Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uniform Circular Motion Lab
Uploaded by
api-249849134Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uniform Circular Motion Lab
Uploaded by
api-249849134Copyright:
Available Formats
SPH4U0!
Names:___________________________________________________!
Uniform Circular Motion Lab
LEARNING GOAL!
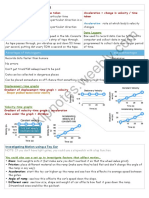
! ! Understand how centripetal force is connected to the radius, velocity and mass. ! ! INTRO! !
65
! Uniform circular motion applications can be found present in product, road and satellite design and engineering. Products, such as washing and drying machines, need to undergo uniform circular motion. If the motion is not uniform, forces are applied to portions of the product that were not designed for such forces which may lead to warping and damage. Road design also involves circular portions, which will involve uniform motion. Many ramps on and off highways are circular in design and are also curbed in order to allow cars to travel on them at higher speeds without skidding off. Satellites orbit the Earth uniformly. Satellite dish cable/internet rely on satellites that orbit the Earth at the same speed in which the Earth rotates. This allows the satellite to remain xed in one position in our sky. Such orbits are called geosynchronous. !
! INVESTIGATION! !
! Secure one rubber stopper to the end of a string 1.15m long. Choose a radius that is between 20 cm and 40 cm, make sure you record it on the table on the following page. Swing the stopper uniformly and calculate the amount of time it takes for the stopper to complete at least 10 full rotations. Determine the speed and acceleration of the stopper and nally the centripetal force. Include units in the headers of the table. Use the space below to show how you found the speed, acceleration and force of the rst row. Make sure it is neat, labeled and include units. You dont have to show your work for the rest. Keeping the radius and mass constant, swing the stopper at 4 other speeds."
Mass
Radius
Rotations
Time
Speed
Acceleration
Force
! Double the radius, keeping the mass the same. Fill out the following table using the same procedure as before. !
Mass Radius Rotations Time Speed Acceleration Force
! Double the mass but use the same radius as you did the rst time. Fill out the following table using the same procedure as before.!
Mass Radius Rotations Time Speed Acceleration Force
! Using the double mass, as in the previous trial, double your radius and ll out the following table using the same procedure as before. "
Mass Radius Rotations Time Speed Acceleration Force
20
! Graph Force vs Speed for each table. Title and label all graphs appropriately. Draw a curve of best t for all graphs."
16
EXTENSION!
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! !
!
1. By what factor does the force change by if the speed is doubled but the mass and radius remain constant? What kind of relation does this point to? Explain your reasoning. !
2. By what factor does the force change by if the mass is doubled but the speed and radius remain constant? What kind of relation does this point to? Explain your reasoning.!
3. By what factor does the force change by if the radius is doubled but the mass and speed remain constant? What kind of relation does this point to? Explain your reasoning.!
4. If the initial centripetal force for an object of mass M, radius R and speed S to undergo uniform circular motion is 75N, what will the centripetal force be if the mass is tripled, the radius doubled and the speed halved? What is the ratio of the nal centripetal force to the initial centripetal force. Show all your work.!
10
22
You might also like
- 15 Impulse TNDocument4 pages15 Impulse TNprisiliamondigirNo ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics (Nicholas Hunter Burns)Document3 pagesRotational Dynamics (Nicholas Hunter Burns)Amber Selwyn BurnsNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Acceleration Lab ReportDocument7 pagesCentripetal Acceleration Lab Reportapi-263389150No ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia ExperimentDocument4 pagesMoment of Inertia Experimentmuhammad faizal akbarNo ratings yet
- Horsepower and TorqueDocument9 pagesHorsepower and TorqueRoberto Lopez RojasNo ratings yet
- The FlywheelDocument9 pagesThe FlywheelMudri MudracNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report - Centripetal AccelerationDocument4 pagesPhysics Lab Report - Centripetal Accelerationapi-257066694No ratings yet
- LAB 3 Newtons 2nd Law of Motion.9!8!06.DchDocument6 pagesLAB 3 Newtons 2nd Law of Motion.9!8!06.DchRodilyn ParreñoNo ratings yet
- MHS Physics Problems Chapter 9Document31 pagesMHS Physics Problems Chapter 9Klaus Danjolli100% (1)
- Lab 8-Impulse and MomentumDocument6 pagesLab 8-Impulse and MomentumlilcommishNo ratings yet
- Lab Newtons 2ndDocument3 pagesLab Newtons 2ndUgur ASİT50% (2)
- Physics 211 Uniform Circular Motion LabDocument6 pagesPhysics 211 Uniform Circular Motion Labtham_psdcNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Force RelationshipDocument8 pagesCentripetal Force RelationshipJoel Christian MascariñaNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Force Calculations and GraphingDocument6 pagesCentripetal Force Calculations and GraphingR MathewNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ReportDocument8 pagesPhysics Lab Reportapi-439858777No ratings yet
