Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problems
Uploaded by
Noor MohdOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problems
Uploaded by
Noor MohdCopyright:
Available Formats
PROBLEMS 1. A soil specimen has a volume of 0.05 m3 and a mass of 87.5 kg. given w = 15%, Gs = 2.68. determine a. b. c. d. e.
Void ratio Porosity Dry unit weight Moist unit weight Degree of saturation
2. The saturated unit weight of a soil is 20.1 kN/m3 at a moisture content of 22%. Determine (a) the dry unit weight and (b) the specific gravity of soil solids, Gs . 3. For a soil, given: void ratio = 0.81, moisture content = 21% and Gs = 2.68. calculate the following a. b. c. d. Porosity Degree of saturation Moist unit weight in kN/m3 Dry unit weight in kN/m3
4. For a given soil, the following are given: moist unit weight= 122 lb/ft 3 , moisture content = 14.7%, and Gs = 2.68. calculate the following: a. b. c. d. Void ratio Porosity Degree of saturation Dry unit weight
5. For the soil described in problem 4: a. What would be the saturated unit weight in lb/ft 3 ? b. How much water, in lb/ft 3 needs to be added to the soil for complete saturation? c. What would be the moist unit weight in lb/ft 3 when the degree of saturation is 80%?
6. For a granular soil, given: = 108 lb/ft 3 , Dr = 82%, w = 8% and Gs = 2.65. For this soil, if emin = 0.44, what would be emax ? What would be the dry unit weight in the loosest state? 7. The laboratory test results of six soils are given in the following table. Classify the soils by the AASHTO Soil Classification System and given the group indices. Sieve Analysis-Percent Passing
A Sieve no. 100 4 95 10 82 40 65 200 42 Liquid limit 26 Plastic limit *NP = nonplastic
B 100 80 61 55 38 25
Soil C 95 80 54 8 NP* NP
D 95 90 79 64 35 26
E 100 94 76 33 38 25
F 100 94 86 76 52 28
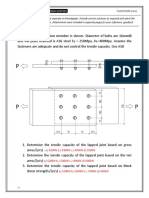
8. Classify the soils given in problem 7 by the United Soil Classification System and determine the group symbols and group names. 9. For a sandy soil given: void ratio, e = 0.63; hydraulic conductivity, k = 0.22 cm/sec; specific gravity of soil solids, Gs = 2.68. Estimate the hydraulic conductivity of the sand (cm/sec) when the dry unit weight of compaction is 117 lb/ft 3 . Use equation (29). 10. A sand has a hydraulic conductivity of 0.25 cm/sec at a void ratio of 0.7. Estimate the void ratio at which its hydraulic conductivity at a void ratio of 0.72? Use equation (28). 11. The in situ hydraulic conductivity of a clay is 5.4 106 cm/sec at a void ratio of 0.92. What would be its hydraulic conductivity at a void ratio of 0.72? Use of equation (31). 12. Refer to the soil profile shown in figure P-12. Determine the total stress, pore water pressure, and effective stress at A, B, C, and D.
Figure P-12 13. A sandy soil (Gs = 2.65), in its densest and loosest states, has void ratios of 0.42 and 0.85, respectively. Estimate the range of the critical hydraulic gradient in this soil at which a quicksand condition might occur. 14. A saturated clay deposit in the field has Liquid limit = 52% Plastic limit = 18% Moisture content = 27% Specific gravity of soil solids, Gs = 2.69 In situ effective overburden pressure = 79 kN/m2 Estimate the preconsolidation pressure, pc a. By using equations (53a and 53b) b. By using equations (54 and 55)
15. For a normally consolidated clay layer, the following are given: Thickness = 3.7 m Void ratio = 0.82 Liquid limit = 42 Average effective stress on the clay layer = 110 kN/m2 How much consolidation settlement would the clay undergo if the average effective stress on the clay layer is increases to 155 kN/m2 as the result of the construction of a foundation?
