Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homework 1
Uploaded by
Itzel A. GuerreroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Homework 1
Uploaded by
Itzel A. GuerreroCopyright:
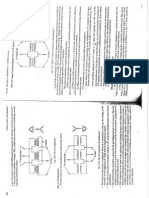
Available Formats
Homework 1 Physical Chemistry II, Semester 2014-1 Due Date: Mon, 03/03, 4:OO PM, in my spot
9. A cup of water at 278 K (the system) is placed in a microwave oven and the oven is turned on for 1 minute during which it begins to boil. Which of q, w, and U are positive, negative, or zero?
10. What is wrong with the following statement?: Burns caused by steam at 100C can be more severe than those caused by water at 100C because steam contains more heat than water. Rewrite the sentence to convey the same information in a correct way. 11. 3.00 moles of an ideal gas at 27.0C expands isothermally from an initial volume of 20.0 dm3 to a final volume of 60.0 dm3. Calculate w for this process a) for expansion against a constant external pressure of 1.00 105 Pa and b) for a reversible expansion. 12. 3.00 moles of an ideal gas are compressed isothermally from 60.0 to 20.0 L using a constant external pressure of 5.00 atm. Calculate q, w, U, and H. 13. For 1 mol of an ideal gas, Pexternal = P = 200 103 Pa. The temperature is changed from 100C to 25.0C, and CV,m = 3/2R. Calculate q, w, U, and H. 14. 3.50 moles of an ideal gas is expanded from 450 K and an initial pressure of 5.00 bar to a final pressure of 1.00 bar, and CP,m = 5/2R. Calculate w for the following two cases.
a) The expansion is isothermal and reversible. b) The expansion is adiabatic and reversible. Without resorting to equations, explain why the result to part (b) is greater than or less than the result to part (a). 15. An ideal gas described by Ti = 300 K, Pi = 1.00 bar, and Vi = 10.0 L is heated at constant volume until P = 10.0 bar. It then undergoes a reversible isothermal expansion until P = 1.00 bar. It is then restored to its original state by the extraction of heat at constant pressure. Depict this closed-cycle process in a P-V diagram. Calculate w for each step and for the total process. What values for w would you calculate if the cycle were traversed in the opposite direction? 16. A nearly flat bicycle tire becomes noticeably warmer after it has been pumped up. Approximate this process as a reversible adiabatic compression. Take the initial pressure and temperature of the air before it is put in the tire to be Pi = 1.00 bar and Ti = 298 K. The final volume of the air in the tire is Vf = 1.00 L and the final pressure is Pf = 5.00 bar. Calculate the final temperature of the air in the tire. Assume that CV,m =5/2R. 17. Because U is a state function, . Using this relationship, show that for an ideal gas.
18. Obtain an expression for the isothermal compressibility 19. if
for a van der Waals gas.
express as a function of and Vm for an ideal gas, and as a function of b, , and Vm for a van der Waals gas. 20. The Joule coefficient is defined as
Calculate the Joule coefficient for an ideal gas and for a van der Waals gas. 21. Use the relation
the cyclic rule, and the van der Waals equation of state to derive an equation for C P,m - C V ,m in terms of Vm and the gas constants R, a, and b.
