Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 15
Uploaded by
Salma BondocCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 15
Uploaded by
Salma BondocCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 15 How Organisms Evolve
15.1 How Are Populations, Genes, And Evolution Related?
Evolution is change in frequencies of alleles in a populations gene pool. Allele
frequencies in a population will remain constant over generations if the following conditions are met: there is no mutation, there is no gene flow, the population is very large, all mating is random, and all genotypes reproduce equally well. These conditions are rarely met in nature. Evolutionary Changes are those that occur from generation to generation and cause descendants to differ from their ancestor. Evolution is a property not of individuals but of populations. Population is a group that includes all the members of a species living in a given area. Gene is a segment of DNA that controls inheritance trait. DNA is a compound in cell nuclei that is the basis of heredity. Allele is one of several alternative forms of a particular gene. Homozygous means having two identical genes. Heterozygous is an individual with different alleles for that gene. Genotype is a genetic group. Phenotype is a visible characteristic of organism. Chromosome is a part of a cell nucleus that contains genes. Diploid means possessing two matched sets of chromosomes in the cell nucleus, one set from each parent. Population Genetic is the study of the allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of the four evolutionary processes: natural selection, genetic drift, mutation, gene flow. Gene Pool is the sum of all the genes in a population. Allele Frequency, it is the number of copies of a particular allele divided by the number of copies of all alleles at the genetic place in a population. Hardy-Weinberg Principle, this model showed that under certain conditions, allele frequencies and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant no matter how many generations pass.
15.2 What Causes Evolution? There are five major causes of evolution: Gene Flow, Mutation, Small Population Size,
Nonrandom mating, and Natural selection. Mutations are random, undirected changes in DNA composition. Although most
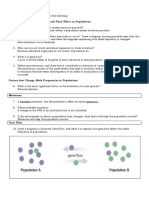
mutations are neutral or harmful to the organism, some prove advantageous in certain environments. Mutations are rare and do not change allele frequencies very much, but they provide the raw material for evolution. Gene flow is the movement of alleles between different populations of a species. Gene flow tends to reduce differences in the genetic composition of different populations. In any population, chance events kill or prevent reproduction by some of the individuals. Genetic drift, if the population is small, chance events may eliminate a disproportionate number of individuals who bear a particular allele, thereby greatly changing the allele frequency in the population. Two causes of genetic drift: Population Bottleneck is an evolutionary event in which a significant percentage of a population or species is killed or prevented from reproducing. Founder Effect occurs when isolated colonies are founded by a small number of organisms. Nonrandom mating, such as assortative mating, can change the distribution of genotypes in a population.
15.3 How Does Natural Selection Works?
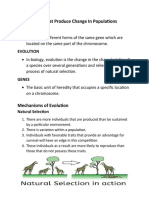
Natural selection is driven by differences in reproductive success among different
genotypes. Natural selection proceeds from the interactions of organisms with both the biotic and abiotic parts of their environments. When two or more species exert mutual environmental pressures on each other for long periods of time, both of them evolve in response. Such coevolution can result from any type of relationship between organisms, including competition and predation. Adaptations are characteristics that help an individual survive and reproduce. Coevolution is mutual feedback between two species. Predation includes any situation in which one organism eats another. Predators are those who do the eating. Preys are those who are eaten. Balanced Polymorphism two or more phenotypes are maintained in a population. Altruism refers to any behavior that endangers an individual organism or reduces its reproductive success but benefits other members of its species. Kin selection is a natural selection that favors self-sacrificing behavior toward relatives because, even if the individual dies, those relatives that survive will carry some of its genes. Selection can influence population in 3 ways Directional selection favors individuals with an extreme value of trait and selects against both average individuals and individuals at the opposite extreme. Stabilizing selection favors individuals with the average value of trait and selects against individuals with extreme values. Disruptive selection favors individuals at both extremes of a trait and selects against individuals with intermediate values.
