Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digital Electronics 8
Uploaded by
Tapas BanerjeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digital Electronics 8
Uploaded by
Tapas BanerjeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Digital Electronics
http://ptuece.loremate.com/die/node/4 March 7, 2012
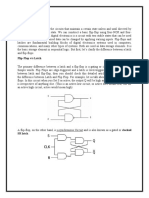
Remember These: 1. Flip-flop is a sequential circuit or device which is used to store single bit of information or data i e either 0 or 1 Single flip-flop stores single bit at a time 2. Flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator as it has two stable states 3. An unclocked flip-flop is called a latch A latch Is that circuit which is constructed using two cross-coupled NAND gates or NOR gates 4. NOR gate S-R latch is called an active High SR latch 5. NAND gate S-R latch is called an active Low SR latch. 6. Flip flops may be level triggered or edge-triggered level triggered are: High level triggered Low level triggered Edge-triggered are Positive edge triggered Negative edge triggered RS, JK D and T type 1. D flip flop is also called as transparent latch as its output follows the input when the clock is high 2. J K flip flop is the most widely used of all flip flops 3. For SR flip-flop When S = R 0 there is NO change condition When, S= 1, R 0, there is SET state. When, S = 0, R = 1, there is RESET state. When S = R = 1, there is invalid state For J-K flip-flop :. When J = K = 0 there is NO change condition When, J = 1, K 0, there is SET state. When J = 0, K = 1, there is RESET state When J K = 1 there is Toggle state 1. Toggle state is that in which the output changes from its previous state with every clock pulse when the inputs are J = K = 1 2. Master slave flip-flop overcomes the problem of race around condition which is common in J-
K flip-flops using level clocks. 3. Register is a set of flip flops used to store binary data or information 4. The registers in which shifting of data takes place are called as shift registers 5. Types of shift registers are: SISO i e Serial in Serial Out SIPO i.e. Serial in Parallel Out. PISO i e Parallel in Serial Out PIPO i e Parallel in Parallel Out 1. Bidirectional shift register is used to shift data from left to right or right to left 2. Universal shift register performs similar function as that of bidirection shift register in addition to it data can be shifted in and out in serial form or in parallel form. 3. Counter is a device used to count clock pulses or number of events 4. Counter types are: Asynchronous Counters Synchronous Counters 1. Asynchronous counters a those in which clock is not simultaneous e output of 1st flip flop acts as clock to the next and so on 2. Synchronous counters are those in which clock is simultaneous i e common to all the flip flops 3. Modulus counters are those which passes through number of states before returning to the starting state 4. A twisted ring counter is known as Johnson counter 5. Monostable multivibrator has only one stable state It is also called as one-shot multivibrator. 6. Astable multivibrator has no stable states It is called as free running multivibrator Q 1. Explain T-flip-flop with suitable internal structure. Ans. The functional block diagram of T flip-flop is as shown in fig.
T flip-flop is known as Toggle flip-flop
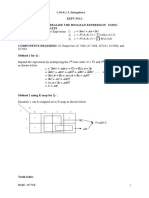
When, T = 1 both NAND Gates 1 and 2 gets high A T flip-flop is designed by combining both the inputs of Gate 1 and 2 together. Thus, when J = K = 0, Q have same previous state i.e. hold state or no change state. When J = K = l, Q have toggle state i.e. invert the previous state. Q 2. Convert SR flip-flop to T flip-flop.