22. Because the change in enthalpy of a gas expanded at constant temperature can be calculated. In order to do so, the functional dependence of on P must be known. Treating Ar as a van der Waals gas, calculate H when 1 mol of Ar is expanded from 400 bar to 1.00 bar at 300 K. Assume that is independent of pressure and is given by
for Ar. What value would H have if the gas exhibited ideal gas behavior? 23. Calculate Hreaction and reaction U at 298.15 K for the following reactions: a) 4NH3(g) + 6NO(g) 5 N2(g) + 6H2O(g) b) 2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) c) TiCl4(l) + 2H2O(l) TiO2(s) + 4HCl(g) d) 2 NaOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l) Assume complete dissociation of NaOH, H2SO4, and Na2SO4 e) CH4(g) + H2O(g) CO(g) + 3H2(g) f) CH3OH(g) + CO(g) CH3COOH(l) 24. Several reactions and their standard reaction enthalpies at 25C are given here. H (kJ mol1) CaC2(s) + 2H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(s) + C2H2(g) 127.9 Ca(s) + O2(g) CaO(s) 635.1 CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(s) 65.2 The standard enthalpies of combustion of graphite and C2H2(g) are 393.51 and 1299.58 kJ mol1, respectively. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of CaC2(s) at 25C. 25. Use the following data at 25C to complete this problem: H H2(g) + O2(g) OH(g) H2(g) + O2(g) H2O(g) H2(g) 2H(g) O2(g) 2O (g) Calculate Hreaction for a) OH(g) H(g) + O(g) b) H2O(g) 2H(g) + O(g) c) H2O(g) H(g) + OH(g) Assuming ideal gas behavior, calculate H reaction and U reaction for all three reactions (kJ mol-1) 38.95 241.814 435.994 498.34
reaction
You might also like
- Chapter 20-The First Law of Thermodynamics: Multiple ChoiceDocument13 pagesChapter 20-The First Law of Thermodynamics: Multiple ChoiceJhajha AlboniaNo ratings yet
- Vaaniyai Saran AdithenDocument108 pagesVaaniyai Saran AdithenLalithaganesanNo ratings yet
- EdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 4 Mark Scheme Results Paper 1 Jan 2006Document11 pagesEdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 4 Mark Scheme Results Paper 1 Jan 2006Neen NaazNo ratings yet
- Tamil Novel LinksDocument1 pageTamil Novel Linksspmeyyammaisp06No ratings yet
- THERMO1 - 4 Control Volume PDFDocument11 pagesTHERMO1 - 4 Control Volume PDFEdmark AldeaNo ratings yet
- Marma VeeduDocument36 pagesMarma VeeduShalomi JacobNo ratings yet
- 2 Forces and MotionDocument42 pages2 Forces and Motion7oda319No ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics For Engineers 7th Edition Solution Manual Chapter 15Document22 pagesProbability and Statistics For Engineers 7th Edition Solution Manual Chapter 15footballp3550% (1)
- A Feedwater Heater Operating at Steady State Has Two Inlets and One ExitDocument1 pageA Feedwater Heater Operating at Steady State Has Two Inlets and One ExitMuthiah Chidambaram Muthiah0% (2)
- Alagumayiladum 1Document10 pagesAlagumayiladum 1Aarthy NavaneethanNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear and Mixed-Integer Optimization Fundament... - (Front Matter)Document15 pagesNonlinear and Mixed-Integer Optimization Fundament... - (Front Matter)Richard YentumiNo ratings yet
- 8 8th Science Term 1 Sura Guide 2019 2020 Sample Materials English MediumDocument61 pages8 8th Science Term 1 Sura Guide 2019 2020 Sample Materials English MediumChandrasegar SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Runge 4 Order Method: Major: All Engineering Majors Authors: Autar Kaw, Charlie BarkerDocument16 pagesRunge 4 Order Method: Major: All Engineering Majors Authors: Autar Kaw, Charlie BarkerjesantNMNo ratings yet
- Soild Waste AmangementDocument75 pagesSoild Waste Amangementhimanshu_agraNo ratings yet
- Masala KurumaDocument16 pagesMasala KurumaBhuvaneshwari Torali Chandrasekaran100% (1)
- Amirdham Thi JanakiraamanDocument92 pagesAmirdham Thi JanakiraamanSangeetha Ravi100% (1)
- Power Plant Engineering by R.K.rajput 940-Upto LastDocument72 pagesPower Plant Engineering by R.K.rajput 940-Upto Lastawdhesh121345621% (14)
- TNPSC Mental Ability and Aptitude Test Question and Answers 2013 PDFDocument23 pagesTNPSC Mental Ability and Aptitude Test Question and Answers 2013 PDFlakshmananNo ratings yet
