Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antibiotics
Uploaded by
Seshu KelamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antibiotics
Uploaded by
Seshu KelamCopyright:
Available Formats
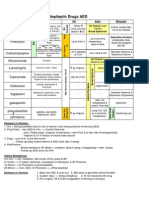
Generic name
Brand names
Common uses
[2]
Possible side [2] effects
Mechanism of action
Aminoglycosides Binding to the bacterial 30S ribos omal subunit (some work by binding to the 50S subunit), inhibiting the translocation of the peptidyl-tRNA from the A-site to the Psite and also causing misreading of mRNA, leaving the bacterium unable to synthesize proteins vital to its growth.
Amikacin Gentamicin Kanamycin Neomycin Netilmicin Tobramycin
Amikin Garamycin Kantrex Neo-Fradin
[3]
Netromycin Nebcin
Paromomycin
Humatin
Infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Klebsiellaparticul arly Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Effective against Aerobic bacteria (not obligate/facultative anaerobes) and tularemia.
Hearing loss Vertigo Kidney damage
Spectinomycin
Trobicin
Gonorrhea Ansamycins
Geldanamycin Herbimycin
Experimental, as antitumor antibiotics Traveler's diarrhea caused by E. coli
Rifaximin
Xifaxan
Streptomycin Carbacephem prevents bacterial cell division by inhibiting cell wall synthesis.
Loracarbef
Lorabid
Discontinued
Carbapenems Ertapenem Invanz Bactericidal for both Gastrointe Inhibition of cell
Doripenem
Doribax
Imipenem/Cilastati Primaxin n
Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms and therefore useful for empiric broadspectrum antibacterial coverage. (Note MRSA resistance to this class.)
stinal upset wall synthesis and diarrhea Nausea Seizures Headache Rash and allergic reactions
Meropenem
Merrem
Cephalosporins (First generation) Cefadroxil Cefazolin Duricef Ancef Gastrointe stinal upset and Same mode of action as Nausea (if other beta-lactam antibiotics: disrupt alcohol the synthesis of taken the peptidoglycan l concurrentl ayer of bacterial cell walls. y) diarrhea Good coverage against Gram-positive infections. Cefalexin Keflex Allergic reactions Cephalosporins (Second generation) Cefaclor Cefamandole Distaclor Mandol(discontin ued) Mefoxin(disconti nued) Cefzil Less Gram-positive cover, improved Gramnegative cover. Gastrointe stinal upset and Same mode of diarrhea action as Nausea (if other beta-lactam antibiotics: disrupt alcohol the synthesis of taken the peptidoglycan l concurrentl ayer of bacterial cell walls. y) Allergic reactions Cephalosporins (Third generation) Cefixime Cefdinir Suprax Improved coverage of Omnicef, Cefdiel Gram-negative Gastrointe Same mode of action as
Cefalotin or Cefalo Keflin(discontinu thin ed)
Cefoxitin Cefprozil
Cefuroxime
Ceftin, Zinnat(U K)
Cefditoren Cefoperazone Cefotaxime Cefpodoxime
Spectracef
organisms, except Pseudomonas. Cefobid(disconti Reduced Gram-positive nued) cover. Claforan Vantin
stinal upset other beta-lactam antibiotics: disrupt and the synthesis of diarrhea the peptidoglycan l Nausea (if ayer of bacterial cell walls. alcohol taken concurrentl y)
Ceftazidime[Unlike most thirdgeneration agents, Ceftazidime is Fortaz active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa] Ceftibuten Ceftizoxime Ceftriaxone Cedax Cefizox (discontinued) Rocephin
Allergic reactions
Cephalosporins (Fourth generation) Gastrointe stinal upset and Same mode of action as Nausea (if other beta-lactam antibiotics: disrupt alcohol the synthesis of taken the peptidoglycan l concurrentl ayer of bacterial cell walls. y) diarrhea Covers pseudomonal infections. Allergic reactions Cephalosporins (Fifth generation) Same mode of action as stinal upset other beta-lactam and antibiotics: disrupt the synthesis of diarrhea the peptidoglycan l Allergic ayer of reaction bacterial cell walls. Gastrointe Same mode of action as stinal upset other beta-lactam Gastrointe
Cefepime
Maxipime
Ceftaroline fosamil Teflaro
Used to treat MRSA
Ceftobiprole
Zeftera
Used to treat MRSA
and diarrhea Nausea (if alcohol taken concurrentl y) Allergic reactions Glycopeptides Teicoplanin Vancomycin Targocid (UK) Vancocin Active against aerobic and anaerobic Grampositive bacteria including MRSA; Vancomycin is used orally for the treatment of C. difficile Lincosamides Clindamycin Cleocin Serious staph-, pneumo-, and streptococcal infections in penicillinallergic patients, also anaerobic infections; clindamycin topically foracne Lipopeptide
antibiotics: disrupt the synthesis of the peptidoglycan l ayer of bacterial cell walls.