16. Refer to problem 16. Assume that the clay layer is preconsolidated, pc = 128 kN/m2 and Cs = 1 C . Estimate the consolidation settlement. 5 c 17. Refer to the soil profile shown in figure P-12. The clay is normally consolidated. A laboratory consolidation test on the clay gave the following results: Pressure (lb/in.2 ) 21 42 If the average effective stress on the clay layer increases by 1000 lb/ft 2 , Void ratio 0.91 0.792
a. What would be the total consolidation settlement? b. If Cv = 1.45 104 in2 /sec, how long will it take for half the consolidation settlement to take place? 18. For a normally consolidated soil, the following is given: Pressure (kN/m2 ) 120 360 Determine the following: a. The compression index, Cc . b. The void ratio corresponding to pressure of 200 kN/m2 . 19. A clay soil specimen, 1.5 in. thick (drained on top only) was tested in the laboratory. For a given load increment, the time for 60% consolidation was 8 min 10 sec. how long will it take for 50% consolidation for a similar clay layer in the field that is 10-ft thick and drained on both sides? 20. Refer to figure P-21. A total of 60 mm consolidation settlement is expected in the two clay layers due to a surcharge of p. Find the duration of surcharge application at which 30 mm of total settlement would take Void ratio 0.82 0.64
Figure P-21 21. A direct shear test was conducted on dry sand. The results were as follows: Area of the specimen= 2 in. 2 in. Normal force (lb) 50 95.5 110 132.0 150 Graph the shear stress at failure against normal stress and determine the soil friction angle. 22. A consolidated-drained triaxial test on a sand yielded the following results: All-around confining pressure = 3 = 30 lb/in2 Added axial stress at failure = = 96 lb/in2 Determine the shear stress parameters. 23. Repeat problem 23 with the following: All-around confining pressure = 3 = 20 lb/in2 Added axial stress at failure = = 40 lb/in2
Shear force at failure (lb) 43.5
24. A consolidated-drained triaxial test on a normally consolidated clay yielded a friction angle, , of 28 . If the al-around confining pressure during the test was140 kN/m2 , what was the major principal stress at failure? 25. Following are the results of two consolidation-drained triaxial tests on a clay: Test I: 3 = 140 kN/m2 ; 1(failure ) = 368 kN/m2 Test II: 3 = 280 kN/m2 ; 1(failure ) = 701 kN/m2 Determine the shear strength parameters, that is, c and .
26. A consolidated-undrianed triaxial test was conducted on a saturated normally consolidated clay. Following are the test results: 3 = 13 lb/in2 1(failure ) = 32 lb/in2 pore pressure at failure = uf = 5.5 lb/in2 Determine Ccu , cu , c, and
27. For a normally consolidated clay, given = 28 and cu = 20 . If a consolidated undrained triaxial test is conducted on the same clay with 3 = 150 kN/m2 , what would be the pore water pressure at failure? 28. A saturated clay layer has Saturated unit weight, sat = 3 = 19.6 kN/m3 Plasticity index = 21 The water table coincides with the ground surface. If the clay is normally consolidated estimate the magnitude of cu ( kN/m2 ) that can be obtained from a vane shear test at a depth of 8 m from the ground surface. Use the Skempton relationship given in table 16.