Ans. Firstly write the truth table for SR to T flip-flop as shown: K maps for S & R are: For S: For R:
Implementation:
Q 3. Give applications of J-K flipflops. Ans.1. J-K flip-flops are used in shift registers. 2. J-K flip-flops are used in counters. Q 4. Give difference between latch and flip-flop. Ans. Q 5. How race around condition can be eliminated? Ans. Race around condition can be eliminated in JK latch by two ways 1. Using the edge triggered J-K flip-flop. 2. Using the master slave J-K flip-flop. Q 6. What is a Glitch? Ans. Glitch is a short duration pulse or spike that appears in the outputs of a counter with MOD number Q 7. How many flip-flops are required to count 16 clock pulses? Why? Ans. To count n clock pulses m flip-flops are required, where,
Thus, for 16 clock pulses to count, 4 flip-flops are required as 2 = 16. Q 8. Give application of D and T flip-flops. Ans. D flip-flops are delay flip flops and are extensively used for temporary storage of data in registers. Hence, registers make use of D flip-flops. T flip-flops are toggle flip-flops and are used in counters. Hence, counter designing make use of T
flip-flops. Q 9. Draw the general block diagram of multivibrator. Ans. It is as shown:
F1 and F2 are the options for the connections of passive components according to the types of multivibrator to design. For example (a) Astable Multivibrator: F1 = C1 and F2 = C2. (b) Monostable Multivibrator: F1 = C and F2 = R. (c) Bistable Multivibrator : F1 = F2 = Parallel combination of R and C of different values. Q 10. For the given state diagram, draw the state reduction diagram. Stats Diagram: Ans. State table is as shown:
For modified reduced state diagram:
Q 11. What do you mean by self starting type counter? Ans. Whenever there is no problem of lock out then the counter is selfstarting type. So, if any time the counter goes into an invalid state, it comes out and goes into a valid state after application of one clock pulse. Q 12. Why is gated D latch called transparent latch? Ans. The edge triggered D flip-flop uses an edge-detector circuits so that the output will respond to D input only when the active transition of clock takes place. It is as shown in fig.
From fig. when enable is 1, the D input will given a 0 at either
the or inputs of NAND latch. Thus, 0 becomes same as D. Thus, when enable is 1 the output Q will look exactly like D. Hence, the D latch is said to be transparent latch. Q 13. A presettable counter has eight flipflops. If the preset number is 125, what is the modulus? Ans. 256 125 = 131 Thus, MOD 131. Q 14. Differentiate between sequential and combination circuits. Ans. Q 15. The clock frequency is 2MHz. How long will it take to serial load the eight shift register? Ans. n=8 Time taken to load serially the eight bit will be given by
Q 16. What is flip-flop? Ans. Flip-flop : Flip-flop is a sequential circuit which is used to store single bit of information at a time i.e. either 1 or 0 at a time. It has two stable output states. It can stay in one of the two stable states unless state is changed by applying external inputs. Thus, it as a basic memory element for storage of data in binary form. There are various types of flip-flops 1. S-R flip flop 2. J-K flip-flop 3. D-type flip flop 4. T-type flip-flop Q 17. Explain about multivibrator.
Ans. Multivibrators : Most of the digital circuits or systems need some kind of a timing waveform for example, all clocked sequential system required a source of trigger pulses. A timing circuit which produces a rectangular waveforms are referred to as multivibrators. There are different types of multivibrators such as: 1. Astable Multivibrator 2. Monostable Multivibrator 3. Bistable Multivibrator. Q 18. What is shift register? Ans. Shift register : A register capable of shifting its binary information either from right to left or left to right is known as shift register. It consists of flip-flops connected is cascade. All flip-flops receive a common clock pulse which causes the shift from one stage to the next stage. It is of four basis types: 1. Serial in serial out register 2. Serial in parallel out register 3. Parallel in serial out register 4. Parallel in parallel out register. Bi-directional shift register and Universal shift registers are also used for different applications. Q 19. What is universal shift register? Ans. Universal shift register performs similar operation and function as that of bidirectional shift register i.e. it can shift data from left to right or right to left, in addition to it data can be shifted in and out and in serial as well as in parallel form. Q 20. Draw a logic symbol for a D-flip-flop and compare with RS flip-flop. Ans. In case of RS two inputs are there hence four possible combined are used. But in case of D flip-flop it has only one input so and two combination are used. Also, in D flipflop what ever we want to store will be put as input. If we want to store 1. 1 is the input and if 0 is input, 0 will be stored in D flip-flop. Q 21. Differentiate between synchronous and asynchronous counters. Ans.