inhibiting peptidogl ycan synthesis
Telavancin
Vibativ
Lincomycin
Lincocin
Possible C. difficilerelatedpseudo membranous enterocolitis
Bind to 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomal RNA the reby inhibiting protein synthesis
Daptomycin
Cubicin
Gram-positive organisms
Bind to the membrane and cause rapid depolarization, resulting in a loss of membrane potential leading to inhibition of protein, DNA and RNA synthesis
Macrolides Azithromycin Clarithromycin Dirithromycin Zithromax,Suma Streptococcal med,Xithrone infections, syphilis, upper Biaxin respiratory tract infections, lower Dynabac(discont Nausea, vomiting, and inhibition of bacterial protein biosynthesis by binding reversibly
inued) Erythromycin Roxithromycin Erythocin,Erythr oped
respiratory tract infections, mycoplasmal infections, Lyme disease
to the subunit 50S of the (especially bacterial ribosome, at higher thereby inhibiting doses) translocation of Prolonged peptidyl tRNA. diarrhea cardiacQT interval(es
Troleandomycin
Tao (discontinued)
pecially erythromyc in) Jaundice
Telithromycin
Ketek
Pneumonia
Visual Disturbance, [4] Liver Toxicity.
Spiramycin
Rovamycine
Mouth infections Monobactams Same mode of action as other beta-lactam antibiotics: disrupt the synthesis of the peptidoglycan l ayer of bacterial cell walls. Nitrofurans Bacterial or protozoal diarrhea or e nteritis
Aztreonam
Azactam
Furazolidone
Furoxone
Nitrofurantoin
Macrodantin,Ma Urinary tract infections crobid Oxazolidonones Thrombocy topenia Peripheral neuropathy Protein synthesis inhibitor; prevents the initiation step
Linezolid
Zyvox
VRSA
Posizolid
Phase II clinical trials Phase II clinical trials
Radezolid
Torezolid
Phase II clinical trials Penicillins
Amoxicillin Ampicillin Azlocillin Carbenicillin
Novamox,Amoxil Principen (discontinued)
Geocillin (discontinued) Tegopen (discontinued) Dynapen (discontinued) Floxapen(Sold to European generics Actavis Group) Mezlin (discontinued) Staphcillin (discontinued) Unipen (discontinued) Prostaphlin (discontinued) Pentids (discontinued) Veetids (PenVee-K) (discontinued) Pipracil (discontinued) Pfizerpen Negaban (UK) (discontinued) Ticar (discontinued) Penicillin combinations Wide range of infections; penicillin used forstreptococcal infections, syphilis, and Lyme disease Gastrointe stinal upset and diarrhea Allergy Same mode of action as other beta-lactam with antibiotics: disrupt seriousana the synthesis of phylactic the peptidoglycan l ayer of reactions bacterial cell walls. Brain and kidney damage (rare)
Cloxacillin
Dicloxacillin
Flucloxacillin
Mezlocillin
Methicillin
Nafcillin
Oxacillin
Penicillin G
Penicillin V
Piperacillin Penicillin G Temocillin
Ticarcillin
Amoxicillin/clavula Augmentin nate
The second component
Ampicillin/sulbacta Unasyn m Piperacillin/tazoba Zosyn ctam Ticarcillin/clavulan Timentin ate Polypeptides
prevents bacterial resistanc e to the first component
Bacitracin
Inhibits isoprenyl pyrophosphate, a molecule that carries the building blocks of the peptidoglycan bacterial cell wall outside of the [5] inner membrane Coly-Mycin-S Eye, ear or bladder infections; usually applied directly to the eye or inhaled into the lungs; rarely given by injection, although the use of intravenous colistin is experiencing a resurgence due to the emergence of multi drug resistant organisms. Interact with the Gramnegative bacterial outer Kidney and membrane andcyto nerve damage plasmic (when given by membrane. It injection) displaces bacterial counter ions, which destabilizes the outer membrane. They act like a detergent against the cytoplasmic membrane, which alters its permeability. Polymyxin B and E are bactericidal even in an isosmotic solution.
