Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yearly Lesson Plan (Biology F4)
Uploaded by
Rossliza YaacobCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yearly Lesson Plan (Biology F4)
Uploaded by
Rossliza YaacobCopyright:
Available Formats
THEME: INTRODUCING BIOLOGY LEARNING AREA: 1.0 INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY DATE 5 9 JAN Learning Objecti e! 1.
.1 Understanding the study of Biology "#gge!te$ Learning Acti itie! Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! what is the study of Biology" #! the importance of Biology with respect to the study of li$ing things% en$ironment% interaction #etween li$ing things and the en$ironment. Construct a concept map #ased on information gathered on the different fields of study and careers related to Biology. &mall group discussion on the importance of the following a! ac'uiring scientific s(ills% #! scientific method% c! practising scientific attitudes and no#le $alues. Learning O#tc%&e! A student is a#le to ? state what the study of Biology is% ? e)plain the importance of Biology% ? list the different fields of study in Biology% ? list the careers related to Biology% ? state $arious ways of studying Biology% fields bidang career kerjaya N%te! '%cab#(ar)
5 9 JAN
1.* Applying scientific in$estigation
+#ser$e a situation and identify all the $aria#les. &uggest a 'uestion that is suita#le for a scientific in$estigation. ,iscuss to a! form a hypothesis% #! plan the method of in$estigation including selection of apparatus and wor( procedures. Carry out an e)periment a! to collect and ta#ulate data% #! present data in a suita#le form% c! interpret the data and draw conclusion% d! write a complete report. Carry out an e)periment on the ma(ing of #read using yeast in the a#sence and presence of sugar. -ecord the time ta(en for the dough to dou#le its si.e. /or further in$estigations% salt is used. ,uring in$estigation% highlight the need to practise scientific attitudes and no#le $alues such as honesty and accuracy in recording and $erifying data.
A student is a#le to ? identify $aria#les in a gi$en situation% ? identify the relationship #etween two $aria#les to form a hypothesis% ? design and carry out a simple e)periment to test the hypothesis% ? record and present data in a suita#le form% ? interpret data to draw conclusions% ? write a report on an e)periment% ? practise scientific attitudes and no#le $alues.
0his acti$ity helps the teacher to assess students1 capa#ilities to carry out a scientific in$estigation. 0hese attitudes and $alues should #e o#ser$ed in all in$estigations in other learning areas.
scientific in$estigation penyiasatan saintifik scientific attitudes sikap saintifik no#le $alues nilai murni
THEME: IN'E"TIGATING THE CELL A" A BA"IC UNIT O* LI'ING THING" LEARNING AREA: 1.0 CELL "TRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANI"ATION DATE 1* 12 JAN Learning Objecti e! 1.1 Understanding cell structure and function "#gge!te$ Learning Acti itie! 3repare and study slides to compare the epidermal cells of onion or cells of Hydrilla leaf with human chee( cells. +#ser$e% draw and la#el diagrams of an animal cell and a plant cell as seen through a light microscope. &tudy electron micrographs of animal cells and plant cells to identify cellular components of cell a! plasma mem#rane and cell wall% #! cytoplasm% c! organelles 4i! nucleus nucleolus% chromosomes% nucleoplasm and nuclear mem#rane% 4ii! rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum% 4iii! mitochondria% 4i$! 5olgi apparatus% 4$! lysosomes% 4$i! ri#osomes% 4$ii! chloroplasts% 4$iii! centrioles% 4i)! $acuoles. Learning O#tc%&e! A student is a#le to ? draw and la#el an animal cell% ? draw and la#el a plant cell% ? identify the cellular components of an animal cell% ? identify the cellular components of a plant cell% 0he structure of the organelles is not re'uired. cellular components komponenkomponen N%te! '%cab#(ar)
6or( in small groups to match cellular components to their functions. &tudents present a comparison #etween the structure of an animal cell and a plant cell. ,iscuss the relationship #etween the density of certain organelles with the function of specific cells a! mitochondria with the function of sperm cells% flight muscle cells in insects and #irds% cells in the meristems% #! chloroplasts with the function of palisade cells. 19 *8 JAN 1.* Understanding cell organisation +#ser$e the li$ing processes of unicellular organisms such as feeding% locomotion and reproduction through computeri.ed animation 9 $ideo 9 microscope. Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! cell specialisation in multicellular organisms% #! the necessity for cell speciali.ation in multicellular organisms c! cell organisation in the formation of tissues% organs and systems in humans%
relate mengaitkan ? state the functions of the cellular components in an animal cell% ? state the functions of the cellular components in a plant cell% ? compare and contrast an animal cell and a plant cell% ? relate the density of certain organelles with the functions of specific cells. A student is a#le to ? state the necessity for cell specialisation in multicellular organism as compared to unicellular organism% ? descri#e cell specialisation in multicellular organisms% ? descri#e cell organisation in the formation of tissues% organs and systems in multicellular organisms% li$ing processes proses proses kehidupan cell specialisation 7pengkhususa n sel density 7 ketumpatan
animals and plants. Construct models of tissues% organs and systems in human% animals and plants. Conduct a discussion on the following a! the meaning of internal en$ironment% #! factors affecting the internal en$ironment including temperature% p:% osmotic pressure and glucose le$el. c! it is important that the organism1s cells always e)perience conditions which permit efficient functioning% the in$ol$ement of $arious systems in maintaining optimal internal en$ironment. 19 *8 JAN 1.8 Appreciating the uni'ueness of the cell ,iscuss and predict the cell condition without a particular cellular component. Conduct a role7play acti$ity to show that cells #ecome adapted for different functions. " state the meaning of internal en$ironment% ? identify factors affecting the internal en$ironment% ? e)plain the necessity to maintain optimal internal en$ironment% ? descri#e the in$ol$ement of $arious systems in maintaining optimal internal en$ironment. A simple e)planation
A student is a#le to ? predict the state of certain cells without a particular cellular component% ? illustrate that most cells are specialised for the ;o# that they perform.
uni'ueness keunikan
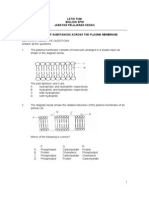
LEARNING AREA: +.0 MO'EMENT O* "UB"TANCE" ACRO"" THE ,LA"MA MEMBRANE ,A0< * 2 /<B Learning Objecti e! *.1 Analysing the of mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane "#gge!te$ Learning Acti itie! ,iscuss the following a! su#stances that are re'uired #y cells% #! su#stances to #e eliminated from cells% c! the necessity for mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane. ,iscuss the structure of the plasma mem#rane as comprising the phospholipid #ilayer% carrier protein and pores. Conduct an e)periment% using starch suspension and glucose solution% to study the mo$ement of su#stances across egg mem#rane or =is(ing tu#ing. ,iscuss the properties of the plasma mem#rane as a semipermea#le mem#rane. ,iscuss the mo$ement of solu#le su#stances across the plasma mem#rane through simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. ? descri#e the permea#ility of the plasma mem#rane% ? e)plain the mo$ement of solu#le su#stances across the plasma mem#rane through the process of passi$e transport% +nly a #rief account of the structure of the plasma mem#rane is re'uired. Learning O#tc%&e! A student is a#le to ? state the su#stances re'uired #y li$ing cells% ? state the su#stances that ha$e to #e eliminated from cells% ? e)plain the necessity for mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane% ? descri#e the structure of the plasma mem#rane% permea#ility 7 ketelapan simple diffusion resapan ringkas facilitated diffusion resapan berbantu passi$e transport pengangkuta n pasif N%te! '%cab#(ar)
Carry out an acti$ity to show osmosis using a simple osmometer. ,iscuss the mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane through acti$e transport. Conduct a simulation acti$ity to show the mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane through passi$e transport and acti$e transport. Use computer simulation to show the mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane. ,iscuss the processes of passi$e transport and acti$e transport in li$ing organisms a! gaseous e)change in the al$eoli and #lood capillaries 4simple diffusion!% #! a#sorption of digested food in the $illus 4facilitated diffusion!% c! a#sorption of water #y root hairs of a plant 4osmosis!% d! ion inta(e #y root hairs of a plant 4acti$e transport!.