- Exp 3 - Rolling Disc and AxleDocument7 pagesExp 3 - Rolling Disc and AxleCoco YapNo ratings yet
- 09 Rotational MotionDocument10 pages09 Rotational MotionBalaram MullapudiNo ratings yet
- Angular Motion LecturesDocument2 pagesAngular Motion LectureseviroyerNo ratings yet
- Centripetal AccelerationDocument4 pagesCentripetal Accelerationapi-263388641No ratings yet
- Unit 3 HomeworkDocument2 pagesUnit 3 HomeworkMiqi ZhangNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines-II Lab Lab Session 01: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesTheory of Machines-II Lab Lab Session 01: ObjectiveMechanical WorkNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion LabDocument8 pagesRotational Motion LabjehrNo ratings yet
- Oscillations: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesOscillations: ObjectivesNanaHanunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Projectiles and Circular MotionDocument56 pagesChapter 11 - Projectiles and Circular Motionascd_msvuNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Force Lab AnalysisDocument10 pagesCentripetal Force Lab AnalysisSuperFly SmithNo ratings yet
- 201 Lab 7. Work and EnergyDocument9 pages201 Lab 7. Work and EnergydermaNo ratings yet
- Physics Homework Review of Mechanics PrinciplesDocument5 pagesPhysics Homework Review of Mechanics PrinciplesNur SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (Simple Harmonic Motion "Pendulum Energy") Using Phet Interactive SimulationDocument2 pagesWorksheet (Simple Harmonic Motion "Pendulum Energy") Using Phet Interactive SimulationSella LubisNo ratings yet
- Six Flags Great Adventure Physics WorkbookDocument51 pagesSix Flags Great Adventure Physics WorkbookPrinces Aurorra0% (1)
- Laboratory Activity No.3Document5 pagesLaboratory Activity No.3NICOLE RUTH RECTONo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion Simulation Lab: ApparatusDocument6 pagesForces and Motion Simulation Lab: ApparatusMatt FerrariNo ratings yet
- P.A Hilton LTD Instruction Manual HTM25 Gear Train ApparatusDocument22 pagesP.A Hilton LTD Instruction Manual HTM25 Gear Train ApparatusAlex AndrangoNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion Lab For Physics 2016 SpringDocument1 pageCircular Motion Lab For Physics 2016 SpringIrwansyah Ramadhani100% (1)
- MOM Lab ReportsDocument17 pagesMOM Lab Reportsfarhan ansarNo ratings yet
- Energy Skate Park - UsedDocument5 pagesEnergy Skate Park - UsedUntold StoriesNo ratings yet
- Measure Centripetal Force in Circular Motion LabDocument6 pagesMeasure Centripetal Force in Circular Motion LabwwzNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Lab PDFDocument19 pagesEngineering Mechanics Lab PDFDeepal Nandy100% (1)
- Module1 - Lab Answer KeyDocument7 pagesModule1 - Lab Answer KeyAudio books LibraryNo ratings yet
- Watermark p1 - Physics Igcse Notes CondensingDocument23 pagesWatermark p1 - Physics Igcse Notes Condensingapi-324122235100% (3)
- MotionDocument14 pagesMotionteerapong onogkNo ratings yet
- Vatsalya Public School, Mandsaur Quarterly Examination (2012-13)Document5 pagesVatsalya Public School, Mandsaur Quarterly Examination (2012-13)Ankit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ebook College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3Rd Edition Knight Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument55 pagesEbook College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3Rd Edition Knight Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFStevenMillersqpe100% (9)
- Rotational Motion ProblemsDocument19 pagesRotational Motion ProblemsShahd MuhamedNo ratings yet
- Understanding Rotational MotionDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Rotational MotionNaN GamingNo ratings yet
- 1101 Lab 8 - OscillationsDocument19 pages1101 Lab 8 - OscillationsManurung DannyNo ratings yet
- 1101 Lab 4 - Circular MotDocument18 pages1101 Lab 4 - Circular MotYi Wei OngNo ratings yet
- Lab 12Document9 pagesLab 12Princes Katherine VergaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 08 Acceleration RPDocument15 pagesLesson 08 Acceleration RPAlya Defa AnindaNo ratings yet
- Lab5 Force & EquilibriumDocument4 pagesLab5 Force & EquilibriumJay NgNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion Acceleration MeasuredDocument4 pagesCircular Motion Acceleration MeasuredJasdeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Spur Gear DesignDocument122 pagesChapter 9 Spur Gear DesignJimmy Silvera OtañeNo ratings yet
- Adaptive MotionDocument77 pagesAdaptive Motionpatrickcjh5236No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument32 pagesPhysicsvzqyr66ck5No ratings yet
- Rotation Learning GuideDocument12 pagesRotation Learning GuideRana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Experiment-3 Balancing of Multiple Mass in Single PlaneDocument5 pagesExperiment-3 Balancing of Multiple Mass in Single PlaneK HNo ratings yet