Colistin
Polymyxin B
Quinolones/Fluoroquinolone Ciprofloxacin Enoxacin Gatifloxacin Gemifloxacin Cipro,Ciproxin, Ciprobay Penetrex Tequin Factive
[6]
Urinary tract infections, bacterial prostatitis, communityacquired pneumonia, bac terial diarrhea, mycoplasmal
Nausea (rare), irreversible damage tocentral nervous system (uncom
inhibit the bacterial DNA gyrase or the topoisomerase IV enzyme, thereby
Levofloxacin Lomefloxacin Moxifloxacin Nalidixic acid Norfloxacin Ofloxacin Trovafloxacin Grepafloxacin Sparfloxacin Temafloxacin
Levaquin Maxaquin Avelox NegGram Noroxin Floxin, Ocuflox Trovan Raxar Zagam Omniflox
infections, gonorrhea
mon), tendinosis (rare)
inhibiting DNA repli cation and transcription.
Withdrawn Withdrawn Withdrawn Withdrawn Sulfonamides
Mafenide Sulfacetamide Sulfadiazine
Sulfamylon Sulamyd, Bleph10 Micro-Sulfon
Silver sulfadiazine Silvadene Sulfadimethoxine Sulfamethizole Di-Methox, Albon Thiosulfil Forte Urinary tract infections (except sulfacetamide, used for eye infections, and mafenide and silver sulfadiazine, used topically for burns)
Sulfamethoxazole Gantanol Sulfanilimide (arch aic) Sulfasalazine Sulfisoxazole Azulfidine Gantrisin
TrimethoprimSulfamethoxazole( Bactrim, Septra Co-trimoxazole) (TMP-SMX)
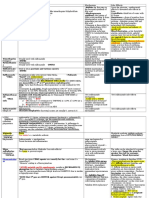
Folate synthesis inhibition Nausea, . They are competitive vomiting, inhibitors of the and enzymedihydropter diarrhea oate synthetase, Allergy (inc DHPS. DHPS luding skin catalyses the conversion of rashes) PABA (paraCrystals in aminobenzoate) to dihydropteroate, urine a key step Kidney in folatesynthesis. failure Folate is Decrease necessary for the cell to in white synthesize nucleic blood acids(nucleic acids cell count are essential Sensitivity building blocks to sunlight of DNA and RNA), and in its absence cells cannot divide.
Sulfonamidochrys Prontosil oidine(archaic) Tetracyclines Demeclocycline Doxycycline Declomycin Vibramycin Syphilis, chlamydial infec tions, Lyme Gastrointe inhibiting the binding
Minocycline Oxytetracycline
Minocin Terramycin
disease,mycoplasmal infections, acne rickettsialinfections, *malaria *Note: Malaria is caused by a protist and not a bacterium.