Q 22. What is buffer register? Ans. Buffer registers are also called as storage registers. They are primarily used for temporary storage, of binary information or data. They provide place to hold data until it is processed. That is why they are known as buffer registers. Q 23. Suggest four applications of shift registers. Ans. Applications of shift registers 1. It is used in ring counters. 2. It is used in sequence generators. 3. It is used for data conversion in computers i.e. serial to parallel, parallel to serial etc. 4. It is used for time delays i.e. serial in serial out shift register are used for this purpose. 5. It is used in Johnson counter / twisted ring counter. Q 24 Give the truth-table for each flip-flop type: (a) J-K ; (b) D ; and (c) T Ans. Truth table of J-K Flip-flop: 2. D Flip-flop: Q output follows D input with each other. 3. T Flip-flop: Toggle means 0 changes to 1 and 1 changes to 0 with the passage of each clock Q 25 Explain why there may be a race condition in a shift register. Ans. There is no race condition in Shift register as it make use of D flip flop, R S flip flop as D and J K flip flop So the condition of J = K = 1 never comes.
Q 26 What is a ripple counter? Ans. Ripple Counter- Ripple counters are also known as asynchronous counters. It is as shown in fig for two bits
For ripple counter input clock is given to first flip-flop and the output of first flip-flop acts as a clock to next flip-flop and so on Q 27. Differentiate between static and dynamic shift registers. Ans. Q 28. What is the Mod of 6 bit Ring Counter ? Ans. The mod of 6 bit ring counter is given by 2 where n = number of bits. 2 = 64. Thus MOD-64.
Q 29. Give expression for maximum frequency of operation of n-bit Asynchronous and synchronous counters. Ans. Max. frequency of operation for asynchorous counter It is same for synchronous counter unless no. of flip-flop, where the maximum frequency of synchronous counter is
Q 30. Compare binary counters with non-binary counters. Ans. Q 31. Draw logic circuit diagram for 3-bit synchronous up-down counter with clear input, start input and done output. The counter should produce done output after completion of
counter in either direction. Ans. 3-bit synchronous up-down counter: Q 32. Specially where Masterslave J-K flip flop is preferred for use. Ans. Master slave J-K flip-flop is preferred where we want to avoid multiple toggling and race around conduction. In this flip-flop, master F/F is positive edge triggered and slave flip-flop is negative edge triggered. The slave ftpflop followed the master flip-flop. Q 33. Applications of D Flip Flop. Ans.1. D Flip-flop can be used as a delay element 2. As a memory element. 3. In counters! timers. 4. in various types of registers, like in SIPO, SIPO etc. Q 34. Draw the logic circuits and the excitation tables for the T, JK flip-flops. Ans. Q 35. Classify the sequential circuits. Ans. Q 36. Describe the difference between a gated S-R latch and an edge-triggered S-R flip flop. Ans. Gated S-R FlipFlop : A gate S-A Flop/flop requires an enable (E) input. When enable is high, the output changes according to the inputs S and R. However when enable is ineffective, no change of state take place. Clock signal may also act as
a enable.