You might also like
- Mechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsDocument44 pagesMechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Chapter 23 Evolution of PopulationsDocument4 pagesAP Biology Chapter 23 Evolution of PopulationsfranciscoNo ratings yet
- Quiz Chap. 11Document4 pagesQuiz Chap. 11Beatrice De LeonNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Chapter 23 PresentationDocument18 pagesAP Biology Chapter 23 PresentationHayleeNo ratings yet
- What Is Genetic Variation?: DNA Single Nucleotide PolymorphismsDocument8 pagesWhat Is Genetic Variation?: DNA Single Nucleotide PolymorphismsVanessa TangonanNo ratings yet
- Micro EvolutionDocument9 pagesMicro EvolutionBryan TanNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms-that-Produce-Change-in-PopulationsDocument45 pagesMechanisms-that-Produce-Change-in-Populationskaren milloNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanism of Evolution Lecture E. SanaDocument6 pagesBasic Mechanism of Evolution Lecture E. SanaEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of MechanismsDocument15 pagesEvolution of MechanismsJesmin ShumiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Natural SelectionDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Natural SelectionKaira JogNo ratings yet
- ,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,MDocument4 pages,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,MAnonymous 51aHkMdNo ratings yet
- Biology WRDocument7 pagesBiology WRElene Grace BarteNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Evolution ExplainedDocument23 pagesMechanisms of Evolution ExplainedVeancy WangNo ratings yet
- Copy Bio (Complete Infos)Document8 pagesCopy Bio (Complete Infos)marcutoy000No ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Microevolution: Genetic Changes Within PopulationsDocument45 pagesChapter 20: Microevolution: Genetic Changes Within Populationsambali1220No ratings yet
- REPORT BIO MicroevolutionDocument35 pagesREPORT BIO Microevolutionmichael tamadoNo ratings yet
- Final EvolutionDocument3 pagesFinal EvolutionJesmin ShumiNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 4 Week 4Document4 pagesGen Bio Module 4 Week 4LouisseNo ratings yet
- Ch. 23 Lecture Outline PDFDocument15 pagesCh. 23 Lecture Outline PDFCSERM UNASNo ratings yet
- SBI 3U Evolution Mechanisms and Their EffectDocument3 pagesSBI 3U Evolution Mechanisms and Their EffectShaun AhujaNo ratings yet
- The Hardy-Weinberg Theorem - AP BiologyDocument2 pagesThe Hardy-Weinberg Theorem - AP BiologyGreyGravityNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Evolution: Natural Selection, Mutation, and Genetic DriftDocument4 pagesMechanisms of Evolution: Natural Selection, Mutation, and Genetic DriftRheena FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Ex. 5. Consequences of Inbreeding On Genetic Structure of Resulting PopulationsDocument3 pagesEx. 5. Consequences of Inbreeding On Genetic Structure of Resulting Populationsmicheal rayapanNo ratings yet
- Breeding Strategies and Genetic ConsequeDocument11 pagesBreeding Strategies and Genetic ConsequeRahadian AhmadNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of EvolutionDocument41 pagesMechanism of EvolutionChristian EstradaNo ratings yet
- ANTH 140 SPR 2016 DVC f-2-f SG2Document5 pagesANTH 140 SPR 2016 DVC f-2-f SG2Lynda TruongNo ratings yet
- The Process in Genetic Engineering (Crops)Document11 pagesThe Process in Genetic Engineering (Crops)Inio JarhylNo ratings yet
- Evolution of PopulationDocument9 pagesEvolution of PopulationUj UmarNo ratings yet
- General Biology II q1 m6Document44 pagesGeneral Biology II q1 m6miradornathaniel71No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument30 pagesUntitledAdugna Mekuria BoteNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Evolution pptDocument26 pagesMechanism of Evolution pptk15014998No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Evo BioDocument8 pagesReviewer in Evo BioMichaela ParalejasNo ratings yet