stinal upset of aminoacyltRNA to Sensitivity the mRNAto sunlight ribosomecomplex. They do so mainly Potential by binding to toxicity to the 30S ribosomal mother and subunit in fetus the mRNA translation comple during x. pregnancy Enamel hypoplasia (staining of teeth; potentially permanent )
Tetracycline Sumycin,Achrom ycin V, Steclin
transient depression of bone growth
Drugs against mycobacteria Clofazimine Dapsone Capreomycin Cycloserine Ethambutol Ethionamide Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Lamprene Avlosulfon Capastat Seromycin Myambutol Trecator I.N.H. Aldinamide Antileprotic Antileprotic Antituberculosis Antituberculosis, urinary tract infections Antituberculosis Antituberculosis Antituberculosis Antituberculosis Binds to the mostly GramReddishsubunit of RNA positive and mycobacteri orange sweat, polymerase to a tears, and urine inhibit transcription Mycobacterium avium complex rash, discolored urine, GI Inhibits peptide synthesis
Rifampicin (Rifam Rifadin, pin in US) Rimactane
Rifabutin
Mycobutin
symptoms Rifapentine Priftin Antituberculosis As Neurotoxicity,ot other aminoglycosi otoxicity des
Streptomycin
Antituberculosis
Others Arsphenamine Salvarsan Spirochaetal infections (obsolete) meningitis, MRSA, topical use, or for low cost internal treatment. Rarely: aplastic Historic: typhus, cholera. anemia. Gram-negative, Grampositive, anaerobes Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of the ribosome Inactivates enolpyr uvyl transferase, thereby blocking cell wall synthesis
Chloramphenicol
Chloromycetin
Fosfomycin
Monurol
Acute cystitis in women
Fusidic acid
Fucidin Produces toxic free radicals that disrupt DNA and Discolored proteins. This nonurine,headache specific , metallic mechanism is taste, nausea; responsible for its alcoholis activity against a contraindicated variety of bacteria, amoebae, and protozoa. Inhibits isoleucine t-RNA synthetase (IleRS) causing inhibition of protein synthesis
Metronidazole
Flagyl
Infections caused by anaerobic bacteria; alsoamoebiasis, trichom oniasis, Giardiasis
Mupirocin
Bactroban
Ointment for impetigo, cr eam for infected cuts
Platensimycin Quinupristin/Dalfo Synercid pristin Gram-negative, GramRash. Lacks positive, anaerobes. known anemic widely used in veterinary side-effects. medicine. A chloramphenicol analog. May inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by
Thiamphenicol
binding to the 50S subunit of the ribosome Indicated for complicated skin/skin structure infections and Tigecycline Tigacyl complicated intraabdominal infections. || Teeth discoloration. || Tindamax Fasigyn Proloprim, Trimpex upset stomach, bitter taste, and itchiness
Tinidazole
protozoan infections
Trimethoprim
Urinary Tract Infections
You might also like
- AntibioticsDocument6 pagesAntibioticsCyrus100% (1)
- List of antibiotics: generic names, brands, classes and usesDocument9 pagesList of antibiotics: generic names, brands, classes and usesprince1500100% (1)
- First Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsDocument23 pagesFirst Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsLaura Lopez RocaNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy NDocument28 pagesChemotherapy NFaisal MehboobNo ratings yet
- Quinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist and Urinary Tract Antitb and LeprosyDocument124 pagesQuinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist and Urinary Tract Antitb and LeprosyrenNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument6 pagesAntibioticsOccamsRazor100% (1)
- Antibiotics 9Document11 pagesAntibiotics 9Beth Morales100% (1)
- Antibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Document40 pagesAntibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Moses MberwaNo ratings yet
- Common infections and recommended antibioticsDocument3 pagesCommon infections and recommended antibioticsNicole BerryNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Summary - DraftDocument10 pagesAntibiotic Summary - DraftStrept Pneumonia100% (1)
- Respiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsDocument4 pagesRespiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsNurse HoomanNo ratings yet
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 pagesNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNo ratings yet
- Mu 002Document10 pagesMu 002chandanNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDocument16 pagesThe Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDianne Chua100% (7)
- Antibiotics Quick ReviewDocument5 pagesAntibiotics Quick Reviewpranjl100% (5)