? e)plain the mo$ement of water molecules across the plasma mem#rane #y osmosis% +nly a #asic e)planation of the acti$e transport process is re'uired.
acti$e transport 7 pengangkuta n aktif
? e)plain the mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane through the process of acti$e transport% ? e)plain the process of passi$e transport in li$ing organisms using e)amples% ? e)plain the process of acti$e transport in li$ing organisms using e)amples%
? compare and contrast passi$e transport and acti$e transport.
Construct a concept map on the mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane. Use a graphic organiser to compare and contrast passi$e transport and acti$e transport. 9 18 /<B *.* Understanding the mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane in e$eryday life Carry out acti$ities to study the effects of hypotonic and hypertonic solutions on plant and animal cells a! plasmolysis and deplasmolysis in plant cells% #! haemolysis and crenation in red #lood cells. ,iscuss the following a! hypotonic% hypertonic and isotonic solutions% #! plasmolysis% deplasmolysis% haemolysis and crenation% c! flaccidity and turgidity of plant cells. Carry out an in$estigation using $arious concentrations of salt or sugar solutions to determine the concentration of e)ternal solution which is isotonic to the cell sap of plant tissues. A student is a#le to ? e)plain what hypotonic% hypertonic and isotonic solutions are% ? e)plain the effects of hypotonic% hypertonic and isotonic solutions on plant cell and animal cell% ? e)plain plasmolysis% deplasmolysis% haemolysis and crenation% ? design an e)periment to determine the concentration of e)ternal solution which is isotonic to cell sap% 0he use of human #lood is discouraged. 0he concentration of the e)ternal solution which is isotonic to the cell sap is determined from the plotted graph. effects 7 kesan turgidity 7 kesegahan
,iscuss and ma(e an inference on the concentration of cell sap in plant tissues which is e'ui$alent to the concentration of isotonic solution. ,iscuss and correlate the mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane with the difference in concentration of the e)ternal solution and that of the cell sap. ,iscuss the following a! wilting of plants caused #y the e)cessi$e use of chemical fertilisers% #! preser$ation of food using salt or sugar. 9718 /<B *.8 Appreciating the mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane Compose poems to appreciate the mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane.
? ma(e an inference on the concentration of cell sap in plant tissues% ? relate the mo$ement of su#stances across plasma mem#rane with concentration gradient% ? e)plain the phenomenon of wilting in plants using e)amples% ? e)plain the preser$ation of food using e)amples.
,iscussion should #e #ased on the concepts of osmosis and plasmolysis.
wilting layu preser$ation 7 pengawetan
A student is a#le to ? e)plain the necessity of mo$ement of su#stances across the plasma mem#rane which occurs in a continuous and controlled manner for sur$i$al of a cell.
LEARNING AREA: -.0 CHEMICAL COM,O"ITION O* THE CELL DATE 127*> /<B Learning Objecti e! 8.1 Understanding the chemical composition of the cell "#gge!te$ Learning Acti itie! Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! elements in the cell% including car#on% hydrogen% o)ygen% nitrogen sulphur% phosphorus% calcium% potassium% magnesium% chlorine% sodium and ferum% #! the presence and importance of chemical compounds in the cell. Learning O#tc%&e! A student is a#le to ? state the elements in the cell% ? list the chemical compounds in the cell% ? e)plain the importance of organic compounds in the cell% ? e)plain the importance of water in the cell. N%te! Chemical compounds in the cell are limited to car#ohydrates% lipids% proteins% nucleic acids and water only. A #rief account on the importance of car#ohydrates% lipids% proteins and nucleic acids is re'uired. A detailed molecular structure is not re'uired. A #rief account of condensation and hydrolysis reactions is re'uired. formation pembentukan #rea(down 7 penguraian '%cab#(ar) organic compounds sebatian organik
127*> /<B
8.* Understanding car#ohydrates
Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! elements in car#ohydrates% #! types of car#ohydrates% i.e. monosaccharides% disaccharides and polysaccharides% using e)amples% c! the formation and
A student is a#le to ? state the elements in car#ohydrates% ? state the types of car#ohydrates% ? e)plain the formation and #rea(down of disaccharides and
#rea(down of disaccharides% such as maltose% sucrose and lactose% d! the formation and #rea(down of polysaccharides% such as starch% glycogen and cellulose. Conduct an acti$ity to differentiate #etween reducing and nonreducing sugars. *87*? /<B 8.8 Understanding proteins Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! elements in protein% such as car#on% hydrogen% o)ygen% sulphur% nitrogen and phosphorus% #! dipeptides and polypeptides% c! the formation and #rea(down of dipeptides and polypeptides% d! essential amino acids and nonessential amino acids. Use charts to illustrate the $arious protein structures% i.e. primary% secondary% tertiary and 'uaternary.
polysaccharides.
reducing sugar gula penurun non7reducing sugar gula bukan penurun
A student is a#le to ? state the elements in proteins% ? state the $arious structures of proteins% ? e)plain the formation and #rea(down of dipeptides and polypeptides% ? e)plain the meaning of essential amino acids and non7 essential amino acids. A detailed molecular structure is not re'uired. A #rief account of condensation and hydrolysis reactions is re'uired.
*72 @AC
8.A Understanding lipids
Bist the main types of lipids a! fat% #! oil% c! wa)% d! phospholipids% e! steroids% such as cholesterol% testosterone% oestrogen% and progesterone. Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! elements in lipids% #! components of fats and oils% c! formation and #rea(down of fats and oils. Use a graphic organiser to compare saturated fats and unsaturated fats.
A student is a#le to ? state the elements in lipids% ? state the main types of lipids% A detailed molecular structure is not re'uired.
? state the components of fats and oils. ? e)plain the formation and #rea(down of fats and oils% ? compare and contrast saturated fats and unsaturated fats.
A #rief account of condensation and hydrolysis reactions is re'uired.
saturated fats lemak tepu unsaturated fats lemak tak tepu
971* @AC
8.5 Understanding en.ymes
,iscuss on the following a! what en.ymes are% #! en.yme re'uirement in the li$ing process% c! general characteristics of en.yme% d! naming of en.yme #ased on the su#strate% e! sites of en.yme synthesis% f! intracellular and e)tracellular en.ymes and e)amples.
A student is a#le to ? state what en.ymes are% ? e)plain why en.ymes are needed in life processes% ? list the general characteristics of en.ymes% ? relate the name of en.yme to su#strate% ? state sites where en.ymes are synthesised% ? state the meaning of
intracellular
Conduct a role7play acti$ity to show the in$ol$ement of ri#osomes% endoplasmic reticulum% and 5olgi #ody in the production of e)tracellular en.yme. Conduct e)periments to study the effects of p: and temperature on the acti$ities of amylase and pepsin. ,iscuss the effects of en.yme concentration and su#strate concentration on en.yme acti$ity. ,iscuss the mechanism of en.yme action using the Cloc( and (ey hypothesis. ,iscuss and correlate p:% temperature% en.yme concentration and su#strate concentration on en.yme acti$ity using the Cloc( and (ey C hypothesis. 5ather information from the Dnternet and other sources on the uses of en.ymes in a! daily life% e.g. tenderising meat #! industry e.g. food processing and detergent manufacturing.
intracellular en.ymes and e)tracellular en.ymes% ? e)plain the in$ol$ement of specific organelles in the production of e)tracellular en.ymes%
en.yme enzim intrasel e)tracellular en.yme enzim luar sel
? e)plain the effects of p:% temperature% en.yme concentration% and su#strate concentration on en.yme acti$ity% ? e)plain the mechanism of en.yme action% ? relate the mechanism of en.yme action with p:% temperature% en.yme concentration and su#strate concentration% ? e)plain the uses of en.ymes in daily life and industry using e)amples.
concentration 7 kepekatan su#strates substrat
971* @A-
8.2 -ealising the importance of the chemical composition in cells
Conduct a role play or story telling session to predict the conse'uences of deficiency in one of the chemical components in the cell.