- Physics 211 Experiment # 10 Measurement of Moment of Inertia ObjectiveDocument7 pagesPhysics 211 Experiment # 10 Measurement of Moment of Inertia ObjectiveKhabi NadaNo ratings yet
- Sample - Memorandum Report Memo ReportDocument6 pagesSample - Memorandum Report Memo ReportVinod BhaskarNo ratings yet
- The Science and Design of the Hybrid Rocket EngineFrom EverandThe Science and Design of the Hybrid Rocket EngineRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Wood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingFrom EverandWood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingNo ratings yet
- Sound ReproductionDocument89 pagesSound Reproductionapi-249849134100% (1)
- Dynamics Test 1Document4 pagesDynamics Test 1api-249849134No ratings yet
- Pendulum Motion LabDocument3 pagesPendulum Motion Labapi-249849134No ratings yet
- Kinematics TestDocument4 pagesKinematics Testapi-249849134No ratings yet
- Pendulum Motion Dummy Data Trial 1Document5 pagesPendulum Motion Dummy Data Trial 1api-249849134No ratings yet
- Pendulum Motion 2Document5 pagesPendulum Motion 2api-249849134No ratings yet
- Pendulum MotionDocument5 pagesPendulum Motionapi-249849134No ratings yet
- Pendulum Motion LabDocument3 pagesPendulum Motion Labapi-249849134No ratings yet
- Participation ProjectDocument1 pageParticipation Projectapi-249849134No ratings yet
- Phy251l FrictionDocument3 pagesPhy251l Frictionapi-249849134No ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Concurrent Forces QDocument2 pagesEquilibrium of Concurrent Forces Qapi-249849134No ratings yet
- Hookes Law LabDocument4 pagesHookes Law Labapi-249849134No ratings yet
- Applied MathematicsDocument119 pagesApplied MathematicsIAMMARKSNo ratings yet
- Numerical Investigation On Detection of PrestressDocument7 pagesNumerical Investigation On Detection of PrestressTrúc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Frequency Control of Inverters Connected in Parallel Forming A Micro-GridDocument6 pagesVoltage and Frequency Control of Inverters Connected in Parallel Forming A Micro-GridShad Rahman100% (1)
- 2 Extracting Knowledge QuestionsDocument27 pages2 Extracting Knowledge QuestionsAzer AliyevNo ratings yet
- Happens To Be A Uniform Ellipsoid: Chapter 16 Gauss' LawDocument7 pagesHappens To Be A Uniform Ellipsoid: Chapter 16 Gauss' LawSamuel PakianathanNo ratings yet
- Analysis AssigmentDocument50 pagesAnalysis AssigmentAliyi MuktarNo ratings yet
- Line-Scanning Laser Scattering System For Fast Defect Inspection of A Large Aperture SurfaceDocument10 pagesLine-Scanning Laser Scattering System For Fast Defect Inspection of A Large Aperture SurfaceAyman IsmailNo ratings yet
- APEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalDocument22 pagesAPEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalbaljinderNo ratings yet
- Change of Order of IntegrationDocument4 pagesChange of Order of IntegrationShubham Teju100% (2)
- Curtain Wall Calculation PDFDocument134 pagesCurtain Wall Calculation PDFAlaaBadwy100% (1)
- De La Salle University Dasmarinas: Experiment No. 4 DC Shunt MotorDocument6 pagesDe La Salle University Dasmarinas: Experiment No. 4 DC Shunt MotorMizhar GerardoNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines Lab Manual 10122015 030654AMDocument51 pagesTheory of Machines Lab Manual 10122015 030654AMAjay Kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 (A) : Cc205 Lab Mechanic of StructuresDocument5 pagesExperiment 3 (A) : Cc205 Lab Mechanic of StructuresZol HasNo ratings yet
- Stefan BoltzmannDocument28 pagesStefan BoltzmannAugusto GloopNo ratings yet
- Resume AyanchattopadhyayDocument2 pagesResume Ayanchattopadhyayapi-163237383No ratings yet
- Errata FE WasimDocument4 pagesErrata FE WasimchafobostonNo ratings yet
- WKST - 1.4 Converting Graphs - ChallengeDocument8 pagesWKST - 1.4 Converting Graphs - Challengefaltu accountNo ratings yet
- Lamp Flicker On Power SystemsDocument22 pagesLamp Flicker On Power SystemsJhon Elmer Luque LuqueNo ratings yet
- IITian Pace Phy1&2Document8 pagesIITian Pace Phy1&2Lokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Energy and Linear and Angular Momenta in Simple Electromagnetic SystemsDocument24 pagesEnergy and Linear and Angular Momenta in Simple Electromagnetic SystemsJennifer RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Cosmos 2007Document38 pagesCosmos 2007Oswaldo NeaveNo ratings yet
- EMI and ACDocument14 pagesEMI and ACbharathNo ratings yet
- torque 정의Document40 pagestorque 정의valmaxjeonNo ratings yet
- Thesis ReportDocument132 pagesThesis ReportOana UdreaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Vectors and Tensors - Lesson4Document22 pages4 - Vectors and Tensors - Lesson4emmanuel FOYETNo ratings yet
- 39 Space Air DistributionDocument25 pages39 Space Air DistributionPRASAD326100% (3)
- Engineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 0809Document10 pagesEngineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 0809Amirul AizatNo ratings yet
- Basic Inertial NavigationDocument38 pagesBasic Inertial Navigationleneneck9057100% (1)
- MomentumDocument2 pagesMomentumMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set - Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesProblem Set - Fluid MechanicsEloisa Mae FundarNo ratings yet