Professional Documents
Culture Documents
09-1 Teleprotection Fundamentals
Uploaded by
dmugalloyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
09-1 Teleprotection Fundamentals
Uploaded by
dmugalloyCopyright:
Available Formats
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
The subjects of these basics are: -The different protection schemes used in Power Systems -The parameters used in Teleprotection Systems
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
Teleprotection is: A discipline between protection and telecommunication. Sometimes under responsibility of the protection organization, sometimes under the responsibility of the communication organization. Sometimes a barrier between the communication engineer and the protection engineer (on customers and on suppliers site !) Teleprotection is used: Mainly at production and transport level where the distances of the transmitted power and short-circuit currents are much larger than at the distribution level. The requirements for network stability are also much more in the transport power systems. At low and medium voltage levels (distribution level) distance protection is usually used without Teleprotection. Arguments for Teleprotection: Minimization of material damage and reduction in time and extent in case of failures Keeping up the supply and distribution of electric power as long and as well as possible under all circumstances
At the production and transport level, clearance of line faults must be absolutely selective and faults must be cleared within the shortest possible time, so called zone 1 time of the Protection Device.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
A Protection System in a Power Network includes the following elements: The Circuit Breaker to isolate the faulty part The Protection Device to detect the fault via Current- and Voltage Transformer and to give the order to trip the Circuit Breaker The Telecommunication and the Teleprotection equipment to transfer the trip to the other end of the Power Line A Teleprotection equipment is: The interface between Protection Device and telecommunication system A converter of the signal from the Protection Device into a signal suitable to transmit over a telecommunication link
For analog channels FSK modulation is used, for digital channels CODING of different models is applied. The Teleprotection Unit is also multiplexing several command signals into one telecom channel.
A Telecommunication System is: A PLC, an optical Multiplexer, a Microwave or a direct link using a copper wire or an optical fiber
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
On this slide the two different signal families used in Teleprotection are listed: Continuous signals are: Longitudinal current differential Phase comparison
Command type signals on/off are: permissive tripping direct intertripping blocking directional comparison
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
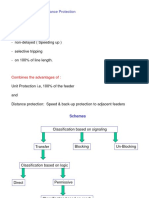
Here you see different protection schemes which are using telecommunication COMMUNICATION IS ESSENTIAL in the following Protection schemes using quantitative signal information: Phase comparison Longitudinal current differential These applications are absolutely selective
COMMUNICATION IS ESSENTIAL in the following Protection schemes using ON/0FF information: Permissive overreach distance Blocking Distance These applications are relatively selective
COMMUNICATION IS SUPPLEMENTARY in the following Protection schemes using ON/0FF information: Permissive underreach distance Accelerated distance
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
The distance line Protection Devices use different zones to detect line faults. The stepped time and distance characteristic of the line protection system provides main protection of the line section in Zone 1 as well as back-up protection of the adjacent Busbars in Zone 2. At the production and transport level, clearance of line faults must be absolutely selective and faults must be cleared within the shortest possible time ,so called ZONE 1 TIME. For example with the underreaching mode, without command transmission, the distance protection cannot clear all faults in the protected line section within the zone 1 time. Faults near the ends of the line section will be cleared at zone 2 time, with additional delay. This is often acceptable at the distribution level, where fast reclosure is not required. Fast coordinated tripping at the ends of the protected line section reduces the effect of short circuit current on network stability as well as the stressing of the plant and finally permits fast auto reclosure. Absolutely selectivity and fast fault clearance for any fault position on the protected line section requires Teleprotection between the ends of the line. Consequently, the reliability of the line protection depends largely on the reliability of the communication link. Protective communication links are often duplicated on important lines to improve the reliability of tripping on internal faults.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
PUTT mode is used in Line Protection were the protected section is more than about 20 km long. . In PUTT mode the zone 1 of the Protection Device is set to underreaching for example 85 percent of the line section without delay. Zone 2 is set for example to 120 percent of the line section and is time delayed of for example 200 milliseconds The sequence of events for this example is:
A
fault occurs at point F in zone 1 of Protection Device RBC, zone 1 has no time delay. line is switched off without any delay by the Circuit Breaker in station B. equipment.