? predict the conse'uences of deficiency in car#ohydrates% protein% lipids or en.ymes in the cell.
deficiency 7 kekurangan
LEARNING AREA: ..0 CELL DI'I"ION DATE *87*? @ALearning Objecti e! A.1 Understanding mitosis "#gge!te$ Learning Acti itie! Conduct a #rainstorming session on the following a! the need for production of new cells in organisms% #! the need for production of new cells identical to parent cells. ,eri$e the meaning and significance of mitosis from the #rainstorming session. &tudy charts to identify the $arious phases of the cell cycle. @a(e models to demonstrate mitosis and cyto(inesis. 3repare and o#ser$e a slide of onion root tip to identify different stages of mitosis. &tudy the process of Learning O#tc%&e! A student is a#le to ? state the necessity for the production of new cells in organisms% ? e)plain the necessity for the production of new cells identical to parent cells% ? state the significance of mitosis% ? identify the phases in the cell cycle% ? e)plain the process of mitosis and cyto(inesis% ? arrange the $arious stages of mitosis in the correct se'uence% identical 7 seiras significance 7 kepentingan N%te! '%cab#(ar)
controlled and uncontrolled mitosis and cyto(inesis through simulation% computerised animation or $ideo. Conduct a #rainstorming session to come up with e)amples on mitosis as a controlled process for the perpetuity of li$ing things such as regeneration of li.ard tail% certain plant parts and the healing of s(in. 5ather information on diseases% including cancer or tumour% caused #y uncontrolled mitosis in li$ing things. @a(e a trip to a research institute to study tissue culture techni'ue. Conduct a de#ate or forum on cloning issues. 8>78 A3A.* Understanding meiosis ,iscuss the following a! trait inheritance in offsprings% #! the need to maintain diploid chromosomal num#er from one generation to another% c! the need to produce
? compare and contrast mitosis and cyto(inesis in animal cell and plant cell% 0echni'ues of Cloning include tissue culture. controlled mitosis mitosis terkawal regeneration7 pertumbuhan / penjanaan semula uncontrolled mitosis mitosis luar kawal
? e)plain the importance of controlled mitosis% ? e)plain the effects of uncontrolled mitosis in li$ing things% ? descri#e the application of (nowledge on mitosis in cloning% ? e)plain the ad$antages and disad$antages of cloning.
A student is a#le to ? state the necessity of trait inheritance in offspring for continuation of life% ? state the necessity to maintain diploid chromosomal num#er trait inheritance pewarisan ciri offspring anak
gametes with haploid num#er of chromosomes% d! the uni'ueness of diploid num#er of chromosomes in organisms% e! the significance of meiosis% f! the type of cell that undergoes meiosis in human% animals and plants. +#ser$e the process of meiosis through computerised animation% photomicrograph% prepared slides% or $ideo. Use simulation acti$ities to show changes in chromosome #eha$iour during meiosis D and meiosis DD Use graphic organisers to compare and contrast a! @eiosis D and meiosis DD% #! @eiosis and mitosis. 271> A3A.8 Appreciating the mo$ement of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. a! conduct a role7play% #! a$oid radioacti$e and carcinogenic su#stances.
from generation to generation% ? state the necessity for production of haploid gametes in se)ual reproduction% ? state the significance of meiosis% ? identify the type of cell that undergoes meiosis% ? e)plain the process of meiosis% ? arrange the $arious stages of meiosis in the correct order% ? compare and contrast meiosis D and meiosis DD% ? compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis.
A detailed e)planation of 3rophase 1 is not re'uired.
A student is a#le to ? descri#e what will happen when the mo$ement of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis do not occur in an orderly manner% ? (now and a$oid things that
may#e harmful. THEME: IN'E"TIGATING THE ,HY"IOLOGY O* LI'ING THING" LEARNING AREA: 1.0 NUTRITION DATE 271> A3Learning Objecti e! 1.1 Understanding types of nutrition "#gge!te$ Learning Acti itie! +#ser$e and identify types of nutrition in $arious organisms. ,iscuss autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition with reference to chemosynthesis% photosynthesis% holo.oic nutrition% saprophytism% and parasitism. Use a graphic organiser to show the types of nutrition. Conduct an acti$ity to classify $arious organisms according to types of nutrition. 1871? A31.* Applying the concept of #alanced diet Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! re'uirements of a #alanced diet% #! factors affecting the daily energy re'uirement such as age% se)% #ody weight and occupation. Conduct an acti$ity to A student is a#le to ? e)plain the necessity for a #alanced diet% ? e)plain the factors affecting the daily energy re'uirement of the human #ody% #alanced diet gizi seimbang Learning O#tc%&e! A student is a#le to ? state the types of nutrition% ? e)plain autotrophic nutrition% ? e)plain heterotrophic nutrition% ? classify organisms according to the types of nutrition. N%te! '%cab#(ar)
The unit for energy used is Joule.
determine the energy $alue in food samples. ,esign acti$ities to test for the presence of starch% reducing sugar% non7 reducing sugar% protein and lipid in food samples. Conduct an e)periment to determine the =itamin C content in $arious fruit ;uices. @atch the $itamins with their sources% functions and effects of deficiency. @atch the minerals with their sources% functions and effects of deficiency. ,iscuss the sources% functions and deficiency of roughage. ,iscuss the sources and functions of water in the #ody. Carry out a group discussion to formulate and ;ustify an appropriate diet menu #ased on a nutrient chart for the following target groups a! pregnant mothers%
? determine the energy $alue in food samples% ? determine the nutrient content in different food samples%
? e)plain the functions and sources of $itamins in a diet to maintain health% ? e)plain the functions and sources of minerals in a diet to maintain health% ? e)plain the functions and sources of roughage 9 dietary fi#re in a diet% ? e)plain the functions of water in the #ody% ? ;ustify the selection of an appropriate #alanced diet for a target group.
roughage 9 dietary fi#re pelawas target group kumpulan sasaran
#! infants% c! children% d! teenagers% e! athletes% f! people with specific diseases% g! the aged% h! $egetarians. *>7*A A31.8 Understanding malnutrition Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! meaning of malnutrition% #! effects of deficiency in proteins% $itamins% minerals% on health% c! effects of e)cessi$e inta(e of car#ohydrates% lipids% $itamins and minerals on health% d! a diet low in saturated fats help reduce the chance of contracting cardio$ascular disease% e! ways to reduce the ris( of high #lood pressure% dia#etes mellitus and osteoporosis. ,iscuss the following a! glucose% amino acids and lipids are always re'uired #y the cell to carry out meta#olic processes% #! comple) su#stances li(e car#ohydrates% proteins and A student is a#le to ? e)plain what malnutrition is% ? e)plain the effects of malnutrition using e)amples% ? descri#e ways to reduce the chance of contracting certain health pro#lems due to one1s diet% ? descri#e ways to reduce the effects of certain health pro#lems.