You might also like
- CHAPTER 1 Soil PropertiesDocument27 pagesCHAPTER 1 Soil PropertiesLyzette LeanderNo ratings yet
- Roofing Materials: Roof ComponentsDocument17 pagesRoofing Materials: Roof ComponentsMero Mero100% (1)
- P5 3B Bernardo KathryneDocument5 pagesP5 3B Bernardo KathryneKATHRYNE BERNARDONo ratings yet
- Determine design wind loads for 3-story concrete houseDocument6 pagesDetermine design wind loads for 3-story concrete houseNedžadDžokoNo ratings yet
- NSCPDocument60 pagesNSCPXylem01 Phloem02No ratings yet
- Mathematics Mock BoardDocument2 pagesMathematics Mock BoardArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- 1 - Hydrostatic PressureDocument15 pages1 - Hydrostatic PressureromasokyNo ratings yet
- Direction: Based On The "Tensile Strength Test" Video Provided, All Data Are Gathered andDocument7 pagesDirection: Based On The "Tensile Strength Test" Video Provided, All Data Are Gathered andErnielle Rae Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- That Sugar Film CritiqueDocument2 pagesThat Sugar Film CritiqueMigz Tolentino100% (1)
- HomeworkDocument17 pagesHomeworksonusk777No ratings yet
- Module-1 Home-Eval 1Document9 pagesModule-1 Home-Eval 1Michael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Machine footing design and analysisDocument5 pagesMachine footing design and analysisJohnmark FormenteraNo ratings yet
- Lateral Force On Non Building StructureDocument18 pagesLateral Force On Non Building Structurefebby016No ratings yet
- Cargamentoaaron Lx3 Hydrostatic-PressureDocument9 pagesCargamentoaaron Lx3 Hydrostatic-PressureAaron CargamentoNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slab Analysis by Coefficient Method PDFDocument7 pagesConcrete Slab Analysis by Coefficient Method PDFJones EdombingoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 4 (Pavement Engineering) PDFDocument1 pageAssignment No. 4 (Pavement Engineering) PDFHumza ShahidNo ratings yet
- EE2224 - Solid Mechanics - Stress StrainDocument63 pagesEE2224 - Solid Mechanics - Stress StrainPreedep BaradidathanNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Problem SetDocument7 pagesSoil Mechanics Problem SetChristine YasaNo ratings yet
- Outline of Topics: Resultant Moments. These Are The Stress Resultants (Also Called Membrane ForcesDocument16 pagesOutline of Topics: Resultant Moments. These Are The Stress Resultants (Also Called Membrane ForcesJosiah FloresNo ratings yet
- Unit Cost Analysis - Rebar WorksDocument14 pagesUnit Cost Analysis - Rebar WorksJhon Walter Ortega CondeNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Beam MethodDocument12 pagesConjugate Beam MethodKobina BondzieNo ratings yet
- Review Innovations: Civil Engineering November 2020 Transportation Engineering 1Document2 pagesReview Innovations: Civil Engineering November 2020 Transportation Engineering 1Krysha RomaineNo ratings yet
- 6 Mitigation On Environmental Impacts of TransportationDocument38 pages6 Mitigation On Environmental Impacts of TransportationRenalyn AndradeNo ratings yet
- Seismic LoadDocument7 pagesSeismic LoadMarc AlamoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Ernielle Rae Dela Cruz BSCE-4ADocument9 pagesQuiz 2 Ernielle Rae Dela Cruz BSCE-4AErnielle Rae Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressDocument12 pagesModule 4 Vertical and Horizontal StressShane IsorenaNo ratings yet
- Building System DesignDocument2 pagesBuilding System DesignBINSAH100% (1)
- Completion SurveyingDocument11 pagesCompletion SurveyingPrincess MerryNo ratings yet
- One-way slab designDocument22 pagesOne-way slab designGhiffa Syauqiyya Harahap 1707113714No ratings yet
- Experiment 16: Tensile Strength of Reinforcing Steel Bars 16.1. Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ExperimentDocument4 pagesExperiment 16: Tensile Strength of Reinforcing Steel Bars 16.1. Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ExperimentJhanyn VivoNo ratings yet
- 6-Beam-Column Members PDFDocument28 pages6-Beam-Column Members PDFKellen Brumbaugh100% (1)
- EASC1081 Soil Mechanics TutorialDocument5 pagesEASC1081 Soil Mechanics TutorialNita NabanitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NodosDocument35 pagesChapter 6 NodosMaria Alejandra ObandoNo ratings yet
- Soil Water Plant RelationshipsDocument29 pagesSoil Water Plant RelationshipsLee CastroNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Soil Mechanics Ready To Print CE PaperDocument6 pagesProblem Set Soil Mechanics Ready To Print CE PaperClein BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Consistency of cement pasteDocument5 pagesConsistency of cement pasteEngel De VillaNo ratings yet