The At
the same time an permissive tripping command is sent to station C by means of the Teleprotection
The
Protection Device RCB in station C has already detected a fault in Zone 2 which is time delayed for example of 200 milliseconds
Additional
after a transmission time delay of typical 10 milliseconds the tripping command is received by Protection Device RCB in station C and the zone 2 time is accelerated to zone 1 time.
The
Circuit Breaker in station C is tripping the power line without any additional delay
In case the fault happens in the common part Zone 1 of both Relay protection, the relays trip the breakers without waiting for the command of the Teleprotection. Advantage: Faster than POTT und Blocking mode Disadvantage: Not selective for short lines Without Teleprotection the breaker in station C would be activated only in the zone 2 time after for example 200 millisecond and therefore auto reclosure of the power line is not assured. As the zone 2 is overreaching the section of the protected line, the selectivity would be not accurate without the communication.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
POTT mode is used in Line Protection were the protected section is less than about 20 km long or on Power Lines where PUTT mode can not be set. In POTT mode the zone 1 of the Protection Device is set to overreaching for example 130 percent of the line section. It has a AND logic therefore both Protection Device must detect the fault in the first zone and must receive the trip from the opposite Teleprotection equipment. Only in this case tripping in first zone time is possible. The sequence of events of the example is: A fault F1 is detected by Distance Relays RBC and RCB. The trips are send to both ends of the line section via Teleprotection equipment. The Relays in station B and station C receiving the tripping command. As they are already started by the fault detection the AND logic is fulfilled and circuit breakers in station B and C trip in zone 1 time. A fault F2 is only detected by distance Relay RCB. Distance relay RBC is not sending a tripping signal to the Station C therefore relay RCB will not trip the Breaker C in zone 1 time.
Advantage: POTT mode has a high selectivity and prevents tripping of a healthy line section in zone 1 time. Disadvantage: It is slower than the PUTT mode because of any fault within the protected section will have the time delay of the Teleprotection equipment. Without telecommunication no tripping in zone 1 is possible.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
The Blocking mode for Line Protection may work for any length of the protected line section. The Zone 1 time is delayed of for example 10 millisecond and is adjusted overreaching for example 130% of the protected line section. Reverse zone towards the Busbars is set for example to -40 percent. The sequence of events of the example is: The fault F1 is detected by Distance Relays RBC and RCB in there Zone 1. After countdown of the delay time both Protection Devices in Station B and C will trip the breakers. The fault F2 is detected by Distance Relay RBC in Zone 1, the delay counter starts counting down. The Protection Device RCB is detecting a fault in the reverse Zone and sends through Teleprotection link a blocking signal DO NOT TRIP to the Protection Device RBC. If this happens within the delay time of Zone 1, the relay will not trip the Breaker. Blocking mode was developed for PLC which is using the Power line to communicate. Advantage: Blocking command is only transferred if the line fault is out of the PLC section and the line for communication is clean. Disadvantage: The first zone is always time delayed for example of 10 milliseconds; if Teleprotection fails zone 1 is not selective any more In new projects the Blocking mode is not used
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
10
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
Breaker Failure Protection is needed to assure the function of the protection system in case of a Line Breaker failure . The local Protection Devices for Busbars, Earth fault and Distance Protection are connected to the Line Breaker. In case of a faulty Breaker the Substation can not be isolated from the power network. The sequence of events of the example is: The Breaker control system blocks the opening of the Breaker B if the SF6 gas pressure is low. Trips from the local Protection system are diverted by the breaker control to the Teleprotection equipment. Through the communication channel L the tripping command is transferred to the station C where the Line Breaker opens and isolates the power flow to station B.