*?71 @AE
1.A Analysing food digestion
A student is a#le to ? state the su#stances re'uired #y the cell to carry out meta#olic processes% ? list the comple) su#stances that need to #e digested% ? e)plain the necessity for
meta#olic processes proses metabolik
lipids need to #e digested. ,raw and la#el parts of the human digesti$e system. ,iscuss the functions of digesti$e ;uices% including sali$a% gastric ;uice% pancreatic ;uice% intestinal ;uice and other su#stances% i.e. hydrochloric acid and #ile that aid the process of digestion. ,iscuss the digestion of car#ohydrates% proteins and fats on the following aspects a! specific location of each digesti$e process% #! chewing of food% c! mo$ement of food% d! glands in$ol$ed% e! digesti$e en.ymes% f! suita#le p: for each en.yme action% g! su#strates and products. Ddentify the parts of digesti$e system in ruminants and rodents. ,iscuss the digestion of cellulose in ruminants 4eg. cow! and rodents 4ra##it!. Use graphic organiser to
digestion of comple) su#stances% ? draw and la#el the human digesti$e system% ? state the digesti$e ;uices and su#stances that aid in the process of digestion in human% ? descri#e the functions of the digesti$e ;uices and su#stances% ? e)plain the digestion of car#ohydrates% proteins and lipids in the human #ody% ? identify parts of digesti$e system in ruminants and rodents in$ol$ed in the digestion of cellulose% ? descri#e the digestion of cellulose in ruminants and rodents% ? compare and contrast the digesti$e process in humans% ruminants and rodents% digesti$e ;uices jus pencernaan #ile 7 hempedu
compare and contrast the process of cellulose digestion in humans% ruminants and rodents. 3lan and conduct e)periments to study the en.yme actions on starch and protein food samples. Collect information and discuss pro#lems related to food digestion #! incomplete digestion of food% c! #ile stones pre$enting the flow of #ile% reduced production of specific digesti$e en.yme. A7F @AE 1.5 Understanding the processes of a#sorption and assimilation of digested food <)amine models or diagrams of the digesti$e system and cross7section of the small intestine. 6ith reference to the models or diagrams discuss the following a! adaptation of the small intestine% #! a#sorption process of amino acids% glucose% fatty acids% glycerol% $itamins and minerals in the $illus. Carry out an acti$ity to study the mo$ement of ? design e)periments to study the digestion of starch and proteins in food samples% ? descri#e pro#lems related to food digestion.
A student is a#le to ? identify the parts of the digesti$e system in$ol$ed in a#sorption of digested food% ? e)plain the adapti$e characteristic of the digesti$e system related to a#sorption% ? draw and la#el the structure of a $illus% ? e)plain the process of a#sorption in the $illus%
adapti$e characteristic ciri-ciri penyesuaian a#sorption 7 penyerapan small intestine usus kecil
su#stances through the =is(ing tu#ing. Based on the a#o$e acti$ity correlate the mo$ement of food su#stances through the =is(ing tu#ing with nutrient a#sorption in the small intestine. ,iscuss the a#sorption of water and minerals in the colon. Using diagrams% charts or computerised animation discuss a! the transport of amino acids% glucose% water solu#le $itamins and minerals #y the circulatory system i! from the small intestine to the li$er through the hepatic portal $ein% ii! from the li$er to the #ody cells% #! transport of lipids and fat solu#le $itamins. @a(e a schematic diagram to show the transport of nutrients from the intestine to the #ody cells. ,iscuss the following
transport pengangkutan circulatory system sistem peredaran ? ma(e an analogy on the process of a#sorption in the small intestine% ? e)plain the a#sorption of water and minerals in the colon% ? descri#e the transport of nutrients #y the circulatory system for assimilation% li$er hati assimilation 7 assimilasi
? e)plain the main functions of the li$er% ? descri#e the process of
functions of the li$er a! storage of nutrients% #! processing the products of digestion i.e. e)cess glucose and amino acids% c! deto)ification. ,iscuss the process of assimilation #y the #ody cells. 11715 @AE 1.2 Understanding the formation of faeces and defecation 6ith reference to diagrams% charts or model of the digesti$e system% identify the colon and rectum. Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! the formation of faeces% #! the role of microorganisms in the colon% c! effects of anti#iotics on the microorganisms in the colon% d! what defecation is% e! the importance of defecation% f! importance of high fi#re diets% g! defecation related pro#lems%i.e. constipation% colon cancer and
assimilation.
A student is a#le to ? identify the part of the digesti$e system where the formation of faeces ta(es place% ? descri#e the formation of faeces% ? e)plain the role of microorganisms in the colon and the effect of anti#iotics on them% ? e)plain what defecation is% ? e)plain the importance of defecation% ? e)plain the importance of high fi#re diets% ? descri#e the pro#lems related to defecation.
defecation penyahtinjaan faeces tinja constipation sembelit haemorrhoids 7 buasir
haemorrhoids. 1?7*8 @AE 1.? <$aluating eating ha#its Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! relationship #etween eating ha#its and health pro#lems such as 4i! gastritis% 4ii! o#esity% 4iii! anore)ia ner$osa% 4i$! #ulimia% #! e$aluate the nutrient contents of food #ased on food la#els or ad$ertisments% c! e$aluate the eating ha#its of classmates. Conduct an acti$ity to predict the effects of a defecti$e digesti$e system. Conduct a discussion on ways to ta(e care of the digesti$e system% such as good eating ha#its% a$oid ;un( food% try to cut down on sweet and fatty foods. Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! the elements re'uired #y plants% #! classify the elements A student is a#le to ? relate eating ha#its with health pro#lems% ? e$aluate critically whether a particular eating ha#it is good or #ad. <ating ha#its in$ol$e the fre'uency and time of eating and the type of food consumed. eating ha#its tabiat makan health pro#lems masalah kesihatan
1?7*8 @AE
1.F -ealising the importance of a healthy digesti$e system
A student is a#le to ? predict the effects of a defecti$e digesti$e system on health% ? ta(e care of the digesti$e system for one1s well7#eing. defecti$e digesti$e system sistem pencernaan yang tidak berfungsi dengan baik
*57*F @AE
1.9 Understanding the importance of macronutrients and
A student is a#le to ? list elements re'uired #y plants% ? classify elements re'uired #y elements unsurunsur
micronutrients in plants
re'uired #y plants #ased on the amount needed 4i! macronutrients consisting of car#on% hydrogen% o)ygen% nitrogen% phosphorus% potassium% calcium% magnesium and sulphur% 4ii! micronutrients consisting of #oron% moly#denum% .inc% manganese% copper and ferum. 3lan and conduct an e)periment on plants to study the effects of macronutrient deficiency i.e. nitrogen% phosphorus% potassium% calcium% magnesium and sulphur. ,iscuss and correlate the effects of macronutrient deficiency with the function of the macronutrients #ased on the results of the e)periment. Collect and interpret data from $arious sources such as the Dnternet on the function of each macronutrient in plants.
plants #ased on the amount needed% ? design an e)periment to study the effects of macronutrient deficiency in plants% ? relate the effects of macronutrient deficiency with the function of macronutrients%
? e)plain the function of each macronutrient in plants% ? state the function of micronutrients in plants%
,iscuss the function of mirconutrients and effects of micronutrient deficiency in plants. 15719 JUN< 1.1> Understanding photosynthesis &tudents read a#out the disco$ery of photosynthesis and e)tract important facts from it. &tudy a cross7sectional model of a leaf. ,raw and la#el it. ,iscuss the following a! functions of the parts of a leaf% #! adaptation of the leaf for optimal photosynthesis. Carry out an acti$ity to in$estigate the adaptation of plants such as hi#iscus% water lily% Hydrilla and cactus with respect to a! distri#ution of stomata% #! distri#ution of chloroplasts. **7*2 JUN< 1.11 Understanding the mechanism of photosynthesis 6ith reference to the structure of chloroplast discuss the light and dar( reactions of photosynthesis with respect to
? state the effects of micronutrient deficiency in plants. A student is a#le to ? descri#e the de$elopment that leads to the disco$ery of photosynthesis% ? state the su#stances re'uired for photosynthesis% ? state the su#stances produced from photosynthesis% ? draw and la#el the cross7 section of a leaf% ? state the function of each part of the leaf with respect to photosynthesis% ? e)plain leaf adaptation to optimise photosynthesis% ? e)plain how plants from different ha#itats are adapted to carry out photosynthesis.