Edge Triggered S-R Flip-flop: In edge-triggered S-R flipflop, the change of state in flip-flop takes place only when edge (either +ve or -ve) of clock pulse takes place. Q 37. What is the difference between level and edge triggering? Explain the working of master slave J-K flip flop. Ans. Master slave JK flip-flop : The master slave flip-flop may be designed using R-S, D and JK flipflops. Following figure shows the functional block diagram of master slave JK flip- flop: In figure m is used for Master and S is used for Slave Working: Case 1: When positive clock pulse goes on leading edge is applied, the CLKm is 1 and CLKs is 0, then data transferred to Qm is held upto CLK = 1
Case 2: When the clock pulse goes negative, trailing edge is applied, the CLKm = 0 and CLKs = 1, then Qm and will be transferred to Q = and at that duration the inputs at J and K should not change This is overcome by the use of data lockout. Internal structures of master slave J-K flip-flop, Truth table is as shown in fig Q 38. Draw a master-slave J-K flip-flop system. Explain its operation and show that the race-around condition is eliminated. Ans. A master-slave J-K flip-flop is constructed from two flip-flops. One flip-flop acts as a master
and the other as a slave and the overall circuit is thus, called as master-slave flip-flop. It make use of J-K master flip-flop and S-A slave flip-flop. The master is positive edge triggered and slave is negative edge triggered. Therefore, master responds to J-K inputs before the slave. V If J = 1 and K = 0, the master sets on the positive clock edge. The high output of the master drives the J input of the slave, so when the negative clock edge arrives, the slave sets, copying the action of the master. If J = 0 and K = 1, the master resets on the positive clock edge. The high output of master i.e. goes to R input of the slave. Therefore, slave resets on arrival of negative clock edge. If J = K = 1 for master, it toggles on positive clock edge and the slave them toggles on the negative clock edge. When J = K = 1 Let clock = 1 then master is active and slave is in active Therefore, output of master toggle. So S and R also will be inverted When clock 0 Master becomes in active and slave is active Therefore, output of the slave will toggle These changed outputs are again returned back to the master inputs as feedback is connected in fig But here clock is 0, the master is still in active So it does not respond to these changed outputs This voids multiple toggling which is responsible for Race Around Condition Hence by using Master-Slave J K Flip-flop RACE AROUND CONDITION will be avoided or eliminated.
Q 39 Explain what is universal shift register? Explain its working. Ans. A universal shift register is one which can function in any of the SISO SIPO PISO or PIPO modes of operation To operate the register universally it contains serial input serial output, parallel inputs, parallel outputs and must be able to serially shift data to the right or to the left, hold the data or to reset Thus, it has bidirectional property also It is a 74194 IC Its internal structure is as shown in figure. Operating modes of IC741 94
You might also like
- Unit-1 - Digital ElectronicsDocument50 pagesUnit-1 - Digital ElectronicsVignesh VigneshNo ratings yet
- Two MarksDocument17 pagesTwo MarksGodwin CNo ratings yet
- JK Flip-Flop and Registers ExplainedDocument21 pagesJK Flip-Flop and Registers ExplainedAce DanielNo ratings yet
- Designing of Flip FlopsDocument8 pagesDesigning of Flip FlopsOni OniNo ratings yet
- STLD TestDocument136 pagesSTLD TestganeshNo ratings yet
- Chp1 - Latches and Flip-FlopsDocument44 pagesChp1 - Latches and Flip-FlopsAbnen OngNo ratings yet