Remark: To assure high security and dependability the processing time in the direct tripping feature is longer. Therefore the total transmission time of the Teleprotection system is more than in the Distance Protection for Permissive and Blocking mode.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
11
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
This a example for direct transfer tripping where the transformer is connected to the system without a Circuit Breaker: Line faults from station A up to connection of transformer at station B are protected by distance relay at station A in overreaching mode. Faults in station B within and beyond the transformer detected by a Buchholtz or a Busbar Protection Device are transferred to the circuit breaker at A by means of the Teleprotection direct tripping signal.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
12
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
Configurable settings in the Teleprotection equipment are the followings: Security is the ability of a equipment to prevent interference and noise from producing unwanted commands Dependability is the ability of a equipment to issue and receive wanted commands in the presence of interference and noise Transmission time is the time elapsed between the instant of change of state at the transmitter input and the instant of the corresponding change of state at the receiver output. Bandwidth is the total frequency range or bit rate utilized by the Teleprotection equipment. In Permissive and Blocking schemes the processing time has to be short and therefore the overall transmission time is also shorter. In the Direct tripping applications the Security and Dependability must be high, therefore the processing and transmission time will be longer.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
13
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
All these impairments may cause unwanted or missing commands In case of interference and noise, more processing time will be needed: feature adaptive transmission time will act in the Teleprotection equipment -The
In case of excessive interference and noise, processing time would be too long and commands not save. To prevent incidents the Teleprotection unit can take different actions: -Puts in operation the feature Unblocking -Activates Contact Freezing for continuous commands -Extends the zone 1 of distance Protection Device in PUTT mode from underreaching to overreaching with the help of the alarm contacts of the Teleprotection equipment Blocks the command outputs of the Teleprotection equipment
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
14
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
On this diagram the available transmission parameters of Teleprotection equipment are shown: The transmission time is the delay between the moment a command initiated on the input of Teleprotection equipment until this command is received at the output of the Teleprotection equipment on the other end of the protection system The Tx Input delay is used in direct tripping mode to make the system more save against EMC interference. With this parameter the command is sent delayed by the Teleprotection equipment at the input side. The Tx and Rx trip duration time can be limited in Permissive tripping applications. With this parameter, the duration of the command coming from the Protection Device can be increased, decreased or fixed by the Teleprotection command. The Rx trip prolongation time is the delay from the moment the transmission of a command from the input of the transmitting Teleprotection equipment stops until the receiver contacts of the receiving Teleprotection equipment are deactivated
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
15
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
This example is valid for permissive tripping scheme and a Power Frequency of 50 Hertz The total fault clearance time is the sum of the Protection Device processing time, the Transmission Time of the Teleprotection equipment and the switching time from the Circuit Breaker.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
16
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
If the Teleprotection equipment is connected to a digital network the addressing facility has to be used. In the worst case mixed up cross connections without using addressing could cause tripping of a wrong Circuit Breaker and a wrong Power Line! In the example in place B, if by mistake of the administrator or the failure of the multiplexer the command of one of the protection devices goes over a wrong communication line, the remote breaker will not trip because of the addressing facility.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
17
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
This summary shows you the Teleprotection products from the ABB portfolio