adaptation 7 penyesuaian
A student is a#le to ? identify the parts of chloroplast related to photosynthesis% ,etailed structure of chloroplast is
a! su#stances re'uired. #! location of reaction. c! products of reaction. ,raw a simple schematic diagram of the light and dar( reactions in photosynthesis. ,iscuss the following a! compare and contrast the light reaction and dar( reaction in photosynthesis% #! correlate light reaction with dar( reaction in photosynthesis. 6rite an e'uation to represent the o$erall process of photosynthesis. *978 JUBE 1.1* &ynthesising factors affecting photosynthesis Conduct a #rainstorming session to identify the factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis i.e. concentration of car#on dio)ide% light intensity and temperature. 3lan and carry out an e)periment to study the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis. Carry out small group discussion on the effects of
not re'uired. ? e)plain the light reaction of photosynthesis% ? e)plain the dar( reaction of photosynthesis% ? compare and contrast light reaction and dar( reaction in photosynthesis% ? relate light reaction with dar( reaction in photosynthesis% ? write an e'uation to represent the process of photosynthesis. ,etailed pathways for light and dar( reactions are not re'uired.
light reaction tindakbalas cahaya dar( reaction tindakbalas gelap
A student is a#le to ? identify the factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis% ? design an e)periment to in$estigate the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis% ? identify the factor that limits the rate of photosynthesis at different light intensity% ? e)plain the effects of temperature and concentration of car#on dio)ide on the rate of
light intensity keamatan cahaya limiting factor7 faktor
light intensity% temperature and concentration of car#on dio)ide on the rate of photosynthesis. 3lan a strategy #ased on factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis to ensure crop production throughout the year in countries with four seasons. 271> JUBE 1.18 3ractising a caring attitude towards plants
photosynthesis% ? e)plain the difference in the rate of photosynthesis in plants throughout the day #ased on the changes in light intensity and temperature% ? identify some ways to meet the need of increasing the producti$ity of crops #ased on factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis.
penghad crops 7 tanaman
Compose a poem or lyric of A student is a#le to a song to show appreciation of the role of ? tell why we need to ta(e photosynthesis in ensuring good care of plants% the perpetuation of life. Conduct a planting pro;ect in the science resource garden or school compound. ? identify cases of mishandling or destruction of plants.
271> JUBE
1.1A Understanding the technology used in food production
Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! the 'uantity of food needed for the present and future population of the country% #! the need for impro$ing the 'uality and 'uantity of food for the country in line with the national food production policy% c! effort #y $arious
A student is a#le to ? e)plain the need for impro$ing the 'uality and 'uantity of food% ? e)plain the effort to di$ersify food production% ? e)plain ways to impro$e the 'uality and 'uantity of food production in the country. impro$ing 7 menambahbaikka n di$ersify 7 mempelbagaikan
agencies to di$ersify food production% d! methods used to impro$e the 'uality and 'uantity of food production through the following 4i! direct seeding for rice% 4ii! hydroponics and aeroponics% 4iii! #reeding% 4i$! tissue culture% 4$! genetic engineering 4$i! soil management% 4$ii! #iological control. Conduct a field trip to rele$ant agencies such as the Dnstitute of Agricultural -esearch and ,e$elopment of @alaysia 4@A-,D!% Agriculture ,epartment and /ishery ,epartment. Carry out a $egeta#le planting pro;ect. 1871? JUBE 1.15 <$aluating the technological de$elopment in food processing ,iscuss the need for food processing #ased on the following a! o$ercoming the factors causing spoilage of food such as the action of microorganisms and o)idation% #! e)tending the lifespan of food% A student is a#le to ? e)plain the necessity for food processing% ? descri#e the de$elopment of food processing technology% food processing pemprosesan makanan de$elopment 7 perkembangan food spoilage kerosakan
c! a$oiding food wastage% d! di$ersifying the uses of food li(e mil( and dairy products% e! ensuring sufficient food supply. 3repare a portfolio on the technological de$elopment of food processing from the early days till the present. Correlate the following food processing methods with factors causing food spoilage i. coo(ing% ii. using salt% sugar and $inegar% iii. fermentation process% i$. drying% $. pasteuri.ation% $i. canning% $ii. refrigeration. Conduct a forum entitled G0he effects of processed food on health.H ? relate food processing methods with factors causing food spoilage% ? assess the methods of food processing to ;ustify the choice of consuming certain processed food.
makanan
LEARNING AREA: +.0 RE",IRATION DATE *>7*A JUBE Learning Objecti e! *.1 Understanding the respiratory process in energy production "#gge!te$ Learning Acti itie! ,iscuss the following a! li$ing processes re'uire energy% #! the main su#strate for respiration% that is glucose% is o#tained from the following 4i! the digestion of car#ohydrates in human and animals% 4ii! the process of photosynthesis in plants. Carry out a discussion on the types of respiration. Carry out an acti$ity to show aero#ic respiration. ,iscuss the energy production in aero#ic respiration. Conduct an e)periment to in$estigate anaero#ic respiration in yeast. ,iscuss the following a! condition leading to anaero#ic respiration in cells% #! the process of anaero#ic respiration in human ? e)plain the process of anaero#ic respiration in human muscles% ? write the chemical e'uations Learning O#tc%&e! A student is a#le to ? state that all li$ing processes re'uire energy% ? identify the main su#strate for producing energy% ? state the two types of respiration% ? e)plain what cell respiration is% ? e)plain the energy production from glucose during the process of aero#ic respiration% ? state the conditions leading to anaero#ic respiration in cells% ? e)plain the process of anaero#ic respiration in yeast% li$ing processes prosesproses kehidupan N%te! '%cab#(ar)
muscles. Use a graphic organiser to compare and contrast aero#ic respiration with anaero#ic respiration. *>7*A JUBE *.* Analysing the respiratory structures and Breathing mechanisms in human and animal +#ser$e graphics and li$e specimens and discuss the respiratory structures in human and other organisms including proto.oa% insects% fish and amphi#ians. Conduct an acti$ity to compare the total surface area of a flat card with a corrugated card% and correlate the increase in total surface area with the modified surface structure. ,iscuss the relationship #etween the total surface area of the respiratory structures and the efficiency of gaseous e)change in $arious organisms. +#ser$e the respiratory structures to generalise the characteristics of the respiratory surfaces in human and other organisms such as proto.oa% insects% fish and amphi#ians.
for aero#ic and anaero#ic respiration% ? compare and contrast aero#ic respiration with anaero#ic respiration. A student is a#le to ? state the respiratory structures in human and some animals% ? ma(e an inference on the $arious adaptations of the respiratory structures% respiratory structures struktur pernafasan corrugated card kad lipatan beralun adaptations penyesuaian
? descri#e the characteristics of respiratory surfaces in human and other organisms%
respiratory surfaces permukaan respirasi
Construct or use a model that can #e manipulated to e)plain the #reathing mechanism in human. ,iscuss the #reathing mechanism of other organisms such as proto.oa% insects% fish and amphi#ians. Use graphic organiser to compare and contrast the human respiratory system with that of other organisms. *?781 JUBE *.8 Understanding the concept of gaseous e)change across the respiratory surfaces and transport of gases in human Using a diagram% discuss the process of gaseous e)change across the surface of the al$eolus and #lood capillaries in the lungs in relation to a! the difference in partial pressure of respiratory gases in the air of the al$eolus and #lood capillaries in the lungs% i.e 4i! partial pressure of o)ygen is higher in the air of the al$eolus compared to the partial pressure of o)ygen in the #lood capillaries% 4ii! partial pressure of car#on dio)ide is lower in the air of the al$eolus compared to the partial pressure of
? descri#e the #reathing mechanism in human and other organisms%
#reathing mechanism mekanisma pernafasan
? compare and contrast the human respiratory system with that of other organisms.
