāiminīya-Brāhma A and Upanishad-Brāhma A, Parallel To Passages of TheDocument20 pagesOertel - Extracts From The Jāiminīya-Brāhma A and Upanishad-Brāhma A, Parallel To Passages of Thespongebob2812No ratings yet
- Asutphin Client Assessment Matrix Fitt Pros Unit 8Document4 pagesAsutphin Client Assessment Matrix Fitt Pros Unit 8api-307235123No ratings yet
- Mensuration Practice SheetDocument1 pageMensuration Practice SheetSonia SabuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics & Machines - by LearnEngineering - inDocument307 pagesFluid Mechanics & Machines - by LearnEngineering - inVishva PatelNo ratings yet
- MHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Document3 pagesMHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Sank DamNo ratings yet
- Stock+List 6ct8.3g2 Esn#30549237 Cpl#2218 GeneradorDocument34 pagesStock+List 6ct8.3g2 Esn#30549237 Cpl#2218 GeneradorAlexis SanchezNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology ApplicationsDocument11 pagesNanotechnology ApplicationsDivya DivyachilaNo ratings yet
- Fuk SecDocument1 pageFuk SecHirushan MenukaNo ratings yet
- Schrodinger Wave EquationsDocument6 pagesSchrodinger Wave EquationsksksvtNo ratings yet
- Model A SOLUTIONSDocument8 pagesModel A SOLUTIONSasdfNo ratings yet
- M.E Construction Engineering ManagementDocument43 pagesM.E Construction Engineering ManagementLeilani JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Jetline: Theoretical Working Point Performance ChartDocument1 pageJetline: Theoretical Working Point Performance ChartMohamed GamalNo ratings yet
- 12.1 ANSYS CompositePrepPostDocument2 pages12.1 ANSYS CompositePrepPostLakmal ArandaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 24 - Laminate Modeling - Rev C PDFDocument20 pagesLesson 24 - Laminate Modeling - Rev C PDFraduga_fbNo ratings yet
- Quran On GeologyDocument10 pagesQuran On GeologyMM NabeelNo ratings yet
- The Redesigning of Junction: Tatya Tope Square BhopalDocument15 pagesThe Redesigning of Junction: Tatya Tope Square BhopalAr Raj YamgarNo ratings yet
- 16950Document16 pages16950uddinnadeemNo ratings yet
- Latest Research Papers On Manet SecurityDocument7 pagesLatest Research Papers On Manet Securitygz9g97haNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems:: Hacking of Electronic EquipmentsDocument76 pagesEmbedded Systems:: Hacking of Electronic EquipmentsKailashi Chandra SekharNo ratings yet
- 2014 Catbalogan Landslide: September, 17, 2014Document6 pages2014 Catbalogan Landslide: September, 17, 2014Jennifer Gapuz GalletaNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Fatima University: College of Business & AccountancyDocument17 pagesOur Lady of Fatima University: College of Business & AccountancyCLARIN GERALDNo ratings yet