- WIND LOADS (Computation of QH For MWFRS, Low Rise BuildingDocument2 pagesWIND LOADS (Computation of QH For MWFRS, Low Rise BuildingRomeo QuerubinNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall Design CalculationsDocument65 pagesRetaining Wall Design CalculationsTAMIL100% (1)
- Soil compaction calculations and test resultsDocument5 pagesSoil compaction calculations and test resultsMikael DionisioNo ratings yet
- Subject 1 Algebra Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Analytic Geometry Probability PhysicsDocument49 pagesSubject 1 Algebra Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Analytic Geometry Probability PhysicsDani LubosNo ratings yet
- Soil mechanics problems on consolidation settlement, stresses, and propertiesDocument8 pagesSoil mechanics problems on consolidation settlement, stresses, and propertiesEarl JyunNo ratings yet
- Compression Only Spring-STAADDocument7 pagesCompression Only Spring-STAADAjaykumar MistryNo ratings yet
- Assesment ExamDocument3 pagesAssesment ExamJulious MacalinaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lateral Earth PressureDocument47 pagesChapter 3 Lateral Earth PressureJiregna Tesfaye100% (2)
- Soil HomeworkDocument29 pagesSoil HomeworkPoopriaw TanapornNo ratings yet
- Kinetic timber design guideDocument3 pagesKinetic timber design guideMark Lehi PalmesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2saifulsabdin0% (1)
- Tutorial Chapter 2Document2 pagesTutorial Chapter 2wendyNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Problems PDFDocument2 pagesSet 1 Problems PDFKristin Argosino0% (1)
- CMT Laboratory 5 Determination of Surface Moisture of Coarse AggregatesDocument6 pagesCMT Laboratory 5 Determination of Surface Moisture of Coarse AggregatesBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic 2Document52 pagesHydraulic 2Othmane BoualamNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations CE Review GuideDocument2 pagesDifferential Equations CE Review GuideNathanielle AndreaNo ratings yet
- Traverse Adjustment - WOLFPackDocument6 pagesTraverse Adjustment - WOLFPackvarunsingh214761100% (1)
- Determining the Center of Gravity of a Floating BodyDocument6 pagesDetermining the Center of Gravity of a Floating BodyDarlin Cara TurquezaNo ratings yet
- MorroofdDocument2 pagesMorroofdAnonymous ym7PJCj0% (1)
- Advanced Math Refresher SetDocument4 pagesAdvanced Math Refresher SetGracielle Nebres100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete - Shear StrengthDocument7 pagesReinforced Concrete - Shear StrengthDenice CastroNo ratings yet
- AssignmentsDocument10 pagesAssignmentsAlsits LvtNo ratings yet
- 620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Document4 pages620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Mona fabrigarNo ratings yet
- Estimating Soil Properties from SPT Tests Using Random NumbersDocument8 pagesEstimating Soil Properties from SPT Tests Using Random NumbersNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Slab Thickness Calculator for Two-Way SlabsDocument2 pagesSlab Thickness Calculator for Two-Way SlabsNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- FF0199 01 Free Flower Diagram PowerpointDocument10 pagesFF0199 01 Free Flower Diagram PowerpointNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Sno Author Year Additive/Replacement 1 2Document2 pagesSno Author Year Additive/Replacement 1 2Noor MohdNo ratings yet
- FF0199 01 Free Flower Diagram PowerpointDocument10 pagesFF0199 01 Free Flower Diagram PowerpointNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Excel Sheet For SieveDocument4 pagesExcel Sheet For SieveNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- FF0221 01 Free Corporate Slides For Powerpoint 16x9Document14 pagesFF0221 01 Free Corporate Slides For Powerpoint 16x9Noor MohdNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Power Point PresentationDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Power Point PresentationNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Power Point PresentationDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Power Point PresentationNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Isolated Footing Design (IS 456-2000)Document12 pagesIsolated Footing Design (IS 456-2000)Divya TadepalliNo ratings yet