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
18
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
In this slide you see the layout of a protection system for an important transmission line. On this type of critical line, most of the protection equipment are doubled. We speak about Main 1 System and Main 2 System.
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
19
Course CHP592 - FOX515
2012-09-17
Questions
Sec 09-1 Teleprotectin Fundamentals
20
You might also like
- A ARTE DA ELETRONICA 3oEDICAO (1) (0001-0050)Document50 pagesA ARTE DA ELETRONICA 3oEDICAO (1) (0001-0050)Baba George71% (7)
- DAC 501 Financial Accounting IDocument11 pagesDAC 501 Financial Accounting IdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Line Protection: Reasons For FaultsDocument13 pagesDifferent Types of Line Protection: Reasons For FaultskarlTronxoNo ratings yet
- 4-Distance ProtectionDocument124 pages4-Distance ProtectionmubarakkirkoNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination of Overcurrent Relay For Chemical Industrial Plant Using ETAPDocument5 pagesCo-Ordination of Overcurrent Relay For Chemical Industrial Plant Using ETAPHimdad Tahir0% (1)
- REB500 Coupler ConfigurationsDocument5 pagesREB500 Coupler ConfigurationsRetratosDeMiVidaNo ratings yet
- Busbar Blocking MicomP140Document44 pagesBusbar Blocking MicomP1401453h100% (1)
- Basic Protection and Relaying SchemesDocument58 pagesBasic Protection and Relaying SchemesputrasejahtraNo ratings yet
- 2014 Line Distance Protection Fundamentals - PriceDocument83 pages2014 Line Distance Protection Fundamentals - PriceRolando Henry Flores CamavilcaNo ratings yet
- Areva KBCH Transformer Diff RelayDocument451 pagesAreva KBCH Transformer Diff RelaybirjueNo ratings yet
- Directional Protection - Course Sample - 589890-591528Document47 pagesDirectional Protection - Course Sample - 589890-591528medanite ashebirNo ratings yet
- FC 81F C 1Document109 pagesFC 81F C 1Stephanie Rasmussen100% (1)
- Overcurrent ProtectionDocument61 pagesOvercurrent ProtectionHuzaifa WasimNo ratings yet
- Bidding Document - Cold Storage For Meat and Associated Facilities Final-1Document184 pagesBidding Document - Cold Storage For Meat and Associated Facilities Final-1dmugalloy100% (1)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationFrom EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- IEC61850-8-1 GOOSE - Basic ENaDocument19 pagesIEC61850-8-1 GOOSE - Basic ENayasadik9No ratings yet
- Technical Offer For 11kv Sm6 SwitchgearDocument6 pagesTechnical Offer For 11kv Sm6 SwitchgeardmugalloyNo ratings yet
- SEL Relays New York Application GuideDocument32 pagesSEL Relays New York Application Guidepistola2No ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SeminarLecture6 ModelingDocument49 pagesSeminarLecture6 ModelingMarco TrovóNo ratings yet
- 2015 Line Distance Protection Fundamentals - Kockott PDFDocument70 pages2015 Line Distance Protection Fundamentals - Kockott PDFIgnacio Lucas Avila ManganoNo ratings yet
- TransformerProtection by Hands On Relay SchoolsDocument63 pagesTransformerProtection by Hands On Relay SchoolshiteshkelaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications Fundamentals and Ap - Bernard Sklar Book Part 1Document310 pagesDigital Communications Fundamentals and Ap - Bernard Sklar Book Part 1Muhammad Waqas ENG Department83% (6)
- AmiranDocument2 pagesAmirandmugalloy100% (1)
- CT Class Very ImportantDocument6 pagesCT Class Very ImportantEngr Fahimuddin QureshiNo ratings yet
- Teleprotection For Distance Protection: To AchieveDocument5 pagesTeleprotection For Distance Protection: To AchievebijoyNo ratings yet
- Protection Technologies of Ultra-High-Voltage AC Transmission SystemsFrom EverandProtection Technologies of Ultra-High-Voltage AC Transmission SystemsNo ratings yet
- Earth Fault Distance Protection (DOCUMENTO)Document150 pagesEarth Fault Distance Protection (DOCUMENTO)DanielAlejandroRamosQueroNo ratings yet
- Distance Protection SchemesDocument11 pagesDistance Protection SchemesParichay GuptoNo ratings yet
- Ldp616 Gender Issues in Development Exam RevsDocument56 pagesLdp616 Gender Issues in Development Exam Revsdmugalloy100% (1)
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Distance Relay ModellingDocument10 pagesDistance Relay ModellingpavanrajhrNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Bank ProtectionDocument17 pagesCapacitor Bank ProtectionskisakNo ratings yet
- Distance Priciples - Basic PrinciplesDocument64 pagesDistance Priciples - Basic PrinciplesRamesh Bakthavachalam100% (1)
- APN-052 Directional Ground-Fault ProtectionDocument17 pagesAPN-052 Directional Ground-Fault ProtectionWalter Andres Estevez VasquezNo ratings yet
- Result Based MonitoringDocument11 pagesResult Based MonitoringdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- The Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsFrom EverandThe Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsNo ratings yet