- Fma3602 Asign1memoDocument15 pagesFma3602 Asign1memoKasturie Pillay100% (1)
- Multivariate Statistical MORRISON 3th PDFDocument85 pagesMultivariate Statistical MORRISON 3th PDFnpunkdayNo ratings yet
- Soup RasamDocument16 pagesSoup Rasampavinami100% (2)
- N26Document45 pagesN26sujathasubramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Problem Session CMPE553 29122010Document4 pagesProblem Session CMPE553 29122010Sundous Hussien100% (1)
- Malika Tiffin VagaigalDocument73 pagesMalika Tiffin VagaigalSumitha RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Books DetailsDocument21 pagesBooks Detailsnarmadhaarasi100% (1)
- KP Basu AlgebraDocument675 pagesKP Basu AlgebraPramurtta Shourjya Majumdar100% (2)
- AnbinthanmaiyaiarindhapinneDocument122 pagesAnbinthanmaiyaiarindhapinnesprachiNo ratings yet
- Problems 2 1st Law PDFDocument10 pagesProblems 2 1st Law PDFKrystel Monica Manalo0% (1)
- Pertemuan 7 ReviewDocument45 pagesPertemuan 7 ReviewAna Sholikhatus Sa'diyah100% (1)
- Taller Fisicoquimica TermoDocument6 pagesTaller Fisicoquimica TermoWilo JaraNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment 2 2014Document5 pagesThermodynamics Assignment 2 2014ravikr950% (1)
- Ideal Gas Equation and EntropyDocument27 pagesIdeal Gas Equation and EntropyJude Roswel GenerilloNo ratings yet
- Example 4Document41 pagesExample 4Akatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Thermo2 MidDocument4 pagesThermo2 MidnoelNo ratings yet
- GisselaBonilla ADocument13 pagesGisselaBonilla AGissela BTNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Thermodynamics (2024)Document4 pagesTutorial 1 - Thermodynamics (2024)kkhimatiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Exercises: o A. e emDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Exercises: o A. e emAnnisa Sylvia SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3Document22 pagesChapter 1-3Aiman LatifNo ratings yet
- BT Hoa Ly 1Document22 pagesBT Hoa Ly 1Minh ThưNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document4 pagesProblem Set 1ash jay100% (1)
- Ideal Gas and Application of Second LawDocument49 pagesIdeal Gas and Application of Second LawAbdulRehman VirkNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Document3 pagesCHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Vicente JonathanNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Heat and The First Law Example ProblemsDocument22 pagesLecture - 3 - Heat and The First Law Example ProblemsifiokNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Pure Substances: Than One Phase, But Each Phase Must Have The Same Chemical CompositionDocument18 pagesBehavior of Pure Substances: Than One Phase, But Each Phase Must Have The Same Chemical CompositionDharmesh PatelNo ratings yet
- TEMA 1 Actividad 1 PROBLEMARIO1de3Document1 pageTEMA 1 Actividad 1 PROBLEMARIO1de3Kari BustamanteNo ratings yet
- HW1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHW1 SolutionsRunner ScottNo ratings yet
- Tuttherm2 PDFDocument6 pagesTuttherm2 PDFPrabir BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 化熱chapt3Document5 pages化熱chapt3卓冠妤No ratings yet
- CHEN 623 Problems Old Examination Problems: 1.: (P + A /V) (V B) RTDocument34 pagesCHEN 623 Problems Old Examination Problems: 1.: (P + A /V) (V B) RTZohaib Ali0% (1)
- Solved - Problems in ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesSolved - Problems in ThermodynamicsAngelica Joyce Benito100% (6)
- Tuttherm 2Document6 pagesTuttherm 2Lin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- WenfengDocument22 pagesWenfengAudina Paramitha AzahraNo ratings yet
- BTE2222 Thermal Science Lab ExperimentsDocument31 pagesBTE2222 Thermal Science Lab ExperimentsFirdaus ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMS of Energy BallanceDocument35 pagesPROBLEMS of Energy BallanceDiah Wulan AyuningtiasNo ratings yet
- Entropy Problems AnswersDocument6 pagesEntropy Problems AnswersTots HolaresNo ratings yet
- Energetica ExaminationDocument11 pagesEnergetica ExaminationDwi NicHeNo ratings yet
- ME2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Nov-Dec 2012 Important Question V+ EditionDocument2 pagesME2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Nov-Dec 2012 Important Question V+ EditionPrasobh ShamohanNo ratings yet