- Creative Business Presentation IdeasDocument4 pagesCreative Business Presentation IdeasNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Etabs For RCC Structures: Welcome To Structural Designing WorldDocument1 pageEtabs For RCC Structures: Welcome To Structural Designing WorldNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Calculation - Universal Calculation: Put The Number To The YELLOW Cells Only !!!!!Document4 pagesWind Load Calculation - Universal Calculation: Put The Number To The YELLOW Cells Only !!!!!Noor MohdNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 SchematicandphotooftestDocument1 pageFigure 1 SchematicandphotooftestNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- TABLE: Joint Reactions Story Joint Label Unique Name Load Case/Combo FZDocument2 pagesTABLE: Joint Reactions Story Joint Label Unique Name Load Case/Combo FZNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Steel Quantity of ColumnDocument1 pageSteel Quantity of ColumnZigzag En.No ratings yet
- Design of Square FootingDocument5 pagesDesign of Square FootingNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Steel Quantity of BeamDocument1 pageSteel Quantity of BeamNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Summary of Column Design Col No Size in MMDocument2 pagesSummary of Column Design Col No Size in MMNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Omitted MeasurementDocument26 pagesOmitted MeasurementNoor Mohd80% (5)
- TABLE: Story Response Story Elevation X-DirDocument2 pagesTABLE: Story Response Story Elevation X-DirNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Area ComputationDocument5 pagesArea ComputationRommel Dave TejanoNo ratings yet
- Unfactored Load CombinationDocument1 pageUnfactored Load CombinationNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- EtabsDocument2 pagesEtabsNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Story Elevation X-DirDocument5 pagesStory Elevation X-DirNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- InstructionsDocument1 pageInstructionsNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Mode Period Mode Period Sec SecDocument2 pagesMode Period Mode Period Sec SecNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument19 pagesContentsNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Unfactored Load CombinationDocument1 pageUnfactored Load CombinationNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionNoor MohdNo ratings yet
- Nano Refrigerants OverviewDocument26 pagesNano Refrigerants Overviewchitta sandeep dattuNo ratings yet
- RPP 04 BFC 34402 Sem II 1415Document7 pagesRPP 04 BFC 34402 Sem II 1415Tikar MengkuangNo ratings yet
- Determining The Velocity of Sound in The Air Using Resonance TubeDocument12 pagesDetermining The Velocity of Sound in The Air Using Resonance TubeRara Aisyah RamadhanyNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Analysis & Performance Based Design FundamentalsDocument86 pagesNonlinear Analysis & Performance Based Design FundamentalsvinujohnpanickerNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient, Peltier Based Portable Cabinet Cooling System For Vaccine Cold ChainDocument4 pagesEnergy Efficient, Peltier Based Portable Cabinet Cooling System For Vaccine Cold ChainVishnuShantanNo ratings yet
- Valve Seat Leakage TestDocument3 pagesValve Seat Leakage Testtaeyun hwngNo ratings yet
- Perrys Chemical Engineers Handbook 1999Document14 pagesPerrys Chemical Engineers Handbook 1999Thirunavuk KarasuNo ratings yet
- Propeller Design Workshop Part I PDFDocument92 pagesPropeller Design Workshop Part I PDFYvessNo ratings yet
- (G6) Orifice Under Varying HeadDocument5 pages(G6) Orifice Under Varying HeadDane JonesNo ratings yet
- Kill Sheet: Prerecorded Infromation Pump Strokes RequiredDocument16 pagesKill Sheet: Prerecorded Infromation Pump Strokes RequiredAbdul Hameed OmarNo ratings yet
- Compute Grid Spacing For A Given Y+: Improve CFD Accuracy With Correct Mesh ResolutionDocument2 pagesCompute Grid Spacing For A Given Y+: Improve CFD Accuracy With Correct Mesh ResolutionAntonio RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Steam TurbineDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Steam TurbineHalil İbrahim KüplüNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To ThermodynamicsEstanislao Amadeo AvogadroNo ratings yet
- Seismic Isolation Product Line-UpDocument9 pagesSeismic Isolation Product Line-UpSyafrul MubaraqNo ratings yet