- Guia de Formación SELDocument72 pagesGuia de Formación SELJefferson Gutama Valladares100% (1)
- C&R Panel (Without Automation) - Aug, 2016Document73 pagesC&R Panel (Without Automation) - Aug, 2016apsNo ratings yet
- UniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eDocument60 pagesUniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eBala MNo ratings yet
- 2 Teleprotection - 2Document21 pages2 Teleprotection - 2sabill arasyidNo ratings yet
- Areva P443 Protection by Areva PaperDocument6 pagesAreva P443 Protection by Areva PaperRajesh BoddunaNo ratings yet
- Distance Relay - Thesis's ProposalDocument5 pagesDistance Relay - Thesis's ProposalQuan DangNo ratings yet
- R5582E RELAY Selection GuideDocument14 pagesR5582E RELAY Selection GuideChandra Hamidi KautsarNo ratings yet
- 03 - RelaySimTest AppNote Line Distance Protection With Teleprotection 2017 ENUDocument20 pages03 - RelaySimTest AppNote Line Distance Protection With Teleprotection 2017 ENUJ100% (1)
- Protection Basics and TerminologyDocument33 pagesProtection Basics and TerminologyMuhammad AbuzarNo ratings yet
- Distance Protection SchemeDocument8 pagesDistance Protection Schemesajjad ramezanzadehNo ratings yet
- (Elearnica - Ir) - Ground Distance Relay Compensation Based On Fault Resistance CADocument6 pages(Elearnica - Ir) - Ground Distance Relay Compensation Based On Fault Resistance CAAnonymous 9VcxlFErfNo ratings yet
- Redundancy in Digital SubstationsDocument14 pagesRedundancy in Digital SubstationsJorge AzabacheNo ratings yet
- SIP5-APN-016 Distance Protection With Tele-Protection On An OHL Feeder enDocument32 pagesSIP5-APN-016 Distance Protection With Tele-Protection On An OHL Feeder enKhajaBurhanNo ratings yet
- 2010 12 PotM Distance Protection IEC 60255 121 IPTS 2010 PDFDocument8 pages2010 12 PotM Distance Protection IEC 60255 121 IPTS 2010 PDFreza515heiNo ratings yet
- ABB Fundamentals of Teleprotection Systems Abril 2011Document28 pagesABB Fundamentals of Teleprotection Systems Abril 2011lazaruzNo ratings yet
- Distance ProtectionDocument14 pagesDistance ProtectionBrenda Naranjo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Line Differential Relay 7SD52Document17 pagesLine Differential Relay 7SD52Anonymous 9VcxlFErfNo ratings yet
- 7SS52 Training 05 - 2009Document115 pages7SS52 Training 05 - 2009Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Advanced-Power-System-Protection-Webinar-Aug-2020Document4 pagesAdvanced-Power-System-Protection-Webinar-Aug-2020nooralhudNo ratings yet
- Power Swing Blocking Function in Distance RelayDocument6 pagesPower Swing Blocking Function in Distance RelayMahmoud AbuziadNo ratings yet
- Use of Travelling Waves Principle in Protection Systems and Related AutomationsDocument52 pagesUse of Travelling Waves Principle in Protection Systems and Related AutomationsUtopia BogdanNo ratings yet
- Mho Relay 2 PDFDocument8 pagesMho Relay 2 PDFArion BaboolalNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Busbar ProtectionDocument45 pagesHigh Voltage Busbar ProtectionabhinavksauravNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection and Control - 1Document5 pagesPower System Protection and Control - 1Pratik Jones KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Protection Signalling: Directional Comparison Distance Protection SchemesDocument12 pagesProtection Signalling: Directional Comparison Distance Protection SchemesnooralhudNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learned Document Library-LL 20130401 Transmission Relaying Undesired BlockingDocument2 pagesLessons Learned Document Library-LL 20130401 Transmission Relaying Undesired Blockingjaackson10No ratings yet
- Schneider Jinko Solar ModuleDocument2 pagesSchneider Jinko Solar ModuledmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Schneider LAPP Solar CablesDocument2 pagesSchneider LAPP Solar CablesdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Bid 1000000297Document6 pagesBid 1000000297dmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Munyoroku - The Role of Organization Structure On Strategy Implementation Among Food Processing Companies in NairobiDocument69 pagesMunyoroku - The Role of Organization Structure On Strategy Implementation Among Food Processing Companies in NairobidmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Types of Evaluation-ReviewedDocument23 pagesTypes of Evaluation-RevieweddmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Issues in Ex-Ante and Ex-Post Evaluations: Outline of This ChapterDocument86 pagesChapter 2 Issues in Ex-Ante and Ex-Post Evaluations: Outline of This ChapterdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- LDP 607-Barriers To Impementation of TQM - February 2016Document1 pageLDP 607-Barriers To Impementation of TQM - February 2016dmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Principles of TQM - February 2016Document3 pagesPrinciples