- Treatment guidelines for common infectionsDocument1 pageTreatment guidelines for common infectionsJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Pharmacology Indications, Mechanism, and Side Effects! PDFDocument1 pageVancomycin Pharmacology Indications, Mechanism, and Side Effects! PDFFrancis PasayNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic GuideDocument6 pagesAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- Chart Antibacterial Drugs PDFDocument1 pageChart Antibacterial Drugs PDFMunaf AlsumaryNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug InteractionsDocument3 pagesDrug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug Interactionsazhar hussinNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Drug ListDocument8 pagesYear 2 Drug ListRay100% (1)
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 pageAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88No ratings yet
- Antibiotics Made EasyDocument116 pagesAntibiotics Made EasyShalini Soorya100% (2)
- SuperDrugs! Simon's Short Drug SummaryDocument5 pagesSuperDrugs! Simon's Short Drug Summarybriancripe100% (2)
- Warfarin Sodium: INR Levels 4.0 or Less Ok To Carry Out Procedure Test Atleast 72 Hrs Prior To ProcedureDocument6 pagesWarfarin Sodium: INR Levels 4.0 or Less Ok To Carry Out Procedure Test Atleast 72 Hrs Prior To ProcedureVimi GeorgeNo ratings yet
- SAR of Macrolides, Penicillins, and Other AntibioticsDocument36 pagesSAR of Macrolides, Penicillins, and Other AntibioticsBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases IDocument7 pagesInfectious Diseases ITiff VoNo ratings yet
- Micro I ReviewDocument15 pagesMicro I ReviewEmilee Tu100% (1)
- Pharmacology Complete Drug TableDocument6 pagesPharmacology Complete Drug Tableninja-2001100% (4)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summaryshenric16No ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibioticsPGI Custodio, Ed KristianNo ratings yet
- Pharm Drug ListDocument17 pagesPharm Drug Listanon_523534678No ratings yet
- AB ClassesDocument4 pagesAB Classesrayooona88100% (2)
- Lang 10 EditionDocument235 pagesLang 10 Editionraju niraulaNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument6 pagesAntiviral DrugsLori MoscaliucNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ChartDocument10 pagesAntibiotics Chartadom09No ratings yet
- Brand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX ReviewDocument72 pagesBrand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX Reviewbapimirab654No ratings yet
- Different Body Receptors PDFDocument1 pageDifferent Body Receptors PDFSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- Classification of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesClassification of AntibioticsdenaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibiotics, The Basics: Classification of Veterinary Antibioticsgalihja100% (1)
- Antiprotozoal Drugs Classification and Mechanism of ActionDocument21 pagesAntiprotozoal Drugs Classification and Mechanism of ActionCurex QANo ratings yet
- INFORMATION ON Group of ANTIBIOTICSDocument8 pagesINFORMATION ON Group of ANTIBIOTICStarun paulNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs TableDocument19 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs TableLaylee ClareNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics - Pathogen ChartDocument3 pagesAntibiotics - Pathogen ChartYanling LiNo ratings yet
- AntimicrobialsDocument1 pageAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Antibiotics Chart 2Document10 pagesAntibiotics Chart 2Vee MendNo ratings yet
- APHA-Chapter-34 - Patient Assessment Laboratory: REVIEW OF SYSTEMS - Physical Assessment, Vital Signs& ObservationsDocument13 pagesAPHA-Chapter-34 - Patient Assessment Laboratory: REVIEW OF SYSTEMS - Physical Assessment, Vital Signs& ObservationsDrSamia El WakilNo ratings yet
- Introduction to commonly used antibioticsDocument2 pagesIntroduction to commonly used antibioticsAmir AmirulNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Chart: National Immunization Schedule For New BornDocument20 pagesVaccination Chart: National Immunization Schedule For New BornsmilealwplzNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsDocument5 pagesAnxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsJohn HolmesNo ratings yet
- Artesunat Injection 2009Document4 pagesArtesunat Injection 2009Franca ImadiyiNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For Antibiotics-2Document10 pagesMnemonics For Antibiotics-2totallyfakeusernameNo ratings yet
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 pageBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testNo ratings yet
- Drug TerminologyDocument5 pagesDrug Terminologyimdaking123No ratings yet
- Anti-Infective Drugs for Bacteria, Viruses and ParasitesDocument28 pagesAnti-Infective Drugs for Bacteria, Viruses and ParasitesMay EvelynNo ratings yet
- Essential Antibiotic Guide for Medical StudentsDocument74 pagesEssential Antibiotic Guide for Medical StudentskaelenNo ratings yet