- Cementing (Sharing Knowledge)Document15 pagesCementing (Sharing Knowledge)Moh Syamsul BahriNo ratings yet
- Latihan Kelompok Mekanika Fluida Dan PartikelDocument2 pagesLatihan Kelompok Mekanika Fluida Dan PartikelrizkaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problem:: A Concrete Gravity Dam Has The Following DimensionsDocument13 pagesNumerical Problem:: A Concrete Gravity Dam Has The Following DimensionsMuhammad Umer Arshad100% (1)
- MOS Endsem Paper 2022 Sem 1Document4 pagesMOS Endsem Paper 2022 Sem 1Xyz XyzNo ratings yet
- Chbe 6300 Graduate Kinetics and Reactor Design: Carsten Sievers 8/20/2020Document27 pagesChbe 6300 Graduate Kinetics and Reactor Design: Carsten Sievers 8/20/2020AnnNo ratings yet
- Flash Point and Fire PointDocument2 pagesFlash Point and Fire PointHitesh N. PanchalNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Irreversible Processes Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesThermodynamics of Irreversible Processes Lecture NotesNatty LopezNo ratings yet
- Questoin Paper JEN Civil Diploma Exam 2016Document29 pagesQuestoin Paper JEN Civil Diploma Exam 2016erparshotamNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation of Shock Absorber (Landcruiser) : AbstractDocument4 pagesDesign Calculation of Shock Absorber (Landcruiser) : AbstractDr. Aung Ko LattNo ratings yet
- Absorption of SO2 by Aqueous NaOH Solutions in The Presence of A SurfactantDocument7 pagesAbsorption of SO2 by Aqueous NaOH Solutions in The Presence of A Surfactantirumor13No ratings yet
- Versafles Liner HangerDocument8 pagesVersafles Liner HangerEdison MontanezNo ratings yet
- (PPT) Fire Resistance Assessment of Concrete StructuresDocument81 pages(PPT) Fire Resistance Assessment of Concrete StructuresGregory Simmon100% (2)
- Outlines: Theory Calculation Conclusion ReferencesDocument31 pagesOutlines: Theory Calculation Conclusion ReferencesYè Paing Oo100% (3)
- Finite Element MethodsDocument8 pagesFinite Element MethodsRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 13 - Design of Compression Members - Bucking 2022Document9 pagesClass 13 - Design of Compression Members - Bucking 2022Engr. Waqas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Design of Packed ColumnDocument4 pagesDesign of Packed Columnمنى عبد المنعم صالح رداد منى عبد المنعم صالح ردادNo ratings yet
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Survival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosFrom EverandSurvival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeFrom EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeFrom EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Into the Planet: My Life as a Cave DiverFrom EverandInto the Planet: My Life as a Cave DiverRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Timefulness: How Thinking Like a Geologist Can Help Save the WorldFrom EverandTimefulness: How Thinking Like a Geologist Can Help Save the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (66)
- A Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersFrom EverandA Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- Zondervan Essential Atlas of the BibleFrom EverandZondervan Essential Atlas of the BibleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- The Story of Stuff: How Our Obsession with Stuff is Trashing the Planet, Our Communities, and Our Health-and a Vision for ChangeFrom EverandThe Story of Stuff: How Our Obsession with Stuff is Trashing the Planet, Our Communities, and Our Health-and a Vision for ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- The Witch's Yearbook: Spells, Stones, Tools and Rituals for a Year of Modern MagicFrom EverandThe Witch's Yearbook: Spells, Stones, Tools and Rituals for a Year of Modern MagicRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Ruthless Tide: The Heroes and Villains of the Johnstown Flood, America's Astonishing Gilded Age DisasterFrom EverandRuthless Tide: The Heroes and Villains of the Johnstown Flood, America's Astonishing Gilded Age DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- The Fourth Phase of Water: Beyond Solid, Liquid, and VaporFrom EverandThe Fourth Phase of Water: Beyond Solid, Liquid, and VaporRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- The Water Kingdom: A Secret History of ChinaFrom EverandThe Water Kingdom: A Secret History of ChinaRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (19)