- Understanding Flip FlopsDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Flip FlopsTech guru MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Module - 3 DSDVDocument40 pagesModule - 3 DSDVHimabindu SanapaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Flip Flop and Registers2020Document25 pagesChapter 7 - Flip Flop and Registers2020SYAFIQAH BATRISYIA MOHD ZAHIRNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: Flip-Flops and Simple Flip-Flop ApplicationsDocument18 pagesChapter - 5: Flip-Flops and Simple Flip-Flop ApplicationsSafeer ParambathNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture 1Document39 pagesComputer Architecture 1ARAFAT GaamanNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Digit Counter GuideDocument7 pagesMini Project Digit Counter GuideMUHAMMAD IZZAT BIN ZULKIFLI STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Flip Flops Behavior & TypesDocument11 pagesAnalyzing Flip Flops Behavior & TypesZakaria JubarnNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document26 pagesModule 4OKNo ratings yet
- Flipflops: Technical Seminar ReportDocument16 pagesFlipflops: Technical Seminar ReportrachitNo ratings yet
- CS302 Mid Term Solved PapersDocument51 pagesCS302 Mid Term Solved PapersattiqueNo ratings yet
- Mini Project DigitDocument7 pagesMini Project DigitMUHAMMAD IZZAT BIN ZULKIFLI STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Logic Design Presentation - Latches & Flip FlopsDocument16 pagesLogic Design Presentation - Latches & Flip FlopsKudzai Russell MutanhaurwaNo ratings yet
- Study of Flip-Flops and Shift RegistersDocument14 pagesStudy of Flip-Flops and Shift RegistersTimoth DevNo ratings yet
- Latches & Flip Flops: Understanding the DifferenceDocument19 pagesLatches & Flip Flops: Understanding the DifferenceTaran ShahNo ratings yet
- Flip FlopDocument6 pagesFlip FlopMuzakki SathorNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Flop FlopsDocument9 pagesBasic Electronics Flop FlopsMegha SaranNo ratings yet
- QB105323Document17 pagesQB105323Noman Ali35No ratings yet
- Shift RegistorsDocument7 pagesShift RegistorsRashid RashNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 DLDDocument189 pagesUnit 5 DLDGuru VelmathiNo ratings yet
- Lec # 06 - DLDDocument30 pagesLec # 06 - DLDSunny 17No ratings yet
- Engg BasicsDocument10 pagesEngg BasicsGnrajesh RajeshNo ratings yet
- How Flip Flops Store Data in ElectronicsDocument19 pagesHow Flip Flops Store Data in ElectronicslidhisijuNo ratings yet
- Understanding Flip-FlopsDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Flip-Flopsamiethurgat100% (2)
- Digital Electronics NotesDocument191 pagesDigital Electronics NotesSatyam ShivamNo ratings yet
- Flip FlopDocument34 pagesFlip Flopqwrr rewqNo ratings yet
- Mcqs cs302Document6 pagesMcqs cs302Abrish AliNo ratings yet
- 6-Registers and CountersDocument40 pages6-Registers and CountersWisdom tabuloNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document6 pagesTest 1kavana a ganigaNo ratings yet
- Flip FlopDocument29 pagesFlip FlopAndleeb juttiNo ratings yet
- Intro to Synchronous Sequential Logic & Storage ElementsDocument49 pagesIntro to Synchronous Sequential Logic & Storage ElementsJames Francis100% (4)
- Digital Design FundamentalsDocument25 pagesDigital Design FundamentalsnileshchaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Flip-Flop and Memory (12328)Document14 pagesFlip-Flop and Memory (12328)red100% (1)
- Registers and CountersDocument13 pagesRegisters and CountersKamal PhyNo ratings yet
- dpsd-2 Mark QBDocument14 pagesdpsd-2 Mark QBpriya100% (2)
- CSE231 Lecture 6Document31 pagesCSE231 Lecture 6Rayhan Amin 2212830042No ratings yet
- Ade Unit 5Document41 pagesAde Unit 5KUMAR SNo ratings yet
- Digital & Logic Design (DLD) : Lab Assignment Report On Implementation of D Flip Flop Ic On BreadboardDocument5 pagesDigital & Logic Design (DLD) : Lab Assignment Report On Implementation of D Flip Flop Ic On BreadboardHaris AmanNo ratings yet
- Java NotesDocument37 pagesJava NotesSandeep Kumar mehtaNo ratings yet
- CounterDocument22 pagesCounterMahesh MahiNo ratings yet
- The Clocked RS Flip-FlopDocument4 pagesThe Clocked RS Flip-Flopabhisheksikka17No ratings yet