A student is a#le to ? descri#e the process of gaseous e)change across the surface of the al$eolus and #lood capillaries in the lungs%
gaseous e)change pertukaran gas #lood capillaries kapilari darah partial pressure tekanan separa
car#on dio)ide in the #lood capillaries. #! the difference in partial pressure of o)ygen and car#on dio)ide in the #lood entering the al$eolus with the #lood lea$ing the al$eolus i.e. 4i! partial pressure of o)ygen is lower in the #lood entering the al$eolus compared to the partial pressure of o)ygen in the #lood lea$ing the al$eolus. 4ii! partial pressure of car#on dio)ide is higher in the #lood entering the al$eolus compared to the partial pressure of car#on dio)ide in the #lood lea$ing the al$eolus. ,iscuss the following a! the transport of respiratory gases in human% #! the e)change of respiratory gases #etween the #lood and #ody cells. Use schematic diagram to e)plain the e)change and transport of respiratory gases in human. Conduct an e)periment to in$estigate the differences ? e)plain the transport of respiratory gases% ? e)plain the process of gaseous e)change #etween the #lood and #ody cells% ? distinguish the composition of inhaled and e)haled air. Caution :andle the following solutions with care Al(aline pyrogallate and concentrated potassium hydro)ide. inhaled air udara sedutan e)haled air udara hembusan
#etween inhaled and e)haled air in terms of o)ygen% car#on dio)ide and heat content. &tudy the process of respiratory gas e)change and transport using simulations and computeri.ed animations. 87? AU5 *.A Understanding the regulatory mechanism in respiration Conduct an e)periment to study the effects of a $igorous e)ercise on the rate of respiration and rate of heart #eat. Conduct a discussion on the following a! correlate the rate of respiration with the o)ygen and car#on dio)ide contents in the #ody% #! regulatory mechanism of o)ygen and car#on dio)ide contents in the #ody. Conduct a discussion on human respiratory response% rate of respiration and rate of heart #eat in different situations a! $igorous acti$ities such as swimming% running% aero#ic e)ercise% mountain clim#ing and playing #adminton% #! rela)ing% A student is a#le to ? descri#e the change in rate of respiration after completing a $igorous e)ercise% $igorous e)ercise senaman cergas
? correlate the rate of respiration with the o)ygen and car#on dio)ide content in the #ody% ? e)plain the regulatory mechanism of o)ygen and car#on dio)ide content in the #ody% ? e)plain the human respiratory response and rate of respiration in different situations% ? correlate the rate of respiration with the rate of heart #eat.
regulatory mechanism mekanisma kawalatur response gerak balas rate of heart #eat kadar denyutan jantung
87? AU5
*.5 -ealising the importance of maintaining a healthy respiratory system
c! fear. ,iscuss the ha#its to #e culti$ated or a$oided to ensure the efficient function of the respiratory organs. Conduct an e)periment to show the effects of cigarette smo(e on white cotton wool and draw an analogy #etween the lungs and the white cotton wool. &how photographs of damaged lungs 4cancer! due to smo(ing.
A student is a#le to ? care and maintain efficient function of the respiratory organs. efficient berkesan
1>71A AU5
*.2 Understanding respiration in plants
,iscuss the following a! the lower energy re'uirement of plants compared to animals for li$ing processes% #! the inta(e of o)ygen #y plants for respiration. ,raw a diagram to show the inta(e of o)ygen in plants. ,iscuss the anaero#ic respiration carried out #y rice plants in a paddy field or other plants in certain situations li(e flooding. Use a graphic organiser to compare the process of
A student is a#le to ? descri#e the energy re'uirement in plants% ? e)plain the inta(e of o)ygen for respiration% ? e)plain aero#ic respiration in plants% ? e)plain anaero#ic respiration in plants under certain conditions% A diagram of the cross7 section of a leaf is re'uired. energy re'uirement keperluan tenaga
? compare and contrast the
respiration with the process of photosynthesis in plants. ,iscuss the following a! meaning of compensation point% #! correlate light intensity with compensation point from graph. =isualise and descri#e the effect on li$ing things when the rate of photosynthesis and rate of respiration remains at compensation point.
process of photosynthesis and respiration% compensation point titik pampasan light intensity keamatan cahaya
? e)plain what compensation point is% ? relate light intensity with the attainment of compensation point% ? predict the situation when the rate of photosynthesis and rate of respiration remains at compensation point.
THEME: IN'E"TIGATING THE RELATION"HI, BET/EEN LI'ING THING" AND THE EN'IRONMENT LEARNING AREA: 1.0 DYNAMIC ECO"Y"TEM DATE 1?7*1 AU5 Learning Objecti e! 1.1 Understanding the a#iotic and #iotic components of the en$ironment "#gge!te$ Learning Acti itie! Conduct a field study to a! identify the a#iotic components including p:% temperature% light intensity% humidity% topography% and the microclimate of an ecosystem% #! identify the #iotic components of an ecosystem% c! in$estigate the feeding relationships of the #iotic Learning O#tc%&e! A student is a#le to ? identify the a#iotic components of an ecosystem% ? identify the #iotic components of an ecosystem% ? classify #iotic components into trophic le$els% N%te! <mphasis is on field study for the students to reinforce their understanding in this area. '%cab#(ar) a#iotic components komponen abiotik #iotic components komponen biotik trophic le$els aras trof
components to construct the food chains and food we#s% and classify the #iotic components into trophic le$els% d! in$estigate the interaction #etween #iotic components as follows 4i! sym#iosis among plants and animals encompassing the following 7 commensalism% 7 parasitism% 7 mutualism% 4ii! saprophytism% 4iii! predator 7 prey interaction. 4e! in$estigate the interaction #etween #iotic components in relation to competition% which are 4i! intraspecific competition% 4ii! interspecific competition. Conduct an e)periment to study the intraspecific competition and interspecific competition of plants% e.g. mai.e and rice. Collect and interpret data to study intraspecific competition and interspecific competition
? e)plain the interactions #etween #iotic components in relation to feeding% using e)amples% ? e)plain the interaction #etween #iotic components in relation to competition% using e)amples.
predator pemangsa prey 7 mangsa competition 7 persaingan
in$ol$ing aramecium% for e)ample aramecium aurelia and aramecium caudatum. 817A &<30 1.* Understanding the processes of colonisation and succession in an ecosystem Conduct a field study on an ecosystem i.e. a mangro$e swamp or a pond to a! identify the niche% ha#itat% community and population% #! in$estigate the process of colonisation% c! in$estigate the process of succession% d! identify pioneer species% successor species% dominant species and clima) community% e! identify the adapti$e characteristics of pioneer species and su#se'uent species in the ha#itat for the processes of colonisation and succession. &tudents present their findings or ma(e a folio. &tudy the processes of coloni.ation and succession through $ideo% computer software and printed material. ,iscuss and correlate the a#iotic component and A student is a#le to ? state what an ecosystem is% ? identify the niche% ha#itat% community and population of an ecosystem% ? e)plain the process of colonisation% ? e)plain the process of succession% ? identify the pioneer species in an ecosystem% ? identify the successors in an ecosystem% ? identify the dominant species in an ecosystem% ? identify the adapti$e characteristics of pioneer species% ? identify the adapti$e characteristics of successors% ? e)plain the changes in ha#itat caused #y pioneer species% ? e)plain the changes in ha#itat caused #y successors at e$ery le$el of succession until a clima) community is reached% mangro$e swamp paya bakau colonisation pengkolonian succession sesaran successors spesies penyesar adapti$e characteristics ciri penyesuaian pioneer spesies perintis clima) community7 komuniti klimaks
#iotic component during the processes of colonisation and succession in an ecosystem.