- Concept of Gene PoolDocument41 pagesConcept of Gene PoolBandook Gamers0% (1)
- AP Biology Complete Study Guide Big Idea #1Document17 pagesAP Biology Complete Study Guide Big Idea #1api-278940778No ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument4 pagesMechanisms of Evolutionchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Micro EvolutionDocument47 pagesLecture 6 - Micro EvolutionirosalejosNo ratings yet
- CH 23 Lecture OutlineDocument6 pagesCH 23 Lecture OutlineZohal Ghulam-JelaniNo ratings yet
- Genetic DiversityDocument20 pagesGenetic Diversityjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Lec 14 PDFDocument4 pagesLec 14 PDFMichael FernoNo ratings yet
- 02 Evolution PDFDocument2 pages02 Evolution PDF24monty24No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Unit I - Evolutionary EcologyDocument2 pagesLecture Notes On Unit I - Evolutionary EcologyCheryl MountainclearNo ratings yet
- Evolution ConceptsDocument2 pagesEvolution ConceptsJavier RosalesNo ratings yet
- Origin of Variation ExplainedDocument4 pagesOrigin of Variation ExplainedBeverlyRose Bueno Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Origin of BiodiversityDocument35 pagesEvolution and Origin of BiodiversityMariel Mae DatanaganNo ratings yet
- hardy weinburg principle and evolutionDocument12 pageshardy weinburg principle and evolutionsamikshachavan8114No ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change in PopulationsDocument6 pagesMechanisms of Evolutionary Change in PopulationsTobias Domenite P.No ratings yet
- EvoultionsDocument1 pageEvoultionsCedieNo ratings yet
- Biology Essay 3 - The Causes of Variation and Its Biological ImportanceDocument3 pagesBiology Essay 3 - The Causes of Variation and Its Biological ImportanceEva Dewsbury67% (3)
- Migrationgene Flow Genetic DriftDocument16 pagesMigrationgene Flow Genetic DriftPhia ViaNo ratings yet
- 15.2 Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument11 pages15.2 Mechanisms of Evolutionslipper_crazy5335No ratings yet
- Lesson 15: Mechanisms in Population: General Biology 2 Nicolites Montessori SchoolDocument3 pagesLesson 15: Mechanisms in Population: General Biology 2 Nicolites Montessori SchoolJohn John SierraNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Consequences of DomesticationDocument10 pagesGenetics and Consequences of DomesticationChandra Sekhar KaranaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 - LESSON 4 - 7 REVIEWERDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology 2 - LESSON 4 - 7 REVIEWERParis ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Genetic VariationDocument18 pagesCauses of Genetic VariationMjGNo ratings yet
- Oscar Marquez-Martinez - CH 9 QuestionsDocument12 pagesOscar Marquez-Martinez - CH 9 Questionsapi-478637931No ratings yet
- Natural Selection 2.5Document26 pagesNatural Selection 2.5DequanNo ratings yet
- Bio CH 17.2 LectureDocument27 pagesBio CH 17.2 LectureAnonymous VShJKF9tCNNo ratings yet
- 1-Evolution Fundamentals Herbers EncyclopediaAnimalBeh2010Document9 pages1-Evolution Fundamentals Herbers EncyclopediaAnimalBeh2010Uriel RodríguezNo ratings yet
- FIVE Agents of Evolutionary ChangeDocument3 pagesFIVE Agents of Evolutionary Changes.felicitas.shaniekadielleNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Hot Air BalloonDocument3 pagesHow To Make A Hot Air BalloonSalma BondocNo ratings yet
- Courtship StylesDocument2 pagesCourtship StylesSalma Bondoc100% (1)
- We Are The WorldDocument2 pagesWe Are The WorldSalma BondocNo ratings yet
- Project in ScienceDocument10 pagesProject in ScienceSalma BondocNo ratings yet
- A Tale of Two CitiesDocument7 pagesA Tale of Two CitiesSalma BondocNo ratings yet