- Flip Flops and Registers ExplainedDocument19 pagesFlip Flops and Registers ExplainedDevi Sharan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Filename-0 Bahan Kuliah Counter Asinkron Dan Counter Sinkron RegisterDocument79 pagesFilename-0 Bahan Kuliah Counter Asinkron Dan Counter Sinkron RegisterYudhaNo ratings yet
- Sequential Logic CircuitsDocument49 pagesSequential Logic CircuitsAffo AlexNo ratings yet
- Flip-Flops: S R Q Q' 1 0 1 0 Set 0 0 1 0 Previous Condition 0 1 0 1 Reset 0 0 0 1 Previous Condition 1 1 0 0 JammedDocument5 pagesFlip-Flops: S R Q Q' 1 0 1 0 Set 0 0 1 0 Previous Condition 0 1 0 1 Reset 0 0 0 1 Previous Condition 1 1 0 0 JammedMatt PrestonNo ratings yet
- FlipflopsDocument38 pagesFlipflopsajith p pNo ratings yet
- Sequential Logic - Flip-Flops: 6.1 SR LatchDocument5 pagesSequential Logic - Flip-Flops: 6.1 SR Latchanon020202No ratings yet
- cs302 Short Notes and Subjetive Paper For MidtermDocument52 pagescs302 Short Notes and Subjetive Paper For MidtermchashmanmuneerNo ratings yet
- Name of The Experiment: Sequential Circuit Design - Latch, Flip Flop and Registers Important: Submit Your Prelab at The Beginning of The LabDocument7 pagesName of The Experiment: Sequential Circuit Design - Latch, Flip Flop and Registers Important: Submit Your Prelab at The Beginning of The LabAurongo NasirNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic and Logic (Cont) : 2.3 Build Sequential Logic CircuitDocument22 pagesArithmetic and Logic (Cont) : 2.3 Build Sequential Logic CircuitBadrul Afif ImranNo ratings yet
- Digital AnswersDocument5 pagesDigital AnswersSachin JunejaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Mole Concept SheetDocument36 pagesMole Concept SheetTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- JescepDocument32 pagesJescepDimla RaniNo ratings yet
- 31 1 3 ScienceDocument32 pages31 1 3 Scienceaswathsiva1192008No ratings yet
- 31 2 1 ScienceDocument27 pages31 2 1 Scienceaswathsiva1192008No ratings yet
- 31 6 2 ScienceDocument32 pages31 6 2 ScienceTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 31 6 3 ScienceDocument32 pages31 6 3 ScienceTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 31 1 2 ScienceDocument32 pages31 1 2 Scienceaswathsiva1192008No ratings yet
- Science 6aDocument32 pagesScience 6aarmyb5863No ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 25Document11 pagesCbjescpu 25Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 31 2 2 ScienceDocument27 pages31 2 2 Scienceaswathsiva1192008No ratings yet
- Science Board Sample PaperDocument27 pagesScience Board Sample Paperskshiarora12No ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 17Document11 pagesCbjescpu 17Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- (DKMZ: Series Z1Xyw/5 Set 1Document27 pages(DKMZ: Series Z1Xyw/5 Set 1AmanNo ratings yet
- 31 5 2 ScienceDocument27 pages31 5 2 Sciencekhandelwalbrother4No ratings yet
- 31 4 3 ScienceDocument24 pages31 4 3 ScienceTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 11Document12 pagesCbjescpu 11Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 20Document10 pagesCbjescpu 20chilledyt243No ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 29Document12 pagesCbjescpu 29Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 18Document10 pagesCbjescpu 18Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 12Document10 pagesCbjescpu 12Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 04Document10 pagesCbjescpu 04Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 30Document10 pagesCbjescpu 30Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Sample Q Paper-5Document10 pages10 Science Sample Q Paper-5msrubber27No ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 05Document11 pagesCbjescpu 05Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 01Document11 pagesCbjescpu 01ahmedmansurr98No ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 24Document10 pagesCbjescpu 24Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 23Document10 pagesCbjescpu 23Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 10Document14 pagesCbjescpu 10Destructive oxeloNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 21Document10 pagesCbjescpu 21Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 22Document9 pagesCbjescpu 22Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan: College of EngineeringDocument3 pagesDhanalakshmi Srinivasan: College of Engineeringhamsalakshmi cNo ratings yet