? relate the a#iotic components with the #iotic components in an ecosystem during the processes of colonisation and succession. A student is a#le to ? identify the appropriate sampling techni'ue to study the population si.e of an organism% ? estimate the population si.e of an organism in a ha#itat% ? determine the distri#ution of organisms in a ha#itat #ased on the density% fre'uency and percentage co$erage of the species% ? correlate the change in population distri#ution of an organism with the changes in each of the a#iotic factors% ? design an e)periment to in$estigate the effect of a change in any one of the a#iotic factors on the population sampling techni'ue teknik persampelan
?711 &<30
1.8 &ynthesising ideas on population ecology
,iscuss the appropriate sampling techni'ues to study the population si.e of an organism. Conduct a field study or use an appropriate analogy to a! estimate the population si.e of animals such as garden snails and wood lice% #! in$estigate the distri#ution of plants using the 'uadrat sampling techni'ue. Based on the a#o$e study discuss the distri#ution of an organism in a ha#itat. ,iscuss and correlate the change in population distri#ution of an organism with the changes in each of the a#iotic factors. 3lan and conduct an e)periment to study the relationship of population distri#ution of an organism
distri#ution taburan density kepadatan fre'uency kekerapan percentage co$erage peratus litupan growth rate kadar pertumbuhan
with changes in any one of the a#iotic factors such as p:% temperature% light intensity and humidity. &uggested organisms leurococcus! "emna 1A71F &<30 1.A Understanding the concept of #iodi$ersity ,iscuss the following a! meaning of #iodi$ersity% #! need for the classification system of organisms. 5ather information on the following a! the fi$e (ingdoms in the classification of organisms% which are @onera% 3rotista% /ungi% 3lantae and Animalia% #! main characteristics of organisms in each (ingdom% c! e)amples of organisms in each (ingdom% ,iscuss the following a! the hierarchy in the classification of organisms from (ingdom to species% #! the method of naming a num#er of $erte#rates and local flowering plants% using the Binnaeus #inomial system% c! the importance of #iodi$ersity.
growth rate of an organism.
A student is a#le to ? e)plain the meaning of #iodi$ersity% ? e)plain the need for classification of organisms% ? state the fi$e (ingdoms used in the classification of organisms% ? identify the main characteristics of organisms in each (ingdom% ? list e)amples of organisms in each (ingdom% ? state the hierarchy in the classification of organisms% using e)amples% ? e)plain through e)amples% the method of naming organisms using the Binnaeus #inomial system%
#iodi$ersity biokepelbagaia n classification pengelasan
Conduct a field trip to create awareness of #iodi$ersity of an ecosystem. *17*5 &<30 1.5 Understanding the impact of microorganisms on life Using charts% slides and photomicrographs% identify and list $arious types of microorganisms i.e. proto.oa% algae% fungi% #acteria and $irus. Conduct an e)periment to study the effects of temperature% p:% light and nutrients on the acti$ity of microorganisms e.g. #acillus subtilis or yeast. 5ather information and discuss the role of useful microorganisms in the following a! decomposition% #! nitrogen cycle% c! alimentary canal of termite% d! digesti$e system in human. 5ather information and discuss the effects of harmful micro 7organisms a! causing diseases% #! spoilage of food and
? e)plain the importance of #iodi$ersity. A student is a#le to ? classify $arious types of microorganisms #ased on their #asic characteristics% ? state the a#iotic components affecting the acti$ity of microorganisms% ? e)plain the effect of a change in each a#iotic component on the acti$ity of microorganisms% ? e)plain the role of useful microorganisms% ? e)plain the effect of harmful micro7organisms% A #rief account of the #asic characteristics of each type of microorganism s is re'uired.
decomposition 7 pereputan alimentary canal salur alimentari
su#stances. 5ather information and present the findings on the following a! pathogens% $ectors% symptoms% and methods in transmission of diseases such as malaria% dengue fe$er% cholera% ringworm% food poisoning% AD,&% hepatitis% and &A-&% #! methods to control pathogens including the use of anti#iotics% $accines% antiseptics and disinfectants. 5ather information and present the uses of microorganisms in #iotechnology% such as a! production of anti#iotics and $accines% #! cleaning of oil spills% c! waste treatment% d! food processing% e! production of #ioplastic% f! production of energy from #iomass. *17*5 &<30 1.2 Appreciating #iodi$ersity Conduct a forum to discuss the importance of preser$ation and conser$ation of #iodi$ersity.
? e)plain the meaning of pathogen% ? identify the pathogen% $ector and symptoms of one particular disease% ? e)plain how the disease spreads% ? descri#e the methods for controlling pathogen% ? e)plain the use of microorganisms in #iotechnology% using e)amples.
0he scientific names of pathogens and life cycle of $ectors are not re'uired.
pathogen 7 patogen transmission 7 pemindahan food poisoning keracunan makanan
oil spills tumpahan minyak waste treatment rawatan kumbahan
A student is a#le to ? ;ustify the importance of preser$ation and conser$ation of #iodi$ersity. preser$ation 7 pemeliharaan
Conduct an acti$ity to preser$e and conser$e $arious li$ing things around us. LEARNING AREA: +.0 ENDANGERED ECO"Y"TEM DATE *F7* +C0 Learning Objecti e! *.1 <$aluating :uman acti$ities that endanger an ecosystem "#gge!te$ Learning Acti itie! Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! human acti$ities that threaten the ecosystem% #! the impact of human acti$ities on the ecosystem% c! the effects of unplanned de$elopment and mismanagement of the ecosystem% such as i. soil erosion% ii. flash flood% iii. landslide% i$. eutrofication% $. water% air% thermal and noise pollution% $i. glo#al warming% $ii. o.one depletion% $iii. climatic change% i). e)tinction of li$ing things% ). deforestation%
? preser$e and conser$e $arious li$ing things around him9her.
conser$ation pemuliharaan
Learning O#tc%&e! A student is a#le to ? identify human acti$ities that threaten the ecosystem% ? e)plain the impact of human acti$ities on the ecosystem% ? e$aluate critically the effects of unplanned de$elopment and mismanagement of the ecosystem%
N%te!
'%cab#(ar) impact impak/kesan threaten 7 mengancam critically secara kritis unplanned tidak terancang mismanagement salah pengurusan de$elopment 7 pembangunan ecosystem ekosistem
? descri#e types of pollution
d! types of pollution and sources of pollution% e! effects of pollution on the following i. human health 4 diseases affecting the respiratory system% s(in pro#lems% con;uncti$itis% cancer and cholera!% ii. animal and plant ha#itats% iii. #uildings% i$. agriculture% $. climate. Conduct an e)periment to compare solid pollutants in the air of different en$ironments and ma(e an inference on the sources of pollution. Conduct an acti$ity to analyse data on air pollution inde) of some cities within and outside the country% and ma(e an inference on the sources of pollution. Conduct an acti$ity to analyse data on water pollution% such as Biochemical +)ygen ,emand 4B+,! $alue and content of hea$y metals in
and sources of pollution%
flash food banjir kilat landslide tanah runtuh glo#al warming pemanasan global o.one depletion penipisan ozon e)tinction kepupusan deforestation 7 penyahutanan pollution 7pencemaran Biochemical +)ygen ,emand keperluan oksigen biokimia
? e)plain the effects of pollution on li$ing things and the en$ironment% ? compare and contrast pollutants in the air from different en$ironments% ? state the sources of air pollution% ? interpret data on the le$el of air pollution in some cities% ? ma(e an inference on the sources of air pollution in some cities% ? interpret data on the le$el of water pollution in some ri$ers% ? ma(e an inference on the sources of water pollution in some ri$ers%
some ri$ers% and ma(e an inference on the sources of pollution. Conduct acti$ities to formulate a strategy to reduce the le$el of air and water pollution in a particular location #y a! analysing information on the population% such as the si.e of population% socio7 economic acti$ities% and le$el of air and water pollution% #! conducting an acti$ity to predict the le$el of air and water pollution at a particular location within the ne)t ten years% c! preparing an action plan consisting of a strategy to reduce the le$el of air and water pollution at that particular location within the ne)t ten years. 579 +C0 *.* Understanding the greenhouse effect and thinning of the o.one layer. Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! greenhouse effect% including its cause and effect% #! concentration of car#on dio)ide in the atmosphere and correlate it with glo#al ? predict the le$el of air and water pollution in a particular location within the ne)t ten years% ? suggest strategies to sol$e pro#lems related to air and water pollution in a particular location within the ne)t ten years.