of TQM - February 2016dmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Facilities Maintenance Training ReportDocument2 pagesFacilities Maintenance Training ReportdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- National TimerDocument193 pagesNational TimerdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- The BMW Group Is The World's Leading Provider of Premium Products and Premium Services For Individual Mobility.Document6 pagesThe BMW Group Is The World's Leading Provider of Premium Products and Premium Services For Individual Mobility.dmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Business Case and Summary 203357Document53 pagesBusiness Case and Summary 203357dmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Cat Part B Answer All The Questions.: TH THDocument2 pagesCat Part B Answer All The Questions.: TH THdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Assignment KUDocument5 pagesFinancial Accounting Assignment KUdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument2 pagesIntroduction To AccountingdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Current Liabilities in Financial AccountingDocument2 pagesCurrent Liabilities in Financial AccountingdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting IIDocument3 pagesFinancial Accounting IIdmugalloyNo ratings yet
- CM P1 11604 en SKF Vibration Sensors CatalogDocument140 pagesCM P1 11604 en SKF Vibration Sensors CatalogErica BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Analog Com (Repaired)Document193 pagesAnalog Com (Repaired)Abinet TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Planning Guideline: Air Interface Dimensioning: Issued by Communication Mobile Networks © Siemens Ag 2006Document55 pagesPlanning Guideline: Air Interface Dimensioning: Issued by Communication Mobile Networks © Siemens Ag 2006AliNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Noise - GATE - CourseDocument24 pagesCH 7 Noise - GATE - CourseDikesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATION SYSTEM - Module-IDocument84 pagesCOMMUNICATION SYSTEM - Module-ICOMPETITIVE GURU JINo ratings yet
- 480E09 DatasheetDocument3 pages480E09 Datasheetram_unltd1518No ratings yet
- Analog Interface Guide IDocument32 pagesAnalog Interface Guide Iarturo53No ratings yet
- Voltright SVS Brochure Aug 08OLLATEKDocument8 pagesVoltright SVS Brochure Aug 08OLLATEKmikaellasyNo ratings yet
- Jitter 1690318488Document46 pagesJitter 1690318488कुनाल सिंहNo ratings yet
- Ailtech 7600 Series Noise Generator Operation and Service Manual, 11-1980.Document26 pagesAiltech 7600 Series Noise Generator Operation and Service Manual, 11-1980.Bob Laughlin, KWØRLNo ratings yet
- The Generalized Contrast-to-Noise Ratio A Formal Definition For Lesion DetectabilityDocument15 pagesThe Generalized Contrast-to-Noise Ratio A Formal Definition For Lesion DetectabilitydsfdsfNo ratings yet
- LM 2896 PDocument10 pagesLM 2896 PEduardo Diaz RoqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - AM ReceptionDocument43 pagesChapter 5 - AM ReceptionmenchieNo ratings yet
- Pricomm FinalsDocument8 pagesPricomm FinalsAllyza Marie BalaneNo ratings yet
- Microlog Accessories Catalog PDFDocument100 pagesMicrolog Accessories Catalog PDFMatt ENo ratings yet
- Noise: Prof V S Patil Head of Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument52 pagesNoise: Prof V S Patil Head of Electrical Engineering DepartmentVijay S PatilNo ratings yet
- Principles Review Notes For PcommsDocument23 pagesPrinciples Review Notes For PcommsJohnny DoeNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document102 pagesUnit 4Manjushree KumaravelNo ratings yet
- Understanding Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Devices For Mobile and Wireless Applications and Design TechniquesDocument51 pagesUnderstanding Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Devices For Mobile and Wireless Applications and Design Techniquesbingwazzup100% (1)
- Adaptive2 CYCBDDocument18 pagesAdaptive2 CYCBD于明杰No ratings yet
- Satellite Communication NotesDocument50 pagesSatellite Communication NotesPreetham SaigalNo ratings yet
- Noise Optimization in Sensor Signal Conditioning Circuit Part IDocument37 pagesNoise Optimization in Sensor Signal Conditioning Circuit Part Iyzhao148No ratings yet
- RF Basics - Part 1: Demystifying The DBDocument6 pagesRF Basics - Part 1: Demystifying The DBRaúl InfanteNo ratings yet
- SINAD - Radio Receiver SensitivityDocument8 pagesSINAD - Radio Receiver SensitivityPaul Adrian Senior CiobanitaNo ratings yet
- 2 Noise1Document294 pages2 Noise1anika tabassumNo ratings yet
- ELEN E6316: Analog-Digital Interfaces: Course Introduction Dynamic Range (Noise and Linearity)Document77 pagesELEN E6316: Analog-Digital Interfaces: Course Introduction Dynamic Range (Noise and Linearity)Wilson PenaNo ratings yet
- Cell Selection SlidesDocument50 pagesCell Selection SlideshaiderifulNo ratings yet