- An 8 Bit Multiplier Project ReportDocument8 pagesAn 8 Bit Multiplier Project ReportAsad Malik0% (1)
- Design Half and Full Adder CircuitsDocument2 pagesDesign Half and Full Adder CircuitsPiyas ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Roll No:: (An Autonomous Institution, Affiliated To Anna University, Chennai)Document1 pageRoll No:: (An Autonomous Institution, Affiliated To Anna University, Chennai)Venkatesh TNo ratings yet
- Digital Circuits & Fundamentals of MicroprocessorDocument86 pagesDigital Circuits & Fundamentals of Microprocessorfree_prog67% (6)
- MOD-10 Counter Truth Table and Logic DiagramDocument11 pagesMOD-10 Counter Truth Table and Logic Diagramroyal brotherNo ratings yet
- Questions On Asynchronous & Synchronous Counters With Solutions (1987 2014)Document11 pagesQuestions On Asynchronous & Synchronous Counters With Solutions (1987 2014)DHRUV CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Digital Techniques VIVA ANSWERS 3rd SEMDocument6 pagesDigital Techniques VIVA ANSWERS 3rd SEMOSA MEMBERNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - 1Document7 pagesTutorial 4 - 1YONIWO EDWARD TSEMINo ratings yet
- Design Asynchronous and Synchronous Counters Using JK Flip FlopsDocument6 pagesDesign Asynchronous and Synchronous Counters Using JK Flip FlopsMani Bharathi40% (5)
- Digital Design Synchronous Sequential LogicDocument61 pagesDigital Design Synchronous Sequential LogicPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Problem - Sheet - 5Document2 pagesProblem - Sheet - 5Shubhanshu ChauhanNo ratings yet
- VLSI Lab ManualDocument68 pagesVLSI Lab ManualadeivaseelanNo ratings yet
- 06ESL38 - Logic Design Lab1Document76 pages06ESL38 - Logic Design Lab1Sachin S ShettyNo ratings yet
- Manual 2018-1Document47 pagesManual 2018-1Deepa JerinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Flip Flops and Their ApplicationsDocument34 pagesCHAPTER 3: Flip Flops and Their ApplicationsFadly ShafiqNo ratings yet
- LOGIC - CIRCUITS Final Exam Q2 2010 - 2011 Problems and Answer KeyDocument2 pagesLOGIC - CIRCUITS Final Exam Q2 2010 - 2011 Problems and Answer KeySimon Gregory Mabanta100% (1)
- Digital Electronics Lab Worksheet 1: Subject Code: 21ECH-101 AimDocument15 pagesDigital Electronics Lab Worksheet 1: Subject Code: 21ECH-101 AimRavinder singhNo ratings yet
- VHDL Codes For Various Combinational CircuitsDocument6 pagesVHDL Codes For Various Combinational CircuitsKaranNo ratings yet
- Digital Lab CS2207 Lab ManualDocument41 pagesDigital Lab CS2207 Lab ManualSingh VelNo ratings yet
- A Design of A Novel ALU Architecture Using Reversible Logic TechniqueDocument5 pagesA Design of A Novel ALU Architecture Using Reversible Logic TechniqueNILAM CHHEDANo ratings yet
- DIgital Electronics Lab Exam Viva QuestionsDocument6 pagesDIgital Electronics Lab Exam Viva Questionsmehek saba100% (18)
- Digital Electronics Chapter 8Document51 pagesDigital Electronics Chapter 8Pious TraderNo ratings yet
- DLD-Chap - 3-Logic GatesDocument40 pagesDLD-Chap - 3-Logic Gatesrizwan0% (1)
- PLD Led LCDDocument37 pagesPLD Led LCDRipan SahaNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics LaboratoryDocument30 pagesDigital Electronics LaboratoryrahulsportyNo ratings yet
- Barrel ShifterDocument79 pagesBarrel ShifterVinay Reddy100% (2)
- BCD CounterDocument22 pagesBCD CounterDarren FerrerNo ratings yet
- Circuit Minimization and Karnaugh MapsDocument62 pagesCircuit Minimization and Karnaugh MapsYONIWO EDWARD TSEMINo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Lab ManualDocument191 pagesDigital Electronics Lab Manuallavanyavinayagam1985No ratings yet