A student is a#le to ? e)plain what greenhouse effect is% ? correlate the concentration of car#on dio)ide in the atmosphere with glo#al warming% ? e)plain the thinning of the o.one layer%
greenhouse effect kesan rumah hijau glo#al warming pemanasan
0he molecular
warming% c! o.one depletion% including its cause and effect% d! impact of o.one depletion and glo#al warming on the ecosystem. 579 +C0 *.8 -ealising the importance of proper management of de$elopment acti$ities and the ecosystem Conduct a de#ate on the need for de$elopment to impro$e the 'uality of life and to meet the re'uirements of an increasing population. ,iscuss the effects of an increase in population on the ecosystem. Carry out small group discussion on the following and present the findings a! implementation of laws% #! use of technology% c! education on the management of resources% including the reduce% reuse% and recycle of resources% d! preser$ation and conser$ation of soil% water% flora and fauna of forests and mangro$e swamps% e! practice of #iological
? e)plain the impact of thinning of the o.one layer and glo#al warming on the ecosystem.
structure of global chlorofluorocar#on and e'uations for chemical reactions are not re'uired.
A student is a#le to ? ;ustify the need for de$elopment% ? e)plain the effects of increase in population on the ecosystem% ? e)plain measures ta(en in the management of de$elopment acti$ities and the ecosystem to ensure a #alance of nature is maintained. #alance of nature keseimbangan alam maintain mengekalkan
? care for the ecosystem%
#iological control kawalan biologi
control% f! use of renewa#le energy% g! efficient use of energy. Conduct acti$ities to care for the following ecosystems in school and at home a! fish ponds% #! gardens. 3lan and conduct a programme related to the management of the ecosystem% for e)ample% G<n$ironment ,ayH. ? participate in acti$ities related to the management of the ecosystem.
renewa#le energy tenaga diperbaharui
You might also like
- Tugas Mingguan 2017Document1 pageTugas Mingguan 2017Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BIO-F5Document9 pagesChapter 1 BIO-F5adele30No ratings yet
- Menembak 2018Document1 pageMenembak 2018Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- Skema Pemarkahan Percubaan Bio k1 k2 - k3Document24 pagesSkema Pemarkahan Percubaan Bio k1 k2 - k3Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BIO-F5Document9 pagesChapter 1 BIO-F5adele30No ratings yet
- Kertas 1 GombakDocument30 pagesKertas 1 GombakRossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- SC Form 1Document1 pageSC Form 1Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 4 K1Document14 pagesBio Form 4 K1Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- IT Bio F5 Final Year Examination (BL)Document13 pagesIT Bio F5 Final Year Examination (BL)Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- RPT Science FRM 2Document12 pagesRPT Science FRM 2Jalil MonNo ratings yet
- Latihan Biologi Tingkatan 4 Dan 5Document12 pagesLatihan Biologi Tingkatan 4 Dan 5Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- Gantt 2011 f4Document4 pagesGantt 2011 f4Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- Latihan Biologi Tingkatan 4 Dan 5Document12 pagesLatihan Biologi Tingkatan 4 Dan 5Rossliza YaacobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BIO-F5Document9 pagesChapter 1 BIO-F5adele30No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Movement of Substances Across Plasma MembraneDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - Movement of Substances Across Plasma MembraneRossliza Yaacob100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- QuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1Document12 pagesQuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1subhrajitm47No ratings yet
- Manual Analizador Fluoruro HachDocument92 pagesManual Analizador Fluoruro HachAitor de IsusiNo ratings yet
- NAT Order of Operations 82Document39 pagesNAT Order of Operations 82Kike PadillaNo ratings yet
- Us Virgin Island WWWWDocument166 pagesUs Virgin Island WWWWErickvannNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Computer ScienceradNo ratings yet
- Photographing Shadow and Light by Joey L. - ExcerptDocument9 pagesPhotographing Shadow and Light by Joey L. - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group75% (4)
- GLF550 Normal ChecklistDocument5 pagesGLF550 Normal ChecklistPetar RadovićNo ratings yet
- Ujian Madrasah Kelas VIDocument6 pagesUjian Madrasah Kelas VIrahniez faurizkaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Interaction Diagrams: Interaction Diagrams Are Used To Model The Dynamic Aspects of A Software SystemDocument13 pages8.1 Interaction Diagrams: Interaction Diagrams Are Used To Model The Dynamic Aspects of A Software SystemSatish JadhaoNo ratings yet
- Obstetrical Hemorrhage: Reynold John D. ValenciaDocument82 pagesObstetrical Hemorrhage: Reynold John D. ValenciaReynold John ValenciaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of School Facilities On The Learning EnvironmentDocument174 pagesThe Impact of School Facilities On The Learning EnvironmentEnrry Sebastian71% (31)
- Sri S T Kalairaj, Chairman: Income Tax TaxesDocument3 pagesSri S T Kalairaj, Chairman: Income Tax TaxesvikramkkNo ratings yet
- ESA Knowlage Sharing - Update (Autosaved)Document20 pagesESA Knowlage Sharing - Update (Autosaved)yared BerhanuNo ratings yet
- April 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesDocument16 pagesApril 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesStrathmore Times100% (1)
- GATE ECE 2006 Actual PaperDocument33 pagesGATE ECE 2006 Actual Paperkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Additional Help With OSCOLA Style GuidelinesDocument26 pagesAdditional Help With OSCOLA Style GuidelinesThabooNo ratings yet
- IDocument2 pagesIsometoiajeNo ratings yet
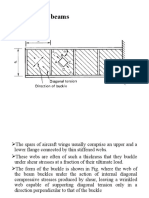
- Tension field beams: Aircraft wing spar analysisDocument19 pagesTension field beams: Aircraft wing spar analysisPrajeesh RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsDocument157 pagesLecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsBảo Châu VươngNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan for Monuro Clothing Store Expansion into CroatiaDocument35 pagesMarketing Plan for Monuro Clothing Store Expansion into CroatiaMuamer ĆimićNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Working CapitalDocument12 pagesEstimation of Working CapitalsnehalgaikwadNo ratings yet
- Fernandez ArmestoDocument10 pagesFernandez Armestosrodriguezlorenzo3288No ratings yet
- The Ultimate Advanced Family PDFDocument39 pagesThe Ultimate Advanced Family PDFWandersonNo ratings yet
- Philippine Coastal Management Guidebook Series No. 8Document182 pagesPhilippine Coastal Management Guidebook Series No. 8Carl100% (1)
- Malware Reverse Engineering Part 1 Static AnalysisDocument27 pagesMalware Reverse Engineering Part 1 Static AnalysisBik AshNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction: Question BankDocument12 pagesUnit-1: Introduction: Question BankAmit BharadwajNo ratings yet
- (23005319 - Acta Mechanica Et Automatica) A Study of The Preload Force in Metal-Elastomer Torsion SpringsDocument6 pages(23005319 - Acta Mechanica Et Automatica) A Study of The Preload Force in Metal-Elastomer Torsion Springsstefan.vince536No ratings yet
- S5-42 DatasheetDocument2 pagesS5-42 Datasheetchillin_in_bots100% (1)
- Oracle Learning ManagementDocument168 pagesOracle Learning ManagementAbhishek Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- 20 Ua412s en 2.0 V1.16 EagDocument122 pages20 Ua412s en 2.0 V1.16 Eagxie samNo ratings yet