- The Expanded Modern Theory of Biological EvolutionDocument22 pagesThe Expanded Modern Theory of Biological EvolutionDiana Itzell G LNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Guided NotesDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Guided Notesapi-280725048No ratings yet
- Biology Pocket Mouse HWDocument3 pagesBiology Pocket Mouse HWZackNo ratings yet
- Interface Computer College 2Nd Unit Exam High School Department Grade 9 ScienceDocument5 pagesInterface Computer College 2Nd Unit Exam High School Department Grade 9 ScienceMara LabanderoNo ratings yet
- Cnvert 1-Halaman-392-397Document6 pagesCnvert 1-Halaman-392-397atma cansNo ratings yet
- 2 7 19 Independent 1Document3 pages2 7 19 Independent 1api-372548146No ratings yet
- The Blind Watchmaker - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesThe Blind Watchmaker - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediastald100% (1)
- Henry Walter BatesDocument6 pagesHenry Walter Batesapi-302616196No ratings yet
- Weekly Evolution Activity SheetsDocument15 pagesWeekly Evolution Activity SheetsShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Rainfall and Bird BeaksDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Rainfall and Bird BeakscokcreNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in General Biology 2: Quarter 1 - Week 4: Evidences of Evolution and Evolutionary Relationships of OrganismsDocument8 pagesWorksheet in General Biology 2: Quarter 1 - Week 4: Evidences of Evolution and Evolutionary Relationships of OrganismsShastine Claor100% (1)
- SpeciationDocument13 pagesSpeciationrabiaNo ratings yet
- Hardy-Weinberg Genetics Take-Home ANSWERSDocument3 pagesHardy-Weinberg Genetics Take-Home ANSWERSAndres JacoboNo ratings yet
- Bio Factsheet: EvolutionDocument3 pagesBio Factsheet: EvolutionsreenitthiNo ratings yet
- Poner en Práctica: Ejercicio 1. Completa Las Oraciones Con oDocument2 pagesPoner en Práctica: Ejercicio 1. Completa Las Oraciones Con oDIEGONo ratings yet
- Pop Genetics & Natural SelectionDocument13 pagesPop Genetics & Natural SelectionAmaniNo ratings yet
- Evidence For EvolutionDocument12 pagesEvidence For Evolutionapi-259727482100% (1)
- Genetika PopulasiDocument48 pagesGenetika PopulasiRoy SinagaNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification 3 PDFDocument1 pageBiological Classification 3 PDFDr-Atin Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1070 AnswersDocument4 pagesBio 1070 AnswersMatthew MilencoffNo ratings yet
- What Is A Species - Carl Zimmer 2008Document8 pagesWhat Is A Species - Carl Zimmer 2008Kinsmir SmNo ratings yet
- (Oxford Series in Ecology and Evolution) Michael L. Arnold - Natural Hybridization and Evolution-Oxford University Press (1997)Document230 pages(Oxford Series in Ecology and Evolution) Michael L. Arnold - Natural Hybridization and Evolution-Oxford University Press (1997)SzutsTamasNo ratings yet
- Leonardo Garcia - The Evolution of Life VocabularyDocument4 pagesLeonardo Garcia - The Evolution of Life Vocabularyapi-450648720No ratings yet
- Randolph Nesse, The Four Areas of BiologyDocument1 pageRandolph Nesse, The Four Areas of BiologyRoque Lazcano VázquezNo ratings yet
- Macroevolution and the Formation of New Species ExplainedDocument19 pagesMacroevolution and the Formation of New Species Explainedmichelle ann sabilonaNo ratings yet
- Ernst Mayr One Long Argument PDFDocument2 pagesErnst Mayr One Long Argument PDFDanNo ratings yet
- Bio IntroDocument41 pagesBio IntrosarahsaurNo ratings yet
- Patrick Bateson - The Active Role of Behaviour in EvolutionDocument16 pagesPatrick Bateson - The Active Role of Behaviour in EvolutionKein BécilNo ratings yet
- TQ Science10 Q3 ST3Document2 pagesTQ Science10 Q3 ST3mae cudal100% (1)
- UCSP Essay (Grade 11)Document2 pagesUCSP Essay (Grade 11)Jane Bardon100% (1)