- List of AntibioticsDocument9 pagesList of Antibioticsdesi_mNo ratings yet
- List of antibiotics by classDocument11 pagesList of antibiotics by classBhanuprakash PuthalapattuNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of ActionDocument13 pagesGeneric Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of Actionangel3424No ratings yet
- IRCTC e-ticket detailsDocument2 pagesIRCTC e-ticket detailsSeshu KelamNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument11 pagesAntibioticsSeshu Kelam100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Image ProcessingDocument72 pagesFundamentals of Image Processingkirthi83No ratings yet
- Developers Best Practices TutorialDocument34 pagesDevelopers Best Practices TutorialVishesh Karunaada SavihrudayaNo ratings yet
- 3D Graphical User InterfacesDocument50 pages3D Graphical User InterfacesSeshu KelamNo ratings yet
- Beta LactamDocument18 pagesBeta LactamCesar Saba0% (1)
- Pharmacology and Toxicology-1Document40 pagesPharmacology and Toxicology-1DR.MAHESHNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument30 pagesChemotherapeutic AgentsAliImadAlKhasaki100% (1)
- Amoxicillin + Clavulanic AcidDocument37 pagesAmoxicillin + Clavulanic Acidsanish tiwariNo ratings yet
- Overview of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesOverview of AntibioticsakshahinbdNo ratings yet
- MICROBIAL GROWTH AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIONDocument43 pagesMICROBIAL GROWTH AND ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIONMichal VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Mechanisms Actions EffectsDocument91 pagesAntibiotics Mechanisms Actions EffectsDareRaymond100% (1)
- Cefuroxime: Drug Information: Special AlertsDocument18 pagesCefuroxime: Drug Information: Special Alertsminhmap90_635122804No ratings yet
- Pharma AIIMSDocument13 pagesPharma AIIMSvkNo ratings yet
- Paparella: Volume I: Basic Sciences and Related Disciplines Section 6: Pharmacology Chapter 28: Antibiotics Leonard P. RybakDocument16 pagesPaparella: Volume I: Basic Sciences and Related Disciplines Section 6: Pharmacology Chapter 28: Antibiotics Leonard P. RybakDiana Mihaela BadescuNo ratings yet
- Antibacterials CMDocument72 pagesAntibacterials CMMike AnnisNo ratings yet
- Units Essential For Maintaining Cell Integrity Prevention ofDocument2 pagesUnits Essential For Maintaining Cell Integrity Prevention ofJayde TabanaoNo ratings yet
- PenicillinDocument75 pagesPenicillinJean CabigaoNo ratings yet
- The Antibiotics: Understanding Their Mechanisms and Appropriate UseDocument56 pagesThe Antibiotics: Understanding Their Mechanisms and Appropriate UseCabdi IshakNo ratings yet
- FDA Guidance Non Penicillin Beta Lactam Risk AssessmentDocument9 pagesFDA Guidance Non Penicillin Beta Lactam Risk Assessmentbvsc77035No ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology Week 3. ABCDDocument21 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology Week 3. ABCDohsehuns wifeuNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeDocument35 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeTiffany Jane Huertas100% (1)
- Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument94 pagesBeta Lactam AntibioticsHely PatelNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Community Pharmacy Training Summer 2018/2019Document23 pagesAntibiotics: Community Pharmacy Training Summer 2018/2019Anfal MNo ratings yet
- Cephalosporins Pharmacology and ChemistryDocument5 pagesCephalosporins Pharmacology and ChemistryIrfan QaisarNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Classification and MechanismsDocument20 pagesAntibiotics Classification and MechanismsSalmanNo ratings yet
- AntimicrobialDocument211 pagesAntimicrobialSanaz Niksefat100% (1)
- Drug Study ICUDocument14 pagesDrug Study ICUAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNo ratings yet
- Beta Lactam Antibiotics Structure, Classification and MechanismDocument15 pagesBeta Lactam Antibiotics Structure, Classification and MechanismNiharika ModiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 2Document53 pagesMicrobiology 2pikachuNo ratings yet
- How Does Penicillin WorkDocument6 pagesHow Does Penicillin WorkJanista FrankNo ratings yet
- Cephalosporins: Generic Names, Brand Names & IndicationsDocument84 pagesCephalosporins: Generic Names, Brand Names & IndicationsCatherine RiaNo ratings yet
- SAR of Macrolides, Penicillins, and Other AntibioticsDocument36 pagesSAR of Macrolides, Penicillins, and Other AntibioticsBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraNo ratings yet
- 2013 - Recent Advances in The Biosynthesis of Penicillins, Cephalosporins and Clavams and Its RegulationDocument25 pages2013 - Recent Advances in The Biosynthesis of Penicillins, Cephalosporins and Clavams and Its RegulationMarie GalvãoNo ratings yet