- MEG 212 Practise QuestionsdocxDocument11 pagesMEG 212 Practise Questionsdocxoyetunde ridwanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 10 Key - Physical Chemistry For Engineers. (Book Work)Document8 pagesProblem Set 10 Key - Physical Chemistry For Engineers. (Book Work)krymxenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MED205Document4 pagesTutorial MED205Anonymous V4jDKjUR6No ratings yet
- Modificadores de ReollogiaDocument16 pagesModificadores de ReollogiaItzel A. GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Viscoptima™ LV: Innovation You Can Build On™Document1 pageViscoptima™ LV: Innovation You Can Build On™Itzel A. GuerreroNo ratings yet
- EjerciciosDocument2 pagesEjerciciosItzel A. GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document2 pagesHomework 2Itzel A. GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Tim1 KelasADocument5 pagesTim1 KelasARiatus SNo ratings yet
- HYSYS TutorialDocument30 pagesHYSYS TutorialEhsan AhzNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument38 pagesGaseshNo ratings yet
- 3.10 Air Compressor Piping Iso DrawingDocument1 page3.10 Air Compressor Piping Iso DrawingCuong Tran0% (1)
- Enabling Assessment Crystal Structure-2Document2 pagesEnabling Assessment Crystal Structure-2Bro KingNo ratings yet
- Gas Pipeline HydraulicsDocument64 pagesGas Pipeline HydraulicsDonald Oseghale OkohNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document4 pagesTutorial 3RagngeNo ratings yet
- 9th SessionDocument13 pages9th SessionAhmed GadNo ratings yet
- Storage Stability of Dry Food Systems Influence ofDocument22 pagesStorage Stability of Dry Food Systems Influence ofcleytonco2211No ratings yet
- PVT Analysis For OilDocument27 pagesPVT Analysis For Oilel hadi100% (1)
- Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChemical BondingChemistry ClassNo ratings yet
- Gas Diffusion in LiquidDocument5 pagesGas Diffusion in LiquidElaine PuiNo ratings yet
- Vle of Hcl-WaterDocument6 pagesVle of Hcl-WaterYaqoob Ali0% (1)
- Fundamentals of Aerodynamics With SolvingDocument180 pagesFundamentals of Aerodynamics With SolvingaerorenNo ratings yet
- Sizing Calculation Turbine Meter Project Perbaikan Dan Penggantian: Sistim Meter LPG Pert Amina Up-Ii DumaiDocument2 pagesSizing Calculation Turbine Meter Project Perbaikan Dan Penggantian: Sistim Meter LPG Pert Amina Up-Ii DumaiNurdeny PribadiNo ratings yet
- 환경유체역학 강의 1Document38 pages환경유체역학 강의 1HyunJoon, KimNo ratings yet
- Section 4 Principle of ESPDocument8 pagesSection 4 Principle of ESPkvsagarNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 PDFDocument15 pagesUnit 11 PDFS M Arshad Rashadi100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Thermal SensorsDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Thermal SensorsAzizIkramNo ratings yet
- XRD Slides. 04.01.2023Document102 pagesXRD Slides. 04.01.2023BhushanNo ratings yet
- FREEMIUM - 11th JEE - Hinglish - Valence Bond Theory - 53Document35 pagesFREEMIUM - 11th JEE - Hinglish - Valence Bond Theory - 53Rathana sabpathyNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bond Formation: General ChemistryDocument20 pagesIonic Bond Formation: General Chemistryyoona stewartNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document31 pagesModule 1Carms GameNo ratings yet
- 4.0 ChemicalbondingDocument219 pages4.0 ChemicalbondingTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- RF Sputtering Manual 2010Document23 pagesRF Sputtering Manual 2010sinytells0% (1)
- Report PPE Assignment 1Document14 pagesReport PPE Assignment 1Libbis SujessyNo ratings yet
- Hydrological CycleDocument17 pagesHydrological CycleSakshi TalmaleNo ratings yet
- 2D System - Nature Nanotech. - Gibertini PDFDocument12 pages2D System - Nature Nanotech. - Gibertini PDFSuchanda MondalNo ratings yet
- Diffusion 2Document30 pagesDiffusion 2Pinlac, Kurt Russel P.No ratings yet
- A Storage Tank Is Used To Store Ammonia at T 33 C and P + 350 MMWC, Atmospheric PressureDocument3 pagesA Storage Tank Is Used To Store Ammonia at T 33 C and P + 350 MMWC, Atmospheric PressureHasnah MalindaNo ratings yet